praetorian prefecture of Africa on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
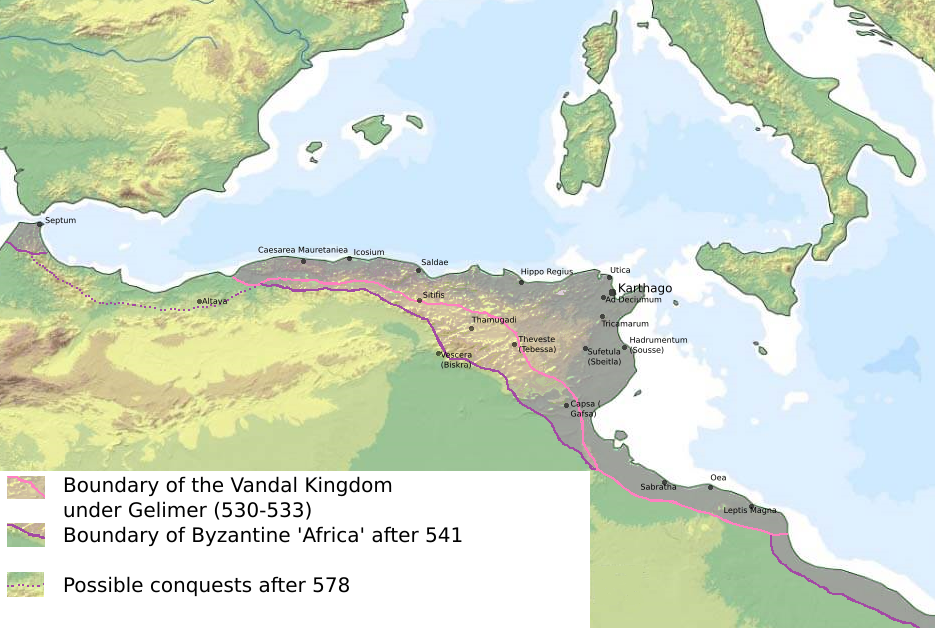
The Praetorian Prefecture of Africa () was an administrative division of the
 In the Easter of 536 however, a large-scale military revolt broke out, caused by dissatisfaction of the soldiers with Solomon. Solomon, together with
In the Easter of 536 however, a large-scale military revolt broke out, caused by dissatisfaction of the soldiers with Solomon. Solomon, together with
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived History of the Roman Empire, the events that caused the ...
in the Maghreb
The Maghreb (; ), also known as the Arab Maghreb () and Northwest Africa, is the western part of the Arab world. The region comprises western and central North Africa, including Algeria, Libya, Mauritania, Morocco, and Tunisia. The Maghreb al ...
. With its seat at Carthage
Carthage was an ancient city in Northern Africa, on the eastern side of the Lake of Tunis in what is now Tunisia. Carthage was one of the most important trading hubs of the Ancient Mediterranean and one of the most affluent cities of the classic ...
, it was established after the reconquest of northwestern Africa from the Vandals
The Vandals were a Germanic people who were first reported in the written records as inhabitants of what is now Poland, during the period of the Roman Empire. Much later, in the fifth century, a group of Vandals led by kings established Vand ...
in 533–534 by the Byzantine Emperor Justinian I
Justinian I (, ; 48214 November 565), also known as Justinian the Great, was Roman emperor from 527 to 565.
His reign was marked by the ambitious but only partly realized ''renovatio imperii'', or "restoration of the Empire". This ambition was ...
. It continued to exist until 591, when it was replaced by the Exarchate of Africa.
History
Establishment
In 533, the Eastern Roman army underBelisarius
BelisariusSometimes called Flavia gens#Later use, Flavius Belisarius. The name became a courtesy title by the late 4th century, see (; ; The exact date of his birth is unknown. March 565) was a military commander of the Byzantine Empire under ...
defeated and destroyed the Vandal Kingdom
The Vandal Kingdom () or Kingdom of the Vandals and Alans () was a confederation of Vandals and Alans, which was a barbarian kingdoms, barbarian kingdom established under Gaiseric, a Vandals, Vandalic warlord. It ruled parts of North Africa and th ...
that had existed in the former Roman territories of Northern Africa. Immediately after the victory, in April 534, the emperor Justinian published a law concerning the administrative organization of the recovered territories. The old provinces of the Roman Diocese of Africa
The Diocese of Africa () was a diocese of the later Roman Empire, incorporating the provinces of North Africa, except Mauretania Tingitana. Its seat was at Carthage, and it was subordinate to the Praetorian prefecture of Italy.
The diocese in ...
had been mostly preserved by the Vandals, but large parts, including almost all of Mauretania Tingitana, much of Mauretania Caesariensis
Mauretania Caesariensis (Latin for "Caesarea, Numidia, Caesarean Mauretania") was a Roman province located in present-day Algeria. The full name refers to its capital Caesarea, Numidia, Caesarea Mauretaniae (modern Cherchell).
The province had ...
and Mauretania Sitifensis and large parts of the interior of Numidia
Numidia was the ancient kingdom of the Numidians in northwest Africa, initially comprising the territory that now makes up Algeria, but later expanding across what is today known as Tunisia and Libya. The polity was originally divided between ...
and Byzacena
Byzacena (or Byzacium) (, ''Byzakion'') was a Late Roman province in the central part of Roman North Africa, which is now roughly Tunisia, split off from Africa Proconsularis.
History
At the end of the 3rd century AD, the Roman emperor Dioclet ...
, had been lost to the inland Berber
Berber or Berbers may refer to:
Ethnic group
* Berbers, an ethnic group native to Northern Africa
* Berber languages, a family of Afro-Asiatic languages
Places
* Berber, Sudan, a town on the Nile
People with the surname
* Ady Berber (1913–196 ...
tribes, collectively called the '' Mauri'' (Moors
The term Moor is an Endonym and exonym, exonym used in European languages to designate the Muslims, Muslim populations of North Africa (the Maghreb) and the Iberian Peninsula (particularly al-Andalus) during the Middle Ages.
Moors are not a s ...
). Nevertheless, Justinian restored the old administrative division, but raised the overall governor at Carthage
Carthage was an ancient city in Northern Africa, on the eastern side of the Lake of Tunis in what is now Tunisia. Carthage was one of the most important trading hubs of the Ancient Mediterranean and one of the most affluent cities of the classic ...
to the supreme administrative rank of Praetorian Prefect
The praetorian prefect (; ) was a high office in the Roman Empire. Originating as the commander of the Praetorian Guard, the office gradually acquired extensive legal and administrative functions, with its holders becoming the Emperor's chief ai ...
, thereby ending the Diocese of Africa's traditional subordination to the Prefecture of Italy (then still under the rule of the Ostrogothic Kingdom
The Ostrogothic Kingdom, officially the Kingdom of Italy (), was a barbarian kingdom established by the Germanic Ostrogoths that controlled Italian peninsula, Italy and neighbouring areas between 493 and 553. Led by Theodoric the Great, the Ost ...
). Seven provinces – four consular, three ''praesides'' – were designated:
It should be assumed that Mauretania Tingitana, traditionally part of the Diocese of Spain (then under the rule of the Visigothic Kingdom
The Visigothic Kingdom, Visigothic Spain or Kingdom of the Goths () was a Barbarian kingdoms, barbarian kingdom that occupied what is now southwestern France and the Iberian Peninsula from the 5th to the 8th centuries. One of the Germanic people ...
), was temporarily extinguished as a separate province in Justinian's arrangement and merged with Mauretania Caesariensis to form the province ruled from Tingi, and that "Mauretania" refers to Mauretania Sitifensis. It is also noteworthy that the island of Sardinia
Sardinia ( ; ; ) is the Mediterranean islands#By area, second-largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, after Sicily, and one of the Regions of Italy, twenty regions of Italy. It is located west of the Italian Peninsula, north of Tunisia an ...
switched to being part of African section in terms of Byzantine provincial administration, rather than Italian section like classical Roman times.
Justinian's intent was to, in the words of the historian J.B. Bury, "wipe out all traces of the Vandal conquest, as if it had never been". The churches were restored to the Chalcedonian clergy, and the remaining Arians suffered persecution. Even the land ownership was reverted to the status prior to the Vandalic conquest, but the scarcity of valid property titles after 100 years of Vandal rule created an administrative and judicial chaos.
The military administration was headed by the new post of ''magister militum
(Latin for "master of soldiers"; : ) was a top-level military command used in the late Roman Empire, dating from the reign of Constantine the Great. The term referred to the senior military officer (equivalent to a war theatre commander, the e ...
Africae'', with a subordinate ''magister peditum'' and four regional frontier commands (Leptis Magna
Leptis or Lepcis Magna, also known by #Names, other names in classical antiquity, antiquity, was a prominent city of the Carthaginian Empire and Roman Libya at the mouth of the Wadi Lebda in the Mediterranean.
Established as a Punic people, Puni ...
for Tripolitania, Capsa or Thelepte for Byzacena, Cirta for Numidia, and Caesarea for Mauretania) under '' duces''. This organization was only gradually established, as the Romans pushed the Mauri back and regained these territories.
The Moorish Wars
When the Romans landed in Africa, the Moors maintained a neutral stance, but after the quick Roman victories, most of their tribes pledged loyalty to the Empire. The most significant tribes were the Leuathae in Tripolitania, and the Frexi in Byzacena. The Frexi and their allies were led by Antalas, while other tribes in the area followed Cutzinas. The Aurasii (the tribes of the Aurès Mountains) in Numidia were ruled by Iaudas, and the Mauretanian Moors were led by Mastigas and Masuna.First Moorish uprising
After Belisarius departed for Constantinople, he was succeeded as ''magister militum
(Latin for "master of soldiers"; : ) was a top-level military command used in the late Roman Empire, dating from the reign of Constantine the Great. The term referred to the senior military officer (equivalent to a war theatre commander, the e ...
Africae'' by his '' domesticus'' (senior aide), the eunuch Solomon
Solomon (), also called Jedidiah, was the fourth monarch of the Kingdom of Israel (united monarchy), Kingdom of Israel and Judah, according to the Hebrew Bible. The successor of his father David, he is described as having been the penultimate ...
from Dara. The tribes of Mauri living in Byzacena
Byzacena (or Byzacium) (, ''Byzakion'') was a Late Roman province in the central part of Roman North Africa, which is now roughly Tunisia, split off from Africa Proconsularis.
History
At the end of the 3rd century AD, the Roman emperor Dioclet ...
and Numidia
Numidia was the ancient kingdom of the Numidians in northwest Africa, initially comprising the territory that now makes up Algeria, but later expanding across what is today known as Tunisia and Libya. The polity was originally divided between ...
almost immediately rose up, and Solomon set out with his forces, which included allied Moorish tribes, against them. The situation was so critical that Solomon was also entrusted with civil authority, replacing the first prefect, Archelaus, in the autumn of 534. Solomon was able to defeat the Mauri of Byzacena at Mamma, and again, decisively, at the Mt. Bourgaon in early 535. In the summer, he campaigned against Iaudas and the Aurasii, who were ravaging Numidia, but failed to achieve any result. Solomon then set about erecting forts along the borders and the main roads, hoping to contain the raids of the Moors.
Military mutiny

 In the Easter of 536 however, a large-scale military revolt broke out, caused by dissatisfaction of the soldiers with Solomon. Solomon, together with
In the Easter of 536 however, a large-scale military revolt broke out, caused by dissatisfaction of the soldiers with Solomon. Solomon, together with Procopius
Procopius of Caesarea (; ''Prokópios ho Kaisareús''; ; – 565) was a prominent Late antiquity, late antique Byzantine Greeks, Greek scholar and historian from Caesarea Maritima. Accompanying the Roman general Belisarius in Justinian I, Empe ...
, who worked as his secretary, was able to escape to Sicily
Sicily (Italian language, Italian and ), officially the Sicilian Region (), is an island in the central Mediterranean Sea, south of the Italian Peninsula in continental Europe and is one of the 20 regions of Italy, regions of Italy. With 4. ...
, which had just been conquered by Belisarius. Solomon's lieutenants Martinus and Theodore were left behind, the first to try to reach the troops at Numidia, and the second to hold Carthage. Upon hearing about the mutiny, Belisarius, with Solomon and 100 picked men, set sail for Africa. Carthage was being besieged by 9,000 rebels, including many Vandals, under a certain Stotzas Stotzas (Greek language, Greek: Στότζας), also Stutias, Theophanes writes him Tzotzas (Τζότζας), was an Byzantine Empire, East Roman (Byzantine) soldier and leader of a military rebellion in the Praetorian prefecture of Africa in the 5 ...
. Theodore was contemplating capitulation, when Belisarius appeared. The news of the famous general's arrival were sufficient for the rebels to abandon the siege and withdraw westwards. Belisarius, although able to muster only 2,000 men, immediately gave pursuit and caught up and defeated the rebel forces at Membresa. The bulk of the rebels however was able to flee, and continued to march towards Numidia, where the local troops decided to join them. Belisarius himself was forced to return to Italy, and Justinian appointed his cousin Germanus as ''magister militum'' to deal with the crisis.
Germanus managed to win over many of the rebels to his side by appearing conciliatory and paying their arrears. Eventually, in the spring of 537, the two armies clashed at Scalae Veteres, resulting in a hard-won victory for Germanus. Stotzas fled to the tribesmen of Mauretania, and Germanus spent the next two years in re-establishing discipline in the army. Finally, Justinian judged the situation to have been stabilized enough, and in 539 Germanus was replaced by Solomon. Solomon carried on Germanus' work by pruning out of the army those of suspect loyalties and strengthening the network of fortifications. This careful organization enabled him to strike successfully against the Aurasii, evicting them from their mountain strongholds, and firmly establish Roman rule in Numidia and Mauretania Sitifensis.
Second Moorish uprising and the revolt of Guntharic
Africa enjoyed peace and prosperity for the next few years, until the arrival of the great plague c. 542. At the same time, the arrogant behaviour of some Roman governors alienated the Mauri leaders, such as Antalas at Byzacena, and provoked them to rise up and raid Roman territory. So it was that during a battle with the Mauri at Cillium in Byzacena in 544, the Romans were defeated and Solomon himself killed. Solomon was succeeded by his nephew, Sergius, who as ''dux'' of Tripolitania had been largely responsible for the Moorish uprising. Sergius was both unpopular and of limited abilities, while the Mauri, joined by the renegade Stotzas, gathered together under the leadership of Antalas. The Moors, aided by Stotzas, were able to enter and sack the coastal city ofHadrumetum
Hadrumetum, also known by #Names, many variant spellings and names, was a Phoenician Phoenician colonies, colony that pre-dated Carthage. It subsequently became one of the most important cities in Roman Africa before Vandal Kingdom, Vandal and Uma ...
by trickery. A priest named Paulus was able to retake the city with a small force without help from Sergius, who refused to march forth against the Moors. Despite this setback, the rebels roamed the provinces at will, while the rural population fled to the fortified cities and to Sicily.
Justinian then sent Areobindus, a man of senatorial rank and husband to his niece Praejecta, but otherwise undistinguished, with a few men to Africa, not to replace Sergius, but to share command with him. Sergius was entrusted with the war in Numidia, while Areobindus undertook to subdue Byzacena. Areobindus sent out a force under the able general John against Antalas and Stotzas. Because Sergius did not come to their aid as requested, the Romans were routed at Thacia, but not before John mortally wounded Stotzas in single combat. The effects of this disaster at least forced Justinian to recall Sergius and restore unity of command in the hands of Areobindus. Soon after, in March 546, Areobindus was overthrown and murdered by Guntharic, the ''dux Numidiae'', who had come into negotiations with the Moors and intended to set himself up as an independent king. Guntharic himself was overthrown by loyal troops under the Armenian Artabanes in early May. Artabanes was elevated to the office of ''magister militum Africae'', but was soon recalled to Constantinople.
The man Justinian sent to replace him was the talented general John Troglita
John Troglita (, ) was a 6th-century Byzantine Empire, Byzantine general. He participated in the Vandalic War and served in North Africa as a regional military governor during the years 533–538, before being sent east to the wars with the Sassan ...
, whose exploits are celebrated in the epic poem ''Iohannis'', written by Flavius Cresconius Corippus. Troglita had already served in Africa under Belisarius and Solomon, and had a distinguished career in the East, where he had been appointed '' dux Mesopotamiae''. Despite his numerically weak forces, he managed to win over several Moorish tribes, and in early 547 he decisively defeated Antalas and his allies, and drove them from Byzacena. As Procopius recounts:
A few months later, however, the tribe of the Leuathae The Laguatan () was a Berbers, Berber clan that inhabited the Cyrenaica area during the Roman Empire, Roman period. They have been described as primarily raiders and nomadic, but others consider them a settled group who also raided.
The Laguatan em ...
, in Tripolitania, rose up, and inflicted a severe defeat upon the imperial forces in the plain of Gallica. The Leuathae were joined by Antalas, and the Moors once again raided freely as far as Carthage. Early in the next year John mustered his forces, and together by several allied Moorish tribes, including the former rebel Cutzinas, utterly defeated the Moors at the battle of the Fields of Cato, killing seventeen of their leaders and putting an end to the revolt that had plagued Africa for almost 15 years.
Peace restored
For the next decades, Africa remained tranquil, allowing it to recover. Peace might not have lasted as long, had not Troglita perceived that the complete eviction of the Mauri from the interior of the provinces, and the complete restoration of the province to its pre-Vandal bounds was impossible. Instead, he opted to accommodate himself with the Moors, promising them autonomy in exchange for becoming the Empire's ''foederati
''Foederati'' ( ; singular: ''foederatus'' ) were peoples and cities bound by a treaty, known as ''foedus'', with Rome. During the Roman Republic, the term identified the '' socii'', but during the Roman Empire, it was used to describe foreign ...
''. The loyalty of these dependent princes of the various Moorish tribes was secured by means of annual pensions and gifts, and the peace was kept by a strong network of fortifications, many of which still survive to the present day.
The only interruption to the province's tranquility was a brief Moorish revolt of 563. It was caused by the unwarranted murder of the aged tribal leader Cutzinas, when he came to Carthage to receive his annual pension, by the ''magister militum'', John Rogathinus. His sons and dependants rose up, until an expeditionary force under the tribune Marcian, nephew of the Emperor, succeeded in restoring the peace.
During the reign of Justin II (565–578), great care was shown to Africa. Under the prefect Thomas, during the period 565–570 the network of fortifications was further strengthened and expanded, the administration reformed and decentralized, and largely successful efforts were made to proselytize the Garamantes
The Garamantes (; ) were ancient peoples, who may have descended from Berbers, Berber tribes, Toubous, Toubou tribes, and Saharan Pastoral period, pastoralists that settled in the Fezzan region by at least 1000 BC and established a civilization t ...
of the Fezzan
Fezzan ( , ; ; ; ) is the southwestern region of modern Libya. It is largely desert, but broken by mountains, uplands, and dry river valleys (wadis) in the north, where oases enable ancient towns and villages to survive deep in the otherwise in ...
and the Gaetuli, living to the south of Mauretania Caesariensis. At the same time, Africa was one of the more tranquil regions of the Empire – which was being assaulted on all sides – and this allowed for troops to be transferred from the province to the East.
Conflict with Moorish kingdom of Garmul
In Mauretania, between the Roman outpost of Septem and the province of Caesariensis, various small Moorish kingdoms, which also ruled over Romanized urban populations, had been established ever since the arrival of the Vandals. Little information exists about them, but these were never subdued by the Vandals, and claimed continuity from the Roman Empire, their leaders styling themselves with titles such as '' imperator'', like the chieftain Masties at Arris (in the Aures) in the late 5th century, or, in the case of king Masuna of Altava (modern Ouled Mimoun, northwestAlgeria
Algeria, officially the People's Democratic Republic of Algeria, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It is bordered to Algeria–Tunisia border, the northeast by Tunisia; to Algeria–Libya border, the east by Libya; to Alger ...
), ''rex gentium Maurorum et Romanorum'' in the early 6th century.
When Belisarius defeated the Vandals, the Romano-Moorish kings had apparently acknowledged Roman suzerainty (at least nominally), but soon, taking advantage of the Moorish revolts, renounced it. In the late 560s, the Moorish king Garmul (probably a successor of the aforementioned Masuna of Altava) launched raids into Roman territory, and although he failed to take any significant town, three successive generals (the praetorian prefect Theodore and the ''magister militum'' Theoctistus in 570, and Theoctistus' successor Amabilis in 571) are recorded by John of Biclaro to have been killed by Garmul's forces. His activities, especially when regarded together with the simultaneous Visigoth
The Visigoths (; ) were a Germanic people united under the rule of a king and living within the Roman Empire during late antiquity. The Visigoths first appeared in the Balkans, as a Roman-allied barbarian military group united under the comman ...
attacks in Spania
Spania () was a Roman province, province of the Eastern Roman Empire from 552 until 624 in the south of the Iberian Peninsula and the Balearic Islands. It was established by the List of Byzantine emperors, Emperor Justinian I in an effort to res ...
, presented a clear threat to the province's authorities. Garmul was not the leader of a mere semi-nomadic tribe, but of a fully-fledged barbarian kingdom, with a standing army. Thus the new emperor, Tiberius II Constantine, re-appointed Thomas as praetorian prefect, and the able general Gennadius was posted as ''magister militum'' with the clear aim of reducing Garmul's kingdom. Preparations were lengthy and careful, but the campaign itself, launched in 577–78, was brief and effective, with Gennadius utilizing terror tactics against Garmul's subjects. Garmul was defeated and killed by 579, and the coastal corridor between Tingitana and Caesariensis secured.
Reorganization into the Exarchate
Gennadius remained in Africa as ''magister militum'' for a long time (until the early 590s), and it was he who became the first ''exarchus'' of Africa, when Emperor Maurice established the exarchate in the late 580s, uniting civil and military authority in his hands. The exarchate extended over North Africa, the possessions in Spain at bay, theBalearic Islands
The Balearic Islands are an archipelago in the western Mediterranean Sea, near the eastern coast of the Iberian Peninsula. The archipelago forms a Provinces of Spain, province and Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Spain, ...
, Sardinia, and Corsica. It prospered greatly, and under Heraclius
Heraclius (; 11 February 641) was Byzantine emperor from 610 to 641. His rise to power began in 608, when he and his father, Heraclius the Elder, the Exarch of Africa, led a revolt against the unpopular emperor Phocas.
Heraclius's reign was ...
, African forces overthrew the tyrant Phocas in 610. The exarchate was de facto a semi-autonomous entity from the 640s on, and survived until the fall of Carthage to the Muslims
Muslims () are people who adhere to Islam, a Monotheism, monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God ...
in 698.
List of known ''praefecti praetorio Africae''
*Archelaus (534) *Solomon
Solomon (), also called Jedidiah, was the fourth monarch of the Kingdom of Israel (united monarchy), Kingdom of Israel and Judah, according to the Hebrew Bible. The successor of his father David, he is described as having been the penultimate ...
(1st time, 534–536)
*Symmachus (536–539)
*Solomon
Solomon (), also called Jedidiah, was the fourth monarch of the Kingdom of Israel (united monarchy), Kingdom of Israel and Judah, according to the Hebrew Bible. The successor of his father David, he is described as having been the penultimate ...
(2nd time, 539–544)
*Sergius (544–545)
* Athanasius (545–548, perhaps up to 550)
*Paul (c. 552)
*John (c. 558)
* Boëthius (560–561)John R.C. Martyn, "A New Family Tree for Boethius", ''Parergon'', 23 (2006), p. 6
*John Rogathinus (c. 563)
*Thomas (1st time, 563–565)
*Theodore (c. 570)
*Thomas (2nd time, 574–578)
*Theodore (c. 582)
References
Sources
* * * * * * Julien, C.A. (1931) ''Histoire de l'Afrique du Nord, vol. 1 – Des origines a la conquête arabe'', 1961 edition, Paris: Payot * * * *Procopius
Procopius of Caesarea (; ''Prokópios ho Kaisareús''; ; – 565) was a prominent Late antiquity, late antique Byzantine Greeks, Greek scholar and historian from Caesarea Maritima. Accompanying the Roman general Belisarius in Justinian I, Empe ...
, ''De Bello Vandalico'' (''BV''), Volume II.
*
*
*
{{DEFAULTSORT:Praetorian Prefecture Africa
Byzantine North Africa
Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent after Asia. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 20% of Earth's land area and 6% of its total surfac ...
Roman provinces in Africa
Justinian I
Medieval history of Algeria
Medieval history of Tunisia
6th century in Africa
6th century in the Byzantine Empire
534 establishments
580s disestablishments