Portal venous system on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
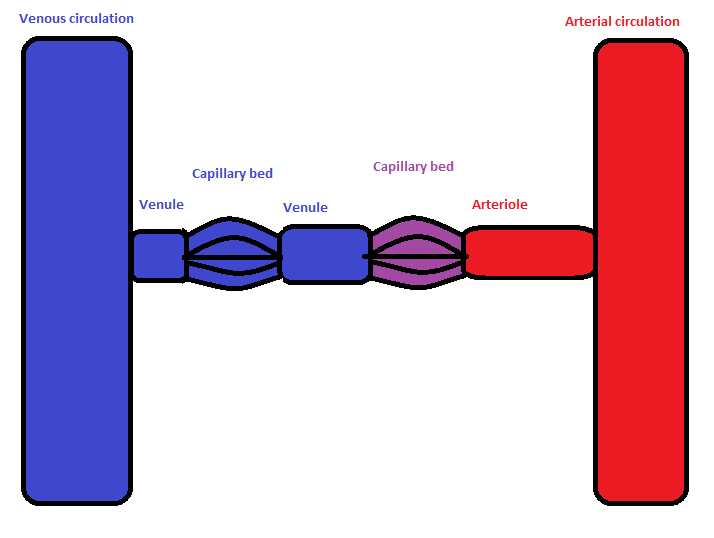 In the
In the
 In the
In the circulatory system
The blood circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the entire body of a human or other vertebrate. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, tha ...
of animals, a portal venous system occurs when a capillary bed
A capillary is a small blood vessel from 5 to 10 micrometres (μm) in diameter. Capillaries are composed of only the tunica intima, consisting of a thin wall of simple squamous endothelial cells. They are the smallest blood vessels in the body: ...
pools into another capillary bed through vein
Veins are blood vessels in humans and most other animals that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are the pulmonary and umbilical veins, both of which carry oxygenated ...
s, without first going through the heart. Both capillary beds and the blood vessel
The blood vessels are the components of the circulatory system that transport blood throughout the human body. These vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to the tissues of the body. They also take waste and carbon dioxide awa ...
s that connect them are considered part of the portal venous system.
They are relatively uncommon as the majority of capillary beds drain into veins which then drain into the heart
The heart is a muscular Organ (biology), organ in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as ca ...
, not into another capillary bed. Portal venous systems are considered venous because the blood vessels that join the two capillary beds are either vein
Veins are blood vessels in humans and most other animals that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are the pulmonary and umbilical veins, both of which carry oxygenated ...
s or venule
A venule is a very small blood vessel in the microcirculation that allows blood to return from the capillary beds to drain into the larger blood vessels, the veins. Venules range from 7μm to 1mm in diameter. Veins contain approximately 70% of ...
s.
Examples of such systems include the hepatic portal system
In human anatomy, the hepatic portal system is the system of veins comprising the hepatic portal vein and its tributaries. It is also called the portal venous system (although it is not the only example of a portal venous system) and splanchnic ...
, the hypophyseal portal system
The hypophyseal portal system is a system of blood vessels in the microcirculation at the base of the brain, connecting the hypothalamus with the anterior pituitary. Its main function is to quickly transport and exchange hormones between the hy ...
, and (in non-mammals) the renal portal system. Unqualified, ''portal venous system'' often refers to the hepatic portal system. For this reason, ''portal vein'' most commonly refers to the hepatic portal vein
The portal vein or hepatic portal vein (HPV) is a blood vessel that carries blood from the gastrointestinal tract, gallbladder, pancreas and spleen to the liver. This blood contains nutrients and toxins extracted from digested contents. Appr ...
.
The functional significance of such a system is that it transports products of one region directly to another region in relatively high concentrations. If the heart were involved in the blood circulation between those two regions, those products would be spread around the rest of the body.
In humans
The humanhepatic portal system
In human anatomy, the hepatic portal system is the system of veins comprising the hepatic portal vein and its tributaries. It is also called the portal venous system (although it is not the only example of a portal venous system) and splanchnic ...
delivers about three-fourths of the blood going to the liver
The liver is a major organ only found in vertebrates which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for digestion and growth. In humans, it i ...
. The final common pathway for transport of venous blood from spleen, pancreas, gallbladder and the abdominal portion of the gastrointestinal tract (with the exception of the inferior part of the anal canal and sigmoid colon) is through the ''hepatic portal vein
The portal vein or hepatic portal vein (HPV) is a blood vessel that carries blood from the gastrointestinal tract, gallbladder, pancreas and spleen to the liver. This blood contains nutrients and toxins extracted from digested contents. Appr ...
''. This portal vein is formed by the union of the ''superior mesenteric vein'' and the ''splenic vein'' posterior to the neck of the pancreas at the level of vertebral body L1. Ascending towards the liver, the portal vein passes posterior to the superior part of the duodenum and enters the right margin of the lesser omentum. It is anterior to the omental foramen and posterior to both the bile duct, which is slightly to the right, and the hepatic artery proper, which is slightly to the left. On approaching the liver, the portal vein divides into right and left branches which enter the liver parenchyma. It gives off the right and left gastric veins, the cystic vein and the para-umbilical veins as tributaries.
The hypophyseal portal system
The hypophyseal portal system is a system of blood vessels in the microcirculation at the base of the brain, connecting the hypothalamus with the anterior pituitary. Its main function is to quickly transport and exchange hormones between the hy ...
portal venous system transports hormones from the hypothalamus to the pituitary gland.
Adrenal medulla capillaries are downstream from adrenal cortex capillaries. This portal system delivers high concentrations of adrenal cortical hormones to the adrenal medulla. In particular, glucocorticoids induce the enzymatic conversion of norepinephrine to epinephrine in the adrenal medulla. By contrast, the ganglia of the sympathetic trunk produce mainly norepinephrine because their cells aren't bathed in high concentrations of glucocorticoids.
Renal tubular capillaries are downstream from renal glomerular capillaries.
The venous blood of the islets of Langerhans is upstream from the capillary system of the exocrine pancreas via ''vasa efferentia''. The acini of the exocrine pancreas are therefore directly exposed to high concentrations of hormones from the endocrine pancreas, forming the pancreatic portal system.
References
{{reflist Angiology