Polylactic acid on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Polylactic acid, also known as poly(lactic acid) or polylactide (PLA), is a thermoplastic
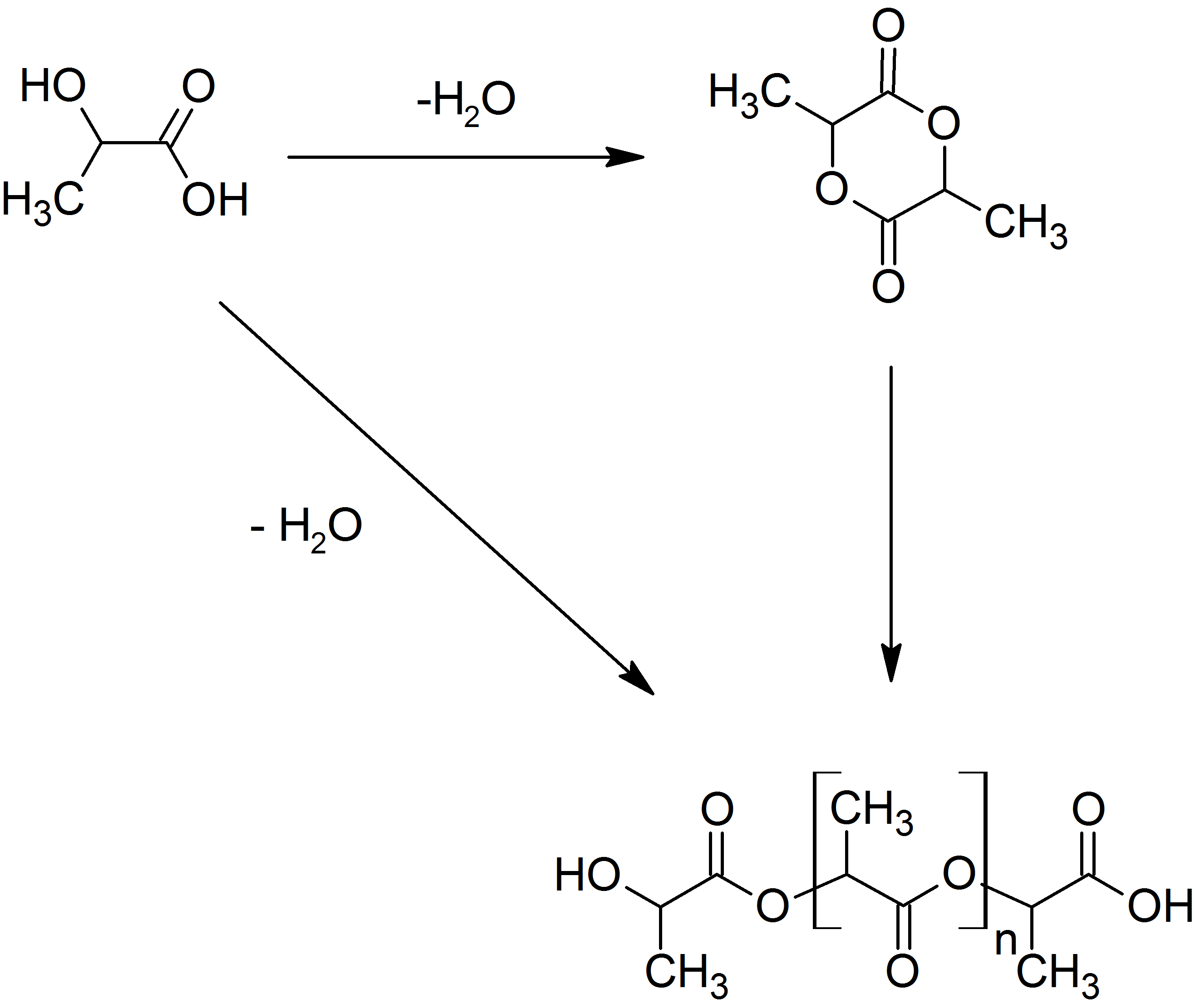 Another method devised is by contacting lactic acid with a zeolite. This condensation reaction is a one-step process, and runs about 100 °C lower in temperature.
Another method devised is by contacting lactic acid with a zeolite. This condensation reaction is a one-step process, and runs about 100 °C lower in temperature.
 PLA is used as a feedstock material in desktop fused filament fabrication by 3D printers, such as RepRap printers.
The boiling point of ethyl acetate is low enough to smooth PLA surfaces in a vapor chamber, similar to using acetone vapor to smooth ABS.
PLA can be solvent welded using
PLA is used as a feedstock material in desktop fused filament fabrication by 3D printers, such as RepRap printers.
The boiling point of ethyl acetate is low enough to smooth PLA surfaces in a vapor chamber, similar to using acetone vapor to smooth ABS.
PLA can be solvent welded using
File:Mulch Film made of PLA-Blend Bio-Flex.jpg, Mulch film made of PLA-blend "bio-flex"
File:Cmglee PLA cups.jpg, Biodegradable PLA cups
File:Teebeutel Polylactid 2009.jpg, Tea bags made of PLA. Peppermint tea is enclosed.
File:3D printing of PLA-CNT microcoil.webm, 3D printing of a
-COO + H2O -> - COOH + -OH-
The degradation rate is very slow in ambient temperatures. A 2017 study found that at 25 °C in seawater, PLA showed no loss of mass over a year, but the study did not measure breakdown of the polymer chains or water absorption. As a result, it degrades poorly in
 Four possible end-of-life scenarios are the most common:
#
Four possible end-of-life scenarios are the most common:
#
"Your plastic pal" , ''The Economist''
{{Use dmy dates, date=January 2018 Biodegradable plastics Bioplastics Polyesters Synthetic fibers Transparent materials Thermoplastics Articles containing video clips Fused filament fabrication
polyester
Polyester is a category of polymers that contain the ester functional group in every repeat unit of their main chain. As a specific material, it most commonly refers to a type called polyethylene terephthalate (PET). Polyesters include natura ...
with backbone formula or , formally obtained by condensation
Condensation is the change of the state of matter from the gas phase into the liquid phase, and is the reverse of vaporization. The word most often refers to the water cycle. It can also be defined as the change in the state of water vapo ...
of lactic acid
Lactic acid is an organic acid. It has a molecular formula . It is white in the solid state and it is miscible with water. When in the dissolved state, it forms a colorless solution. Production includes both artificial synthesis as well as nat ...
with loss of water (hence its name). It can also be prepared by ring-opening polymerization of lactide , the cyclic dimer of the basic repeating unit.
PLA has become a popular material due to it being economically produced from renewable resource
A renewable resource, also known as a flow resource, is a natural resource which will replenish to replace the portion depleted by usage and consumption, either through natural reproduction or other recurring processes in a finite amount of ti ...
s. In 2021, PLA had the highest consumption volume of any bioplastic of the world, although it is still not a commodity polymer. Its widespread application has been hindered by numerous physical and processing shortcomings. PLA is the most widely used plastic filament material in 3D printing. Its low melting point, high strength, low thermal expansion, good layer adhesion, and high heat resistance when annealed make it an ideal material for this purpose. Without annealing, however, PLA has the lowest heat resistance of the common 3D printing plastics.
Although the name "polylactic acid" is widely used, it does not comply with IUPAC
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC ) is an international federation of National Adhering Organizations working for the advancement of the chemical sciences, especially by developing nomenclature and terminology. It is ...
standard nomenclature, which is "poly(lactic acid)". The name "polylactic acid" is potentially ambiguous or confusing, because PLA is not a polyacid ( polyelectrolyte), but rather a polyester.
Chemical properties
Synthesis
The monomer is typically made from fermented plant starch such as from corn,cassava
''Manihot esculenta'', commonly called cassava (), manioc, or yuca (among numerous regional names), is a woody shrub of the spurge family, Euphorbiaceae, native to South America. Although a perennial plant, cassava is extensively cultivated ...
, sugarcane
Sugarcane or sugar cane is a species of (often hybrid) tall, perennial grass (in the genus '' Saccharum'', tribe Andropogoneae) that is used for sugar production. The plants are 2–6 m (6–20 ft) tall with stout, jointed, fibrous stalk ...
or sugar beet pulp
Beet pulp is a byproduct from the processing of sugar beet which is used as fodder for horses and other livestock. Beet pulp is the fibrous material left over after the sugar is extracted from sugar beets. It is supplied either as dried flakes or ...
.
Several industrial routes afford usable (i.e. high molecular weight) PLA. Two main monomers are used: lactic acid
Lactic acid is an organic acid. It has a molecular formula . It is white in the solid state and it is miscible with water. When in the dissolved state, it forms a colorless solution. Production includes both artificial synthesis as well as nat ...
, and the cyclic di-ester, lactide. The most common route to PLA is the ring-opening polymerization
In polymer chemistry, polymerization (American English), or polymerisation (British English), is a process of reacting monomer molecules together in a chemical reaction to form polymer chains or three-dimensional networks. There are many f ...
of lactide with various metal catalyst
Catalysis () is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by adding a substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed in the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recyc ...
s (typically tin octoate
Tin(II) 2-ethylhexanoate or tin(II) octoate or stannous octoate (Sn(Oct)2) is a compound of tin. Produced by the reaction of tin(II) oxide and 2-ethylhexanoic acid, it is a clear colorless liquid at room temperature, though often appears yellow due ...
) in solution or as a suspension. The metal-catalyzed reaction tends to cause racemization of the PLA, reducing its stereoregularity compared to the starting material (usually corn starch).
The direct condensation of lactic acid monomers can also be used to produce PLA. This process needs to be carried out at less than 200 °C; above that temperature, the entropically favored lactide monomer is generated. This reaction generates one equivalent of water for every condensation ( esterification) step. The condensation reaction is reversible and subject to equilibrium, so removal of water is required to generate high molecular weight species. Water removal by application of a vacuum or by azeotropic distillation
In chemistry, azeotropic distillation is any of a range of techniques used to break an azeotrope in distillation. In chemical engineering, ''azeotropic distillation'' usually refers to the specific technique of adding another component to gene ...
is required to drive the reaction toward polycondensation. Molecular weights of 130 kDa can be obtained this way. Even higher molecular weights can be attained by carefully crystallizing the crude polymer from the melt. Carboxylic acid and alcohol end groups are thus concentrated in the amorphous region of the solid polymer, and so they can react. Molecular weights of 128–152 kDa are obtainable thus.
: Another method devised is by contacting lactic acid with a zeolite. This condensation reaction is a one-step process, and runs about 100 °C lower in temperature.
Another method devised is by contacting lactic acid with a zeolite. This condensation reaction is a one-step process, and runs about 100 °C lower in temperature.
Stereoisomers
Due to the chiral nature of lactic acid, several distinct forms of polylactide exist: poly-L-lactide (PLLA) is the product resulting from polymerization of L,L-lactide (also known as L-lactide). Progress in biotechnology has resulted in the development of commercial production of the D enantiomer form. Polymerization of aracemic mixture
In chemistry, a racemic mixture, or racemate (), is one that has equal amounts of left- and right-handed enantiomers of a chiral molecule or salt. Racemic mixtures are rare in nature, but many compounds are produced industrially as racemates. ...
of L- and D-lactides usually leads to the synthesis of poly-DL-lactide (PDLLA), which is amorphous. Use of stereospecific catalysts can lead to heterotactic PLA which has been found to show crystallinity. The degree of crystallinity, and hence many important properties, is largely controlled by the ratio of D to L enantiomers used, and to a lesser extent on the type of catalyst used. Apart from lactic acid and lactide, lactic acid ''O''-carboxyanhydride ("lac-OCA"), a five-membered cyclic compound has been used academically as well. This compound is more reactive than lactide, because its polymerization is driven by the loss of one equivalent of carbon dioxide per equivalent of lactic acid. Water is not a co-product.
The direct biosynthesis of PLA, in a manner similar to production of poly(hydroxyalkanoate)s, has been reported.
Physical and mechanical properties
PLA polymers range from amorphous glassy polymer to semi-crystalline and highly crystalline polymer with a glass transition 60–65 °C, a melting temperature 130-180 °C, and aYoung's modulus
Young's modulus E, the Young modulus, or the modulus of elasticity in tension or compression (i.e., negative tension), is a mechanical property that measures the tensile or compressive stiffness of a solid material when the force is applied ...
2.7–16 GPa. Heat-resistant PLA can withstand temperatures of 110 °C. The basic mechanical properties of PLA are between those of polystyrene
Polystyrene (PS) is a synthetic polymer made from monomers of the Aromatic hydrocarbon, aromatic hydrocarbon styrene. Polystyrene can be solid or foamed. General-purpose polystyrene is clear, hard, and brittle. It is an inexpensive resin pe ...
and PET. The melting temperature of PLLA can be increased by 40–50 °C and its heat deflection temperature can be increased from approximately 60 °C to up to 190 °C by physically blending the polymer with PDLA (poly-D-lactide). PDLA and PLLA form a highly regular stereocomplex with increased crystallinity. The temperature stability is maximised when a 1:1 blend is used, but even at lower concentrations of 3–10% of PDLA, there is still a substantial improvement. In the latter case, PDLA acts as a nucleating agent, thereby increasing the crystallization rate. Biodegradation
Biodegradation is the breakdown of organic matter by microorganisms, such as bacteria and fungi. It is generally assumed to be a natural process, which differentiates it from composting. Composting is a human-driven process in which biodegra ...
of PDLA is slower than for PLA due to the higher crystallinity of PDLA. The flexural modulus of PLA is higher than polystyrene and PLA has good heat sealability.
Several technologies such as annealing, adding nucleating
In thermodynamics, nucleation is the first step in the formation of either a new thermodynamic phase or structure via self-assembly or self-organization within a substance or mixture. Nucleation is typically defined to be the process that deter ...
agents, forming composites with fibers or nano-particles, chain extending and introducing crosslink structures have been used to enhance the mechanical properties of PLA polymers. Polylactic acid can be processed like most thermoplastics into fiber
Fiber or fibre (from la, fibra, links=no) is a natural or artificial substance that is significantly longer than it is wide. Fibers are often used in the manufacture of other materials. The strongest engineering materials often incorporate ...
(for example, using conventional melt spinning processes) and film. PLA has similar mechanical properties to PETE polymer, but has a significantly lower maximum continuous use temperature.
Racemic PLA and pure PLLA have low glass transition temperatures, making them undesirable because of low strength and melting point. A stereocomplex of PDLA and PLLA has a higher glass transition temperature, lending it more mechanical strength.
The high surface energy of PLA results in good printability, making it widely used in 3D printing. The tensile strength for 3D printed PLA was previously determined.
Solvents
PLA is soluble in a range of organic solvents. Ethyl acetate is widely used because of its ease of access and low risk. It is useful in 3D printers for cleaning the extruder heads and for removing PLA supports. Other safe solvents includepropylene carbonate
Propylene carbonate (often abbreviated PC) is an organic compound with the formula C4H6O3. It is a cyclic carbonate ester derived from propylene glycol. This colorless and odorless liquid is useful as a polar, aprotic solvent. Propylene carbonat ...
, which is safer than ethyl acetate but is difficult to purchase commercially. Pyridine
Pyridine is a basic heterocyclic organic compound with the chemical formula . It is structurally related to benzene, with one methine group replaced by a nitrogen atom. It is a highly flammable, weakly alkaline, water-miscible liquid w ...
can be used, but it has a distinct fish odor and is less safe than ethyl acetate. PLA is also soluble in hot benzene
Benzene is an organic chemical compound with the molecular formula C6H6. The benzene molecule is composed of six carbon atoms joined in a planar ring with one hydrogen atom attached to each. Because it contains only carbon and hydrogen atoms ...
, tetrahydrofuran
Tetrahydrofuran (THF), or oxolane, is an organic compound with the formula (CH2)4O. The compound is classified as heterocyclic compound, specifically a cyclic ether. It is a colorless, water- miscible organic liquid with low viscosity. It is ...
, and dioxane.
Fabrication
PLA objects can be fabricated by 3D printing, casting, injection moulding,extrusion
Extrusion is a process used to create objects of a fixed cross-sectional profile by pushing material through a die of the desired cross-section. Its two main advantages over other manufacturing processes are its ability to create very complex c ...
, machining, and solvent welding.
 PLA is used as a feedstock material in desktop fused filament fabrication by 3D printers, such as RepRap printers.
The boiling point of ethyl acetate is low enough to smooth PLA surfaces in a vapor chamber, similar to using acetone vapor to smooth ABS.
PLA can be solvent welded using
PLA is used as a feedstock material in desktop fused filament fabrication by 3D printers, such as RepRap printers.
The boiling point of ethyl acetate is low enough to smooth PLA surfaces in a vapor chamber, similar to using acetone vapor to smooth ABS.
PLA can be solvent welded using dichloromethane
Dichloromethane (DCM or methylene chloride, methylene bichloride) is an organochlorine compound with the formula . This colorless, volatile liquid with a chloroform-like, sweet odour is widely used as a solvent. Although it is not miscible wit ...
. Acetone
Acetone (2-propanone or dimethyl ketone), is an organic compound with the formula . It is the simplest and smallest ketone (). It is a colorless, highly volatile and flammable liquid with a characteristic pungent odour.
Acetone is miscibl ...
also softens the surface of PLA, making it sticky without dissolving it, for welding to another PLA surface.
PLA-printed solids can be encased in plaster-like moulding materials, then burned out in a furnace, so that the resulting void can be filled with molten metal. This is known as "lost PLA casting", a type of investment casting
Investment casting is an industrial process based on lost-wax casting, one of the oldest known metal-forming techniques. The term "lost-wax casting" can also refer to modern investment casting processes.
Investment casting has been used in vari ...
.
Applications
Consumer goods
PLA is used in a large variety of consumer products such as disposable tableware, cutlery, housings for kitchen appliances and electronics such as laptops and handheld devices, and microwavable trays. (However, PLA is not suitable for microwavable containers because of its low glass transition temperature.) It is used for compost bags, food packaging and loose-fill packaging material that is cast, injection molded, or spun. In the form of a film, it shrinks upon heating, allowing it to be used in shrink tunnels. In the form of fibers, it is used for monofilament fishing line and netting. In the form of nonwoven fabrics, it is used forupholstery
Upholstery is the work of providing furniture, especially seats, with padding, springs, webbing, and fabric or leather covers. The word also refers to the materials used to upholster something.
''Upholstery'' comes from the Middle English ...
, disposable garments, awning
An awning or overhang is a secondary covering attached to the exterior wall of a building. It is typically composed of canvas woven of acrylic, cotton or polyester yarn, or vinyl laminated to polyester fabric that is stretched tightly over a li ...
s, feminine hygiene products, and diapers.
PLA has applications in engineering plastics, where the stereocomplex is blended with a rubber-like polymer such as ABS. Such blends have good form stability and visual transparency, making them useful in low-end packaging applications.
PLA is used for automotive parts such as floor mats, panels, and covers. Its heat resistance and durability are inferior to the widely used polypropylene
Polypropylene (PP), also known as polypropene, is a thermoplastic polymer used in a wide variety of applications. It is produced via chain-growth polymerization from the monomer propylene.
Polypropylene
belongs to the group of polyolefins a ...
(PP), but its properties are improved by means such as capping of the end groups to reduce hydrolysis.
Agricultural
In the form of fibers, PLA is used for monofilament fishing line and netting for vegetation and weed prevention. It is used for sandbags, planting pots, binding tape and ropes .Medical
PLA can degrade into innocuous lactic acid, making it suitable for use as medical implants in the form of anchors, screws, plates, pins, rods, and mesh. Depending on the type used, it breaks down inside the body within 6 months to 2 years. This gradual degradation is desirable for a support structure, because it gradually transfers the load to the body (e.g., to the bone) as that area heals. The strength characteristics of PLA and PLLA implants are well documented. Thanks to its bio-compatibility and biodegradability, PLA found interest as a polymeric scaffold for drug delivery purposes. The composite blend of poly(L-lactide-''co''-D,L-lactide) (PLDLLA) with tricalcium phosphate (TCP) is used as PLDLLA/TCP scaffolds for bone engineering. Poly-L-lactic acid (PLLA) is the main ingredient inSculptra Sculptra, , is a proprietary formulation of poly-L-lactic acid (PLLA) that is an FDA-approved dermal filler manufactured by Dermik Laboratories, which conducts the American business of Aventis Dermatology, the global dermatology unit of Aventis ( ...
, a facial volume enhancer used for treating lipoatrophy of the cheeks.
PLLA is used to stimulate collagen synthesis in fibroblasts via foreign body reaction in the presence of macrophages. Macrophages act as a stimulant in secretion of cytokines and mediators such as TGF-β
Transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) is a multifunctional cytokine belonging to the transforming growth factor superfamily that includes three different mammalian isoforms (TGF-β 1 to 3, HGNC symbols TGFB1, TGFB2, TGFB3) and many other s ...
, which stimulate the fibroblast to secrete collagen into the surrounding tissue. Therefore, PLLA has potential applications in the dermatological studies.
PLLA is under investigation as a scaffold that can generate a small amount of electric current
An electric current is a stream of charged particles, such as electrons or ions, moving through an electrical conductor or space. It is measured as the net rate of flow of electric charge through a surface or into a control volume. The movi ...
via the piezoelectric effect that stimulates the growth of mechanically robust cartilage in multiple animal models.
microcoil
A microcoil is a tiny electrical conductor such as a wire in the shape of a spiral or helix which could be a solenoid or a planar structure.
Uses
NMR spectroscopy and micro-MRI
One field where these are found is nuclear magnetic resonance ( ...
using a conductive mixture of polylactide and carbon nanotubes.
File:3D Printed Macrognathism.jpg, 3D printed human skull with data from computed tomography. Transparent PLA.
Degradation
PLA is degraded abiotically by three mechanisms: #Hydrolysis
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water is the nucleophile.
Biological hydrolysi ...
: The ester groups of the main chain are cleaved, thus reducing molecular weight.
# Thermal decomposition: A complex phenomenon leading to the appearance of different compounds such as lighter molecules and linear and cyclic oligomers with different ''Mw'', and lactide.
# Photodegradation: UV radiation induces degradation. This is a factor mainly where PLA is exposed to sunlight in its applications in plasticulture, packaging containers and films.
The hydrolytic reaction is: landfill
A landfill site, also known as a tip, dump, rubbish dump, garbage dump, or dumping ground, is a site for the disposal of waste materials. Landfill is the oldest and most common form of waste disposal, although the systematic burial of the wast ...
s and household composts, but is effectively digested in hotter industrial composts, usually degrading best at temperatures of over .
Pure PLA foams are selectively hydrolysed in Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium (DMEM) supplemented with fetal bovine serum (FBS) (a solution mimicking body fluid). After 30 days of submersion in DMEM+FBS, a PLLA scaffold lost about 20% of its weight.
PLA samples of various molecular weights were degraded into methyl lactate (a green solvent) by using a metal complex catalyst.
PLA can also be degraded by some bacteria, such as ''Amycolatopsis
''Amycolatopsis'' is a genus of high GC-content bacteria within the family Pseudonocardiaceae.
The genus is known for producing many types of antibiotics, including
* Epoxyquinomicin, related to ''Amycolatopsis sulphurea'', are a class of weak ...
'' and '' Saccharothrix''. A purified protease from ''Amycolatopsis
''Amycolatopsis'' is a genus of high GC-content bacteria within the family Pseudonocardiaceae.
The genus is known for producing many types of antibiotics, including
* Epoxyquinomicin, related to ''Amycolatopsis sulphurea'', are a class of weak ...
'' sp., PLA depolymerase, can also degrade PLA. Enzymes such as pronase and most effectively proteinase K from '' Tritirachium album'' degrade PLA.
End of life
Recycling
Recycling is the process of converting waste materials into new materials and objects. The Energy recycling, recovery of energy from waste materials is often included in this concept. The recyclability of a material depends on its ability t ...
: which can be either chemical or mechanical. Currently, the SPI resin identification code 7 ("others") is applicable for PLA. In Belgium, Galactic started the first pilot unit to chemically recycle PLA (Loopla). Unlike mechanical recycling, waste material can hold various contaminants. Polylactic acid can be chemically recycled to monomer by thermal depolymerization or hydrolysis. When purified, the monomer can be used for the manufacturing of virgin PLA with no loss of original properties ( cradle-to-cradle recycling). End-of-life PLA can be chemically recycled to methyl lactate by transesterification.
# Compost
Compost is a mixture of ingredients used as plant fertilizer and to improve soil's physical, chemical and biological properties. It is commonly prepared by decomposing plant, food waste, recycling organic materials and manure. The resulting ...
ing: PLA is biodegradable under industrial composting conditions, starting with chemical hydrolysis process, followed by microbial digestion, to ultimately degrade the PLA. Under industrial composting conditions (), PLA can partly (about half) decompose into water and carbon dioxide in 60 days, after which the remainder decomposes much more slowly, with the rate depending on the material's degree of crystallinity. Environments without the necessary conditions will see very slow decomposition akin to that of non-bioplastics, not fully decomposing for hundreds or thousands of years.
# Incineration: PLA can be incinerated without producing chlorine-containing chemicals or heavy metals because it contains only carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent—its atom making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds. It belongs to group 14 of the periodic table. Carbon ma ...
, oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements ...
, and hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-to ...
atoms. Since it does not contain chlorine it does not produce dioxins or hydrochloric acid
Hydrochloric acid, also known as muriatic acid, is an aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride. It is a colorless solution with a distinctive pungent smell. It is classified as a strong acid. It is a component of the gastric acid in the dige ...
during incineration. PLA can be combusted with no remaining residue. This and other results suggest that incineration is an environmentally friendly disposal of waste PLA.
# Landfill
A landfill site, also known as a tip, dump, rubbish dump, garbage dump, or dumping ground, is a site for the disposal of waste materials. Landfill is the oldest and most common form of waste disposal, although the systematic burial of the wast ...
: the least preferable option is landfilling because PLA degrades very slowly in ambient temperatures, often as slowly as other plastics.
See also
*Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) ( chemical formula (C8H8)''x''·(C4H6)''y''·(C3H3N)''z'' is a common thermoplastic polymer. Its glass transition temperature is approximately . ABS is amorphous and therefore has no true melting point.
...
(ABS) - also used for 3D printing
* Cellophane, polyglycolide, plastarch material, poly-3-hydroxybutyrate – biologically derived polymers
* Polilactofate
Polilactofate (PLF) is a copolymer of PDLL (poly(d,l-lactide)) and a phosphoester
In chemistry, a phosphodiester bond occurs when exactly two of the hydroxyl groups () in phosphoric acid react with hydroxyl groups on other molecules to form t ...
* Polycaprolactone
Polycaprolactone (PCL) is a biodegradable polyester with a low melting point of around 60 °C and a glass transition temperature of about −60 °C. The most common use of polycaprolactone is in the production of speciality polyu ...
* Zein
Zein is a class of prolamine protein found in maize (corn). It is usually manufactured as a powder from corn gluten meal. Zein is one of the best understood plant proteins.Momany, Frank A.; Sessa, David J.; Lawton, John C.; Selling, Gordon W.; ...
, shellac – biologically derived coating materials
References
External links
"Your plastic pal" , ''The Economist''
{{Use dmy dates, date=January 2018 Biodegradable plastics Bioplastics Polyesters Synthetic fibers Transparent materials Thermoplastics Articles containing video clips Fused filament fabrication