polio on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Poliomyelitis ( ), commonly shortened to polio, is an
 Poliomyelitis does not affect any species other than humans. The disease is caused by infection with a member of the
Poliomyelitis does not affect any species other than humans. The disease is caused by infection with a member of the
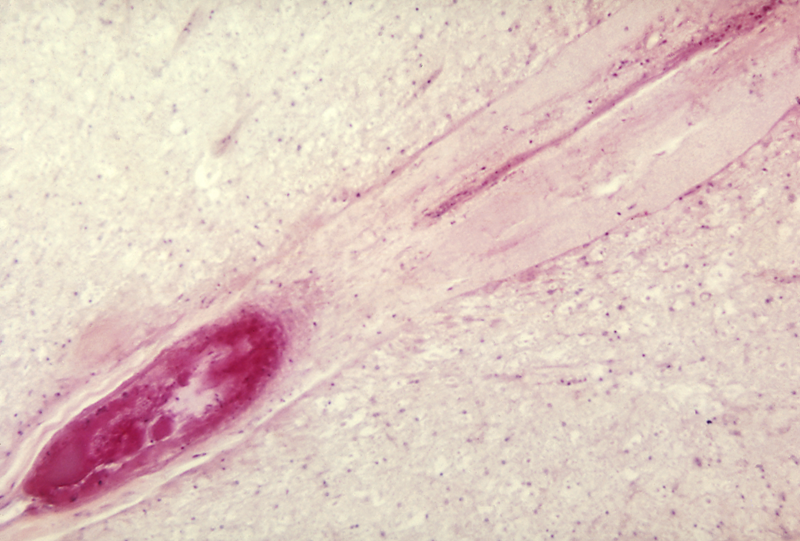 Poliovirus enters the body through the mouth, infecting the first cells with which it comes in contact – the
Poliovirus enters the body through the mouth, infecting the first cells with which it comes in contact – the
 In around one percent of infections, poliovirus spreads along certain nerve fiber pathways, preferentially replicating in and destroying
In around one percent of infections, poliovirus spreads along certain nerve fiber pathways, preferentially replicating in and destroying
 Spinal polio, the most common form of paralytic poliomyelitis, results from viral invasion of the motor neurons of the anterior horn cells, or the
Spinal polio, the most common form of paralytic poliomyelitis, results from viral invasion of the motor neurons of the anterior horn cells, or the
 Making up about two percent of cases of paralytic polio, bulbar polio occurs when poliovirus invades and destroys nerves within the bulbar region of the
Making up about two percent of cases of paralytic polio, bulbar polio occurs when poliovirus invades and destroys nerves within the bulbar region of the
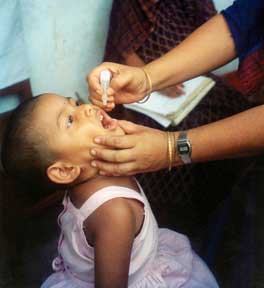 Two types of vaccine are used throughout the world to combat polio: an inactivated poliovirus given by injection, and a weakened poliovirus given by mouth. Both types induce immunity to polio and are effective in protecting individuals from disease.
The inactivated polio vaccine (IPV) was developed in 1952 by Jonas Salk at the University of Pittsburgh, and announced to the world on 12 April 1955. The Salk vaccine is based on poliovirus grown in a type of monkey kidney
Two types of vaccine are used throughout the world to combat polio: an inactivated poliovirus given by injection, and a weakened poliovirus given by mouth. Both types induce immunity to polio and are effective in protecting individuals from disease.
The inactivated polio vaccine (IPV) was developed in 1952 by Jonas Salk at the University of Pittsburgh, and announced to the world on 12 April 1955. The Salk vaccine is based on poliovirus grown in a type of monkey kidney  Because the oral polio vaccine is inexpensive, easy to administer, and produces excellent immunity in the intestine (which helps prevent infection with wild virus in areas where it is
Because the oral polio vaccine is inexpensive, easy to administer, and produces excellent immunity in the intestine (which helps prevent infection with wild virus in areas where it is
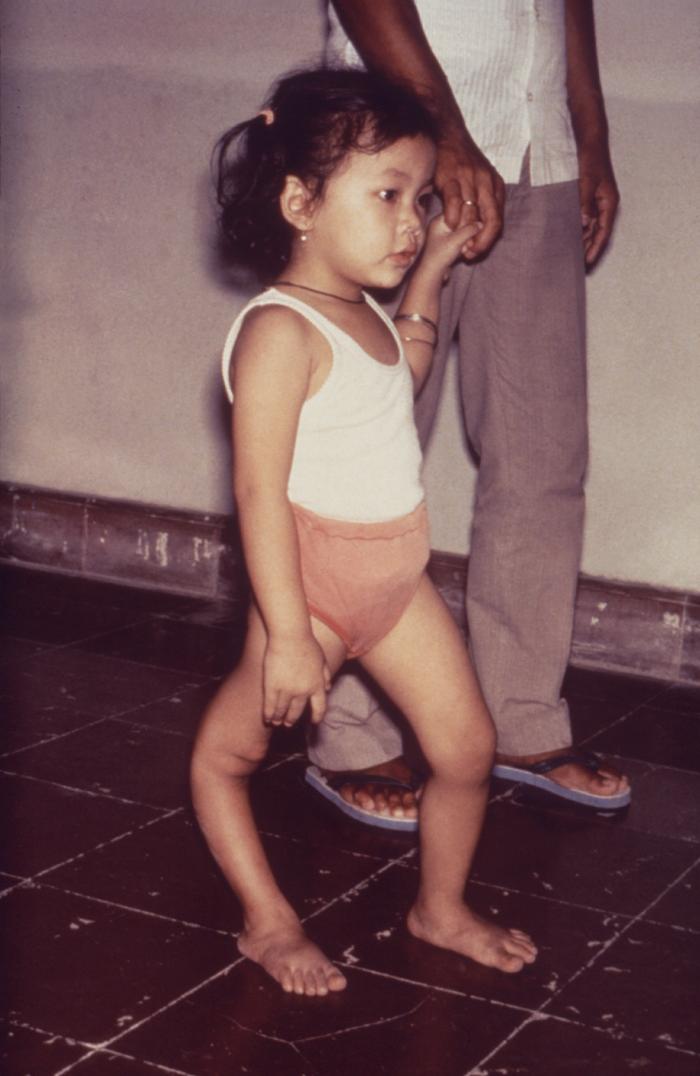 Patients with abortive polio infections recover completely. In those who develop only aseptic meningitis, the symptoms can be expected to persist for two to ten days, followed by complete recovery. In cases of spinal polio, if the affected nerve cells are completely destroyed, paralysis will be permanent; cells that are not destroyed, but lose function temporarily, may recover within four to six weeks after onset. Reproduced online with permission by Post-Polio Health International; retrieved on 10 November 2007. Half the patients with spinal polio recover fully; one-quarter recover with mild disability, and the remaining quarter are left with severe disability. The degree of both acute paralysis and residual paralysis is likely to be proportional to the degree of viremia, and
Patients with abortive polio infections recover completely. In those who develop only aseptic meningitis, the symptoms can be expected to persist for two to ten days, followed by complete recovery. In cases of spinal polio, if the affected nerve cells are completely destroyed, paralysis will be permanent; cells that are not destroyed, but lose function temporarily, may recover within four to six weeks after onset. Reproduced online with permission by Post-Polio Health International; retrieved on 10 November 2007. Half the patients with spinal polio recover fully; one-quarter recover with mild disability, and the remaining quarter are left with severe disability. The degree of both acute paralysis and residual paralysis is likely to be proportional to the degree of viremia, and
 Paralysis, length differences and deformations of the lower extremities can lead to a hindrance when walking with compensation mechanisms that lead to a severe impairment of the gait pattern. In order to be able to stand and walk safely and to improve the gait pattern, orthotics can be included in the therapy concept. Today, modern materials and functional elements enable the orthosis to be specifically adapted to the requirements resulting from the patient's gait. Mechanical stance phase control knee joints may secure the knee joint in the early stance phases and release again for knee flexion when the swing phase is initiated. With the help of an orthotic treatment with a stance phase control knee joint, a natural gait pattern can be achieved despite mechanical protection against unwanted knee flexion. In these cases, locked knee joints are often used, which have a good safety function, but do not allow knee flexion when walking during swing phase. With such joints, the knee joint remains mechanically blocked during the swing phase. Patients with locked knee joints must swing the leg forward with the knee extended even during the swing phase. This only works if the patient develops compensatory mechanisms, e.g. by raising the body's center of gravity in the swing phase (Duchenne limping) or by swinging the orthotic leg to the side (circumduction).
Paralysis, length differences and deformations of the lower extremities can lead to a hindrance when walking with compensation mechanisms that lead to a severe impairment of the gait pattern. In order to be able to stand and walk safely and to improve the gait pattern, orthotics can be included in the therapy concept. Today, modern materials and functional elements enable the orthosis to be specifically adapted to the requirements resulting from the patient's gait. Mechanical stance phase control knee joints may secure the knee joint in the early stance phases and release again for knee flexion when the swing phase is initiated. With the help of an orthotic treatment with a stance phase control knee joint, a natural gait pattern can be achieved despite mechanical protection against unwanted knee flexion. In these cases, locked knee joints are often used, which have a good safety function, but do not allow knee flexion when walking during swing phase. With such joints, the knee joint remains mechanically blocked during the swing phase. Patients with locked knee joints must swing the leg forward with the knee extended even during the swing phase. This only works if the patient develops compensatory mechanisms, e.g. by raising the body's center of gravity in the swing phase (Duchenne limping) or by swinging the orthotic leg to the side (circumduction).
 The effects of polio have been known since
The effects of polio have been known since
online
* * Hecht, Alan, and I. Edward Alcamo. ''Polio'' (2003
online copy
for middle schools * * , a major scholarly history. * Rai, Anushree, et al. "Polio returns to the USA: An epidemiological alert." ''Annals of Medicine and Surgery'' 82 (2022)
online
* * * * * Zimmermann, Jonas. "War on Disease: Polio Eradication in the United States." ''Historia. scriber'' 15 (2023): 263-280
online
infectious disease
An infection is the invasion of tissue (biology), tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host (biology), host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmis ...
caused by the poliovirus. Approximately 75% of cases are asymptomatic
Asymptomatic (or clinically silent) is an adjective categorising the medical conditions (i.e., injuries or diseases) that patients carry but without experiencing their symptoms, despite an explicit diagnosis (e.g., a positive medical test).
P ...
; mild symptoms which can occur include sore throat and fever; in a proportion of cases more severe symptoms develop such as headache
A headache, also known as cephalalgia, is the symptom of pain in the face, head, or neck. It can occur as a migraine, tension-type headache, or cluster headache. There is an increased risk of Depression (mood), depression in those with severe ...
, neck stiffness, and paresthesia
Paresthesia is a sensation of the skin that may feel like numbness (''hypoesthesia''), tingling, pricking, chilling, or burning. It can be temporary or Chronic condition, chronic and has many possible underlying causes. Paresthesia is usually p ...
. These symptoms usually pass within one or two weeks. A less common symptom is permanent paralysis
Paralysis (: paralyses; also known as plegia) is a loss of Motor skill, motor function in one or more Skeletal muscle, muscles. Paralysis can also be accompanied by a loss of feeling (sensory loss) in the affected area if there is sensory d ...
, and possible death in extreme cases.. Years after recovery, post-polio syndrome may occur, with a slow development of muscle weakness similar to what the person had during the initial infection.
Polio occurs naturally only in humans. It is highly infectious, and is spread from person to person either through fecal–oral transmission (e.g. poor hygiene, or by ingestion of food or water contaminated by human feces), or via the oral–oral route. Those who are infected may spread the disease for up to six weeks even if no symptoms are present. The disease may be diagnosed by finding the virus in the feces
Feces (also known as faeces American and British English spelling differences#ae and oe, or fæces; : faex) are the solid or semi-solid remains of food that was not digested in the small intestine, and has been broken down by bacteria in the ...
or detecting antibodies
An antibody (Ab) or immunoglobulin (Ig) is a large, Y-shaped protein belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily which is used by the immune system to identify and neutralize antigens such as bacteria and viruses, including those that caus ...
against it in the blood.
Poliomyelitis has existed for thousands of years, with depictions of the disease in ancient art. The disease was first recognized as a distinct condition by the English physician
A physician, medical practitioner (British English), medical doctor, or simply doctor is a health professional who practices medicine, which is concerned with promoting, maintaining or restoring health through the Medical education, study, Med ...
Michael Underwood in 1789, and the virus that causes it was first identified in 1909 by the Austrian immunologist Karl Landsteiner. Major outbreaks started to occur in the late 19th century in Europe and the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
, and in the 20th century, it became one of the most worrying childhood diseases. Following the introduction of polio vaccines in the 1950s, polio incidence declined rapidly. , only Pakistan and Afghanistan remain endemic for wild poliovirus (WPV).
Once infected, there is no specific treatment. The disease can be prevented by the polio vaccine
Polio vaccines are vaccines used to prevent poliomyelitis (polio). Two types are used: an inactivated vaccine, inactivated poliovirus given by injection (IPV) and a attenuated vaccine, weakened poliovirus given by mouth (OPV). The World Healt ...
, with multiple doses required for lifelong protection. There are two broad types of polio vaccine; an injected polio vaccine (IPV) using inactivated poliovirus and an oral polio vaccine (OPV) containing attenuated (weakened) live virus. Through the use of both types of vaccine, incidence of wild polio has decreased from an estimated 350,000 cases in 1988 to 30 confirmed cases in 2022, confined to just three countries. In rare cases, the traditional OPV was able to revert to a virulent form. An improved oral vaccine with greater genetic stability (nOPV2) was developed and granted full licensure and prequalification by the World Health Organization in December 2023.
Signs and symptoms
The term "poliomyelitis" is used to identify the disease caused by any of the three serotypes of poliovirus. Two basic patterns of polio infection are described: a minor illness that does not involve thecentral nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain, spinal cord and retina. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity o ...
(CNS), sometimes called abortive poliomyelitis, and a major illness involving the CNS, which may be paralytic or nonparalytic. Adults are more likely to develop symptoms, including severe symptoms, than children.
In most people with a normal immune system, a poliovirus infection is asymptomatic
Asymptomatic (or clinically silent) is an adjective categorising the medical conditions (i.e., injuries or diseases) that patients carry but without experiencing their symptoms, despite an explicit diagnosis (e.g., a positive medical test).
P ...
. In about 25% of cases, the infection produces minor symptoms which may include sore throat
Sore throat, also known as throat pain, is pain or irritation of the throat. The majority of sore throats are caused by a virus, for which antibiotics are not helpful.
For sore throat caused by bacteria (GAS), treatment with antibiotics may hel ...
and low fever. These symptoms are temporary and full recovery occurs within one or two weeks.
In about 1 percent of infections the virus can migrate from the gastrointestinal tract into the central nervous system (CNS). Most patients with CNS involvement develop nonparalytic aseptic meningitis, with symptoms of headache, neck, back, abdominal and extremity pain, fever, vomiting, stomach pain, lethargy
Lethargy is a state of tiredness, sleepiness, weariness, fatigue, sluggishness, or lack of energy. It can be accompanied by depression, decreased motivation, or apathy. Lethargy can be a normal response to inadequate sleep, overexertion, overw ...
, and irritability. About one to five in 1,000 cases progress to paralytic disease, in which the muscles become weak, floppy and poorly controlled, and, finally, completely paralyzed; this condition is known as acute flaccid paralysis. The weakness most often involves the legs, but may less commonly involve the muscles of the head, neck, and diaphragm. Depending on the site of paralysis, paralytic poliomyelitis is classified as spinal, bulbar, or bulbospinal. In those who develop paralysis, between 2 and 10 percent die as the paralysis affects the breathing muscles.
Encephalitis
Encephalitis is inflammation of the Human brain, brain. The severity can be variable with symptoms including reduction or alteration in consciousness, aphasia, headache, fever, confusion, a stiff neck, and vomiting. Complications may include se ...
, an infection of the brain tissue itself, can occur in rare cases, and is usually restricted to infants. It is characterized by confusion, changes in mental status, headaches, fever, and, less commonly, seizure
A seizure is a sudden, brief disruption of brain activity caused by abnormal, excessive, or synchronous neuronal firing. Depending on the regions of the brain involved, seizures can lead to changes in movement, sensation, behavior, awareness, o ...
s and spastic paralysis.
Etymology
The term ''poliomyelitis'' derives from theAncient Greek
Ancient Greek (, ; ) includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the classical antiquity, ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Greek ...
(), meaning "grey", ( "marrow"), referring to the grey matter of the spinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue that extends from the medulla oblongata in the lower brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone) of vertebrate animals. The center of the spinal c ...
, and the suffix ''-itis
Inflammation (from ) is part of the biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. The five cardinal signs are heat, pain, redness, swelling, and loss of function (Latin ''calor'', '' ...
'', which denotes inflammation
Inflammation (from ) is part of the biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. The five cardinal signs are heat, pain, redness, swelling, and loss of function (Latin ''calor'', '' ...
, i.e., inflammation of the spinal cord's grey matter. The word was first used in 1874 and is attributed to the German physician Adolf Kussmaul. The first recorded use of the abbreviated version ''polio'' was in the '' Indianapolis Star'' in 1911.
Cause
genus
Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family (taxonomy), family as used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In bino ...
'' Enterovirus'' known as poliovirus (PV). This group of RNA virus
An RNA virus is a virus characterized by a ribonucleic acid (RNA) based genome. The genome can be single-stranded RNA (ssRNA) or double-stranded (Double-stranded RNA, dsRNA). Notable human diseases caused by RNA viruses include influenza, SARS, ...
es colonize the gastrointestinal tract
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the Digestion, digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The tract is the largest of the body's systems, after the cardiovascula ...
– specifically the oropharynx
The pharynx (: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the mouth and nasal cavity, and above the esophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs respectively). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though its ...
and the intestine
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The tract is the largest of the body's systems, after the cardiovascular system. T ...
. Its structure
A structure is an arrangement and organization of interrelated elements in a material object or system, or the object or system so organized. Material structures include man-made objects such as buildings and machines and natural objects such as ...
is quite simple, composed of a single (+) sense RNA
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule that is essential for most biological functions, either by performing the function itself (non-coding RNA) or by forming a template for the production of proteins (messenger RNA). RNA and deoxyrib ...
genome
A genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding genes, other functional regions of the genome such as ...
enclosed in a protein shell called a capsid
A capsid is the protein shell of a virus, enclosing its genetic material. It consists of several oligomeric (repeating) structural subunits made of protein called protomers. The observable 3-dimensional morphological subunits, which may or m ...
. In addition to protecting the virus' genetic material, the capsid proteins enable poliovirus to infect certain types of cells. Three serotypes of poliovirus have been identified – wild poliovirus type 1 (WPV1), type 2 (WPV2), and type 3 (WPV3) – each with a slightly different capsid protein. All three are extremely virulent and produce the same disease symptoms. WPV1 is the most commonly encountered form, and the one most closely associated with paralysis. (Available free on Medscape; registration required.) WPV2 was certified as eradicated in 2015 and WPV3 certified as eradicated in 2019.
The incubation period
Incubation period (also known as the latent period or latency period) is the time elapsed between exposure to a pathogenic organism, a chemical, or ionizing radiation, radiation, and when symptoms and signs are first apparent. In a typical infect ...
(from exposure to the first signs and symptoms) ranges from three to six days for nonparalytic polio. If the disease progresses to cause paralysis, this occurs within 7 to 21 days.
Individuals who are exposed to the virus, either through infection or by immunization
Immunization, or immunisation, is the process by which an individual's immune system becomes fortified against an infectious agent (known as the antigen, immunogen). When this system is exposed to molecules that are foreign to the body, called ' ...
via polio vaccine
Polio vaccines are vaccines used to prevent poliomyelitis (polio). Two types are used: an inactivated vaccine, inactivated poliovirus given by injection (IPV) and a attenuated vaccine, weakened poliovirus given by mouth (OPV). The World Healt ...
, develop immunity. In immune individuals, IgA antibodies
An antibody (Ab) or immunoglobulin (Ig) is a large, Y-shaped protein belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily which is used by the immune system to identify and neutralize antigens such as bacteria and viruses, including those that caus ...
against poliovirus are present in the tonsils and gastrointestinal tract
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the Digestion, digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The tract is the largest of the body's systems, after the cardiovascula ...
and able to block virus replication; IgG and IgM antibodies against PV can prevent the spread of the virus to motor neurons of the central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain, spinal cord and retina. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity o ...
. Infection or vaccination with one serotype of poliovirus does not provide immunity against the other serotypes, and full immunity requires exposure to each serotype.
A rare condition with a similar presentation, nonpoliovirus poliomyelitis, may result from infections with enteroviruses other than poliovirus.
The oral polio vaccine, which has been in use since 1961, contains weakened viruses that can replicate. On rare occasions, these may be transmitted from the vaccinated person to other people; in communities with good vaccine coverage, transmission is limited, and the virus dies out. In communities with low vaccine coverage, this weakened virus may continue to circulate and, over time may mutate and revert to a virulent form. Polio arising from this cause is referred to as ''circulating vaccine-derived poliovirus'' (cVDPV) or ''variant poliovirus'' in order to distinguish it from the natural or "wild" poliovirus (WPV).
Transmission
Poliomyelitis is highly contagious. The disease is transmitted primarily via thefecal–oral route
The fecal–oral route (also called the oral–fecal route or orofecal route) describes a particular route of transmission of a disease wherein pathogens in fecal particles pass from one person to the mouth of another person. Main causes of fec ...
, by ingesting contaminated food or water. It is occasionally transmitted via the oral–oral route. It is seasonal in temperate climate
In geography, the temperate climates of Earth occur in the middle latitudes (approximately 23.5° to 66.5° N/S of the Equator), which span between the tropics and the polar regions of Earth. These zones generally have wider temperature ra ...
s, with peak transmission occurring in summer and autumn. These seasonal differences are far less pronounced in tropical
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the equator, where the sun may shine directly overhead. This contrasts with the temperate or polar regions of Earth, where the Sun can never be directly overhead. This is because of Earth's ax ...
areas. Polio is most infectious between 7 and 10 days before and after the appearance of symptoms, but transmission is possible as long as the virus remains in the saliva or feces. Virus particles can be excreted in the feces
Feces (also known as faeces American and British English spelling differences#ae and oe, or fæces; : faex) are the solid or semi-solid remains of food that was not digested in the small intestine, and has been broken down by bacteria in the ...
for up to six weeks.
Factors that increase the risk of polio infection include pregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring gestation, gestates inside a woman's uterus. A multiple birth, multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Conception (biology), Conception usually occurs ...
, being very old or very young, immune deficiency, and malnutrition
Malnutrition occurs when an organism gets too few or too many nutrients, resulting in health problems. Specifically, it is a deficiency, excess, or imbalance of energy, protein and other nutrients which adversely affects the body's tissues a ...
. Although the virus can cross the maternal-fetal barrier during pregnancy, the fetus does not appear to be affected by either maternal infection or polio vaccination. Maternal antibodies also cross the placenta
The placenta (: placentas or placentae) is a temporary embryonic and later fetal organ that begins developing from the blastocyst shortly after implantation. It plays critical roles in facilitating nutrient, gas, and waste exchange between ...
, providing passive immunity that protects the infant from polio infection during the first few months of life.
Pathophysiology
 Poliovirus enters the body through the mouth, infecting the first cells with which it comes in contact – the
Poliovirus enters the body through the mouth, infecting the first cells with which it comes in contact – the pharynx
The pharynx (: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the human mouth, mouth and nasal cavity, and above the esophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs respectively). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates ...
and intestinal mucosa. It gains entry by binding to an immunoglobulin-like receptor, known as the poliovirus receptor or CD155, on the cell membrane. The virus then hijacks the host cell's own machinery, and begins to replicate. Poliovirus divides within gastrointestinal cells for about a week, from where it spreads to the tonsils (specifically the follicular dendritic cells residing within the tonsilar germinal centers), the intestinal lymphoid tissue including the M cells of Peyer's patches, and the deep cervical and mesenteric lymph nodes, where it multiplies abundantly. The virus is subsequently absorbed into the bloodstream.
Known as viremia, the presence of a virus in the bloodstream enables it to be widely distributed throughout the body. Poliovirus can survive and multiply within the blood and lymphatics for long periods of time, sometimes as long as 17 weeks. In a small percentage of cases, it can spread and replicate in other sites, such as brown fat, the reticuloendothelial tissues, and muscle. This sustained replication causes a major viremia, and leads to the development of minor influenza-like symptoms. Rarely, this may progress and the virus may invade the central nervous system, provoking a local inflammatory response. In most cases, this causes a self-limiting inflammation of the meninges
In anatomy, the meninges (; meninx ; ) are the three membranes that envelop the brain and spinal cord. In mammals, the meninges are the dura mater, the arachnoid mater, and the pia mater. Cerebrospinal fluid is located in the subarachnoid spac ...
, the layers of tissue surrounding the brain
The brain is an organ (biology), organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It consists of nervous tissue and is typically located in the head (cephalization), usually near organs for ...
, which is known as nonparalytic aseptic meningitis. Penetration of the CNS provides no known benefit to the virus, and is quite possibly an incidental deviation of a normal gastrointestinal infection. The mechanisms by which poliovirus spreads to the CNS are poorly understood, but it appears to be primarily a chance event – largely independent of the age, gender, or socioeconomic
Economics () is a behavioral science that studies the Production (economics), production, distribution (economics), distribution, and Consumption (economics), consumption of goods and services.
Economics focuses on the behaviour and interac ...
position of the individual.
Paralytic polio
 In around one percent of infections, poliovirus spreads along certain nerve fiber pathways, preferentially replicating in and destroying
In around one percent of infections, poliovirus spreads along certain nerve fiber pathways, preferentially replicating in and destroying motor neuron
A motor neuron (or motoneuron), also known as efferent neuron is a neuron whose cell body is located in the motor cortex, brainstem or the spinal cord, and whose axon (fiber) projects to the spinal cord or outside of the spinal cord to directly o ...
s within the spinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue that extends from the medulla oblongata in the lower brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone) of vertebrate animals. The center of the spinal c ...
, brain stem
The brainstem (or brain stem) is the posterior stalk-like part of the brain that connects the cerebrum with the spinal cord. In the human brain the brainstem is composed of the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata. The midbrain is co ...
, or motor cortex
The motor cortex is the region of the cerebral cortex involved in the planning, motor control, control, and execution of voluntary movements.
The motor cortex is an area of the frontal lobe located in the posterior precentral gyrus immediately ...
. This leads to the development of paralytic poliomyelitis, the various forms of which (spinal, bulbar, and bulbospinal) vary only with the amount of neuronal damage and inflammation that occurs, and the region of the CNS affected.
The destruction of neuronal cells produces lesion
A lesion is any damage or abnormal change in the tissue of an organism, usually caused by injury or diseases. The term ''Lesion'' is derived from the Latin meaning "injury". Lesions may occur in both plants and animals.
Types
There is no de ...
s within the spinal ganglia; these may also occur in the reticular formation
The reticular formation is a set of interconnected nuclei in the brainstem that spans from the lower end of the medulla oblongata to the upper end of the midbrain. The neurons of the reticular formation make up a complex set of neural networks ...
, vestibular nuclei
The vestibular nuclei (VN) are the cranial nuclei for the vestibular nerve located in the brainstem.
In Terminologia Anatomica, they are grouped in both the pons and the medulla in the brainstem
The brainstem (or brain stem) is the poste ...
, cerebellar vermis
The cerebellar vermis (from Latin ''vermis,'' "worm") is located in the medial, cortico-nuclear zone of the cerebellum, which is in the posterior cranial fossa, posterior fossa of the cranium. The primary fissure in the vermis curves ventrolatera ...
, and deep cerebellar nuclei. Inflammation associated with nerve cell
A neuron (American English), neurone (British English), or nerve cell, is an excitable cell that fires electric signals called action potentials across a neural network in the nervous system. They are located in the nervous system and help to ...
destruction often alters the color and appearance of the gray matter in the spinal column
The spinal column, also known as the vertebral column, spine or backbone, is the core part of the axial skeleton in vertebrates. The vertebral column is the defining and eponymous characteristic of the vertebrate. The spinal column is a segmen ...
, causing it to appear reddish and swollen. Other destructive changes associated with paralytic disease occur in the forebrain
In the anatomy of the brain of vertebrates, the forebrain or prosencephalon is the rostral (forward-most) portion of the brain. The forebrain controls body temperature, reproductive functions, eating, sleeping, and the display of emotions.
Ve ...
region, specifically the hypothalamus
The hypothalamus (: hypothalami; ) is a small part of the vertebrate brain that contains a number of nucleus (neuroanatomy), nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions is to link the nervous system to the endocrin ...
and thalamus
The thalamus (: thalami; from Greek language, Greek Wikt:θάλαμος, θάλαμος, "chamber") is a large mass of gray matter on the lateral wall of the third ventricle forming the wikt:dorsal, dorsal part of the diencephalon (a division of ...
.
Early symptoms of paralytic polio include high fever, headache, stiffness in the back and neck, asymmetrical weakness of various muscles, sensitivity to touch, difficulty swallowing, muscle pain, loss of superficial and deep reflexes, paresthesia
Paresthesia is a sensation of the skin that may feel like numbness (''hypoesthesia''), tingling, pricking, chilling, or burning. It can be temporary or Chronic condition, chronic and has many possible underlying causes. Paresthesia is usually p ...
(pins and needles), irritability, constipation, or difficulty urinating. Paralysis generally develops one to ten days after early symptoms begin, progresses for two to three days, and is usually complete by the time the fever breaks.
The likelihood of developing paralytic polio increases with age, as does the extent of paralysis. In children, nonparalytic meningitis is the most likely consequence of CNS involvement, and paralysis occurs in only one in 1000 cases. In adults, paralysis occurs in one in 75 cases. Reproduced online with permission by Lincolnshire Post-Polio Library; retrieved on 10 November 2007. In children under five years of age, paralysis of one leg is most common; in adults, extensive paralysis of the chest
The thorax (: thoraces or thoraxes) or chest is a part of the anatomy of mammals and other tetrapod animals located between the neck and the abdomen.
In insects, crustaceans, and the extinct trilobites, the thorax is one of the three main di ...
and abdomen
The abdomen (colloquially called the gut, belly, tummy, midriff, tucky, or stomach) is the front part of the torso between the thorax (chest) and pelvis in humans and in other vertebrates. The area occupied by the abdomen is called the abdominal ...
also affecting all four limbs – quadriplegia – is more likely. Paralysis rates also vary depending on the serotype of the infecting poliovirus; the highest rates of paralysis (one in 200) are associated with poliovirus type 1, the lowest rates (one in 2,000) are associated with type 2.
Spinal polio
ventral
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to describe unambiguously the anatomy of humans and other animals. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position prov ...
(front) grey matter section in the spinal column
The spinal column, also known as the vertebral column, spine or backbone, is the core part of the axial skeleton in vertebrates. The vertebral column is the defining and eponymous characteristic of the vertebrate. The spinal column is a segmen ...
, which are responsible for movement of the muscles, including those of the trunk, limbs, and the intercostal muscles. Virus invasion causes inflammation of the nerve cells, leading to damage or destruction of motor neuron ganglia
A ganglion (: ganglia) is a group of neuron cell bodies in the peripheral nervous system. In the somatic nervous system, this includes dorsal root ganglia and trigeminal ganglia among a few others. In the autonomic nervous system, there a ...
. When spinal neurons die, Wallerian degeneration takes place, leading to weakness of those muscles formerly innervated by the now-dead neurons. With the destruction of nerve cells, the muscles no longer receive signals from the brain or spinal cord; without nerve stimulation, the muscles atrophy
Atrophy is the partial or complete wasting away of a part of the body. Causes of atrophy include mutations (which can destroy the gene to build up the organ), malnutrition, poor nourishment, poor circulatory system, circulation, loss of hormone, ...
, becoming weak, floppy and poorly controlled, and finally completely paralyzed. Maximum paralysis progresses rapidly (two to four days), and usually involves fever and muscle pain. Deep tendon reflexes are also affected, and are typically absent or diminished; sensation (the ability to feel) in the paralyzed limbs, however, is not affected.
The extent of spinal paralysis depends on the region of the cord affected, which may be cervical, thoracic
The thorax (: thoraces or thoraxes) or chest is a part of the anatomy of mammals and other tetrapod animals located between the neck and the abdomen.
In insects, crustaceans, and the extinct trilobites, the thorax is one of the three main ...
, or lumbar
In tetrapod anatomy, lumbar is an adjective that means of or pertaining to the abdominal segment of the torso, between the diaphragm (anatomy), diaphragm and the sacrum.
Naming and location
The lumbar region is sometimes referred to as the lowe ...
. The virus may affect muscles on both sides of the body, but more often the paralysis is asymmetrical. Any limb or combination of limbs may be affected – one leg, one arm, or both legs and both arms. Paralysis is often more severe proximally (where the limb joins the body) than distally (the fingertips and toes).
Bulbar polio
brain stem
The brainstem (or brain stem) is the posterior stalk-like part of the brain that connects the cerebrum with the spinal cord. In the human brain the brainstem is composed of the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata. The midbrain is co ...
. The bulbar region is a white matter
White matter refers to areas of the central nervous system that are mainly made up of myelinated axons, also called Nerve tract, tracts. Long thought to be passive tissue, white matter affects learning and brain functions, modulating the distr ...
pathway that connects the cerebral cortex
The cerebral cortex, also known as the cerebral mantle, is the outer layer of neural tissue of the cerebrum of the brain in humans and other mammals. It is the largest site of Neuron, neural integration in the central nervous system, and plays ...
to the brain stem. The destruction of these nerves weakens the muscles supplied by the cranial nerves, producing symptoms of encephalitis
Encephalitis is inflammation of the Human brain, brain. The severity can be variable with symptoms including reduction or alteration in consciousness, aphasia, headache, fever, confusion, a stiff neck, and vomiting. Complications may include se ...
, and causes difficulty breathing, speaking and swallowing. Critical nerves affected are the glossopharyngeal nerve
The glossopharyngeal nerve (), also known as the ninth cranial nerve, cranial nerve IX, or simply CN IX, is a cranial nerve that exits the brainstem from the sides of the upper Medulla oblongata, medulla, just anterior (closer to the nose) to t ...
(which partially controls swallowing and functions in the throat, tongue movement, and taste), the vagus nerve
The vagus nerve, also known as the tenth cranial nerve (CN X), plays a crucial role in the autonomic nervous system, which is responsible for regulating involuntary functions within the human body. This nerve carries both sensory and motor fibe ...
(which sends signals to the heart, intestines, and lungs), and the accessory nerve (which controls upper neck movement). Due to the effect on swallowing, secretions of mucus
Mucus (, ) is a slippery aqueous secretion produced by, and covering, mucous membranes. It is typically produced from cells found in mucous glands, although it may also originate from mixed glands, which contain both Serous fluid, serous and muc ...
may build up in the airway, causing suffocation. Other signs and symptoms include facial weakness (caused by destruction of the trigeminal nerve
In neuroanatomy, the trigeminal nerve (literal translation, lit. ''triplet'' nerve), also known as the fifth cranial nerve, cranial nerve V, or simply CN V, is a cranial nerve responsible for Sense, sensation in the face and motor functions ...
and facial nerve
The facial nerve, also known as the seventh cranial nerve, cranial nerve VII, or simply CN VII, is a cranial nerve that emerges from the pons of the brainstem, controls the muscles of facial expression, and functions in the conveyance of ta ...
, which innervate the cheeks, tear ducts, gums, and muscles of the face, among other structures), double vision, difficulty in chewing, and abnormal respiratory rate, depth, and rhythm (which may lead to respiratory arrest). Pulmonary edema
Pulmonary edema (British English: oedema), also known as pulmonary congestion, is excessive fluid accumulation in the tissue or air spaces (usually alveoli) of the lungs. This leads to impaired gas exchange, most often leading to shortness ...
and shock are also possible and may be fatal.
Bulbospinal polio
Approximately 19 percent of all paralytic polio cases have both bulbar and spinal symptoms; this subtype is called respiratory or bulbospinal polio. Here, the virus affects the upper part of the cervical spinal cord (cervical vertebrae
In tetrapods, cervical vertebrae (: vertebra) are the vertebrae of the neck, immediately below the skull. Truncal vertebrae (divided into thoracic and lumbar vertebrae in mammals) lie caudal (toward the tail) of cervical vertebrae. In saurop ...
C3 through C5), and paralysis of the diaphragm occurs. The critical nerves affected are the phrenic nerve (which drives the diaphragm to inflate the lungs
The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in many animals, including humans. In mammals and most other tetrapods, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of the heart. Their function in the respiratory syste ...
) and those that drive the muscles needed for swallowing. By destroying these nerves, this form of polio affects breathing, making it difficult or impossible for the patient to breathe without the support of a ventilator. It can lead to paralysis of the arms and legs and may also affect swallowing and heart functions.
Diagnosis
Paralytic poliomyelitis may be clinically suspected in individuals experiencing acute onset of flaccid paralysis in one or more limbs with decreased or absent tendon reflexes in the affected limbs that cannot be attributed to another apparent cause, and without sensory orcognitive
Cognition is the "mental action or process of acquiring knowledge and understanding through thought, experience, and the senses". It encompasses all aspects of intellectual functions and processes such as: perception, attention, thought, ...
loss.
A laboratory diagnosis is usually made based on the recovery of poliovirus from a stool sample or a swab of the pharynx
The pharynx (: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the human mouth, mouth and nasal cavity, and above the esophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs respectively). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates ...
. Rarely, it may be possible to identify poliovirus in the blood or in the cerebrospinal fluid
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear, colorless Extracellular fluid#Transcellular fluid, transcellular body fluid found within the meninges, meningeal tissue that surrounds the vertebrate brain and spinal cord, and in the ventricular system, ven ...
. Poliovirus samples are further analysed using reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) or genomic sequencing to determine the serotype (i.e., 1, 2, or 3), and whether the virus is a wild or vaccine-derived strain.
Prevention
Passive immunization
In 1950, William Hammon at theUniversity of Pittsburgh
The University of Pittsburgh (Pitt) is a Commonwealth System of Higher Education, state-related research university in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, United States. The university is composed of seventeen undergraduate and graduate schools and colle ...
purified the gamma globulin component of the blood plasma
Blood plasma is a light Amber (color), amber-colored liquid component of blood in which blood cells are absent, but which contains Blood protein, proteins and other constituents of whole blood in Suspension (chemistry), suspension. It makes up ...
of polio survivors. Hammon proposed the gamma globulin, which contained antibodies to poliovirus, could be used to halt poliovirus infection, prevent disease, and reduce the severity of disease in other patients who had contracted polio. The results of a large clinical trial
Clinical trials are prospective biomedical or behavioral research studies on human subject research, human participants designed to answer specific questions about biomedical or behavioral interventions, including new treatments (such as novel v ...
were promising; the gamma globulin was shown to be about 80 percent effective in preventing the development of paralytic poliomyelitis. It was also shown to reduce the severity of the disease in patients who developed polio. Due to the limited supply of blood plasma gamma globulin was later deemed impractical for widespread use and the medical community focused on the development of a polio vaccine.
Vaccine
 Two types of vaccine are used throughout the world to combat polio: an inactivated poliovirus given by injection, and a weakened poliovirus given by mouth. Both types induce immunity to polio and are effective in protecting individuals from disease.
The inactivated polio vaccine (IPV) was developed in 1952 by Jonas Salk at the University of Pittsburgh, and announced to the world on 12 April 1955. The Salk vaccine is based on poliovirus grown in a type of monkey kidney
Two types of vaccine are used throughout the world to combat polio: an inactivated poliovirus given by injection, and a weakened poliovirus given by mouth. Both types induce immunity to polio and are effective in protecting individuals from disease.
The inactivated polio vaccine (IPV) was developed in 1952 by Jonas Salk at the University of Pittsburgh, and announced to the world on 12 April 1955. The Salk vaccine is based on poliovirus grown in a type of monkey kidney tissue culture
Tissue culture is the growth of tissue (biology), tissues or cell (biology), cells in an artificial medium separate from the parent organism. This technique is also called micropropagation. This is typically facilitated via use of a liquid, semi-s ...
(vero cell
Vero cells are a lineage of cells used in cell cultures. The 'Vero' lineage was isolated from kidney epithelial cells extracted from an African green monkey ('' Chlorocebus'' sp.; formerly called ''Cercopithecus aethiops'', this group of monk ...
line), which is chemically inactivated with formalin. After two doses of IPV (given by injection), 90 percent or more of individuals develop protective antibody to all three serotype
A serotype or serovar is a distinct variation within a species of bacteria or virus or among immune cells of different individuals. These microorganisms, viruses, or Cell (biology), cells are classified together based on their shared reactivity ...
s of poliovirus, and at least 99 percent are immune to poliovirus following three doses.
Subsequently, Albert Sabin developed a polio vaccine that can be administered orally (oral polio vaccine - OPV), comprising a live, attenuated virus. It was produced by the repeated passage of the virus through nonhuman cells at subphysiological
Physiology (; ) is the science, scientific study of function (biology), functions and mechanism (biology), mechanisms in a life, living system. As a branches of science, subdiscipline of biology, physiology focuses on how organisms, organ syst ...
temperatures. The attenuated poliovirus in the Sabin vaccine replicates very efficiently in the gut, the primary site of wild poliovirus infection and replication, but the vaccine strain is unable to replicate efficiently within nervous system
In biology, the nervous system is the complex system, highly complex part of an animal that coordinates its behavior, actions and sense, sensory information by transmitting action potential, signals to and from different parts of its body. Th ...
tissue. A single dose of Sabin's trivalent OPV produces immunity to all three poliovirus serotypes in about 50 percent of recipients. Three doses of OPV produce protective antibody to all three poliovirus types in more than 95 percent of recipients. Human trials of Sabin's vaccine began in 1957, and in 1958, it was selected, in competition with the live attenuated vaccines of Koprowski and other researchers, by the US National Institutes of Health. Accessed 16 December 2009. Licensed in 1962, it rapidly became the only oral polio vaccine used worldwide.
OPV efficiently blocks person-to-person transmission of wild poliovirus by oral–oral and fecal–oral routes, thereby protecting both individual vaccine recipients and the wider community. The live attenuated virus may be transmitted from vaccinees to their unvaccinated contacts, resulting in wider community immunity. IPV confers good immunity but is less effective at preventing spread of wild poliovirus by the fecal–oral route.
endemic
Endemism is the state of a species being found only in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also foun ...
), it has been the vaccine of choice for controlling poliomyelitis in many countries. On very rare occasions, the attenuated virus in the Sabin OPV can revert into a form that can paralyze. In 2017, cases caused by vaccine-derived poliovirus (cVDPV) outnumbered wild poliovirus cases for the first time, due to wild polio cases hitting record lows. Most industrialized countries have switched to inactivated polio vaccine, which cannot revert, either as the sole vaccine against poliomyelitis or in combination with oral polio vaccine.
An improved oral vaccine (Novel oral polio vaccine type 2 - nOPV2) began development in 2011 and was granted emergency licensing in 2021, and subsequently full licensure in December 2023. This has greater genetic stability than the traditional oral vaccine and is less likely to revert to a virulent form.
Treatment
There is nocure
A cure is a substance or procedure that resolves a medical condition. This may include a medication, a surgery, surgical operation, a lifestyle change, or even a philosophical shift that alleviates a person's suffering or achieves a state of heali ...
for polio, but there are treatments. The focus of modern treatment has been on providing relief of symptoms, speeding recovery and preventing complications. Supportive measures include antibiotics
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy ...
to prevent infections in weakened muscles, analgesics for pain, moderate exercise and a nutritious diet. Treatment of polio often requires long-term rehabilitation, including occupational therapy
Occupational therapy (OT), also known as ergotherapy, is a healthcare profession. Ergotherapy is derived from the Greek wiktionary:ergon, ergon which is allied to work, to act and to be active. Occupational therapy is based on the assumption t ...
, physical therapy
Physical therapy (PT), also known as physiotherapy, is a healthcare profession, as well as the care provided by physical therapists who promote, maintain, or restore health through patient education, physical intervention, disease preventio ...
, braces, corrective shoes and, in some cases, orthopedic surgery.
Portable ventilators may be required to support breathing. Historically, a noninvasive, negative-pressure ventilator, more commonly called an iron lung, was used to artificially maintain respiration during an acute polio infection until a person could breathe independently (generally about one to two weeks). The use of iron lungs is largely obsolete in modern medicine as more modern breathing therapies have been developed and due to the eradication of polio in most of the world.
Other historical treatments for polio include hydrotherapy
Hydrotherapy, formerly called hydropathy and also called water cure, is a branch of alternative medicine (particularly naturopathy), occupational therapy, and Physical therapy, physiotherapy, that involves the use of water for pain relief and ...
, electrotherapy, massage and passive motion exercises, and surgical treatments, such as tendon lengthening and nerve grafting.
Prognosis
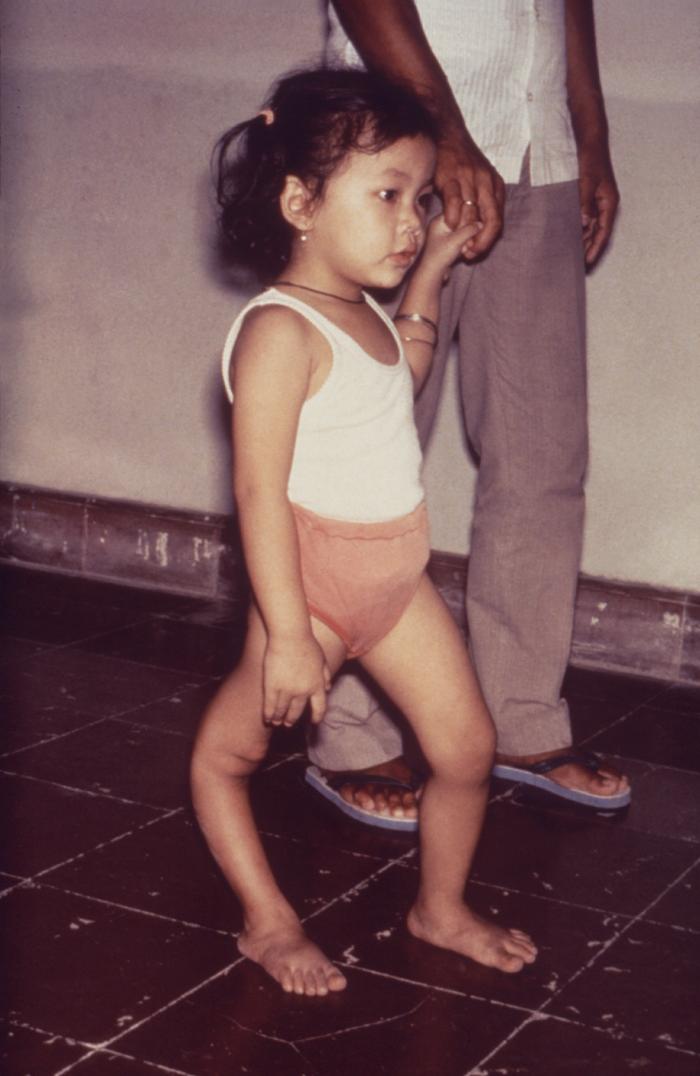 Patients with abortive polio infections recover completely. In those who develop only aseptic meningitis, the symptoms can be expected to persist for two to ten days, followed by complete recovery. In cases of spinal polio, if the affected nerve cells are completely destroyed, paralysis will be permanent; cells that are not destroyed, but lose function temporarily, may recover within four to six weeks after onset. Reproduced online with permission by Post-Polio Health International; retrieved on 10 November 2007. Half the patients with spinal polio recover fully; one-quarter recover with mild disability, and the remaining quarter are left with severe disability. The degree of both acute paralysis and residual paralysis is likely to be proportional to the degree of viremia, and
Patients with abortive polio infections recover completely. In those who develop only aseptic meningitis, the symptoms can be expected to persist for two to ten days, followed by complete recovery. In cases of spinal polio, if the affected nerve cells are completely destroyed, paralysis will be permanent; cells that are not destroyed, but lose function temporarily, may recover within four to six weeks after onset. Reproduced online with permission by Post-Polio Health International; retrieved on 10 November 2007. Half the patients with spinal polio recover fully; one-quarter recover with mild disability, and the remaining quarter are left with severe disability. The degree of both acute paralysis and residual paralysis is likely to be proportional to the degree of viremia, and inversely proportional
In mathematics, two sequences of numbers, often experimental data, are proportional or directly proportional if their corresponding elements have a constant ratio. The ratio is called ''coefficient of proportionality'' (or ''proportionality ...
to the degree of immunity. Spinal polio is rarely fatal.
Without respiratory support, consequences of poliomyelitis with respiratory involvement include suffocation or pneumonia from aspiration of secretions. Overall, 5 to 10 percent of patients with paralytic polio die due to the paralysis of muscles used for breathing. The case fatality rate (CFR) varies by age: 2 to 5 percent of children and up to 15 to 30 percent of adults die. Bulbar polio often causes death if respiratory support is not provided; with support, its CFR ranges from 25 to 75 percent, depending on the age of the patient. When intermittent positive pressure ventilation is available, the fatalities can be reduced to 15 percent.
Recovery
Many cases of poliomyelitis result in only temporary paralysis. Generally in these cases, nerve impulses return to the paralyzed muscle within a month, and recovery is complete in six to eight months. The neurophysiological processes involved in recovery following acute paralytic poliomyelitis are quite effective; muscles are able to retain normal strength even if half the original motor neurons have been lost. Paralysis remaining after one year is likely to be permanent, although some recovery of muscle strength is possible up to 18 months after infection. One mechanism involved in recovery is nerve terminal sprouting, in which remaining brainstem and spinal cord motor neurons develop new branches, or axonal sprouts. These sprouts can reinnervate orphaned muscle fibers that have been denervated by acute polio infection, restoring the fibers' capacity to contract and improving strength. Terminal sprouting may generate a few significantly enlarged motor neurons doing work previously performed by as many as four or five units: a single motor neuron that once controlled 200 muscle cells might control 800 to 1000 cells. Other mechanisms that occur during the rehabilitation phase, and contribute to muscle strength restoration, include myofiber hypertrophy – enlargement of muscle fibers through exercise and activity – and transformation of type II muscle fibers to type I muscle fibers. In addition to these physiological processes, the body can compensate for residual paralysis in other ways. Weaker muscles can be used at a higher than usual intensity relative to the muscle's maximal capacity, little-used muscles can be developed, andligament
A ligament is a type of fibrous connective tissue in the body that connects bones to other bones. It also connects flight feathers to bones, in dinosaurs and birds. All 30,000 species of amniotes (land animals with internal bones) have liga ...
s can enable stability and mobility.
Complications
Residual complications of paralytic polio often occur following the initial recovery process. Muscleparesis
In medicine, paresis (), compound word from Greek , (πᾰρᾰ- “beside” + ἵημι “let go, release”), is a condition typified by a weakness of voluntary movement, or by partial loss of voluntary movement or by impaired movement. Whe ...
and paralysis can sometimes result in skeletal
A skeleton is the structural frame that supports the body of most animals. There are several types of skeletons, including the exoskeleton, which is a rigid outer shell that holds up an organism's shape; the endoskeleton, a rigid internal fram ...
deformities, tightening of the joints, and movement disability. Once the muscles in the limb become flaccid, they may interfere with the function of other muscles. A typical manifestation of this problem is equinus foot (similar to club foot). This deformity develops when the muscles that pull the toes downward are working, but those that pull it upward are not, and the foot naturally tends to drop toward the ground. If the problem is left untreated, the Achilles tendon
The Achilles tendon or heel cord, also known as the calcaneal tendon, is a tendon at the back of the lower leg, and is the thickest in the human body. It serves to attach the plantaris, gastrocnemius (calf) and soleus muscles to the calcane ...
s at the back of the foot retract and the foot cannot take on a normal position. People with polio that develop equinus foot cannot walk properly because they cannot put their heels on the ground. A similar situation can develop if the arms become paralyzed.
In some cases the growth of an affected leg is slowed by polio, while the other leg continues to grow normally. The result is that one leg is shorter than the other and the person limps and leans to one side, in turn leading to deformities of the spine (such as scoliosis
Scoliosis (: scolioses) is a condition in which a person's Vertebral column, spine has an irregular curve in the coronal plane. The curve is usually S- or C-shaped over three dimensions. In some, the degree of curve is stable, while in others ...
). Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a systemic skeletal disorder characterized by low bone mass, micro-architectural deterioration of bone tissue leading to more porous bone, and consequent increase in Bone fracture, fracture risk.
It is the most common reason f ...
and increased likelihood of bone fracture
A bone fracture (abbreviated FRX or Fx, Fx, or #) is a medical condition in which there is a partial or complete break in the continuity of any bone in the body. In more severe cases, the bone may be broken into several fragments, known as a ''c ...
s may occur. An intervention to prevent or lessen length disparity can be to perform an epiphysiodesis on the distal femoral and proximal tibial/fibular condyles, so that limb's growth is artificially stunted, and by the time of epiphyseal (growth) plate closure, the legs are more equal in length. Alternatively, a person can be fitted with custom-made footwear which corrects the difference in leg lengths. Other surgery to re-balance muscular agonist/antagonist imbalances may also be helpful. Extended use of braces or wheelchairs may cause compression neuropathy, as well as a loss of proper function of the vein
Veins () are blood vessels in the circulatory system of humans and most other animals that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are those of the pulmonary and feta ...
s in the legs, due to pooling of blood in paralyzed lower limbs. Complications from prolonged immobility involving the lungs
The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in many animals, including humans. In mammals and most other tetrapods, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of the heart. Their function in the respiratory syste ...
, kidney
In humans, the kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped blood-filtering organ (anatomy), organs that are a multilobar, multipapillary form of mammalian kidneys, usually without signs of external lobulation. They are located on the left and rig ...
s and heart
The heart is a muscular Organ (biology), organ found in humans and other animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels. The heart and blood vessels together make the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrie ...
include pulmonary edema
Pulmonary edema (British English: oedema), also known as pulmonary congestion, is excessive fluid accumulation in the tissue or air spaces (usually alveoli) of the lungs. This leads to impaired gas exchange, most often leading to shortness ...
, aspiration pneumonia
Aspiration pneumonia is a type of lung infection that is due to a relatively large amount of material from the stomach or mouth entering the lungs. Signs and symptoms often include fever and cough of relatively rapid onset. Complications may incl ...
, urinary tract infections, kidney stone
Kidney stone disease (known as nephrolithiasis, renal calculus disease, or urolithiasis) is a crystallopathy and occurs when there are too many minerals in the urine and not enough liquid or hydration. This imbalance causes tiny pieces of cr ...
s, paralytic ileus, myocarditis
Myocarditis is inflammation of the cardiac muscle. Myocarditis can progress to inflammatory cardiomyopathy when there is associated ventricular remodeling and cardiac dysfunction due to chronic inflammation. Symptoms can include shortness of bre ...
and cor pulmonale.
Post-polio syndrome
Between 25 percent and 50 percent of individuals who have recovered from paralytic polio in childhood can develop additional symptoms decades after recovering from the acute infection, notably new muscle weakness and extreme fatigue. This condition is known as post-polio syndrome (PPS) or post-polio sequelae. The symptoms of PPS are thought to involve a failure of the oversizedmotor unit
In biology, a motor unit is made up of a motor neuron and all of the skeletal muscle fibers innervated by the neuron's axon terminals, including the neuromuscular junctions between the neuron and the fibres. Groups of motor units often work tog ...
s created during the recovery phase of the paralytic disease. Contributing factors that increase the risk of PPS include aging with loss of neuron units, the presence of a permanent residual impairment after recovery from the acute illness, and both overuse and disuse of neurons. PPS is a slow, progressive disease, and there is no specific treatment for it. Post-polio syndrome is not an infectious process, and persons experiencing the syndrome do not shed poliovirus.
Orthotics
 Paralysis, length differences and deformations of the lower extremities can lead to a hindrance when walking with compensation mechanisms that lead to a severe impairment of the gait pattern. In order to be able to stand and walk safely and to improve the gait pattern, orthotics can be included in the therapy concept. Today, modern materials and functional elements enable the orthosis to be specifically adapted to the requirements resulting from the patient's gait. Mechanical stance phase control knee joints may secure the knee joint in the early stance phases and release again for knee flexion when the swing phase is initiated. With the help of an orthotic treatment with a stance phase control knee joint, a natural gait pattern can be achieved despite mechanical protection against unwanted knee flexion. In these cases, locked knee joints are often used, which have a good safety function, but do not allow knee flexion when walking during swing phase. With such joints, the knee joint remains mechanically blocked during the swing phase. Patients with locked knee joints must swing the leg forward with the knee extended even during the swing phase. This only works if the patient develops compensatory mechanisms, e.g. by raising the body's center of gravity in the swing phase (Duchenne limping) or by swinging the orthotic leg to the side (circumduction).
Paralysis, length differences and deformations of the lower extremities can lead to a hindrance when walking with compensation mechanisms that lead to a severe impairment of the gait pattern. In order to be able to stand and walk safely and to improve the gait pattern, orthotics can be included in the therapy concept. Today, modern materials and functional elements enable the orthosis to be specifically adapted to the requirements resulting from the patient's gait. Mechanical stance phase control knee joints may secure the knee joint in the early stance phases and release again for knee flexion when the swing phase is initiated. With the help of an orthotic treatment with a stance phase control knee joint, a natural gait pattern can be achieved despite mechanical protection against unwanted knee flexion. In these cases, locked knee joints are often used, which have a good safety function, but do not allow knee flexion when walking during swing phase. With such joints, the knee joint remains mechanically blocked during the swing phase. Patients with locked knee joints must swing the leg forward with the knee extended even during the swing phase. This only works if the patient develops compensatory mechanisms, e.g. by raising the body's center of gravity in the swing phase (Duchenne limping) or by swinging the orthotic leg to the side (circumduction).
Epidemiology
Major polio epidemics were unknown before the 20th century; up until that time, polio was an endemic disease worldwide. Mothers who had survived polio infection passed on temporary immunity to their babies in the womb and through breast milk. As a result, an infant who encountered a polio infection generally suffered only mild symptoms and acquired a long-term immunity to the disease. With improvements in sanitation and hygiene during the 19th century, the general level of herd immunity in the population declined; this provided circumstances where epidemics of polio became frequent. It is estimated that epidemic polio killed or paralysed over half a million people every year. Following the widespread use of poliovirus vaccine in the mid-1950s, new cases of poliomyelitis declined dramatically in many industrialized countries. Efforts to completely eradicate the disease started in 1988 and are ongoing.Circulating vaccine-derived polioviruses
The oral polio vaccine, while highly effective, has the disadvantage that it contains a live virus which has been attenuated so that it cannot cause severe illness. The vaccine virus is excreted in the stool, and in under-immunized communities it can spread from person to person. This is known as circulating vaccine-derived poliovirus (cVDPV) or more simply as variant poliovirus. With prolonged transmission of this kind, the weakened virus can mutate and revert to a form that causes illness and paralysis. Cases of cVDPV now exceed wild-type cases, making it desirable to discontinue the use of the oral polio vaccine as soon as safely possible and instead use other types of polio vaccines.Eradication
A global effort to eradicate polio – theGlobal Polio Eradication Initiative
The Global Polio Eradication Initiative is an initiative created in 1988, just after the World Health Assembly resolved to eradicate the disease poliomyelitis. Led by the World Health Organization, it is the largest international public health ...
– began in 1988, led by the World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a list of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations which coordinates responses to international public health issues and emergencies. It is headquartered in Gen ...
, UNICEF
UNICEF ( ), originally the United Nations International Children's Emergency Fund, officially United Nations Children's Fund since 1953, is an agency of the United Nations responsible for providing Humanitarianism, humanitarian and Development a ...
, and The Rotary Foundation. Polio is one of only two diseases currently the subject of a global eradication program, the other being Guinea worm disease
Dracunculiasis, also called Guinea-worm disease, is a parasitic infection by the Dracunculus medinensis, Guinea worm (''Dracunculus medinensis).'' A person becomes infected by drinking Water pollution, water contaminated with Guinea-worm larv ...
. So far, the only diseases completely eradicated by humankind are smallpox
Smallpox was an infectious disease caused by Variola virus (often called Smallpox virus), which belongs to the genus '' Orthopoxvirus''. The last naturally occurring case was diagnosed in October 1977, and the World Health Organization (W ...
, declared eradicated in 1980, and rinderpest
Rinderpest (also cattle plague or steppe murrain) was an infectious viral disease of cattle, domestic water buffalo, and many other species of even-toed ungulates, including gaurs, African Buffalo, buffaloes, large antelope, deer, giraffes, wilde ...
, declared eradicated in 2011. In April 2012, the World Health Assembly declared that the failure to completely eradicate polio would be a programmatic emergency for global public health, and that it "must not happen".
These efforts have hugely reduced the number of cases; from an estimated 350,000 cases in 1988 to a low of 483 cases in 2001, after which it remained at a level of about 1,000–2000 cases per year for a number of years.
By 2015, polio was believed to remain naturally spreading in only two countries, Pakistan
Pakistan, officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of over 241.5 million, having the Islam by country# ...
and Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. It is bordered by Pakistan to the Durand Line, east and south, Iran to the Afghanistan–Iran borde ...
, although it continued to cause outbreaks in other nearby countries due to hidden or re-established transmission.
Global surveillance for polio takes two forms. Cases of acute flaccid paralysis (AFP) are tested for the presence and type of poliovirus. In addition, environmental and wastewater
Wastewater (or waste water) is water generated after the use of freshwater, raw water, drinking water or saline water in a variety of deliberate applications or processes. Another definition of wastewater is "Used water from any combination of do ...
samples are tested for the presence of poliovirus - this is an effective method of detecting circulating virus which has not given rise to severe symptoms. Here is a summary of both wild polio (WPV) and variant polio (cVDPV) prevalence over the last 5 years:
* 2019 - 147 cases of WPV1 in Pakistan, and 29 cases in Afghanistan. None were reported elsewhere in the world. cVDPV was detected in 19 countries with 378 confirmed cases.
* 2020 - 84 WPV1 cases in Pakistan, 56 in Afghanistan. 32 countries reported cVDPV detection, and there were 1,103 cVDPV cases.
* In 2021, there were just six confirmed cases of wild poliovirus — one in Pakistan, four in Afghanistan, and one in Malawi. The case in Malawi, the country's first in almost three decades and the first in Africa in five years, was seen as a significant setback to the eradication effort. 23 countries detected cVDPV, with 698 cases.
* In 2022, there were 30 confirmed cases of WPV1 reported to WHO, with two cases in Pakistan and 20 Afghanistan respectively, while eight non-endemic cases were recorded in Mozambique, the first cases in the country since 1992. The Mozambique cases derived from the strain of Pakistani origin that caused two confirmed cases in Malawi in 2021. 24 countries detected cVDPV, with 881 cases.
* In 2023, twelve cases of WPV1 were reported, six each in Afghanistan and Pakistan. 32 countries reported cVDPV, with 524 cases.
Afghanistan and Pakistan
The last remaining region with wild polio cases are theSouth Asia
South Asia is the southern Subregion#Asia, subregion of Asia that is defined in both geographical and Ethnicity, ethnic-Culture, cultural terms. South Asia, with a population of 2.04 billion, contains a quarter (25%) of the world's populatio ...
n countries Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. It is bordered by Pakistan to the Durand Line, east and south, Iran to the Afghanistan–Iran borde ...
and Pakistan
Pakistan, officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of over 241.5 million, having the Islam by country# ...
.
During 2011, the CIA ran a fake hepatitis vaccination clinic in Abbottabad, Pakistan, in an attempt to locate Osama bin Laden
Osama bin Laden (10 March 19572 May 2011) was a militant leader who was the founder and first general emir of al-Qaeda. Ideologically a pan-Islamist, Bin Laden participated in the Afghan ''mujahideen'' against the Soviet Union, and support ...
. This destroyed trust in vaccination programs in the region. There were attacks and deaths among vaccination workers; 66 vaccinators were killed in 2013 and 2014. In Afghanistan, the Taliban
, leader1_title = Supreme Leader of Afghanistan, Supreme leaders
, leader1_name = {{indented plainlist,
* Mullah Omar{{Natural Causes{{nbsp(1994–2013)
* Akhtar Mansour{{Assassinated (2015–2016)
* Hibatullah Akhundzada (2016–present) ...
banned house-to-house polio vaccination between 2018 and 2021. These factors have set back efforts to eliminate polio by means of vaccination in these countries.
In Afghanistan, 80 cases of polio were reported from 35 districts during 2011. Incidence over the subsequent 10 years has declined to just 4 cases in 2 districts during 2021.
In Pakistan, cases dropped by 97 percent from 2014 to 2018; reasons include 440 million dirham
The dirham, dirhem or drahm is a unit of currency and of mass. It is the name of the currencies of Moroccan dirham, Morocco, the United Arab Emirates dirham, United Arab Emirates and Armenian dram, Armenia, and is the name of a currency subdivisi ...
support from the United Arab Emirates
The United Arab Emirates (UAE), or simply the Emirates, is a country in West Asia, in the Middle East, at the eastern end of the Arabian Peninsula. It is a Federal monarchy, federal elective monarchy made up of Emirates of the United Arab E ...
to vaccinate more than ten million children, changes in the military situation, and arrests of some of those who attacked polio workers.
Americas
TheAmericas
The Americas, sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North America and South America.''Webster's New World College Dictionary'', 2010 by Wiley Publishing, Inc., Cleveland, Ohio. When viewed as a sing ...
were declared polio-free in 1994. The last known case was a boy in Peru
Peru, officially the Republic of Peru, is a country in western South America. It is bordered in the north by Ecuador and Colombia, in the east by Brazil, in the southeast by Bolivia, in the south by Chile, and in the south and west by the Pac ...
in 1991. The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is the National public health institutes, national public health agency of the United States. It is a Federal agencies of the United States, United States federal agency under the United S ...
recommends polio vaccination boosters for travelers and those who live in countries where the disease is endemic.
In July 2022, the US state of New York reported a polio case for the first time in almost a decade in the country; this was attributed to a vaccine-derived strain of the virus.
Western Pacific
In 2000, polio was declared to have been officially eliminated in 37 Western Pacific countries, including China and Australia. Despite eradication ten years earlier, an outbreak was confirmed in China in September 2011, involving a strain common in Pakistan. In September 2019, the Department of Health of the Philippines declared a polio outbreak in the country after a single case in a 3-year-old girl. In December 2019, acute poliomyelitis was confirmed in an infant in Sabah state,Borneo
Borneo () is the List of islands by area, third-largest island in the world, with an area of , and population of 23,053,723 (2020 national censuses). Situated at the geographic centre of Maritime Southeast Asia, it is one of the Greater Sunda ...
, Malaysia
Malaysia is a country in Southeast Asia. Featuring the Tanjung Piai, southernmost point of continental Eurasia, it is a federation, federal constitutional monarchy consisting of States and federal territories of Malaysia, 13 states and thre ...
. Subsequently, a further three polio cases were reported, with the last case reported in January 2020. Both outbreaks were found to be linked instances of vaccine-derived poliomyelitis.
Europe
Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
was declared polio-free in 2002.
Southeast Asia
On 27 March 2014, the WHO announced the eradication of poliomyelitis in the South-East Asia Region, which includes eleven countries:Bangladesh
Bangladesh, officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, eighth-most populous country in the world and among the List of countries and dependencies by ...
, Bhutan
Bhutan, officially the Kingdom of Bhutan, is a landlocked country in South Asia, in the Eastern Himalayas between China to the north and northwest and India to the south and southeast. With a population of over 727,145 and a territory of , ...
, North Korea
North Korea, officially the Democratic People's Republic of Korea (DPRK), is a country in East Asia. It constitutes the northern half of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and borders China and Russia to the north at the Yalu River, Yalu (Amnok) an ...
, India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
, Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania, between the Indian Ocean, Indian and Pacific Ocean, Pacific oceans. Comprising over List of islands of Indonesia, 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, ...
, Maldives
The Maldives, officially the Republic of Maldives, and historically known as the Maldive Islands, is an Archipelagic state, archipelagic country in South Asia located in the Indian Ocean. The Maldives is southwest of Sri Lanka and India, abou ...
, Myanmar
Myanmar, officially the Republic of the Union of Myanmar; and also referred to as Burma (the official English name until 1989), is a country in northwest Southeast Asia. It is the largest country by area in Mainland Southeast Asia and has ...
, Nepal
Nepal, officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal, is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is mainly situated in the Himalayas, but also includes parts of the Indo-Gangetic Plain. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China Ch ...
, Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka, officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, also known historically as Ceylon, is an island country in South Asia. It lies in the Indian Ocean, southwest of the Bay of Bengal, separated from the Indian subcontinent, ...
, Thailand
Thailand, officially the Kingdom of Thailand and historically known as Siam (the official name until 1939), is a country in Southeast Asia on the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese Peninsula. With a population of almost 66 million, it spa ...
and Timor-Leste. With the addition of this region, 80 per cent of the world population was considered to be living in polio-free regions.
Middle East
InSyria
Syria, officially the Syrian Arab Republic, is a country in West Asia located in the Eastern Mediterranean and the Levant. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the west, Turkey to Syria–Turkey border, the north, Iraq to Iraq–Syria border, t ...
, difficulties in executing immunization programs in the ongoing civil war
A civil war is a war between organized groups within the same Sovereign state, state (or country). The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies.J ...
led to a return of polio, probably in 2012, acknowledged by the WHO in 2013. 15 cases were confirmed among children in Syria
Syria, officially the Syrian Arab Republic, is a country in West Asia located in the Eastern Mediterranean and the Levant. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the west, Turkey to Syria–Turkey border, the north, Iraq to Iraq–Syria border, t ...
between October and November 2013 in Deir Ezzor. Later, two more cases, one each in rural Damascus
Damascus ( , ; ) is the capital and List of largest cities in the Levant region by population, largest city of Syria. It is the oldest capital in the world and, according to some, the fourth Holiest sites in Islam, holiest city in Islam. Kno ...
and Aleppo
Aleppo is a city in Syria, which serves as the capital of the Aleppo Governorate, the most populous Governorates of Syria, governorate of Syria. With an estimated population of 2,098,000 residents it is Syria's largest city by urban area, and ...
, were identified. It was the first outbreak in Syria since 1999. Doctors and international public health agencies report more than 90 cases of polio in Syria, with fears of contagion in rebel areas from lack of sanitation and safe-water services. A vaccination campaign in Syria operated under gunfire and led to the deaths of several vaccinators, but returned vaccination coverage to pre-war levels. Syria is currently free of polio, but is considered "at risk".
In 2024, the Gaza Health Ministry reported that several children have shown symptoms consistent with polio, with laboratory tests confirming that a 10-month-old child is infected with the virus. In 2022, prior to the Israel-Hamas conflict, routine immunization coverage of eligible children exceeded 99%, but fell to less than 90% by the first quarter of 2024, according to the WHO. United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is the Earth, global intergovernmental organization established by the signing of the Charter of the United Nations, UN Charter on 26 June 1945 with the stated purpose of maintaining international peace and internationa ...
Secretary-General António Guterres
António Manuel de Oliveira Guterres (born 30 April 1949) is a Portuguese politician and diplomat who is serving as the ninth and current secretary-general of the United Nations since 2017. A member of the Socialist Party (Portugal), ...
urged for a weeklong cease-fire in Gaza to facilitate vaccinations and prevent a potential polio outbreak, emphasizing the risk faced by many children.
Africa
In 2003, innorthern Nigeria
Northern Nigeria (or Arewa, Arewancin Nijeriya) was an autonomous division within Nigeria, distinctly different from the southern part of the country, with independent customs, foreign relations and security structures. In 1962, it acquired t ...
– a country that at that time was considered provisionally polio free – a fatwa
A fatwa (; ; ; ) is a legal ruling on a point of Islamic law (sharia) given by a qualified Islamic jurist ('' faqih'') in response to a question posed by a private individual, judge or government. A jurist issuing fatwas is called a ''mufti'', ...
was issued declaring that the polio vaccine was designed to render children sterile. Subsequently, polio reappeared in Nigeria and spread from there to several other countries. In 2013, nine health workers administering polio vaccine were targeted and killed by gunmen on motorcycles in Kano, but this was the only attack. Local traditional and religious leaders and polio survivors worked to revive the campaign, and Nigeria was removed from the polio-endemic list in September 2015 after more than a year without any cases, only to be restored to the list in 2016 when two cases were detected.
Africa was declared free of wild polio in August 2020, although cases of circulating vaccine-derived poliovirus type 2 continue to appear in several countries.
A single case of wild polio that was detected in Malawi
Malawi, officially the Republic of Malawi, is a landlocked country in Southeastern Africa. It is bordered by Zambia to the west, Tanzania to the north and northeast, and Mozambique to the east, south, and southwest. Malawi spans over and ...
in February 2022, and another in Mozambique
Mozambique, officially the Republic of Mozambique, is a country located in Southeast Africa bordered by the Indian Ocean to the east, Tanzania to the north, Malawi and Zambia to the northwest, Zimbabwe to the west, and Eswatini and South Afr ...
in May 2022 were both of a strain imported from Pakistan and do not affect the African region's wild poliovirus-free certification status.
History
 The effects of polio have been known since
The effects of polio have been known since prehistory
Prehistory, also called pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the first known use of stone tools by hominins million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use ...
; Egyptian paintings and carvings depict otherwise healthy people with withered limbs, and young children walking with canes. The earliest known case of polio is indicated by the remains of a teenage girl discovered in a 4000-year-old burial site in the United Arab Emirates
The United Arab Emirates (UAE), or simply the Emirates, is a country in West Asia, in the Middle East, at the eastern end of the Arabian Peninsula. It is a Federal monarchy, federal elective monarchy made up of Emirates of the United Arab E ...
, exhibiting characteristic symptoms of the condition.
The first clinical description was provided by the English physician Michael Underwood in 1789, where he refers to polio as "a debility of the lower extremities". The work of physicians Jakob Heine in 1840 and Karl Oskar Medin in 1890 led to it being known as ''Heine–Medin disease''. The disease was later called ''infantile paralysis'', based on its propensity to affect children.
Before the 20th century, polio infections were rarely seen in infants before six months of age, most cases occurring in children six months to four years of age. Poorer sanitation
Sanitation refers to public health conditions related to clean drinking water and treatment and disposal of human excreta and sewage. Preventing human contact with feces is part of sanitation, as is hand washing with soap. Sanitation systems ...
of the time resulted in constant exposure to the virus, which enhanced a natural immunity within the population. In developed countries during the late 19th and early 20th centuries, improvements were made in community sanitation, including better sewage
Sewage (or domestic sewage, domestic wastewater, municipal wastewater) is a type of wastewater that is produced by a community of people. It is typically transported through a sewerage, sewer system. Sewage consists of wastewater discharged fro ...
disposal and clean water supplies. These changes drastically increased the proportion of children and adults at risk of paralytic polio infection, by reducing childhood exposure and immunity to the disease.
Small localized paralytic polio epidemics began to appear in Europe and the United States around 1900. Outbreaks reached pandemic
A pandemic ( ) is an epidemic of an infectious disease that has a sudden increase in cases and spreads across a large region, for instance multiple continents or worldwide, affecting a substantial number of individuals. Widespread endemic (epi ...
proportions in Europe, North America, Australia, and New Zealand during the first half of the 20th century. By 1950, the peak age incidence of paralytic poliomyelitis in the United States had shifted from infants to children aged five to nine years, when the risk of paralysis is greater; about one-third of the cases were reported in persons over 15 years of age. Accordingly, the rate of paralysis and death due to polio infection also increased during this time. In the United States, the 1952 polio epidemic became the worst outbreak in the nation's history. Of the nearly 58,000 cases reported that year, 3,145 died and 21,269 were left with mild to disabling paralysis. Intensive care medicine
Intensive care medicine, usually called critical care medicine, is a medical specialty that deals with seriously or critically ill patients who have, are at risk of, or are recovering from conditions that may be life-threatening. It includes p ...
has its origin in the fight against polio. Most hospitals in the 1950s had limited access to iron lungs for patients unable to breathe without mechanical assistance. Respiratory centers designed to assist the most severe polio patients, first established in 1952 at the Blegdam Hospital of Copenhagen
Copenhagen ( ) is the capital and most populous city of Denmark, with a population of 1.4 million in the Urban area of Copenhagen, urban area. The city is situated on the islands of Zealand and Amager, separated from Malmö, Sweden, by the ...
by Danish anesthesiologist
Anesthesiology, anaesthesiology or anaesthesia is the medical specialty concerned with the total perioperative medicine, perioperative care of patients before, during and after surgery. It encompasses anesthesia, intensive care medicine, critica ...
Bjørn Ibsen, were the precursors of modern intensive care unit
An intensive care unit (ICU), also known as an intensive therapy unit or intensive treatment unit (ITU) or critical care unit (CCU), is a special department of a hospital or health care facility that provides intensive care medicine.
An inten ...
s (ICU). (A year later, Ibsen would establish the world's first dedicated ICU.)
The polio epidemics not only altered the lives of those who survived them, but also brought profound cultural changes, spurring grassroots
A grassroots movement is one that uses the people in a given district, region or community as the basis for a political or continent movement. Grassroots movements and organizations use collective action from volunteers at the local level to imp ...
fund-raising campaigns that would revolutionize medical philanthropy
Philanthropy is a form of altruism that consists of "private initiatives for the Public good (economics), public good, focusing on quality of life". Philanthropy contrasts with business initiatives, which are private initiatives for private goo ...
, and giving rise to the modern field of rehabilitation therapy. As one of the largest disabled groups in the world, polio survivors also helped to advance the modern disability rights movement
The disability rights movement is a global social movement that seeks to secure equal opportunities and equal rights for all disabled people.
It is made up of organizations of disability activists, also known as disability advocates, around ...
through campaigns for the social and civil rights of the disabled
Disability is the experience of any condition that makes it more difficult for a person to do certain activities or have equitable access within a given society. Disabilities may be cognitive, developmental, intellectual, mental, physica ...
. The World Health Organization estimates that there are 10 to 20 million polio survivors worldwide. In 1977, there were 254,000 persons living in the United States who had been paralyzed by polio. According to doctors and local polio support groups, some 40,000 polio survivors with varying degrees of paralysis were living in Germany, 30,000 in Japan, 24,000 in France, 16,000 in Australia, 12,000 in Canada and 12,000 in the United Kingdom in 2001. Many notable individuals have survived polio and often credit the prolonged immobility and residual paralysis associated with polio as a driving force in their lives and careers.
The disease was very well publicized during the polio epidemics of the 1950s, with extensive media coverage of any scientific advancements that might lead to a cure. Thus, the scientists working on polio became some of the most famous of the century. Fifteen scientists and two laymen who made important contributions to the knowledge and treatment of poliomyelitis are honored by the Polio Hall of Fame, which was dedicated in 1957 at the Roosevelt Warm Springs Institute for Rehabilitation in Warm Springs, Georgia, US. In 2008 four organizations (Rotary International, the World Health Organization, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and UNICEF) were added to the Hall of Fame.
World Polio Day (24 October) as an annual day of awareness was established by Rotary International
Rotary International is one of the largest service organizations in the world. The self-declared mission of Rotary, as stated on its website, is to "provide service to others, promote integrity, and advance world understanding, goodwill, and p ...
to commemorate the birth of Jonas Salk, who led the first team to develop a vaccine against poliomyelitis.
A global effort to eradicate polio – the Global Polio Eradication Initiative
The Global Polio Eradication Initiative is an initiative created in 1988, just after the World Health Assembly resolved to eradicate the disease poliomyelitis. Led by the World Health Organization, it is the largest international public health ...
(GPEI) – began in 1988, led by the World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a list of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations which coordinates responses to international public health issues and emergencies. It is headquartered in Gen ...
, UNICEF
UNICEF ( ), originally the United Nations International Children's Emergency Fund, officially United Nations Children's Fund since 1953, is an agency of the United Nations responsible for providing Humanitarianism, humanitarian and Development a ...
, and The Rotary Foundation. Since then, international cooperation led by GPEI has reduced polio worldwide by 99 percent, and the campaign is ongoing.
In 2010, wild poliovirus was discovered through importation in 13 different countries. They were Chad
Chad, officially the Republic of Chad, is a landlocked country at the crossroads of North Africa, North and Central Africa. It is bordered by Libya to Chad–Libya border, the north, Sudan to Chad–Sudan border, the east, the Central Afric ...
, the Democratic Republic of Congo
The Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), also known as the DR Congo, Congo-Kinshasa, or simply the Congo (the last ambiguously also referring to the neighbouring Republic of the Congo), is a country in Central Africa. By land area, it is t ...
, the Republic of Congo, Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a landlocked country primarily in Central Asia, with a European Kazakhstan, small portion in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the Kazakhstan–Russia border, north and west, China to th ...
, Liberia
Liberia, officially the Republic of Liberia, is a country on the West African coast. It is bordered by Sierra Leone to Liberia–Sierra Leone border, its northwest, Guinea to Guinea–Liberia border, its north, Ivory Coast to Ivory Coast–Lib ...
, Mali
Mali, officially the Republic of Mali, is a landlocked country in West Africa. It is the List of African countries by area, eighth-largest country in Africa, with an area of over . The country is bordered to the north by Algeria, to the east b ...
, Nepal
Nepal, officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal, is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is mainly situated in the Himalayas, but also includes parts of the Indo-Gangetic Plain. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China Ch ...
, Niger
Niger, officially the Republic of the Niger, is a landlocked country in West Africa. It is a unitary state Geography of Niger#Political geography, bordered by Libya to the Libya–Niger border, north-east, Chad to the Chad–Niger border, east ...
, the Russian Federation
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
, Senegal
Senegal, officially the Republic of Senegal, is the westernmost country in West Africa, situated on the Atlantic Ocean coastline. It borders Mauritania to Mauritania–Senegal border, the north, Mali to Mali–Senegal border, the east, Guinea t ...
, Tajikistan
Tajikistan, officially the Republic of Tajikistan, is a landlocked country in Central Asia. Dushanbe is the capital city, capital and most populous city. Tajikistan borders Afghanistan to the Afghanistan–Tajikistan border, south, Uzbekistan to ...
, Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan is a landlocked country in Central Asia bordered by Kazakhstan to the northwest, Uzbekistan to the north, east and northeast, Afghanistan to the southeast, Iran to the south and southwest and the Caspian Sea to the west. Ash ...
, and Uganda
Uganda, officially the Republic of Uganda, is a landlocked country in East Africa. It is bordered to the east by Kenya, to the north by South Sudan, to the west by the Democratic Republic of the Congo, to the south-west by Rwanda, and to the ...
.
In 2021, Types 2 and 3 were fully eradicated from every country; however, type 1 cases still remain in Pakistan and Afghanistan. A majority of countries have successfully eradicated polio, with Pakistan and Afghanistan being the last countries with endemic cases of poliovirus. The following countries have been considered polio-free, but not confirmed as of April 2024: Somalia, Djibouti, Sudan, Egypt, Libya, Tunisia, Morocco, Palestine, Lebanon, Syria, Jordan, Saudi Arabia, Bahrain, Qatar, Oman, Yemen, the UAE, Iraq, Kuwait, and Iran.
Research
Since 2018,Global Polio Eradication Initiative
The Global Polio Eradication Initiative is an initiative created in 1988, just after the World Health Assembly resolved to eradicate the disease poliomyelitis. Led by the World Health Organization, it is the largest international public health ...
(GPEI) has coordinated efforts both to eliminate polio and to research means of improving surveillance and prevention. At the peak of its work, the programme directly employed 4000 people across 75 countries and managed a budget of nearly U.S. $1 billion.
, the GPEI had raised 18 billion dollars in funding, with annual contributions around 800 million to 1 billion dollars. Around 30% of the funding came from the Gates Foundation 30% from developed governments, 27% from countries at risk of polio, and the rest was made up of donations from nonprofits, private funders, and other foundations.
The GPEI has identified six directions for continuing research:
* Optimizing oral polio vaccine efficacy
* Developing affordable inactivated polio vaccine
* Managing risks associated with vaccine-derived polioviruses and vaccine-associated paralytic polio (including OPV cessation)
* Antivirals
* Polio diagnostics
* Surveillance research
Even if polio can be eliminated from the world population, vaccination programs should continue for at least ten years. The retention of live poliovirus samples in laboratories and vaccine manufacturing facilities (which carry a risk of escape of the virus) should progressively be reduced. To support these two objectives, vaccines are under development which either utilise a virus-like particle, or which derive from a modified virus which cannot reproduce in a human host.
References
Further reading
* Benison, Saul. “The Enigma of Poliomyelitis: 1910,” in ''Freedom and Reform: Essays in Honor of Henry Steele Commager,'' ed. Harold Hyman, (1967). * Benison, Saul. “The History of Polio Research in the United States: Appraisal and Lessons,” in ''The Twentieth Century Sciences: Studies in the Biography of Ideas,'' ed. Gerald Holton, (1972). * Black, Kathryn. ''In the shadow of polio : a personal and social history'' (1996online
* * Hecht, Alan, and I. Edward Alcamo. ''Polio'' (2003
online copy
for middle schools * * , a major scholarly history. * Rai, Anushree, et al. "Polio returns to the USA: An epidemiological alert." ''Annals of Medicine and Surgery'' 82 (2022)
online
* * * * * Zimmermann, Jonas. "War on Disease: Polio Eradication in the United States." ''Historia. scriber'' 15 (2023): 263-280
online
External links
* * * {{Authority control Infectious diseases with eradication efforts Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate Wikipedia infectious disease articles ready to translate Vaccine-preventable diseases Central nervous system disorders Myelin disorders