Polar Vortex on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A circumpolar vortex, or simply polar vortex, is a large region of cold, rotating air that encircles both of Earth's
 Polar vortices are weakest during summer and strongest during winter.
Polar vortices are weakest during summer and strongest during winter.
Cold enough for snow, and more's on the way
. ''
 Other astronomical bodies are also known to have polar vortices, including
Other astronomical bodies are also known to have polar vortices, including
polar regions
The polar regions, also called the frigid zones or polar zones, of Earth are the regions of the planet that surround its geographical poles (the North and South Poles), lying within the polar circles. These high latitudes are dominated by floa ...
. Polar vortices also exist on other rotating, low-obliquity
In astronomy, axial tilt, also known as obliquity, is the angle between an object's rotational axis and its orbital axis, which is the line perpendicular to its orbital plane; equivalently, it is the angle between its equatorial plane and orbi ...
planetary bodies. The term polar vortex can be used to describe two distinct phenomena; the stratospheric
The stratosphere () is the second layer of the atmosphere of the Earth, located above the troposphere and below the mesosphere. The stratosphere is an atmospheric layer composed of stratified temperature layers, with the warm layers of air h ...
polar vortex, and the tropospheric
The troposphere is the first and lowest layer of the atmosphere of the Earth, and contains 75% of the total mass of the planetary atmosphere, 99% of the total mass of water vapour and aerosols, and is where most weather phenomena occur. From t ...
polar vortex. The stratospheric and tropospheric polar vortices both rotate in the direction of the Earth's spin, but they are distinct phenomena that have different sizes, structures, seasonal cycles, and impacts on weather.
The stratospheric polar vortex is an area of high-speed, cyclonically rotating winds around 15 km to 50 km high, poleward of 50°, and is strongest in winter. It forms in Autumn when Arctic or Antarctic temperatures cool rapidly as the polar night
The polar night is a phenomenon where the nighttime lasts for more than 24 hours that occurs in the northernmost and southernmost regions of Earth. This occurs only inside the polar circles. The opposite phenomenon, the polar day, or midni ...
begins. The increased temperature difference between the pole and the tropics causes strong winds and the Coriolis effect
In physics, the Coriolis force is an inertial or fictitious force that acts on objects in motion within a frame of reference that rotates with respect to an inertial frame. In a reference frame with clockwise rotation, the force acts to the ...
causes the vortex to spin up. The stratospheric polar vortex breaks down in Spring as the polar night ends. A sudden stratospheric warming
A sudden stratospheric warming (SSW) is an event in which the polar stratospheric temperature rises by several tens of kelvins (up to increases of about 50 °C (90 °F)) over the course of a few days. The warming is preceded by a slowing ...
(SSW) is an event that occurs when the stratospheric vortex breaks down during winter, and can have significant impacts on surface weather.
The tropospheric polar vortex is often defined as the area poleward of the tropospheric jet stream
Jet streams are fast flowing, narrow, meandering air currents in the atmospheres of some planets, including Earth. On Earth, the main jet streams are located near the altitude of the tropopause and are westerly winds (flowing west to east) ...
. The equatorward edge is around 40° to 50°, and it extends from the surface up to around 10 km to 15 km. Its yearly cycle differs from the stratospheric vortex because the tropospheric vortex exists all year, but is similar to the stratospheric vortex since it is also strongest in winter when the polar regions are coldest.
The tropospheric polar vortex was first described as early as 1853. The stratospheric vortex's SSWs were discovered in 1952 with radiosonde
A radiosonde is a battery-powered telemetry instrument carried into the atmosphere usually by a weather balloon that measures various atmospheric parameters and transmits them by radio to a ground receiver. Modern radiosondes measure or calcula ...
observations at altitudes higher than 20 km. The tropospheric polar vortex was mentioned frequently in the news and weather media in the cold North American winter of 2013–2014, popularizing the term as an explanation of very cold temperatures. The tropospheric vortex increased in public visibility in 2021 as a result of extreme frigid temperatures in the central United States, with experts linking its effects to climate change
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to ...
.
Ozone depletion
Ozone depletion consists of two related events observed since the late 1970s: a steady lowering of about four percent in the total amount of ozone in Earth's atmosphere, and a much larger springtime decrease in stratospheric ozone (the ozone lay ...
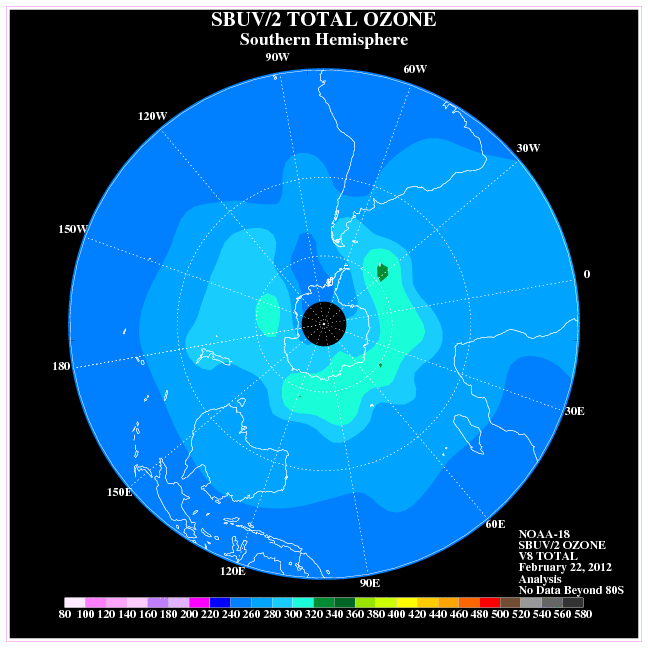
occurs within the polar vortices – particularly over the Southern Hemisphere – reaching a maximum depletion in the spring.
Arctic and Antarctic vortices
Northern Hemisphere
When the tropospheric vortex of the Arctic is strong, it has a well defined and nearly circular shape, there is a single vortex with ajet stream
Jet streams are fast flowing, narrow, meandering air currents in the atmospheres of some planets, including Earth. On Earth, the main jet streams are located near the altitude of the tropopause and are westerly winds (flowing west to east) ...
that is well constrained near the polar front
In meteorology, the polar front is the weather front boundary between the polar cell and the Ferrel cell around the 60° latitude, near the polar regions, in both hemisphere. At this boundary a sharp gradient in temperature occurs between the ...
, and the Arctic air is well contained. When the northern tropospheric vortex weakenes, it breaks into two or more smaller vortices, the strongest of which are near Baffin Island
Baffin Island (formerly Baffin Land), in the Canadian territory of Nunavut, is the largest island in Canada and the fifth-largest island in the world. Its area is , slightly larger than Spain; its population was 13,039 as of the 2021 Canadia ...
, Nunavut, and the other over northeast Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part ...
. When it is very weak, the flow of Arctic air becomes more disorganized, and masses of cold Arctic air can push equatorward, bringing with them a rapid and sharp temperature drop.
A deep freeze that gripped much of the United States and Canada in late January 2019 has been blamed on a "polar vortex". This is not the scientifically correct use of the term polar vortex, but instead is referring to outbreaks of cold Arctic air caused by a weakened polar vortex. The US National Weather Service warned that frostbite is possible within just 10 minutes of being outside in such extreme temperatures, and hundreds of schools, colleges and universities in the affected areas were closed. Around 21 people died in US due to severe frostbite. States within the midwest region of the United States had windchills just above -50 °F (-45 °C). The Polar vortex is also thought to have had effects in Europe. For example, the 2013–14 United Kingdom winter floods
The 2013–2014 United Kingdom winter floods saw areas of Ireland and the United Kingdom inundated following severe storms. The south of England saw heavy rainfalls associated with these storms which caused widespread flooding, power cuts an ...
were blamed on the Polar vortex bringing severe cold in the United States and Canada. Similarly, the severe cold in the United Kingdom in the winters of 2009/10 and 2010/11 were also blamed on the Polar vortex.
Southern Hemisphere
TheAntarctic
The Antarctic ( or , American English also or ; commonly ) is a polar region around Earth's South Pole, opposite the Arctic region around the North Pole. The Antarctic comprises the continent of Antarctica, the Kerguelen Plateau and othe ...
vortex of the Southern Hemisphere is a single low-pressure zone that is found near the edge of the Ross ice shelf
The Ross Ice Shelf is the largest ice shelf of Antarctica (, an area of roughly and about across: about the size of France). It is several hundred metres thick. The nearly vertical ice front to the open sea is more than long, and between h ...
, near 160 west longitude. When the polar vortex is strong, the mid-latitude Westerlies
The westerlies, anti-trades, or prevailing westerlies, are prevailing winds from the west toward the east in the middle latitudes between 30 and 60 degrees latitude. They originate from the high-pressure areas in the horse latitudes and tren ...
(winds at the surface level between 30° and 60° latitude from the west) increase in strength and are persistent. When the polar vortex is weak, high-pressure zones of the mid-latitudes may push poleward, moving the polar vortex, jet stream
Jet streams are fast flowing, narrow, meandering air currents in the atmospheres of some planets, including Earth. On Earth, the main jet streams are located near the altitude of the tropopause and are westerly winds (flowing west to east) ...
, and polar front equatorward. The jet stream is seen to "buckle" and deviate south. This rapidly brings cold dry air into contact with the warm, moist air of the mid-latitudes, resulting in a rapid and dramatic change of weather known as a " cold snap".
In Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands. With an area of , Australia is the largest country by ...
, the polar vortex, known there as a "polar blast" or "polar plunge", is a cold front
A cold front is the leading edge of a cooler mass of air at ground level that replaces a warmer mass of air and lies within a pronounced surface trough of low pressure. It often forms behind an extratropical cyclone (to the west in the Northern ...
that drags air from Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest cont ...
which brings rain showers, snow (typically inland, with blizzard
A blizzard is a severe snowstorm characterized by strong sustained winds and low visibility, lasting for a prolonged period of time—typically at least three or four hours. A ground blizzard is a weather condition where snow is not falling ...
s occurring in the highlands), gusty icy winds, and hail
Hail is a form of solid precipitation. It is distinct from ice pellets (American English "sleet"), though the two are often confused. It consists of balls or irregular lumps of ice, each of which is called a hailstone. Ice pellets generally fal ...
in the south-eastern parts of the country, such as in Victoria, Tasmania
)
, nickname =
, image_map = Tasmania in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of Tasmania in AustraliaCoordinates:
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdi ...
, the southeast coast of South Australia
South Australia (commonly abbreviated as SA) is a States and territories of Australia, state in the southern central part of Australia. It covers some of the most arid parts of the country. With a total land area of , it is the fourth-largest o ...
and the southern half of New South Wales
)
, nickname =
, image_map = New South Wales in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of New South Wales in AustraliaCoordinates:
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Australia
, established_title = Before federation
, es ...
(but only on the windward
Windward () and leeward () are terms used to describe the direction of the wind. Windward is ''upwind'' from the point of reference, i.e. towards the direction from which the wind is coming; leeward is ''downwind'' from the point of reference ...
side of the Great Dividing Range
The Great Dividing Range, also known as the East Australian Cordillera or the Eastern Highlands, is a cordillera system in eastern Australia consisting of an expansive collection of mountain ranges, plateaus and rolling hills, that runs rough ...
, whereas the leeward side will be affected by foehn wind
A Foehn or Föhn (, , ), is a type of dry, relatively warm, downslope wind that occurs in the lee (downwind side) of a mountain range.
It is a rain shadow wind that results from the subsequent adiabatic warming of air that has dropped most of ...
s).
Identification
The bases of the two polar vortices are located in the middle and uppertroposphere
The troposphere is the first and lowest layer of the atmosphere of the Earth, and contains 75% of the total mass of the planetary atmosphere, 99% of the total mass of water vapour and aerosols, and is where most weather phenomena occur. Fro ...
and extend into the stratosphere
The stratosphere () is the second layer of the atmosphere of the Earth, located above the troposphere and below the mesosphere. The stratosphere is an atmospheric layer composed of stratified temperature layers, with the warm layers of air h ...
. Beneath that lies a large mass of cold, dense Arctic air. The interface between the cold dry air mass of the pole and the warm moist air mass farther south defines the location of the polar front. The polar front is centered, roughly at 60° latitude. A polar vortex strengthens in the winter and weakens in the summer because of its dependence on the temperature difference between the equator and the poles.Halldór Björnsson. . Veðurstofa Íslands. Retrieved on 2008-06-15.
Polar cyclones are low-pressure zones embedded within the polar air masses, and exist year-round. The stratospheric polar vortex develops at latitudes above the subtropical jet stream. Horizontally, most polar vortices have a radius of less than . Since polar vortices exist from the stratosphere downward into the mid-troposphere, a variety of heights/pressure levels are used to mark its position. The 50 hPa pressure surface is most often used to identify its stratospheric location. At the level of the tropopause, the extent of closed contours of potential temperature
The potential temperature of a parcel of fluid at pressure P is the temperature that the parcel would attain if adiabatically brought to a standard reference pressure P_, usually . The potential temperature is denoted \theta and, for a gas well-ap ...
can be used to determine its strength. Others have used levels down to the 500 hPa pressure level (about above sea level during the winter) to identify the polar vortex.
Duration and strength
 Polar vortices are weakest during summer and strongest during winter.
Polar vortices are weakest during summer and strongest during winter. Extratropical cyclone
Extratropical cyclones, sometimes called mid-latitude cyclones or wave cyclones, are low-pressure areas which, along with the anticyclones of high-pressure areas, drive the weather over much of the Earth. Extratropical cyclones are capable ...
s that migrate into higher latitudes when the polar vortex is weak can disrupt the single vortex creating smaller vortices (cold-core low
A cold-core low, also known as an upper level low or cold-core cyclone, is a cyclone aloft which has an associated cold pool of air residing at high altitude within the Earth's troposphere, without a frontal structure. It is a low pressure syste ...
s) within the polar air mass. Those individual vortices can persist for more than a month.
Volcanic
A volcano is a rupture in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.
On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where tectonic plat ...
eruptions in the tropics
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the Equator. They are defined in latitude by the Tropic of Cancer in the Northern Hemisphere at N and the Tropic of Capricorn in
the Southern Hemisphere at S. The tropics are also refer ...
can lead to a stronger polar vortex during winter for as long as two years afterwards. The strength and position of the polar vortex shapes the flow pattern in a broad area about it. An index which is used in the northern hemisphere
The Northern Hemisphere is the half of Earth that is north of the Equator. For other planets in the Solar System, north is defined as being in the same celestial hemisphere relative to the invariable plane of the solar system as Earth's Nort ...
to gauge its magnitude is the Arctic oscillation
The Arctic oscillation (AO) or Northern Annular Mode/Northern Hemisphere Annular Mode (NAM) is a weather phenomenon at the Arctic pole north of 20 degrees latitude. It is an important mode of climate variability for the Northern Hemisphere. The s ...
.
When the Arctic vortex is at its strongest, there is a single vortex, but normally, the Arctic vortex is elongated in shape, with two cyclone centers, one over Baffin Island in Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by to ...
and the other over northeast Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part ...
. When the Arctic pattern is at its weakest, subtropic air masses can intrude poleward causing the Arctic air masses to move equatorward, as during the Winter 1985 Arctic outbreak
The 1985 North America cold wave was a meteorological event which occurred in January, 1985, as a result of the shifting of the polar vortex farther south than is normally seen. Blocked from its normal movement, polar air from the north pushed ...
.Kevin Myatt (2005-01-17)Cold enough for snow, and more's on the way
. ''
Roanoke Times
''The Roanoke Times'' is the primary newspaper in Southwestern Virginia and is based in Roanoke, Virginia, United States. It is published by Lee Enterprises. In addition to its headquarters in Roanoke, it maintains a bureau in Christiansburg, ...
''. Retrieved on 2012-02-24. The Antarctic
The Antarctic ( or , American English also or ; commonly ) is a polar region around Earth's South Pole, opposite the Arctic region around the North Pole. The Antarctic comprises the continent of Antarctica, the Kerguelen Plateau and othe ...
polar vortex is more pronounced and persistent than the Arctic
The Arctic ( or ) is a polar regions of Earth, polar region located at the northernmost part of Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean, adjacent seas, and parts of Canada (Yukon, Northwest Territories, Nunavut), Danish Realm (Greenla ...
one. In the Arctic the distribution of land masses at high latitudes in the Northern Hemisphere gives rise to Rossby wave
Rossby waves, also known as planetary waves, are a type of inertial wave naturally occurring in rotating fluids. They were first identified by Sweden-born American meteorologist Carl-Gustaf Arvid Rossby. They are observed in the atmospheres an ...
s which contribute to the breakdown of the polar vortex, whereas in the Southern Hemisphere the vortex is less disturbed. The breakdown of the polar vortex is an extreme event known as a sudden stratospheric warming
A sudden stratospheric warming (SSW) is an event in which the polar stratospheric temperature rises by several tens of kelvins (up to increases of about 50 °C (90 °F)) over the course of a few days. The warming is preceded by a slowing ...
, here the vortex completely breaks down and an associated warming of 30–50 °C (54–90 °F) over a few days can occur.
The waxing and waning of the polar vortex is driven by the movement of mass and the transfer of heat in the polar region. In the autumn, the circumpolar winds increase in speed and the polar vortex rises into the stratosphere
The stratosphere () is the second layer of the atmosphere of the Earth, located above the troposphere and below the mesosphere. The stratosphere is an atmospheric layer composed of stratified temperature layers, with the warm layers of air h ...
. The result is that the polar air forms a coherent rotating air mass: the polar vortex. As winter approaches, the vortex core cools, the winds decrease, and the vortex energy declines. Once late winter and early spring approach the vortex is at its weakest. As a result, during late winter, large fragments of the vortex air can be diverted into lower latitudes by stronger weather systems intruding from those latitudes. In the lowest level of the stratosphere, strong potential vorticity
In fluid mechanics, potential vorticity (PV) is a quantity which is proportional to the dot product of vorticity and stratification. This quantity, following a parcel of air or water, can only be changed by diabatic or frictional processes. I ...
gradients remain, and the majority of that air remains confined within the polar air mass into December in the Southern Hemisphere and April in the Northern Hemisphere, well after the breakup of the vortex in the mid-stratosphere.
The breakup of the northern polar vortex occurs between mid March to mid May. This event signifies the transition from winter to spring, and has impacts on the hydrological cycle
The water cycle, also known as the hydrologic cycle or the hydrological cycle, is a biogeochemical cycle that describes the continuous movement of water on, above and below the surface of the Earth. The mass of water on Earth remains fairly const ...
, growing seasons of vegetation, and overall ecosystem productivity. The timing of the transition also influences changes in sea ice, ozone, air temperature, and cloudiness. Early and late polar breakup episodes have occurred, due to variations in the stratospheric flow structure and upward spreading of planetary waves from the troposphere. As a result of increased waves into the vortex, the vortex experiences more rapid warming than normal, resulting in an earlier breakup and spring. When the breakup comes early, it is characterized by with persistent of remnants of the vortex. When the breakup is late, the remnants dissipate rapidly. When the breakup is early, there is one warming period from late February to middle March. When the breakup is late, there are two warming periods, one January, and one in March. Zonal mean temperature, wind, and geopotential height exert varying deviations from their normal values before and after early breakups, while the deviations remain constant before and after late breakups. Scientists are connecting a delay in the Arctic vortex breakup with a reduction of planetary wave activities, few stratospheric sudden warming events, and depletion of ozone.

Sudden stratospheric warming
A sudden stratospheric warming (SSW) is an event in which the polar stratospheric temperature rises by several tens of kelvins (up to increases of about 50 °C (90 °F)) over the course of a few days. The warming is preceded by a slowing ...
events are associated with weaker polar vortices. This warming of stratospheric air can reverse the circulation in the Arctic Polar Vortex from counter-clockwise to clockwise. These changes aloft force changes in the troposphere below. An example of an effect on the troposphere is the change in speed of the Atlantic Ocean circulation pattern. A soft spot just south of Greenland is where the initial step of downwelling
Downwelling is the process of accumulation and sinking of higher density material beneath lower density material, such as cold or saline water beneath warmer or fresher water or cold air beneath warm air. It is the ''sinking'' limb of a convecti ...
occurs, nicknamed the "Achilles Heel of the North Atlantic". Small amounts of heating or cooling traveling from the polar vortex can trigger or delay downwelling
Downwelling is the process of accumulation and sinking of higher density material beneath lower density material, such as cold or saline water beneath warmer or fresher water or cold air beneath warm air. It is the ''sinking'' limb of a convecti ...
, altering the Gulf Stream Current of the Atlantic, and the speed of other ocean currents. Since all other oceans depend on the Atlantic Ocean's movement of heat energy, climates across the planet can be dramatically affected. The weakening or strengthening of the polar vortex can alter the sea circulation more than a mile beneath the waves. Strengthening storm systems within the troposphere that cool the poles, intensify the polar vortex. La Niña–related climate anomalies significantly strengthen the polar vortex. Intensification of the polar vortex produces changes in relative humidity as downward intrusions of dry, stratospheric air enter the vortex core. With a strengthening of the vortex comes a longwave cooling due to a decrease in water vapor concentration near the vortex. The decreased water content is a result of a lower tropopause within the vortex, which places dry stratospheric air above moist tropospheric air. Instability is caused when the vortex tube, the line of concentrated vorticity, is displaced. When this occurs, the vortex rings become more unstable and prone to shifting by planetary waves. The planetary wave activity in both hemispheres varies year-to-year, producing a corresponding response in the strength and temperature of the polar vortex. The number of waves around the perimeter of the vortex are related to the core size; as the vortex core decreases, the number of waves increase.
The degree of the mixing of polar and mid-latitude air depends on the evolution and position of the polar night jet. In general, the mixing is less inside the vortex than outside. Mixing occurs with unstable planetary waves that are characteristic of the middle and upper stratosphere in winter. Prior to vortex breakdown, there is little transport of air out of the Arctic Polar Vortex due to strong barriers above 420 km (261 miles). The polar night jet which exists below this, is weak in the early winter. As a result, it does not deviate any descending polar air, which then mixes with air in the mid-latitudes. In the late winter, air parcels do not descend as much, reducing mixing. After the vortex is broken up, the ex-vortex air is dispersed into the middle latitudes within a month.
Sometimes, a mass of the polar vortex breaks off before the end of the final warming period. If large enough, the piece can move into Canada and the Midwestern, Central, Southern, and Northeastern United States. This diversion of the polar vortex can occur due to the displacement of the polar jet stream; for example, the significant northwestward direction of the polar jet stream in the western part of the United States during the winters of 2013–2014, and 2014–2015. This caused warm, dry conditions in the west, and cold, snowy conditions in the north-central and northeast. Occasionally, the high-pressure air mass, called the Greenland Block, can cause the polar vortex to divert to the south, rather than follow its normal path over the North Atlantic.
Extreme weather
A study in 2001 found that stratospheric circulation can have anomalous effects on weather regimes. In the same year, researchers found a statistical correlation between weak polar vortex and outbreaks of severe cold in the Northern Hemisphere. In later years, scientists identified interactions withArctic sea ice decline
Arctic sea ice decline has occurred in recent decades due to the effects of climate change on oceans, with declines in sea ice area, extent, and volume. Sea ice in the Arctic Ocean has been melting more in summer than it refreezes in the winter. ...
, reduced snow cover, evapotranspiration
Evapotranspiration (ET) is the combined processes by which water moves from the earth’s surface into the atmosphere. It covers both water evaporation (movement of water to the air directly from soil, canopies, and water bodies) and transp ...
patterns, NAO anomalies or weather anomalies which are linked to the polar vortex and jet stream
Jet streams are fast flowing, narrow, meandering air currents in the atmospheres of some planets, including Earth. On Earth, the main jet streams are located near the altitude of the tropopause and are westerly winds (flowing west to east) ...
configuration.
Climate change

Ozone depletion
The chemistry of the Antarctic polar vortex has created severeozone depletion
Ozone depletion consists of two related events observed since the late 1970s: a steady lowering of about four percent in the total amount of ozone in Earth's atmosphere, and a much larger springtime decrease in stratospheric ozone (the ozone lay ...
, although the effect has been weakening since the 2000s. It is expected to return to 1980 levels in about 2075. The nitric acid in polar stratospheric clouds reacts with chlorofluorocarbon
Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs) are fully or partly halogenated hydrocarbons that contain carbon (C), hydrogen (H), chlorine (Cl), and fluorine (F), produced as volatile derivatives of methane, ethane, and p ...
s to form chlorine
Chlorine is a chemical element with the symbol Cl and atomic number 17. The second-lightest of the halogens, it appears between fluorine and bromine in the periodic table and its properties are mostly intermediate between them. Chlorine i ...
, which catalyzes the photochemical destruction of ozone
Ozone (), or trioxygen, is an inorganic molecule with the chemical formula . It is a pale blue gas with a distinctively pungent smell. It is an allotrope of oxygen that is much less stable than the diatomic allotrope , breaking down in the l ...
. Chlorine concentrations build up during the polar winter, and the consequent ozone destruction is greatest when the sunlight returns in spring. These clouds can only form at temperatures below about .
Since there is greater air exchange between the Arctic and the mid-latitudes, ozone depletion at the north pole is much less severe than at the south. Accordingly, the seasonal reduction of ozone levels over the Arctic is usually characterized as an "ozone dent", whereas the more severe ozone depletion over the Antarctic is considered an "ozone hole". That said, chemical ozone destruction in the 2011 Arctic polar vortex attained, for the first time, a level clearly identifiable as an Arctic " ozone hole".
Outside Earth
 Other astronomical bodies are also known to have polar vortices, including
Other astronomical bodies are also known to have polar vortices, including Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun. It is sometimes called Earth's "sister" or "twin" planet as it is almost as large and has a similar composition. As an interior planet to Earth, Venus (like Mercury) appears in Earth's sky never f ...
(double vortex – that is, two polar vortices at a pole), Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System, only being larger than Mercury. In the English language, Mars is named for the Roman god of war. Mars is a terrestrial planet with a thin at ...
, Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a mass more than two and a half times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined, but slightly less than one-thousand ...
, Saturn
Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second-largest in the Solar System, after Jupiter. It is a gas giant with an average radius of about nine and a half times that of Earth. It has only one-eighth the average density of Earth; h ...
, and Saturn's moon Titan
Titan most often refers to:
* Titan (moon), the largest moon of Saturn
* Titans, a race of deities in Greek mythology
Titan or Titans may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Fictional entities
Fictional locations
* Titan in fiction, fictiona ...
.
Saturn
Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second-largest in the Solar System, after Jupiter. It is a gas giant with an average radius of about nine and a half times that of Earth. It has only one-eighth the average density of Earth; h ...
's south pole is the only known hot polar vortex in the solar system.
See also
*Polar amplification
Polar amplification is the phenomenon that any change in the net radiation balance (for example greenhouse intensification) tends to produce a larger change in temperature near the poles than in the planetary average. This is commonly referred to a ...
* Saturn's hexagon
Saturn's hexagon is a persistent approximately hexagonal cloud pattern around the north pole of the planet Saturn, located at about 78°N.
The sides of the hexagon are about long, which is about longer than the diameter of Earth.
The hexagon m ...
– a persisting hexagonal cloud pattern around the north pole of Saturn
* Windward Performance Perlan II – will be used to study the northern polar vortex
* Polar front
In meteorology, the polar front is the weather front boundary between the polar cell and the Ferrel cell around the 60° latitude, near the polar regions, in both hemisphere. At this boundary a sharp gradient in temperature occurs between the ...
* Cut-off low
A cut-off low (or cutoff low), sometimes referred to as the weatherman's woe, is defined as "a closed upper-level low which has become completely displaced (cut off) from basic westerly current, and moves independently of that current" by the Nat ...
References
Further reading
* * * * * * * *External links
* * * * * * * * {{Authority control Atmospheric dynamics Regional climate effects Polar regions of the Earth Vortices