phenotypic trait on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A phenotypic trait, simply trait, or character state is a distinct variant of a phenotypic characteristic of an
A phenotypic trait, simply trait, or character state is a distinct variant of a phenotypic characteristic of an
 A phenotypic trait, simply trait, or character state is a distinct variant of a phenotypic characteristic of an
A phenotypic trait, simply trait, or character state is a distinct variant of a phenotypic characteristic of an organism
An organism is any life, living thing that functions as an individual. Such a definition raises more problems than it solves, not least because the concept of an individual is also difficult. Many criteria, few of them widely accepted, have be ...
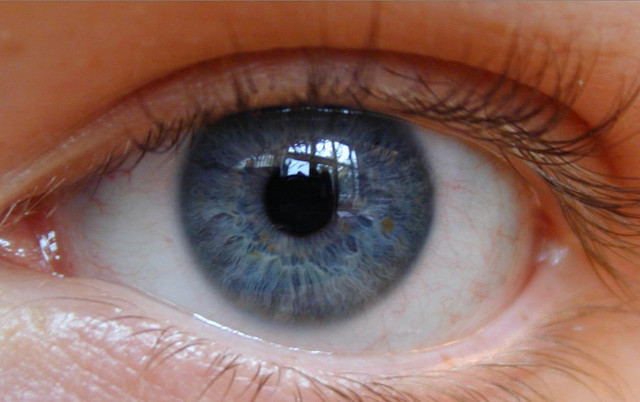
; it may be either inherited or determined environmentally, but typically occurs as a combination of the two.Lawrence, Eleanor (2005) ''Henderson's Dictionary of Biology''. Pearson, Prentice Hall. For example, having eye color
Eye color is a polygene, polygenic phenotypic trait determined by two factors: the pigmentation of the eye's Iris (anatomy), iris and the frequency-dependence of the scattering of light by the Turbidity, turbid medium in the Stroma of iris, str ...
is a ''character'' of an organism, while blue, brown and hazel versions of eye color are ''traits''. The term ''trait'' is generally used in genetics
Genetics is the study of genes, genetic variation, and heredity in organisms.Hartl D, Jones E (2005) It is an important branch in biology because heredity is vital to organisms' evolution. Gregor Mendel, a Moravian Augustinians, Augustinian ...
, often to describe the phenotypic expression of different combinations of allele
An allele is a variant of the sequence of nucleotides at a particular location, or Locus (genetics), locus, on a DNA molecule.
Alleles can differ at a single position through Single-nucleotide polymorphism, single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP), ...
s in different individual organisms within a single population
Population is a set of humans or other organisms in a given region or area. Governments conduct a census to quantify the resident population size within a given jurisdiction. The term is also applied to non-human animals, microorganisms, and pl ...
, such as the famous purple vs. white flower coloration in Gregor Mendel
Gregor Johann Mendel Order of Saint Augustine, OSA (; ; ; 20 July 1822 – 6 January 1884) was an Austrian Empire, Austrian biologist, meteorologist, mathematician, Augustinians, Augustinian friar and abbot of St Thomas's Abbey, Brno, St. Thom ...
's pea plants. By contrast, in systematics
Systematics is the study of the diversification of living forms, both past and present, and the relationships among living things through time. Relationships are visualized as evolutionary trees (synonyms: phylogenetic trees, phylogenies). Phy ...
, the term ''character state'' is employed to describe features that represent fixed diagnostic differences among taxa
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; : taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and ...
, such as the absence of tails in great apes, relative to other primate
Primates is an order (biology), order of mammals, which is further divided into the Strepsirrhini, strepsirrhines, which include lemurs, galagos, and Lorisidae, lorisids; and the Haplorhini, haplorhines, which include Tarsiiformes, tarsiers a ...
groups.
Definition
A phenotypic trait is an obvious, observable, and measurable characteristic of an organism; it is the expression of genes in an observable way. An example of a phenotypic trait is a specific hair color or eye color. Underlying genes, that make up thegenotype
The genotype of an organism is its complete set of genetic material. Genotype can also be used to refer to the alleles or variants an individual carries in a particular gene or genetic location. The number of alleles an individual can have in a ...
, determine the hair color, but the hair color observed is the phenotype.
The phenotype is dependent on the genetic make-up of the organism, but is also influenced by the environmental conditions that the organism was subjected to during its ontogenetic development, including various epigenetic processes.
Regardless of the degree of influence of genotype versus environment, the phenotype encompasses all of the characteristics of an organism, including traits at multiple levels of biological organization, ranging from behavior
Behavior (American English) or behaviour (British English) is the range of actions of Individual, individuals, organisms, systems or Artificial intelligence, artificial entities in some environment. These systems can include other systems or or ...
and evolutionary history of life
The history of life on Earth traces the processes by which living and extinct organisms evolved, from the earliest emergence of life to the present day. Earth formed about 4.5 billion years ago (abbreviated as ''Ga'', for '' gigaannum'') and ...
traits (e.g., litter size), through morphology (e.g., body height and composition), physiology (e.g., blood pressure), cellular characteristics (e.g., membrane lipid composition, mitochondrial densities), components of biochemical
Biochemistry, or biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. A sub-discipline of both chemistry and biology, biochemistry may be divided into three fields: structural biology, enzymology, ...
pathways, and even messenger RNA
In molecular biology, messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) is a single-stranded molecule of RNA that corresponds to the genetic sequence of a gene, and is read by a ribosome in the process of synthesizing a protein.
mRNA is created during the ...
.
Genetic origin of traits in diploid organisms
Different phenotypic traits are caused by different forms ofgenes
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protei ...
, or allele
An allele is a variant of the sequence of nucleotides at a particular location, or Locus (genetics), locus, on a DNA molecule.
Alleles can differ at a single position through Single-nucleotide polymorphism, single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP), ...
s, which arise by mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, ...
in a single individual and are passed on to successive generations.
Biochemistry of dominance and extensions to expression of traits
Thebiochemistry
Biochemistry, or biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. A sub-discipline of both chemistry and biology, biochemistry may be divided into three fields: structural biology, enzymology, a ...
of the intermediate proteins determines how they interact in the cell. Therefore, biochemistry predicts how different combinations of alleles will produce varying traits.
Extended expression patterns seen in diploid organisms include facets of incomplete dominance, codominance, and multiple alleles. Incomplete dominance is the condition in which neither allele dominates the other in one heterozygote. Instead the phenotype is intermediate in heterozygotes. Thus you can tell that each allele is present in the heterozygote. Codominance refers to the allelic relationship that occurs when two alleles are both expressed in the heterozygote, and both phenotypes are seen simultaneously. Multiple alleles refers to the situation when there are more than 2 common alleles of a particular gene. Blood groups in humans is a classic example. The ABO blood group proteins are important in
determining blood type in humans, and this is determined by different alleles of the one locus.
Continuum versus categorical traits
Schizotypy is an example of a psychological phenotypic trait found in schizophrenia-spectrum disorders. Studies have shown that gender and age influences the expression of schizotypal traits. For instance, certain schizotypal traits may develop further during adolescence, whereas others stay the same during this period.See also
* Allometric engineering of traits *Character displacement
Character or Characters may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Literature
* ''Character'' (novel), a 1936 Dutch novel by Ferdinand Bordewijk
* ''Characters'' (Theophrastus), a classical Greek set of character sketches attributed to Theoph ...
* Eye color
Eye color is a polygene, polygenic phenotypic trait determined by two factors: the pigmentation of the eye's Iris (anatomy), iris and the frequency-dependence of the scattering of light by the Turbidity, turbid medium in the Stroma of iris, str ...
* Phene
* Phenotype
In genetics, the phenotype () is the set of observable characteristics or traits of an organism. The term covers the organism's morphology (physical form and structure), its developmental processes, its biochemical and physiological propert ...
* Race (biology)
In Taxonomy (biology), biological taxonomy, race is an informal group (taxonomy), informal Taxonomic rank, rank in the taxonomic hierarchy for which various definitions exist. Sometimes it is used to denote a level below that of subspecies, whi ...
* Skill
A skill is the learned or innate
ability to act with determined results with good execution often within a given amount of time, energy, or both.
Skills can often be divided into domain-general and domain-specific skills. Some examples of gen ...
Citations
References
* Lawrence, Eleanor (2005) ''Henderson's Dictionary of Biology''. Pearson, Prentice Hall. * {{genarch Classical genetics