payroll tax on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Payroll taxes are taxes imposed on employers or employees. They are usually calculated as a percentage of the salaries that employers pay their employees. By law, some payroll taxes are the responsibility of the employee and others fall on the employer, but almost all economists agree that the true economic incidence of a payroll tax is unaffected by this distinction, and falls largely or entirely on workers in the form of lower wages. Because payroll taxes fall exclusively on wages and not on returns to financial or physical investments, payroll taxes may contribute to underinvestment in
Payroll taxes are taxes imposed on employers or employees. They are usually calculated as a percentage of the salaries that employers pay their employees. By law, some payroll taxes are the responsibility of the employee and others fall on the employer, but almost all economists agree that the true economic incidence of a payroll tax is unaffected by this distinction, and falls largely or entirely on workers in the form of lower wages. Because payroll taxes fall exclusively on wages and not on returns to financial or physical investments, payroll taxes may contribute to underinvestment in
 In the United States, payroll taxes are also called employment taxes by the Internal Revenue Service.
In the United States, payroll taxes are assessed by the federal government, some of the 50 states and numerous cities. These taxes are imposed on employers and employees and on various compensation bases and are collected and paid to the taxing jurisdiction by the employers. Most jurisdictions imposing payroll taxes require reporting quarterly and annually in most cases, and electronic reporting is generally required for all but small employers.
In the United States, payroll taxes are also called employment taxes by the Internal Revenue Service.
In the United States, payroll taxes are assessed by the federal government, some of the 50 states and numerous cities. These taxes are imposed on employers and employees and on various compensation bases and are collected and paid to the taxing jurisdiction by the employers. Most jurisdictions imposing payroll taxes require reporting quarterly and annually in most cases, and electronic reporting is generally required for all but small employers.
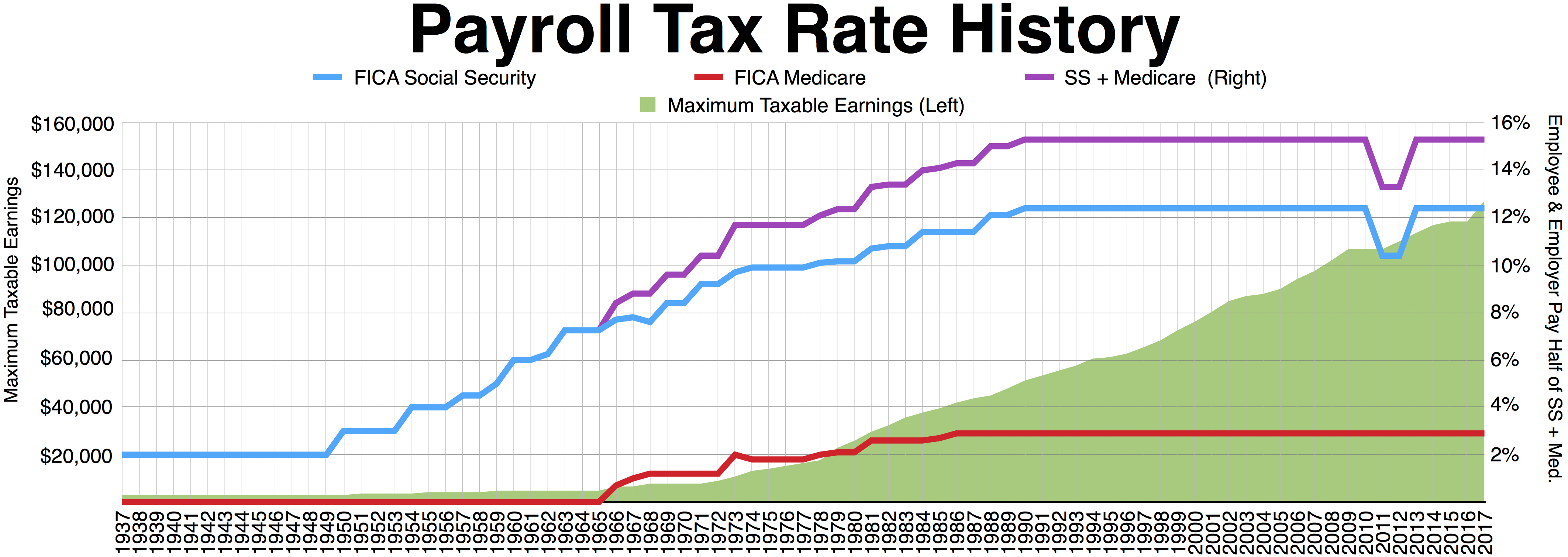 Federal social insurance taxes are imposed on employers and employees, ordinarily consisting of a tax of 12.4% of wages up to an annual wage maximum ($118,500 in wages, for a maximum contribution of $14,694 in 2016) for
Federal social insurance taxes are imposed on employers and employees, ordinarily consisting of a tax of 12.4% of wages up to an annual wage maximum ($118,500 in wages, for a maximum contribution of $14,694 in 2016) for
26 USC 6672
Payroll tax in ChinaIRS publication 15
- detailed information on federal payroll tax in the U.S.
Trust Fund Recovery Penalty
irs.gov Wages and salaries Withholding taxes Taxation-related lists Payroll
 Payroll taxes are taxes imposed on employers or employees. They are usually calculated as a percentage of the salaries that employers pay their employees. By law, some payroll taxes are the responsibility of the employee and others fall on the employer, but almost all economists agree that the true economic incidence of a payroll tax is unaffected by this distinction, and falls largely or entirely on workers in the form of lower wages. Because payroll taxes fall exclusively on wages and not on returns to financial or physical investments, payroll taxes may contribute to underinvestment in
Payroll taxes are taxes imposed on employers or employees. They are usually calculated as a percentage of the salaries that employers pay their employees. By law, some payroll taxes are the responsibility of the employee and others fall on the employer, but almost all economists agree that the true economic incidence of a payroll tax is unaffected by this distinction, and falls largely or entirely on workers in the form of lower wages. Because payroll taxes fall exclusively on wages and not on returns to financial or physical investments, payroll taxes may contribute to underinvestment in human capital
Human capital or human assets is a concept used by economists to designate personal attributes considered useful in the production process. It encompasses employee knowledge, skills, know-how, good health, and education. Human capital has a subs ...
, such as higher education.
National payroll tax systems
Australia
The Australian federal government ( ATO) requires withholding tax on employment income (payroll taxes of the first type), under a system known as pay-as-you-go (PAYG). The individual states impose payroll taxes of the second type.Bermuda
InBermuda
Bermuda is a British Overseas Territories, British Overseas Territory in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean. The closest land outside the territory is in the American state of North Carolina, about to the west-northwest.
Bermuda is an ...
, payroll tax accounts for over a third of the annual national budget, making it the primary source of government revenue. The tax is paid by employers based on the total remuneration (salary and benefits) paid to all employees, at a standard rate of 14% (though, under certain circumstances, can be as low as 4.75%). Employers are allowed to deduct a small percentage of an employee's pay (around 4%). Another tax, social insurance
Social insurance is a form of Social protection, social welfare that provides insurance against economic risks. The insurance may be provided publicly or through the subsidizing of private insurance. In contrast to other forms of Welfare spend ...
, is withheld by the employer.
Brazil
InBrazil
Brazil, officially the Federative Republic of Brazil, is the largest country in South America. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, fifth-largest country by area and the List of countries and dependencies by population ...
, employers are required to withhold 11% of the employee's wages for Social Security and a certain percentage as Income Tax (according to the applicable tax bracket). The employer is required to contribute an additional 20% of the total payroll value to the Social Security system. Depending on the company's main activity, the employer must also contribute to federally funded insurance and educational programs.
There is also a required deposit of 8% of the employee's wages (not withheld from him) into a bank account that can be withdrawn only when the employee is fired, or under certain other extraordinary circumstances, such as serious illness (called a "Security Fund for Duration of Employment"). All these contributions amount to a total tax burden of almost 40% of the payroll for the employer and 15% of the employee's wages.
Canada
TheNorthwest Territories
The Northwest Territories is a federal Provinces and territories of Canada, territory of Canada. At a land area of approximately and a 2021 census population of 41,070, it is the second-largest and the most populous of Provinces and territorie ...
in Canada applies a payroll tax of 2% to all employees. It is an example of the second type of payroll tax, but unlike in other jurisdictions, it is paid directly by employees rather than employers. Unlike the first type of payroll tax as it is applied in Canada, though, there is no basic personal exemption below which employees are not required to pay the tax.
Ontario
Ontario is the southernmost Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada. Located in Central Canada, Ontario is the Population of Canada by province and territory, country's most populous province. As of the 2021 Canadian census, it ...
applies a health premium tax to all payrolls on a sliding scale up to $900 per year.
China
InChina
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
, the payroll tax is a specific tax that is paid to provinces and territories by employers, not by employees. The tax is deducted from the worker's pay. The Chinese Government itself requires only one tax to be withheld from paychecks: the PAYG (or pay-as-you-go) tax, which includes medicare levies and insurances.
Tax calculations and contributions differ from city to city in China, and each city's data will be updated yearly.
Taxable Income = Gross Salary – Social Benefits – ¥3,500 IIT = Taxable Income x Tax Rate – Quick Deduction Net Salary = Gross Salary – Social Benefits – IIT
Croatia
InCroatia
Croatia, officially the Republic of Croatia, is a country in Central Europe, Central and Southeast Europe, on the coast of the Adriatic Sea. It borders Slovenia to the northwest, Hungary to the northeast, Serbia to the east, Bosnia and Herze ...
, the payroll tax is composed of several items:
* national income tax on personal income (), which is applied incrementally with rates of 0% (personal exemption = 3800 HRK), 24% (3800-30000 HRK) and 36% (30000 HRK - )
* optional local surcharge on personal income (), which is applied by some cities and municipalities on the amount of national tax, currently up to 18% (in Zagreb
Zagreb ( ) is the capital (political), capital and List of cities and towns in Croatia#List of cities and towns, largest city of Croatia. It is in the Northern Croatia, north of the country, along the Sava river, at the southern slopes of the ...
)
* pension insurance (), universal 20%, for some people divided into two different funds, one of which is government-managed (15%) and the other is a personal pension fund (5%)
* health insurance (), universal 16.5%
* health insurance exemption exists for the population below 30 years of age as part of government policy to encourage youth employment.
Czech Republic
The income tax in the Czech Republic is progressive. The primary tax rate is 15% of gross income, but for an annual salary that is 48 times bigger than the average monthly salary (38.911 CZK in 2022, around 1.600 EUR), the rate is 23%. That applies only to the difference. The minimum wage to pay income tax is 27.840CZK in 2021 (approx. 1140EUR). For people with trade certificates, the rate applies only to 40% of their revenue. The remaining 60% can be deducted as a standard expense. Freelancers also have to file an Income tax return every year. Taxpayers can apply a few tax deductions, such as a deduction for a child (starting at approx. 600EUR annually in 2021), for being a student (approx. 160EUR in 2021), for a dependent spouse (approx. 1000EUR in 2021) and more. Health and social insurance are mandatory and a part of a payroll tax. The health insurance rate is 13,5%. For employees with a salary higher than the minimum wage (16.200CZK in 2022, approximately 660EUR), 9% pay the employers, and only 4,5% pay the employees. Trade license workers pay it themselves. Categories that do not have to pay health and social insurance are, for example, students or people registered at the unemployment department. The social insurance rate is 31,5% for employees (6,5% paid by the employee and 25% by the employer) and 29,2% for freelancers. The income tax makes up to half of the national income. The health and social insurance make another 30-40%.Finland
In Finland, there are several payroll taxes: *paid by employees on their income: :* pension insurance fee (''työeläkevakuutusmaksu''): employeesThe Employees Pensions Act (first link) provides that the employee contributes to a pension fund by paying a part from their ''compensation for employment'' – i.d., from their wages or their salary. What constitutes ''employment'' is defined in the Employment Contracts Act (second link): * * 17–68 years of age pay a 7,15% fee on their gross earned income :* unemployment insurance fee (''työttömyysvakuutusmaksu''): employees 18–65 years of ageThe Act on the Financing of Unemployment Benefits (555/1998) section 12 subsection 1 (first link) provides that everyone employed in Finland is required to pay unemployment insurance fee. The section 12a subsection 1 paragraphs 1–2 (second link) provide for the age limit: * * pay a 0.79% fee on their gross earned income :* health insurance daily allowance contribution (''sairausvakuutuksen päivärahamaksu''): employees 16–68 years of age pay a 1.01% contribution on their entire gross earned income if it equals to, or exceeds €16,499France
In France, statutory payroll tax only covers employee and employer contributions to the social security system. Income tax deductions from the payroll are voluntary and may be requested by the employee, otherwise, employees are billed 2 mandatory income tax prepayments during the year directly by the tax authority (set at 1/3 of the prior year's final tax bill). Employee payroll tax is made up of assigned taxes for the three branches of the social security system and includes both basic and supplementary coverage. Different percentages apply depending on thresholds that are multiples of the social security earnings ceiling (in 2012 = 36,372 euro per year). Contributions for salaries between the minimum wage and 1.6 times the minimum wage are eligible to relief (known as Fillon relief) of up to 28 percentage points of employer contributions, effectively halving employer non-wage costs.Germany
German employers are obliged to withhold wage tax on a monthly basis. The wage tax withheld will be qualified as prepayment of the income tax of the employee in case the taxpayer files an annual income tax return. The actual tax rate depends on the personal income of the employee and the tax class the employee (and his/her partner) has chosen. The choice of tax class is only important for withholding tax, and therefore for immediately disposable income. The choice of tax class has no effect on tax refunds. In addition to income tax withheld, employees and employers in Germany must pay contributions to finance social security benefits. The social security system consists of four insurances, for which the contribution will be (nearly) equally shared between employer and employee (old age insurance, unemployment insurance, health insurance and nursing care insurance). Contributions are payable only on wages up to the social security threshold: In addition, there are some insurances which are covered by the employee only (accident insurance, insolvency insurance, contribution to the maternity allocation, contribution for sick pay allocation for small companies). The following table shows employee and employer contributions by category for the year 2015.Greece
An employer is obligated to deduct tax at source from an employee and to make additional contributions to social security as in many other EU member states. The employer's contribution amounts to 28.06% of the salary. The employee's contribution is 16%.Hong Kong
InHong Kong
Hong Kong)., Legally Hong Kong, China in international treaties and organizations. is a special administrative region of China. With 7.5 million residents in a territory, Hong Kong is the fourth most densely populated region in the wor ...
, salaries tax is capped at 15%. Depending on income, employers fall into different tax brackets.
Sweden
In 2018, the Swedish social security contribution paid by the employer is 31.42 percent, calculated on top of the employee's salary. The percentage is lower for old employees. The other type of Swedish payroll tax is the income tax withheld ( PAYE), which consists of municipal, county, and, for higher income brackets, state tax. In most municipalities, the income tax comes to approximately 32 percent, with the two higher income brackets also paying a state tax of 20 or 25 percent respectively. The combination of the two types is a total marginal tax effect of 52 to 60 percent. According to a 2019 study in the ''American Economic Review'', a large employee payroll tax cut for young workers did not lead to increases in wages for young workers, but it did lead to an increase in employment, capital, sales, and profits of firms with many young workers.United Kingdom
In theUnited Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
, pay as you earn (PAYE) income tax and Employees' National Insurance contributions are examples of the first kind of payroll tax, while Employers' National Insurance contributions are an example of the second kind of payroll tax. There are currently (February 2022) five PAYE income tax bands in Scotland and four elsewhere; see for details. Both income tax and National Insurance contributions are paid only on income above a lower threshold. This threshold is progressively eliminated for the highest earners, beginning at £100,000 per year.
United States
 In the United States, payroll taxes are also called employment taxes by the Internal Revenue Service.
In the United States, payroll taxes are assessed by the federal government, some of the 50 states and numerous cities. These taxes are imposed on employers and employees and on various compensation bases and are collected and paid to the taxing jurisdiction by the employers. Most jurisdictions imposing payroll taxes require reporting quarterly and annually in most cases, and electronic reporting is generally required for all but small employers.
In the United States, payroll taxes are also called employment taxes by the Internal Revenue Service.
In the United States, payroll taxes are assessed by the federal government, some of the 50 states and numerous cities. These taxes are imposed on employers and employees and on various compensation bases and are collected and paid to the taxing jurisdiction by the employers. Most jurisdictions imposing payroll taxes require reporting quarterly and annually in most cases, and electronic reporting is generally required for all but small employers.
Social Security and Medicare taxes
 Federal social insurance taxes are imposed on employers and employees, ordinarily consisting of a tax of 12.4% of wages up to an annual wage maximum ($118,500 in wages, for a maximum contribution of $14,694 in 2016) for
Federal social insurance taxes are imposed on employers and employees, ordinarily consisting of a tax of 12.4% of wages up to an annual wage maximum ($118,500 in wages, for a maximum contribution of $14,694 in 2016) for Social Security
Welfare spending is a type of government support intended to ensure that members of a society can meet basic human needs such as food and shelter. Social security may either be synonymous with welfare, or refer specifically to social insurance ...
and a tax of 2.9% (half imposed on employer and half withheld from the employee's pay) of all wages for Medicare. The Social Security tax is divided into 6.2% that is visible to employees (the "employee contribution") and 6.2% that is visible only to employers (the "employer's contribution"). For the years 2011 and 2012, the employee's contribution had been temporarily reduced to 4.2%, while the employer's portion remained at 6.2%, but Congress allowed the rate to return to 6.2% for the individual in 2013. To the extent an employee's portion of the 6.2% tax exceeded the maximum by reason of multiple employers, the employee is entitled to a refundable tax credit
A tax credit is a tax incentive which allows certain taxpayers to subtract the amount of the credit they have accrued from the total they owe the state. It may also be a credit granted in recognition of taxes already paid or a form of state "dis ...
upon filing an income tax return for the year.
Income tax withholding
Federal, state, and localwithholding tax
Tax withholding, also known as tax retention, pay-as-you-earn tax or tax deduction at source, is income tax paid to the government by the payer of the income rather than by the recipient of the income. The tax is thus withheld or deducted from the ...
es are required in those jurisdictions imposing an income tax. Employers having contact with the jurisdiction must withhold the tax from wages paid to their employees in those jurisdictions. Computation of the amount of tax to withhold is performed by the employer based on representations by the employee regarding their tax status on IRS Form W-4.
Amounts of income tax so withheld must be paid to the taxing jurisdiction, and are available as refundable tax credits to the employees. Income taxes withheld from payroll are not final taxes, merely prepayments. Employees must still file income tax returns and self assess tax, claiming amounts withheld as payments.
Unemployment taxes
Employers are subject to unemployment taxes by the federal and all state governments. The tax is a percentage of taxable wages with a cap. The tax rate and cap vary by jurisdiction and by employer's industry and experience rating. For 2009, the typical maximum tax per employee was under $1,000. Some states also impose unemployment, disability insurance, or similar taxes on employees.Reporting and payment
Employers must report payroll taxes to the appropriate taxing jurisdiction in the manner each jurisdiction provides. Quarterly reporting of aggregate income tax withholding and Social Security taxes is required in most jurisdictions. Employers must file reports of aggregate unemployment tax quarterly and annually with each applicable state, and annually at the Federal level. Each employer is required to provide each employee an annual report on IRS Form W-2 of wages paid and Federal, state and local taxes withheld. A copy must be sent to the IRS, and some state governments also require a copy. These are due by January 31 and February 28 (March 31 if filed electronically), respectively, following the calendar year in which wages are paid. The Form W-2 constitutes proof of payment of tax for the employee. Employers are required to pay payroll taxes to the taxing jurisdiction under varying rules, in many cases within one banking day. Payment of Federal and many state payroll taxes is required to be made byelectronic funds transfer
Electronic funds transfer (EFT) is the transfer of money from one bank account to another, either within a single financial institution or across multiple institutions, via computer-based systems.
The funds transfer process generally consists ...
if certain dollar thresholds are met, or by deposit with a bank for the benefit of the taxing jurisdiction.
Penalties
Failure to timely and properly pay federal payroll taxes results in an automatic penalty of 2% to 10%. This is called the Trust Fund Recovery Penalty. Similar state and local penalties apply. Failure to properly file monthly or quarterly returns may result in additional penalties. Failure to file Forms W-2 results in an automatic penalty of up to $50 per form not timely filed. State and local penalties vary by jurisdiction. A particularly severe penalty applies where federal income tax withholding and Social Security taxes are not paid to the IRS. The penalty of up to 100% of the amount not paid can be assessed against the employer entity as well as any person (such as a corporate officer) having control or custody of the funds from which payment should have been made.See also
*List of countries by tax rates
A comparison of tax rates by countries is difficult and somewhat subjective, as tax laws in most countries are extremely complex and the Tax incidence, tax burden falls differently on different groups in each country and sub-national unit. The l ...
References
{{Reflist, colwidth=30emExternal links
Payroll tax in China
- detailed information on federal payroll tax in the U.S.
Trust Fund Recovery Penalty
irs.gov Wages and salaries Withholding taxes Taxation-related lists Payroll