Partition Of The Ottoman Empire on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The partition of the Ottoman Empire (30 October 19181 November 1922) was a geopolitical event that occurred after
 During the Great War, Britain produced three contrasting, but feasibly compatible, statements regarding their ambitions for Palestine. Britain had supported, through British intelligence officer T. E. Lawrence (aka Lawrence of Arabia), the establishment of a united Arab state covering a large area of the Arab Middle East in exchange for Arab support of the British during the war. The
During the Great War, Britain produced three contrasting, but feasibly compatible, statements regarding their ambitions for Palestine. Britain had supported, through British intelligence officer T. E. Lawrence (aka Lawrence of Arabia), the establishment of a united Arab state covering a large area of the Arab Middle East in exchange for Arab support of the British during the war. The

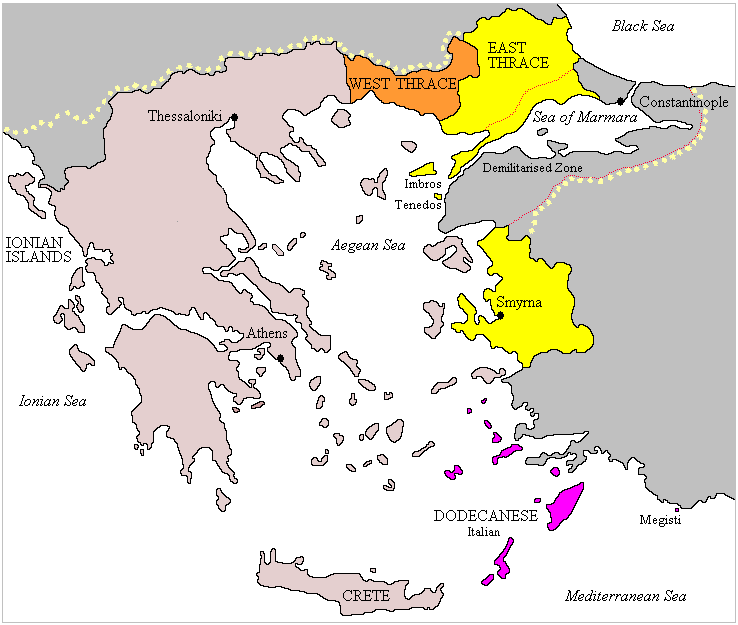 The western Allies, particularly Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, British Prime Minister David Lloyd George, promised Greece territorial gains at the expense of the
The western Allies, particularly Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, British Prime Minister David Lloyd George, promised Greece territorial gains at the expense of the
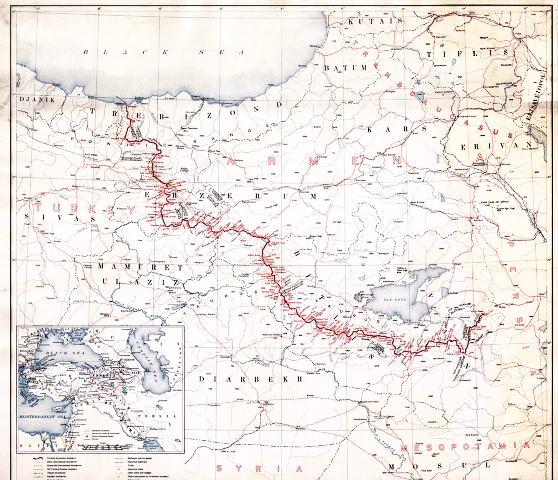 In the later years of World War I, the Armenians in Russia established a provisional government in the south-west of the Russian Empire. Military conflicts between the Turks and Armenians both during and after the war eventually determined the borders of the state of
In the later years of World War I, the Armenians in Russia established a provisional government in the south-west of the Russian Empire. Military conflicts between the Turks and Armenians both during and after the war eventually determined the borders of the state of
Occupation during and after the War (Ottoman Empire)
in
* Smith, Leonard V.
Post-war Treaties (Ottoman Empire/ Middle East)
in
{{Turkish War of Independence History of Greece (1909–1924) Modern history of Turkey 20th century in Iraq Ottoman Syria Ottoman Greece Partition (politics) 20th century in Armenia Aftermath of World War I in Turkey Turkey–United Kingdom relations Ottoman Empire–United Kingdom relations 20th century in Syria Ottoman period in Armenia Iraq–Turkey relations Dissolution of the Ottoman Empire 1920s in Islam
World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
and the occupation of Constantinople
The occupation of Istanbul ( tr, İstanbul'un İşgali; 12 November 1918 – 4 October 1923), the capital of the Ottoman Empire, by British, French, Italian, and Greek forces, took place in accordance with the Armistice of Mudros, which ended O ...
by British, French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
and Italian troops in November 1918. The partitioning was planned in several agreements made by the Allied Powers early in the course of World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
, notably the Sykes–Picot Agreement
The Sykes–Picot Agreement () was a 1916 secret treaty between the United Kingdom and France, with assent from the Russian Empire and the Kingdom of Italy, to define their mutually agreed spheres of influence and control in an eventual partition ...
, after the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University ...
had joined Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwee ...
to form the Ottoman–German Alliance. The huge conglomeration of territories and peoples that formerly comprised the Ottoman Empire was divided into several new states. The Ottoman Empire had been the leading Islamic state
An Islamic state is a state that has a form of government based on Islamic law (sharia). As a term, it has been used to describe various historical polities and theories of governance in the Islamic world. As a translation of the Arabic ter ...
in geopolitical, cultural and ideological terms. The partitioning of the Ottoman Empire after the war led to the domination of the Middle East
The Middle East ( ar, الشرق الأوسط, ISO 233: ) is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabian Peninsula, Arabia (including the Arabian Peninsula and Bahrain), Anatolia, Asia Minor (Asian part of Turkey except Hatay Pro ...
by Western powers such as Britain and France, and saw the creation of the modern Arab world
The Arab world ( ar, اَلْعَالَمُ الْعَرَبِيُّ '), formally the Arab homeland ( '), also known as the Arab nation ( '), the Arabsphere, or the Arab states, refers to a vast group of countries, mainly located in Western A ...
and the Republic of Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula ...
. Resistance to the influence of these powers came from the Turkish National Movement
The Turkish National Movement ( tr, Türk Ulusal Hareketi) encompasses the political and military activities of the Turkish revolutionaries that resulted in the creation and shaping of the modern Republic of Turkey, as a consequence of the def ...
but did not become widespread in the other post-Ottoman states until the period of rapid decolonization after World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
.
The sometimes-violent creation of protectorate
A protectorate, in the context of international relations, is a state that is under protection by another state for defence against aggression and other violations of law. It is a dependent territory that enjoys autonomy over most of its in ...
s in Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq ...
and Palestine, and the proposed division of Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
along communal lines, is thought to have been a part of the larger strategy of ensuring tension in the Middle East, thus necessitating the role of Western colonial powers (at that time Britain, France and Italy) as peace brokers and arms suppliers. The League of Nations mandate
A League of Nations mandate was a legal status for certain territories transferred from the control of one country to another following World War I, or the legal instruments that contained the internationally agreed-upon terms for administ ...
granted the French Mandate for Syria and the Lebanon, the British Mandate for Mesopotamia (later Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq ...
) and the British Mandate for Palestine
The Mandate for Palestine was a League of Nations mandate for British administration of the territories of Mandatory Palestine, Palestine and Emirate of Transjordan, Transjordan, both of which had been conceded by the Ottoman Empire following ...
, later divided into Mandatory Palestine
Mandatory Palestine ( ar, فلسطين الانتدابية '; he, פָּלֶשְׂתִּינָה (א״י) ', where "E.Y." indicates ''’Eretz Yiśrā’ēl'', the Land of Israel) was a geopolitical entity established between 1920 and 1948 ...
and the Emirate of Transjordan
The Emirate of Transjordan ( ar, إمارة شرق الأردن, Imārat Sharq al-Urdun, Emirate of East Jordan), officially known as the Amirate of Trans-Jordan, was a British protectorate established on 11 April 1921,
(1921–1946). The Ottoman Empire's possessions in the Arabian Peninsula
The Arabian Peninsula, (; ar, شِبْهُ الْجَزِيرَةِ الْعَرَبِيَّة, , "Arabian Peninsula" or , , "Island of the Arabs") or Arabia, is a peninsula of Western Asia, situated northeast of Africa on the Arabian Plat ...
became the Kingdom of Hejaz
The Hashemite Kingdom of Hejaz ( ar, المملكة الحجازية الهاشمية, ''Al-Mamlakah al-Ḥijāziyyah Al-Hāshimiyyah'') was a state in the Hejaz region in the Middle East that included the western portion of the Arabian Penins ...
, which the Sultanate of Nejd (today Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country in Western Asia. It covers the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula, and has a land area of about , making it the fifth-largest country in Asia, the second-largest in the Ara ...
) was allowed to annex, and the Mutawakkilite Kingdom of Yemen. The Empire's possessions on the western shores of the Persian Gulf
The Persian Gulf ( fa, خلیج فارس, translit=xalij-e fârs, lit=Gulf of Fars, ), sometimes called the ( ar, اَلْخَلِيْجُ ٱلْعَرَبِيُّ, Al-Khalīj al-ˁArabī), is a mediterranean sea in Western Asia. The bo ...
were variously annexed by Saudi Arabia ( al-Ahsa and Qatif), or remained British protectorates (Kuwait
Kuwait (; ar, الكويت ', or ), officially the State of Kuwait ( ar, دولة الكويت '), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated in the northern edge of Eastern Arabia at the tip of the Persian Gulf, bordering Iraq to Iraq–Ku ...
, Bahrain
Bahrain ( ; ; ar, البحرين, al-Bahrayn, locally ), officially the Kingdom of Bahrain, ' is an island country in Western Asia. It is situated on the Persian Gulf, and comprises a small archipelago made up of 50 natural islands and a ...
, and Qatar
Qatar (, ; ar, قطر, Qaṭar ; local vernacular pronunciation: ), officially the State of Qatar,) is a country in Western Asia. It occupies the Qatar Peninsula on the northeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula in the Middle East; it sh ...
) and became the Arab States of the Persian Gulf.
After the Ottoman government collapsed completely, its representatives signed the Treaty of Sèvres
The Treaty of Sèvres (french: Traité de Sèvres) was a 1920 treaty signed between the Allies of World War I and the Ottoman Empire. The treaty ceded large parts of Ottoman territory to France, the United Kingdom, Greece and Italy, as well ...
in 1920, which would have partitioned much of the territory of present-day Turkey among France, the United Kingdom, Greece and Italy. The Turkish War of Independence
The Turkish War of Independence "War of Liberation", also known figuratively as ''İstiklâl Harbi'' "Independence War" or ''Millî Mücadele'' "National Struggle" (19 May 1919 – 24 July 1923) was a series of military campaigns waged by th ...
forced the Western European powers to return to the negotiating table before the treaty could be ratified. The Western Europeans and the Grand National Assembly of Turkey
The Grand National Assembly of Turkey ( tr, ), usually referred to simply as the TBMM or Parliament ( tr, or ''Parlamento''), is the unicameral Turkish legislature. It is the sole body given the legislative prerogatives by the Turkish Cons ...
signed and ratified the new Treaty of Lausanne in 1923, superseding the Treaty of Sèvres and agreeing on most of the territorial issues. One unresolved issue, the dispute between the Kingdom of Iraq and the Republic of Turkey over the former province of Mosul, was later negotiated under the auspices of the League of Nations
The League of Nations (french: link=no, Société des Nations ) was the first worldwide intergovernmental organisation whose principal mission was to maintain world peace. It was founded on 10 January 1920 by the Paris Peace Conference th ...
in 1926. The British and French partitioned Greater Syria between them in the Sykes-Picot Agreement. Other secret agreements were concluded with Italy and Russia. The Balfour Declaration
The Balfour Declaration was a public statement issued by the British government in 1917 during the First World War announcing its support for the establishment of a "national home for the Jewish people" in Palestine, then an Ottoman regio ...
encouraged the international Zionist
Zionism ( he, צִיּוֹנוּת ''Tsiyyonut'' after '' Zion'') is a nationalist movement that espouses the establishment of, and support for a homeland for the Jewish people centered in the area roughly corresponding to what is known in Je ...
movement to push for a Jewish homeland in Palestine. While a part of the Triple Entente, Russia also had wartime agreements Agreement may refer to:
Agreements between people and organizations
* Gentlemen's agreement, not enforceable by law
* Trade agreement, between countries
* Consensus, a decision-making process
* Contract, enforceable in a court of law
** Meeting of ...
preventing it from participating in the partitioning of the Ottoman Empire after the Russian Revolution
The Russian Revolution was a period of political and social revolution that took place in the former Russian Empire which began during the First World War. This period saw Russia abolish its monarchy and adopt a socialist form of government ...
. The Treaty of Sèvres formally acknowledged the new League of Nations mandates in the region, the independence of Yemen
Yemen (; ar, ٱلْيَمَن, al-Yaman), officially the Republic of Yemen,, ) is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula, and borders Saudi Arabia to the north and Oman to the northeast and ...
, and British sovereignty over Cyprus.
Background
The Western powers had long believed that they would eventually become dominant in the area claimed by the weak central government of the Ottoman Empire. Britain anticipated a need to secure the area because of its strategic position on the route to Colonial India and perceived itself as locked in a struggle with Russia for imperial influence known as The Great Game. These powers disagreed over their contradictory post-war aims and made several dual and triple agreements.French Mandates
Syria and Lebanon became a Frenchprotectorate
A protectorate, in the context of international relations, is a state that is under protection by another state for defence against aggression and other violations of law. It is a dependent territory that enjoys autonomy over most of its in ...
(thinly disguised as a League of Nations Mandate
A League of Nations mandate was a legal status for certain territories transferred from the control of one country to another following World War I, or the legal instruments that contained the internationally agreed-upon terms for administ ...
). French control was met immediately with armed resistance, and, to combat Arab nationalism
Arab nationalism ( ar, القومية العربية, al-Qawmīya al-ʿArabīya) is a nationalist ideology that asserts the Arabs are a nation and promotes the unity of Arab people, celebrating the glories of Arab civilization, the language ...
, France divided the Mandate area into Lebanon and four sub-states.
Mandate of Syria
Compared to the mandate of Lebanon, the situation in Syria was more chaotic. The Entities stated are the ones that are united. * Syrian Federation: Included State of Damascus, Alawite State, and State of Aleppo (including Sanjak of Alexandretta), which were the former territorial components of the briefly existingArab Kingdom of Syria
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, No ...
.
* State of Syria (1925–1930): Successor to the Syrian Federation era (Not including the Alawite State).
*First Syrian Republic
The First Syrian Republic, officially the Syrian Republic, '; french: République syrienne was formed in 1930 as a component of the Mandate for Syria and the Lebanon, succeeding the State of Syria. A treaty of independence was made in 1936 t ...
: State of Syria (1925–1930) with the territories of Jabal Druze State and Alawite State incorporated ( Hatay State later merged with Turkey).
Mandate of Lebanon
Greater Lebanon was the name of aterritory
A territory is an area of land, sea, or space, particularly belonging or connected to a country, person, or animal.
In international politics, a territory is usually either the total area from which a state may extract power resources or a ...
created by France. It was the precursor of modern Lebanon
Lebanon ( , ar, لُبْنَان, translit=lubnān, ), officially the Republic of Lebanon () or the Lebanese Republic, is a country in Western Asia. It is located between Syria to the north and east and Israel to the south, while Cyprus lie ...
. It existed between 1 September 1920 and 23 May 1926. France carved its territory from the Levant
The Levant () is an approximate historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is ...
ine landmass (mandated by the League of Nations
The League of Nations (french: link=no, Société des Nations ) was the first worldwide intergovernmental organisation whose principal mission was to maintain world peace. It was founded on 10 January 1920 by the Paris Peace Conference th ...
) to create a "haven" for the Maronite
The Maronites ( ar, الموارنة; syr, ܡܖ̈ܘܢܝܐ) are a Christian ethnoreligious group native to the Eastern Mediterranean and Levant region of the Middle East, whose members traditionally belong to the Maronite Church, with the lar ...
Christian population. Maronites gained self-rule and secured their position in independent Lebanon in 1943.
French intervention on behalf of the Maronite
The Maronites ( ar, الموارنة; syr, ܡܖ̈ܘܢܝܐ) are a Christian ethnoreligious group native to the Eastern Mediterranean and Levant region of the Middle East, whose members traditionally belong to the Maronite Church, with the lar ...
s had begun with the capitulations of the Ottoman Empire, agreements made during the 16th to the 19th centuries. In 1866, when Youssef Bey Karam led a Maronite uprising in Mount Lebanon, a French-led naval force arrived to help, making threats against the governor, Dawood Pasha, at the Sultan's Porte and later removing Karam to safety.
British Mandates
The British were awarded three mandated territories, with one ofSharif Hussein
Hussein bin Ali al-Hashimi ( ar, الحسين بن علي الهاشمي, al-Ḥusayn bin ‘Alī al-Hāshimī; 1 May 18544 June 1931) was an Arab leader from the Banu Hashim clan who was the Sharif and Emir of Mecca from 1908 and, after procl ...
's sons, Faisal, installed as King of Iraq
The king of Iraq ( ar, ملك العراق, ''Malik al-‘Irāq'') was Iraq's head of state and monarch from 1921 to 1958. He served as the head of the Iraqi monarchy—the Hashemite dynasty. The king was addressed as His Majesty (صاحب � ...
and Transjordan providing a throne for another of Hussein's sons, Abdullah. Mandatory Palestine
Mandatory Palestine ( ar, فلسطين الانتدابية '; he, פָּלֶשְׂתִּינָה (א״י) ', where "E.Y." indicates ''’Eretz Yiśrā’ēl'', the Land of Israel) was a geopolitical entity established between 1920 and 1948 ...
was placed under direct British administration, and the Jewish population was allowed to increase, initially under British protection. Most of the Arabian peninsula fell to another British ally, Ibn Saud
Abdulaziz bin Abdul Rahman Al Saud ( ar, عبد العزيز بن عبد الرحمن آل سعود, ʿAbd al ʿAzīz bin ʿAbd ar Raḥman Āl Suʿūd; 15 January 1875Ibn Saud's birth year has been a source of debate. It is generally accepted ...
, who created the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country in Western Asia. It covers the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula, and has a land area of about , making it the fifth-largest country in Asia, the second-largest in the Ara ...
in 1932.
Mandate for Mesopotamia
Mosul was allocated to France under the 1916 Sykes-Picot Agreement and was subsequently given to Britain under the 1918 Clemenceau–Lloyd George Agreement. Great Britain and Turkey disputed control of the former Ottoman province ofMosul
Mosul ( ar, الموصل, al-Mawṣil, ku, مووسڵ, translit=Mûsil, Turkish: ''Musul'', syr, ܡܘܨܠ, Māwṣil) is a major city in northern Iraq, serving as the capital of Nineveh Governorate. The city is considered the second larg ...
in the 1920s. Under the 1923 Treaty of Lausanne Mosul fell under the British Mandate of Mesopotamia, but the new Turkish republic claimed the province as part of its historic heartland. A three-person League of Nations committee went to the region in 1924 to study the case and in 1925 recommended the region remain connected to Iraq, and that the UK should hold the mandate for another 25 years, to assure the autonomous rights of the Kurd ug:كۇردلار
Kurds ( ku, کورد ,Kurd, italic=yes, rtl=yes) or Kurdish people are an Iranian ethnic group native to the mountainous region of Kurdistan in Western Asia, which spans southeastern Turkey, northwestern Iran, northern Ira ...
ish population. Turkey rejected this decision. Nonetheless, Britain, Iraq and Turkey made a treaty on 5 June 1926, that mostly followed the decision of the League Council. Mosul stayed under British Mandate of Mesopotamia until Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq ...
was granted independence in 1932 by the urging of King Faisal, though the British retained military bases and transit rights for their forces in the country.
Mandate for Palestine
 During the Great War, Britain produced three contrasting, but feasibly compatible, statements regarding their ambitions for Palestine. Britain had supported, through British intelligence officer T. E. Lawrence (aka Lawrence of Arabia), the establishment of a united Arab state covering a large area of the Arab Middle East in exchange for Arab support of the British during the war. The
During the Great War, Britain produced three contrasting, but feasibly compatible, statements regarding their ambitions for Palestine. Britain had supported, through British intelligence officer T. E. Lawrence (aka Lawrence of Arabia), the establishment of a united Arab state covering a large area of the Arab Middle East in exchange for Arab support of the British during the war. The Balfour Declaration
The Balfour Declaration was a public statement issued by the British government in 1917 during the First World War announcing its support for the establishment of a "national home for the Jewish people" in Palestine, then an Ottoman regio ...
of 1917 encouraged Jewish ambitions for a national home. Lastly, the British promised via the Hussein–McMahon Correspondence that the Hashemite family would have lordship over most land in the region in return for their support in the Great Arab Revolt.
The Arab Revolt, which was in part orchestrated by Lawrence, resulted in British forces under General Edmund Allenby defeating the Ottoman forces in 1917 in the Sinai and Palestine Campaign and occupying Palestine and Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
. The land was administered by the British for the remainder of the war.
The United Kingdom was granted control of Palestine by the Versailles Peace Conference which established the League of Nations
The League of Nations (french: link=no, Société des Nations ) was the first worldwide intergovernmental organisation whose principal mission was to maintain world peace. It was founded on 10 January 1920 by the Paris Peace Conference th ...
in 1919. Herbert Samuel, a former Postmaster General in the British cabinet who was instrumental in drafting the Balfour Declaration
The Balfour Declaration was a public statement issued by the British government in 1917 during the First World War announcing its support for the establishment of a "national home for the Jewish people" in Palestine, then an Ottoman regio ...
, was appointed the first High Commissioner in Palestine. In 1920 at the San Remo conference
The San Remo conference was an international meeting of the post- World War I Allied Supreme Council as an outgrowth of the Paris Peace Conference, held at Villa Devachan in Sanremo, Italy, from 19 to 26 April 1920. The San Remo Resolution pa ...
, in Italy, the League of Nations mandate
A League of Nations mandate was a legal status for certain territories transferred from the control of one country to another following World War I, or the legal instruments that contained the internationally agreed-upon terms for administ ...
over Palestine was assigned to Britain. In 1923 Britain transferred a part of the Golan Heights
The Golan Heights ( ar, هَضْبَةُ الْجَوْلَانِ, Haḍbatu l-Jawlān or ; he, רמת הגולן, ), or simply the Golan, is a region in the Levant spanning about . The region defined as the Golan Heights differs between di ...
to the French Mandate of Syria
The Mandate for Syria and the Lebanon (french: Mandat pour la Syrie et le Liban; ar, الانتداب الفرنسي على سوريا ولبنان, al-intidāb al-fransi 'ala suriya wa-lubnān) (1923−1946) was a League of Nations mandate foun ...
, in exchange for the Metula region.
Independence movements
When the Ottomans departed, the Arabs proclaimed an independent state inDamascus
)), is an adjective which means "spacious".
, motto =
, image_flag = Flag of Damascus.svg
, image_seal = Emblem of Damascus.svg
, seal_type = Seal
, map_caption =
, ...
, but were too weak, militarily and economically, to resist the European powers for long, and Britain and France soon re-established control.
During the 1920s and 1930s Iraq, Syria and Egypt moved towards independence, although the British and French did not formally depart the region until after World War II. But in Palestine, the conflicting forces of Arab nationalism and Zionism created a situation from which the British could neither resolve nor extricate themselves from. The rise to power of Nazism
Nazism ( ; german: Nazismus), the common name in English for National Socialism (german: Nationalsozialismus, ), is the far-right totalitarian political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) i ...
in Germany created a new urgency in the Zionist quest to create a Jewish state in Palestine, leading to the Israeli–Palestinian conflict.
Arabian Peninsula
On the Arabian Peninsula, the Arabs were able to establish several independent states. In 1916 Hussein bin Ali, Sharif of Mecca, established theKingdom of Hejaz
The Hashemite Kingdom of Hejaz ( ar, المملكة الحجازية الهاشمية, ''Al-Mamlakah al-Ḥijāziyyah Al-Hāshimiyyah'') was a state in the Hejaz region in the Middle East that included the western portion of the Arabian Penins ...
, while the Emirate of Riyadh was transformed into the Sultanate of Nejd. In 1926 the Kingdom of Nejd and Hejaz was formed, which in 1932 became the kingdom of Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country in Western Asia. It covers the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula, and has a land area of about , making it the fifth-largest country in Asia, the second-largest in the Ara ...
. The Mutawakkilite Kingdom of Yemen became independent in 1918, while the Arab States of the Persian Gulf became ''de facto'' British protectorates, with some internal autonomy.
Anatolia
The Russians, British, Italians, French,Greeks
The Greeks or Hellenes (; el, Έλληνες, ''Éllines'' ) are an ethnic group and nation indigenous to the Eastern Mediterranean and the Black Sea regions, namely Greece, Cyprus, Albania, Italy, Turkey, Egypt, and, to a lesser extent, ot ...
, Assyrians and Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ''O ...
ns all made claims to Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
, based on a collection of wartime promises, military actions, secret agreements, and treaties. According to the Treaty of Sèvres, all but the Assyrians would have had their wishes honoured. Armenia was to be given a significant portion of the east, known as Wilsonian Armenia
Wilsonian Armenia () refers to the unimplemented boundary configuration of the First Republic of Armenia in the Treaty of Sèvres, as drawn by U.S. President Woodrow Wilson's Department of State. The Treaty of Sèvres was a peace treaty that ha ...
, extending as far down as the Lake Van area and as far west as Muş, Mush, Greece was to be given Smyrna and the area around it (and likely would have gained Constantinople and all of Thrace, which was administered as internationally controlled and demilitarized territory), Italy was to be given control over the south-central and western coast of Anatolia around Antalya, France to be given the area of Cilicia, and Britain to be given all the area south of Armenia. The Treaty of Lausanne, by contrast, forfeited all arrangements and territorial annexations.
Russia
In March 1915, Foreign Minister of the Russian Empire, Sergey Sazonov, told British and French Ambassadors George Buchanan (diplomat), George Buchanan and Maurice Paléologue that a lasting postwar settlement demanded Russian possession of "the city of Constantinople, the western shore of the Bosporus, Sea of Marmara, and Dardanelles, as well as southern Thrace up to the Enos-Media line", and "a part of the Asiatic coast between the Bosporus, the Sakarya River, and a point to be determined on the shore of the Bay of İzmit."''Armenia on the Road to Independence'', 1967, p. 59 The Constantinople Agreement was made public by the Russian newspaper ''Izvestiya'' in November 1917, to gain the support of the Armenian public for theRussian Revolution
The Russian Revolution was a period of political and social revolution that took place in the former Russian Empire which began during the First World War. This period saw Russia abolish its monarchy and adopt a socialist form of government ...
. However, said revolution effectively ended Russian plans.
United Kingdom
The British seeking control over the straits of Marmara led to the Occupation of Constantinople, with French assistance, from 13 November 1918 to 23 September 1923. After theTurkish War of Independence
The Turkish War of Independence "War of Liberation", also known figuratively as ''İstiklâl Harbi'' "Independence War" or ''Millî Mücadele'' "National Struggle" (19 May 1919 – 24 July 1923) was a series of military campaigns waged by th ...
and the signing of the Treaty of Lausanne, the troops left the city.
Italy
Under the 1917 Agreement of Saint-Jean-de-Maurienne between France, Italy, and the United Kingdom, Italy was to receive all southwestern Anatolia except the Adana region, including İzmir. However, in 1919 the Greek Prime Minister Eleftherios Venizelos obtained the permission of the Paris Peace Conference, 1919, Paris Peace Conference to Occupation of İzmir, occupy İzmir, overriding the provisions of the agreement.France
Under the secretSykes–Picot Agreement
The Sykes–Picot Agreement () was a 1916 secret treaty between the United Kingdom and France, with assent from the Russian Empire and the Kingdom of Italy, to define their mutually agreed spheres of influence and control in an eventual partition ...
of 1916, the French obtained Hatay Province, Hatay, Lebanon
Lebanon ( , ar, لُبْنَان, translit=lubnān, ), officially the Republic of Lebanon () or the Lebanese Republic, is a country in Western Asia. It is located between Syria to the north and east and Israel to the south, while Cyprus lie ...
and Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
and expressed a desire for the part of South-Eastern Anatolia. The 1917 Agreement of St. Jean-de-Maurienne between France, Italy and the United Kingdom allotted France the Adana region.
The French army, along with the British, occupied parts of Anatolia from 1919 to 1921 in the Franco-Turkish War, including coal mines, railways, the Black Sea ports of Zonguldak, Karadeniz Ereğli and Constantinople, Uzunköprü in Eastern Thrace and the region of Cilicia. France eventually withdrew from all these areas, after the Armistice of Mudanya, the Treaty of Ankara (1921), Treaty of Ankara and the Treaty of Lausanne.
Greece

 The western Allies, particularly Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, British Prime Minister David Lloyd George, promised Greece territorial gains at the expense of the
The western Allies, particularly Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, British Prime Minister David Lloyd George, promised Greece territorial gains at the expense of the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University ...
if Greece entered the war on the Allied side. The promised territories included eastern Thrace, the islands of Imbros (Gökçeada) and Tenedos (Bozcaada), and parts of western Anatolia around the city of İzmir.
In May 1917, after the exile of Constantine I of Greece, Greek prime minister Eleuthérios Venizélos returned to Athens and allied with the Entente. Greek military forces (though divided between supporters of the monarchy and supporters of Venizélos) began to take part in military operations against the Bulgarian army on the border. That same year, İzmir was promised to Italy under the Agreement of Saint-Jean-de-Maurienne between France, Italy and the United Kingdom.
At the 1918 Paris Peace Conference, based on the wartime promises, Venizélos lobbied hard for an expanded Hellas (the Megali Idea) that would include the small Greek-speaking community in far Southern Albania, the Orthodox Greek-speaking community in Thrace (including Constantinople) and the Orthodox community in Asia Minor. In 1919, despite Italian opposition, he obtained the permission of the Paris Peace Conference of 1919 for Greece to occupy İzmir.
South West Caucasian Republic
The South West Caucasian Republic was an entity established on Russian territory in 1918, after the withdrawal of Ottoman troops to the pre-World War I border as a result of the Armistice of Mudros. It had a nominally independent provisional government headed by Fakhr al-Din Pirioghlu and based in Kars. After fighting broke out between it and both Georgia and Armenia, British High Commissioner Admiral Somerset Arthur Gough-Calthorpe occupied Kars on 19 April 1919, abolishing its parliament and arresting 30 members of its government. He placed Kars province under Armenian rule.Armenia
 In the later years of World War I, the Armenians in Russia established a provisional government in the south-west of the Russian Empire. Military conflicts between the Turks and Armenians both during and after the war eventually determined the borders of the state of
In the later years of World War I, the Armenians in Russia established a provisional government in the south-west of the Russian Empire. Military conflicts between the Turks and Armenians both during and after the war eventually determined the borders of the state of Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ''O ...
.
Administration for Western Armenia
In April 1915, Russia supported the establishment of the Armenian provisional government under Russian-Armenian Governor Aram Manukian, leader of the resistance in the Defense of Van (1915), Defense of Van. The Armenian national liberation movement hoped that Armenia could be liberated from the Ottoman regime in exchange for helping the Russian army. However, the Tsarist regime had a secret wartime agreement with the other members of the Triple Entente about the eventual fate of several Anatolian territories, named theSykes–Picot Agreement
The Sykes–Picot Agreement () was a 1916 secret treaty between the United Kingdom and France, with assent from the Russian Empire and the Kingdom of Italy, to define their mutually agreed spheres of influence and control in an eventual partition ...
. These plans were made public by the Armenian revolutionaries in 1917 to gain the support of the Armenian public.
In the meantime, the provisional government was becoming more stable as more Armenians were moving into its territory. In 1917, 150,000 Armenians relocated to the provinces of Erzurum Province, Erzurum, Bitlis Province, Bitlis, Muş Province, Muş and Van Province, Van. And Armen Garo (known as Karekin Pastirmaciyan) and other Armenian leaders asked for the Armenian regulars in the European theatre to be transferred to the Caucasian front.
The Russian revolution left the front in eastern Turkey in a state of flux. In December 1917, a truce was signed by representatives of the Ottoman Empire and the Transcaucasian Commissariat. However, the Ottoman Empire began to reinforce its Third Army (Ottoman Empire), Third Army on the eastern front. Fighting began in mid-February 1918. Armenians, under heavy pressure from the Ottoman army and Kurdish irregulars, were forced to withdraw from Erzincan to Erzurum and then to Kars, eventually evacuating even Kars on 25 April. As a response to the Ottoman advances, the Transcaucasian Commissariat evolved into the short-lived Transcaucasian Federation; its disintegration resulted in Armenians forming the Democratic Republic of Armenia on 30 May 1918. The Treaty of Batum, signed on 4 June, reduced the Armenian republic to an area of only 11,000 km2.
Wilsonian Armenia
At the Paris Peace Conference, 1919, the Armenian Diaspora and the Armenian Revolutionary Federation argued that Historical Armenia, the region which had remained outside the control of theOttoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University ...
from 1915 to 1918, should be part of the Democratic Republic of Armenia. Arguing from the principles in Woodrow Wilson's "Fourteen Points" speech, the Armenian Diaspora argued Armenia had "the ability to control the region", based on the Armenian control established after the Russian Revolution. The Armenians also argued that the dominant population of the region was becoming more Armenian as Turkish inhabitants were moving to the western provinces. Boghos Nubar, the president of the Armenian National Delegation, added: "In the Caucasus, where, without mentioning the 150,000 Armenians in the Imperial Russian Army, more than 40,000 of their volunteers contributed to the liberation of a portion of the Armenian vilayets, and where, under the command of their leaders, Antranik and Nazerbekoff, they, alone among the peoples of the Caucasus, offered resistance to the Turkish armies, from the beginning of the Bolshevist withdrawal right up to the signing of an armistice."
President Wilson accepted the Armenian arguments for drawing the frontier and wrote: "The world expects of them (the Armenians), that they give every encouragement and help within their power to those Turkish refugees who may desire to return to their former homes in the districts of Trabzon, Trebizond, Erzurum, Erzerum, Van, Turkey, Van and Bitlis remembering that these peoples, too, have suffered greatly."President Wilson's Acceptance letter for drawing the frontier given to the Paris Peace Conference, Washington, 22 November 1920. The conference agreed with his suggestion that the Democratic Republic of Armenia should expand into present-day eastern Turkey.
Georgia
After the fall of the Russian Empire, Georgia became an Democratic Republic of Georgia, independent republic and sought to maintain control of Batumi as well as Ardahan, Artvin, and Oltu, the areas with Muslim Georgian elements, which had been acquired by Russia from the Ottomans in 1878. The Ottoman forces occupied the disputed territories by June 1918, forcing Georgia to sign the Treaty of Batum. After the demise of the Ottoman power, Georgia regained Ardahan and Artvin from local Muslim militias in 1919 and Batum from the British administration of that maritime city in 1920. It claimed but never attempted to control Oltu, which was also contested by Armenia. Soviet Russia and Turkey launched a Red Army invasion of Georgia, near-simultaneous attack on Georgia in February–March 1921, leading to new territorial rearrangements finalized in the Treaty of Kars, by which Batumi remained within the borders of now-Georgian SSR, Soviet Georgia, while Ardahan and Artvin were recognized as parts of Turkey.Republic of Turkey
Between 1918 and 1923, Turkish resistance movements led by Mustafa Kemal Atatürk forced the Greeks and Armenians out of Anatolia, while the Italians never established a presence. The Turkish revolutionaries also suppressed Kurdish attempts to become independent in the 1920s. After the Turkish resistance gained control over Anatolia, there was no hope of meeting the conditions of theTreaty of Sèvres
The Treaty of Sèvres (french: Traité de Sèvres) was a 1920 treaty signed between the Allies of World War I and the Ottoman Empire. The treaty ceded large parts of Ottoman territory to France, the United Kingdom, Greece and Italy, as well ...
.
Before joining the Soviet Union, the Democratic Republic of Armenia signed the Treaty of Alexandropol, on 3 December 1920, agreeing to the current border between the two countries, though the Armenian government had already collapsed due to a concurrent Soviet invasion on 2 December. Afterwards Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ''O ...
became an integral part of the Soviet Union. This border was ratified again with the Treaty of Moscow (1921), in which the Bolsheviks ceded the already Turkish-occupied provinces of Kars Province, Kars, Iğdır Province, Iğdır, Ardahan Province, Ardahan, and Artvin Province, Artvin to Turkey in exchange for the Adjara region with its capital city of Batumi.
Turkey and the newly formed Soviet Union, along with the Armenian Soviet Socialist Republic and Georgian Soviet Socialist Republic, ratified the Treaty of Kars on 11 September 1922, establishing the north-eastern border of Turkey and bringing peace to the region, despite none of them being internationally recognized at the time. Finally, the Treaty of Lausanne, signed in 1923, formally ended all hostilities and led to the creation of the modern Turkey, Turkish Republic.
See also
* Abolition of the Ottoman sultanate * Dissolution of the Ottoman EmpireNotes
Bibliography
* David Fromkin, Fromkin, David. ''A Peace to End All Peace, A Peace to End All Peace: Creating the Modern Middle East''. New York: Henry Holt and Company, 1989. * Quilliam, Neil. ''Syria and the New World Order''. Reading, UK: Ithaca Press (Garnet), 1999.External links
*Criss, Nur BilgeOccupation during and after the War (Ottoman Empire)
in
* Smith, Leonard V.
Post-war Treaties (Ottoman Empire/ Middle East)
in
{{Turkish War of Independence History of Greece (1909–1924) Modern history of Turkey 20th century in Iraq Ottoman Syria Ottoman Greece Partition (politics) 20th century in Armenia Aftermath of World War I in Turkey Turkey–United Kingdom relations Ottoman Empire–United Kingdom relations 20th century in Syria Ottoman period in Armenia Iraq–Turkey relations Dissolution of the Ottoman Empire 1920s in Islam