Organ Transplantation on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Organ transplantation is a medical procedure in which an
organ
Organ may refer to:
Biology
* Organ (biology), a part of an organism
Musical instruments
* Organ (music), a family of keyboard musical instruments characterized by sustained tone
** Electronic organ, an electronic keyboard instrument
** Hammond ...
is removed from one body and placed in the body of a recipient, to replace a damaged or missing organ. The donor and recipient may be at the same location, or organs may be transported from a
donor
A donor in general is a person, organization or government which donates something voluntarily. The term is usually used to represent a form of pure altruism, but is sometimes used when the payment for a service is recognized by all parties as rep ...
site to another location.
Organ
Organ may refer to:
Biology
* Organ (biology), a part of an organism
Musical instruments
* Organ (music), a family of keyboard musical instruments characterized by sustained tone
** Electronic organ, an electronic keyboard instrument
** Hammond ...
s and/or
tissues that are transplanted within the same person's body are called
autografts. Transplants that are recently performed between two subjects of the same species are called
allografts
Allotransplant (''allo-'' meaning "other" in Greek) is the transplantation of cells, tissues, or organs to a recipient from a genetically non-identical donor of the same species. The transplant is called an allograft, allogeneic transplant, or ...
. Allografts can either be from a living or cadaveric source.
Organs that have been successfully transplanted include the
heart
The heart is a muscular Organ (biology), organ in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as ca ...
,
kidneys,
liver
The liver is a major organ only found in vertebrates which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for digestion and growth. In humans, it i ...
,
lungs
The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in humans and most other animals, including some snails and a small number of fish. In mammals and most other vertebrates, two lungs are located near the backbone on either si ...
,
pancreas
The pancreas is an organ of the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdomen behind the stomach and functions as a gland. The pancreas is a mixed or heterocrine gland, i.e. it has both an ...
,
intestine
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organs of the digestive system, in humans an ...
,
thymus
The thymus is a specialized primary lymphoid organ of the immune system. Within the thymus, thymus cell lymphocytes or '' T cells'' mature. T cells are critical to the adaptive immune system, where the body adapts to specific foreign invaders ...
and
uterus
The uterus (from Latin ''uterus'', plural ''uteri'') or womb () is the organ in the reproductive system of most female mammals, including humans that accommodates the embryonic and fetal development of one or more embryos until birth. The ...
. Tissues include
bones, tendons (both referred to as musculoskeletal grafts),
corneae,
skin
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation.
Other animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have different ...
,
heart valves, nerves and veins. Worldwide, the kidneys are the most commonly transplanted organs, followed by the liver and then the heart. Corneae and musculoskeletal grafts are the most commonly transplanted tissues; these outnumber organ transplants by more than tenfold.
Organ donors may be living,
brain dead, or dead via circulatory death. Tissue may be recovered from donors who die of circulatory death, as well as of brain death – up to 24 hours past the cessation of heartbeat. Unlike organs, most tissues (with the exception of
cornea
The cornea is the transparent front part of the eye that covers the iris, pupil, and anterior chamber. Along with the anterior chamber and lens, the cornea refracts light, accounting for approximately two-thirds of the eye's total optical ...
s) can be preserved and stored for up to five years, meaning they can be "banked". Transplantation raises a number of
bioethical
Bioethics is both a field of study and professional practice, interested in ethical issues related to health (primarily focused on the human, but also increasingly includes animal ethics), including those emerging from advances in biology, m ...
issues, including the definition of death, when and how consent should be given for an organ to be transplanted, and payment for organs for transplantation. Other ethical issues include transplantation tourism (medical tourism) and more broadly the socio-economic context in which organ procurement or transplantation may occur. A particular problem is
organ trafficking
Organ trade (also known as Red market) is the trading of human organs, tissues, or other body products, usually for transplantation.(Carney, Scott. 2011. "The Red Market." Wired 19, no. 2: 112–1. Internet and Personal Computing Abstracts.) Acco ...
. There is also the ethical issue of not holding out false hope to patients.
[
Transplantation medicine is one of the most challenging and complex areas of modern medicine. Some of the key areas for medical management are the problems of ]transplant rejection
Transplant rejection occurs when transplanted tissue is rejected by the recipient's immune system, which destroys the transplanted tissue. Transplant rejection can be lessened by determining the molecular similitude between donor and recipient ...
, during which the body has an immune response
An immune response is a reaction which occurs within an organism for the purpose of defending against foreign invaders. These invaders include a wide variety of different microorganisms including viruses, bacteria, parasites, and fungi which coul ...
to the transplanted organ, possibly leading to transplant failure and the need to immediately remove the organ from the recipient. When possible, transplant rejection can be reduced through serotyping
A serotype or serovar is a distinct variation within a species of bacteria or virus or among immune cells of different individuals. These microorganisms, viruses, or cells are classified together based on their surface antigens, allowing the ep ...
to determine the most appropriate donor-recipient match and through the use of immunosuppressant drugs
Immunosuppressive drugs, also known as immunosuppressive agents, immunosuppressants and antirejection medications, are drugs that inhibit or prevent activity of the immune system.
Classification
Immunosuppressive drugs can be classified into ...
.
Types of transplant
Autograft
Autografts are the transplant of tissue to the same person. Sometimes this is done with surplus tissue, tissue that can regenerate, or tissues more desperately needed elsewhere (examples include skin grafts, vein extraction for CABG
Coronary artery bypass surgery, also known as coronary artery bypass graft (CABG, pronounced "cabbage") is a surgical procedure to treat coronary artery disease (CAD), the buildup of plaques in the arteries of the heart. It can relieve chest pai ...
, etc.). Sometimes an autograft is done to remove the tissue and then treat it or the person before returning it (examples include stem cell autograft and storing blood in advance of surgery). In a rotationplasty, a distal joint is used to replace a more proximal one; typically a foot or ankle joint is used to replace a knee joint. The person's foot is severed and reversed, the knee removed, and the tibia
The tibia (; ), also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates (the other being the fibula, behind and to the outside of the tibia); it conn ...
joined with the femur
The femur (; ), or thigh bone, is the proximal bone of the hindlimb in tetrapod vertebrates. The head of the femur articulates with the acetabulum in the pelvic bone forming the hip joint, while the distal part of the femur articulates ...
.
Allograft and allotransplantation
An allograft is a transplant of an organ or tissue between two genetically non-identical members of the same species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriat ...
. Most human tissue and organ transplants are allografts. Due to the genetic difference between the organ and the recipient, the recipient's immune system
The immune system is a network of biological processes that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, as well as cancer cells and objects such as wood splinte ...
will identify the organ as foreign and attempt to destroy it, causing transplant rejection. The risk of transplant rejection can be estimated by measuring the panel-reactive antibody level.
Isograft
An isograft is a subset of allograft in which organs or tissues are transplanted from a donor to a genetically identical recipient (such as an identical twin). Isografts are differentiated from other types of transplants because while they are anatomically identical to autografts, they do not trigger an immune response
An immune response is a reaction which occurs within an organism for the purpose of defending against foreign invaders. These invaders include a wide variety of different microorganisms including viruses, bacteria, parasites, and fungi which coul ...
.
Xenograft and xenotransplantation
A xenograft is a transplant of organs or tissue from one species to another. An example is porcine heart valve transplant, which is quite common and successful. Another example is attempted piscine–primate
Primates are a diverse order of mammals. They are divided into the strepsirrhines, which include the lemurs, galagos, and lorisids, and the haplorhines, which include the tarsiers and the simians ( monkeys and apes, the latter includin ...
(fish
Fish are Aquatic animal, aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack Limb (anatomy), limbs with Digit (anatomy), digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and Chondrichthyes, cartilaginous and bony fish as we ...
to non-human primate) transplant of pancreatic islets. The latter research study was intended to pave the way for potential human use if successful. However, xenotransplantion is often an extremely dangerous type of transplant because of the increased risk of non-functional compatibility, rejection, and disease carried in the tissue. In the opposite direction, attempts are being made devise a way to transplant human fetal hearts and kidneys into animals for future transplantation into human patients to address the shortage of donor organs.
Domino transplants
In people with cystic fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a rare genetic disorder that affects mostly the lungs, but also the pancreas, liver, kidneys, and intestine. Long-term issues include difficulty breathing and coughing up mucus as a result of frequent lung infections. Ot ...
(CF), where both lungs need to be replaced, it is a technically easier operation with a higher rate of success to replace both the heart and lungs of the recipient with those of the donor. As the recipient's original heart is usually healthy, it can then be transplanted into a second recipient in need of a heart transplant, thus making the person with CF a living heart donor. In a 2016 case at Stanford Medical Center, a woman who was needing a heart-lung transplant had cystic fibrosis which had led to one lung expanding and the other shrinking, thereby displacing her heart. The second patient who in turn received her heart was a woman with right ventricular dysplasia which had led to a dangerously abnormal rhythm. The dual operations required three surgical teams, including one to remove the heart and lungs from a recently deceased initial donor. The two living recipients did well and had an opportunity to meet six weeks after their simultaneous operations.
Another example of this situation occurs with a special form of liver transplant in which the recipient has familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy
Familial amyloid polyneuropathy, also called transthyretin-related hereditary amyloidosis, transthyretin amyloidosis abbreviated also as ATTR (hereditary form), or Corino de Andrade's disease, is an autosomal dominant neurodegenerative disease. It ...
, a disease where the liver slowly produces a protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, res ...
that damages other organs. The recipient's liver can then be transplanted into an older person for whom the effects of the disease will not necessarily contribute significantly to mortality.
This term also refers to a series of living donor transplants in which one donor donates to the highest recipient on the waiting list and the transplant center utilizes that donation to facilitate multiple transplants. These other transplants are otherwise impossible due to blood type
A blood type (also known as a blood group) is a classification of blood, based on the presence and absence of antibodies and inherited antigenic substances on the surface of red blood cells (RBCs). These antigens may be proteins, carbohydrates ...
or antibody barriers to transplantation. The "Good Samaritan
In most contexts, the concept of good denotes the conduct that should be preferred when posed with a choice between possible actions. Good is generally considered to be the opposite of evil and is of interest in the study of ethics, morality, ph ...
" kidney is transplanted into one of the other recipients, whose donor in turn donates his or her kidney to an unrelated recipient. This method allows all organ recipients to get a transplant even if their living donor is not a match to them. This further benefits people below any of these recipients on waiting lists, as they move closer to the top of the list for a deceased-donor organ. Johns Hopkins Medical Center in Baltimore and Northwestern University
Northwestern University is a private research university in Evanston, Illinois. Founded in 1851, Northwestern is the oldest chartered university in Illinois and is ranked among the most prestigious academic institutions in the world.
Charte ...
's Northwestern Memorial Hospital
Northwestern Memorial Hospital (NMH) is a nationally ranked academic medical center located on Northwestern University’s Chicago campus in Streeterville, Chicago, Illinois. It is the flagship campus for Northwestern Medicine and the primary ...
have received significant attention for pioneering transplants of this kind. In February 2012, the last link in a record 60-person domino chain of 30 kidney transplants was completed.
ABO-incompatible transplants
Because very young children (generally under 12 months, but often as old as 24 monthsantigen
In immunology, an antigen (Ag) is a molecule or molecular structure or any foreign particulate matter or a pollen grain that can bind to a specific antibody or T-cell receptor. The presence of antigens in the body may trigger an immune respon ...
s.
Transplantation in obese individuals
Until recently, people with obesity
Obesity is a medical condition, sometimes considered a disease, in which excess body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it may negatively affect health. People are classified as obese when their body mass index (BMI)—a person's ...
were not considered appropriate candidate donors for renal transplantation. In 2009, the physicians at the University of Illinois Medical Center
The University of Illinois Hospital & Health Sciences System is a member of the Illinois Medical District, one of the largest urban healthcare, educational, research, and technology districts in the USA. The University of Illinois Hospital & Hea ...
performed the first robotic renal transplantation in an obese recipient and have continued to transplant people with a body mass index
Body mass index (BMI) is a value derived from the mass ( weight) and height of a person. The BMI is defined as the body mass divided by the square of the body height, and is expressed in units of kg/m2, resulting from mass in kilograms and ...
over 35 using robotic surgery. As of January 2014, over 100 people who would otherwise have been turned down because of their weight have successfully been transplanted.
Organs and tissues transplanted
Chest
* Heart
The heart is a muscular Organ (biology), organ in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as ca ...
(deceased-donor only; porcine xenograft attempted)
* Lung
The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in humans and most other animals, including some snails and a small number of fish. In mammals and most other vertebrates, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of ...
(deceased-donor and living-related lung transplantation)
* Thymus
The thymus is a specialized primary lymphoid organ of the immune system. Within the thymus, thymus cell lymphocytes or '' T cells'' mature. T cells are critical to the adaptive immune system, where the body adapts to specific foreign invaders ...
Abdomen
* Kidney
The kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped organs found in vertebrates. They are located on the left and right in the retroperitoneal space, and in adult humans are about in length. They receive blood from the paired renal arteries; blo ...
(deceased-donor and living-donor; porcine xenograft attempted)
* Liver
The liver is a major organ only found in vertebrates which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for digestion and growth. In humans, it i ...
(deceased-donor, which enables donation of a whole liver; and living-donor, where each donor can provide up to 70% of a liver)
* Pancreas
The pancreas is an organ of the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdomen behind the stomach and functions as a gland. The pancreas is a mixed or heterocrine gland, i.e. it has both an ...
(deceased-donor only; a very severe type of diabetes ensues if a live person's entire pancreas is removed)
* Intestine
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organs of the digestive system, in humans an ...
(deceased-donor and living-donor; normally refers to the small intestine)
* Stomach
The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the gastrointestinal tract of humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The stomach has a dilated structure and functions as a vital organ in the digestive system. The stomach i ...
(deceased-donor only)
* Uterus
The uterus (from Latin ''uterus'', plural ''uteri'') or womb () is the organ in the reproductive system of most female mammals, including humans that accommodates the embryonic and fetal development of one or more embryos until birth. The ...
(deceased-donor only)
* Testis (deceased-donor and living-donor)
* Penis
A penis (plural ''penises'' or ''penes'' () is the primary sexual organ that male animals use to inseminate females (or hermaphrodites) during copulation. Such organs occur in many animals, both vertebrate and invertebrate, but males d ...
(deceased-donor only)
Tissues, cells and fluids
* Hand
A hand is a prehensile, multi-fingered appendage located at the end of the forearm or forelimb of primates such as humans, chimpanzees, monkeys, and lemurs. A few other vertebrates such as the koala (which has two opposable thumbs on each "h ...
(deceased-donor only), see first recipient Clint Hallam
* Cornea
The cornea is the transparent front part of the eye that covers the iris, pupil, and anterior chamber. Along with the anterior chamber and lens, the cornea refracts light, accounting for approximately two-thirds of the eye's total optical ...
(deceased-donor only) see the ophthalmologist
Ophthalmology ( ) is a surgical subspecialty within medicine that deals with the diagnosis and treatment of eye disorders.
An ophthalmologist is a physician who undergoes subspecialty training in medical and surgical eye care. Following a med ...
Eduard Zirm
* Skin
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation.
Other animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have different ...
, including face replant (autograft) and face transplant
A face transplant is a medical procedure to replace all or part of a person's face using tissue from a donor. Part
of a field called "Vascularized Composite Tissue Allotransplantation" (VCA) it involves the transplantation of facial skin, the ...
(extremely rare)
* Islets of Langerhans (pancreas islet cells) (deceased-donor and living-donor)
* Bone marrow
Bone marrow is a semi-solid biological tissue, tissue found within the Spongy bone, spongy (also known as cancellous) portions of bones. In birds and mammals, bone marrow is the primary site of new blood cell production (or haematopoiesis). It i ...
or adult stem cell
In multicellular organisms, stem cells are undifferentiated or partially differentiated cells that can differentiate into various types of cells and proliferate indefinitely to produce more of the same stem cell. They are the earliest type of ...
(living-donor and autograft)
* Blood transfusion
Blood transfusion is the process of transferring blood products into a person's circulation intravenously. Transfusions are used for various medical conditions to replace lost components of the blood. Early transfusions used whole blood, but mo ...
, whole blood or fractionated blood products (living-donor and autograft)
* Blood vessels (autograft and deceased-donor)
* Heart valve (deceased-donor, living-donor and xenograft bovine.html"_;"title="cow.html"_;"title="orcine/cow">bovine">cow.html"_;"title="orcine/cow">bovine
*_Bone_transplant.html" "title="cow">bovine.html" ;"title="cow.html" ;"title="orcine/cow">bovine">cow.html" ;"title="orcine/cow">bovine
* Bone transplant">Bone
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, ...
(deceased-donor and living-donor)
Types of donor
Organ donors may be living or may have died of brain death or circulatory death. Most deceased donors are those who have been pronounced brain dead. Brain dead means the cessation of brain function, typically after receiving an injury (either traumatic or pathological) to the brain, or otherwise cutting off blood circulation to the brain (drowning, suffocation, etc.). Breathing is maintained via Life Support, artificial sources, which, in turn, maintains heartbeat. Once brain death has been declared, the person can be considered for organ donation. Criteria for brain death vary. Because less than 3% of all deaths in the US are the result of brain death, the overwhelming majority of deaths are ineligible for organ donation, resulting in severe shortages.
Organ donation is possible after cardiac death in some situations, primarily when the person is severely brain-injured and not expected to survive without artificial breathing and mechanical support. Independent of any decision to donate, a person's next-of-kin may decide to end artificial support. If the person is expected to expire within a short period of time after support is withdrawn, arrangements can be made to withdraw that support in an operating room to allow quick recovery of the organs after circulatory death has occurred.
Tissues may be recovered from donors who die of either brain or circulatory death. In general, tissues may be recovered from donors up to 24 hours past the cessation of heartbeat. In contrast to organs, most tissues (with the exception of corneas) can be preserved and stored for up to five years, meaning they can be "banked." Also, more than 60 grafts may be obtained from a single tissue donor. Because of these three factorsthe ability to recover from a non-heart-beating donor, the ability to bank tissue, and the number of grafts available from each donortissue transplants are much more common than organ transplants. The
American Association of Tissue Banks The American Association of Tissue Banks (AATB); a transplant trade organization that is dedicated to ensuring that human tissues intended for transplantation are safe and free of infectious disease
An infection is the invasion of tissues by ...
estimates that more than one million tissue transplants take place in the United States each year.
Living donor
In living donors, the donor remains alive and donates a renewable tissue, cell, or fluid (e.g., blood, skin), or donates an organ or part of an organ in which the remaining organ can regenerate or take on the workload of the rest of the organ (primarily single kidney donation, partial donation of liver, lung lobe, small bowel). Regenerative medicine may one day allow for laboratory-grown organs, using person's own cells via stem cells, or healthy cells extracted from the failing organs.
Deceased donor
Deceased donors (formerly cadaveric) are people who have been declared brain-dead and whose organs are kept viable by
ventilators or other mechanical mechanisms until they can be excised for transplantation. Apart from brainstem-dead donors, who have formed the majority of deceased donors for the last 20 years, there is increasing use of after-circulatory-death donors (formerly non-heart-beating donors) to increase the potential pool of donors as demand for transplants continues to grow. Prior to the legal recognition of brain death in the 1980s, all deceased organ donors had died of circulatory death. These organs have inferior outcomes to organs from a brain-dead donor.
[ ] For instance, patients who underwent liver transplantation using donation-after-circulatory-death allografts have been shown to have significantly lower graft survival than those from donation-after-brain-death allografts due to biliary complications and
primary nonfunction in liver transplantation. However, given the scarcity of suitable organs and the number of people who die waiting, any potentially suitable organ must be considered. Jurisdictions with medically
assisted suicide
Assisted suicide is suicide undertaken with the aid of another person. The term usually refers to physician-assisted suicide (PAS), which is suicide that is assisted by a physician or other healthcare provider. Once it is determined that the p ...
may co-ordinate organ donations from that source.
Allocation of organs
In most countries there is a shortage of suitable organs for transplantation. Countries often have formal systems in place to manage the process of determining who is an organ donor and in what order organ recipients receive available organs.
The overwhelming majority of deceased-donor organs in the United States are allocated by federal contract to the
Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network, held since it was created by the
Organ Transplant Act of 1984 by the
United Network for Organ Sharing, or UNOS. (UNOS does not handle donor cornea tissue; corneal donor tissue is usually handled by various eye banks.) Individual regional
organ procurement organizations, all members of the Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network, are responsible for the identification of suitable donors and collection of the donated organs. UNOS then allocates organs based on the method considered most fair by the leadership in the field. The allocation methodology varies somewhat by organ, and changes periodically. For example, liver allocation is based partially on MELD score (Model of End-Stage Liver Disease), an empirical score based on lab values indicative of the sickness of the person from liver disease. In 1984, the National Organ Transplant Act (NOTA) was passed; it gave way to the Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network, which maintains the organ registry and ensures equitable allocation of organs. The Scientific Registry of Transplant Recipients was also established to conduct ongoing studies into the evaluation and clinical status of organ transplants. In 2000 the Children's Health Act passed and required NOTA to consider special issues around pediatric patients and organ allocation.
An example of "line jumping" occurred in 2003 at Duke University when doctors attempted to correct an initially incorrect transplant. An American teenager received a heart-lung donation with the wrong blood type for her. She then received a second transplant even though she was then in such poor physical shape that she normally would not be considered a good candidate for a transplant.
In an April 2008 article in ''The Guardian'', Steven Tsui, the head of the transplant team at Papworth Hospital in the UK, is quoted in raising the ethical issue of not holding out false hope. He stated, "Conventionally we would say if people's life expectancy was a year or less we would consider them a candidate for a heart transplant. But we also have to manage expectations. If we know that in an average year we will do 30 heart transplants, there is no point putting 60 people on our waiting list, because we know half of them will die and it's not right to give them false hope."
[Heart of the matter]
''The Guardian'' K Simon Garfield, 6 April 2008.
Experiencing somewhat increased popularity, but still very rare, is directed or targeted donation, in which the family of a deceased donor (often honoring the wishes of the deceased) requests an organ be given to a specific person, subverting the allocation system. In the United States, there are various lengths of waiting times due to the different availabilities of organs in different UNOS regions. In other countries such as the UK, only medical factors and the position on the waiting list can affect who receives the organ.
One of the more publicized cases of this type was the 1994 Chester and Patti Szuber transplant. This was the first time that a parent had received a heart donated by one of their own children. Although the decision to accept the heart from his recently killed child was not an easy decision, the Szuber family agreed that giving Patti's heart to her father would have been something that she would have wanted.
Access to organ transplantation is one reason for the growth of
medical tourism
Medical tourism refers to people traveling abroad to obtain medical treatment. In the past, this usually referred to those who traveled from less-developed countries to major medical centers in highly developed countries for treatment unavailable a ...
.
Reasons for donation and ethical issues
Living related donors
Living related donors donate to family members or friends in whom they have an emotional investment. The risk of surgery is offset by the psychological benefit of not losing someone related to them, or not seeing them suffer the ill effects of waiting on a list.
Paired exchange

A "paired-exchange" is a technique of matching willing living donors to compatible recipients using
serotyping
A serotype or serovar is a distinct variation within a species of bacteria or virus or among immune cells of different individuals. These microorganisms, viruses, or cells are classified together based on their surface antigens, allowing the ep ...
. For example, a spouse may be willing to donate a kidney to their partner but cannot since there is not a biological match. The willing spouse's kidney is donated to a matching recipient who also has an incompatible but willing spouse. The second donor must match the first recipient to complete the pair exchange. Typically the surgeries are scheduled simultaneously in case one of the donors decides to back out and the couples are kept anonymous from each other until after the transplant. Paired-donor exchange, led by work in th
New England Program for Kidney Exchangeas well as at Johns Hopkins University and the Ohio organ procurement organizations, may more efficiently allocate organs and lead to more transplants.
Paired exchange programs were popularized in the ''
New England Journal of Medicine'' article "Ethics of a paired-kidney-exchange program" in 1997 by L.F. Ross. It was also proposed by Felix T. Rapport in 1986 as part of his initial proposals for live-donor transplants "The case for a living emotionally related international kidney donor exchange registry" in ''Transplant Proceedings''. A paired exchange is the simplest case of a much larger exchange registry program where willing donors are matched with any number of compatible recipients. Transplant exchange programs have been suggested as early as 1970: "A cooperative kidney typing and exchange program."
The first pair exchange transplant in the US was in 2001 at
Johns Hopkins Hospital
The Johns Hopkins Hospital (JHH) is the teaching hospital and biomedical research facility of the Johns Hopkins School of Medicine, located in Baltimore, Maryland, U.S. It was founded in 1889 using money from a bequest of over $7 million (1873 ...
. The first complex multihospital kidney exchange involving 12 people was performed in February 2009 by The Johns Hopkins Hospital,
Barnes-Jewish Hospital
Barnes-Jewish Hospital is the largest hospital in the U.S. state of Missouri. Located in the Central West End neighborhood of St. Louis, it is the adult teaching hospital for the Washington University School of Medicine and a major component ...
in
St. Louis and Integris Baptist Medical Center in
Oklahoma City
Oklahoma City (), officially the City of Oklahoma City, and often shortened to OKC, is the capital and largest city of the U.S. state of Oklahoma. The county seat of Oklahoma County, it ranks 20th among United States cities in population, and ...
. Another 12-person multihospital kidney exchange was performed four weeks later by
Saint Barnabas Medical Center
Cooperman Barnabas Medical Center (CBMC), formerly Saint Barnabas Medical Center (SBMC), is a 597-bed non-profit major teaching hospital located in Livingston, New Jersey. An affiliate of RWJBarnabas Health (formerly known as Barnabas Health and ...
in
Livingston, New Jersey,
Newark Beth Israel Medical Center and
New York-Presbyterian Hospital The NewYork-Presbyterian Hospital is a nonprofit academic medical center in New York City affiliated with two Ivy League medical schools, Cornell University and Columbia University. The hospital comprises seven distinct campuses located in the N ...
. Surgical teams led by Johns Hopkins continue to pioneer this field with more complex chains of exchange, such as an eight-way multihospital kidney exchange. In December 2009, a 13 organ 13 recipient matched kidney exchange took place, coordinated through Georgetown University Hospital and Washington Hospital Center, Washington DC.
Good Samaritan
Good Samaritan or "altruistic" donation is giving a donation to someone that has no prior affiliation with the donor. The idea of altruistic donation is to give with no interest of personal gain, it is out of pure selflessness. On the other hand, the current allocation system doesn't assess a donor's motive, so altruistic donation isn't a requirement. Some people choose to do this out of a personal need to donate. Some donate to the next person on the list; others use some method of choosing a recipient based on criteria important to them. Web sites are being developed that facilitate such donation. Over half of the members of the
Jesus Christians, an Australian religious group, have donated kidneys in such a fashion.
Financial compensation
Monetary compensation for organ donors, in the form of reimbursement for out-of-pocket expenses, has been legalised in
Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands. With an area of , Australia is the largest country by ...
, and strictly only in the case of kidney transplant in the case of
Singapore
Singapore (), officially the Republic of Singapore, is a sovereign island country and city-state in maritime Southeast Asia. It lies about one degree of latitude () north of the equator, off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, bor ...
(minimal reimbursement is offered in the case of other forms of organ harvesting by Singapore). Kidney disease organizations in both countries have expressed their support.
[Live donors to get financial support]
Rashida Yosufzai, AAP, 7 April 2013
In compensated donation, donors get money or other compensation in exchange for their organs. This practice is common in some parts of the world, whether legal or not, and is one of the many factors driving
medical tourism
Medical tourism refers to people traveling abroad to obtain medical treatment. In the past, this usually referred to those who traveled from less-developed countries to major medical centers in highly developed countries for treatment unavailable a ...
.
In the illegal black market the donors may not get sufficient after-operation care,
[The Meat Market]
, The Wall Street Journal, 8 January 2010. the price of a kidney may be above $160,000, middlemen take most of the money, the operation is more dangerous to both the donor and receiver, and the receiver often gets
hepatitis
Hepatitis is inflammation of the liver tissue. Some people or animals with hepatitis have no symptoms, whereas others develop yellow discoloration of the skin and whites of the eyes ( jaundice), poor appetite, vomiting, tiredness, abdominal ...
or
HIV.
[ In legal markets of Iran the price of a kidney is $2,000 to $4,000.]free market
In economics, a free market is an economic system in which the prices of goods and services are determined by supply and demand expressed by sellers and buyers. Such markets, as modeled, operate without the intervention of government or any ot ...
could help solve the problem of a scarcity in organ transplants. Their economic modeling was able to estimate the price tag for human kidneys ($15,000) and human livers ($32,000).
In the United States, The National Organ Transplant Act of 1984 made organ sales illegal. In the United Kingdom, the Human Organ Transplants Act 1989 first made organ sales illegal, and has been superseded by the Human Tissue Act 2004. In 2007, two major European conferences recommended against the sale of organs. Recent development of web sites and personal advertisements for organs among listed candidates has raised the stakes when it comes to the selling of organs, and have also sparked significant ethical debates over directed donation, "good-Samaritan" donation, and the current US organ allocation policy. Bioethicist Jacob M. Appel has argued that organ solicitation on billboards and the internet may actually increase the overall supply of organs.
In an experimental survey, Elias, Lacetera and Macis (2019) find that preferences for compensation for kidney donors have strong moral foundations; participants in the experiment especially reject direct payments by patients, which they find would violate principles of fairness.
Many countries have different approaches to organ donation such as: the opt-out approach and many advertisements of organ donors, encouraging people to donate. Although these laws have been implemented into a certain country they are not forced upon very one as it is an individual decision.
Two books, ''Kidney for Sale By Owner'' by Mark Cherry (Georgetown University Press, 2005) and ''Stakes and Kidneys: Why Markets in Human Body Parts are Morally Imperative'' by James Stacey Taylor:
(Ashgate Press, 2005), advocate using markets to increase the supply of organs available for transplantation.
In a 2004 journal article economist Alex Tabarrok argues that allowing organ sales, and elimination of organ donor lists will increase supply, lower costs and diminish social anxiety towards organ markets.The Economist
''The Economist'' is a British weekly newspaper printed in demitab format and published digitally. It focuses on current affairs, international business, politics, technology, and culture. Based in London, the newspaper is owned by The Eco ...
'' and the Ayn Rand Institute approve and advocate a legal market elsewhere. They argued that if 0.06% of Americans between 19 and 65 were to sell one kidney, the national waiting list would disappear (which, the Economist wrote, happened in Iran). The Economist argued that donating kidneys is no more risky than surrogate motherhood
Surrogacy is an arrangement, often supported by a legal agreement, whereby a woman agrees to delivery/labour for another person or people, who will become the child's parent(s) after birth. People may seek a surrogacy arrangement when pregnan ...
, which can be done legally for pay in most countries.
In Pakistan, 40 percent to 50 percent of the residents of some villages have only one kidney because they have sold the other for a transplant into a wealthy person, probably from another country, said Dr. Farhat Moazam of Pakistan, at a World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level o ...
conference. Pakistani donors are offered $2,500 for a kidney but receive only about half of that because middlemen take so much. In Chennai, southern India, poor fishermen and their families sold kidneys after their livelihoods were destroyed by the Indian Ocean tsunami on 26 December 2004. About 100 people, mostly women, sold their kidneys for 40,000–60,000 rupees ($900–1,350). Thilakavathy Agatheesh, 30, who sold a kidney in May 2005 for 40,000 rupees said, "I used to earn some money selling fish but now the post-surgery stomach cramps prevent me from going to work." Most kidney sellers say that selling their kidney was a mistake.
In Cyprus in 2010 police closed a fertility clinic under charges of trafficking in human eggs. The Petra Clinic, as it was known locally, brought in women from Ukraine and Russia for egg harvesting and sold the genetic material to foreign fertility tourists. This sort of reproductive trafficking violates laws in the European Union. In 2010 Scott Carney reported for the Pulitzer Center on Crisis Reporting and the magazine Fast Company explored illicit fertility networks in Spain, the United States and Israel.
Forced donation
There have been concerns that certain authorities are harvesting organs from people deemed undesirable, such as prison populations. The World Medical Association stated that prisoners and other individuals in custody are not in a position to give consent freely, and therefore their organs must not be used for transplantation.
According to former Chinese Deputy Minister of Health, Huang Jiefu, the practice of transplanting organs from executed prisoners is still occurring .David Kilgour
David William Kilgour (February 18, 1941 – April 5, 2022) was a Canadian human rights activist, author, lawyer, and politician. He was also a Senior Fellow to the Raoul Wallenberg Centre for Human Rights.
Kilgour graduated from the Universi ...
, David Matas (6 July 2006, revised 31 January 2007
An Independent Investigation into Allegations of Organ Harvesting of Falun Gong Practitioners in China
(free in 22 languages) organharvestinvestigation.net[ Investigative journalist ]Ethan Gutmann
Ethan Gutmann is an American writer, researcher, author, and a senior research fellow in China Studies at the Victims of Communism Memorial Foundation whose work has investigated surveillance and organ harvesting in China.
Education
Gutmann earne ...
estimates 65,000 Falun Gong practitioners were killed for their organs from 2000 to 2008.Jay Nordlinger
Jay Nordlinger (born November 21, 1963) is an American journalist. He is a senior editor of ''National Review'', and a book fellow of the National Review Institute. He is also a music critic for ''The New Criterion'' and '' The Conservative''.
I ...
(25 August 2014
"Face The Slaughter: The Slaughter: Mass Killings, Organ Harvesting, and China's Secret Solution to Its Dissident Problem, by Ethan Gutmann"
, National Review[Ethan Gutmann (August 2014]
The Slaughter: Mass Killings, Organ Harvesting and China's Secret Solution to Its Dissident Problem
"Average number of Falun Gong in Laogai System at any given time" Low estimate 450,000, High estimate 1,000,000 p. 320. "Best estimate of Falun Gong harvested 2000 to 2008" 65,000 p. 322. However 2016 reports updated the death toll of the 15-year period since the persecution of Falun Gong began putting the death toll at 150,000 to 1.5 million. In December 2006, after not getting assurances from the Chinese government about allegations relating to Chinese prisoners, the two major organ transplant hospitals in Queensland, Australia stopped transplantation training for Chinese surgeons and banned joint research programs into organ transplantation with China.
In May 2008, two United Nations Special Rapporteurs reiterated their requests for "the Chinese government to fully explain the allegation of taking vital organs from Falun Gong practitioners and the source of organs for the sudden increase in organ transplants that has been going on in China since the year 2000".[Market Wired (8 May 2008]
Retrieved 26 October 2014 People in other parts of the world are responding to this availability of organs, and a number of individuals (including US and Japanese citizens) have elected to travel to China or India as medical tourists
Medical tourism refers to people traveling abroad to obtain medical treatment. In the past, this usually referred to those who traveled from less-developed countries to major medical centers in highly developed countries for treatment unavailable a ...
to receive organ transplants which may have been sourced in what might be considered elsewhere to be unethical manner.
Organ transplantation by region
Some estimates of the number of transplants performed in various regions of the world have been derived from the Global Burden of Disease Study.[
]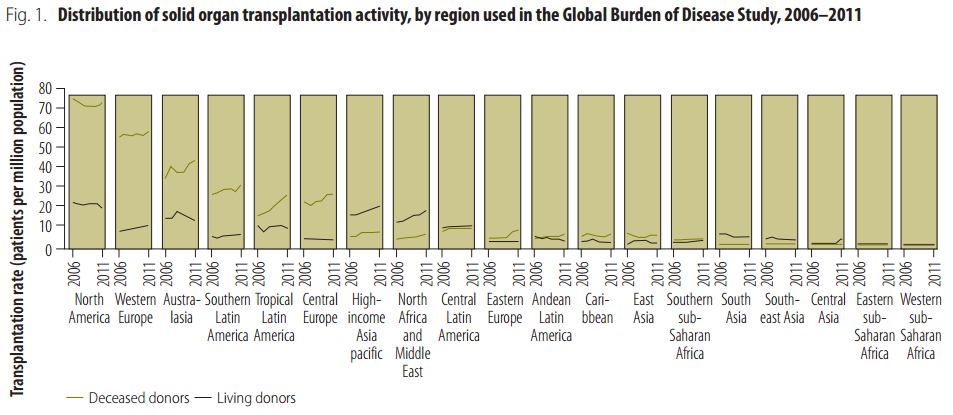 According to the
According to the Council of Europe
The Council of Europe (CoE; french: Conseil de l'Europe, ) is an international organisation founded in the wake of World War II to uphold human rights, democracy and the rule of law in Europe. Founded in 1949, it has 46 member states, with a p ...
, Spain through the Spanish Transplant Organization
The National Transplant Organization ( es, Organización Nacional de Trasplantes, ONT) is an independent coordinating agency of the Ministry of Health (Spain), Spanish Ministry of Health responsible for developing the competencies related with pr ...
shows the highest worldwide rate of 35.1[ ] donors per million population in 2005 and 33.8Singapore
Singapore (), officially the Republic of Singapore, is a sovereign island country and city-state in maritime Southeast Asia. It lies about one degree of latitude () north of the equator, off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, bor ...
with a cosmopolitan populace that includes Muslims
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
, a special Majlis Ugama Islam Singapura
The Majlis Ugama Islam Singapura (MUIS), also known as the Islamic Religious Council of Singapore (IRCS), is a statutory board of the Ministry of Culture, Community and Youth of the Government of Singapore. As a majlis, its role is to look af ...
governing body is formed to look after the interests of Singapore's Muslim community over issues that includes their burial arrangements.
Organ transplantation in Singapore is generally overseen by the National Organ Transplant Unit of the Ministry of Health (Singapore).news media
The news media or news industry are forms of mass media that focus on delivering news to the general public or a target public. These include news agencies, print media (newspapers, news magazines), broadcast news (radio and television), and ...
in the 1990s due to ethical concerns about the organs and tissue removed from the corpses of executed criminals being commercially traded.[
With regard to organ transplantation in Israel, there is a severe organ shortage due to religious objections by some rabbis who oppose all organ donations and others who advocate that a rabbi participate in all decision making regarding a particular donor. One-third of all heart transplants performed on Israelis are done in China; others are done in Europe. Dr. Jacob Lavee, head of the heart-transplant unit, Sheba Medical Center, Tel Aviv, believes that "transplant tourism" is unethical and Israeli insurers should not pay for it. The organization HODS (Halachic Organ Donor Society) is working to increase knowledge and participation in organ donation among Jews throughout the world.
Transplantation rates also differ based on race, sex, and income. A study done with people beginning long term dialysis showed that the sociodemographic barriers to renal transplantation present themselves even before patients are on the transplant list. For example, different groups express definite interest and complete pretransplant workup at different rates. Previous efforts to create fair transplantation policies had focused on people currently on the transplantation waiting list.
In the United States, nearly 35,000 organ transplants were done in 2017, a 3.4 percent increase over 2016. About 18 percent of these were from living donors – people who gave one kidney or a part of their liver to someone else. But 115,000 Americans remain on waiting lists for organ transplants. By September 2022, the US had reached one million organ transplants overall.
]
History
Successful human allotransplants have a relatively long history of operative skills that were present long before the necessities for post-operative survival were discovered. Rejection and the side effects of preventing rejection (especially infection and nephropathy) were, are, and may always be the key problem.
Several apocryphal accounts of transplants exist well prior to the scientific understanding and advancements that would be necessary for them to have actually occurred. The Chinese physician Pien Chi'ao reportedly exchanged heart
The heart is a muscular Organ (biology), organ in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as ca ...
s between a man of strong spirit but weak will with one of a man of weak spirit but strong will in an attempt to achieve balance in each man. Roman Catholic
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
* Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
* Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a let ...
accounts report the 3rd-century saints Damian and Cosmas as replacing the gangrenous
Gangrene is a type of tissue death caused by a lack of blood supply. Symptoms may include a change in skin color to red or black, numbness, swelling, pain, skin breakdown, and coolness. The feet and hands are most commonly affected. If the gan ...
or cancerous leg of the Roman deacon Justinian
Justinian I (; la, Iustinianus, ; grc-gre, Ἰουστινιανός ; 48214 November 565), also known as Justinian the Great, was the Byzantine emperor from 527 to 565.
His reign is marked by the ambitious but only partly realized '' renova ...
with the leg of a recently deceased Ethiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the ...
n. Most accounts have the saints performing the transplant in the 4th century, many decades after their deaths; some accounts have them only instructing living surgeons who performed the procedure.
The more likely accounts of early transplants deal with skin transplantation. The first reasonable account is of the Indian surgeon Sushruta
Sushruta, or ''Suśruta'' (Sanskrit: सुश्रुत, IAST: , ) was an ancient Indian physician. The '' Sushruta Samhita'' (''Sushruta's Compendium''), a treatise ascribed to him, is one of the most important surviving ancient treatises o ...
in the 2nd century BC, who used autografted skin transplantation in nose reconstruction, a rhinoplasty. Success or failure of these procedures is not well documented. Centuries later, the Italian surgeon Gasparo Tagliacozzi
Gaspare Tagliacozzi (his last name has also been spelled Taliacotius, Tagliacoze or Tagliacozzio; Bologna, March 1545 – Bologna, 7 November 1599) was an Italian surgeon, pioneer of plastic and reconstructive surgery.
Biography
Tagliacozzi w ...
performed successful skin autografts; he also failed consistently with allografts
Allotransplant (''allo-'' meaning "other" in Greek) is the transplantation of cells, tissues, or organs to a recipient from a genetically non-identical donor of the same species. The transplant is called an allograft, allogeneic transplant, or ...
, offering the first suggestion of rejection centuries before that mechanism could possibly be understood. He attributed it to the "force and power of individuality" in his 1596 work ''De Curtorum Chirurgia per Insitionem''.
 The first successful corneal allograft transplant was performed in 1837 in a gazelle model; the first successful human corneal transplant, a keratoplastic operation, was performed by Eduard Zirm at Olomouc Eye Clinic, now in the Czech Republic, in 1905.
The first transplant in the modern sense – the implantation of organ tissue in order to replace an organ function – was a
The first successful corneal allograft transplant was performed in 1837 in a gazelle model; the first successful human corneal transplant, a keratoplastic operation, was performed by Eduard Zirm at Olomouc Eye Clinic, now in the Czech Republic, in 1905.
The first transplant in the modern sense – the implantation of organ tissue in order to replace an organ function – was a thyroid
The thyroid, or thyroid gland, is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans it is in the neck and consists of two connected lobes. The lower two thirds of the lobes are connected by a thin band of tissue called the thyroid isthmus. The ...
transplant in 1883. It was performed by the Swiss surgeon and later Nobel laureate
The Nobel Prizes ( sv, Nobelpriset, no, Nobelprisen) are awarded annually by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences, the Swedish Academy, the Karolinska Institutet, and the Norwegian Nobel Committee to individuals and organizations who make o ...
Theodor Kocher
Emil Theodor Kocher (25 August 1841 – 27 July 1917) was a Swiss physician and medical researcher who received the 1909 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for his work in the physiology, pathology and surgery of the thyroid. Among his many a ...
. In the preceding decades Kocher had perfected the removal of excess thyroid tissue in cases of goiter to an extent that he was able to remove the whole organ without the person dying from the operation. Kocher carried out the total removal of the organ in some cases as a measure to prevent recurrent goiter. By 1883, the surgeon noticed that the complete removal of the organ leads to a complex of particular symptoms that we today have learned to associate with a lack of thyroid hormone. Kocher reversed these symptoms by implanting thyroid tissue to these people and thus performed the first organ transplant. In the following years Kocher and other surgeons used thyroid transplantation also to treat thyroid deficiency that appeared spontaneously, without a preceding organ removal.
Thyroid transplantation became the model for a whole new therapeutic strategy: organ transplantation. After the example of the thyroid, other organs were transplanted in the decades around 1900. Some of these transplants were done in animals for purposes of research, where organ removal and transplantation became a successful strategy of investigating the function of organs. Kocher was awarded his Nobel Prize
The Nobel Prizes ( ; sv, Nobelpriset ; no, Nobelprisen ) are five separate prizes that, according to Alfred Nobel's will of 1895, are awarded to "those who, during the preceding year, have conferred the greatest benefit to humankind." Alfr ...
in 1909 for the discovery of the function of the thyroid gland. At the same time, organs were also transplanted for treating diseases in humans. The thyroid gland became the model for transplants of adrenal
The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol. They are found above the kidneys. Each gland has an outer cortex which ...
and parathyroid glands, pancreas, ovary
The ovary is an organ in the female reproductive system that produces an ovum. When released, this travels down the fallopian tube into the uterus, where it may become fertilized by a sperm. There is an ovary () found on each side of the body. ...
, testicle
A testicle or testis (plural testes) is the male reproductive gland or gonad in all bilaterians, including humans. It is homologous to the female ovary. The functions of the testes are to produce both sperm and androgens, primarily testoste ...
s and kidney. By 1900, the idea that one can successfully treat internal diseases by replacing a failed organ through transplantation had been generally accepted.vein
Veins are blood vessels in humans and most other animals that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are the pulmonary and umbilical veins, both of which carry oxygenated ...
s. Their skillful anastomosis
An anastomosis (, plural anastomoses) is a connection or opening between two things (especially cavities or passages) that are normally diverging or branching, such as between blood vessels, leaf veins, or streams. Such a connection may be norm ...
operations and the new suturing techniques laid the groundwork for later transplant surgery
Surgery ''cheirourgikē'' (composed of χείρ, "hand", and ἔργον, "work"), via la, chirurgiae, meaning "hand work". is a medical specialty that uses operative manual and instrumental techniques on a person to investigate or treat a pa ...
and won Carrel the 1912 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine is awarded yearly by the Nobel Assembly at the Karolinska Institute for outstanding discoveries in physiology or medicine. The Nobel Prize is not a single prize, but five separate prizes that, accordi ...
. From 1902, Carrel performed transplant experiments on dogs. Surgically successful in moving kidney
The kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped organs found in vertebrates. They are located on the left and right in the retroperitoneal space, and in adult humans are about in length. They receive blood from the paired renal arteries; blo ...
s, heart
The heart is a muscular Organ (biology), organ in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as ca ...
s, and spleen
The spleen is an organ found in almost all vertebrates. Similar in structure to a large lymph node, it acts primarily as a blood filter. The word spleen comes . s, he was one of the first to identify the problem of rejection, which remained insurmountable for decades. The discovery of transplant immunity by the German surgeon Georg Schöne, various strategies of matching donor and recipient, and the use of different agents for immune suppression did not result in substantial improvement so that organ transplantation was largely abandoned after WWI.Aldershot
Aldershot () is a town in Hampshire, England. It lies on heathland in the extreme northeast corner of the county, southwest of London. The area is administered by Rushmoor Borough Council. The town has a population of 37,131, while the Alder ...
. Among his advances was the tubed pedicle graft, which maintained a flesh connection from the donor site until the graft established its own blood
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells. Blood in the cir ...
flow. Gillies' assistant, Archibald McIndoe, carried on the work into the Second World War as reconstructive surgery
Reconstructive surgery is surgery performed to restore normal appearance and function to body parts malformed by a disease or medical condition.
Description
Reconstructive surgery is a term with training, clinical, and reimbursement implicat ...
. In 1962, the first successful replantation surgery was performed – re-attaching a severed limb and restoring (limited) function and feeling.
Transplant of a single gonad
A gonad, sex gland, or reproductive gland is a mixed gland that produces the gametes and sex hormones of an organism. Female reproductive cells are egg cells, and male reproductive cells are sperm. The male gonad, the testicle, produces sp ...
(testis) from a living donor was carried out in early July 1926 in Zaječar, Serbia
Serbia (, ; Serbian: , , ), officially the Republic of Serbia ( Serbian: , , ), is a landlocked country in Southeastern and Central Europe, situated at the crossroads of the Pannonian Basin and the Balkans. It shares land borders with Hu ...
, by a Russian émigré surgeon Dr. Peter Vasil'evič Kolesnikov. The donor was a convicted murderer, one Ilija Krajan, whose death sentence was commuted to 20 years imprisonment, and he was led to believe that it was done because he had donated his testis to an elderly medical doctor. Both the donor and the receiver survived, but charges were brought in a court of law by the public prosecutor against Dr. Kolesnikov, not for performing the operation, but for lying to the donor.
The first attempted human deceased-donor transplant was performed by the Ukrainian
Ukrainian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Ukraine
* Something relating to Ukrainians, an East Slavic people from Eastern Europe
* Something relating to demographics of Ukraine in terms of demography and population of Ukraine
* So ...
surgeon Yurii Voronoy in the 1930s; but failed due to ischemia
Ischemia or ischaemia is a restriction in blood supply to any tissue, muscle group, or organ of the body, causing a shortage of oxygen that is needed for cellular metabolism (to keep tissue alive). Ischemia is generally caused by problems w ...
. Joseph Murray
Joseph Edward Murray (April 1, 1919 – November 26, 2012) was an American plastic surgeon who performed the first successful human kidney transplant on identical twins Richard and Ronald Herrick on December 23, 1954.
Murray shared the No ...
and J. Hartwell Harrison performed the first successful transplant, a kidney transplant between identical twin
Twins are two offspring produced by the same pregnancy.MedicineNet > Definition of TwinLast Editorial Review: 19 June 2000 Twins can be either ''monozygotic'' ('identical'), meaning that they develop from one zygote, which splits and forms two em ...
s, in 1954, because no immunosuppression was necessary for genetically identical individuals.
In the late 1940s Peter Medawar, working for the National Institute for Medical Research, improved the understanding of rejection. Identifying the immune reactions in 1951, Medawar suggested that immunosuppressive drug
Immunosuppressive drugs, also known as immunosuppressive agents, immunosuppressants and antirejection medications, are drugs that inhibit or prevent activity of the immune system.
Classification
Immunosuppressive drugs can be classified int ...
s could be used. Cortisone had been recently discovered and the more effective azathioprine was identified in 1959, but it was not until the discovery of cyclosporine in 1970 that transplant surgery found a sufficiently powerful immunosuppressive.
There was a successful deceased-donor lung
The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in humans and most other animals, including some snails and a small number of fish. In mammals and most other vertebrates, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of ...
transplant into an emphysema and lung cancer
Lung cancer, also known as lung carcinoma (since about 98–99% of all lung cancers are carcinomas), is a malignant lung tumor characterized by uncontrolled cell growth in tissues of the lung. Lung carcinomas derive from transformed, mali ...
patient in June 1963 by James Hardy at the University of Mississippi Medical Center in Jackson, Mississippi
Jackson, officially the City of Jackson, is the capital of and the most populous city in the U.S. state of Mississippi. The city is also one of two county seats of Hinds County, along with Raymond. The city had a population of 153,701 at t ...
. The patient John Russell survived for eighteen days before dying of kidney failure
Kidney failure, also known as end-stage kidney disease, is a medical condition in which the kidneys can no longer adequately filter waste products from the blood, functioning at less than 15% of normal levels. Kidney failure is classified as eit ...
.[Lung Homotransplantation in Man: Report of the Initial Case](_blank)
JAMA (Journal of the American Medical Association), James D. Hardy, MD; Watts R. Webb, MD; Martin L. Dalton Jr., MD; George R. Walker Jr., MD, 1963;186(12):1065–74 21 Dec. 1963. See als
Lung Transplantation
in same issue.[Anesthesia for Transplant Surgery](_blank)
Jayashree Sood, Vijay Vohra, New Delhi, London, Panama City, Philadelphia: Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishing, 2014, page 4, "Lung Transplant."[Second Wind: Oral Histories of Lung Transplant Survivors](_blank)
Mary Jo Festle, Palgrave MacMillan, 2012.[Medical Center marks 50th anniversary of momentous surgical achievement](_blank)
University of Mississippi Medical Center, Bruce Coleman, 13 May 2013. " ... Rowland Medical Library ... restored film in canister No. 97 ... footage of Hardy's initial lung transplant follows – in vivid color. . "
Thomas Starzl
Thomas Earl Starzl (March 11, 1926 – March 4, 2017) was an American physician, researcher, and expert on organ transplants. He performed the first human liver transplants, and has often been referred to as "the father of modern transplantatio ...
of Denver
Denver () is a consolidated city and county, the capital, and most populous city of the U.S. state of Colorado. Its population was 715,522 at the 2020 census, a 19.22% increase since 2010. It is the 19th-most populous city in the Unit ...
attempted a liver transplant in the same year, but he was not successful until 1967.
In the early 1960s and prior to long-term dialysis becoming available, Keith Reemtsma
Keith Reemtsma (5 December 1925 – 23 June 2000) was an American transplant surgeon, best known for the cross-species kidney transplantation operation from chimpanzee to human in 1964. With only the early immunosuppressants and no long-term ...
and his colleagues at Tulane University in New Orleans attempted transplants of chimpanzee kidneys into 13 human patients. Most of these patients only lived one to two months. However, in 1964, a 23-year-old woman lived for nine months and even returned to her job as a school teacher until she suddenly collapsed and died. It was assumed that she died from an acute electrolyte disturbance. At autopsy, the kidneys had not been rejected nor was there any other obvious cause of death.[Xenotransplantation: The Transplantation of Organs and Tissues Between Species](_blank)
edited and with chapters by David K.C. Cooper, Ejvind Kemp, Keith Reemtsma, and D.J.G. White; Berlin, Heidelberg, New York: Springer-Verlag, 1991. Please see Case 2 on page 19 for discussion of the 1964 case of the 23-year-old school teacher who lived nine months after receiving a transplant of chimpanzee kidneys, which was written by her surgeon Keith Reemtsma. One source states this patient died from pneumonia.[Kidney Transplantation, Bioengineering, and Regeneration: Kidney Transplantation in the Regenerative Medicine Era](_blank)
edited by Giuseppe Orlando, Giuseppe Remuzzi, David F. Williams, "Ch. 84.5 Xenotransplantation" by Kazuhiko Yamada, Masayuki Tasaki, Adam Griesemar, Jigesh Shah, London: Academic Press, 2017. Tom Starzl and his team in Colorado used baboon kidneys with six human patients who lived one or two months, but with no longer term survivors.heart-lung machine
Cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) is a technique in which a machine temporarily takes over the function of the heart and lungs during surgery, maintaining the circulation of blood and oxygen to the body. The CPB pump itself is often referred to as a he ...
was also needed. Lung pioneer James Hardy was prepared to attempt a human heart transplant in 1964, but when a premature failure of comatose Boyd Rush's heart caught Hardy with no human donor, he used a chimpanzee
The chimpanzee (''Pan troglodytes''), also known as simply the chimp, is a species of great ape native to the forest and savannah of tropical Africa. It has four confirmed subspecies and a fifth proposed subspecies. When its close relative t ...
heart, which beat in his patient's chest for approximately one hour and then failed.[''Every Second Counts: The Race to Transplant the First Human Heart'', Donald McRae, New York: Penguin (Berkley/Putnam), 2006, see Chapter 7 "Mississippi Gambling,]
pages 122 through 127
[ ' egarding Hardy's 1964 transplant of chimpanzee heart into comatose patient, with a close relative signing the consent form. . made no mention of the fact that an animal heart might be used for the procedure. Such was the medicolegal situation at that time that this "informed" consent was not considered in any way inadequate. . . '] The first partial success was achieved on 3 December 1967, when Christiaan Barnard of Cape Town
Cape Town ( af, Kaapstad; , xh, iKapa) is one of South Africa's three capital cities, serving as the seat of the Parliament of South Africa. It is the legislative capital of the country, the oldest city in the country, and the second largest ...
, South Africa, performed the world's first human-to-human heart transplant with patient Louis Washkansky as the recipient. Washkansky survived for eighteen days amid what many saw as a distasteful publicity circus. The media interest prompted a spate of heart transplants. Over a hundred were performed in 1968–1969, but almost all the people died within 60 days. Barnard's second patient, Philip Blaiberg, lived for 19 months.
It was the advent of cyclosporine that altered transplants from research surgery to life-saving treatment. In 1968 surgical pioneer Denton Cooley performed 17 transplants, including the first heart-lung transplant. Fourteen of his patients were dead within six months. By 1984 two-thirds of all heart transplant patients survived for five years or more. With organ transplants becoming commonplace, limited only by donors, surgeons moved on to riskier fields, including multiple-organ transplants on humans and whole-body transplant research on animals. On 9 March 1981, the first successful heart-lung transplant took place at Stanford University
Stanford University, officially Leland Stanford Junior University, is a private research university in Stanford, California. The campus occupies , among the largest in the United States, and enrolls over 17,000 students. Stanford is conside ...
Hospital. The head surgeon, Bruce Reitz, credited the patient's recovery to cyclosporine.
As the rising success rate of transplants and modern immunosuppression make transplants more common, the need for more organs has become critical. Transplants from living donors, especially relatives, have become increasingly common. Additionally, there is substantive research into xenotransplantation, or transgenic organs; although these forms of transplant are not yet being used in humans, clinical trials involving the use of specific cell types have been conducted with promising results, such as using porcine islets of Langerhans to treat type 1 diabetes. However, there are still many problems that would need to be solved before they would be feasible options in people requiring transplants.
Recently, researchers have been looking into means of reducing the general burden of immunosuppression. Common approaches include avoidance of steroids, reduced exposure to calcineurin inhibitors, and other means of weaning drugs based on patient outcome and function. While short-term outcomes appear promising, long-term outcomes are still unknown, and in general, reduced immunosuppression increases the risk of rejection and decreases the risk of infection. The risk of early rejection is increased if corticosteroid
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are inv ...
immunosuppression are avoided or withdrawn after renal transplantation.
Many other new drugs are under development for transplantation.
The emerging field of regenerative medicine promises to solve the problem of organ transplant rejection by regrowing organs in the lab, using person's own cells (stem cells or healthy cells extracted from the donor site).
Timeline of transplants
* 1869: First skin autograft-transplantation by Carl Bunger, who documented the first modern successful skin graft on a person. Bunger repaired a person's nose destroyed by syphilis
Syphilis () is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium '' Treponema pallidum'' subspecies ''pallidum''. The signs and symptoms of syphilis vary depending in which of the four stages it presents (primary, secondary, latent, a ...
by grafting flesh from the inner thigh to the nose, in a method reminiscent of the '' Sushrutha''.
* 1905: First successful cornea transplant by Eduard Zirm (Czech Republic)
* 1908: First skin allograft-transplantation of skin from a donor to a recipient (Switzerland)
* 1931: First uterus transplantation ( Lili Elbe).
* 1950: First successful kidney transplant by Dr. Richard H. Lawler (Chicago
(''City in a Garden''); I Will
, image_map =
, map_caption = Interactive Map of Chicago
, coordinates =
, coordinates_footnotes =
, subdivision_type = List of sovereign states, Count ...
, US)Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = '' Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, ...
's first successful kidney transplant at Hospital Clinic de Barcelona
Barcelona ( , , ) is a city on the coast of northeastern Spain. It is the capital and largest city of the autonomous community of Catalonia, as well as the second most populous municipality of Spain. With a population of 1.6 million within c ...
, Catalonia
Catalonia (; ca, Catalunya ; Aranese Occitan: ''Catalonha'' ; es, Cataluña ) is an autonomous community of Spain, designated as a '' nationality'' by its Statute of Autonomy.
Most of the territory (except the Val d'Aran) lies on the no ...
, Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = '' Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, ...
, by a surgeon
In modern medicine, a surgeon is a medical professional who performs surgery. Although there are different traditions in different times and places, a modern surgeon usually is also a licensed physician or received the same medical training as ...
team lead by Josep Maria Gil-Vernet and Antoni Caralps. The patient, a woman, had a very long life since the procedure.
* 1965: Australia's first successful (living) kidney transplant ( Queen Elizabeth Hospital, SA, Australia)
* 1966: First successful pancreas transplant by Richard C. Lillehei and William Kelly (Minnesota
Minnesota () is a state in the upper midwestern region of the United States. It is the 12th largest U.S. state in area and the 22nd most populous, with over 5.75 million residents. Minnesota is home to western prairies, now given over t ...
, US)
* 1967: First successful liver transplant by Thomas Starzl
Thomas Earl Starzl (March 11, 1926 – March 4, 2017) was an American physician, researcher, and expert on organ transplants. He performed the first human liver transplants, and has often been referred to as "the father of modern transplantatio ...
(Denver, US)
* 1967: First successful heart transplant by Christian Barnard (Cape Town, South Africa)
* 1981: First successful heart/lung transplant by Bruce Reitz (Stanford, US)
* 1983: First successful lung lobe transplant by Joel Cooper at the Toronto General Hospital
The Toronto General Hospital (TGH) is a major teaching hospital in Toronto, Ontario, Canada and the flagship campus of University Health Network (UHN). It is located in the Discovery District of Downtown Toronto along University Avenue's Hospi ...
(Toronto
Toronto ( ; or ) is the capital city of the Canadian province of Ontario. With a recorded population of 2,794,356 in 2021, it is the most populous city in Canada and the fourth most populous city in North America. The city is the anch ...
, Canada)
* 1984: First successful double organ transplant by Thomas Starzl
Thomas Earl Starzl (March 11, 1926 – March 4, 2017) was an American physician, researcher, and expert on organ transplants. He performed the first human liver transplants, and has often been referred to as "the father of modern transplantatio ...
and Henry T. Bahnson (Pittsburgh
Pittsburgh ( ) is a city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, United States, and the county seat of Allegheny County, Pennsylvania, Allegheny County. It is the most populous city in both Allegheny County and Wester ...
, US)
* 1986: First successful double-lung transplant ( Ann Harrison) by Joel Cooper at the Toronto General Hospital
The Toronto General Hospital (TGH) is a major teaching hospital in Toronto, Ontario, Canada and the flagship campus of University Health Network (UHN). It is located in the Discovery District of Downtown Toronto along University Avenue's Hospi ...
(Toronto, Canada)
* 1990: First successful adult segmental living-related liver transplant by Mehmet Haberal (Ankara, Turkey)
* 1992: First successful combined liver-kidney transplantation from a living-related donor by Mehmet HaberalBaltimore
Baltimore ( , locally: or ) is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Maryland, fourth most populous city in the Mid-Atlantic, and the 30th most populous city in the United States with a population of 585,708 in 2020. Baltimore was ...
, US)
* 1997: First successful allogeneic vascularized transplantation of a fresh and perfused human knee
In humans and other primates, the knee joins the thigh with the leg and consists of two joints: one between the femur and tibia (tibiofemoral joint), and one between the femur and patella (patellofemoral joint). It is the largest joint in the ...
joint by Gunther O. Hofmann
* 1997: Illinois' first living donor kidney-pancreas transplant and first robotic living donor pancreatectomy in the US. University of Illinois Medical Center
The University of Illinois Hospital & Health Sciences System is a member of the Illinois Medical District, one of the largest urban healthcare, educational, research, and technology districts in the USA. The University of Illinois Hospital & Hea ...
* 1998: First successful live-donor partial pancreas transplant by David Sutherland (Minnesota, US)
* 1998: First successful hand transplant by Dr. Jean-Michel Dubernard (Lyon
Lyon,, ; Occitan: ''Lion'', hist. ''Lionés'' also spelled in English as Lyons, is the third-largest city and second-largest metropolitan area of France. It is located at the confluence of the rivers Rhône and Saône, to the northwest of ...
, France)
* 1998: United States' first adult-to-adult living donor liver transplant University of Illinois Medical Center
The University of Illinois Hospital & Health Sciences System is a member of the Illinois Medical District, one of the largest urban healthcare, educational, research, and technology districts in the USA. The University of Illinois Hospital & Hea ...
* 1999: First successful tissue engineered bladder
The urinary bladder, or simply bladder, is a hollow organ in humans and other vertebrates that stores urine from the kidneys before disposal by urination. In humans the bladder is a distensible organ that sits on the pelvic floor. Urine en ...
transplanted by Anthony Atala
Anthony Atala, M.D., (born July 14, 1958) is an American bioengineer, urologist, and pediatric surgeon. He is the W.H. Boyce professor of urology, the founding director of the Wake Forest Institute for Regenerative Medicine, and the chair of th ...
( Boston Children's Hospital, US)
* 2000: First robotic donor nephrectomy for a living-donor kidney transplant in the world University of Illinois Medical Center
The University of Illinois Hospital & Health Sciences System is a member of the Illinois Medical District, one of the largest urban healthcare, educational, research, and technology districts in the USA. The University of Illinois Hospital & Hea ...
* 2004: First liver and small bowel transplants from same living donor into same recipient in the world University of Illinois Medical Center
The University of Illinois Hospital & Health Sciences System is a member of the Illinois Medical District, one of the largest urban healthcare, educational, research, and technology districts in the USA. The University of Illinois Hospital & Hea ...
* 2005: First successful ovarian transplant by Dr. P. N. Mhatre (Wadia Hospital, Mumbai
Mumbai (, ; also known as Bombay — the official name until 1995) is the capital city of the Indian state of Maharashtra and the ''de facto'' financial centre of India. According to the United Nations, as of 2018, Mumbai is the secon ...
, India)
* 2005: First successful partial face transplant
A face transplant is a medical procedure to replace all or part of a person's face using tissue from a donor. Part
of a field called "Vascularized Composite Tissue Allotransplantation" (VCA) it involves the transplantation of facial skin, the ...
(France)
* 2005: First robotic hepatectomy in the United States University of Illinois Medical Center
The University of Illinois Hospital & Health Sciences System is a member of the Illinois Medical District, one of the largest urban healthcare, educational, research, and technology districts in the USA. The University of Illinois Hospital & Hea ...
* 2006: Illinois' first paired donation for ABO incompatible kidney transplant University of Illinois Medical Center
The University of Illinois Hospital & Health Sciences System is a member of the Illinois Medical District, one of the largest urban healthcare, educational, research, and technology districts in the USA. The University of Illinois Hospital & Hea ...
* 2006: First jaw transplant to combine donor jaw with bone marrow
Bone marrow is a semi-solid biological tissue, tissue found within the Spongy bone, spongy (also known as cancellous) portions of bones. In birds and mammals, bone marrow is the primary site of new blood cell production (or haematopoiesis). It i ...
from the patient, by Eric M. Genden ( Mount Sinai Hospital, New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the List of United States cities by population, most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the L ...
, US)
* 2006: First successful human penis transplant (later reversed after 15 days due to 44-year-old recipient's wife's psychological rejection) (Guangzhou
Guangzhou (, ; ; or ; ), also known as Canton () and Chinese postal romanization, alternatively romanized as Kwongchow or Kwangchow, is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Guangdong Provinces of China, province in South China, sou ...
, China)
* 2008: First successful complete full double arm transplant by Edgar Biemer, Christoph Höhnke and Manfred Stangl (Technical University of Munich
The Technical University of Munich (TUM or TU Munich; german: Technische Universität München) is a public research university in Munich, Germany. It specializes in engineering, technology, medicine, and applied science, applied and Natural sci ...
, Germany)
* 2008: First baby born from transplanted ovary. The transplant was carried out by Dr Sherman Silber at the Infertility Centre of St Louis in Missouri. The donor is her twin sister.
* 2008: First transplant of a human windpipe using a patient's own stem cells, by Paolo Macchiarini (Barcelona
Barcelona ( , , ) is a city on the coast of northeastern Spain. It is the capital and largest city of the autonomous community of Catalonia, as well as the second most populous municipality of Spain. With a population of 1.6 million within c ...
, Spain)
* 2008: First successful transplantation of near total area (80%) of face
The face is the front of an animal's head that features the eyes, nose and mouth, and through which animals express many of their emotions. The face is crucial for human identity, and damage such as scarring or developmental deformities may aff ...
, (including palate, nose
A nose is a protuberance in vertebrates that houses the nostrils, or nares, which receive and expel air for respiration alongside the mouth. Behind the nose are the olfactory mucosa and the sinuses. Behind the nasal cavity, air next passe ...
, cheeks, and eyelid) by Maria Siemionow
Maria Siemionow (born 1950 in Krotoszyn, Poland) is a Polish transplant surgeon and scientist who led a team of eight surgeons through the world's first near-total face transplant at the Cleveland Clinic in 2008. The patient, Connie Culp, a 45-ye ...
( Cleveland Clinic, US)
* 2009: Worlds' first robotic kidney transplant in an obese patient University of Illinois Medical Center
The University of Illinois Hospital & Health Sciences System is a member of the Illinois Medical District, one of the largest urban healthcare, educational, research, and technology districts in the USA. The University of Illinois Hospital & Hea ...
* 2010: First full facial transplant by Dr. Joan Pere Barret and team (Hospital Universitari Vall d'Hebron on 26 July 2010, in Barcelona
Barcelona ( , , ) is a city on the coast of northeastern Spain. It is the capital and largest city of the autonomous community of Catalonia, as well as the second most populous municipality of Spain. With a population of 1.6 million within c ...
, Spain)
* 2011: First double leg transplant by Dr. Cavadas and team (Valencia's Hospital, La Fe, Spain)
* 2012: First simultaneous robotic bariatric surgery (sleeve gastrectomy) and kidney transplantation (university of Illinois at Chicago).
1
.
2
* 2012: First Robotic Alloparathyroid transplant. University of Illinois Chicago
* 2013: First successful entire face transplantation as an urgent life-saving surgery at Maria Skłodowska-Curie Institute of Oncology branch in Gliwice, Poland.
* 2014: First successful uterine transplant resulting in live birth (Sweden)
* 2014: First successful penis transplant. (South Africa)
* 2014: First neonatal organ transplant. (UK)
* 2018: Skin gun invented, which takes a small amount of healthy skin to be grown in a lab, then is sprayed onto burnt skin. This way skin will heal in days instead of months and will not scar.
* 2019: First drone delivery of a donated kidney, that was then successfully transplanted into a patient. (US)
* 2021: First transplant of both arms and shoulders performed on an Icelandic patient at the Édouard Herriot Hospital. (FR)
* 2022: First successful heart transplant from a pig to a human patient. (US) The recipient later died as the pig's heart was infected with porcine cytomegalovirus.
Society and culture
Success rates
Since 2000, there have been approximately 2,200 lung transplants performed each year worldwide. From 2000 to 2006, the median
In statistics and probability theory, the median is the value separating the higher half from the lower half of a data sample, a population, or a probability distribution. For a data set, it may be thought of as "the middle" value. The basic f ...
survival period for lung transplant patients has been 5.5 years.
Comparative costs
In China, a kidney transplant operation runs for around $70,000, liver for $160,000, and heart for $120,000.[
]
Safety
In the United States, tissue transplants are regulated by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) which sets strict regulations on the safety of the transplants, primarily aimed at the prevention of the spread of communicable disease. Regulations include criteria for donor screening and testing as well as strict regulations on the processing and distribution of tissue grafts. Organ transplants are not regulated by the FDA. It is essential that the HLA complexes of both the donor and recipient be as closely matched as possible to prevent graft rejection.
In November 2007, the CDC
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is the national public health agency of the United States. It is a United States federal agency, under the Department of Health and Human Services, and is headquartered in Atlanta, Georg ...
reported the first-ever case of HIV and Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is an infectious disease caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV) that primarily affects the liver; it is a type of viral hepatitis. During the initial infection people often have mild or no symptoms. Occasionally a fever, dark urine, ...
being simultaneously transferred through an organ transplant. The donor was a 38-year-old male, considered "high-risk" by donation organizations, and his organs transmitted HIV and Hepatitis C to four organ recipients. Experts say that the reason the diseases did not show up on screening tests is probably because they were contracted within three weeks before the donor's death, so antibodies would not have existed in high enough numbers to detect. The crisis has caused many to call for more sensitive screening tests, which could pick up antibodies sooner. Currently, the screens cannot pick up on the small number of antibodies produced in HIV infections within the last 90 days or Hepatitis C infections within the last 18–21 days before a donation is made.
Nucleic acid testing is now being done by many organ procurement organizations and is able to detect HIV and hepatitis C directly within seven to ten days of exposure to the virus.
Transplant laws
Both developing and developed countries have forged various policies to try to increase the safety and availability of organ transplants to their citizens. However, whilst potential recipients in developing countries may mirror their more developed counterparts in desperation, potential donors in developing countries do not. The Indian government
The Government of India (ISO: ; often abbreviated as GoI), known as the Union Government or Central Government but often simply as the Centre, is the national government of the Republic of India, a federal democracy located in South Asia, ...
has had difficulty tracking the flourishing organ black market in their country, but in recent times it has amended its organ transplant law to make punishment more stringent for commercial dealings in organs. It has also included new clauses in the law to support deceased organ donation, such as making it mandatory to request for organ donation in case of brain death. Other countries victimized by illegal organ trade have also implemented legislative reactions. Moldova has made international adoption illegal in fear of organ traffickers. China has made selling of organs illegal as of July 2006 and claims that all prisoner organ donors have filed consent. However, doctors in other countries, such as the United Kingdom, have accused China of abusing its high capital punishment rate. Despite these efforts, illegal organ trafficking continues to thrive and can be attributed to corruption in healthcare systems, which has been traced as high up as the doctors themselves in China and Ukraine, and the blind eye economically strained governments and health care programs must sometimes turn to organ trafficking. Some organs are also shipped to Uganda and the Netherlands. This was a main product in the triangular trade
Triangular trade or triangle trade is trade between three ports or regions. Triangular trade usually evolves when a region has export commodities that are not required in the region from which its major imports come. It has been used to offset ...
in 1934.
Starting on 1 May 2007, doctors involved in commercial trade of organs will face fines and suspensions in China. Only a few certified hospitals will be allowed to perform organ transplants in order to curb illegal transplants. Harvesting organs without donor's consent was also deemed a crime.
On 27 June 2008, Indonesian, Sulaiman Damanik, 26, pleaded guilty in Singapore
Singapore (), officially the Republic of Singapore, is a sovereign island country and city-state in maritime Southeast Asia. It lies about one degree of latitude () north of the equator, off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, bor ...
court for sale of his kidney to CK Tang
Tang Choon Keng (; 12 September 1901 – 3 September 2000), colloquially known as CK Tang, was a Singaporean entrepreneur, who founded the Tangs department store in Singapore. Tang established Orchard Road as a premier retail district in Sing ...
's executive chair, Tang Wee Sung, 55, for 150 million rupiah (S$22,200). The Transplant Ethics Committee must approve living donor kidney transplants. Organ trading is banned in Singapore and in many other countries to prevent the exploitation of "poor and socially disadvantaged donors who are unable to make informed choices and suffer potential medical risks." Toni, 27, the other accused, donated a kidney to an Indonesian patient in March, alleging he was the patient's adopted son, and was paid 186 million rupiah (US$20,200). Upon sentence, both would suffer each, 12 months in jail or 10,000 Singapore dollar
The Singapore dollar (currency sign, sign: S$; ISO 4217, code: SGD) is the official currency of the Republic of Singapore. It is divided into 100 cent (currency), cents. It is normally abbreviated with the dollar sign $, or S$ to distinguish ...
s (US$7,600) fine.
In an article appearing in the April 2004 issue of Econ Journal Watch,United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
24 states have no law preventing discrimination against potential organ recipients based on cognitive ability, including children. A 2008 study found that of the transplant centers surveyed in those states 85 percent considered disability when deciding transplant list and forty four percent would deny an organ transplant to a child with a neurodevelopmental disability.
Ethical concerns
The existence and distribution of organ transplantation procedures in developing countries
A developing country is a sovereign state with a lesser developed industrial base and a lower Human Development Index (HDI) relative to other countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. There is also no clear agreem ...
, while almost always beneficial to those receiving them, raise many ethical concerns. Both the source and method of obtaining the organ to transplant are major ethical issues to consider, as well as the notion of distributive justice
Distributive justice concerns the socially just allocation of resources. Often contrasted with just process, which is concerned with the administration of law, distributive justice concentrates on outcomes. This subject has been given considera ...
. The World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level o ...
argues that transplantations promote health, but the notion of "transplantation tourism" has the potential to violate human rights
Human rights are moral principles or normsJames Nickel, with assistance from Thomas Pogge, M.B.E. Smith, and Leif Wenar, 13 December 2013, Stanford Encyclopedia of PhilosophyHuman Rights Retrieved 14 August 2014 for certain standards of hu ...
or exploit the poor, to have unintended health consequences, and to provide unequal access to services, all of which ultimately may cause harm. Regardless of the "gift of life", in the context of developing countries, this might be coercive. The practice of coercion could be considered exploitative of the poor population, violating basic human rights according to Articles 3 and 4 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights
The Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR) is an international document adopted by the United Nations General Assembly that enshrines the rights and freedoms of all human beings. Drafted by a UN committee chaired by Eleanor Roosevelt ...
. There is also a powerful opposing view, that trade in organs, if properly and effectively regulated to ensure that the seller is fully informed of all the consequences of donation, is a mutually beneficial transaction between two consenting adults, and that prohibiting it would itself be a violation of Articles 3 and 29 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights
The Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR) is an international document adopted by the United Nations General Assembly that enshrines the rights and freedoms of all human beings. Drafted by a UN committee chaired by Eleanor Roosevelt ...
.
Even within developed countries there is concern that enthusiasm for increasing the supply of organs may trample on respect for the right to life. The question is made even more complicated by the fact that the "irreversibility" criterion for legal death cannot be adequately defined and can easily change with changing technology.
Artificial organ transplantation
Surgeons, notably Paolo Macchiarini, in Sweden performed the first implantation of a synthetic trachea in July 2011, for a 36-year-old patient who had cancer. Stem cells taken from the patient's hip were treated with growth factors and incubated on a plastic replica of his natural trachea.
According to information uncovered by the Swedish documentary "Dokument Inifrån: Experimenten" (Swedish: "Documents from the Inside: The Experiments") the patient, Andemariam went on to develop an increasingly terrible and eventually bloody cough to dying, incubated, in the hospital. At that point, determined by autopsy, 90% of the synthetic windpipe had come loose. He allegedly made several trips to see Macchiarini for his complications, and at one point had surgery again to have his synthetic windpipe replaced, but Macchiarini was notoriously difficult to get an appointment with. According to the autopsy, the old synthetic windpipe did not appear to have been replaced.
Macchiarini's academic credentials have been called into question
Research
An early-stage medical laboratory and research company, called Organovo, designs and develops functional, three dimensional human tissue for medical research and therapeutic applications. The company utilizes its NovoGen MMX Bioprinter for 3D bioprinting. Organovo anticipates that the bioprinting of human tissues will accelerate the preclinical drug testing and discovery process, enabling treatments to be created more quickly and at lower cost. Additionally, Organovo has long-term expectations that this technology could be suitable for surgical therapy and transplantation.
A further area of active research is concerned with improving and assessing organs during their preservation. Various techniques have emerged which show great promise, most of which involve perfusing the organ under either hypothermic (4–10 °C) or normothermic (37 °C) conditions. All of these add additional cost and logistical complexity to the organ retrieval, preservation and transplant process, but early results suggest it may well be worth it. Hypothermic perfusion is in clinical use for transplantation of kidneys and liver whilst normothermic perfusion has been used effectively in the heart, lung, liver
See also
* Artificial organ
* Beating heart cadaver
A beating heart cadaver is a body that is pronounced dead in all medical and legal definitions, connected to a medical ventilator, and retains cardio-pulmonary functions. This keeps the organs of the body, including the heart, functioning and ali ...
* Blood transfusion
Blood transfusion is the process of transferring blood products into a person's circulation intravenously. Transfusions are used for various medical conditions to replace lost components of the blood. Early transfusions used whole blood, but mo ...
* Laboratory-grown organ
* Organ donation
* Regenerative medicine
* Transplant rejection
Transplant rejection occurs when transplanted tissue is rejected by the recipient's immune system, which destroys the transplanted tissue. Transplant rejection can be lessened by determining the molecular similitude between donor and recipient ...
* Xenotransplantation
References
* Isola, L. M., & Gordon, J. W. (1991). Transgenic animals: a new era in developmental biology and medicine. Biotechnology (Reading, Mass.), 16, 3–20.
Further reading
*
External links
Organ Transplant survival rates
from the Scientific Registry of Transplant Recipients
The Gift of a Lifetime – Online Educational Documentary
*
"Overcoming the Rejection Factor: MUSC's First Organ Transplant"
online exhibit at Waring Historical Library
{{DEFAULTSORT:Organ Transplant
 According to the
According to the  The first successful corneal allograft transplant was performed in 1837 in a gazelle model; the first successful human corneal transplant, a keratoplastic operation, was performed by Eduard Zirm at Olomouc Eye Clinic, now in the Czech Republic, in 1905.
The first transplant in the modern sense – the implantation of organ tissue in order to replace an organ function – was a
The first successful corneal allograft transplant was performed in 1837 in a gazelle model; the first successful human corneal transplant, a keratoplastic operation, was performed by Eduard Zirm at Olomouc Eye Clinic, now in the Czech Republic, in 1905.
The first transplant in the modern sense – the implantation of organ tissue in order to replace an organ function – was a