order-6 tetrahedral honeycomb on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In
 The order-6 tetrahedral honeycomb has a second construction as a uniform honeycomb, with
The order-6 tetrahedral honeycomb has a second construction as a uniform honeycomb, with
 The order-6 tetrahedral honeycomb is also a regular hyperbolic honeycomb in 3-space, and one of 11 which are paracompact.
This honeycomb is one of 15 uniform paracompact honeycombs in the ,3,3Coxeter group, along with its dual, the
The order-6 tetrahedral honeycomb is also a regular hyperbolic honeycomb in 3-space, and one of 11 which are paracompact.
This honeycomb is one of 15 uniform paracompact honeycombs in the ,3,3Coxeter group, along with its dual, the




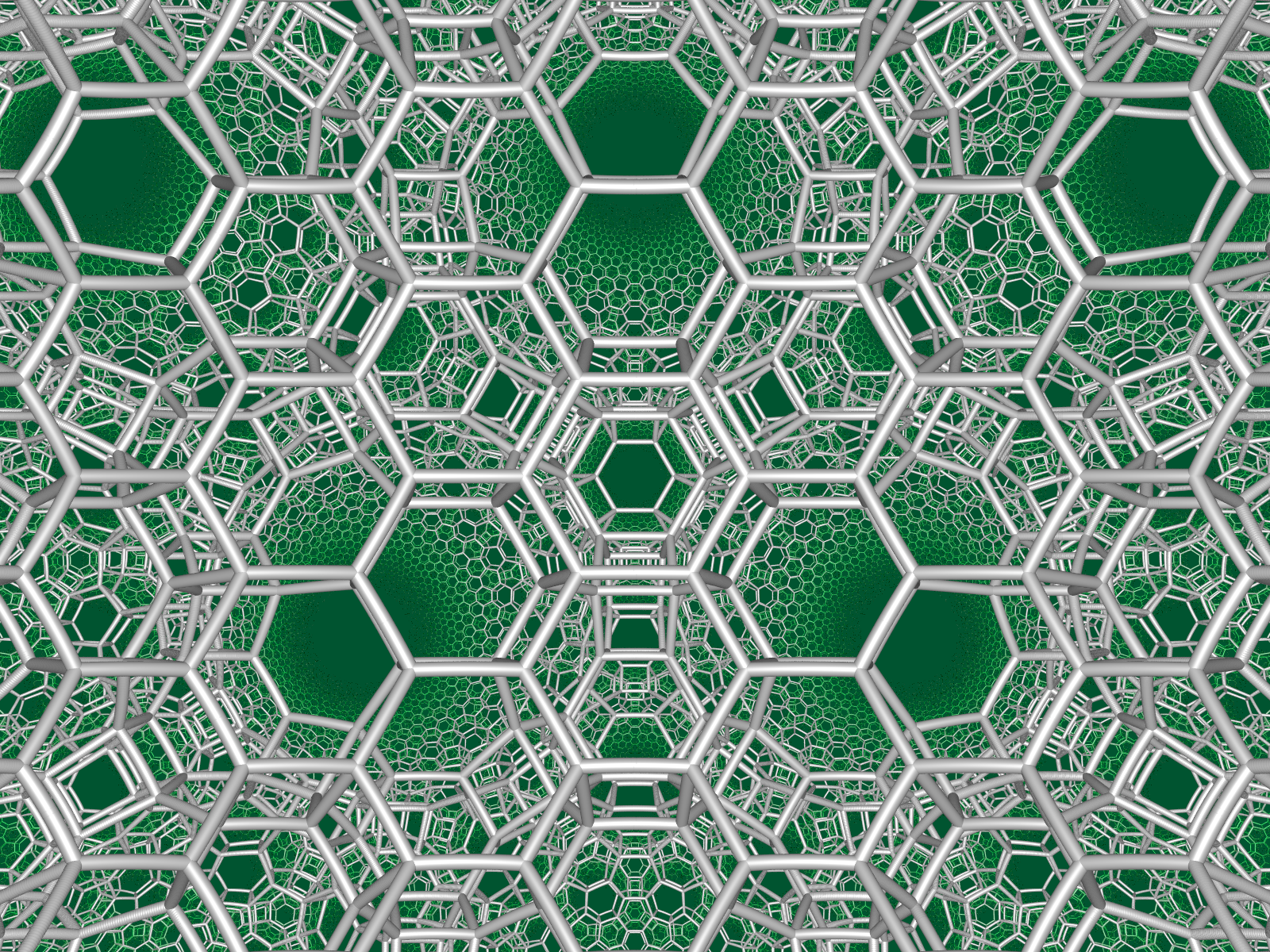
Regular Honeycombs in Hyperbolic Space
Table III * Jeffrey R. Weeks ''The Shape of Space, 2nd edition'' {{isbn, 0-8247-0709-5 (Chapter 16-17: Geometries on Three-manifolds I,II) * Norman Johnson ''Uniform Polytopes'', Manuscript ** N.W. Johnson: ''The Theory of Uniform Polytopes and Honeycombs'', Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Toronto, 1966 ** N.W. Johnson: ''Geometries and Transformations'', (2018) Chapter 13: Hyperbolic Coxeter groups Honeycombs (geometry)
hyperbolic 3-space
In mathematics, hyperbolic space of dimension n is the unique simply connected, n-dimensional Riemannian manifold of constant sectional curvature equal to -1. It is homogeneous, and satisfies the stronger property of being a symmetric space. ...
, the order-6 tetrahedral honeycomb is a paracompact regular space-filling tessellation
A tessellation or tiling is the covering of a surface, often a plane (mathematics), plane, using one or more geometric shapes, called ''tiles'', with no overlaps and no gaps. In mathematics, tessellation can be generalized to high-dimensional ...
(or honeycomb
A honeycomb is a mass of Triangular prismatic honeycomb#Hexagonal prismatic honeycomb, hexagonal prismatic Beeswax, wax cells built by honey bees in their beehive, nests to contain their larvae and stores of honey and pollen.
beekeeping, Beekee ...
). It is ''paracompact'' because it has vertex figures
In geometry, a vertex figure, broadly speaking, is the figure exposed when a corner of a polyhedron or polytope is sliced off.
Definitions
Take some corner or vertex of a polyhedron. Mark a point somewhere along each connected edge. Draw lines ...
composed of an infinite number of faces, and has all vertices as ideal point
In hyperbolic geometry, an ideal point, omega point or point at infinity is a well-defined point outside the hyperbolic plane or space.
Given a line ''l'' and a point ''P'' not on ''l'', right- and left-limiting parallels to ''l'' through ''P'' ...
s at infinity. With Schläfli symbol
In geometry, the Schläfli symbol is a notation of the form \ that defines regular polytopes and tessellations.
The Schläfli symbol is named after the 19th-century Swiss mathematician Ludwig Schläfli, who generalized Euclidean geometry to more ...
, the order-6 tetrahedral honeycomb has six ideal
Ideal may refer to:
Philosophy
* Ideal (ethics), values that one actively pursues as goals
* Platonic ideal, a philosophical idea of trueness of form, associated with Plato
Mathematics
* Ideal (ring theory), special subsets of a ring considere ...
tetrahedra
In geometry, a tetrahedron (plural: tetrahedra or tetrahedrons), also known as a triangular pyramid, is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, six straight edges, and four vertex corners. The tetrahedron is the simplest of all the o ...
around each edge. All vertices are ideal
Ideal may refer to:
Philosophy
* Ideal (ethics), values that one actively pursues as goals
* Platonic ideal, a philosophical idea of trueness of form, associated with Plato
Mathematics
* Ideal (ring theory), special subsets of a ring considere ...
, with infinitely many tetrahedra existing around each vertex in a triangular tiling
In geometry, the triangular tiling or triangular tessellation is one of the three regular tilings of the Euclidean plane, and is the only such tiling where the constituent shapes are not parallelogons. Because the internal angle of the equilater ...
vertex figure
In geometry, a vertex figure, broadly speaking, is the figure exposed when a corner of a polyhedron or polytope is sliced off.
Definitions
Take some corner or Vertex (geometry), vertex of a polyhedron. Mark a point somewhere along each connect ...
.Coxeter ''The Beauty of Geometry'', 1999, Chapter 10, Table III
Symmetry constructions
 The order-6 tetrahedral honeycomb has a second construction as a uniform honeycomb, with
The order-6 tetrahedral honeycomb has a second construction as a uniform honeycomb, with Schläfli symbol
In geometry, the Schläfli symbol is a notation of the form \ that defines regular polytopes and tessellations.
The Schläfli symbol is named after the 19th-century Swiss mathematician Ludwig Schläfli, who generalized Euclidean geometry to more ...
. This construction contains alternating types, or colors, of tetrahedral cells. In Coxeter notation
In geometry, Coxeter notation (also Coxeter symbol) is a system of classifying symmetry groups, describing the angles between fundamental reflections of a Coxeter group in a bracketed notation expressing the structure of a Coxeter-Dynkin diagram ...
, this half symmetry is represented as ,3,6,1+↔ ,((3,3,3)) or ,3[3/sup>">.html" ;"title=",3[3">,3[3/sup> ↔ .
Related polytopes and honeycombs
The order-6 tetrahedral honeycomb is similar to the two-dimensional infinite-order triangular tiling, . Both tessellations are regular, and only contain triangles and ideal vertices. :hexagonal tiling honeycomb
In the field of hyperbolic geometry, the hexagonal tiling honeycomb is one of 11 regular paracompact honeycombs in 3-dimensional hyperbolic space. It is ''paracompact'' because it has cells composed of an infinite number of faces. Each cell is a ...
.
The order-6 tetrahedral honeycomb is part of a sequence of regular polychora
In mathematics, a regular 4-polytope is a regular four-dimensional polytope. They are the four-dimensional analogues of the regular polyhedra in three dimensions and the regular polygons in two dimensions.
There are six convex and ten star regu ...
and honeycombs with tetrahedral
In geometry, a tetrahedron (plural: tetrahedra or tetrahedrons), also known as a triangular pyramid, is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, six straight edges, and four vertex corners. The tetrahedron is the simplest of all the o ...
cells
Cell most often refers to:
* Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life
Cell may also refer to:
Locations
* Monastic cell, a small room, hut, or cave in which a religious recluse lives, alternatively the small precursor of a monastery w ...
.
It is also part of a sequence of honeycombs with triangular tiling
In geometry, the triangular tiling or triangular tessellation is one of the three regular tilings of the Euclidean plane, and is the only such tiling where the constituent shapes are not parallelogons. Because the internal angle of the equilater ...
vertex figure
In geometry, a vertex figure, broadly speaking, is the figure exposed when a corner of a polyhedron or polytope is sliced off.
Definitions
Take some corner or Vertex (geometry), vertex of a polyhedron. Mark a point somewhere along each connect ...
s.
Rectified order-6 tetrahedral honeycomb
The rectified order-6 tetrahedral honeycomb, t1 hasoctahedral
In geometry, an octahedron (plural: octahedra, octahedrons) is a polyhedron with eight faces. The term is most commonly used to refer to the regular octahedron, a Platonic solid composed of eight equilateral triangles, four of which meet at ea ...
and triangular tiling
In geometry, the triangular tiling or triangular tessellation is one of the three regular tilings of the Euclidean plane, and is the only such tiling where the constituent shapes are not parallelogons. Because the internal angle of the equilater ...
cells arranged in a hexagonal prism
In geometry, the hexagonal prism is a prism with hexagonal base. Prisms are polyhedrons; this polyhedron has 8 faces, 18 edges, and 12 vertices..
Since it has 8 faces, it is an octahedron. However, the term ''octahedron'' is primarily used to ...
vertex figure
In geometry, a vertex figure, broadly speaking, is the figure exposed when a corner of a polyhedron or polytope is sliced off.
Definitions
Take some corner or Vertex (geometry), vertex of a polyhedron. Mark a point somewhere along each connect ...
.
: 

Perspective projection
Linear or point-projection perspective (from la, perspicere 'to see through') is one of two types of graphical projection perspective in the graphic arts; the other is parallel projection. Linear perspective is an approximate representation, ...
view within Poincaré disk model
In geometry, the Poincaré disk model, also called the conformal disk model, is a model of 2-dimensional hyperbolic geometry in which all points are inside the unit disk, and straight lines are either circular arcs contained within the disk th ...
Truncated order-6 tetrahedral honeycomb
The truncated order-6 tetrahedral honeycomb, t0,1 hastruncated tetrahedron
In geometry, the truncated tetrahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 4 regular hexagonal faces, 4 equilateral triangle faces, 12 vertices and 18 edges (of two types). It can be constructed by truncating all 4 vertices of a regular tetrahedro ...
and triangular tiling
In geometry, the triangular tiling or triangular tessellation is one of the three regular tilings of the Euclidean plane, and is the only such tiling where the constituent shapes are not parallelogons. Because the internal angle of the equilater ...
cells arranged in a hexagonal pyramid
In geometry, a hexagonal pyramid is a pyramid with a hexagonal base upon which are erected six isosceles triangular faces that meet at a point (the apex). Like any pyramid, it is self- dual.
A right hexagonal pyramid with a regular hexagon base ...
vertex figure
In geometry, a vertex figure, broadly speaking, is the figure exposed when a corner of a polyhedron or polytope is sliced off.
Definitions
Take some corner or Vertex (geometry), vertex of a polyhedron. Mark a point somewhere along each connect ...
.

Bitruncated order-6 tetrahedral honeycomb
The bitruncated order-6 tetrahedral honeycomb is equivalent to the bitruncated hexagonal tiling honeycomb.Cantellated order-6 tetrahedral honeycomb
The cantellated order-6 tetrahedral honeycomb, t0,2 hascuboctahedron
A cuboctahedron is a polyhedron with 8 triangular faces and 6 square faces. A cuboctahedron has 12 identical vertices, with 2 triangles and 2 squares meeting at each, and 24 identical edges, each separating a triangle from a square. As such, it ...
, trihexagonal tiling
In geometry, the trihexagonal tiling is one of 11 uniform tilings of the Euclidean plane by regular polygons. See in particular Theorem 2.1.3, p. 59 (classification of uniform tilings); Figure 2.1.5, p.63 (illustration of this tiling), Theorem 2. ...
, and hexagonal prism
In geometry, the hexagonal prism is a prism with hexagonal base. Prisms are polyhedrons; this polyhedron has 8 faces, 18 edges, and 12 vertices..
Since it has 8 faces, it is an octahedron. However, the term ''octahedron'' is primarily used to ...
cells arranged in an isosceles triangular prism
In geometry, a triangular prism is a three-sided prism; it is a polyhedron made of a triangular base, a translated copy, and 3 faces joining corresponding sides. A right triangular prism has rectangular sides, otherwise it is ''oblique''. A unif ...
vertex figure
In geometry, a vertex figure, broadly speaking, is the figure exposed when a corner of a polyhedron or polytope is sliced off.
Definitions
Take some corner or Vertex (geometry), vertex of a polyhedron. Mark a point somewhere along each connect ...
.

Cantitruncated order-6 tetrahedral honeycomb
The cantitruncated order-6 tetrahedral honeycomb, t0,1,2 hastruncated octahedron
In geometry, the truncated octahedron is the Archimedean solid that arises from a regular octahedron by removing six pyramids, one at each of the octahedron's vertices. The truncated octahedron has 14 faces (8 regular hexagon, hexagons and 6 Squa ...
, hexagonal tiling
In geometry, the hexagonal tiling or hexagonal tessellation is a regular tiling of the Euclidean plane, in which exactly three hexagons meet at each vertex. It has Schläfli symbol of or (as a truncated triangular tiling).
English mathemat ...
, and hexagonal prism
In geometry, the hexagonal prism is a prism with hexagonal base. Prisms are polyhedrons; this polyhedron has 8 faces, 18 edges, and 12 vertices..
Since it has 8 faces, it is an octahedron. However, the term ''octahedron'' is primarily used to ...
cells connected in a mirrored sphenoid
In geometry, a tetrahedron (plural: tetrahedra or tetrahedrons), also known as a triangular pyramid, is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, six straight edges, and four vertex corners. The tetrahedron is the simplest of all the o ...
vertex figure
In geometry, a vertex figure, broadly speaking, is the figure exposed when a corner of a polyhedron or polytope is sliced off.
Definitions
Take some corner or Vertex (geometry), vertex of a polyhedron. Mark a point somewhere along each connect ...
.

Runcinated order-6 tetrahedral honeycomb
The bitruncated order-6 tetrahedral honeycomb is equivalent to the bitruncated hexagonal tiling honeycomb.Runcitruncated order-6 tetrahedral honeycomb
The runcitruncated order-6 tetrahedral honeycomb is equivalent to the runcicantellated hexagonal tiling honeycomb.Runcicantellated order-6 tetrahedral honeycomb
The runcicantellated order-6 tetrahedral honeycomb is equivalent to the runcitruncated hexagonal tiling honeycomb.Omnitruncated order-6 tetrahedral honeycomb
The omnitruncated order-6 tetrahedral honeycomb is equivalent to the omnitruncated hexagonal tiling honeycomb.See also
*Convex uniform honeycombs in hyperbolic space
In hyperbolic geometry, a uniform honeycomb in hyperbolic space is a uniform tessellation of uniform polyhedral cells. In 3-dimensional hyperbolic space there are nine Coxeter group families of compact convex uniform honeycombs, generated as Wyt ...
* Regular tessellations of hyperbolic 3-space
* Paracompact uniform honeycomb
In geometry, uniform honeycombs in hyperbolic space are tessellations of convex uniform polyhedron Cell (geometry), cells. In 3-dimensional hyperbolic space there are 23 Coxeter group families of Coxeter diagram#Paracompact (Koszul simplex groups), ...
s
References
*Coxeter
Harold Scott MacDonald "Donald" Coxeter, (9 February 1907 – 31 March 2003) was a British and later also Canadian geometer. He is regarded as one of the greatest geometers of the 20th century.
Biography
Coxeter was born in Kensington to ...
, ''Regular Polytopes
In mathematics, a regular polytope is a polytope whose symmetry group acts transitively on its flags, thus giving it the highest degree of symmetry. All its elements or -faces (for all , where is the dimension of the polytope) — cells, f ...
'', 3rd. ed., Dover Publications, 1973. . (Tables I and II: Regular polytopes and honeycombs, pp. 294–296)
* ''The Beauty of Geometry: Twelve Essays'' (1999), Dover Publications, , (Chapter 10Regular Honeycombs in Hyperbolic Space
Table III * Jeffrey R. Weeks ''The Shape of Space, 2nd edition'' {{isbn, 0-8247-0709-5 (Chapter 16-17: Geometries on Three-manifolds I,II) * Norman Johnson ''Uniform Polytopes'', Manuscript ** N.W. Johnson: ''The Theory of Uniform Polytopes and Honeycombs'', Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Toronto, 1966 ** N.W. Johnson: ''Geometries and Transformations'', (2018) Chapter 13: Hyperbolic Coxeter groups Honeycombs (geometry)