Open Reading Frame on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In
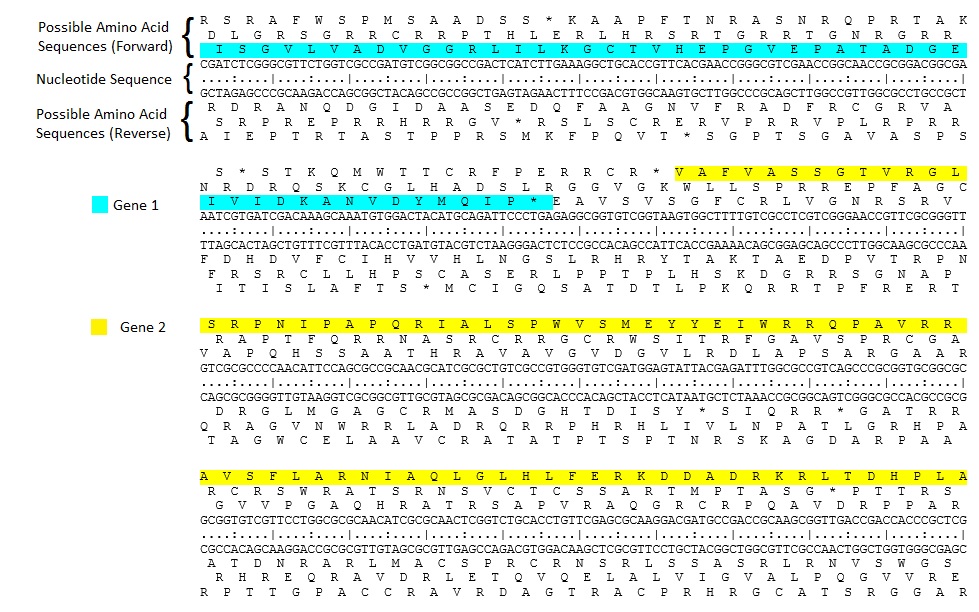
Translation and Open Reading Frames
hORFeome V5.1
- A web-based interactive tool for CCSB Human ORFeome Collection
- A free, fast and multi-platform desktop GUI tool for predicting and analyzing ORFs
StarORF
- A multi-platform, java-based, GUI tool for predicting and analyzing ORFs and obtaining reverse complement sequence
{{Webarchive, url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151222082631/http://bioinformatics.ysu.edu/tools/OrfPredictor.html , date=2015-12-22 - A webserver designed for ORF prediction and translation of a batch of EST or cDNA sequences Molecular genetics Bioinformatics he:מסגרת קריאה#מסגרת קריאה פתוחה
 In
In molecular biology
Molecular biology is the branch of biology that seeks to understand the molecular basis of biological activity in and between cells, including biomolecular synthesis, modification, mechanisms, and interactions. The study of chemical and physi ...
, open reading frames (ORFs) are defined as spans of DNA sequence between the start and stop codons. Usually, this is considered within a studied region of a prokaryotic
A prokaryote () is a single-celled organism that lacks a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. The word ''prokaryote'' comes from the Greek πρό (, 'before') and κάρυον (, 'nut' or 'kernel').Campbell, N. "Biology:Concepts & Connec ...
DNA sequence, where only one of the six possible reading frames will be "open" (the "reading", however, refers to the RNA produced by transcription of the DNA and its subsequent interaction with the ribosome in translation
Translation is the communication of the meaning of a source-language text by means of an equivalent target-language text. The English language draws a terminological distinction (which does not exist in every language) between ''transla ...
). Such an ORF may contain a start codon (usually AUG in terms of RNA) and by definition cannot extend beyond a stop codon
In molecular biology (specifically protein biosynthesis), a stop codon (or termination codon) is a codon (nucleotide triplet within messenger RNA) that signals the termination of the translation process of the current protein. Most codons in mess ...
(usually UAA, UAG or UGA in RNA). That start codon (not necessarily the first) indicates where translation may start. The transcription termination site is located after the ORF, beyond the translation
Translation is the communication of the meaning of a source-language text by means of an equivalent target-language text. The English language draws a terminological distinction (which does not exist in every language) between ''transla ...
stop codon
In molecular biology (specifically protein biosynthesis), a stop codon (or termination codon) is a codon (nucleotide triplet within messenger RNA) that signals the termination of the translation process of the current protein. Most codons in mess ...
. If transcription were to cease before the stop codon, an incomplete protein would be made during translation.
In eukaryotic
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose Cell (biology), cells have a cell nucleus, nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the ...
gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a b ...
s with multiple exons, introns are removed and exons are then joined together after transcription to yield the final mRNA
In molecular biology, messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) is a single-stranded molecule of RNA that corresponds to the genetic sequence of a gene, and is read by a ribosome in the process of synthesizing a protein.
mRNA is created during the ...
for protein translation. In the context of gene finding, the start-stop definition of an ORF therefore only applies to spliced mRNAs, not genomic DNA, since introns may contain stop codons and/or cause shifts between reading frames. An alternative definition says that an ORF is a sequence that has a length divisible by three and is bounded by stop codons. This more general definition can be useful in the context of transcriptomics
Transcriptomics technologies are the techniques used to study an organism's transcriptome, the sum of all of its RNA transcripts. The information content of an organism is recorded in the DNA of its genome and expressed through transcription. H ...
and metagenomics
Metagenomics is the study of genetic material recovered directly from environmental or clinical samples by a method called sequencing. The broad field may also be referred to as environmental genomics, ecogenomics, community genomics or microb ...
, where a start or stop codon may not be present in the obtained sequences. Such an ORF corresponds to parts of a gene rather than the complete gene.
Biological significance
One common use of open reading frames (ORFs) is as one piece of evidence to assist ingene prediction
In computational biology, gene prediction or gene finding refers to the process of identifying the regions of genomic DNA that encode genes. This includes protein-coding genes as well as RNA genes, but may also include prediction of other functiona ...
. Long ORFs are often used, along with other evidence, to initially identify candidate protein-coding regions or functional RNA-coding regions in a DNA sequence. The presence of an ORF does not necessarily mean that the region is always translated. For example, in a randomly generated DNA sequence with an equal percentage of each nucleotide
Nucleotides are organic molecules consisting of a nucleoside and a phosphate. They serve as monomeric units of the nucleic acid polymers – deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), both of which are essential biomolecule ...
, a stop-codon
In molecular biology (specifically protein biosynthesis), a stop codon (or termination codon) is a codon (nucleotide triplet within messenger RNA) that signals the termination of the translation process of the current protein. Most codons in mess ...
would be expected once every 21 codons. A simple gene prediction
In computational biology, gene prediction or gene finding refers to the process of identifying the regions of genomic DNA that encode genes. This includes protein-coding genes as well as RNA genes, but may also include prediction of other functiona ...
algorithm for prokaryotes might look for a start codon followed by an open reading frame that is long enough to encode a typical protein, where the codon usage of that region matches the frequency characteristic for the given organism's coding regions. Therefore, some authors say that an ORF should have a minimal length, e.g. 100 codons or 150 codons. By itself even a long open reading frame is not conclusive evidence for the presence of a gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a b ...
.
Short ORFs (sORFs). Some short ORFs (sORFs) that lack the classical hallmarks of protein-coding genes (both from ncRNAs and mRNAs) can produce functional peptides. 5’-UTR of about 50% of mammal mRNAs are known to contain one or several sORFs, also called upstream ORFs or uORFs. However, less than 10% of the vertebrate mRNAs surveyed in an older study contained AUG codons in front of the major ORF. Interestingly, uORFs were found in two thirds of proto-oncogenes and related proteins. 64–75% of experimentally found translation initiation sites of sORFs are conserved in the genomes of human and mouse and may indicate that these elements have function. However, sORFs can often be found only in the minor forms of mRNAs and avoid selection; the high conservation of initiation sites may be connected with their location inside promoters of the relevant genes. This is characteristic of SLAMF1
Signaling lymphocytic activation molecule 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SLAMF1'' gene. Recently SLAMF1 has also been designated CD150 (cluster of differentiation 150).
SLAMF1 belongs to the signaling lymphocytic activation mo ...
gene, for example.
Six-frame translation
Since DNA is interpreted in groups of three nucleotides (codons), a DNA strand has three distinct reading frames. The double helix of a DNA molecule has two anti-parallel strands; with the two strands having three reading frames each, there are six possible frame translations.
Software
Finder
The ORF Finder (Open Reading Frame Finder) is a graphical analysis tool which finds all open reading frames of a selectable minimum size in a user's sequence or in a sequence already in the database. This tool identifies all open reading frames using the standard or alternative genetic codes. The deduced amino acid sequence can be saved in various formats and searched against the sequence database using thebasic local alignment search tool
In bioinformatics, BLAST (basic local alignment search tool) is an algorithm and program for comparing Primary structure, primary biological sequence information, such as the amino acid, amino-acid sequences of proteins or the nucleotides of DN ...
(BLAST) server. The ORF Finder should be helpful in preparing complete and accurate sequence submissions. It is also packaged with the Sequin sequence submission software (sequence analyser).
Investigator
ORF Investigator is a program which not only gives information about the coding and non coding sequences but also can perform pairwise global alignment of different gene/DNA regions sequences. The tool efficiently finds the ORFs for corresponding amino acid sequences and converts them into their single letter amino acid code, and provides their locations in the sequence. The pairwise global alignment between the sequences makes it convenient to detect the different mutations, including single nucleotide polymorphism.Needleman–Wunsch algorithm
The Needleman–Wunsch algorithm is an algorithm used in bioinformatics to align protein or nucleotide sequences. It was one of the first applications of dynamic programming to compare biological sequences. The algorithm was developed by Saul ...
s are used for the gene alignment. The ORF Investigator is written in the portable Perl
Perl is a family of two high-level, general-purpose, interpreted, dynamic programming languages. "Perl" refers to Perl 5, but from 2000 to 2019 it also referred to its redesigned "sister language", Perl 6, before the latter's name was offic ...
programming language
A programming language is a system of notation for writing computer programs. Most programming languages are text-based formal languages, but they may also be graphical. They are a kind of computer language.
The description of a programming ...
, and is therefore available to users of all common operating systems.
Predictor
OrfPredictor is a web server designed for identifying protein-coding regions in expressed sequence tag (EST)-derived sequences. For query sequences with a hit in BLASTX, the program predicts the coding regions based on the translation reading frames identified in BLASTX alignments, otherwise, it predicts the most probable coding region based on the intrinsic signals of the query sequences. The output is the predicted peptide sequences in the FASTA format, and a definition line that includes the query ID, the translation reading frame and the nucleotide positions where the coding region begins and ends. OrfPredictor facilitates the annotation of EST-derived sequences, particularly, for large-scale EST projects. ORF Predictor uses a combination of the two different ORF definitions mentioned above. It searches stretches starting with a start codon and ending at a stop codon. As an additional criterion, it searches for a stop codon in the 5'untranslated region
In molecular genetics, an untranslated region (or UTR) refers to either of two sections, one on each side of a coding sequence on a strand of mRNA. If it is found on the 5' side, it is called the 5' UTR (or leader sequence), or if it is foun ...
(UTR or NTR, ''nontranslated region''.)
ORFik
ORFik is a R-package in Bioconductor for finding open reading frames and using Next generation sequencing technologies for justification of ORFs.orfipy
orfipy is a tool written inPython
Python may refer to:
Snakes
* Pythonidae, a family of nonvenomous snakes found in Africa, Asia, and Australia
** ''Python'' (genus), a genus of Pythonidae found in Africa and Asia
* Python (mythology), a mythical serpent
Computing
* Python (pro ...
/ Cython
Cython () is a programming language that aims to be a superset of the Python programming language, designed to give C-like performance with code that is written mostly in Python with optional additional C-inspired syntax.
Cython is a compiled ...
to extract ORFs in an extremely and fast and flexible manner. orfipy can work with plain or gzipped FASTA and FASTQ sequences, and provides several options to fine-tune ORF searches; these include specifying the start and stop codons, reporting partial ORFs, and using custom translation tables. The results can be saved in multiple formats, including the space-efficient BED format. orfipy is particularly faster for data containing multiple smaller FASTA sequences, such as de-novo transcriptome assemblies.
See also
* Coding region * Putative gene * Sequerome – Asequence profiling tool
A sequence profiling tool in bioinformatics is a type of software that presents information related to a genetic sequence, gene name, or keyword input. Such tools generally take a query such as a DNA, RNA, or protein sequence or ‘keyword’ an ...
that links each BLAST
Blast or The Blast may refer to:
*Explosion, a rapid increase in volume and release of energy in an extreme manner
*Detonation, an exothermic front accelerating through a medium that eventually drives a shock front
Film
* ''Blast'' (1997 film), ...
record to the NCBI
The National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) is part of the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM), a branch of the National Institutes of Health (NIH). It is approved and funded by the government of the United States. The ...
ORF enabling complete ORF analysis of a BLAST report.
References
External links
Translation and Open Reading Frames
hORFeome V5.1
- A web-based interactive tool for CCSB Human ORFeome Collection
- A free, fast and multi-platform desktop GUI tool for predicting and analyzing ORFs
StarORF
- A multi-platform, java-based, GUI tool for predicting and analyzing ORFs and obtaining reverse complement sequence
{{Webarchive, url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151222082631/http://bioinformatics.ysu.edu/tools/OrfPredictor.html , date=2015-12-22 - A webserver designed for ORF prediction and translation of a batch of EST or cDNA sequences Molecular genetics Bioinformatics he:מסגרת קריאה#מסגרת קריאה פתוחה