Oncotic Pressure on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
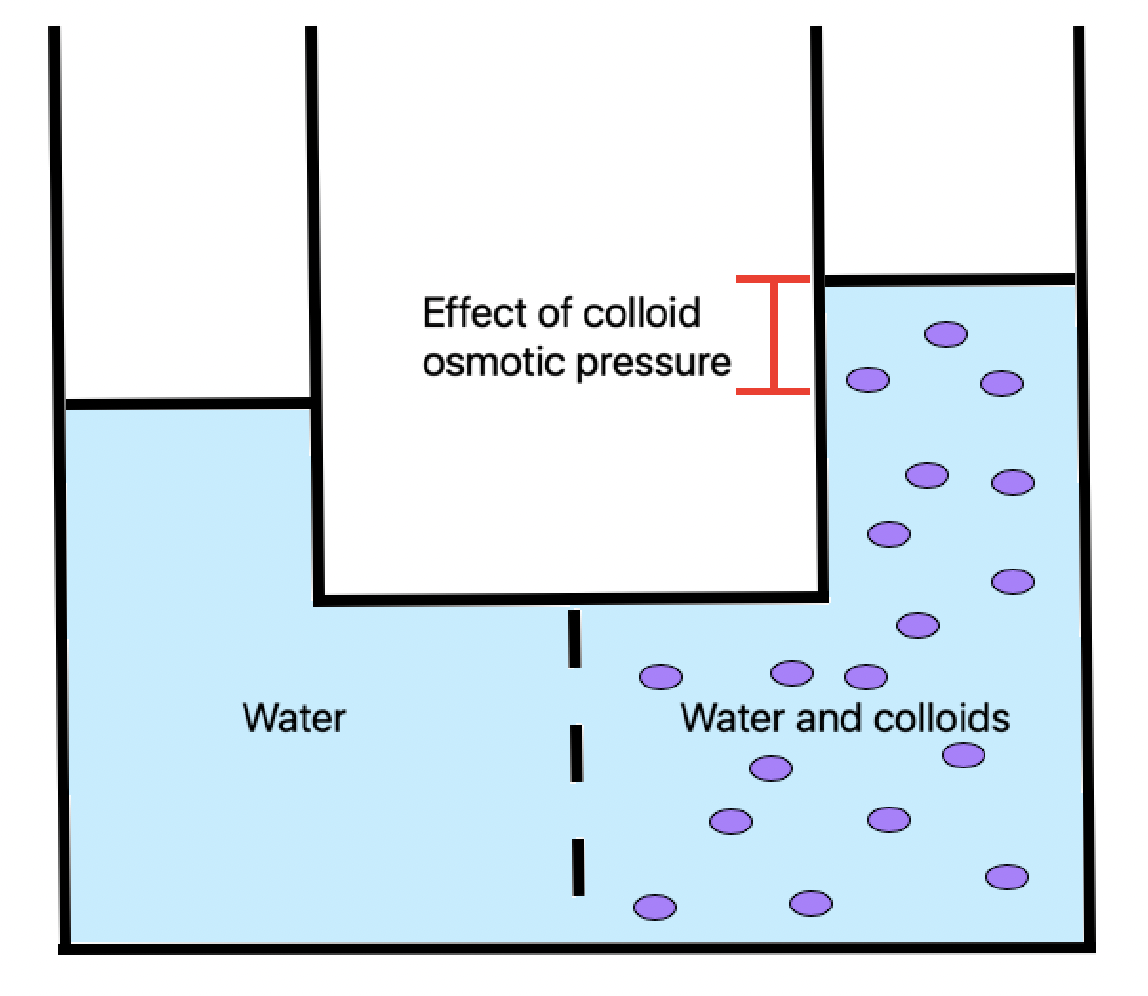 Oncotic pressure, or colloid osmotic-pressure, is a form of
Oncotic pressure, or colloid osmotic-pressure, is a form of
Overview at cvphysiology.com
Physiology
 Oncotic pressure, or colloid osmotic-pressure, is a form of
Oncotic pressure, or colloid osmotic-pressure, is a form of osmotic pressure
Osmotic pressure is the minimum pressure which needs to be applied to a solution to prevent the inward flow of its pure solvent across a semipermeable membrane.
It is also defined as the measure of the tendency of a solution to take in a pure ...
induced by the protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, res ...
s, notably albumin
Albumin is a family of globular proteins, the most common of which are the serum albumins. All the proteins of the albumin family are water- soluble, moderately soluble in concentrated salt solutions, and experience heat denaturation. Album ...
, in a blood vessel's plasma (blood/liquid) that causes a pull on fluid back into the capillary. Participating colloids displace water molecules, thus creating a relative water
Water (chemical formula ) is an inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living organisms (in which it acts as ...
molecule deficit with water molecules moving back into the circulatory system within the lower venous pressure end of capillaries.
It has the opposing effect of both hydrostatic blood pressure
Blood pressure (BP) is the pressure of circulating blood against the walls of blood vessels. Most of this pressure results from the heart pumping blood through the circulatory system. When used without qualification, the term "blood pressure ...
pushing water and small molecules out of the blood into the interstitial spaces within the arterial end of capillaries and interstitial
An interstitial space or interstice is a space between structures or objects.
In particular, interstitial may refer to:
Biology
* Interstitial cell tumor
* Interstitial cell, any cell that lies between other cells
* Interstitial collagenase ...
colloidal osmotic pressure. These interacting factors determine the partition balancing of extracellular water between the blood plasma and outside the blood stream.
Oncotic pressure strongly affects the physiological function of the circulatory system. It is suspected to have a major effect on the pressure across the glomerular filter. However, this concept has been strongly criticised and attention has been shifted to the impact of the intravascular glycocalyx layer as the major player.
Etymology
'Oncotic' by definition is termed as 'pertaining to swelling', indicating the effect of oncotic imbalance on the swelling of tissues. The word itself is derived from onco- and -ic; 'onco-' meaning 'pertaining to mass or tumors' and '-ic', which forms an adjective.Description
Throughout the body, dissolved compounds have an osmotic pressure. Because largeplasma proteins
Blood-proteins, also termed plasma proteins, are proteins present in blood plasma. They serve many different functions, including transport of lipids, hormones, vitamins and minerals in activity and functioning of the immune system. Other blood p ...
cannot easily cross through the capillary
A capillary is a small blood vessel from 5 to 10 micrometres (μm) in diameter. Capillaries are composed of only the tunica intima, consisting of a thin wall of simple squamous endothelial cells. They are the smallest blood vessels in the bod ...
walls, their effect on the osmotic pressure of the capillary interiors will, to some extent, balance out the tendency for fluid to leak out of the capillaries. In other words, the oncotic pressure tends to pull fluid into the capillaries. In conditions where plasma proteins are reduced, e.g. from being lost in the urine
Urine is a liquid by-product of metabolism in humans and in many other animals. Urine flows from the kidneys through the ureters to the urinary bladder. Urination results in urine being excreted from the body through the urethra.
Cellul ...
(proteinuria
Proteinuria is the presence of excess proteins in the urine. In healthy persons, urine contains very little protein; an excess is suggestive of illness. Excess protein in the urine often causes the urine to become foamy (although this symptom ma ...
), there will be a reduction in oncotic pressure and an increase in filtration across the capillary, resulting in excess fluid buildup in the tissues (edema
Edema, also spelled oedema, and also known as fluid retention, dropsy, hydropsy and swelling, is the build-up of fluid in the body's tissue. Most commonly, the legs or arms are affected. Symptoms may include skin which feels tight, the area ma ...
).
The large majority of oncotic pressure in capillaries is generated by the presence of high quantities of albumin
Albumin is a family of globular proteins, the most common of which are the serum albumins. All the proteins of the albumin family are water- soluble, moderately soluble in concentrated salt solutions, and experience heat denaturation. Album ...
, a protein that constitutes approximately 80% of the total oncotic pressure exerted by blood plasma on interstitial fluid . The total oncotic pressure of an average capillary is about 28 mmHg with albumin contributing approximately 22 mmHg of this oncotic pressure, despite only representing 50% of all protein in blood plasma at 35-50 g/L. Because blood proteins cannot escape through capillary endothelium, oncotic pressure of capillary beds tends to draw water into the vessels. It is necessary to understand the oncotic pressure as a balance; because the blood proteins reduce interior permeability, less plasma fluid can exit the vessel.
Oncotic pressure is represented by the symbol Π or π in the Starling equation and elsewhere. The Starling equation in particular describes filtration in volume/s (Jv) by relating oncotic pressure (πp) to capillary hydrostatic pressure (Pc), interstitial fluid hydrostatic pressure (Pi), and interstitial fluid oncotic pressure (πi), as well as several descriptive coefficients, as shown below:
At the arteriolar end of the capillary, blood pressure starts at about 36 mm Hg and decreases to around 15 mm Hg at the venous end, with oncotic pressure at a stable 25–28 mm Hg. Within the capillary, reabsorption due to this venous pressure difference is estimated to be around 90% that of the filtered fluid, with the extra 10% being returned via lymphatics in order to maintain stable blood volume.
Physiological impact
In tissues, physiological disruption can arise with decreased oncotic pressure, which can be determined using blood tests for protein concentration. Decreased colloidal osmotic pressure, most notably seen in hypoalbuminemia, can cause edema and decrease in blood volume as fluid is not reabsorbed into the bloodstream. Colloid pressure in these cases can be lost due to a number of different factors, but primarily decreased colloid production or increased loss of colloids through glomerular filtration. This low pressure often correlates with poor surgical outcomes. In the clinical setting, there are two types of fluids that are used for intravenous drips: crystalloids andcolloid
A colloid is a mixture in which one substance consisting of microscopically dispersed insoluble particles is suspended throughout another substance. Some definitions specify that the particles must be dispersed in a liquid, while others extend ...
s. Crystalloids are aqueous solution
An aqueous solution is a solution in which the solvent is water. It is mostly shown in chemical equations by appending (aq) to the relevant chemical formula. For example, a solution of table salt, or sodium chloride (NaCl), in water would be r ...
s of mineral salts or other water-soluble molecules. Colloids contain larger insoluble molecules, such as gelatin
Gelatin or gelatine (from la, gelatus meaning "stiff" or "frozen") is a translucent, colorless, flavorless food ingredient, commonly derived from collagen taken from animal body parts. It is brittle when dry and rubbery when moist. It may also ...
. There is some debate concerning the advantages and disadvantages of using biological vs. synthetic colloid solutions. Oncotic pressure values are approximately 290 mOsm per kg of water, which slightly differs from the osmotic pressure of the blood that has values approximating 300 mOsm /L. These colloidal solutions are typically used to remedy low colloid concentration, such as in hypoalbuminemia, but is also suspected to assist in injuries that typically increase fluid loss, such as burns.
References
{{reflistExternal links
Overview at cvphysiology.com
Physiology