northern gannet on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The northern gannet (''Morus bassanus'') is a
Northern gannet (Morus bassanus) juvenile Sagres.jpg, juvenile
Northern gannet (Morus bassanus) juvenile in flight Sagres.jpg, juvenile
Northern Gannet juvenile RWD.jpg, immature
Morus bassanus juv.jpg, sub adult
Northern gannet (Morus bassanus) in flight Sagres.jpg, adult
Northern gannets are slightly larger and thicker-billed than Cape or Australian gannets. The northern gannet has more white in the wings and an all-white tail, the other species having black tips to their tail feathers. Individuals on the west coast of Africa could be confused with vagrant masked boobies, though the latter is smaller overall, lacks the buff tinge to the head, and has a black tail. From a distance, or in poor visibility, albatrosses can be confused with northern gannets, particularly those with immature plumage that have more black on the wings.
 The northern gannet's breeding range is on both sides of the
The northern gannet's breeding range is on both sides of the
 Some northern gannet breeding colonies have been recorded as being located in the same place for hundreds of years. The cliffs containing the colonies appear white when seen from a distance, due to the number of nesting birds present on them. There is a written record of a colony on the island of
Some northern gannet breeding colonies have been recorded as being located in the same place for hundreds of years. The cliffs containing the colonies appear white when seen from a distance, due to the number of nesting birds present on them. There is a written record of a colony on the island of  :*
:*
 The wings of the northern gannet are long and narrow and are positioned towards the front of the body, allowing efficient use of air currents when flying. Even in calm weather they can attain velocities of between although their flying muscles are relatively small: in other birds flying muscles make up around 20% of total weight, while in northern gannets the flying muscles are less than 13%. Despite their speed, they cannot manoeuvre in flight as well as other seabirds. Northern gannets need to warm up before flying. They also walk with difficulty and this means that they have problems getting airborne from a flat area. They take off from water by facing into the wind and strongly beating their wings. In light winds and high waves they are sometimes unable to take off and they can become beached.
Northern gannets alight on land using angled wings, fanned tail and raised feet to control their speed, not always successfully, since damaged or broken wings were recorded as a frequent cause of death in adults at one colony.
The wings of the northern gannet are long and narrow and are positioned towards the front of the body, allowing efficient use of air currents when flying. Even in calm weather they can attain velocities of between although their flying muscles are relatively small: in other birds flying muscles make up around 20% of total weight, while in northern gannets the flying muscles are less than 13%. Despite their speed, they cannot manoeuvre in flight as well as other seabirds. Northern gannets need to warm up before flying. They also walk with difficulty and this means that they have problems getting airborne from a flat area. They take off from water by facing into the wind and strongly beating their wings. In light winds and high waves they are sometimes unable to take off and they can become beached.
Northern gannets alight on land using angled wings, fanned tail and raised feet to control their speed, not always successfully, since damaged or broken wings were recorded as a frequent cause of death in adults at one colony.
 Gannets will follow
Gannets will follow
 The oldest birds are the first to return to the northern gannet's breeding colonies. Birds not of breeding age arrive a few weeks later. In general, birds first return to a colony (not uncommonly the one in which they were hatched) when they are two or three years old. Once an individual has successfully bred in a colony it will not normally change to another. Nesting starts in March or April.
Immature birds stay on the edges of the colony. They may even make a nest but they do not breed until they are 4 or 5 years old. Some birds of this age occupy empty nests that they will aggressively defend if they have sat on them for two or three days. If an apparently empty nest has an owner, the immature bird will leave without a struggle when the owner arrives to take possession.
The preferred nesting sites are on coastal hillsides or cliffs. If these are not available northern gannets will nest in groups on islands or flat surfaces. As they find it more difficult to take off from such locations they will often cross the area occupied by an adjacent nest causing an aggressive reaction from the sitting pair; this means that the stress levels are higher in this type of colony than in those on steeper surfaces. Notwithstanding this, nests are always built close together and otherwise ideal nesting sites will not be used if they are some distance from a colony. On average there are 2.3 nests per square metre (1.9 per square yard). Both sexes fiercely defend the area around their nest. Where space allows, the distance between nests is double the reach of an individual.
The oldest birds are the first to return to the northern gannet's breeding colonies. Birds not of breeding age arrive a few weeks later. In general, birds first return to a colony (not uncommonly the one in which they were hatched) when they are two or three years old. Once an individual has successfully bred in a colony it will not normally change to another. Nesting starts in March or April.
Immature birds stay on the edges of the colony. They may even make a nest but they do not breed until they are 4 or 5 years old. Some birds of this age occupy empty nests that they will aggressively defend if they have sat on them for two or three days. If an apparently empty nest has an owner, the immature bird will leave without a struggle when the owner arrives to take possession.
The preferred nesting sites are on coastal hillsides or cliffs. If these are not available northern gannets will nest in groups on islands or flat surfaces. As they find it more difficult to take off from such locations they will often cross the area occupied by an adjacent nest causing an aggressive reaction from the sitting pair; this means that the stress levels are higher in this type of colony than in those on steeper surfaces. Notwithstanding this, nests are always built close together and otherwise ideal nesting sites will not be used if they are some distance from a colony. On average there are 2.3 nests per square metre (1.9 per square yard). Both sexes fiercely defend the area around their nest. Where space allows, the distance between nests is double the reach of an individual.
 Nests are made from
Nests are made from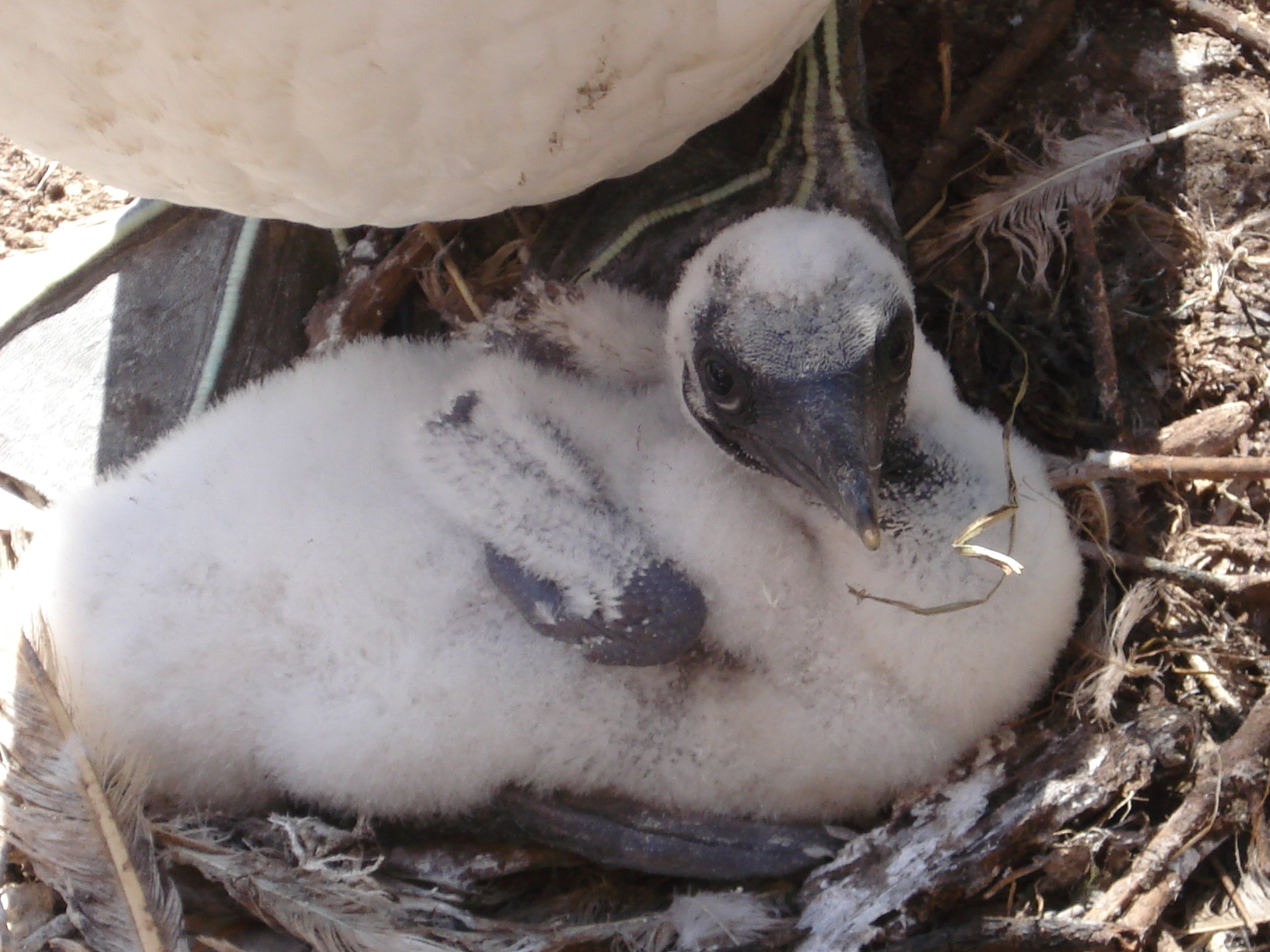  Newly hatched chicks are featherless and are dark blue or black in colour. In the second week of life they are covered in white down, replaced over the next five weeks by dark brown feathers flecked with white. Young chicks are fed regurgitated semi-digested fish by their parents, who open their mouths wide for their young to fetch the food from the back of their throats. Older chicks receive whole fish. Unlike the chicks of other species, northern gannet chicks do not move about the nest or flap their wings to ask for food: this reduces the likelihood that they will fall from the nest.
The adults feed their offspring for around 13 weeks, right up until the time they leave. The young birds
Newly hatched chicks are featherless and are dark blue or black in colour. In the second week of life they are covered in white down, replaced over the next five weeks by dark brown feathers flecked with white. Young chicks are fed regurgitated semi-digested fish by their parents, who open their mouths wide for their young to fetch the food from the back of their throats. Older chicks receive whole fish. Unlike the chicks of other species, northern gannet chicks do not move about the nest or flap their wings to ask for food: this reduces the likelihood that they will fall from the nest.
The adults feed their offspring for around 13 weeks, right up until the time they leave. The young birds
 Northern gannets exhibit many types of aggressive behaviour while they are nesting. Confrontations normally only take place between birds of the same sex. Females will lower their heads before an aggressive male that is defending its nest: this will expose the back of the female's neck and the male will take it in its beak and expel the female from the nest. A female will not react if a male approaches a nest but it will react fiercely if another female approaches. The fights between males occupying nests for the first time are particularly intense. Such fights can last for up to two hours and lead to serious injuries. Birds lunge at each other and lock bills, wrestling for extended periods while neighbours peck at them. The fights are preceded by threatening gestures, which are also seen outside the breeding season. Males demonstrate ownership of a nest by gesturing towards their neighbours in a ''bowing display''; their heads and beaks point down, and their wings are held up and away from the body, yet folded backwards. The male moves his head from side to side before bowing forwards.
Males try to attract an available female after establishing a territory. The females will fly over the colony several times before landing. Their posture, with the neck stretched out, tells the male that they are available for courtship. The male will then shake their heads in a similar way to when they are guarding their nest, but with their wings closed. Mated pairs engage in a ''fencing display'' when the male arrives back at the nest. The two birds stand breast to breast with wings spread and bills extended vertically. They
Northern gannets exhibit many types of aggressive behaviour while they are nesting. Confrontations normally only take place between birds of the same sex. Females will lower their heads before an aggressive male that is defending its nest: this will expose the back of the female's neck and the male will take it in its beak and expel the female from the nest. A female will not react if a male approaches a nest but it will react fiercely if another female approaches. The fights between males occupying nests for the first time are particularly intense. Such fights can last for up to two hours and lead to serious injuries. Birds lunge at each other and lock bills, wrestling for extended periods while neighbours peck at them. The fights are preceded by threatening gestures, which are also seen outside the breeding season. Males demonstrate ownership of a nest by gesturing towards their neighbours in a ''bowing display''; their heads and beaks point down, and their wings are held up and away from the body, yet folded backwards. The male moves his head from side to side before bowing forwards.
Males try to attract an available female after establishing a territory. The females will fly over the colony several times before landing. Their posture, with the neck stretched out, tells the male that they are available for courtship. The male will then shake their heads in a similar way to when they are guarding their nest, but with their wings closed. Mated pairs engage in a ''fencing display'' when the male arrives back at the nest. The two birds stand breast to breast with wings spread and bills extended vertically. They
 The northern gannet is not heavily predated. The only known habitual natural predators of adults are
The northern gannet is not heavily predated. The only known habitual natural predators of adults are
 A 2004 survey counted 45 gannet breeding colonies and some 361,000 nests. The population is apparently growing between 3% and 5% a year, although this growth is concentrated in just a few colonies. Although northern gannet populations are now stable, their numbers were once greatly reduced due to
A 2004 survey counted 45 gannet breeding colonies and some 361,000 nests. The population is apparently growing between 3% and 5% a year, although this growth is concentrated in just a few colonies. Although northern gannet populations are now stable, their numbers were once greatly reduced due to
 In Homer's ''
In Homer's '' Northern gannets have long been eaten for food. Birds, mainly the young, were taken from Bass Rock for at least 350 years until 1885, when the annual cull of about 1,500 individuals finally ceased, and Shetland gannets were sold as "Highland goose" in London restaurants during
Northern gannets have long been eaten for food. Birds, mainly the young, were taken from Bass Rock for at least 350 years until 1885, when the annual cull of about 1,500 individuals finally ceased, and Shetland gannets were sold as "Highland goose" in London restaurants during
seabird
Seabirds (also known as marine birds) are birds that are adapted to life within the marine environment. While seabirds vary greatly in lifestyle, behaviour and physiology, they often exhibit striking convergent evolution, as the same envir ...
, the largest species of the gannet
Gannets are seabirds comprising the genus ''Morus'' in the family Sulidae, closely related to boobies.
Gannets are large white birds with yellowish heads; black-tipped wings; and long bills. Northern gannets are the largest seabirds in the ...
family, Sulidae
The bird family Sulidae comprises the gannets and boobies. Collectively called sulids, they are medium-large coastal seabirds that plunge-dive for fish and similar prey. The 10 species in this family are often considered congeneric in older ...
. It is native to the coasts of the Atlantic Ocean, breeding in Western Europe and Northeastern North America. It is the largest seabird in the northern Atlantic. The sexes are similar in appearance. The adult northern gannet has a mainly white streamlined body with a long neck, and long and slender wings. It is long with a wingspan. The head and nape have a buff tinge that is more prominent in breeding season, and the wings are edged with dark brown-black feathers. The long, pointed bill is blue-grey, contrasting with black, bare skin around the mouth and eyes. Juveniles are mostly grey-brown, becoming increasingly white in the five years it takes them to reach maturity.
Nesting takes place in colonies
In modern parlance, a colony is a territory subject to a form of foreign rule. Though dominated by the foreign colonizers, colonies remain separate from the administration of the original country of the colonizers, the '' metropolitan state'' ...
on both sides of the North Atlantic
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe ...
, the largest of which are at Bass Rock
The Bass Rock, or simply the Bass (), ( gd, Creag nam Bathais or gd, Am Bas) is an island in the outer part of the Firth of Forth in the east of Scotland. Approximately offshore, and north-east of North Berwick, it is a steep-sided volca ...
(75,000 pairs as of 2014), St. Kilda (60,000 pairs as of 2013) and Ailsa Craig
Ailsa Craig (; sco, Ailsae Craig; gd, Creag Ealasaid) is an island of in the outer Firth of Clyde, west of mainland Scotland, upon which microgranite has long been quarried to make curling stones. The now-uninhabited island comprises the ...
(33,000 pairs as of 2014) in Scotland, Grassholm
Grassholm ( cy, Gwales or ) or Grassholm Island is a small uninhabited island situated off the southwestern Pembrokeshire coast in Wales, lying west of Skomer, in the community of Marloes and St Brides. It is the westernmost point in Wales ...
in Wales, and Bonaventure Island (60,000 pairs in 2009) off the coast of Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirte ...
. Its breeding range has extended northward and eastward, with colonies being established on Russia's Kola Peninsula
The Kola Peninsula (russian: Кольский полуостров, Kolsky poluostrov; sjd, Куэлнэгк нёа̄ррк) is a peninsula in the extreme northwest of Russia, and one of the largest peninsulas of Europe. Constituting the bulk ...
in 1995 and Bear Island (the southernmost island of Svalbard
Svalbard ( , ), also known as Spitsbergen, or Spitzbergen, is a Norwegian archipelago in the Arctic Ocean. North of mainland Europe, it is about midway between the northern coast of Norway and the North Pole. The islands of the group rang ...
), in 2011. Colonies are mostly located on offshore islands with cliff
In geography and geology, a cliff is an area of rock which has a general angle defined by the vertical, or nearly vertical. Cliffs are formed by the processes of weathering and erosion, with the effect of gravity. Cliffs are common on co ...
s, from which the birds can more easily launch into the air. The northern gannet undertakes seasonal migrations and catches fish (which are the mainstay of its diet) by making high-speed dives into the sea.
The northern gannet was previously hunted for food in certain parts of its range, and although that practice still continues in the Outer Hebrides
The Outer Hebrides () or Western Isles ( gd, Na h-Eileanan Siar or or ("islands of the strangers"); sco, Waster Isles), sometimes known as the Long Isle/Long Island ( gd, An t-Eilean Fada, links=no), is an island chain off the west coas ...
of Scotland and the Faroe Islands
The Faroe Islands ( ), or simply the Faroes ( fo, Føroyar ; da, Færøerne ), are a North Atlantic island group and an autonomous territory of the Kingdom of Denmark.
They are located north-northwest of Scotland, and about halfway bet ...
, the bird faces few other natural or man-made threats. Since its population is growing, the International Union for Conservation of Nature
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN; officially International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources) is an international organization working in the field of nature conservation and sustainable use of natu ...
considers it a least-concern species
A least-concern species is a species that has been categorized by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) as evaluated as not being a focus of species conservation because the specific species is still plentiful in the wild. T ...
. Because it is both a conspicuous and a common bird, it is referred to in several ancient myths and legends.
Taxonomy
The Swiss naturalistConrad Gessner
Conrad Gessner (; la, Conradus Gesnerus 26 March 1516 – 13 December 1565) was a Swiss physician, naturalist, bibliographer, and philologist. Born into a poor family in Zürich, Switzerland, his father and teachers quickly realised his tale ...
gave the northern gannet the name ''Anser bassanus'' or ''scoticus'' in the 16th century, and noted that the Scots called it a ''solendguse''. The former name was also used by the English naturalist Francis Willughby
Francis Willughby (sometimes spelt Willoughby, la, Franciscus Willughbeius) FRS (22 November 1635 – 3 July 1672) was an English ornithologist and ichthyologist, and an early student of linguistics and games.
He was born and raised at ...
in the 17th century; the species was known to him from a colony in the Firth of Forth
The Firth of Forth () is the estuary, or firth, of several Scottish rivers including the River Forth. It meets the North Sea with Fife on the north coast and Lothian on the south.
Name
''Firth'' is a cognate of ''fjord'', a Norse word meani ...
and from a stray bird that was found near Coleshill, Warwickshire
Coleshill ( ) is a market town in the North Warwickshire district of Warwickshire, England, taking its name from the River Cole, on which it stands. It had a population of 6,481 in the 2011 Census and is situated east-northeast of Birmingham ...
. It was one of the many species originally described by the Swedish zoologist
Zoology ()The pronunciation of zoology as is usually regarded as nonstandard, though it is not uncommon. is the branch of biology that studies the animal kingdom, including the structure, embryology, evolution, classification, habits, and d ...
Carl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (; 23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after his ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné Blunt (2004), p. 171. (), was a Swedish botanist, zoologist, taxonomist, and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, ...
in the landmark 1758 10th edition
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number representing a single or the only entity. 1 is also a numerical digit and represents a single unit of counting or measurement. For example, a line segment of ''unit length'' is a line segment of length 1. ...
of his ''Systema Naturae
' (originally in Latin written ' with the ligature æ) is one of the major works of the Swedish botanist, zoologist and physician Carl Linnaeus (1707–1778) and introduced the Linnaean taxonomy. Although the system, now known as binomial ...
'', where it was given the binomial
Binomial may refer to:
In mathematics
*Binomial (polynomial), a polynomial with two terms
*Binomial coefficient, numbers appearing in the expansions of powers of binomials
*Binomial QMF, a perfect-reconstruction orthogonal wavelet decomposition
* ...
name ''Pelecanus bassanus''. The French biologist Brisson placed it in the genus '' Sula'' in 1760, and his compatriot Louis Vieillot moved the species to his new genus ''Morus Morus may refer to:
People
* Alexander Morus (1616–1670), Franco-Scottish Protestant preacher
* Henryk Moruś (1943–2013), Polish serial killer
* Huw Morus (1622–1709), Welsh poet
* Thomas More or Morus (1478–1535), English philosopher
* M ...
'' in 1816. ''Morus'' is derived from Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic pe ...
''moros'', meaning "foolish", and refers to the lack of fear shown by breeding gannets and boobies
A booby is a seabird in the genus ''Sula'', part of the family Sulidae. Boobies are closely related to the gannets (''Morus''), which were formerly included in ''Sula''.
Systematics and evolution
The genus ''Sula'' was introduced by the Fren ...
, which enables them to be easily killed. The specific name ''bassanus'' is from the Bass Rock
The Bass Rock, or simply the Bass (), ( gd, Creag nam Bathais or gd, Am Bas) is an island in the outer part of the Firth of Forth in the east of Scotland. Approximately offshore, and north-east of North Berwick, it is a steep-sided volca ...
in the Firth of Forth. The ornithologist
Ornithology is a branch of zoology that concerns the "methodological study and consequent knowledge of birds with all that relates to them." Several aspects of ornithology differ from related disciplines, due partly to the high visibility and th ...
Bryan Nelson in 1978 supported the species' inclusion in ''Sula'' as he felt the differences in anatomy, behaviour, ecology
Ecology () is the study of the relationships between living organisms, including humans, and their physical environment. Ecology considers organisms at the individual, population, community, ecosystem, and biosphere level. Ecology overl ...
and morphology between gannets and boobies were not sufficient to warrant separate genera.
Charles Lucian Bonaparte described the American populations as ''Sula americana'' in 1838, though the basis for distinguishing them from the European species was unclear and the name is now considered to be a synonym.
"Northern gannet" has been designated as the official common name for the species by the International Ornithologists' Union
The International Ornithologists' Union, formerly known as the International Ornithological Committee, is a group of about 200 international ornithologists, and is responsible for the International Ornithological Congress and other international ...
(IOC). It is also known as the North Atlantic gannet. ''Gannet'' is derived from Old English
Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlers in the mid-5th ...
''ganot'', meaning "strong or masculine", which is ultimately from the same Old Germanic
Proto-Germanic (abbreviated PGmc; also called Common Germanic) is the reconstructed proto-language of the Germanic branch of the Indo-European languages.
Proto-Germanic eventually developed from pre-Proto-Germanic into three Germanic branc ...
root as ''gander''. ''Soland goose'' and similar old names for the northern gannet such as ''solan'' or ''solan goose'' derive from a hypothetical Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic ( gd, Gàidhlig ), also known as Scots Gaelic and Gaelic, is a Goidelic language (in the Celtic branch of the Indo-European language family) native to the Gaels of Scotland. As a Goidelic language, Scottish Gaelic, as well as ...
''sulan'', itself borrowed from the Old Norse
Old Norse, Old Nordic, or Old Scandinavian, is a stage of development of North Germanic dialects before their final divergence into separate Nordic languages. Old Norse was spoken by inhabitants of Scandinavia and their overseas settlement ...
''sula''. The literal meaning is "cleft stick", referring to the appearance of the conspicuous crossed black wing tips on a perched northern gannet. Old regional names such as Norfolk's "herring gant" or Yorkshire's "mackerel gant" refer to typical fish prey. Lincolnshire's ''gaunt'', although derived from the same Germanic root, usually applies to the great crested grebe
The great crested grebe (''Podiceps cristatus'') is a member of the grebe family of water birds noted for its elaborate mating display.
Taxonomy
The great crested grebe was formally described by the Swedish naturalist Carl Linnaeus in 1758 in t ...
, but the English writer Richard Hakluyt
Richard Hakluyt (; 1553 – 23 November 1616) was an English writer. He is known for promoting the English colonization of North America through his works, notably ''Divers Voyages Touching the Discoverie of America'' (1582) and ''The Pri ...
used the term in 1600 to refer to the gannet, "a great White foule". Young birds have been called "spotted booby" or "parliament goose", the former term referring to their plumage. The feeding habits of the gannet have led to its name being used as slang for a gluttonous person, a usage first recorded in 1929.
The Sulidae
The bird family Sulidae comprises the gannets and boobies. Collectively called sulids, they are medium-large coastal seabirds that plunge-dive for fish and similar prey. The 10 species in this family are often considered congeneric in older ...
, the gannet
Gannets are seabirds comprising the genus ''Morus'' in the family Sulidae, closely related to boobies.
Gannets are large white birds with yellowish heads; black-tipped wings; and long bills. Northern gannets are the largest seabirds in the ...
s and boobies, appeared about 30 million years ago. Early Sulidae fossils resembled the boobies, although they were more aquatic, the gannets splitting off later, about 16 million years ago. The gannets evolved in the northern hemisphere, later colonising the southern oceans. The most ancient extant species may be the Abbott's booby
Abbott's booby (''Papasula abbotti'') is an endangered seabird of the sulid family, which includes gannets and boobies. It is a large booby and is placed within its own monotypic genus. It was first identified from a specimen collected by Will ...
, possibly the sole survivor of an otherwise extinct separate lineage. A 2011 genetic study of nuclear
Nuclear may refer to:
Physics
Relating to the nucleus of the atom:
*Nuclear engineering
*Nuclear physics
*Nuclear power
*Nuclear reactor
*Nuclear weapon
*Nuclear medicine
*Radiation therapy
*Nuclear warfare
Mathematics
*Nuclear space
*Nuclear ...
and mitochondrial DNA
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA or mDNA) is the DNA located in mitochondria, cellular organelles within eukaryotic cells that convert chemical energy from food into a form that cells can use, such as adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Mitochondrial D ...
suggests that the ancestor of the gannets arose around 2.5 million years ago before splitting into northern and southern lineages. The latter then split into the Cape
A cape is a clothing accessory or a sleeveless outer garment which drapes the wearer's back, arms, and chest, and connects at the neck.
History
Capes were common in medieval Europe, especially when combined with a hood in the chaperon. Th ...
and Australasian gannet
The Australasian gannet (''Morus serrator''), also known as the Australian gannet or tākapu, is a large seabird of the booby and gannet family, Sulidae. Adults are mostly white, with black flight feathers at the wingtips and lining the trailin ...
s around 0.5 million years ago. The three gannets are generally considered to be separate species forming a superspecies, though they have also formerly been classified as subspecies
In biological classification, subspecies is a rank below species, used for populations that live in different areas and vary in size, shape, or other physical characteristics ( morphology), but that can successfully interbreed. Not all specie ...
of ''Sula bassanus''.
Description
An adult northern gannet has a wingspan, and is long and weighs , making it the largest gannet and the largest seabird native to the westernPalearctic
The Palearctic or Palaearctic is the largest of the eight biogeographic realms of the Earth. It stretches across all of Eurasia north of the foothills of the Himalayas, and North Africa.
The realm consists of several bioregions: the Euro-Sib ...
. The two sexes are generally of a similar size and appearance. The plumage
Plumage ( "feather") is a layer of feathers that covers a bird and the pattern, colour, and arrangement of those feathers. The pattern and colours of plumage differ between species and subspecies and may vary with age classes. Within species, ...
is white with dark brown to black wing tips; the primary
Primary or primaries may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Music Groups and labels
* Primary (band), from Australia
* Primary (musician), hip hop musician and record producer from South Korea
* Primary Music, Israeli record label
Works
...
flight feathers, primary coverts
A covert feather or tectrix on a bird is one of a set of feathers, called coverts (or ''tectrices''), which, as the name implies, cover other feathers. The coverts help to smooth airflow over the wings and tail. Ear coverts
The ear coverts are ...
and alula
The alula , or bastard wing, (plural ''alulae'') is a small projection on the anterior edge of the wing of modern birds and a few non-avian dinosaurs. The word is Latin and means "winglet"; it is the diminutive of ''ala'', meaning "wing". The al ...
e are dark. The head and neck are tinged buff-yellow, becoming much more prominent in the breeding season. Males are more deeply coloured than females. The eyes are surrounded by black bare skin and have a cobalt blue orbital ring, the iris is light blue-grey with a fine dark outer ring. The beak
The beak, bill, or rostrum is an external anatomical structure found mostly in birds, but also in turtles, non-avian dinosaurs and a few mammals. A beak is used for eating, preening, manipulating objects, killing prey, fighting, probing for fo ...
is long, strong and conical with a slight downcurve at the end and a sharp cutting edge. In adults, the beak is blue-grey with dark grey or black edges. There is a black groove running the length of the mandible that merges into the skin around the eyes. A black band of bare skin also separates the pale feathers of the forehead and throat from the bill, which gives the gannet its distinctive face markings. The four-toed feet are joined by a membrane that can vary in colour from dark grey to dark brown. There are coloured lines running along the toes that continue along up the legs. These are typically greenish-yellow in males and bluish in females and probably have a role in mating
In biology, mating is the pairing of either opposite- sex or hermaphroditic organisms for the purposes of sexual reproduction. ''Fertilization'' is the fusion of two gametes. ''Copulation'' is the union of the sex organs of two sexually reprod ...
.
Fledglings are dark grey to slate-grey with upperparts and wings finely speckled with white. There is a prominent V-shaped white area under the rump. The wing tips and tail are dark brown-black, partly tipped with white. The bill and iris are dark brown. They can weigh more than by the time they leave the nest at about 10 weeks of age. In the second year, the bird's appearance changes depending on the different phases of moulting: they can have adult plumage at the front and continue to be brown at the rear. Gannets gradually acquire more white in subsequent seasons until they reach maturity after five years.
Adaptations for diving
Northern gannets have streamlined bodies adapted for plunge-diving at high speed, including powerful neck muscles, and a spongy bone plate at the base of the bill. The nostrils are inside the bill and can be closed to prevent water entry; the eyes are protected by strongnictitating membrane
The nictitating membrane (from Latin '' nictare'', to blink) is a transparent or translucent third eyelid present in some animals that can be drawn across the eye from the medial canthus to protect and moisten it while maintaining vision. All ...
s. There are subcutaneous air sacs in the lower body and along the sides. Other air sacs are located between the sternum and the pectoral muscles and between the rib
In vertebrate anatomy, ribs ( la, costae) are the long curved bones which form the rib cage, part of the axial skeleton. In most tetrapods, ribs surround the chest, enabling the lungs to expand and thus facilitate breathing by expanding the ches ...
s and the intercostal muscles. These sacs are connected to the lungs and are filled with air when the bird breathes in. The air can be returned to the lungs by muscle contractions.
The feather
Feathers are epidermal growths that form a distinctive outer covering, or plumage, on both avian (bird) and some non-avian dinosaurs and other archosaurs. They are the most complex integumentary structures found in vertebrates and a premie ...
s are waterproof, which allows the birds to spend long periods in water. A water-impermeable secretion produced by a sebaceous gland
A sebaceous gland is a microscopic exocrine gland in the skin that opens into a hair follicle to secrete an oily or waxy matter, called sebum, which lubricates the hair and skin of mammals. In humans, sebaceous glands occur in the greatest n ...
covers the feathers and the birds spread it across their body using their beak or head. Individuals have a subcutaneous fat layer, dense down feather
The down of birds is a layer of fine feathers found under the tougher exterior feathers. Very young birds are clad only in down. Powder down is a specialized type of down found only in a few groups of birds. Down is a fine thermal insulator an ...
s and tightly overlapping feathers that help them withstand low temperatures. A reduced blood flow in the webbing on their feet outside of the breeding season also helps to maintain body temperature when the birds swim.
Call
The northern gannet is a loud and vocal bird, particularly in the colony. Its typical call is a harsh ''arrah-arrah'' or ''urrah-urrah'', which is emitted upon arriving or when challenging other gannets at the colony. The call is shortened to a ''rah'' ''rah'' when fishing or collecting nesting material, and lengthened to a ''ooo-ah'' when taking off. The calls of the sexes are similar. According to Nelson northern gannets can recognize the call of their breeding partner, their chicks and birds in neighbouring nests. Individuals from outside this sphere are treated with more aggression.Distribution and habitat
 The northern gannet's breeding range is on both sides of the
The northern gannet's breeding range is on both sides of the North Atlantic
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe a ...
on coasts influenced by the Gulf Stream
The Gulf Stream, together with its northern extension the North Atlantic Drift, is a warm and swift Atlantic ocean current that originates in the Gulf of Mexico and flows through the Straits of Florida and up the eastern coastline of the Unit ...
, There are colonies in the Gulf of Saint Lawrence
, image = Baie de la Tour.jpg
, alt =
, caption = Gulf of St. Lawrence from Anticosti National Park, Quebec
, image_bathymetry = Golfe Saint-Laurent Depths fr.svg
, alt_bathymetry = Bathymetry ...
and on the islands off the east coast of Canada. They normally nest
A nest is a structure built for certain animals to hold eggs or young. Although nests are most closely associated with birds, members of all classes of vertebrates and some invertebrates construct nests. They may be composed of organic materi ...
in large colonies
In modern parlance, a colony is a territory subject to a form of foreign rule. Though dominated by the foreign colonizers, colonies remain separate from the administration of the original country of the colonizers, the '' metropolitan state'' ...
, on cliffs overlooking the ocean or on small rocky islands. The water needs to be cool enough for Atlantic mackerel
The Atlantic mackerel (''Scomber scombrus''), also known as Boston mackerel, Norwegian mackerel, Scottish mackerel or just mackerel, is a species of mackerel found in the temperate waters of the Mediterranean Sea, the Black Sea, and the northern ...
and herring
Herring are forage fish, mostly belonging to the family of Clupeidae.
Herring often move in large schools around fishing banks and near the coast, found particularly in shallow, temperate waters of the North Pacific and North Atlantic Ocean ...
, which are the main food source for the northern gannet. These areas also overlie the continental shelf
A continental shelf is a portion of a continent that is submerged under an area of relatively shallow water, known as a shelf sea. Much of these shelves were exposed by drops in sea level during glacial periods. The shelf surrounding an island ...
. Northern gannet colonies can be found in the far north in regions that are very cold and stormy, and Nelson has suggested that they can survive in these regions for several reasons, including the combination of body weight and a powerful beak that allows them to capture strong muscular fish, and the ability to dive to great depths and capture prey far from the cliffs. Their fat reserves act as weight when diving and as reserves during extended periods without food.
The northern limit of their breeding area depends on the presence of waters that are free of sea ice during the breeding season. Therefore, while Greenland
Greenland ( kl, Kalaallit Nunaat, ; da, Grønland, ) is an island country in North America that is part of the Kingdom of Denmark. It is located between the Arctic and Atlantic oceans, east of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. Greenland ...
and Svalbard offer suitable breeding sites, the Arctic regions have summers that are too short to allow the northern gannets to lay their eggs and raise a brood, which requires between 26 and 30 weeks. The southern limit of their distribution mainly depends on the presence of sufficient prey. There is fossil evidence of northern gannets breeding on Crete in the Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological Epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was fina ...
.
Breeding colonies
 Some northern gannet breeding colonies have been recorded as being located in the same place for hundreds of years. The cliffs containing the colonies appear white when seen from a distance, due to the number of nesting birds present on them. There is a written record of a colony on the island of
Some northern gannet breeding colonies have been recorded as being located in the same place for hundreds of years. The cliffs containing the colonies appear white when seen from a distance, due to the number of nesting birds present on them. There is a written record of a colony on the island of Lundy
Lundy is an English island in the Bristol Channel. It was a micronation from 1925–1969. It forms part of the district of Torridge in the county of Devon.
About long and wide, Lundy has had a long and turbulent history, frequently chang ...
from 1274. There were only 70 nests by 1871, and the colony finally disappeared by 1909 at the latest. More than two-thirds of the world population breeds around the coasts of the British Isles
The British Isles are a group of islands in the North Atlantic Ocean off the north-western coast of continental Europe, consisting of the islands of Great Britain, Ireland, the Isle of Man, the Inner and Outer Hebrides, the Northern Isl ...
. Colonies include:
*Scotland
:* Bass Rock, off the Firth of Forth
The Firth of Forth () is the estuary, or firth, of several Scottish rivers including the River Forth. It meets the North Sea with Fife on the north coast and Lothian on the south.
Name
''Firth'' is a cognate of ''fjord'', a Norse word meani ...
, first recorded in 1493. In 2004, it contained more than 48,000 nests. By 2014 this had increased to over 75,000, making it the largest colony in the world.
:* Northern gannets began a colony at Troup Head in Aberdeenshire
Aberdeenshire ( sco, Aiberdeenshire; gd, Siorrachd Obar Dheathain) is one of the 32 council areas of Scotland.
It takes its name from the County of Aberdeen which has substantially different boundaries. The Aberdeenshire Council area inclu ...
in 1988, and by 2014 it held an estimated 6,456 pairs.
:* Saint Kilda and Sula Sgeir
Sula Sgeir is a small, uninhabited Scottish island in the North Atlantic, west of Rona. One of the most remote islands of the British Isles, it lies approximately north of Lewis and is best known for its population of gannets. It has a narr ...
, in the Hebrides
The Hebrides (; gd, Innse Gall, ; non, Suðreyjar, "southern isles") are an archipelago off the west coast of the Scottish mainland. The islands fall into two main groups, based on their proximity to the mainland: the Inner and Outer Hebri ...
, Scotland. The former colony was estimated at 60,290 pairs and the latter 11,230 pairs in 2013. A colony on the Flannan Isles
The Flannan Isles ( gd, Na h-Eileanan Flannach) or alternatively, the Seven Hunters are a small island group in the Outer Hebrides of Scotland, approximately west of the Isle of Lewis. They may take their name from Saint Flannan, the 7th centur ...
almost doubled in size to 5,280 pairs in 2013. Further south, the island of Ailsa Craig
Ailsa Craig (; sco, Ailsae Craig; gd, Creag Ealasaid) is an island of in the outer Firth of Clyde, west of mainland Scotland, upon which microgranite has long been quarried to make curling stones. The now-uninhabited island comprises the ...
in the Firth of Clyde
The Firth of Clyde is the mouth of the River Clyde. It is located on the west coast of Scotland and constitutes the deepest coastal waters in the British Isles (it is 164 metres deep at its deepest). The firth is sheltered from the Atlantic ...
hosted an estimated 33,226 pairs in 2014. Ailsa Craig has been known as a colony since 1583.
:* In Shetland
Shetland, also called the Shetland Islands and formerly Zetland, is a subarctic archipelago in Scotland lying between Orkney, the Faroe Islands and Norway. It is the northernmost region of the United Kingdom.
The islands lie about to the n ...
, there were an estimated 25,580 breeding pairs at Hermaness
Hermaness is the northernmost headland of Unst, the most northerly inhabited island of Shetland, Scotland. It consists of huge sea cliffs and moorland, making it an ideal habitat for a variety of birds. Hermaness was designated a national nature ...
, 11,786 on Noss, and 3,591 on Fair Isle
Fair Isle (; sco, Fair Isle; non, Friðarey; gd, Fara) is an island in Shetland, in northern Scotland. It lies about halfway between mainland Shetland and Orkney. It is known for its bird observatory and a traditional style of knitting. Th ...
in 2013, while Orkney
Orkney (; sco, Orkney; on, Orkneyjar; nrn, Orknøjar), also known as the Orkney Islands, is an archipelago in the Northern Isles of Scotland, situated off the north coast of the island of Great Britain. Orkney is 10 miles (16 km) north ...
had an estimated 4,550 pairs at Sule Stack. Sule Skerry's breeding population rose from 57 to 1,870 pairs between 2003 and 2013.
*Wales
:* Grassholm
Grassholm ( cy, Gwales or ) or Grassholm Island is a small uninhabited island situated off the southwestern Pembrokeshire coast in Wales, lying west of Skomer, in the community of Marloes and St Brides. It is the westernmost point in Wales ...
off the Pembrokeshire
Pembrokeshire ( ; cy, Sir Benfro ) is a county in the south-west of Wales. It is bordered by Carmarthenshire to the east, Ceredigion to the northeast, and the rest by sea. The county is home to Pembrokeshire Coast National Park. The Park oc ...
coast in Wales had an estimated 36,011 pairs in 2015. Gannets began nesting here between 1820 and 1860, though never in great numbers, only exceeding 300 pairs by 1913.
*England
:* Bempton Cliffs
Bempton Cliffs is a section of precipitous coast at Bempton in the East Riding of Yorkshire, England. It is run by the RSPB as a nature reserve and is known for its breeding seabirds, including northern gannet, Atlantic puffin, razorbill, comm ...
hosted an estimated 12,494 pairs in 2015, more than tripling in size in 12 years.
*Ireland
 :*
:*Little Skellig
Little Skellig (Irish: ''Sceilig Bheag'') is an unhabitable island in the Atlantic Ocean, 11 km south-west of Valentia Island in County Kerry, Ireland. It is small than Skellig Michael (54 acres)) its twin island. The two islands rose c ...
, a small island located about off the Iveragh Peninsula
The Iveragh Peninsula () is located in County Kerry in Ireland. It is the largest peninsula in southwestern Ireland. A mountain range, the MacGillycuddy's Reeks, lies in the centre of the peninsula. Carrauntoohil, its highest mountain, is als ...
of County Kerry
County Kerry ( gle, Contae Chiarraí) is a county in Ireland. It is located in the South-West Region and forms part of the province of Munster. It is named after the Ciarraige who lived in part of the present county. The population of the co ...
is the largest colony in Ireland, hosting around 30,000 breeding pairs. Known as a gannetry before 1700, human impact had reduced the population to 30 pairs by 1880 before rapidly increasing to around 10,000 pairs by 1906, the fastest recovery ever recorded at a gannet colony. There are small colonies on Ireland's southern coast, on Bull Rock
Dursey Island ( ga, Baoi Bhéarra or ') lies at the southwestern tip of the Beara Peninsula in the west of County Cork in Ireland. Dursey Island is 6.5 kilometres long and 1.5 kilometres wide. The island is separated from the mainland by a narro ...
, County Cork
County Cork ( ga, Contae Chorcaí) is the largest and the southernmost county of Ireland, named after the city of Cork, the state's second-largest city. It is in the province of Munster and the Southern Region. Its largest market towns a ...
, Clare Island
Clare Island ( or ''Oileán Chliara''), also historically Inishcleer, is a mountainous island guarding the entrance to Clew Bay in County Mayo, Ireland. Historically part of the kingdom of Umhaill, it is famous as the home of the 15th century pi ...
, County Mayo
County Mayo (; ga, Contae Mhaigh Eo, meaning "Plain of the yew trees") is a county in Ireland. In the West of Ireland, in the province of Connacht, it is named after the village of Mayo, now generally known as Mayo Abbey. Mayo County Counci ...
and Great Saltee Island, County Wexford
County Wexford ( ga, Contae Loch Garman) is a county in Ireland. It is in the province of Leinster and is part of the Southern Region. Named after the town of Wexford, it was based on the historic Gaelic territory of Hy Kinsella (''Uí C ...
.
:*Alderney. Around 7,500 pairs nest on two islets—Ortac
Ortac is a small uninhabited islet about west of the coast of Alderney near to the islet of Burhou. It measures roughly , and rises above the sea level.Les Etacs
Alderney (; french: Aurigny ; Auregnais: ) is the northernmost of the inhabited Channel Islands. It is part of the Bailiwick of Guernsey, a British Crown dependency. It is long and wide.
The island's area is , making it the third-largest ...
—off the coast of Alderney
Alderney (; french: Aurigny ; Auregnais: ) is the northernmost of the inhabited Channel Islands. It is part of the Bailiwick of Guernsey, a British Crown Dependencies, Crown dependency. It is long and wide.
The island's area is , making i ...
in the English Channel
The English Channel, "The Sleeve"; nrf, la Maunche, "The Sleeve" ( Cotentinais) or ( Jèrriais), ( Guernésiais), "The Channel"; br, Mor Breizh, "Sea of Brittany"; cy, Môr Udd, "Lord's Sea"; kw, Mor Bretannek, "British Sea"; nl, Het Ka ...
, the first birds only nesting there in the 1940s. These birds migrate further south to the Mediterranean and west coast of Africa than more northerly breeding colonies.
*France. The French island of Rouzic in the Jentilez
''For the city in Quebec, see Sept-Îles, Quebec''
Sept-Îles ( French for ''seven islands'') or Jentilez (in Breton) is a small archipelago off the north coast of Brittany, in the Perros-Guirec commune of Côtes-d'Armor. This group of island ...
archipelago off the coast of Brittany
Brittany (; french: link=no, Bretagne ; br, Breizh, or ; Gallo: ''Bertaèyn'' ) is a peninsula, historical country and cultural area in the west of modern France, covering the western part of what was known as Armorica during the period ...
hosts the southernmost breeding colony of northern gannets. Established in the late 1930s, it had grown to over 11,500 breeding pairs by 1995. Pairs have nested sporadically with varying success along the Mediterranean coast.
*Germany. Northern gannets have reappeared on Heligoland
Heligoland (; german: Helgoland, ; Heligolandic Frisian: , , Mooring Frisian: , da, Helgoland) is a small archipelago in the North Sea. A part of the German state of Schleswig-Holstein since 1890, the islands were historically possession ...
in 1991 and around 680 breeding pairs have been counted in 2016.
*Italy. A pair raised a chick successfully for three successive seasons from 2013 to 2015 on a moored boat at Porto Venere
Porto Venere (; until 1991 ''Portovenere''; lij, Pòrtivene) is a town and ''comune'' (municipality) located on the Ligurian coast of Italy in the province of La Spezia. It comprises the three villages of Fezzano, Le Grazie and Porto Venere, an ...
in northern Italy, after birds had been seen there since 1993.
*The Faroe Islands. Mykines in the Faroe Islands
The Faroe Islands ( ), or simply the Faroes ( fo, Føroyar ; da, Færøerne ), are a North Atlantic island group and an autonomous territory of the Kingdom of Denmark.
They are located north-northwest of Scotland, and about halfway bet ...
held about 2,000 breeding pairs in 2000, although that had risen to 2,500 pairs by 2014.
*Iceland. Eldey
Eldey () is a small island about off the coast of the Reykjanes Peninsula in southwest Iceland. Located west-southwest of Reykjavík, the island of Eldey covers an area of about , and rises to a height of . Its sheer cliffs are home to la ...
, a small island located about off the coast of the Reykjanesskagi Peninsula, Iceland, hosting around 16,300 breeding pairs in 1962, and a similar number in 2008. Iceland has several small colonies along its coast, and on Grimsey, around north.
*Norway. As of 2016, there are an estimated 6,900 breeding pairs in Norway. Northern gannets first bred in the south of the country in the mid 1940s at Runde
Runde is an island in the municipality of Herøy in Møre og Romsdal county, Norway. The island has a population of 113 people (as of 2015), and it is connected by the Runde Bridge to the island of Remøya to the south.
Runde is famous for it ...
in Møre og Romsdal
Møre og Romsdal (; en, Møre and Romsdal) is a county in the northernmost part of Western Norway. It borders the counties of Trøndelag, Innlandet, and Vestland. The county administration is located in the town of Molde, while Ålesund is t ...
. In 1967 a colony was established at Syltefjord, within the Arctic Circle
The Arctic Circle is one of the two polar circles, and the most northerly of the five major circles of latitude as shown on maps of Earth. Its southern equivalent is the Antarctic Circle.
The Arctic Circle marks the southernmost latitude at ...
at 70°N. Colonies were also established on low islets in Lofoten
Lofoten () is an archipelago and a traditional district in the county of Nordland, Norway. Lofoten has distinctive scenery with dramatic mountains and peaks, open sea and sheltered bays, beaches and untouched lands. There are two towns, Svolv� ...
and Vesterålen
Vesterålen is a district and archipelago in Nordland county, Norway. It is located just north of Lofoten and west of Harstad. It is the northernmost part of Nordland county. Sortland is the largest town, situated near the center of the arch ...
, but declined due to increasing numbers of white-tailed eagle
The white-tailed eagle (''Haliaeetus albicilla'') is a very large species of sea eagle widely distributed across temperate Eurasia. Like all eagles, it is a member of the family Accipitridae (or accipitrids) which includes other diurnal raptors ...
s. Once rare, these were protected in 1968 and their numbers have risen. It is unclear why the eagles have not impacted on gannet numbers further north. In 2011, gannets began breeding on Bear Island, southernmost island of Svalbard
Svalbard ( , ), also known as Spitsbergen, or Spitzbergen, is a Norwegian archipelago in the Arctic Ocean. North of mainland Europe, it is about midway between the northern coast of Norway and the North Pole. The islands of the group rang ...
, likely due to the warming of the Barents Sea
The Barents Sea ( , also ; no, Barentshavet, ; russian: Баренцево море, Barentsevo More) is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean, located off the northern coasts of Norway and Russia and divided between Norwegian and Russian terr ...
and influx of fish. The colony numbered 52 pairs in 2016.
*Russia. There are around 250 pairs in a colony at Kharlov on the Kola Peninsula
The Kola Peninsula (russian: Кольский полуостров, Kolsky poluostrov; sjd, Куэлнэгк нёа̄ррк) is a peninsula in the extreme northwest of Russia, and one of the largest peninsulas of Europe. Constituting the bulk ...
in Russia. Established in 1995, this is also thought to be due to the warming of the Barents Sea.
*North America. There are six breeding colonies along the coast of Canada. The Gulf of Saint Lawrence
, image = Baie de la Tour.jpg
, alt =
, caption = Gulf of St. Lawrence from Anticosti National Park, Quebec
, image_bathymetry = Golfe Saint-Laurent Depths fr.svg
, alt_bathymetry = Bathymetry ...
hosts three colonies— Bonaventure Island, Bird Rocks and Anticosti Island—and there are three off the eastern and southeastern coast of Newfoundland (Cape St. Mary's Ecological Reserve
Cape St. Mary's Ecological Reserve is an ecological reserve located near Cape St. Mary's on the Cape Shore, on the southwestern Avalon Peninsula of Newfoundland.
It is home to one of North America's largest seabird colonies. The government o ...
, Funk Island, Baccalieu Island Ecological Reserve. Bonaventure Island off the south coast of the Gaspé Peninsula
The Gaspé Peninsula, also known as Gaspesia (; ), is a peninsula along the south shore of the Saint Lawrence River that extends from the Matapedia Valley in Quebec, Canada, into the Gulf of Saint Lawrence. It is separated from New Brunswick ...
of Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirte ...
is the largest colony with 60,000 nests as of 2009.
Migration
After the breeding season, adult northern gannets disperse over a wide area although they travel no more than from the breeding colony. It is not known if all birds from one colony migrate to the same over-wintering area. Many adults migrate to the west of theMediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on ...
, passing over the Strait of Gibraltar
The Strait of Gibraltar ( ar, مضيق جبل طارق, Maḍīq Jabal Ṭāriq; es, Estrecho de Gibraltar, Archaic: Pillars of Hercules), also known as the Straits of Gibraltar, is a narrow strait that connects the Atlantic Ocean to the Medi ...
and flying over land as little as possible. Other birds follow Africa's Atlantic coastline to arrive in the Gulf of Guinea
The Gulf of Guinea is the northeasternmost part of the tropical Atlantic Ocean from Cape Lopez in Gabon, north and west to Cape Palmas in Liberia. The intersection of the Equator and Prime Meridian (zero degrees latitude and longitude) is i ...
. Immature northern gannets from colonies in Canada fly to the Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico ( es, Golfo de México) is an ocean basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, largely surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United ...
, much further south than the adults.
The immature gannets migrate southwards for great distances and have been recorded as far south as Ecuador. In their second year some birds return to the colony they were born in, where they arrive later than the mature birds. They then migrate south again at the end of the breeding season, but travel shorter distances in this second migration. Gannets from Alderney have been tracked since 2015 to gain better knowledge of their movements. One individual was found to have travelled from its colony in Alderney to Scandinavian waters, a round trip of around .
The species has been recorded as a vagrant in many central and eastern European countries as far south and west as the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Rom ...
, and also in Bermuda, Cuba, Cyprus, Egypt, Kazakhstan, Jan Mayen
Jan Mayen () is a Norwegian volcanic island in the Arctic Ocean with no permanent population. It is long (southwest-northeast) and in area, partly covered by glaciers (an area of around the Beerenberg volcano). It has two parts: larger ...
and Syria. In February 2016, one was recorded from Ceará
Ceará (, pronounced locally as or ) is one of the 26 states of Brazil, located in the northeastern part of the country, on the Atlantic coast. It is the eighth-largest Brazilian State by population and the 17th by area. It is also one of the ...
in northeastern Brazil—the first sighting in the Southern Hemisphere.
Behaviour
 The wings of the northern gannet are long and narrow and are positioned towards the front of the body, allowing efficient use of air currents when flying. Even in calm weather they can attain velocities of between although their flying muscles are relatively small: in other birds flying muscles make up around 20% of total weight, while in northern gannets the flying muscles are less than 13%. Despite their speed, they cannot manoeuvre in flight as well as other seabirds. Northern gannets need to warm up before flying. They also walk with difficulty and this means that they have problems getting airborne from a flat area. They take off from water by facing into the wind and strongly beating their wings. In light winds and high waves they are sometimes unable to take off and they can become beached.
Northern gannets alight on land using angled wings, fanned tail and raised feet to control their speed, not always successfully, since damaged or broken wings were recorded as a frequent cause of death in adults at one colony.
The wings of the northern gannet are long and narrow and are positioned towards the front of the body, allowing efficient use of air currents when flying. Even in calm weather they can attain velocities of between although their flying muscles are relatively small: in other birds flying muscles make up around 20% of total weight, while in northern gannets the flying muscles are less than 13%. Despite their speed, they cannot manoeuvre in flight as well as other seabirds. Northern gannets need to warm up before flying. They also walk with difficulty and this means that they have problems getting airborne from a flat area. They take off from water by facing into the wind and strongly beating their wings. In light winds and high waves they are sometimes unable to take off and they can become beached.
Northern gannets alight on land using angled wings, fanned tail and raised feet to control their speed, not always successfully, since damaged or broken wings were recorded as a frequent cause of death in adults at one colony.
Feeding
Northern gannets forage for food during the day, generally by diving at high speed into the sea. They search for food both near to their nesting sites but also further out to sea. Birds that are feeding young have been recorded searching for food up to from their nest. It has been found that 2% of birds nesting in the colony on Bass Rock search for fish atDogger Bank
Dogger Bank ( Dutch: ''Doggersbank'', German: ''Doggerbank'', Danish: ''Doggerbanke'') is a large sandbank in a shallow area of the North Sea about off the east coast of England.
During the last ice age the bank was part of a large landmass ...
, between away. It is likely that they fly further than this while foraging, possibly up to double the distance; normally they fly less than . Some studies have found that the duration and direction of flights made while foraging for food are similar for both sexes, although there are significant differences in the search behaviour of males and females. Female northern gannets are not only more selective than males in choosing a search area: they also make longer and deeper dives and spend more time floating on the surface than males.
fishing boats
A fishing vessel is a boat or ship used to catch fish in the sea, or on a lake or river. Many different kinds of vessels are used in commercial, artisanal and recreational fishing.
The total number of fishing vessels in the world in 2016 was e ...
or cetacea
Cetacea (; , ) is an infraorder of aquatic mammals that includes whales, dolphins, and porpoises. Key characteristics are their fully aquatic lifestyle, streamlined body shape, often large size and exclusively carnivorous diet. They propel th ...
ns to find discarded or injured fish.
They forage from heights of up to with no clear preference, and typically dive between . They dive with their bodies straight and rigid, wings tucked close to the body but angled back, extending beyond the tail, before piercing the water like an arrow. They control the direction of the dive using their wings and tail, and fold their wings against the body just before impact. Birds can hit the water at speeds of up to . This allows them to penetrate up to below the surface, and they will swim down to an average , sometimes deeper than . The bird's subcutaneous air sacs may have a role in controlling their buoyancy.
Gannets usually push their prey deeper into the water and capture it as they return to the surface. When a dive is successful, they swallow the fish underwater before surfacing, and never fly with the fish in their bill. Larger fish are swallowed headfirst, smaller fish are swallowed sideways or tail-first. The fish is stored in a branched bag in the throat and does not cause drag when in flight.
Their white colour helps other gannets to identify one of their kind and they can deduce the presence of a shoal
In oceanography, geomorphology, and geoscience, a shoal is a natural submerged ridge, bank, or bar that consists of, or is covered by, sand or other unconsolidated material and rises from the bed of a body of water to near the surface. It ...
of fish by this diving behaviour; this in turn facilitates group foraging, which makes capturing their prey easier. The colour also makes the gannet less visible to the fish underneath. Northern gannets also forage for fish while swimming with their head under water.
They eat mainly fish in length that shoal near the surface. Virtually any small fish (roughly 80–90% of their diet) or other small pelagic
The pelagic zone consists of the water column of the open ocean, and can be further divided into regions by depth (as illustrated on the right). The word ''pelagic'' is derived . The pelagic zone can be thought of as an imaginary cylinder or w ...
species (largely squid
True squid are molluscs with an elongated soft body, large eyes, eight arms, and two tentacles in the superorder Decapodiformes, though many other molluscs within the broader Neocoleoidea are also called squid despite not strictly fittin ...
) will be taken opportunistically. Sardine
"Sardine" and "pilchard" are common names for various species of small, oily forage fish in the herring family Clupeidae. The term "sardine" was first used in English during the early 15th century, a folk etymology says it comes from the It ...
s, anchovies
An anchovy is a small, common forage fish of the family Engraulidae. Most species are found in marine waters, but several will enter brackish water, and some in South America are restricted to fresh water.
More than 140 species are placed in 1 ...
, haddock, smelt
Smelt may refer to:
* Smelting, chemical process
* The common name of various fish:
** Smelt (fish), a family of small fish, Osmeridae
** Australian smelt in the family Retropinnidae and species ''Retropinna semoni''
** Big-scale sand smelt ''A ...
, Atlantic cod
The Atlantic cod (''Gadus morhua'') is a benthopelagic fish of the family Gadidae, widely consumed by humans. It is also commercially known as cod or codling.Newfoundland
Newfoundland and Labrador (; french: Terre-Neuve-et-Labrador; frequently abbreviated as NL) is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region ...
for the energy requirements of their growing chicks. Given the economic importance of the prey taken, whether they are in competition with human fishing industry in the area is an important question which remains unassessed. (But given the small amount taken, NL's cod take is probably unaffected.)
On the other hand, they profit off of discarded bycatch and processed parts p.728 and the reduction in competition if humans are taking predatory fish. . p.61
''M. bassanus'' inflicts significant wasteage on the northwest Atlantic ''Salmo salar'' fishery, but does not actually eat much of them. This makes it difficult to resolve this conflict with the fishing industry in the area, as the only option would be to exterminate the birds, which is ecologically unacceptable.p.542, "A recent..."
Breeding
 The oldest birds are the first to return to the northern gannet's breeding colonies. Birds not of breeding age arrive a few weeks later. In general, birds first return to a colony (not uncommonly the one in which they were hatched) when they are two or three years old. Once an individual has successfully bred in a colony it will not normally change to another. Nesting starts in March or April.
Immature birds stay on the edges of the colony. They may even make a nest but they do not breed until they are 4 or 5 years old. Some birds of this age occupy empty nests that they will aggressively defend if they have sat on them for two or three days. If an apparently empty nest has an owner, the immature bird will leave without a struggle when the owner arrives to take possession.
The preferred nesting sites are on coastal hillsides or cliffs. If these are not available northern gannets will nest in groups on islands or flat surfaces. As they find it more difficult to take off from such locations they will often cross the area occupied by an adjacent nest causing an aggressive reaction from the sitting pair; this means that the stress levels are higher in this type of colony than in those on steeper surfaces. Notwithstanding this, nests are always built close together and otherwise ideal nesting sites will not be used if they are some distance from a colony. On average there are 2.3 nests per square metre (1.9 per square yard). Both sexes fiercely defend the area around their nest. Where space allows, the distance between nests is double the reach of an individual.
The oldest birds are the first to return to the northern gannet's breeding colonies. Birds not of breeding age arrive a few weeks later. In general, birds first return to a colony (not uncommonly the one in which they were hatched) when they are two or three years old. Once an individual has successfully bred in a colony it will not normally change to another. Nesting starts in March or April.
Immature birds stay on the edges of the colony. They may even make a nest but they do not breed until they are 4 or 5 years old. Some birds of this age occupy empty nests that they will aggressively defend if they have sat on them for two or three days. If an apparently empty nest has an owner, the immature bird will leave without a struggle when the owner arrives to take possession.
The preferred nesting sites are on coastal hillsides or cliffs. If these are not available northern gannets will nest in groups on islands or flat surfaces. As they find it more difficult to take off from such locations they will often cross the area occupied by an adjacent nest causing an aggressive reaction from the sitting pair; this means that the stress levels are higher in this type of colony than in those on steeper surfaces. Notwithstanding this, nests are always built close together and otherwise ideal nesting sites will not be used if they are some distance from a colony. On average there are 2.3 nests per square metre (1.9 per square yard). Both sexes fiercely defend the area around their nest. Where space allows, the distance between nests is double the reach of an individual.
 Nests are made from
Nests are made from seaweed
Seaweed, or macroalgae, refers to thousands of species of macroscopic, multicellular, marine algae. The term includes some types of '' Rhodophyta'' (red), ''Phaeophyta'' (brown) and '' Chlorophyta'' (green) macroalgae. Seaweed species such as ...
, plants, earth and debris from the sea. The males usually collect the materials. Nests are compact cups typically in height. The area which a nest occupies grows throughout the breeding season as the breeding pairs throw their excrement outside the nest. Over years, nests can reach in height.
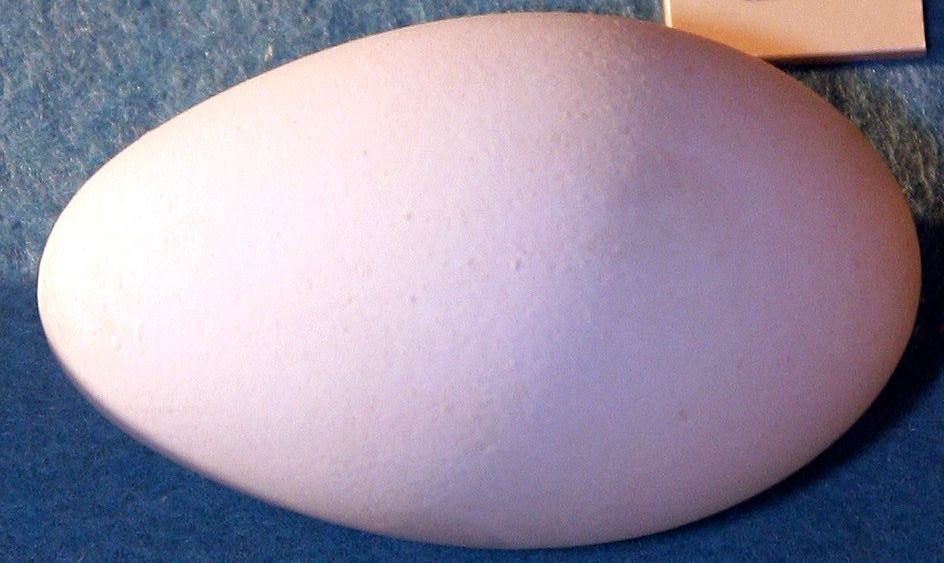
Northern gannets lay one egg that on average weighs , which is light for such a large seabird. The egg is around long by wide and the shell is pale blue and translucent initially before fading to a chalky white surface that is easily stained. ''M. bassanus'' was among those birds most affected by the shell-thinning effect of DDT, which contributed in large degree to its ban.p.502, "...''Sula bassanus''..." Where two eggs are found in a nest this is the result of two females laying an egg in the same nest or one egg being stolen from another nest. Northern gannets will lay a replacement egg if the first is lost. Incubation takes 42 to 46 days, during which time the egg is surrounded by the brooding bird's warm, webbed feet. Just before hatching begins, the brooding bird releases the egg from its feet to prevent the egg from breaking under the adult's weight as the chick breaks it open. This is a frequent cause of death for chicks of birds that are breeding for the first time. The process of breaking the eggshell can take up to 36 hours. The webbed feet are also used to cover the chicks, which are only rarely left alone by their parents. Chicks that are left unattended are often attacked and killed by other northern gannets.
fledge
Fledging is the stage in a flying animal's life between hatching or birth and becoming capable of flight.
This term is most frequently applied to birds, but is also used for bats. For altricial birds, those that spend more time in vulnera ...
between 84 and 97 days old, departing by launching themselves off a cliff and flying—a procedure for which it is impossible to practice beforehand. If they leave the nest in bad weather they can be mortally wounded as they can be blown against the rocks. The young birds are attacked by adults if unattended. Once they leave the nest they stay at sea learning to fish and fly, their flight skills being too poor for them to return to the breeding ledges.
Northern gannets have only one brood a year. The survival rate for young birds for their first four years is 30% and the annual survival rate for adults is 91.9%. The typical lifespan after becoming adult is 17 years, and the maximum known age is 37 years 4 months 16 days. Gannet pairs are monogamous and may remain together over several seasons, if not for all of their lives. The pairs separate when their chicks leave the nest but they bond again the following year. Should one of the pair die, the other bird will find another mate.
Displays
 Northern gannets exhibit many types of aggressive behaviour while they are nesting. Confrontations normally only take place between birds of the same sex. Females will lower their heads before an aggressive male that is defending its nest: this will expose the back of the female's neck and the male will take it in its beak and expel the female from the nest. A female will not react if a male approaches a nest but it will react fiercely if another female approaches. The fights between males occupying nests for the first time are particularly intense. Such fights can last for up to two hours and lead to serious injuries. Birds lunge at each other and lock bills, wrestling for extended periods while neighbours peck at them. The fights are preceded by threatening gestures, which are also seen outside the breeding season. Males demonstrate ownership of a nest by gesturing towards their neighbours in a ''bowing display''; their heads and beaks point down, and their wings are held up and away from the body, yet folded backwards. The male moves his head from side to side before bowing forwards.
Males try to attract an available female after establishing a territory. The females will fly over the colony several times before landing. Their posture, with the neck stretched out, tells the male that they are available for courtship. The male will then shake their heads in a similar way to when they are guarding their nest, but with their wings closed. Mated pairs engage in a ''fencing display'' when the male arrives back at the nest. The two birds stand breast to breast with wings spread and bills extended vertically. They
Northern gannets exhibit many types of aggressive behaviour while they are nesting. Confrontations normally only take place between birds of the same sex. Females will lower their heads before an aggressive male that is defending its nest: this will expose the back of the female's neck and the male will take it in its beak and expel the female from the nest. A female will not react if a male approaches a nest but it will react fiercely if another female approaches. The fights between males occupying nests for the first time are particularly intense. Such fights can last for up to two hours and lead to serious injuries. Birds lunge at each other and lock bills, wrestling for extended periods while neighbours peck at them. The fights are preceded by threatening gestures, which are also seen outside the breeding season. Males demonstrate ownership of a nest by gesturing towards their neighbours in a ''bowing display''; their heads and beaks point down, and their wings are held up and away from the body, yet folded backwards. The male moves his head from side to side before bowing forwards.
Males try to attract an available female after establishing a territory. The females will fly over the colony several times before landing. Their posture, with the neck stretched out, tells the male that they are available for courtship. The male will then shake their heads in a similar way to when they are guarding their nest, but with their wings closed. Mated pairs engage in a ''fencing display'' when the male arrives back at the nest. The two birds stand breast to breast with wings spread and bills extended vertically. They fence
A fence is a structure that encloses an area, typically outdoors, and is usually constructed from posts that are connected by boards, wire, rails or netting. A fence differs from a wall in not having a solid foundation along its whole length.
...
and scissor with their bills rapidly, calling loudly at the same time. Fencing is interspersed with bill bowing.
Predators and parasites
 The northern gannet is not heavily predated. The only known habitual natural predators of adults are
The northern gannet is not heavily predated. The only known habitual natural predators of adults are bald eagle
The bald eagle (''Haliaeetus leucocephalus'') is a bird of prey found in North America. A sea eagle, it has two known subspecies and forms a species pair with the white-tailed eagle (''Haliaeetus albicilla''), which occupies the same niche as ...
s and white-tailed eagle
The white-tailed eagle (''Haliaeetus albicilla'') is a very large species of sea eagle widely distributed across temperate Eurasia. Like all eagles, it is a member of the family Accipitridae (or accipitrids) which includes other diurnal raptors ...
s. Predators of eggs and nestlings include the great black-backed gull
The great black-backed gull (''Larus marinus'') is the largest member of the gull family. Described by the Cornell Lab of Ornithology as "the king of the Atlantic waterfront", it is a very aggressive hunter, pirate, and scavenger. It breeds on t ...
and American herring gull
The American herring gull or Smithsonian gull (''Larus smithsonianus'' or ''Larus argentatus smithsonianus'') is a large gull that breeds in North America, where it is treated by the American Ornithological Society as a subspecies of herring ...
, common raven
The common raven (''Corvus corax'') is a large all-black passerine bird. It is the most widely distributed of all corvids, found across the Northern Hemisphere. It is a raven known by many names at the subspecies level; there are at least ...
s, ermine, and red fox
The red fox (''Vulpes vulpes'') is the largest of the true foxes and one of the most widely distributed members of the Order (biology), order Carnivora, being present across the entire Northern Hemisphere including most of North America, Europe ...
. Attacks at sea are insignificant, though large shark
Sharks are a group of elasmobranch fish characterized by a cartilaginous skeleton, five to seven gill slits on the sides of the head, and pectoral fins that are not fused to the head. Modern sharks are classified within the clade Selachi ...
s and seal
Seal may refer to any of the following:
Common uses
* Pinniped, a diverse group of semi-aquatic marine mammals, many of which are commonly called seals, particularly:
** Earless seal, or "true seal"
** Fur seal
* Seal (emblem), a device to imp ...
s may rarely snatch a gannet out at sea.
Kleptoparasitism
Kleptoparasitism (etymologically, parasitism by theft) is a form of feeding in which one animal deliberately takes food from another. The strategy is evolutionarily stable when stealing is less costly than direct feeding, which can mean when ...
by skua
The skuas are a group of predatory seabirds with seven species forming the genus ''Stercorarius'', the only genus in the family Stercorariidae. The three smaller skuas, the long-tailed skua, the Arctic skua, and the pomarine skua are calle ...
s, particularly the great skua
The great skua (''Stercorarius skua''), sometimes known by the name bonxie in Britain, is a large seabird in the skua family Stercorariidae. It is roughly the size of a herring gull. It mainly eats fish caught at the sea surface or taken fr ...
, occurs at breeding sites. The skua chases its victim until it disgorges its stomach contents, providing a meal for the attacker. Skuas may catch the tip of the gannet's wing, causing it to fall into the sea, or seize the tail to tip its victim into the water. The gannet is only released when it has regurgitated its catch.
External parasites include feather lice
A bird louse is any chewing louse (small, biting insects) of order Phthiraptera which parasitizes warm-blooded animals, especially birds. Bird lice may feed on feathers, skin, or blood. They have no wings, and their biting mouth parts distingui ...
, although there are relatively few species and none are found on the head. As with grebe
Grebes () are aquatic diving birds in the order Podicipediformes . Grebes are widely distributed freshwater birds, with some species also found in marine habitats during migration and winter. Some flightless species exist as well, most notably ...
s and divers, it may be that the short head feathers provide insufficient cover for the parasite. In one species, '' Michaelichus bassani'', immature lice are found in the membranes lining the subcutaneous air-cells. ''Ixodes
''Ixodes'' is a genus of hard-bodied ticks (family Ixodidae). It includes important disease vectors of animals and humans ( tick-borne disease), and some species (notably '' Ixodes holocyclus'') inject toxins that can cause paralysis. Som ...
'' mite
Mites are small arachnids (eight-legged arthropods). Mites span two large orders of arachnids, the Acariformes and the Parasitiformes, which were historically grouped together in the subclass Acari, but genetic analysis does not show clear e ...
s include the widespread '' I. uriae''.
The spiny-headed worm '' Corynosoma tunitae'' appears to occur only in gannets and closely related seabird families such as the cormorants. The tapeworm
Eucestoda, commonly referred to as tapeworms, is the larger of the two subclasses of flatworms in the class Cestoda (the other subclass is Cestodaria). Larvae have six posterior hooks on the scolex (head), in contrast to the ten-hooked Cesto ...
'' Tetrabothrius bassani'' absorbs toxic heavy metal
A toxic heavy metal is any relatively dense metal or metalloid that is noted for its potential toxicity, especially in environmental contexts. The term has particular application to cadmium, mercury and lead, all of which appear in the World ...
s at a higher concentration than the gannet's own tissues, with an average 12 times as much cadmium
Cadmium is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Cd and atomic number 48. This soft, silvery-white metal is chemically similar to the two other stable metals in group 12 element, group 12, zinc and mercury (element), mercury. Li ...
as the gannet's pectoral muscle
Pectoral muscles (colloquially referred to as "pecs") are the muscles that connect the front of the human chest with the bones of the upper arm and shoulder. This region contains four muscles that provide movements to the upper limbs or ribs.
Pe ...
s and 7–10 times the lead
Lead is a chemical element with the symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metal that is denser than most common materials. Lead is soft and malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cut, ...
level of the bird's kidney and liver. Since levels of these toxic metals are detectable in the parasite earlier than in the host, the tapeworm might be used as an early indicator of marine pollution.
Conservation status
 A 2004 survey counted 45 gannet breeding colonies and some 361,000 nests. The population is apparently growing between 3% and 5% a year, although this growth is concentrated in just a few colonies. Although northern gannet populations are now stable, their numbers were once greatly reduced due to
A 2004 survey counted 45 gannet breeding colonies and some 361,000 nests. The population is apparently growing between 3% and 5% a year, although this growth is concentrated in just a few colonies. Although northern gannet populations are now stable, their numbers were once greatly reduced due to loss of habitat
Habitat destruction (also termed habitat loss and habitat reduction) is the process by which a natural habitat becomes incapable of supporting its native species. The organisms that previously inhabited the site are displaced or dead, thereby ...
, removal of eggs and killing of adults for their meat and feathers. In 1939, there were 22 colonies and some 83,000 nests, which means that the populations have increased fourfold since that time.
In 1992, the International Union for Conservation of Nature
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN; officially International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources) is an international organization working in the field of nature conservation and sustainable use of natu ...
(IUCN) estimated the bird's population to be some 526,000. After taking into account an estimate produced for BirdLife International
BirdLife International is a global partnership of non-governmental organizations that strives to conserve birds and their habitats. BirdLife International's priorities include preventing extinction of bird species, identifying and safeguarding ...
in 2004 of the European population, the IUCN revised its global population to between 950,000 and 1,200,000 individuals.
The IUCN lists northern gannets as a species of least concern
A least-concern species is a species that has been categorized by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) as evaluated as not being a focus of species conservation because the specific species is still plentiful in the wild. ...
, as they are widely distributed and as there is a large population that appears to be growing due to high breeding success, with 75% of eggs producing fledged young.
In culture
 In Homer's ''
In Homer's ''Odyssey
The ''Odyssey'' (; grc, Ὀδύσσεια, Odýsseia, ) is one of two major ancient Greek epic poems attributed to Homer. It is one of the oldest extant works of literature still widely read by modern audiences. As with the '' Iliad'', ...
'', the sea goddess Leucothea ( el, Λευκοθέα "white goddess"), appears "in the likeness of a Gannet" and tells the shipwrecked Odysseus
Odysseus ( ; grc-gre, Ὀδυσσεύς, Ὀδυσεύς, OdysseúsOdyseús, ), also known by the Latin variant Ulysses ( , ; lat, UlyssesUlixes), is a legendary Greek king of Ithaca and the hero of Homer's epic poem the ''Odyssey''. Odys ...
to discard his cloak and raft, instead offering him her veil to wind round himself which will save his life and enable him to reach land.
Another early reference to the gannet is in the 7th-century Old English
Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlers in the mid-5th ...
epic poem '' The Seafarer''.
An old myth from Mykines in the Faroe Islands tells of the giant Tórur seeking mercy following defeat at the hands of Óli, the islanders' head man and magician. In return, he gave them whales, driftwood logs and a bird unique to the archipelago, on condition that the inhabitants did not laugh at his gifts. Over time, the islanders forgot their promise, and lost the whales and logs, but fearful of losing a valuable food source, they never mocked the gannets that Tórur had given them.
 Northern gannets have long been eaten for food. Birds, mainly the young, were taken from Bass Rock for at least 350 years until 1885, when the annual cull of about 1,500 individuals finally ceased, and Shetland gannets were sold as "Highland goose" in London restaurants during
Northern gannets have long been eaten for food. Birds, mainly the young, were taken from Bass Rock for at least 350 years until 1885, when the annual cull of about 1,500 individuals finally ceased, and Shetland gannets were sold as "Highland goose" in London restaurants during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
. Views of the palatability of this bird are mixed, but as well as being a food for the poor it also regularly featured in Scottish royal banquets. In Scotland gannets were traditionally salted to preserve them until they got to market, this technique being replaced by partially cooking or smoking in the era of modern transport. They are normally served roasted, although sometimes raw when pickled or dried.
The best-known site was the remote island of St. Kilda, where adults and eggs were taken in the spring. The fat chicks, known locally as "gugas", were harvested from the precipitous cliffs in August, just before they could fly, and thrown to waiting boats far below. Much of the meat was salted in barrels for storage, but the rest of the bird was also used. Islanders paid their rent in feathers for stuffing pillows and furniture, the gannet stomachs were used to hold oil derived from the carcasses, and the breastbones served as lamp wicks.
Hunting on St. Kilda ceased in 1910, but the gannetry on Sula Sgeir is still exploited under a licence that permits 2,200 chicks to be taken each year. During the hunt, 10 men live on the island, and the cleaned birds are singed on a fire fuelled by their own oil-rich offal. The filleted birds are then taken to Stornoway
Stornoway (; gd, Steòrnabhagh; sco, Stornowa) is the main town of the Western Isles and the capital of Lewis and Harris in Scotland.
The town's population is around 6,953, making it by far the largest town in the Outer Hebrides, as well ...
, where each hunter receives 200 skins to give away or sell. The continuing existence of the practice of hunting and eating gannets attracts criticism in some quarters. The island's name "Sula Sgeir" itself derives from ''sula'', meaning "gannet", and the Old Norse ''skerr'', a skerry
A skerry is a small rocky island, or islet, usually too small for human habitation. It may simply be a rocky reef. A skerry can also be called a low sea stack.
A skerry may have vegetative life such as moss and small, hardy grasses. They ar ...
. Other sites that continued hunting into the 20th century were Eldey
Eldey () is a small island about off the coast of the Reykjanes Peninsula in southwest Iceland. Located west-southwest of Reykjavík, the island of Eldey covers an area of about , and rises to a height of . Its sheer cliffs are home to la ...
in Iceland, where the activity ceased in 1939, and Mykines, where small-scale culling still persists. About 500 young are culled for consumption each year in Mykines, using techniques similar to those of the Sula Sgeir hunts.
Although the Bass Rock population fell to fewer than 4,000 pairs in the early 19th century, the population soon recovered once hunting ceased, and St. Kilda was harvested sustainably for hundreds of years. Elsewhere, the recovery was less complete. The Bird Rocks colony in the Gulf of St Lawrence may once have held 250,000 birds, but unchecked hunting, including for fish bait, meant that the population was only 1,000 birds by 1932, despite government protection since 1904.
Explanatory notes
Citations
General and cited references
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
* {{Authority controlnorthern gannet
The northern gannet (''Morus bassanus'') is a seabird, the largest species of the gannet family, Sulidae. It is native to the coasts of the Atlantic Ocean, breeding in Western Europe and Northeastern North America. It is the largest seabird in t ...
Birds of Europe
Birds of North America
Birds of the Atlantic Ocean
northern gannet
The northern gannet (''Morus bassanus'') is a seabird, the largest species of the gannet family, Sulidae. It is native to the coasts of the Atlantic Ocean, breeding in Western Europe and Northeastern North America. It is the largest seabird in t ...
northern gannet
The northern gannet (''Morus bassanus'') is a seabird, the largest species of the gannet family, Sulidae. It is native to the coasts of the Atlantic Ocean, breeding in Western Europe and Northeastern North America. It is the largest seabird in t ...
Articles containing video clips