Myelitis on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Myelitis is

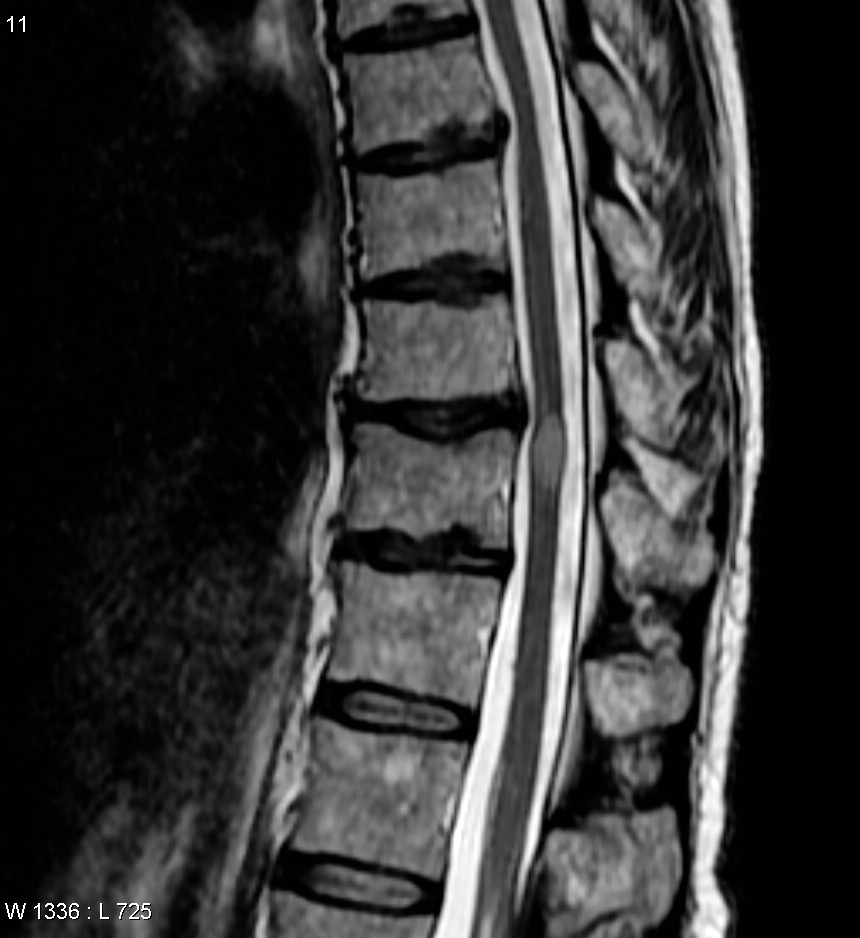 Myelitis lesions usually occur in a narrow region but can be spread and affect many areas.
* Acute flaccid myelitis: a polio-like syndrome that causes muscle weakness and paralysis.
*
Myelitis lesions usually occur in a narrow region but can be spread and affect many areas.
* Acute flaccid myelitis: a polio-like syndrome that causes muscle weakness and paralysis.
*
* Viral myelitis
Most viral myelitis is acute, but the
inflammation
Inflammation (from la, inflammatio) is part of the complex biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants, and is a protective response involving immune cells, blood vessels, and molec ...
of the spinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue, which extends from the medulla oblongata in the brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone). The backbone encloses the central canal of the sp ...
which can disrupt the normal responses from the brain
A brain is an organ (biology), organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as Visual perception, vision. I ...
to the rest of the body, and from the rest of the body to the brain. Inflammation in the spinal cord, can cause the myelin
Myelin is a lipid-rich material that surrounds nerve cell axons (the nervous system's "wires") to insulate them and increase the rate at which electrical impulses (called action potentials) are passed along the axon. The myelinated axon can ...
and axon
An axon (from Greek ἄξων ''áxōn'', axis), or nerve fiber (or nerve fibre: see spelling differences), is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, in vertebrates, that typically conducts electrical impulses known as action p ...
to be damaged resulting in symptoms such as paralysis and sensory loss. Myelitis is classified to several categories depending on the area or the cause of the lesion; however, any inflammatory attack on the spinal cord is often referred to as transverse myelitis.
Types of myelitis

 Myelitis lesions usually occur in a narrow region but can be spread and affect many areas.
* Acute flaccid myelitis: a polio-like syndrome that causes muscle weakness and paralysis.
*
Myelitis lesions usually occur in a narrow region but can be spread and affect many areas.
* Acute flaccid myelitis: a polio-like syndrome that causes muscle weakness and paralysis.
* Poliomyelitis
Poliomyelitis, commonly shortened to polio, is an infectious disease caused by the poliovirus. Approximately 70% of cases are asymptomatic; mild symptoms which can occur include sore throat and fever; in a proportion of cases more severe sym ...
: disease caused by viral infection in the gray matter with symptoms of muscle paralysis or weakness
* Transverse myelitis: caused by axonal demyelination encompassing both sides of the spinal cord
* Leukomyelitis Leukomyelitis, also known as acute spasmodic paraplegia, is a disorder of the central nervous system. It affects only the "white matter" of the spinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue, which exten ...
: lesions in the white matter
* Meningococcal myelitis (or meningomyelitis): lesions occurring in the region of meninges
In anatomy, the meninges (, ''singular:'' meninx ( or ), ) are the three membranes that envelop the brain and spinal cord. In mammals, the meninges are the dura mater, the arachnoid mater, and the pia mater. Cerebrospinal fluid is located in ...
and the spinal cord
Osteomyelitis of the vertebra
The spinal column, a defining synapomorphy shared by nearly all vertebrates, Hagfish are believed to have secondarily lost their spinal column is a moderately flexible series of vertebrae (singular vertebra), each constituting a characteristi ...
l bone surrounding the spinal cord (that is, vertebral osteomyelitis
Vertebral osteomyelitis is a type of osteomyelitis (infection and inflammation of the bone and bone marrow) that affects the vertebrae. It is a rare bone infection concentrated in the vertebral column. Cases of vertebral osteomyelitis are so rare ...
) is a separate condition, although some infections (for example, ''Staphylococcus aureus
''Staphylococcus aureus'' is a Gram-positive spherically shaped bacterium, a member of the Bacillota, and is a usual member of the microbiota of the body, frequently found in the upper respiratory tract and on the skin. It is often posit ...
'' infection) can occasionally cause both at once. The similarity of the words reflects that the combining form '' myel(o)-'' has multiple (homonym
In linguistics, homonyms are words which are homographs (words that share the same spelling, regardless of pronunciation), or homophones ( equivocal words, that share the same pronunciation, regardless of spelling), or both. Using this definitio ...
ous) senses referring to bone marrow or the spinal cord.
Symptoms
Depending on the cause of the disease, such clinical conditions manifest different speed in progression of symptoms in a matter of hours to days. Most myelitis manifests fast progression in muscle weakness or paralysis starting with the legs and then arms with varying degrees of severity. Sometimes the dysfunction of arms or legs cause instability of posture and difficulty in walking or any movement. Also symptoms generally includeparesthesia
Paresthesia is an abnormal sensation of the skin (tingling, pricking, chilling, burning, numbness) with no apparent physical cause. Paresthesia may be transient or chronic, and may have any of dozens of possible underlying causes. Paresthesias a ...
which is a sensation of tickling, tingling, burning, pricking, or numbness of a person's skin with no apparent long-term physical effect. Adult patients often report pain in the back, extremities, or abdomen. Patients also present increased urinary urgency, bowel or bladder dysfunctions such as bladder incontinence, difficulty or inability to void, and incomplete evacuation of bowel or constipation. Others also report fever, respiratory problems and intractable vomiting.
Diseases associated with myelitis
Conditions associated with myelitis include: *Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis
Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis (ADEM), or acute demyelinating encephalomyelitis, is a rare autoimmune disease marked by a sudden, widespread attack of inflammation in the brain and spinal cord. As well as causing the brain and spinal co ...
: autoimmune demyelination of the brain causing severe neurological signs and symptoms
* Multiple sclerosis
Multiple (cerebral) sclerosis (MS), also known as encephalomyelitis disseminata or disseminated sclerosis, is the most common demyelinating disease, in which the insulating covers of nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord are damaged. This ...
: demyelination of the brain and spinal cord
* Neuromyelitis optica
Neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders (NMOSD), including neuromyelitis optica (NMO), are autoimmune diseases characterized by acute inflammation of the optic nerve ( optic neuritis, ON) and the spinal cord ( myelitis). Episodes of ON and myeli ...
or Devic's disease
Neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders (NMOSD), including neuromyelitis optica (NMO), are autoimmune diseases characterized by acute inflammation of the optic nerve (optic neuritis, ON) and the spinal cord (myelitis). Episodes of ON and myelitis ...
: immune attack on optic nerve
In neuroanatomy, the optic nerve, also known as the second cranial nerve, cranial nerve II, or simply CN II, is a paired cranial nerve that transmits visual information from the retina to the brain. In humans, the optic nerve is derived fro ...
and spinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue, which extends from the medulla oblongata in the brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone). The backbone encloses the central canal of the sp ...
* Sjögren's syndrome: destruction of the exocrine system of the body
* Systemic lupus erythematosus
Lupus, technically known as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), is an autoimmune disease in which the body's immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue in many parts of the body. Symptoms vary among people and may be mild to severe. Commo ...
: a systemic autoimmune disease featuring a wide variety of neurological signs and symptoms
* Sarcoidosis
Sarcoidosis (also known as ''Besnier-Boeck-Schaumann disease'') is a disease involving abnormal collections of inflammatory cells that form lumps known as granulomata. The disease usually begins in the lungs, skin, or lymph nodes. Less commonly af ...
: chronic inflammatory cells form as nodules in multiple organs
* Atopy
Atopy is the tendency to produce an exaggerated immunoglobulin E (IgE) immune response to otherwise harmless substances in the environment. Allergic diseases are clinical manifestations of such inappropriate, atopic responses.
Atopy may have a ...
: an immune disorder of children manifesting as eczema
Dermatitis is inflammation of the skin, typically characterized by itchiness, redness and a rash. In cases of short duration, there may be small blisters, while in long-term cases the skin may become thickened. The area of skin involved c ...
or other allergic conditions. It can include atopic myelitis, which causes weakness.
* Immune-mediated myelopathies, heterogeneous group of inflammatory spinal cord disorders including autoimmune disorders with known antibodies
Cause
Myelitis occurs due to various reasons such as infections. Direct infection by viruses, bacteria, mold, or parasites such as human immunodeficiency virus ( HIV),human T-lymphotropic virus
The human T-lymphotropic virus, human T-cell lymphotropic virus, or human T-cell leukemia-lymphoma virus (HTLV) family of viruses are a group of human retroviruses that are known to cause a type of cancer called adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma and ...
types I and II (HTLV-I/II), syphilis
Syphilis () is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium '' Treponema pallidum'' subspecies ''pallidum''. The signs and symptoms of syphilis vary depending in which of the four stages it presents (primary, secondary, latent, a ...
, lyme disease, and tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease usually caused by '' Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, ...
can cause myelitis but it can also be caused due to non-infectious or inflammatory pathway. Myelitis often follows after the infections or after vaccination. These phenomena can be explained by a theory of autoimmune attack which states that the autoimmune bodies attack its spinal cord in response to immune reaction.
Mechanism of myelitis
The theory of autoimmune attack claims that a person with neuroimmunologic disorders have genetic predisposition to auto-immune disorder, and the environmental factors would trigger the disease. The specific genetics in myelitis is not completely understood. It is believed that the immune system response could be to viral, bacterial, fungal, or parasitic infection; however, it is not known why the immune system attacks itself. Especially, for the immune system to cause inflammatory response anywhere in the central nervous system, the cells from the immune system must pass through theblood brain barrier
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells. Blood in the ...
. In the case of myelitis, not only is the immune system dysfunctional, but the dysfunction also crosses this protective blood brain barrier to affect the spinal cord.
retrovirus
A retrovirus is a type of virus that inserts a DNA copy of its RNA genome into the DNA of a host cell that it invades, thus changing the genome of that cell. Once inside the host cell's cytoplasm, the virus uses its own reverse transcriptas ...
es (such as HIV and HTLV) can cause chronic myelitis. Poliomyelitis
Poliomyelitis, commonly shortened to polio, is an infectious disease caused by the poliovirus. Approximately 70% of cases are asymptomatic; mild symptoms which can occur include sore throat and fever; in a proportion of cases more severe sym ...
, or gray matter myelitis, is usually caused by infection of anterior horn of the spinal cord by the enteroviruses (poliovirus
A poliovirus, the causative agent of polio (also known as poliomyelitis), is a serotype of the species '' Enterovirus C'', in the family of '' Picornaviridae''. There are three poliovirus serotypes: types 1, 2, and 3.
Poliovirus is composed of ...
es, enteroviruses (EV) 70 and 71, echovirus
Echovirus is a polyphyletic group of viruses associated with enteric disease in humans. The name is derived from "enteric cytopathic human orphan virus". These viruses were originally not associated with disease, but many have since been identif ...
es, coxsackievirus
Coxsackieviruses are a few related enteroviruses that belong to the ''Picornaviridae'' family of nonenveloped, linear, positive-sense single-stranded RNA viruses, as well as its genus ''Enterovirus'', which also includes poliovirus and echovir ...
es A and B) and the flaviviruses (West Nile, Japanese encephalitis
Japanese encephalitis (JE) is an infection of the brain caused by the Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV). While most infections result in little or no symptoms, occasional inflammation of the brain occurs. In these cases, symptoms may include he ...
, tick-borne encephalitis
Tick-borne encephalitis (TBE) is a viral infectious disease involving the central nervous system. The disease most often manifests as meningitis, encephalitis or meningoencephalitis. Myelitis and spinal paralysis also occurs. In about one third ...
). On the other hand, transverse myelitis or leukomyelitis Leukomyelitis, also known as acute spasmodic paraplegia, is a disorder of the central nervous system. It affects only the "white matter" of the spinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue, which exten ...
, or white matter myelitis, are often caused by the herpesviruses and influenza virus
''Orthomyxoviridae'' (from Greek ὀρθός, ''orthós'' 'straight' + μύξα, ''mýxa'' 'mucus') is a family of negative-sense RNA viruses. It includes seven genera: ''Alphainfluenzavirus'', ''Betainfluenzavirus'', '' Gammainfluenzavirus'', ' ...
. It can be due to direct viral invasion or via immune mediated mechanisms.
* Bacterial myelitis
Bacterial myelitis includes '' Mycoplasma pneumoniae'', which is a common agent for respiratory tract. Studies have shown respiratory tract infections within 4–39 days prior to the onset of transverse myelitis. Or, tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease usually caused by '' Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, ...
, syphilis
Syphilis () is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium '' Treponema pallidum'' subspecies ''pallidum''. The signs and symptoms of syphilis vary depending in which of the four stages it presents (primary, secondary, latent, a ...
, and brucellosis
Brucellosis is a highly contagious zoonosis caused by ingestion of unpasteurized milk or undercooked meat from infected animals, or close contact with their secretions. It is also known as undulant fever, Malta fever, and Mediterranean fever.
The ...
are also known to cause myelitis in immune-compromised individuals. Myelitis is a rare manifestation of bacterial infection.
* Fungal myelitis
Fungi
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately fr ...
have been reported to cause spinal cord disease either by forming abscesses inside the bone or by granuloma
A granuloma is an aggregation of macrophages that forms in response to chronic inflammation. This occurs when the immune system attempts to isolate foreign substances that it is otherwise unable to eliminate. Such substances include infectious o ...
. In general, there are two groups of fungi that may infect the CNS and cause myelitis - primary and secondary pathogens. Primary pathogens include the following: ''Cryptococcus neoformans
''Cryptococcus neoformans'' is an encapsulated yeast belonging to the class Tremellomycetes and an obligate aerobe that can live in both plants and animals. Its teleomorph is a filamentous fungus, formerly referred to ''Filobasidiella neoformans ...
'', '' Coccidioides immitis'', '' Blastomyces dermatitides'', and '' Hystoplasma capsulatum''. Secondary pathogens are opportunistic agents that primarily infect immunocompromised hosts such as Candida species, Aspergillus
' () is a genus consisting of several hundred mold species found in various climates worldwide.
''Aspergillus'' was first catalogued in 1729 by the Italian priest and biologist Pier Antonio Micheli. Viewing the fungi under a microscope, Mic ...
species, and zygomycetes.
* Parasitic myelitis
Parasitic species infect human hosts through larvae that penetrate the skin. Then they enter the lymphatic and circulatory system, and migrate to liver and lung. Some reach the spinal cord. Parasitic infections have been reported with Schistosoma
''Schistosoma'' is a genus of trematodes, commonly known as blood flukes. They are parasitic flatworms responsible for a highly significant group of infections in humans termed '' schistosomiasis'', which is considered by the World Health Org ...
species, '' Toxocara canis'', Echinococcus
''Echinococcus'' is a genus within Cestoda, a parasitic class of the platyhelminthes phylum (colloquially known as flatworms). Human echinococcosis is an infectious disease caused by the following species: E. granulosus, E. multilocularis, or ...
species, '' Taenia solium'', ''Trichinella spiralis
''Trichinella spiralis'' is a viviparous nematode parasite, occurring in rodents, pigs, bears, hyenas and humans, and is responsible for the disease trichinosis. It is sometimes referred to as the "pork worm" due to it being typically encount ...
'', and Plasmodium
''Plasmodium'' is a genus of unicellular eukaryotes that are obligate parasites of vertebrates and insects. The life cycles of ''Plasmodium'' species involve development in a blood-feeding insect host which then injects parasites into a ve ...
species.
Autoimmune myelitis
In 2016, it was identified inMayo clinic
The Mayo Clinic () is a nonprofit American academic medical center focused on integrated health care, education, and research. It employs over 4,500 physicians and scientists, along with another 58,400 administrative and allied health staf ...
an autoimmune form of myelitis due to the presence of anti- GFAP autoantibodies. Immunoglobulin
An antibody (Ab), also known as an immunoglobulin (Ig), is a large, Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as pathogenic bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique molecule of th ...
s directed against the α-isoform of glial fibrillary acidic protein
Glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) is a protein that is encoded by the ''GFAP'' gene in humans. It is a type III intermediate filament (IF) protein that is expressed by numerous cell types of the central nervous system (CNS), including astro ...
(GFAP-IgG) predicted a special meningoencephalomyelitis termed autoimmune GFAP Astrocytopathy that later was found also to be able to appear as a myelitis.
Diagnosis
Myelitis has an extensive differential diagnosis. The type of onset (acute versus subacute/chronic) along with associated symptoms such as the presence of pain, constitutional symptoms that encompass fever,malaise
As a medical term, malaise is a feeling of general discomfort, uneasiness or lack of wellbeing and often the first sign of an infection or other disease. The word has existed in French since at least the 12th century.
The term is often used ...
, weight loss or a cutaneous rash may help identify the cause of myelitis. In order to establish a diagnosis of myelitis, one has to localize the spinal cord level, and exclude cerebral and neuromuscular diseases. Also a detailed medical history, a careful neurologic examination, and imaging studies using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are needed. In respect to the cause of the process, further work-up would help identify the cause and guide treatment. Full spine MRI is warranted, especially with acute onset myelitis, to evaluate for structural lesions that may require surgical intervention, or disseminated disease. Adding gadolinium further increases diagnostic sensitivity. A brain MRI may be needed to identify the extent of central nervous system (CNS) involvement. Lumbar puncture is important for the diagnosis of acute myelitis when a tumoral process, inflammatory or infectious cause are suspected, or the MRI is normal or non-specific. Complementary blood tests are also of value in establishing a firm diagnosis. Rarely, a biopsy of a mass lesion may become necessary when the cause is uncertain. However, in 15–30% of people with subacute or chronic myelitis, a clear cause is never uncovered.
Treatment
Since each case is different, the following are possible treatments that patients might receive in the management of myelitis. * Intravenous steroids High-dose intravenous methyl-prednisolone for 3–5 days is considered as a standard of care for patients suspected to have acute myelitis, unless there are compelling reasons otherwise. The decision to offer continued steroids or add a new treatment is often based on the clinical course and MRI appearance at the end of five days of steroids. *Plasma exchange
Plasmapheresis (from the Greek πλάσμα, ''plasma'', something molded, and ἀφαίρεσις ''aphairesis'', taking away) is the removal, treatment, and return or exchange of blood plasma or components thereof from and to the blood circula ...
(PLEX)
Patients with moderate to aggressive forms of disease who do not show much improvement after being treated with intravenous and oral steroids will be treated with PLEX. Retrospective studies of patients with TM treated with IV steroids followed by PLEX showed a positive outcome. It also has been shown to be effective with other autoimmune or inflammatory central nervous system disorders. Particular benefit has been shown with patients who are in the acute or subacute stage of the myelitis showing active inflammation on MRI. However, because of the risks implied by the lumbar puncture procedure, this intervention is determined by the treating physician on a case-by-case basis.
* Immunosuppressants
Immunosuppressive drugs, also known as immunosuppressive agents, immunosuppressants and antirejection medications, are drugs that inhibit or prevent activity of the immune system.
Classification
Immunosuppressive drugs can be classified in ...
/ Immunomodulatory agents
Myelitis with no definite cause seldom recurs, but for others, myelitis may be a manifestation of other diseases that are mentioned above. In these cases, ongoing treatment with medications that modulate or suppress the immune system may be necessary. Sometimes there is no specific treatment. Either way, aggressive rehabilitation and long-term symptom management are an integral part of the healthcare plan.
Prospective research direction
Central nervous system nerve regeneration would be able to repair or regenerate the damage caused to the spinal cord. It would restore functions lost due to the disease.Karumbaiah, L., Bellamkonda, R.. ''Neural Tissue Engineering''. * Engineering endogenous repair Currently, there exists ahydrogel
A hydrogel is a crosslinked hydrophilic polymer that does not dissolve in water. They are highly absorbent yet maintain well defined structures. These properties underpin several applications, especially in the biomedical area. Many hydrogels ar ...
based scaffold which acts as a channel to deliver nerve growth-enhancing substrates while providing structural support. These factors would promote nerve repairs to the target area. Hydrogels' macroporous properties would enable attachment of cells and enhance ion and nutrient exchange. In addition, hydrogels' biodegradability or bioresolvability would prevent the need for surgical removal of the hydrogel after drug delivery. It means that it would be dissolved naturally by the body's enzymatic reaction.
* Biochemical repair
:*Neurotropic factor therapy and gene therapy
:*Neurotropic growth factors regulate growth, survival, and plasticity of the axon
An axon (from Greek ἄξων ''áxōn'', axis), or nerve fiber (or nerve fibre: see spelling differences), is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, in vertebrates, that typically conducts electrical impulses known as action p ...
. They benefit nerve regeneration after injury to the nervous system. They are a potent initiator of sensory axon growth and are up-regulated at the lesion site. The continuous delivery of neurotropic growth factor (NGF) would increase the nerve regeneration in the spinal cord. However, the excessive dosing of NGF often leads to undesired plasticity and sprouting of uninjured sensory nerves. Gene therapy would be able to increase the NGF efficacy by the controlled and sustained delivery in a site-specific manner.
* Stem cell
In multicellular organisms, stem cells are undifferentiated or partially differentiated cells that can differentiate into various types of cells and proliferate indefinitely to produce more of the same stem cell. They are the earliest type of ...
-based therapies
The possibility for nerve regeneration after injury to the spinal cord was considered to be limited because of the absence of major neurogenesis
Neurogenesis is the process by which nervous system cells, the neurons, are produced by neural stem cells (NSCs). It occurs in all species of animals except the porifera (sponges) and placozoans. Types of NSCs include neuroepithelial cells (NEC ...
. However, Joseph Altman showed that cell division does occur in the brain which allowed potential for stem cell therapy for nerve regeneration. The stem cell-based therapies are used in order to replace cells lost and injured due to inflammation, to modulate the immune system, and to enhance regeneration and remyelination of axons. Neural stem cells (NSC) have the potential to integrate with the spinal cord because in the recent past investigations have demonstrated their potential for differentiation into multiple cell types that are crucial to the spinal cord. Studies show that NSCs that were transplanted into a demyelinating spinal cord lesion were found to regenerate oligodendrocytes and Schwann cells, and completely remyelinated axons.
See also
*Encephalomyelitis
Encephalomyelitis is inflammation of the brain and spinal cord. Various types of encephalomyelitis include:
* '' Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis'' or ''postinfectious encephalomyelitis'', a demyelinating disease of the brain and spinal cord, ...
* Myalgic encephalomyelitis – also known as chronic fatigue syndrome
Chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS), also called myalgic encephalomyelitis (ME) or ME/CFS, is a complex, debilitating, long-term medical condition. The causes and mechanisms of the disease are not fully understood. Distinguishing core symptoms are ...
* Transverse myelitis
References
External links
{{Spinal cord lesions Inflammations Central nervous system disorders