mitochondrion on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A mitochondrion (; ) is an organelle found in the
A mitochondrion (; ) is an organelle found in the
 Mitochondria may have a number of different shapes.
A mitochondrion contains outer and inner membranes composed of phospholipid bilayers and
Mitochondria may have a number of different shapes.
A mitochondrion contains outer and inner membranes composed of phospholipid bilayers and
 The inner mitochondrial membrane is compartmentalized into numerous folds called cristae, which expand the surface area of the inner mitochondrial membrane, enhancing its ability to produce ATP. For typical liver mitochondria, the area of the inner membrane is about five times as large as the outer membrane. This ratio is variable and mitochondria from cells that have a greater demand for ATP, such as muscle cells, contain even more cristae. Mitochondria within the same cell can have substantially different crista-density, with the ones that are required to produce more energy having much more crista-membrane surface. These folds are studded with small round bodies known as F particles or oxysomes.
The inner mitochondrial membrane is compartmentalized into numerous folds called cristae, which expand the surface area of the inner mitochondrial membrane, enhancing its ability to produce ATP. For typical liver mitochondria, the area of the inner membrane is about five times as large as the outer membrane. This ratio is variable and mitochondria from cells that have a greater demand for ATP, such as muscle cells, contain even more cristae. Mitochondria within the same cell can have substantially different crista-density, with the ones that are required to produce more energy having much more crista-membrane surface. These folds are studded with small round bodies known as F particles or oxysomes.
 The electrons from NADH and FADH are transferred to oxygen (O) and hydrogen (protons) in several steps via an electron transport chain. NADH and FADH molecules are produced within the matrix via the citric acid cycle and in the cytoplasm by glycolysis. Reducing equivalents from the cytoplasm can be imported via the malate-aspartate shuttle system of
The electrons from NADH and FADH are transferred to oxygen (O) and hydrogen (protons) in several steps via an electron transport chain. NADH and FADH molecules are produced within the matrix via the citric acid cycle and in the cytoplasm by glycolysis. Reducing equivalents from the cytoplasm can be imported via the malate-aspartate shuttle system of O2 + 4H+(aq) + 4 Fe^(cyt\,c) -> 2H2O + 4 Fe^(cyt\,c)
releasing a lot of free energy from the reactants without breaking bonds of an organic fuel. The free energy put in to remove an electron from Fe2+ is released at complex III when Fe3+ of cytochrome c reacts to oxidize 2 Fe^(cyt\,c) + QH2 -> 2 Fe^(cyt\,c) + Q + 2H+(aq)
The ubiquinone (Q) generated reacts, in complex I, with NADH:
Q + H+(aq) + NADH -> QH2 + NAD+
While the reactions are controlled by an electron transport chain, free electrons are not amongst the reactants or products in the three reactions shown and therefore do not affect the free energy released, which is used to pump
 The concentrations of free calcium in the cell can regulate an array of reactions and is important for signal transduction in the cell. Mitochondria can transiently store calcium, a contributing process for the cell's homeostasis of calcium.
Their ability to rapidly take in calcium for later release makes them good "cytosolic buffers" for calcium. The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is the most significant storage site of calcium, and there is a significant interplay between the mitochondrion and ER with regard to calcium. The calcium is taken up into the
The concentrations of free calcium in the cell can regulate an array of reactions and is important for signal transduction in the cell. Mitochondria can transiently store calcium, a contributing process for the cell's homeostasis of calcium.
Their ability to rapidly take in calcium for later release makes them good "cytosolic buffers" for calcium. The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is the most significant storage site of calcium, and there is a significant interplay between the mitochondrion and ER with regard to calcium. The calcium is taken up into the
 A few groups of unicellular eukaryotes have only vestigial mitochondria or derived structures: The
A few groups of unicellular eukaryotes have only vestigial mitochondria or derived structures: The
 Mitochondria contain their own genome. The human mitochondrial genome is a circular double-stranded DNA molecule of about 16 kilobases. It encodes 37 genes: 13 for subunits of respiratory complexes I, III, IV and V, 22 for mitochondrial tRNA (for the 20 standard amino acids, plus an extra gene for leucine and serine), and 2 for
Mitochondria contain their own genome. The human mitochondrial genome is a circular double-stranded DNA molecule of about 16 kilobases. It encodes 37 genes: 13 for subunits of respiratory complexes I, III, IV and V, 22 for mitochondrial tRNA (for the 20 standard amino acids, plus an extra gene for leucine and serine), and 2 for
While slight variations on the standard genetic code had been predicted earlier, none was discovered until 1979, when researchers studying human mitochondrial genes determined that they used an alternative code. Nonetheless, the mitochondria of many other eukaryotes, including most plants, use the standard code. Many slight variants have been discovered since, including various alternative mitochondrial codes. Further, the AUA, AUC, and AUU codons are all allowable start codons.
Some of these differences should be regarded as pseudo-changes in the genetic code due to the phenomenon of RNA editing, which is common in mitochondria. In higher plants, it was thought that CGG encoded for tryptophan and not arginine; however, the codon in the processed RNA was discovered to be the UGG codon, consistent with the standard genetic code for tryptophan. Of note, the arthropod mitochondrial genetic code has undergone parallel evolution within a phylum, with some organisms uniquely translating AGG to lysine.
Powering the Cell Mitochondria
– XVIVO Scientific Animation
Mitodb.com
– The mitochondrial disease database.
at University of Mainz
Mitochondria Research Portal
at mitochondrial.net
at cytochemistry.net
at
MIP
Mitochondrial Physiology Society
3D structures of proteins from inner mitochondrial membrane
at
3D structures of proteins associated with outer mitochondrial membrane
at
Mitochondrial Protein Partnership
at University of Wisconsin
MitoMiner – A mitochondrial proteomics database
at
Mitochondrion – Cell Centered Database
at San Diego State University
Video Clip of Rat-liver Mitochondrion from Cryo-electron Tomography
{{Authority control Cellular respiration Endosymbiotic events
 A mitochondrion (; ) is an organelle found in the
A mitochondrion (; ) is an organelle found in the cells
Cell most often refers to:
* Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life
Cell may also refer to:
Locations
* Monastic cell, a small room, hut, or cave in which a religious recluse lives, alternatively the small precursor of a monastery w ...
of most Eukaryotes, such as animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals consume organic material, breathe oxygen, are able to move, can reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage ...
s, plant
Plants are predominantly photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae. Historically, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi; however, all current definitions of Plantae excl ...
s and fungi
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately fr ...
. Mitochondria have a double membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosine triphosphate
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is an organic compound that provides energy to drive many processes in living cells, such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, condensate dissolution, and chemical synthesis. Found in all known forms ...
(ATP), which is used throughout the cell as a source of chemical energy
Chemical energy is the energy of chemical substances that is released when they undergo a chemical reaction and transform into other substances. Some examples of storage media of chemical energy include batteries, Schmidt-Rohr, K. (2018). "How ...
. They were discovered by Albert von Kölliker
Albert von Kölliker (born Rudolf Albert Kölliker'';'' 6 July 18172 November 1905) was a Swiss anatomist, physiologist, and histologist.
Biography
Albert Kölliker was born in Zurich, Switzerland. His early education was carried on in Zurich, ...
in 1857 in the voluntary muscles of insects. The term ''mitochondrion'' was coined by Carl Benda in 1898. The mitochondrion is popularly nicknamed the "powerhouse of the cell", a phrase coined by Philip Siekevitz in a 1957 article of the same name.
Some cells in some multicellular organisms lack mitochondria (for example, mature mammalian red blood cell
Red blood cells (RBCs), also referred to as red cells, red blood corpuscles (in humans or other animals not having nucleus in red blood cells), haematids, erythroid cells or erythrocytes (from Greek ''erythros'' for "red" and ''kytos'' for "hol ...
s). A large number of unicellular organisms, such as microsporidia
Microsporidia are a group of spore-forming unicellular parasites. These spores contain an extrusion apparatus that has a coiled polar tube ending in an anchoring disc at the apical part of the spore. They were once considered protozoans or pr ...
, parabasalid
The parabasalids are a group of flagellated protists within the supergroup Excavata. Most of these eukaryotic organisms form a symbiotic relationship in animals. These include a variety of forms found in the intestines of termites and cockroach ...
s and diplomonad
The diplomonads (Greek for "two units") are a group of flagellates, most of which are parasitic. They include ''Giardia duodenalis'', which causes giardiasis in humans. They are placed among the metamonads, and appear to be particularly close ...
s, have reduced or transformed their mitochondria into other structures. One eukaryote, ''Monocercomonoides
''Monocercomonoides'' is a genus of flagellate Excavata belonging to the order Oxymonadida. It was established by Bernard V. Travis and was first described as those with "polymastiginid flagellates having three anterior flagella and a trailing ...
'', is known to have completely lost its mitochondria, and one multicellular organism, '' Henneguya salminicola'', is known to have retained mitochondrion-related organelles in association with a complete loss of their mitochondrial genome.
Mitochondria are commonly between 0.75 and 3 μm
The micrometre ( international spelling as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures; SI symbol: μm) or micrometer ( American spelling), also commonly known as a micron, is a unit of length in the International System of Uni ...
in crossection, but vary considerably in size and structure. Unless specifically stained
A stain is a discoloration that can be clearly distinguished from the surface, material, or medium it is found upon. They are caused by the chemical or physical interaction of two dissimilar materials. Accidental staining may make materials app ...
, they are not visible. In addition to supplying cellular energy, mitochondria are involved in other tasks, such as signaling, cellular differentiation, and cell death, as well as maintaining control of the cell cycle
The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the series of events that take place in a cell that cause it to divide into two daughter cells. These events include the duplication of its DNA (DNA replication) and some of its organelles, and sub ...
and cell growth. Mitochondrial biogenesis is in turn temporally coordinated with these cellular processes. Mitochondria have been implicated in several human disorders and conditions, such as mitochondrial diseases, cardiac dysfunction, heart failure and autism.
The number of mitochondria in a cell can vary widely by organism
In biology, an organism () is any living system that functions as an individual entity. All organisms are composed of cells ( cell theory). Organisms are classified by taxonomy into groups such as multicellular animals, plants, and fu ...
, tissue, and cell type. A mature red blood cell has no mitochondria, whereas a liver cell
A hepatocyte is a cell of the main parenchymal tissue of the liver. Hepatocytes make up 80% of the liver's mass.
These cells are involved in:
* Protein synthesis
* Protein storage
* Transformation of carbohydrates
* Synthesis of cholesterol, ...
can have more than 2000. The mitochondrion is composed of compartments that carry out specialized functions. These compartments or regions include the outer membrane, intermembrane space, inner membrane, cristae, and matrix
Matrix most commonly refers to:
* ''The Matrix'' (franchise), an American media franchise
** '' The Matrix'', a 1999 science-fiction action film
** "The Matrix", a fictional setting, a virtual reality environment, within ''The Matrix'' (franchi ...
.
Although most of a eukaryotic cell's DNA is contained in the cell nucleus
The cell nucleus (pl. nuclei; from Latin or , meaning ''kernel'' or ''seed'') is a membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types, such as mammalian red blood cells, h ...
, the mitochondrion has its own genome ("mitogenome") that is substantially similar to bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were am ...
l genomes. This finding has led to general acceptance of the endosymbiotic hypothesis
Symbiogenesis (endosymbiotic theory, or serial endosymbiotic theory,) is the leading evolutionary theory of the origin of eukaryotic cells from prokaryotic organisms. The theory holds that mitochondria, plastids such as chloroplasts, and possibly ...
- that free-living prokaryotic ancestors of modern mitochondria permanently fused with eukaryotic cells in the distant past, evolving such that modern animals, plants, fungi, and other eukaryotes are able to respire to generate cellular energy.
Structure
protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, res ...
s. The two membranes have different properties. Because of this double-membraned organization, there are five distinct parts to a mitochondrion:
# The outer mitochondrial membrane,
# The intermembrane space (the space between the outer and inner membranes),
# The inner mitochondrial membrane,
# The cristae space (formed by infoldings of the inner membrane), and
# The matrix
Matrix most commonly refers to:
* ''The Matrix'' (franchise), an American media franchise
** '' The Matrix'', a 1999 science-fiction action film
** "The Matrix", a fictional setting, a virtual reality environment, within ''The Matrix'' (franchi ...
(space within the inner membrane), which is a fluid.
Mitochondria have folding to increase surface area, which in turn increases ATP (adenosine triphosphate) production.
Mitochondria stripped of their outer membrane are called mitoplast
A mitoplast is a mitochondrion that has been stripped of its outer membrane leaving the inner membrane and matrix intact.
How Mitoplasts Are Most Commonly Created
To begin the process, mitochondria must first be separated from cultured cells ...
s.
Outer membrane
The outer mitochondrial membrane, which encloses the entire organelle, is 60 to 75angstrom
The angstromEntry "angstrom" in the Oxford online dictionary. Retrieved on 2019-03-02 from https://en.oxforddictionaries.com/definition/angstrom.Entry "angstrom" in the Merriam-Webster online dictionary. Retrieved on 2019-03-02 from https://www.m ...
s (Å) thick. It has a protein-to-phospholipid ratio similar to that of the cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane (PM) or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of all cells from the outside environment (t ...
(about 1:1 by weight). It contains large numbers of integral membrane proteins called porins. A major trafficking protein is the pore-forming voltage-dependent anion channel (VDAC). The VDAC is the primary transporter of nucleotide
Nucleotides are organic molecules consisting of a nucleoside and a phosphate. They serve as monomeric units of the nucleic acid polymers – deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), both of which are essential biomolecu ...
s, ions and metabolites between the cytosol and the intermembrane space. It is formed as a beta barrel that spans the outer membrane, similar to that in the gram-negative bacterial membrane. Larger proteins can enter the mitochondrion if a signaling sequence at their N-terminus binds to a large multisubunit protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, res ...
called translocase in the outer membrane, which then actively moves them across the membrane. Mitochondrial pro-proteins are imported through specialised translocation complexes.
The outer membrane also contains enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products ...
s involved in such diverse activities as the elongation of fatty acid
In chemistry, particularly in biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with an aliphatic chain, which is either saturated or unsaturated. Most naturally occurring fatty acids have an unbranched chain of an even number of carbon atoms, f ...
s, oxidation
Redox (reduction–oxidation, , ) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of substrate change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is the gain of electrons or ...
of epinephrine, and the degradation of tryptophan. These enzymes include monoamine oxidase, rotenone-insensitive NADH-cytochrome c-reductase, kynurenine hydroxylase and fatty acid Co-A ligase. Disruption of the outer membrane permits proteins in the intermembrane space to leak into the cytosol, leading to cell death. The outer mitochondrial membrane can associate with the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane, in a structure called MAM (mitochondria-associated ER-membrane). This is important in the ER-mitochondria calcium signaling and is involved in the transfer of lipids between the ER and mitochondria. Outside the outer membrane are small (diameter: 60 Å) particles named sub-units of Parson.
Intermembrane space
The mitochondrial intermembrane space is the space between the outer membrane and the inner membrane. It is also known as perimitochondrial space. Because the outer membrane is freely permeable to small molecules, the concentrations of small molecules, such as ions and sugars, in the intermembrane space is the same as in the cytosol. However, large proteins must have a specific signaling sequence to be transported across the outer membrane, so the protein composition of this space is different from the protein composition of the cytosol. Oneprotein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, res ...
that is localized to the intermembrane space in this way is cytochrome c.
Inner membrane
The inner mitochondrial membrane contains proteins with three types of functions: # Those that perform the electron transport chainredox
Redox (reduction–oxidation, , ) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of substrate change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is the gain of electrons or ...
reactions
# ATP synthase, which generates ATP in the matrix
# Specific transport proteins that regulate metabolite passage into and out of the mitochondrial matrix
It contains more than 151 different polypeptides, and has a very high protein-to-phospholipid ratio (more than 3:1 by weight, which is about 1 protein for 15 phospholipids). The inner membrane is home to around 1/5 of the total protein in a mitochondrion. Additionally, the inner membrane is rich in an unusual phospholipid, cardiolipin
Cardiolipin (IUPAC name 1,3-bis(''sn''-3’-phosphatidyl)-''sn''-glycerol) is an important component of the inner mitochondrial membrane, where it constitutes about 20% of the total lipid composition. It can also be found in the membranes of most ...
. This phospholipid was originally discovered in cow hearts in 1942, and is usually characteristic of mitochondrial and bacterial plasma membranes. Cardiolipin contains four fatty acids rather than two, and may help to make the inner membrane impermeable, and its disruption can lead to multiple clinical disorders including neurological disorders and cancer. Unlike the outer membrane, the inner membrane does not contain porins, and is highly impermeable to all molecules. Almost all ions and molecules require special membrane transporters to enter or exit the matrix. Proteins are ferried into the matrix via the translocase of the inner membrane (TIM) complex or via OXA1L
Mitochondrial inner membrane protein OXA1L is a protein that in humans is encoded by the OXA1L gene located on 14q11.2. The C-terminus of this protein interacts with mitochondrial
A mitochondrion (; ) is an organelle found in the cells of ...
. In addition, there is a membrane potential across the inner membrane, formed by the action of the enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products ...
s of the electron transport chain. Inner membrane fusion is mediated by the inner membrane protein OPA1
Dynamin-like 120 kDa protein, mitochondrial is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''OPA1'' gene. This protein regulates mitochondrial fusion and cristae structure in the inner mitochondrial membrane (IMM) and contributes to ATP synthesis a ...
.
Cristae
 The inner mitochondrial membrane is compartmentalized into numerous folds called cristae, which expand the surface area of the inner mitochondrial membrane, enhancing its ability to produce ATP. For typical liver mitochondria, the area of the inner membrane is about five times as large as the outer membrane. This ratio is variable and mitochondria from cells that have a greater demand for ATP, such as muscle cells, contain even more cristae. Mitochondria within the same cell can have substantially different crista-density, with the ones that are required to produce more energy having much more crista-membrane surface. These folds are studded with small round bodies known as F particles or oxysomes.
The inner mitochondrial membrane is compartmentalized into numerous folds called cristae, which expand the surface area of the inner mitochondrial membrane, enhancing its ability to produce ATP. For typical liver mitochondria, the area of the inner membrane is about five times as large as the outer membrane. This ratio is variable and mitochondria from cells that have a greater demand for ATP, such as muscle cells, contain even more cristae. Mitochondria within the same cell can have substantially different crista-density, with the ones that are required to produce more energy having much more crista-membrane surface. These folds are studded with small round bodies known as F particles or oxysomes.
Matrix
The matrix is the space enclosed by the inner membrane. It contains about 2/3 of the total proteins in a mitochondrion. The matrix is important in the production of ATP with the aid of the ATP synthase contained in the inner membrane. The matrix contains a highly concentrated mixture of hundreds of enzymes, special mitochondrial ribosomes, tRNA, and several copies of the mitochondrial DNAgenome
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding ...
. Of the enzymes, the major functions include oxidation of pyruvate and fatty acids, and the citric acid cycle
The citric acid cycle (CAC)—also known as the Krebs cycle or the TCA cycle (tricarboxylic acid cycle)—is a series of chemical reactions to release stored energy through the oxidation of acetyl-CoA derived from carbohydrates, fats, and prot ...
. The DNA molecules are packaged into nucleoids by proteins, one of which is TFAM.
Function
The most prominent roles of mitochondria are to produce the energy currency of the cell, ATP (i.e., phosphorylation ofADP
Adp or ADP may refer to:
Aviation
* Aéroports de Paris, airport authority for the Parisian region in France
* Aeropuertos del Perú, airport operator for airports in northern Peru
* SLAF Anuradhapura, an airport in Sri Lanka
* Ampara Airp ...
), through respiration and to regulate cellular metabolism
Metabolism (, from el, μεταβολή ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run ...
. The central set of reactions involved in ATP production are collectively known as the citric acid cycle
The citric acid cycle (CAC)—also known as the Krebs cycle or the TCA cycle (tricarboxylic acid cycle)—is a series of chemical reactions to release stored energy through the oxidation of acetyl-CoA derived from carbohydrates, fats, and prot ...
, or the Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. However, the mitochondrion has many other functions in addition to the production of ATP.
Energy conversion
A dominant role for the mitochondria is the production of ATP, as reflected by the large number of proteins in the inner membrane for this task. This is done by oxidizing the major products ofglucose
Glucose is a simple sugar with the molecular formula . Glucose is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. Glucose is mainly made by plants and most algae during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, u ...
: pyruvate, and NADH, which are produced in the cytosol. This type of cellular respiration
Cellular respiration is the process by which biological fuels are oxidised in the presence of an inorganic electron acceptor such as oxygen to produce large amounts of energy, to drive the bulk production of ATP. Cellular respiration may be des ...
, known as aerobic respiration, is dependent on the presence of oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements ...
. When oxygen is limited, the glycolytic products will be metabolized by anaerobic fermentation, a process that is independent of the mitochondria. The production of ATP from glucose and oxygen has an approximately 13-times higher yield during aerobic respiration compared to fermentation. Plant mitochondria can also produce a limited amount of ATP either by breaking the sugar produced during photosynthesis or without oxygen by using the alternate substrate nitrite. ATP crosses out through the inner membrane with the help of a specific protein, and across the outer membrane via porins. ADP returns via the same route.
Pyruvate and the citric acid cycle
Pyruvate molecules produced by glycolysis are actively transported across the inner mitochondrial membrane, and into the matrix where they can either beoxidized
Redox (reduction–oxidation, , ) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of substrate change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is the gain of electrons or a ...
and combined with coenzyme A to form CO, acetyl-CoA, and NADH, or they can be carboxylated (by pyruvate carboxylase) to form oxaloacetate. This latter reaction "fills up" the amount of oxaloacetate in the citric acid cycle and is therefore an anaplerotic reaction
Anaplerotic reactions, a term coined by Hans Kornberg and originating from the Greeἀνά 'up' anπληρόω 'to fill', are chemical reactions that form intermediates of a metabolic pathway. Examples of such are found in the citric acid cycle (TC ...
, increasing the cycle's capacity to metabolize acetyl-CoA when the tissue's energy needs (e.g., in muscle) are suddenly increased by activity.
In the citric acid cycle, all the intermediates (e.g. citrate, iso-citrate, alpha-ketoglutarate, succinate, fumarate, malate and oxaloacetate) are regenerated during each turn of the cycle. Adding more of any of these intermediates to the mitochondrion therefore means that the additional amount is retained within the cycle, increasing all the other intermediates as one is converted into the other. Hence, the addition of any one of them to the cycle has an anaplerotic effect, and its removal has a cataplerotic effect. These anaplerotic and cataplerotic reactions will, during the course of the cycle, increase or decrease the amount of oxaloacetate available to combine with acetyl-CoA to form citric acid. This in turn increases or decreases the rate of ATP production by the mitochondrion, and thus the availability of ATP to the cell.
Acetyl-CoA, on the other hand, derived from pyruvate oxidation, or from the beta-oxidation
In biochemistry and metabolism, beta-oxidation is the catabolic process by which fatty acid molecules are broken down in the cytosol in prokaryotes and in the mitochondria in eukaryotes to generate acetyl-CoA, which enters the citric acid cycle, ...
of fatty acids, is the only fuel to enter the citric acid cycle. With each turn of the cycle one molecule of acetyl-CoA is consumed for every molecule of oxaloacetate present in the mitochondrial matrix, and is never regenerated. It is the oxidation of the acetate portion of acetyl-CoA that produces CO and water, with the energy thus released captured in the form of ATP.
In the liver, the carboxylation of cytosolic pyruvate into intra-mitochondrial oxaloacetate is an early step in the gluconeogenic pathway, which converts lactate
Lactate may refer to:
* Lactation, the secretion of milk from the mammary glands
* Lactate, the conjugate base of lactic acid
Lactic acid is an organic acid. It has a molecular formula . It is white in the solid state and it is miscible with w ...
and de-aminated alanine into glucose, under the influence of high levels of glucagon and/or epinephrine in the blood. Here, the addition of oxaloacetate to the mitochondrion does not have a net anaplerotic effect, as another citric acid cycle intermediate (malate) is immediately removed from the mitochondrion to be converted to cytosolic oxaloacetate, and ultimately to glucose, in a process that is almost the reverse of glycolysis.
The enzymes of the citric acid cycle are located in the mitochondrial matrix, with the exception of succinate dehydrogenase
Succinate dehydrogenase (SDH) or succinate-coenzyme Q reductase (SQR) or respiratory complex II is an enzyme complex, found in many bacterial cells and in the inner mitochondrial membrane of eukaryotes. It is the only enzyme that participates ...
, which is bound to the inner mitochondrial membrane as part of Complex II. The citric acid cycle oxidizes the acetyl-CoA to carbon dioxide, and, in the process, produces reduced cofactors (three molecules of NADH and one molecule of FADH) that are a source of electrons for the electron transport chain, and a molecule of GTP (which is readily converted to an ATP).
O and NADH: Energy-releasing reactions
antiporter
An antiporter (also called exchanger or counter-transporter) is a cotransporter and integral membrane protein involved in secondary active transport of two or more different molecules or ions across a phospholipid membrane such as the plasma membr ...
proteins or fed into the electron transport chain using a glycerol phosphate shuttle.
The major energy-releasing reactions Voet, D.; Voet, J. G. (2004). ''Biochemistry'', 3rd edition, p. 804, Wiley. Atkins, P.; de Paula, J. (2006) "Physical Chemistry", 8th ed.; pp. 225-229, Freeman: New York, 2006. that make the mitochondrion the "powerhouse of the cell" occur at protein complexes I, III and IV in the inner mitochondrial membrane ( NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone), cytochrome c reductase, and cytochrome c oxidase). At complex IV, O2 reacts with the reduced form of iron in cytochrome c:
ubiquinol
A ubiquinol is an electron-rich (reduced) form of coenzyme Q (ubiquinone). The term most often refers to ubiquinol-10, with a 10-unit tail most commonly found in humans.
The natural ubiquinol form of coenzyme Q is 2,3-dimethoxy-5-methyl-6-poly p ...
(QH2):
protons
A proton is a stable subatomic particle, symbol , H+, or 1H+ with a positive electric charge of +1 ''e'' elementary charge. Its mass is slightly less than that of a neutron and 1,836 times the mass of an electron (the proton–electron m ...
(H) into the intermembrane space. This process is efficient, but a small percentage of electrons may prematurely reduce oxygen, forming reactive oxygen species such as superoxide. This can cause oxidative stress in the mitochondria and may contribute to the decline in mitochondrial function associated with aging.
As the proton concentration increases in the intermembrane space, a strong electrochemical gradient is established across the inner membrane. The protons can return to the matrix through the ATP synthase complex, and their potential energy is used to synthesize ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate (P). This process is called chemiosmosis, and was first described by Peter Mitchell, who was awarded the 1978 Nobel Prize in Chemistry
)
, image = Nobel Prize.png
, alt = A golden medallion with an embossed image of a bearded man facing left in profile. To the left of the man is the text "ALFR•" then "NOBEL", and on the right, the text (smaller) "NAT•" then "M ...
for his work. Later, part of the 1997 Nobel Prize in Chemistry was awarded to Paul D. Boyer
Paul Delos Boyer (July 31, 1918 – June 2, 2018) was an American biochemist, analytical chemist, and a professor of chemistry at University of California Los Angeles (UCLA). He shared the 1997 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for research on the "enzy ...
and John E. Walker
Sir John Ernest Walker One or more of the preceding sentences incorporates text from the royalsociety.org website where: (born 7 January 1941) is a British chemist who won the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1997. Walker is Emeritus Director an ...
for their clarification of the working mechanism of ATP synthase.
Heat production
Under certain conditions, protons can re-enter the mitochondrial matrix without contributing to ATP synthesis. This process is known as ''proton leak'' ormitochondrial uncoupling An uncoupler or uncoupling agent is a molecule that disrupts oxidative phosphorylation in prokaryotes and mitochondria or photophosphorylation in chloroplasts and cyanobacteria by dissociating the reactions of ATP synthesis from the electron transp ...
and is due to the facilitated diffusion
Facilitated diffusion (also known as facilitated transport or passive-mediated transport) is the process of spontaneous passive transport (as opposed to active transport) of molecules or ions across a biological membrane via specific transmembra ...
of protons into the matrix. The process results in the unharnessed potential energy of the proton electrochemical gradient being released as heat. The process is mediated by a proton channel called thermogenin, or UCP1. Thermogenin is primarily found in brown adipose tissue, or brown fat, and is responsible for non-shivering thermogenesis. Brown adipose tissue is found in mammals, and is at its highest levels in early life and in hibernating animals. In humans, brown adipose tissue is present at birth and decreases with age.
Storage of calcium ions
 The concentrations of free calcium in the cell can regulate an array of reactions and is important for signal transduction in the cell. Mitochondria can transiently store calcium, a contributing process for the cell's homeostasis of calcium.
Their ability to rapidly take in calcium for later release makes them good "cytosolic buffers" for calcium. The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is the most significant storage site of calcium, and there is a significant interplay between the mitochondrion and ER with regard to calcium. The calcium is taken up into the
The concentrations of free calcium in the cell can regulate an array of reactions and is important for signal transduction in the cell. Mitochondria can transiently store calcium, a contributing process for the cell's homeostasis of calcium.
Their ability to rapidly take in calcium for later release makes them good "cytosolic buffers" for calcium. The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is the most significant storage site of calcium, and there is a significant interplay between the mitochondrion and ER with regard to calcium. The calcium is taken up into the matrix
Matrix most commonly refers to:
* ''The Matrix'' (franchise), an American media franchise
** '' The Matrix'', a 1999 science-fiction action film
** "The Matrix", a fictional setting, a virtual reality environment, within ''The Matrix'' (franchi ...
by the mitochondrial calcium uniporter
The mitochondrial calcium uniporter (MCU) is a transmembrane protein that allows the passage of calcium ions from a cell's cytosol into mitochondria. Its activity is regulated by MICU1 and MICU2, which together with the MCU make up the mitochon ...
on the inner mitochondrial membrane. It is primarily driven by the mitochondrial membrane potential. Release of this calcium back into the cell's interior can occur via a sodium-calcium exchange protein or via "calcium-induced-calcium-release" pathways. This can initiate calcium spikes or calcium waves with large changes in the membrane potential. These can activate a series of second messenger system proteins that can coordinate processes such as neurotransmitter release in nerve cells and release of hormone
A hormone (from the Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of signaling molecules in multicellular organisms that are sent to distant organs by complex biological processes to regulate physiology and behavior. Hormones are required ...
s in endocrine cells.
Ca influx to the mitochondrial matrix has recently been implicated as a mechanism to regulate respiratory bioenergetics
Bioenergetics is a field in biochemistry and cell biology that concerns energy flow through living systems. This is an active area of biological research that includes the study of the transformation of energy in living organisms and the study of ...
by allowing the electrochemical potential across the membrane to transiently "pulse" from ΔΨ-dominated to pH-dominated, facilitating a reduction of oxidative stress. In neurons, concomitant increases in cytosolic and mitochondrial calcium act to synchronize neuronal activity with mitochondrial energy metabolism. Mitochondrial matrix calcium levels can reach the tens of micromolar levels, which is necessary for the activation of isocitrate dehydrogenase, one of the key regulatory enzymes of the Krebs cycle.
Cellular proliferation regulation
The relationship between cellular proliferation and mitochondria has been investigated. Tumor cells require ample ATP to synthesize bioactive compounds such aslipid
Lipids are a broad group of naturally-occurring molecules which includes fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids in ...
s, protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, res ...
s, and nucleotide
Nucleotides are organic molecules consisting of a nucleoside and a phosphate. They serve as monomeric units of the nucleic acid polymers – deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), both of which are essential biomolecu ...
s for rapid proliferation. The majority of ATP in tumor cells is generated via the oxidative phosphorylation pathway (OxPhos). Interference with OxPhos cause cell cycle
The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the series of events that take place in a cell that cause it to divide into two daughter cells. These events include the duplication of its DNA (DNA replication) and some of its organelles, and sub ...
arrest suggesting that mitochondria play a role in cell proliferation. Mitochondrial ATP production is also vital for cell division
Cell division is the process by which a parent cell divides into two daughter cells. Cell division usually occurs as part of a larger cell cycle in which the cell grows and replicates its chromosome(s) before dividing. In eukaryotes, there ...
and differentiation in infection in addition to basic functions in the cell including the regulation of cell volume, solute concentration
In chemistry, concentration is the abundance of a constituent divided by the total volume of a mixture. Several types of mathematical description can be distinguished: '' mass concentration'', '' molar concentration'', ''number concentration'', ...
, and cellular architecture. ATP levels differ at various stages of the cell cycle suggesting that there is a relationship between the abundance of ATP and the cell's ability to enter a new cell cycle. ATP's role in the basic functions of the cell make the cell cycle
The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the series of events that take place in a cell that cause it to divide into two daughter cells. These events include the duplication of its DNA (DNA replication) and some of its organelles, and sub ...
sensitive to changes in the availability of mitochondrial derived ATP. The variation in ATP levels at different stages of the cell cycle support the hypothesis that mitochondria play an important role in cell cycle regulation. Although the specific mechanisms between mitochondria and the cell cycle regulation is not well understood, studies have shown that low energy cell cycle checkpoints monitor the energy capability before committing to another round of cell division.
Additional functions
Mitochondria play a central role in many other metabolic tasks, such as: * Signaling through mitochondrial reactive oxygen species * Regulation of the membrane potential *Apoptosis
Apoptosis (from grc, ἀπόπτωσις, apóptōsis, 'falling off') is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes ( morphology) and death. These changes in ...
-programmed cell death
* Calcium signaling (including calcium-evoked apoptosis)
* Regulation of cellular metabolism
Metabolism (, from el, μεταβολή ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run ...
* Certain heme synthesis reactions ''(see also: porphyrin)''
* Steroid
A steroid is a biologically active organic compound with four rings arranged in a specific molecular configuration. Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes that alter membrane fluidity; and ...
synthesis.
* Hormonal signaling Mitochondria are sensitive and responsive to hormones, in part by the action of mitochondrial estrogen receptors (mtERs). These receptors have been found in various tissues and cell types, including brain and heart
* Immune signaling
* Neuronal mitochondria also contribute to cellular quality control by reporting neuronal status towards microglia through specialised somatic-junctions.
* Mitochondria of developing neurons contribute to intercellular signaling towards microglia, which communication is indispensable for proper regulation of brain development.
Some mitochondrial functions are performed only in specific types of cells. For example, mitochondria in liver cell
A hepatocyte is a cell of the main parenchymal tissue of the liver. Hepatocytes make up 80% of the liver's mass.
These cells are involved in:
* Protein synthesis
* Protein storage
* Transformation of carbohydrates
* Synthesis of cholesterol, ...
s contain enzymes that allow them to detoxify ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . A stable binary hydride, and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinct pungent smell. Biologically, it is a common nitrogenous ...
, a waste product of protein metabolism. A mutation in the genes regulating any of these functions can result in mitochondrial diseases.
Mitochondrial proteins (proteins transcribed from mitochondrial DNA) vary depending on the tissue and the species. In humans, 615 distinct types of proteins have been identified from cardiac mitochondria, whereas in rats
Rats are various medium-sized, long-tailed rodents. Species of rats are found throughout the order Rodentia, but stereotypical rats are found in the genus ''Rattus''. Other rat genera include ''Neotoma'' (pack rats), '' Bandicota'' (bandicoot ...
, 940 proteins have been reported. The mitochondrial proteome is thought to be dynamically regulated.Organization and distribution
Mitochondria (or related structures) are found in all eukaryotes (except theOxymonad
The Oxymonads (or Oxymonadida) are a group of flagellated protozoa found exclusively in the intestines of termites and other wood-eating insects. Along with the similar parabasalid flagellates, they harbor the symbiotic bacteria that are respons ...
''Monocercomonoides
''Monocercomonoides'' is a genus of flagellate Excavata belonging to the order Oxymonadida. It was established by Bernard V. Travis and was first described as those with "polymastiginid flagellates having three anterior flagella and a trailing ...
''). Although commonly depicted as bean-like structures they form a highly dynamic network in the majority of cells where they constantly undergo fission and fusion. The population of all the mitochondria of a given cell constitutes the chondriome. Mitochondria vary in number and location according to cell type. A single mitochondrion is often found in unicellular organisms, while human liver cells have about 1000–2000 mitochondria per cell, making up 1/5 of the cell volume. The mitochondrial content of otherwise similar cells can vary substantially in size and membrane potential, with differences arising from sources including uneven partitioning at cell division, leading to extrinsic differences in ATP levels and downstream cellular processes. The mitochondria can be found nestled between myofibril
A myofibril (also known as a muscle fibril or sarcostyle) is a basic rod-like organelle of a muscle cell. Skeletal muscles are composed of long, tubular cells known as muscle fibers, and these cells contain many chains of myofibrils. Each myofi ...
s of muscle or wrapped around the sperm flagellum
A flagellum (; ) is a hairlike appendage that protrudes from certain plant and animal sperm cells, and from a wide range of microorganisms to provide motility. Many protists with flagella are termed as flagellates.
A microorganism may have f ...
. Often, they form a complex 3D branching network inside the cell with the cytoskeleton
The cytoskeleton is a complex, dynamic network of interlinking protein filaments present in the cytoplasm of all cells, including those of bacteria and archaea. In eukaryotes, it extends from the cell nucleus to the cell membrane and is co ...
. The association with the cytoskeleton determines mitochondrial shape, which can affect the function as well: different structures of the mitochondrial network may afford the population a variety of physical, chemical, and signalling advantages or disadvantages. Mitochondria in cells are always distributed along microtubules and the distribution of these organelles is also correlated with the endoplasmic reticulum. Recent evidence suggests that vimentin, one of the components of the cytoskeleton, is also critical to the association with the cytoskeleton.
Mitochondria-associated ER membrane (MAM)
The mitochondria-associated ER membrane (MAM) is another structural element that is increasingly recognized for its critical role in cellular physiology andhomeostasis
In biology, homeostasis ( British also homoeostasis) (/hɒmɪə(ʊ)ˈsteɪsɪs/) is the state of steady internal, physical, and chemical conditions maintained by living systems. This is the condition of optimal functioning for the organism and ...
. Once considered a technical snag in cell fractionation techniques, the alleged ER vesicle contaminants that invariably appeared in the mitochondrial fraction have been re-identified as membranous structures derived from the MAM—the interface between mitochondria and the ER. Physical coupling between these two organelles had previously been observed in electron micrographs and has more recently been probed with fluorescence microscopy. Such studies estimate that at the MAM, which may comprise up to 20% of the mitochondrial outer membrane, the ER and mitochondria are separated by a mere 10–25 nm and held together by protein tethering complexes.
Purified MAM from subcellular fractionation is enriched in enzymes involved in phospholipid exchange, in addition to channels associated with Ca signaling. These hints of a prominent role for the MAM in the regulation of cellular lipid stores and signal transduction have been borne out, with significant implications for mitochondrial-associated cellular phenomena, as discussed below. Not only has the MAM provided insight into the mechanistic basis underlying such physiological processes as intrinsic apoptosis and the propagation of calcium signaling, but it also favors a more refined view of the mitochondria. Though often seen as static, isolated 'powerhouses' hijacked for cellular metabolism through an ancient endosymbiotic event, the evolution of the MAM underscores the extent to which mitochondria have been integrated into overall cellular physiology, with intimate physical and functional coupling to the endomembrane system.
Phospholipid transfer
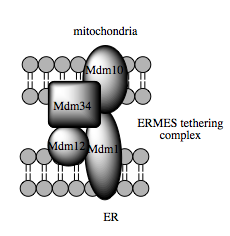
The MAM is enriched in enzymes involved in lipid biosynthesis, such as phosphatidylserine synthase on the ER face and phosphatidylserine decarboxylase on the mitochondrial face. Because mitochondria are dynamic organelles constantly undergoing fission and fusion events, they require a constant and well-regulated supply of phospholipids for membrane integrity. But mitochondria are not only a destination for the phospholipids they finish synthesis of; rather, this organelle also plays a role in inter-organelle trafficking of the intermediates and products of phospholipid biosynthetic pathways, ceramide and cholesterol metabolism, and glycosphingolipid anabolism. Such trafficking capacity depends on the MAM, which has been shown to facilitate transfer of lipid intermediates between organelles. In contrast to the standard vesicular mechanism of lipid transfer, evidence indicates that the physical proximity of the ER and mitochondrial membranes at the MAM allows for lipid flipping between opposed bilayers. Despite this unusual and seemingly energetically unfavorable mechanism, such transport does not require ATP. Instead, in yeast, it has been shown to be dependent on a multiprotein tethering structure termed the ER-mitochondria encounter structure, or ERMES, although it remains unclear whether this structure directly mediates lipid transfer or is required to keep the membranes in sufficiently close proximity to lower theenergy barrier
In chemistry and physics, activation energy is the minimum amount of energy that must be provided for compounds to result in a chemical reaction. The activation energy (''E''a) of a reaction is measured in joules per mole (J/mol), kilojoules pe ...
for lipid
Lipids are a broad group of naturally-occurring molecules which includes fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids in ...
flipping.
The MAM may also be part of the secretory pathway, in addition to its role in intracellular lipid trafficking. In particular, the MAM appears to be an intermediate destination between the rough ER and the Golgi in the pathway that leads to very-low-density lipoprotein, or VLDL, assembly and secretion. The MAM thus serves as a critical metabolic and trafficking hub in lipid metabolism.
Calcium signaling
A critical role for the ER in calcium signaling was acknowledged before such a role for the mitochondria was widely accepted, in part because the low affinity of Ca channels localized to the outer mitochondrial membrane seemed to contradict this organelle's purported responsiveness to changes in intracellular Ca flux. But the presence of the MAM resolves this apparent contradiction: the close physical association between the two organelles results in Ca microdomains at contact points that facilitate efficient Ca transmission from the ER to the mitochondria. Transmission occurs in response to so-called "Ca puffs" generated by spontaneous clustering and activation of IP3R, a canonical ER membrane Ca channel. The fate of these puffs—in particular, whether they remain restricted to isolated locales or integrated into Ca waves for propagation throughout the cell—is determined in large part by MAM dynamics. Although reuptake of Ca by the ER (concomitant with its release) modulates the intensity of the puffs, thus insulating mitochondria to a certain degree from high Ca exposure, the MAM often serves as a firewall that essentially buffers Ca puffs by acting as a sink into which free ions released into the cytosol can be funneled. This Ca tunneling occurs through the low-affinity Ca receptor VDAC1, which recently has been shown to be physically tethered to the IP3R clusters on the ER membrane and enriched at the MAM. The ability of mitochondria to serve as a Ca sink is a result of the electrochemical gradient generated during oxidative phosphorylation, which makes tunneling of the cation an exergonic process. Normal, mild calcium influx from cytosol into the mitochondrial matrix causes transient depolarization that is corrected by pumping out protons. But transmission of Ca is not unidirectional; rather, it is a two-way street. The properties of the Ca pump SERCA and the channel IP3R present on the ER membrane facilitate feedback regulation coordinated by MAM function. In particular, the clearance of Ca by the MAM allows forspatio-temporal pattern
Spatiotemporal patterns are patterns that occur in a wide range of natural phenoma and are characterized by a spatial and a temporal patterning. The general rules of pattern formation hold. In contrast to "static", pure spatial patterns, the ...
ing of Ca signaling because Ca alters IP3R activity in a biphasic manner. SERCA is likewise affected by mitochondrial feedback: uptake of Ca by the MAM stimulates ATP production, thus providing energy that enables SERCA to reload the ER with Ca for continued Ca efflux at the MAM. Thus, the MAM is not a passive buffer for Ca puffs; rather it helps modulate further Ca signaling through feedback loops that affect ER dynamics.
Regulating ER release of Ca at the MAM is especially critical because only a certain window of Ca uptake sustains the mitochondria, and consequently the cell, at homeostasis. Sufficient intraorganelle Ca signaling is required to stimulate metabolism by activating dehydrogenase enzymes critical to flux through the citric acid cycle. However, once Ca signaling in the mitochondria passes a certain threshold, it stimulates the intrinsic pathway of apoptosis in part by collapsing the mitochondrial membrane potential required for metabolism. Studies examining the role of pro- and anti-apoptotic factors support this model; for example, the anti-apoptotic factor Bcl-2 has been shown to interact with IP3Rs to reduce Ca filling of the ER, leading to reduced efflux at the MAM and preventing collapse of the mitochondrial membrane potential post-apoptotic stimuli. Given the need for such fine regulation of Ca signaling, it is perhaps unsurprising that dysregulated mitochondrial Ca has been implicated in several neurodegenerative diseases, while the catalogue of tumor suppressors includes a few that are enriched at the MAM.
Molecular basis for tethering
Recent advances in the identification of the tethers between the mitochondrial and ER membranes suggest that the scaffolding function of the molecular elements involved is secondary to other, non-structural functions. In yeast, ERMES, a multiprotein complex of interacting ER- and mitochondrial-resident membrane proteins, is required for lipid transfer at the MAM and exemplifies this principle. One of its components, for example, is also a constituent of the protein complex required for insertion of transmembrane beta-barrel proteins into the lipid bilayer. However, a homologue of the ERMES complex has not yet been identified in mammalian cells. Other proteins implicated in scaffolding likewise have functions independent of structural tethering at the MAM; for example, ER-resident and mitochondrial-resident mitofusins form heterocomplexes that regulate the number of inter-organelle contact sites, although mitofusins were first identified for their role in fission and fusion events between individual mitochondria.Glucose
Glucose is a simple sugar with the molecular formula . Glucose is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. Glucose is mainly made by plants and most algae during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, u ...
-related protein 75 (grp75) is another dual-function protein. In addition to the matrix pool of grp75, a portion serves as a chaperone that physically links the mitochondrial and ER Ca channels VDAC and IP3R for efficient Ca transmission at the MAM. Another potential tether is Sigma-1R, a non-opioid receptor whose stabilization of ER-resident IP3R may preserve communication at the MAM during the metabolic stress response.

Perspective
The MAM is a critical signaling, metabolic, and trafficking hub in the cell that allows for the integration of ER and mitochondrial physiology. Coupling between these organelles is not simply structural but functional as well and critical for overall cellular physiology andhomeostasis
In biology, homeostasis ( British also homoeostasis) (/hɒmɪə(ʊ)ˈsteɪsɪs/) is the state of steady internal, physical, and chemical conditions maintained by living systems. This is the condition of optimal functioning for the organism and ...
. The MAM thus offers a perspective on mitochondria that diverges from the traditional view of this organelle as a static, isolated unit appropriated for its metabolic capacity by the cell. Instead, this mitochondrial-ER interface emphasizes the integration of the mitochondria, the product of an endosymbiotic event, into diverse cellular processes. Recently it has also been shown, that mitochondria and MAM-s in neurons are anchored to specialised intercellular communication sites (so called somatic-junctions). Microglial processes monitor and protect neuronal functions at these sites, and MAM-s are supposed to have an important role in this type of cellular quality-control.
Origin and evolution
There are two hypotheses about the origin of mitochondria: endosymbiotic and autogenous. The endosymbiotic hypothesis suggests that mitochondria were originally prokaryotic cells, capable of implementing oxidative mechanisms that were not possible for eukaryotic cells; they became endosymbionts living inside the eukaryote. In the autogenous hypothesis, mitochondria were born by splitting off a portion of DNA from the nucleus of the eukaryotic cell at the time of divergence with the prokaryotes; this DNA portion would have been enclosed by membranes, which could not be crossed by proteins. Since mitochondria have many features in common withbacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were am ...
, the endosymbiotic hypothesis is the more widely accepted of the two accounts.
A mitochondrion contains DNA, which is organized as several copies of a single, usually circular chromosome
A chromosome is a long DNA molecule with part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells the most important of these proteins ar ...
. This mitochondrial chromosome contains genes for redox
Redox (reduction–oxidation, , ) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of substrate change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is the gain of electrons or ...
proteins, such as those of the respiratory chain. The CoRR hypothesis proposes that this co-location is required for redox regulation. The mitochondrial genome
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding ...
codes for some RNAs of ribosomes, and the 22 tRNAs necessary for the translation of mRNA
In molecular biology, messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) is a single-stranded molecule of RNA that corresponds to the genetic sequence of a gene, and is read by a ribosome in the process of synthesizing a protein.
mRNA is created during the ...
s into protein. The circular structure is also found in prokaryotes. The proto-mitochondrion
The proto-mitochondrion is the hypothetical ancestral bacterial endosymbiont from which all mitochondria in eukaryotes are thought to descend, after an episode of symbiogenesis which created the aerobic eukaryotes.
Phylogeny
The phylogenetic ana ...
was probably closely related to ''Rickettsia
''Rickettsia'' is a genus of nonmotile, gram-negative, nonspore-forming, highly pleomorphic bacteria that may occur in the forms of cocci (0.1 μm in diameter), bacilli (1–4 μm long), or threads (up to about 10 μm long). The term "ricke ...
''. However, the exact relationship of the ancestor of mitochondria to the alphaproteobacteria and whether the mitochondrion was formed at the same time or after the nucleus, remains controversial. For example, it has been suggested that the SAR11 clade of bacteria shares a relatively recent common ancestor with the mitochondria, while phylogenomic analyses indicate that mitochondria evolved from a Pseudomonadota lineage that is closely related to or a member of alphaproteobacteria. Some papers describe mitochondria as sister to the alphaproteobactera, together forming the sister the marineproteo1 group, together forming the sister to Magnetococcidae
The Magnetococcales were an order of Alphaproteobacteria, but now the mitochondria are considered as sister to the alphaproteobactera, together forming the sister the marineproteo1 group, together forming the sister to Magnetococcidae.
See a ...
.
The ribosomes coded for by the mitochondrial DNA are similar to those from bacteria in size and structure. They closely resemble the bacterial 70S ribosome and not the 80S cytoplasm
In cell biology, the cytoplasm is all of the material within a eukaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, except for the cell nucleus. The material inside the nucleus and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. ...
ic ribosomes, which are coded for by nuclear
Nuclear may refer to:
Physics
Relating to the nucleus of the atom:
*Nuclear engineering
*Nuclear physics
*Nuclear power
*Nuclear reactor
*Nuclear weapon
*Nuclear medicine
*Radiation therapy
*Nuclear warfare
Mathematics
*Nuclear space
*Nuclear ...
DNA.
The endosymbiotic relationship of mitochondria with their host cells was popularized by Lynn Margulis. The endosymbiotic hypothesis
Symbiogenesis (endosymbiotic theory, or serial endosymbiotic theory,) is the leading evolutionary theory of the origin of eukaryotic cells from prokaryotic organisms. The theory holds that mitochondria, plastids such as chloroplasts, and possibly ...
suggests that mitochondria descended from aerobic bacteria that somehow survived endocytosis by another cell, and became incorporated into the cytoplasm
In cell biology, the cytoplasm is all of the material within a eukaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, except for the cell nucleus. The material inside the nucleus and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. ...
. The ability of these bacteria to conduct respiration in host cells that had relied on glycolysis and fermentation would have provided a considerable evolutionary advantage. This symbiotic relationship probably developed 1.7 to 2 billion years ago.
 A few groups of unicellular eukaryotes have only vestigial mitochondria or derived structures: The
A few groups of unicellular eukaryotes have only vestigial mitochondria or derived structures: The microsporidia
Microsporidia are a group of spore-forming unicellular parasites. These spores contain an extrusion apparatus that has a coiled polar tube ending in an anchoring disc at the apical part of the spore. They were once considered protozoans or pr ...
ns, metamonads, and archamoebae
The Archamoebae are a group of protists originally thought to have evolved before the acquisition of mitochondria by eukaryotes. They include genera that are internal parasites or commensals of animals (''Entamoeba'' and ''Endolimax''). A few s ...
. These groups appear as the most primitive eukaryotes on phylogenetic trees constructed using rRNA
Ribosomal ribonucleic acid (rRNA) is a type of non-coding RNA which is the primary component of ribosomes, essential to all cells. rRNA is a ribozyme which carries out protein synthesis in ribosomes. Ribosomal RNA is transcribed from ribos ...
information, which once suggested that they appeared before the origin of mitochondria. However, this is now known to be an artifact of ''long-branch attraction
In phylogenetics, long branch attraction (LBA) is a form of systematic error whereby distantly related lineages are incorrectly inferred to be closely related. LBA arises when the amount of molecular or morphological change accumulated within a lin ...
'': They are derived groups and retain genes or organelles derived from mitochondria (e. g., mitosomes and hydrogenosomes). Hydrogenosomes, mitosomes, and related organelles as found in some loricifera (e. g. '' Spinoloricus'') and myxozoa (e. g. '' Henneguya zschokkei'') are together classified as MROs, mitochondrion-related organelles.
Monocercomonoides
''Monocercomonoides'' is a genus of flagellate Excavata belonging to the order Oxymonadida. It was established by Bernard V. Travis and was first described as those with "polymastiginid flagellates having three anterior flagella and a trailing ...
appear to have lost their mitochondria completely and at least some of the mitochondrial functions seem to be carried out by cytoplasmic proteins now''.''
Mitochondrial genetics
rRNA
Ribosomal ribonucleic acid (rRNA) is a type of non-coding RNA which is the primary component of ribosomes, essential to all cells. rRNA is a ribozyme which carries out protein synthesis in ribosomes. Ribosomal RNA is transcribed from ribos ...
(12S and 16S rRNA). One mitochondrion can contain two to ten copies of its DNA. One of the two mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) strands has a disproportionately higher ratio of the heavier nucleotides adenine and guanine, and this is termed the heavy strand (or H strand), whereas the other strand is termed the light strand (or L strand). The weight difference allows the two strands to be separated by centrifugation. mtDNA has one long non-coding stretch known as the non-coding region (NCR), which contains the heavy strand promoter (HSP) and light strand promoter (LSP) for RNA transcription, the origin of replication for the H strand (OriH) localized on the L strand, three conserved sequence boxes (CSBs 1–3), and a termination-associated sequence (TAS). The origin of replication for the L strand (OriL) is localized on the H strand 11,000 bp downstream of OriH, located within a cluster of genes coding for tRNA.
As in prokaryotes, there is a very high proportion of coding DNA and an absence of repeats. Mitochondrial genes are transcribed as multigenic transcripts, which are cleaved and polyadenylated to yield mature mRNA
In molecular biology, messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) is a single-stranded molecule of RNA that corresponds to the genetic sequence of a gene, and is read by a ribosome in the process of synthesizing a protein.
mRNA is created during the ...
s. Most proteins necessary for mitochondrial function are encoded by genes in the cell nucleus
The cell nucleus (pl. nuclei; from Latin or , meaning ''kernel'' or ''seed'') is a membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types, such as mammalian red blood cells, h ...
and the corresponding proteins are imported into the mitochondrion. The exact number of genes encoded by the nucleus and the mitochondrial genome differs between species. Most mitochondrial genomes are circular. In general, mitochondrial DNA lacks introns, as is the case in the human mitochondrial genome; however, introns have been observed in some eukaryotic mitochondrial DNA, such as that of yeast
Yeasts are eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms classified as members of the fungus kingdom. The first yeast originated hundreds of millions of years ago, and at least 1,500 species are currently recognized. They are estimated to constit ...
and protist
A protist () is any eukaryotic organism (that is, an organism whose cells contain a cell nucleus) that is not an animal, plant, or fungus. While it is likely that protists share a common ancestor (the last eukaryotic common ancestor), the e ...
s, including '' Dictyostelium discoideum''. Between protein-coding regions, tRNAs are present. Mitochondrial tRNA genes have different sequences from the nuclear tRNAs, but lookalikes of mitochondrial tRNAs have been found in the nuclear chromosomes with high sequence similarity.
In animals, the mitochondrial genome is typically a single circular chromosome that is approximately 16 kb long and has 37 genes. The genes, while highly conserved, may vary in location. Curiously, this pattern is not found in the human body louse (''Pediculus humanus
''Pediculus humanus'' is a species of louse that infects humans. It comprises two subspecies:
*''Pediculus humanus humanus'' Linnaeus, 1758 – body louse
The body louse (''Pediculus humanus humanus'', also known as ''Pediculus humanus cor ...
''). Instead, this mitochondrial genome is arranged in 18 minicircular chromosomes, each of which is 3–4 kb long and has one to three genes. This pattern is also found in other sucking lice
Sucking lice (Anoplura, formerly known as Siphunculata) have around 500 species and represent the smaller of the two traditional superfamilies of lice. As opposed to the paraphyletic chewing lice, which are now divided among three suborders, th ...
, but not in chewing lice
The Mallophaga are a possibly paraphyletic section of lice
Louse ( : lice) is the common name for any member of the clade Phthiraptera, which contains nearly 5,000 species of wingless parasitic insects. Phthiraptera has variously been reco ...
. Recombination has been shown to occur between the minichromosomes.
Human population genetic studies
The near-absence of genetic recombination in mitochondrial DNA makes it a useful source of information for studyingpopulation genetics
Population genetics is a subfield of genetics that deals with genetic differences within and between populations, and is a part of evolutionary biology. Studies in this branch of biology examine such phenomena as adaptation, speciation, and po ...
and evolutionary biology
Evolutionary biology is the subfield of biology that studies the evolutionary processes (natural selection, common descent, speciation) that produced the diversity of life on Earth. It is also defined as the study of the history of life ...
. Because all the mitochondrial DNA is inherited as a single unit, or haplotype, the relationships between mitochondrial DNA from different individuals can be represented as a gene tree
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a ba ...
. Patterns in these gene trees can be used to infer the evolutionary history of populations. The classic example of this is in human evolutionary genetics
Human evolutionary genetics studies how one human genome differs from another human genome, the evolutionary past that gave rise to the human genome, and its current effects. Differences between genomes have anthropological, medical, historical a ...
, where the molecular clock
The molecular clock is a figurative term for a technique that uses the mutation rate of biomolecules to deduce the time in prehistory when two or more life forms diverged. The biomolecular data used for such calculations are usually nucleo ...
can be used to provide a recent date for mitochondrial Eve. This is often interpreted as strong support for a recent modern human expansion out of Africa. Another human example is the sequencing of mitochondrial DNA from Neanderthal
Neanderthals (, also ''Homo neanderthalensis'' and erroneously ''Homo sapiens neanderthalensis''), also written as Neandertals, are an Extinction, extinct species or subspecies of archaic humans who lived in Eurasia until about 40,000 years ag ...
bones. The relatively large evolutionary distance between the mitochondrial DNA sequences of Neanderthals and living humans has been interpreted as evidence for the lack of interbreeding between Neanderthals and modern humans.
However, mitochondrial DNA reflects only the history of the females in a population. This can be partially overcome by the use of paternal genetic sequences, such as the non-recombining region of the Y-chromosome
The Y chromosome is one of two sex chromosomes ( allosomes) in therian mammals, including humans, and many other animals. The other is the X chromosome. Y is normally the sex-determining chromosome in many species, since it is the presence or ...
.
Recent measurements of the molecular clock
The molecular clock is a figurative term for a technique that uses the mutation rate of biomolecules to deduce the time in prehistory when two or more life forms diverged. The biomolecular data used for such calculations are usually nucleo ...
for mitochondrial DNA reported a value of 1 mutation every 7884 years dating back to the most recent common ancestor of humans and apes, which is consistent with estimates of mutation rates of autosomal DNA (10 per base per generation).
Alternative genetic code
Replication and inheritance
Mitochondria divide by mitochondrial fission, a form of binary fission that is also done by bacteria although the process is tightly regulated by the host eukaryotic cell and involves communication between and contact with several other organelles. The regulation of this division differs between eukaryotes. In many single-celled eukaryotes, their growth and division are linked to thecell cycle
The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the series of events that take place in a cell that cause it to divide into two daughter cells. These events include the duplication of its DNA (DNA replication) and some of its organelles, and sub ...
. For example, a single mitochondrion may divide synchronously with the nucleus. This division and segregation process must be tightly controlled so that each daughter cell receives at least one mitochondrion. In other eukaryotes (in mammals for example), mitochondria may replicate their DNA and divide mainly in response to the energy needs of the cell, rather than in phase with the cell cycle. When the energy needs of a cell are high, mitochondria grow and divide. When energy use is low, mitochondria are destroyed or become inactive. In such examples mitochondria are apparently randomly distributed to the daughter cells during the division of the cytoplasm
In cell biology, the cytoplasm is all of the material within a eukaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, except for the cell nucleus. The material inside the nucleus and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. ...
. Mitochondrial dynamics, the balance between mitochondrial fusion and fission, is an important factor in pathologies associated with several disease conditions.
The hypothesis of mitochondrial binary fission has relied on the visualization by fluorescence microscopy and conventional transmission electron microscopy
Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) is a microscopy technique in which a beam of electrons is transmitted through a specimen to form an image. The specimen is most often an ultrathin section less than 100 nm thick or a suspension on a ...
(TEM). The resolution of fluorescence microscopy (~200 nm) is insufficient to distinguish structural details, such as double mitochondrial membrane in mitochondrial division or even to distinguish individual mitochondria when several are close together. Conventional TEM has also some technical limitations in verifying mitochondrial division. Cryo-electron tomography
Electron cryotomography (CryoET) is an imaging technique used to produce high-resolution (~1–4 nm) three-dimensional views of samples, often (but not limited to) biological macromolecules and cells. CryoET is a specialized application of tra ...
was recently used to visualize mitochondrial division in frozen hydrated intact cells. It revealed that mitochondria divide by budding.
An individual's mitochondrial genes are inherited only from the mother, with rare exceptions. In humans, when an egg cell is fertilized by a sperm, the mitochondria, and therefore the mitochondrial DNA, usually come from the egg only. The sperm's mitochondria enter the egg, but do not contribute genetic information to the embryo. Instead, paternal mitochondria are marked with ubiquitin to select them for later destruction inside the embryo
An embryo is an initial stage of development of a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male spe ...
. The egg cell contains relatively few mitochondria, but these mitochondria divide to populate the cells of the adult organism. This mode is seen in most organisms, including the majority of animals. However, mitochondria in some species can sometimes be inherited paternally. This is the norm among certain coniferous plants, although not in pine tree
A pine is any conifer tree or shrub in the genus ''Pinus'' () of the family Pinaceae. ''Pinus'' is the sole genus in the subfamily Pinoideae. The World Flora Online created by the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew and Missouri Botanical Garden ac ...
s and yew
Yew is a common name given to various species of trees.
It is most prominently given to any of various coniferous trees and shrubs in the genus ''Taxus'':
* European yew or common yew (''Taxus baccata'')
* Pacific yew or western yew (''Taxus br ...
s. For Mytilids, paternal inheritance only occurs within males of the species. It has been suggested that it occurs at a very low level in humans.
Uniparental inheritance Uniparental inheritance is a non-Mendelian form of inheritance that consists of the transmission of genotypes from one parental type to all progeny. That is, all the genes in offspring will originate from only the mother or only the father. This phe ...
leads to little opportunity for genetic recombination between different lineages of mitochondria, although a single mitochondrion can contain 2–10 copies of its DNA. What recombination does take place maintains genetic integrity rather than maintaining diversity. However, there are studies showing evidence of recombination in mitochondrial DNA. It is clear that the enzymes necessary for recombination are present in mammalian cells. Further, evidence suggests that animal mitochondria can undergo recombination. The data are more controversial in humans, although indirect evidence of recombination exists.
Entities undergoing uniparental inheritance and with little to no recombination may be expected to be subject to Muller's ratchet, the accumulation of deleterious mutations until functionality is lost. Animal populations of mitochondria avoid this buildup through a developmental process known as the mtDNA bottleneck. The bottleneck exploits stochastic processes in the cell to increase the cell-to-cell variability in mutant load as an organism develops: a single egg cell with some proportion of mutant mtDNA thus produces an embryo where different cells have different mutant loads. Cell-level selection may then act to remove those cells with more mutant mtDNA, leading to a stabilization or reduction in mutant load between generations. The mechanism underlying the bottleneck is debated, with a recent mathematical and experimental metastudy providing evidence for a combination of random partitioning of mtDNAs at cell divisions and random turnover of mtDNA molecules within the cell.
DNA repair
Mitochondria can repair oxidativeDNA damage
DNA repair is a collection of processes by which a cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. In human cells, both normal metabolic activities and environmental factors such as radiation can cause DNA d ...
by mechanisms analogous to those occurring in the cell nucleus
The cell nucleus (pl. nuclei; from Latin or , meaning ''kernel'' or ''seed'') is a membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types, such as mammalian red blood cells, h ...
. The proteins employed in mtDNA repair are encoded by nuclear gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a b ...
s, and are translocated to the mitochondria. The DNA repair
DNA repair is a collection of processes by which a cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. In human cells, both normal metabolic activities and environmental factors such as radiation can cause DNA d ...
pathways in mammalian mitochondria include base excision repair
Base excision repair (BER) is a cellular mechanism, studied in the fields of biochemistry and genetics, that repairs damaged DNA throughout the cell cycle. It is responsible primarily for removing small, non-helix-distorting base lesions from ...
, double-strand break repair, direct reversal and mismatch repair. Alternatively, DNA damage may be bypassed, rather than repaired, by translesion synthesis.
Of the several DNA repair process in mitochondria, the base excision repair pathway has been most comprehensively studied. Base excision repair is carried out by a sequence of enzyme-catalyzed steps that include recognition and excision of a damaged DNA base, removal of the resulting abasic site, end processing, gap filling and ligation. A common damage in mtDNA that is repaired by base excision repair is 8-oxoguanine produced by oxidation of guanine
Guanine () ( symbol G or Gua) is one of the four main nucleobases found in the nucleic acids DNA and RNA, the others being adenine, cytosine, and thymine ( uracil in RNA). In DNA, guanine is paired with cytosine. The guanine nucleoside is ...
.
Double-strand breaks can be repaired by homologous recombination
Homologous recombination is a type of genetic recombination in which genetic information is exchanged between two similar or identical molecules of double-stranded or single-stranded nucleic acids (usually DNA as in cellular organisms but may ...
al repair in both mammalian mtDNA and plant mtDNA. Double-strand breaks in mtDNA can also be repaired by microhomology-mediated end joining. Although there is evidence for the repair processes of direct reversal and mismatch repair in mtDNA, these processes are not well characterized.
Lack of mitochondrial DNA
Some organisms have lost mitochondrial DNA altogether. In these cases, genes encoded by the mitochondrial DNA have been lost or transferred to the nucleus. '' Cryptosporidium'' have mitochondria that lack any DNA, presumably because all their genes have been lost or transferred. In ''Cryptosporidium'', the mitochondria have an altered ATP generation system that renders the parasite resistant to many classical mitochondrial inhibitors such ascyanide
Cyanide is a naturally occurring, rapidly acting, toxic chemical that can exist in many different forms.
In chemistry, a cyanide () is a chemical compound that contains a functional group. This group, known as the cyano group, consists of ...
, azide, and atovaquone. Mitochondria that lack their own DNA have been found in a marine parasitic dinoflagellate from the genus '' Amoebophyra''. This microorganism, ''A. cerati'', has functional mitochondria that lack a genome. In related species, the mitochondrial genome still has three genes, but in ''A. cerati'' only a single mitochondrial gene — the cytochrome c oxidase I gene (''cox1'') — is found, and it has migrated to the genome of the nucleus.
Dysfunction and disease
Mitochondrial diseases
Damage and subsequent dysfunction in mitochondria is an important factor in a range of human diseases due to their influence in cell metabolism. Mitochondrial disorders often present as neurological disorders, including autism. They can also manifest as myopathy,diabetes
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level ( hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased ...
, multiple endocrinopathy, and a variety of other systemic disorders. Diseases caused by mutation in the mtDNA include Kearns–Sayre syndrome, MELAS syndrome
Mitochondrial encephalopathy, lactic acidosis, and stroke-like episodes (MELAS) is one of the family of mitochondrial diseases, which also include MIDD (maternally inherited diabetes and deafness, MERRF syndrome, and Leber's hereditary optic n ...
and Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy. In the vast majority of cases, these diseases are transmitted by a female to her children, as the zygote
A zygote (, ) is a eukaryotic cell formed by a fertilization event between two gametes. The zygote's genome is a combination of the DNA in each gamete, and contains all of the genetic information of a new individual organism.
In multicell ...
derives its mitochondria and hence its mtDNA from the ovum. Diseases such as Kearns-Sayre syndrome, Pearson syndrome
Pearson syndrome is a mitochondrial disease characterized by sideroblastic anemia and exocrine pancreas dysfunction. Other clinical features are failure to thrive, pancreatic fibrosis with insulin-dependent diabetes and exocrine pancreatic defici ...
, and progressive external ophthalmoplegia are thought to be due to large-scale mtDNA rearrangements, whereas other diseases such as MELAS syndrome, Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy, MERRF syndrome, and others are due to point mutations in mtDNA.
It has also been reported that drug tolerant cancer cells have an increased number and size of mitochondria which suggested an increase in mitochondrial biogenesis. Interestingly, a recent study in ''Nature Nanotechnology'' has reported that cancer cells can hijack the mitochondria from immune cells via physical tunneling nanotubes.
In other diseases, defects in nuclear genes lead to dysfunction of mitochondrial proteins. This is the case in Friedreich's ataxia
Friedreich's ataxia (FRDA or FA) is an autosomal-recessive genetic disease that causes difficulty walking, a loss of sensation in the arms and legs, and impaired speech that worsens over time. Symptoms generally start between 5 and 20 year ...
, hereditary spastic paraplegia, and Wilson's disease. These diseases are inherited in a dominance relationship, as applies to most other genetic diseases. A variety of disorders can be caused by nuclear mutations of oxidative phosphorylation enzymes, such as coenzyme Q10 deficiency and Barth syndrome
Barth syndrome (BTHS) is a rare but serious X-linked genetic disorder, caused by changes in phospholipid structure and metabolism. It may affect multiple body systems (though mainly characterized by pronounced pediatric-onset cardiomyopathy), and ...
. Environmental influences may interact with hereditary predispositions and cause mitochondrial disease. For example, there may be a link between pesticide exposure and the later onset of Parkinson's disease
Parkinson's disease (PD), or simply Parkinson's, is a long-term degenerative disorder of the central nervous system that mainly affects the motor system. The symptoms usually emerge slowly, and as the disease worsens, non-motor symptoms beco ...
. Other pathologies with etiology involving mitochondrial dysfunction include schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a mental disorder characterized by continuous or relapsing episodes of psychosis. Major symptoms include hallucinations (typically hearing voices), delusions, and disorganized thinking. Other symptoms include social w ...
, bipolar disorder
Bipolar disorder, previously known as manic depression, is a mental disorder characterized by periods of Depression (mood), depression and periods of abnormally elevated Mood (psychology), mood that last from days to weeks each. If the elevat ...
, dementia
Dementia is a disorder which manifests as a set of related symptoms, which usually surfaces when the brain is damaged by injury or disease. The symptoms involve progressive impairments in memory, thinking, and behavior, which negatively affe ...
, Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, epilepsy
Epilepsy is a group of non-communicable neurological disorders characterized by recurrent epileptic seizures. Epileptic seizures can vary from brief and nearly undetectable periods to long periods of vigorous shaking due to abnormal electrica ...
, stroke
A stroke is a disease, medical condition in which poor cerebral circulation, blood flow to the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: brain ischemia, ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and intracranial hemorrhage, hemorr ...
, cardiovascular disease, chronic fatigue syndrome, retinitis pigmentosa, and diabetes mellitus
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level ( hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased ...
.
Mitochondria-mediated oxidative stress plays a role in cardiomyopathy in type 2 diabetics
Type 2 diabetes, formerly known as adult-onset diabetes, is a form of diabetes mellitus that is characterized by high blood sugar, insulin resistance, and relative lack of insulin. Common symptoms include increased thirst, frequent urination, ...
. Increased fatty acid delivery to the heart increases fatty acid uptake by cardiomyocytes, resulting in increased fatty acid oxidation in these cells. This process increases the reducing equivalents available to the electron transport chain of the mitochondria, ultimately increasing reactive oxygen species (ROS) production. ROS increases uncoupling proteins (UCPs) and potentiate proton leakage through the adenine nucleotide translocator (ANT), the combination of which uncouples the mitochondria. Uncoupling then increases oxygen consumption by the mitochondria, compounding the increase in fatty acid oxidation. This creates a vicious cycle of uncoupling; furthermore, even though oxygen consumption increases, ATP synthesis does not increase proportionally because the mitochondria are uncoupled. Less ATP availability ultimately results in an energy deficit presenting as reduced cardiac efficiency and contractile dysfunction. To compound the problem, impaired sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium release and reduced mitochondrial reuptake limits peak cytosolic levels of the important signaling ion during muscle contraction. Decreased intra-mitochondrial calcium concentration increases dehydrogenase activation and ATP synthesis. So in addition to lower ATP synthesis due to fatty acid oxidation, ATP synthesis is impaired by poor calcium signaling as well, causing cardiac problems for diabetics.
Relationships to aging
There may be some leakage of the electrons transferred in the respiratory chain to form reactive oxygen species. This was thought to result in significant oxidative stress in the mitochondria with high mutation rates of mitochondrial DNA. Hypothesized links between aging and oxidative stress are not new and were proposed in 1956, which was later refined into the mitochondrial free radical theory of aging. A vicious cycle was thought to occur, as oxidative stress leads to mitochondrial DNA mutations, which can lead to enzymatic abnormalities and further oxidative stress. A number of changes can occur to mitochondria during the aging process. Tissues from elderly humans show a decrease in enzymatic activity of the proteins of the respiratory chain. However, mutated mtDNA can only be found in about 0.2% of very old cells. Large deletions in the mitochondrial genome have been hypothesized to lead to high levels of oxidative stress and neuronal death inParkinson's disease
Parkinson's disease (PD), or simply Parkinson's, is a long-term degenerative disorder of the central nervous system that mainly affects the motor system. The symptoms usually emerge slowly, and as the disease worsens, non-motor symptoms beco ...
. Mitochondrial dysfunction has also been shown to occur in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.
Since mitochondria cover a pivotal role in the ovarian function, by providing ATP necessary for the development from germinal vesicle to mature oocyte
An oocyte (, ), oöcyte, or ovocyte is a female gametocyte or germ cell involved in reproduction. In other words, it is an immature ovum, or egg cell. An oocyte is produced in a female fetus in the ovary during female gametogenesis. The female ...
, a decreased mitochondria function can lead to inflammation, resulting in premature ovarian failure and accelerated ovarian aging. The resulting dysfunction is then reflected in quantitative (such as mtDNA copy number and mtDNA deletions), qualitative (such as mutations and strand breaks) and oxidative damage (such as dysfunctional mitochondria due to ROS), which are not only relevant in ovarian aging, but perturb oocyte-cumulus crosstalk in the ovary, are linked to genetic disorders (such as Fragile X) and can interfere with embryo selection.
History
The first observations of intracellular structures that probably represented mitochondria were published in 1857, by the physiologist Albert von Kolliker.Richard Altmann
Richard Altmann (12 March 1852 – 8 December 1900) was a German pathologist and histologist from Deutsch Eylau in the Province of Prussia.
Altmann studied medicine in Greifswald, Königsberg, Marburg, and Giessen, obtaining a doctorate at ...
, in 1890, established them as cell organelles and called them "bioblasts." In 1898, Carl Benda coined the term "mitochondria" from the Greek , , "thread", and , , "granule." Leonor Michaelis
Leonor Michaelis (16 January 1875 – 8 October 1949) was a German biochemist, physical chemist, and physician, known for his work with Maud Menten on enzyme kinetics in 1913, as well as for work on enzyme inhibition, pH and quinones.
Ear ...
discovered that Janus green can be used as a supravital stain for mitochondria in 1900. In 1904, Friedrich Meves, made the first recorded observation of mitochondria in plants in cells of the white waterlily, ''Nymphaea alba
''Nymphaea alba'', the white waterlily, European white water lily or white nenuphar , is an aquatic flowering plant in the family Nymphaeaceae. It is native to North Africa, temperate Asia, Europe and tropical Asia (Jammu and Kashmir).
Descript ...
'' and in 1908, along with Claudius Regaud
Claudius Regaud (born 30 January 1870 in Lyons, France; died 29 December 1940 in Couzon-au-Mont-d'Or, France) was a French doctor and biologist, one of the pioneers in radiotherapy at the Curie Institute.
Scientific work
In 1906, Regaud disc ...
, suggested that they contain proteins and lipids. Benjamin F. Kingsbury, in 1912, first related them with cell respiration, but almost exclusively based on morphological observations. In 1913, particles from extracts of guinea-pig liver were linked to respiration by Otto Heinrich Warburg, which he called "grana." Warburg and Heinrich Otto Wieland
Heinrich Otto Wieland (; 4 June 1877 – 5 August 1957) was a German chemist. He won the 1927 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for his research into the bile acids.
Career
In 1901 Wieland received his doctorate at the University of Munich while studyin ...
, who had also postulated a similar particle mechanism, disagreed on the chemical nature of the respiration. It was not until 1925, when David Keilin discovered cytochromes, that the respiratory chain was described.
In 1939, experiments using minced muscle cells demonstrated that cellular respiration using one oxygen molecule can form four adenosine triphosphate
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is an organic compound that provides energy to drive many processes in living cells, such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, condensate dissolution, and chemical synthesis. Found in all known forms ...
(ATP) molecules, and in 1941, the concept of the phosphate bonds of ATP being a form of energy in cellular metabolism was developed by Fritz Albert Lipmann
Fritz Albert Lipmann (; June 12, 1899 – July 24, 1986) was a German-American biochemist and a co-discoverer in 1945 of coenzyme A. For this, together with other research on coenzyme A, he was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in ...
. In the following years, the mechanism behind cellular respiration was further elaborated, although its link to the mitochondria was not known. The introduction of tissue fractionation by Albert Claude allowed mitochondria to be isolated from other cell fractions and biochemical analysis to be conducted on them alone. In 1946, he concluded that cytochrome oxidase and other enzymes responsible for the respiratory chain were isolated to the mitochondria. Eugene Kennedy
Eugene Cullen Kennedy (August 28, 1928 – June 3, 2015) was a psychologist, writer, columnist, and professor emeritus of Loyola University Chicago. Kennedy was a laicized Catholic priest and a long-time observer of the Catholic Church, but his ...
and Albert Lehninger discovered in 1948 that mitochondria are the site of oxidative phosphorylation in eukaryotes. Over time, the fractionation method was further developed, improving the quality of the mitochondria isolated, and other elements of cell respiration were determined to occur in the mitochondria.
The first high-resolution electron micrographs
A micrograph or photomicrograph is a photograph or digital image taken through a microscope or similar device to show a magnified image of an object. This is opposed to a macrograph or photomacrograph, an image which is also taken on a m ...
appeared in 1952, replacing the Janus Green stains as the preferred way to visualize mitochondria. This led to a more detailed analysis of the structure of the mitochondria, including confirmation that they were surrounded by a membrane. It also showed a second membrane inside the mitochondria that folded up in ridges dividing up the inner chamber and that the size and shape of the mitochondria varied from cell to cell.
The popular term "powerhouse of the cell" was coined by Philip Siekevitz in 1957.
In 1967, it was discovered that mitochondria contained ribosomes. In 1968, methods were developed for mapping the mitochondrial genes, with the genetic and physical map of yeast mitochondrial DNA completed in 1976.
See also
* Anti-mitochondrial antibodies * Mitochondrial metabolic rates *Mitochondrial permeability transition pore
The mitochondrial permeability transition pore (mPTP or MPTP; also referred to as PTP, mTP or MTP) is a protein that is formed in the inner membrane of the mitochondria under certain pathological conditions such as traumatic brain injury and st ...
* Mitophagy
* Nebenkern The nebenkern is a mitochondrial formation in the sperm of some insects such as Drosophila. After the completion of meiosis, spermatid mitochondria wrap around each other to form a spherical aggregate, adjacent to the nucleus. The nebenkern proceeds ...
* Oncocyte
An oncocyte is an epithelial cell characterized by an excessive number of mitochondria, resulting in an abundant acidophilic, granular cytoplasm. Oncocytes can be benign or malignant.
Other names
Also known as:
*'' Hürthle cell'' (thyroid gland ...
* Oncocytoma
* Paternal mtDNA transmission In genetics, paternal mtDNA transmission and paternal mtDNA inheritance refer to the incidence of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) being passed from a father to his offspring. Paternal mtDNA inheritance is observed in a small proportion of species; in g ...
* Plastid
* Submitochondrial particle
References
General *External links
*Powering the Cell Mitochondria
– XVIVO Scientific Animation
Mitodb.com
– The mitochondrial disease database.
at University of Mainz
Mitochondria Research Portal
at mitochondrial.net
at cytochemistry.net
at
University of Alabama
The University of Alabama (informally known as Alabama, UA, or Bama) is a public research university in Tuscaloosa, Alabama. Established in 1820 and opened to students in 1831, the University of Alabama is the oldest and largest of the publ ...
MIP
Mitochondrial Physiology Society
3D structures of proteins from inner mitochondrial membrane
at
University of Michigan
, mottoeng = "Arts, Knowledge, Truth"
, former_names = Catholepistemiad, or University of Michigania (1817–1821)
, budget = $10.3 billion (2021)
, endowment = $17 billion (2021)As o ...
3D structures of proteins associated with outer mitochondrial membrane
at
University of Michigan
, mottoeng = "Arts, Knowledge, Truth"
, former_names = Catholepistemiad, or University of Michigania (1817–1821)
, budget = $10.3 billion (2021)
, endowment = $17 billion (2021)As o ...
Mitochondrial Protein Partnership
at University of Wisconsin
MitoMiner – A mitochondrial proteomics database
at
MRC Mitochondrial Biology Unit
The MRC Mitochondrial Biology Unit (formerly the MRC Dunn Human Nutrition Unit) is a department of the School of Clinical Medicine at the University of Cambridge, funded through a strategic partnership between the Medical Research Council and th ...
Mitochondrion – Cell Centered Database
at San Diego State University
Video Clip of Rat-liver Mitochondrion from Cryo-electron Tomography
{{Authority control Cellular respiration Endosymbiotic events