millipede on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Millipedes (originating from the
Other vernacular names include "thousand-legger" or simply "diplopod". The science of millipede biology and taxonomy is called diplopodology: the study of diplopods.
 Approximately 12,000 millipede
Approximately 12,000 millipede
 Although the relationships of millipede orders are still the subject of debate, the class Diplopoda as a whole is considered a monophyletic group of arthropods: all millipedes are more closely related to each other than to any other arthropods. Diplopoda is a class within the arthropod subphylum Myriapoda, the myriapods, which includes centipedes (class Chilopoda) as well as the lesser-known pauropods (class Pauropoda) and symphylans (class Symphyla). Within myriapods, the closest relatives or
Although the relationships of millipede orders are still the subject of debate, the class Diplopoda as a whole is considered a monophyletic group of arthropods: all millipedes are more closely related to each other than to any other arthropods. Diplopoda is a class within the arthropod subphylum Myriapoda, the myriapods, which includes centipedes (class Chilopoda) as well as the lesser-known pauropods (class Pauropoda) and symphylans (class Symphyla). Within myriapods, the closest relatives or


 Millipedes come in a variety of body shapes and sizes, ranging from to around in length, and can have as few as eleven to over three hundred segments. They are generally black or brown in colour, although there are a few brightly coloured species, and some have aposematic colouring to warn that they are toxic. Species of '' Motyxia'' produce cyanide as a chemical defence and are bioluminescent.
Body styles vary greatly between major millipede groups. In the basal subclass Penicillata, consisting of the tiny bristle millipedes, the exoskeleton is soft and uncalcified, and is covered in prominent setae or bristles. All other millipedes, belonging to the subclass Chilognatha, have a hardened exoskeleton. The chilognaths are in turn divided into two infraclasses: the Pentazonia, containing relatively short-bodied groups such as pill millipedes, and the Helminthomorpha ("worm-like" millipedes), which contains the vast majority of species, with long, many-segmented bodies.
They have also lost the gene that codes for the JHAMTl enzyme, which is responsible for catalysing the last step of the production of a juvenile hormone that regulates the development and reproduction in other arthropods like crustaceans, centipedes and insects.
Millipedes come in a variety of body shapes and sizes, ranging from to around in length, and can have as few as eleven to over three hundred segments. They are generally black or brown in colour, although there are a few brightly coloured species, and some have aposematic colouring to warn that they are toxic. Species of '' Motyxia'' produce cyanide as a chemical defence and are bioluminescent.
Body styles vary greatly between major millipede groups. In the basal subclass Penicillata, consisting of the tiny bristle millipedes, the exoskeleton is soft and uncalcified, and is covered in prominent setae or bristles. All other millipedes, belonging to the subclass Chilognatha, have a hardened exoskeleton. The chilognaths are in turn divided into two infraclasses: the Pentazonia, containing relatively short-bodied groups such as pill millipedes, and the Helminthomorpha ("worm-like" millipedes), which contains the vast majority of species, with long, many-segmented bodies.
They have also lost the gene that codes for the JHAMTl enzyme, which is responsible for catalysing the last step of the production of a juvenile hormone that regulates the development and reproduction in other arthropods like crustaceans, centipedes and insects.
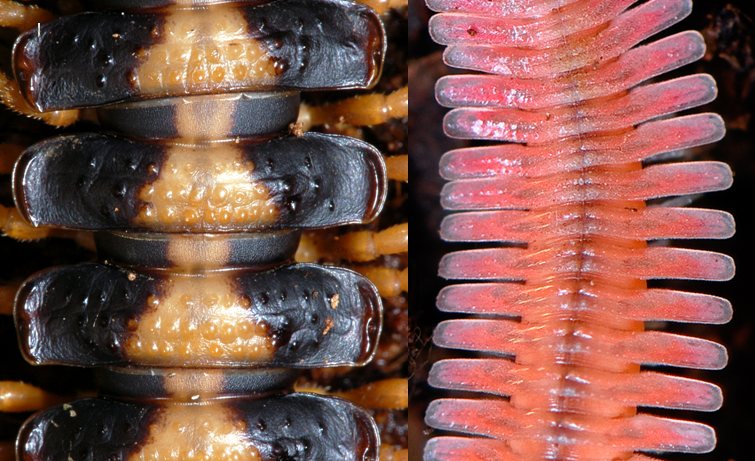 Millipede bodies may be flattened or cylindrical, and are composed of numerous metameric segments, each with an
Millipede bodies may be flattened or cylindrical, and are composed of numerous metameric segments, each with an
 Millipedes show a diversity of mating styles and structures. In the basal order Polyxenida (bristle millipedes), mating is indirect: males deposit spermatophores onto webs they secrete with special glands, and the spermatophores are subsequently picked up by females. In all other millipede groups, males possess one or two pairs of modified legs called gonopods which are used to transfer sperm to the female during copulation. The location of the gonopods differs between groups: in males of the Pentazonia they are located at the rear of the body and known as telopods and may also function in grasping females, while in the Helminthomorpha – the vast majority of species – they are located on the seventh body segment. A few species are
Millipedes show a diversity of mating styles and structures. In the basal order Polyxenida (bristle millipedes), mating is indirect: males deposit spermatophores onto webs they secrete with special glands, and the spermatophores are subsequently picked up by females. In all other millipede groups, males possess one or two pairs of modified legs called gonopods which are used to transfer sperm to the female during copulation. The location of the gonopods differs between groups: in males of the Pentazonia they are located at the rear of the body and known as telopods and may also function in grasping females, while in the Helminthomorpha – the vast majority of species – they are located on the seventh body segment. A few species are 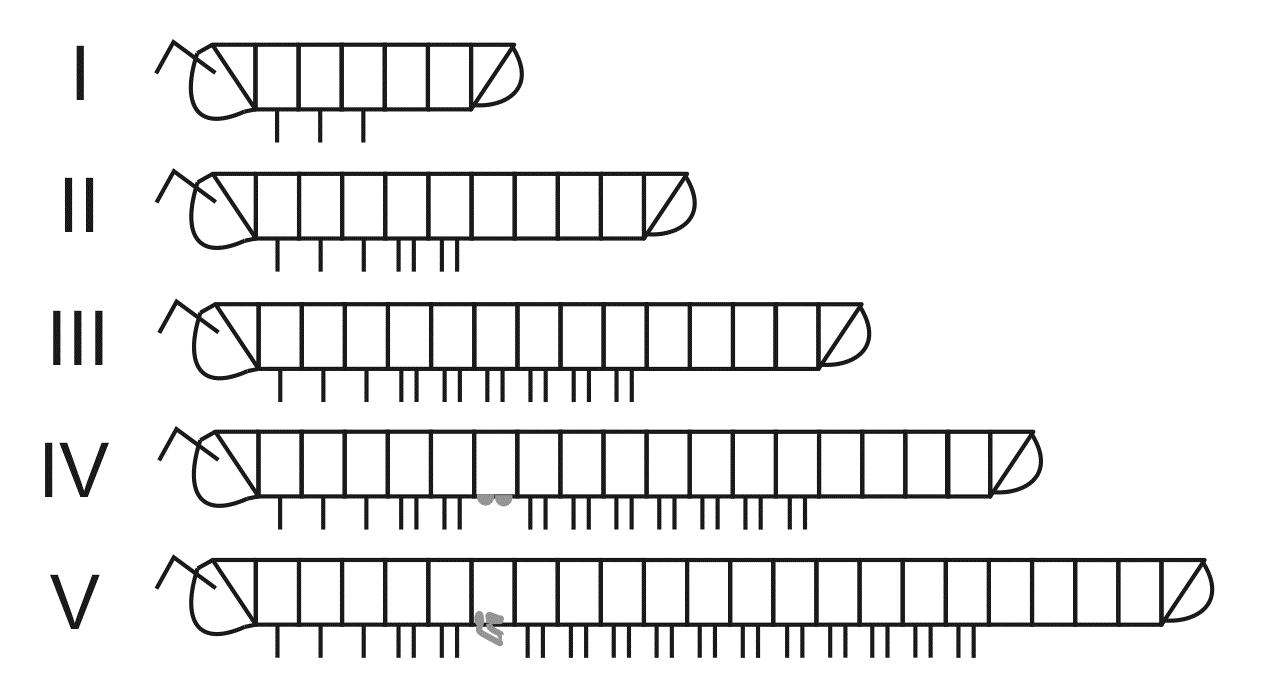 The genital openings ( gonopores) of both sexes are located on the underside of the third body segment (near the second pair of legs) and may be accompanied in the male by one or two penes which deposit the sperm packets onto the gonopods. In the female, the genital pores open into paired small sacs called cyphopods or vulvae, which are covered by small hood-like lids, and are used to store the sperm after copulation. The cyphopod morphology can also be used to identify species. Millipede
The genital openings ( gonopores) of both sexes are located on the underside of the third body segment (near the second pair of legs) and may be accompanied in the male by one or two penes which deposit the sperm packets onto the gonopods. In the female, the genital pores open into paired small sacs called cyphopods or vulvae, which are covered by small hood-like lids, and are used to store the sperm after copulation. The cyphopod morphology can also be used to identify species. Millipede

 Millipedes are preyed on by a wide range of animals, including various
Millipedes are preyed on by a wide range of animals, including various
 Some millipedes form mutualistic relationships with organisms of other species, in which both species benefit from the interaction, or commensal relationships, in which only one species benefits while the other is unaffected. Several species form close relationships with ants, a relationship known as myrmecophily, especially within the family Pyrgodesmidae (Polydesmida), which contains "obligate myrmecophiles", species which have only been found in ant colonies. More species are "facultative myrmecophiles", non-exclusively associated with ants, including many species of Polyxenida that have been found in ant nests around the world.
Many millipede species have commensal relationships with
Some millipedes form mutualistic relationships with organisms of other species, in which both species benefit from the interaction, or commensal relationships, in which only one species benefits while the other is unaffected. Several species form close relationships with ants, a relationship known as myrmecophily, especially within the family Pyrgodesmidae (Polydesmida), which contains "obligate myrmecophiles", species which have only been found in ant colonies. More species are "facultative myrmecophiles", non-exclusively associated with ants, including many species of Polyxenida that have been found in ant nests around the world.
Many millipede species have commensal relationships with
 Some millipedes are considered household pests, including '' Xenobolus carnifex'' which can infest thatched roofs in India, and '' Ommatoiulus moreleti'', which periodically invades homes in Australia. Other species exhibit periodical swarming behaviour, which can result in home invasions, crop damage, and train delays when the tracks become slippery with the crushed remains of hundreds of millipedes. Some millipedes can cause significant damage to crops: the spotted snake millipede (''Blaniulus guttulatus'') is a pest of
Some millipedes are considered household pests, including '' Xenobolus carnifex'' which can infest thatched roofs in India, and '' Ommatoiulus moreleti'', which periodically invades homes in Australia. Other species exhibit periodical swarming behaviour, which can result in home invasions, crop damage, and train delays when the tracks become slippery with the crushed remains of hundreds of millipedes. Some millipedes can cause significant damage to crops: the spotted snake millipede (''Blaniulus guttulatus'') is a pest of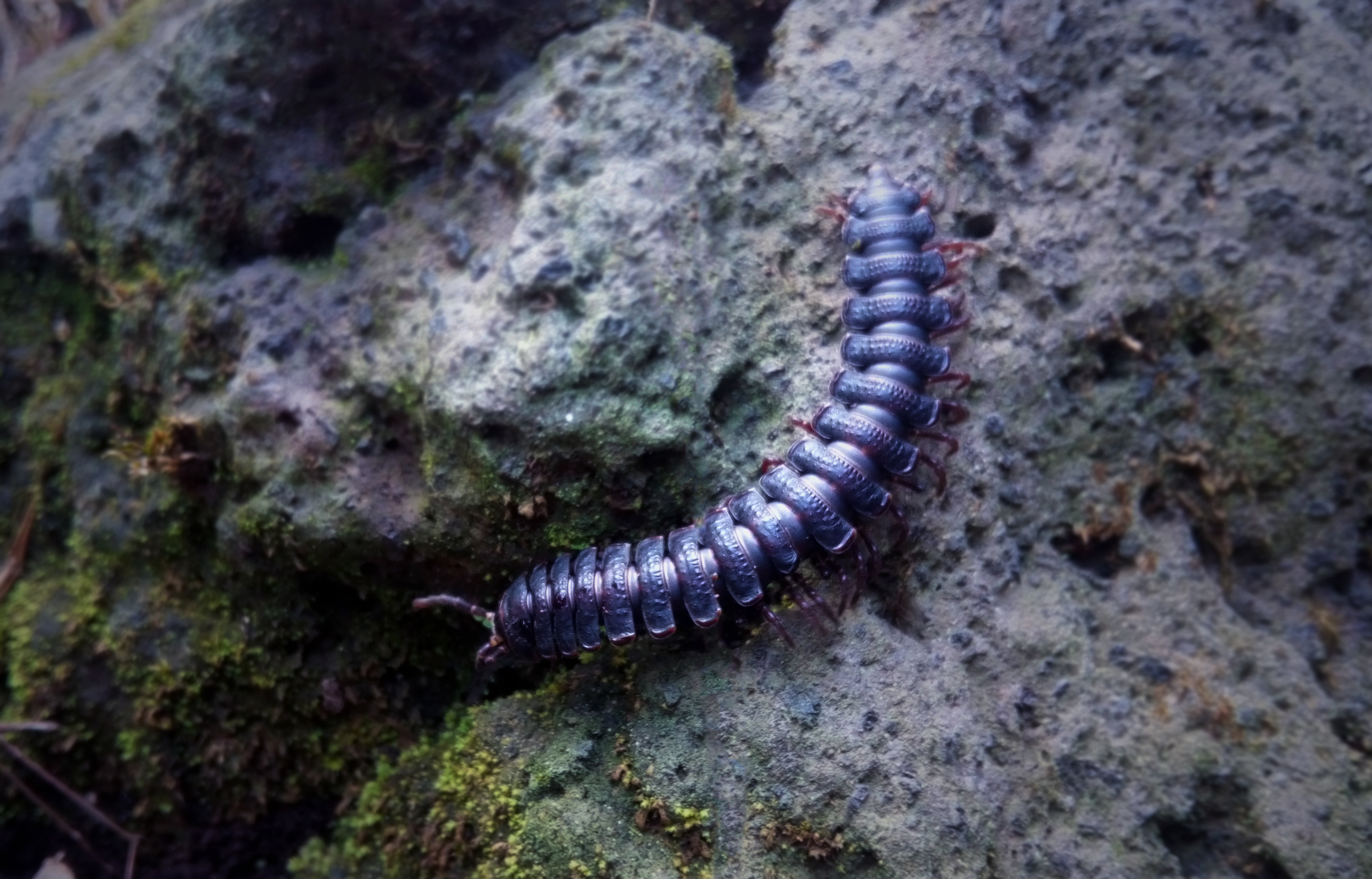  Millipedes appear in
Millipedes appear in Millicompost: an alternate biocompost for forest nurseries
/ref>
Milli-PEET: The Class Diplopoda
– The Field Museum, Chicago
Diplopoda: Guide to New Zealand Soil Invertebrates
– Massey University
British Myriapod & Isopod Group
{{DEFAULTSORT:Millipede Detritivores Wenlock first appearances Extant Silurian first appearances Myriapods Taxa named by Henri Marie Ducrotay de Blainville
Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
, "thousand", and , "foot") are a group of arthropod
Arthropods ( ) are invertebrates in the phylum Arthropoda. They possess an arthropod exoskeleton, exoskeleton with a cuticle made of chitin, often Mineralization (biology), mineralised with calcium carbonate, a body with differentiated (Metam ...
s that are characterised by having two pairs of jointed legs on most body segments; they are known scientifically as the class
Class, Classes, or The Class may refer to:
Common uses not otherwise categorized
* Class (biology), a taxonomic rank
* Class (knowledge representation), a collection of individuals or objects
* Class (philosophy), an analytical concept used d ...
Diplopoda, the name derived from this feature. Each double-legged segment is a result of two single segments fused together. Most millipedes have very elongated cylindrical or flattened bodies with more than 20 segments, while pill millipedes are shorter and can roll into a tight ball. Although the name "millipede" derives from Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
for "thousand feet", no species was known to have 1,000 or more until the discovery in 2020 of '' Eumillipes persephone'', which can have over 1,300 legs. There are approximately 12,000 named species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), ...
classified into 16 orders and around 140 families, making Diplopoda the largest class of myriapods, an arthropod group which also includes centipedes and other multi-legged creatures.
Most millipedes are slow-moving detritivores, eating decaying leaves and other dead plant matter; however, some eat fungi
A fungus (: fungi , , , or ; or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as one ...
or drink plant fluid. Millipedes are generally harmless to humans, although some can become household or garden pests. Millipedes can be an unwanted nuisance particularly in greenhouses where they can potentially cause severe damage to emergent seedlings. Most millipedes defend themselves with a variety of chemicals secreted from pores along the body, although the tiny bristle millipedes are covered with tufts of detachable bristles. Its primary defence mechanism is to curl into a tight coil, thereby protecting its legs and other vital delicate areas on the body behind a hard exoskeleton. Reproduction
Reproduction (or procreation or breeding) is the biological process by which new individual organisms – "offspring" – are produced from their "parent" or parents. There are two forms of reproduction: Asexual reproduction, asexual and Sexual ...
in most species is carried out by modified male legs called gonopods, which transfer packets of sperm to females.
First appearing in the Silurian
The Silurian ( ) is a geologic period and system spanning 23.5 million years from the end of the Ordovician Period, at million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Devonian Period, Mya. The Silurian is the third and shortest period of t ...
period, millipedes are some of the oldest known land animals. Some members of prehistoric groups, such as '' Arthropleura'', grew to over ; the largest modern species reach maximum lengths of . The longest extant species is the giant African millipede ('' Archispirostreptus gigas'').
Among myriapods, millipedes have traditionally been considered most closely related to the tiny pauropods, although some molecular studies challenge this relationship. Millipedes can be distinguished from the somewhat similar but only distantly related centipedes (class Chilopoda), which move rapidly, are venom
Venom or zootoxin is a type of toxin produced by an animal that is actively delivered through a wound by means of a bite, sting, or similar action. The toxin is delivered through a specially evolved ''venom apparatus'', such as fangs or a sti ...
ous, carnivorous, and have only a single pair of legs on each body segment.
The scientific study of millipedes is known as diplopodology, and a scientist who studies them is called a diplopodologist.
Etymology and names
The term "millipede" is widespread in popular and scientific literature, but among North American scientists, the term "milliped" (without the terminal e) is also used.Other vernacular names include "thousand-legger" or simply "diplopod". The science of millipede biology and taxonomy is called diplopodology: the study of diplopods.
Classification
 Approximately 12,000 millipede
Approximately 12,000 millipede species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), ...
have been described. Estimates of the true number of species on earth range from 15,000 to as high as 80,000. Few species of millipede are at all widespread; they have very poor dispersal abilities, depending as they do on terrestrial locomotion and humid habitats. These factors have favoured genetic isolation and rapid speciation, producing many lineages with restricted ranges.
The living members of the Diplopoda are divided into sixteen orders in two subclasses. The basal subclass Penicillata contains a single order, Polyxenida (bristle millipedes). All other millipedes belong to the subclass Chilognatha consisting of two infraclasses: Pentazonia, containing the short-bodied pill millipedes, and Helminthomorpha (worm-like millipedes), containing the great majority of the species.
Outline of classification
The higher-level classification of millipedes is presented below, based on Shear, 2011, and Shear & Edgecombe, 2010 (extinct groups). Recent cladistic and molecular studies have challenged the traditional classification schemes above, and in particular the position of the orders Siphoniulida and Polyzoniida is not yet well established. The placement and positions of extinct groups (†) known only from fossils is tentative and not fully resolved. After each name is listed the author citation: the name of the person who coined the name or defined the group, even if not at the current rank. Class Diplopoda de Blainville in Gervais, 1844 * Subclass Penicillata Latreille, 1831 ** Order Polyxenida Verhoeff, 1934 * Subclass † Arthropleuridea (placed in Penicillata by some authors) **Order † Arthropleurida Waterlot, 1934 ** Order † Eoarthropleurida Shear & Selden, 1995 ** Order † Microdecemplicida Wilson & Shear, 2000 * Subclass Chilognatha Latreille, 1802 ** Order † Zosterogrammida Wilson, 2005 (Chilognatha '' incertae sedis'') ** Infraclass Pentazonia Brandt, 1833 *** Order † Amynilyspedida Hoffman, 1969 *** Superorder Limacomorpha Pocock, 1894 **** Order Glomeridesmida Cook, 1895 *** Superorder Oniscomorpha Pocock, 1887 **** Order Glomerida Brandt, 1833 **** OrderSphaerotheriida
Sphaerotheriida is an order (biology), order of millipedes in the infraclass Pentazonia, sometimes known as giant pill millipedes. They inhabit Southern Africa, Madagascar, South and Southeast Asia, Australia and New Zealand. Like the Northern He ...
Brandt, 1833
** Infraclass Helminthomorpha Pocock, 1887
*** Superorder † Archipolypoda Scudder, 1882
**** Order † Archidesmida Wilson & Anderson 2004
**** Order † Cowiedesmida Wilson & Anderson 2004
**** Order † Euphoberiida Hoffman, 1969
**** Order † Palaeosomatida Hannibal & Krzeminski, 2005
*** Order † Pleurojulida Schneider & Werneburg, 1998 (possibly sister to Colobognatha)
*** Subterclass Colobognatha Brandt, 1834
**** Order Platydesmida Cook, 1895
**** Order Polyzoniida Cook, 1895
**** Order Siphonocryptida Cook, 1895
**** Order Siphonophorida Newport, 1844
*** Subterclass Eugnatha Attems, 1898
**** Superorder Juliformia Attems, 1926
***** Order Julida Brandt, 1833
***** Order Spirobolida Cook, 1895
***** Order Spirostreptida Brandt, 1833
*****Superfamily † Xyloiuloidea Cook, 1895 (Sometimes aligned with Spirobolida)
**** Superorder Nematophora Verhoeff, 1913
***** Order Callipodida Pocock, 1894
***** Order Chordeumatida Pocock 1894
***** Order Stemmiulida Cook, 1895
***** Order Siphoniulida Cook, 1895
**** Superorder Merocheta Cook, 1895
***** Order Polydesmida Pocock, 1887
Evolution
Millipedes are among the first animals to have colonised land during the Silurian period. Early forms probably atemoss
Mosses are small, non-vascular plant, non-vascular flowerless plants in the taxonomic phylum, division Bryophyta (, ) ''sensu stricto''. Bryophyta (''sensu lato'', Wilhelm Philippe Schimper, Schimp. 1879) may also refer to the parent group bryo ...
es and primitive vascular plant
Vascular plants (), also called tracheophytes (, ) or collectively tracheophyta (; ), are plants that have lignin, lignified tissues (the xylem) for conducting water and minerals throughout the plant. They also have a specialized non-lignified Ti ...
s. There are two major groups of millipedes whose members are all extinct: the Archipolypoda ("ancient, many-legged ones") which contain the oldest known terrestrial animals, and Arthropleuridea, which contain the largest known land invertebrates. '' Pneumodesmus newmani'' is the earliest member of the millipedes from the late Wenlock epoch of the late Silurian
The Silurian ( ) is a geologic period and system spanning 23.5 million years from the end of the Ordovician Period, at million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Devonian Period, Mya. The Silurian is the third and shortest period of t ...
around , or early Lochkovian
The Lochkovian is one of three faunal stages in the Early Devonian Epoch. It lasted from 419.2 ± 3.2 million years ago to 410.8 ± 2.8 million years ago. It marked the beginning of the Devonian Period, and was followed by the Pragian Stage. It is ...
of the early Devonian
The Devonian ( ) is a period (geology), geologic period and system (stratigraphy), system of the Paleozoic era (geology), era during the Phanerozoic eon (geology), eon, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the preceding Silurian per ...
around 414 million years ago, known from long fragment and has clear evidence of spiracles (breathing holes) attesting to its air-breathing habits. Other early fossils of millipedes are '' Kampecaris obanensis'' and '' Archidesmus'' sp. from 425 millions years ago in the late Silurian
The Silurian ( ) is a geologic period and system spanning 23.5 million years from the end of the Ordovician Period, at million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Devonian Period, Mya. The Silurian is the third and shortest period of t ...
. During the Carboniferous
The Carboniferous ( ) is a Geologic time scale, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), system of the Paleozoic era (geology), era that spans 60 million years, from the end of the Devonian Period Ma (million years ago) to the beginning of the ...
, '' Arthropleura'' became the largest known land-dwelling invertebrate on record, length exceeding . The reason that ''Arthropleura'' was able to achieve this size is not clearly known; early studies posited that it was a result of high atmospheric oxygen levels, while later studies consider that the lack of competition is more probable. Millipedes also exhibit the earliest evidence of chemical defence, as some Devonian
The Devonian ( ) is a period (geology), geologic period and system (stratigraphy), system of the Paleozoic era (geology), era during the Phanerozoic eon (geology), eon, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the preceding Silurian per ...
fossils have defensive gland openings called ozopores.
Living groups
The history of scientific millipede classification began withCarl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné,#Blunt, Blunt (2004), p. 171. was a Swedish biologist and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, the modern system of naming o ...
, who in his 10th edition of ''Systema Naturae'', 1758, named seven species of '' Julus'' as "Insecta Aptera" (wingless insects). In 1802, the French zoologist Pierre André Latreille
Pierre André Latreille (; 29 November 1762 – 6 February 1833) was a French zoology, zoologist, specialising in arthropods. Having trained as a Roman Catholic priest before the French Revolution, Latreille was imprisoned, and only regained hi ...
proposed the name Chilognatha as the first group of what are now the Diplopoda, and in 1840 the German naturalist Johann Friedrich von Brandt produced the first detailed classification. The name Diplopoda itself was coined in 1844 by the French zoologist Henri Marie Ducrotay de Blainville
Henri Marie Ducrotay de Blainville (; 12 September 1777 – 1 May 1850) was a French zoologist and anatomist.
Life
Blainville was born at Arques-la-Bataille, Arques, near Dieppe, Seine-Maritime, Dieppe. As a young man, he went to Paris to study a ...
. From 1890 to 1940, millipede taxonomy was driven by relatively few researchers at any given time, with major contributions by Carl Attems, Karl Wilhelm Verhoeff and Ralph Vary Chamberlin
Ralph Vary Chamberlin (January 3, 1879October 31, 1967) was an American biologist, Ethnography, ethnographer, and historian from Salt Lake City, Utah. He was a faculty member of the University of Utah for over 25 years, where he helped establish ...
, who each described over 1,000 species, as well as Orator F. Cook, Filippo Silvestri, R. I. Pocock, and Henry W. Brölemann. This was a period when the science of diplopodology flourished: rates of species descriptions were on average the highest in history, sometimes exceeding 300 per year.
In 1971, the Dutch biologist C. A. W. Jeekel published a comprehensive listing of all known millipede genera and families described between 1758 and 1957 in his ''Nomenclator Generum et Familiarum Diplopodorum'', a work credited as launching the "modern era" of millipede taxonomy. In 1980, the American biologist Richard L. Hoffman published a classification of millipedes which recognized the Penicillata, Pentazonia, and Helminthomorpha, and the first phylogenetic analysis of millipede orders using modern cladistic methods was published in 1984 by Henrik Enghoff of Denmark. A 2003 classification by the American myriapodologist Rowland Shelley is similar to the one originally proposed by Verhoeff, and remains the currently accepted classification scheme (shown below), despite more recent molecular studies proposing conflicting relationships. A 2011 summary of millipede family diversity by William A. Shear placed the order Siphoniulida within the larger group Nematophora.
Fossil record
In addition to the 16 living orders, there are 9 extinct orders and one superfamily known only from fossils. The relationship of these to living groups and to each other is controversial. The extinct Arthropleuridea was long considered a distinct myriapod class, although work in the early 21st century established the group as a subclass of millipedes. Several living orders also appear in the fossil record. Below are two proposed arrangements of fossil millipede groups. Extinct groups are indicated with adagger
A dagger is a fighting knife with a very sharp point and usually one or two sharp edges, typically designed or capable of being used as a cutting or stabbing, thrusting weapon.State v. Martin, 633 S.W.2d 80 (Mo. 1982): This is the dictionary or ...
(†). The extinct order Zosterogrammida, a chilognath of uncertain position, is not shown.
Relation to other myriapods
 Although the relationships of millipede orders are still the subject of debate, the class Diplopoda as a whole is considered a monophyletic group of arthropods: all millipedes are more closely related to each other than to any other arthropods. Diplopoda is a class within the arthropod subphylum Myriapoda, the myriapods, which includes centipedes (class Chilopoda) as well as the lesser-known pauropods (class Pauropoda) and symphylans (class Symphyla). Within myriapods, the closest relatives or
Although the relationships of millipede orders are still the subject of debate, the class Diplopoda as a whole is considered a monophyletic group of arthropods: all millipedes are more closely related to each other than to any other arthropods. Diplopoda is a class within the arthropod subphylum Myriapoda, the myriapods, which includes centipedes (class Chilopoda) as well as the lesser-known pauropods (class Pauropoda) and symphylans (class Symphyla). Within myriapods, the closest relatives or sister group
In phylogenetics, a sister group or sister taxon, also called an adelphotaxon, comprises the closest relative(s) of another given unit in an evolutionary tree.
Definition
The expression is most easily illustrated by a cladogram:
Taxon A and ...
of millipedes has long been considered the pauropods, which also have a collum and diplosegments.
Distinction from centipedes
The differences between millipedes and centipedes are a common question from the general public. Both groups of myriapods share similarities, such as long, multi-segmented bodies, many legs, a single pair of antennae, and the presence of postantennal organs, but have many differences and distinct evolutionary histories, as the most recent common ancestor of centipedes and millipedes lived around 450 to 475 million years ago in the Silurian. The head alone exemplifies the differences; millipedes have short, geniculate (elbowed) antennae for probing the substrate, a pair of robust mandibles and a single pair of maxillae fused into a lip; centipedes have long, threadlike antennae, a pair of small mandibles, two pairs of maxillae and a pair of large poison claws.
Characteristics

 Millipedes come in a variety of body shapes and sizes, ranging from to around in length, and can have as few as eleven to over three hundred segments. They are generally black or brown in colour, although there are a few brightly coloured species, and some have aposematic colouring to warn that they are toxic. Species of '' Motyxia'' produce cyanide as a chemical defence and are bioluminescent.
Body styles vary greatly between major millipede groups. In the basal subclass Penicillata, consisting of the tiny bristle millipedes, the exoskeleton is soft and uncalcified, and is covered in prominent setae or bristles. All other millipedes, belonging to the subclass Chilognatha, have a hardened exoskeleton. The chilognaths are in turn divided into two infraclasses: the Pentazonia, containing relatively short-bodied groups such as pill millipedes, and the Helminthomorpha ("worm-like" millipedes), which contains the vast majority of species, with long, many-segmented bodies.
They have also lost the gene that codes for the JHAMTl enzyme, which is responsible for catalysing the last step of the production of a juvenile hormone that regulates the development and reproduction in other arthropods like crustaceans, centipedes and insects.
Millipedes come in a variety of body shapes and sizes, ranging from to around in length, and can have as few as eleven to over three hundred segments. They are generally black or brown in colour, although there are a few brightly coloured species, and some have aposematic colouring to warn that they are toxic. Species of '' Motyxia'' produce cyanide as a chemical defence and are bioluminescent.
Body styles vary greatly between major millipede groups. In the basal subclass Penicillata, consisting of the tiny bristle millipedes, the exoskeleton is soft and uncalcified, and is covered in prominent setae or bristles. All other millipedes, belonging to the subclass Chilognatha, have a hardened exoskeleton. The chilognaths are in turn divided into two infraclasses: the Pentazonia, containing relatively short-bodied groups such as pill millipedes, and the Helminthomorpha ("worm-like" millipedes), which contains the vast majority of species, with long, many-segmented bodies.
They have also lost the gene that codes for the JHAMTl enzyme, which is responsible for catalysing the last step of the production of a juvenile hormone that regulates the development and reproduction in other arthropods like crustaceans, centipedes and insects.Head
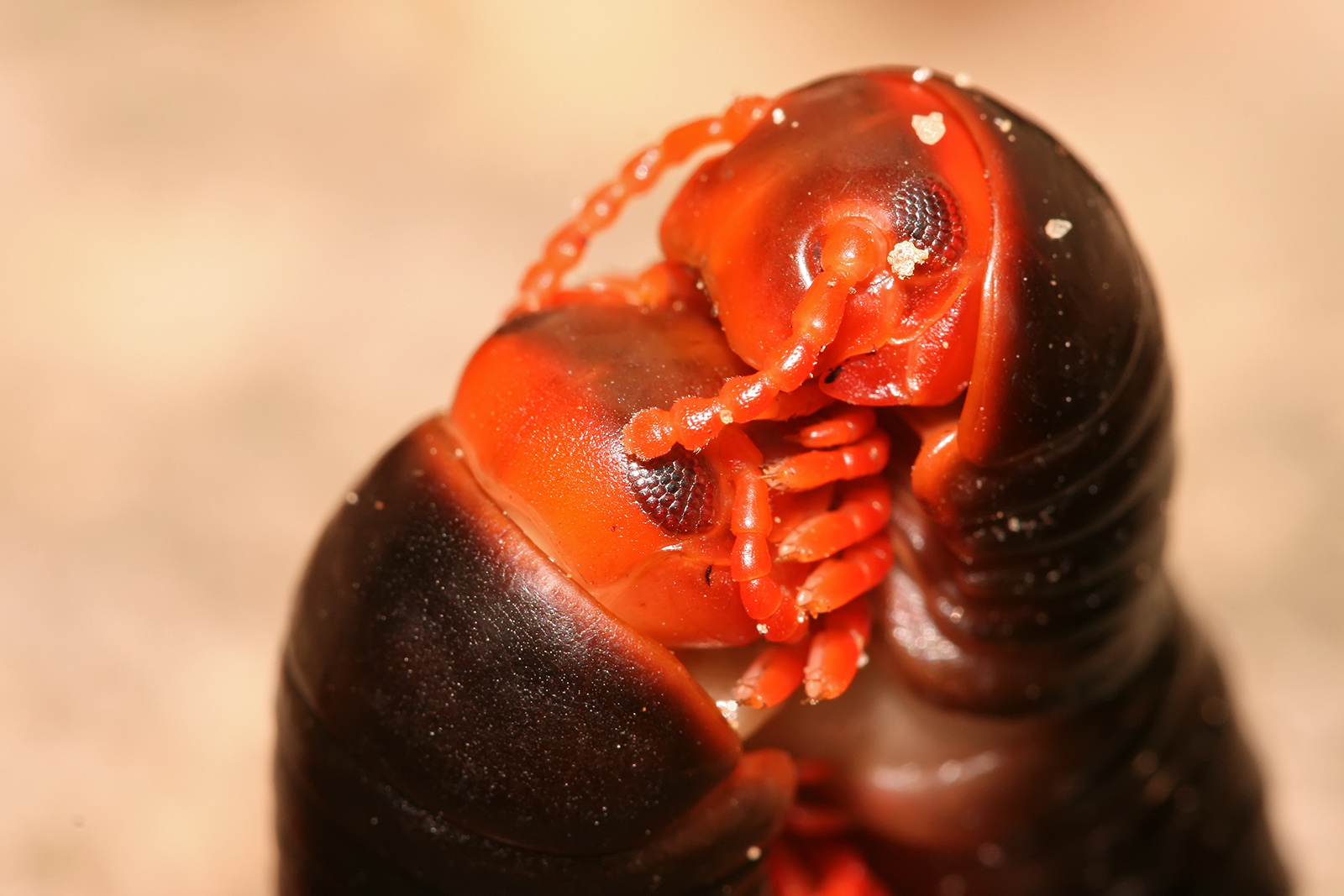
The head of a millipede is typically rounded above and flattened below and bears a pair of large mandibles in front of a plate-like structure called a gnathochilarium ("jaw lip"). The head contains a single pair of antennae with seven or eight segments and a group of sensory cones at the tip. Many orders also possess a pair of sensory organs known as the Tömösváry organs, shaped as small oval rings posterior and lateral to the base of the antennae. Their function is unknown, but they also occur in some centipedes, and are possibly used to measure humidity or light levels in the surrounding environment. Millipede eyes consist of several simple flat-lensed ocelli arranged in a group or patch on each side of the head. These patches are also called ocular fields or ocellaria. Many species of millipedes, including the entire orders Polydesmida, Siphoniulida, Glomeridesmida, Siphonophorida and Platydesmida, and cave-dwelling millipedes such as '' Causeyella'' and '' Trichopetalum'', had ancestors that could see but have subsequently lost their eyes and are blind.Body
 Millipede bodies may be flattened or cylindrical, and are composed of numerous metameric segments, each with an
Millipede bodies may be flattened or cylindrical, and are composed of numerous metameric segments, each with an exoskeleton
An exoskeleton () . is a skeleton that is on the exterior of an animal in the form of hardened integument, which both supports the body's shape and protects the internal organs, in contrast to an internal endoskeleton (e.g. human skeleton, that ...
consisting of four chitin
Chitin (carbon, C8hydrogen, H13oxygen, O5nitrogen, N)n ( ) is a long-chain polymer of N-Acetylglucosamine, ''N''-acetylglucosamine, an amide derivative of glucose. Chitin is the second most abundant polysaccharide in nature (behind only cell ...
ous plates: a single plate above (the tergite), one at each side ( pleurites), and a plate on the underside ( sternite) where the legs attach. In many millipedes, such as Merocheta and Juliformia, these plates are fused to varying degrees, sometimes forming a single cylindrical ring. The plates are typically hard, impregnated with calcium salts. Because they can't close their permanently open spiracles and most species lack a waxy cuticle, millipedes are susceptible to water loss and with a few exceptions must spend most of their time in moist or humid environments.
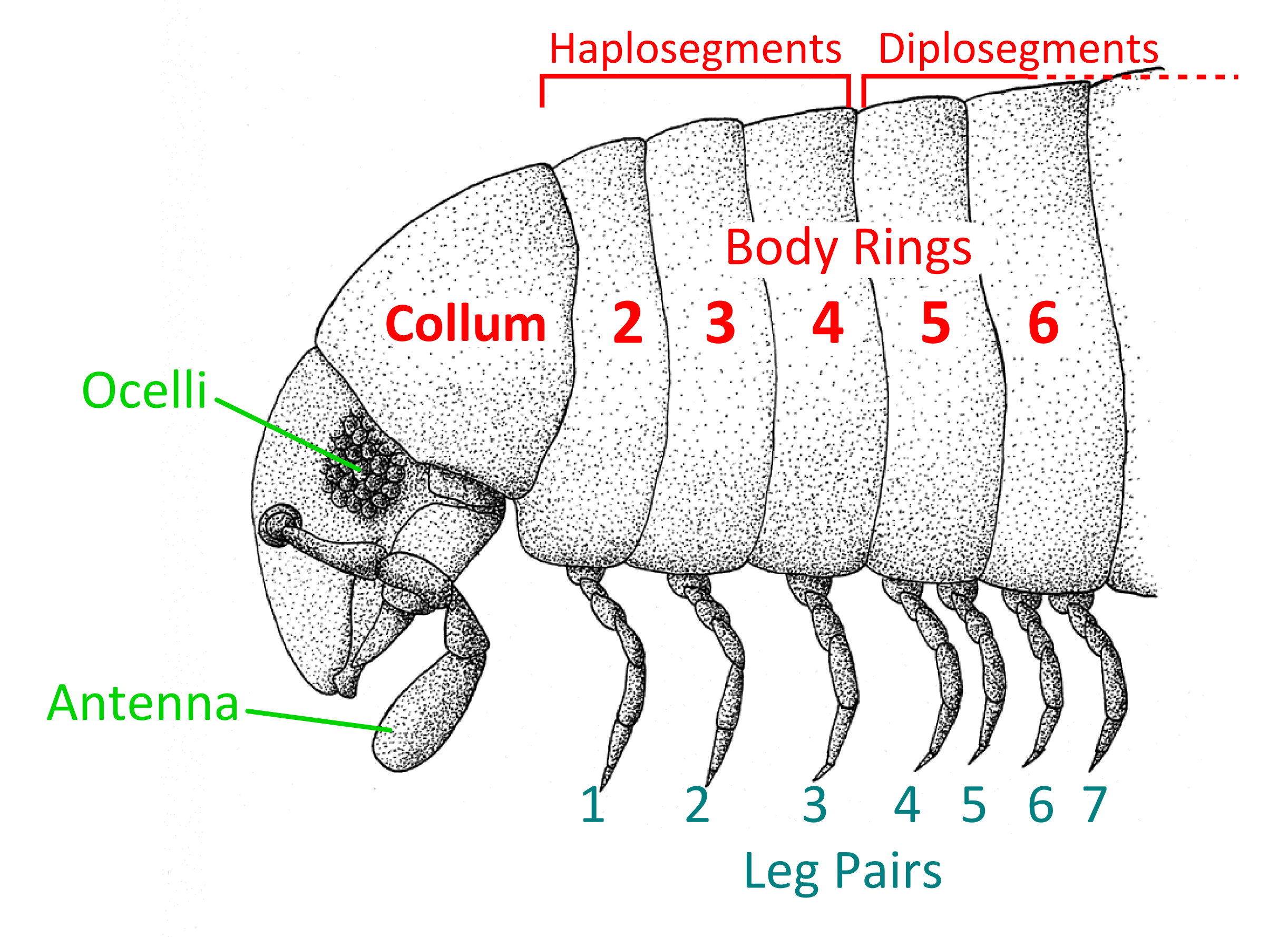
The first segment behind the head is legless and known as a collum (from the Latin for neck or collar). The second, third, and fourth body segments bear a single pair of legs each and are known as "haplosegments" (the three haplosegments are sometimes referred to as a " thorax"). The remaining segments, from the fifth to the posterior, are properly known as diplosegments or double segments, formed by the fusion of two embryonic segments. Each diplosegment bears two pairs of legs, rather than just one as in centipedes. In some millipedes, the last few segments may be legless. The terms "segment" or "body ring" are often used interchangeably to refer to both haplo- and diplosegments. The final segment is known as the telson and consists of a legless preanal ring, a pair of anal valves (closeable plates around the anus), and a small scale below the anus.
Millipedes in several orders have keel-like extensions of the body-wall known as paranota, which can vary widely in shape, size, and texture; modifications include lobes, papillae, ridges, crests, spines and notches. Paranota may allow millipedes to wedge more securely into crevices, protect the legs, or make the millipede more difficult for predators to swallow.
The legs are composed of seven segments, and attach on the underside of the body. The legs of an individual are generally rather similar to each other, although often longer in males than females, and males of some species may have a reduced or enlarged first pair of legs. The most conspicuous leg modifications are involved in reproduction, discussed below. Despite the common name, no millipede was known to have 1,000 legs until 2021: common species have between 34 and 400 legs, and the record is held by '' Eumillipes persephone'', with individuals possessing up to 1,306 legs – more than any other creature on Earth.
Internal organs
Millipedes breathe through two pairs of spiracles located ventrally on each segment near the base of the legs. Each opens into an internal pouch, and connects to a system of tracheae. The heart runs the entire length of the body, with anaorta
The aorta ( ; : aortas or aortae) is the main and largest artery in the human body, originating from the Ventricle (heart), left ventricle of the heart, branching upwards immediately after, and extending down to the abdomen, where it splits at ...
stretching into the head. The excretory organs are two pairs of malpighian tubules, located near the mid-part of the gut. The digestive tract is a simple tube with two pairs of salivary glands to help digest the food.
Reproduction and growth
 Millipedes show a diversity of mating styles and structures. In the basal order Polyxenida (bristle millipedes), mating is indirect: males deposit spermatophores onto webs they secrete with special glands, and the spermatophores are subsequently picked up by females. In all other millipede groups, males possess one or two pairs of modified legs called gonopods which are used to transfer sperm to the female during copulation. The location of the gonopods differs between groups: in males of the Pentazonia they are located at the rear of the body and known as telopods and may also function in grasping females, while in the Helminthomorpha – the vast majority of species – they are located on the seventh body segment. A few species are
Millipedes show a diversity of mating styles and structures. In the basal order Polyxenida (bristle millipedes), mating is indirect: males deposit spermatophores onto webs they secrete with special glands, and the spermatophores are subsequently picked up by females. In all other millipede groups, males possess one or two pairs of modified legs called gonopods which are used to transfer sperm to the female during copulation. The location of the gonopods differs between groups: in males of the Pentazonia they are located at the rear of the body and known as telopods and may also function in grasping females, while in the Helminthomorpha – the vast majority of species – they are located on the seventh body segment. A few species are parthenogenetic
Parthenogenesis (; from the Greek + ) is a natural form of asexual reproduction in which the embryo develops directly from an egg without need for fertilization. In animals, parthenogenesis means the development of an embryo from an unfertiliz ...
, having few, if any, males.
Gonopods occur in a diversity of shapes and sizes, and in the range from closely resembling walking legs to complex structures quite unlike legs at all. In some groups, the gonopods are kept retracted within the body; in others they project forward parallel to the body. Gonopod morphology is the predominant means of determining species among millipedes: the structures may differ greatly between closely related species but very little within a species. The gonopods develop gradually from walking legs through successive moults until reproductive maturity.
 The genital openings ( gonopores) of both sexes are located on the underside of the third body segment (near the second pair of legs) and may be accompanied in the male by one or two penes which deposit the sperm packets onto the gonopods. In the female, the genital pores open into paired small sacs called cyphopods or vulvae, which are covered by small hood-like lids, and are used to store the sperm after copulation. The cyphopod morphology can also be used to identify species. Millipede
The genital openings ( gonopores) of both sexes are located on the underside of the third body segment (near the second pair of legs) and may be accompanied in the male by one or two penes which deposit the sperm packets onto the gonopods. In the female, the genital pores open into paired small sacs called cyphopods or vulvae, which are covered by small hood-like lids, and are used to store the sperm after copulation. The cyphopod morphology can also be used to identify species. Millipede sperm
Sperm (: sperm or sperms) is the male reproductive Cell (biology), cell, or gamete, in anisogamous forms of sexual reproduction (forms in which there is a larger, female reproductive cell and a smaller, male one). Animals produce motile sperm ...
lack flagella, a unique trait among myriapods.
In all except the bristle millipedes, copulation occurs with the two individuals facing one another. Copulation may be preceded by male behaviours such as tapping with antennae, running along the back of the female, offering edible glandular secretions, or in the case of some pill-millipedes, stridulation or "chirping". During copulation in most millipedes, the male positions his seventh segment in front of the female's third segment, and may insert his gonopods to extrude the vulvae before bending his body to deposit sperm onto his gonopods and reinserting the "charged" gonopods into the female.
Females lay from ten to three hundred eggs at a time, depending on species, fertilising them with the stored sperm as they do so. Many species deposit the eggs on moist soil or organic detritus, but some construct nests lined with dried faeces
Feces (also known as faeces American and British English spelling differences#ae and oe, or fæces; : faex) are the solid or semi-solid remains of food that was not digested in the small intestine, and has been broken down by bacteria in the ...
, and may protect the eggs within silk cocoons. In most species, the female abandons the eggs after they are laid, but some species in the orders Platydesmida and Stemmiulida provide parental care for eggs and young.
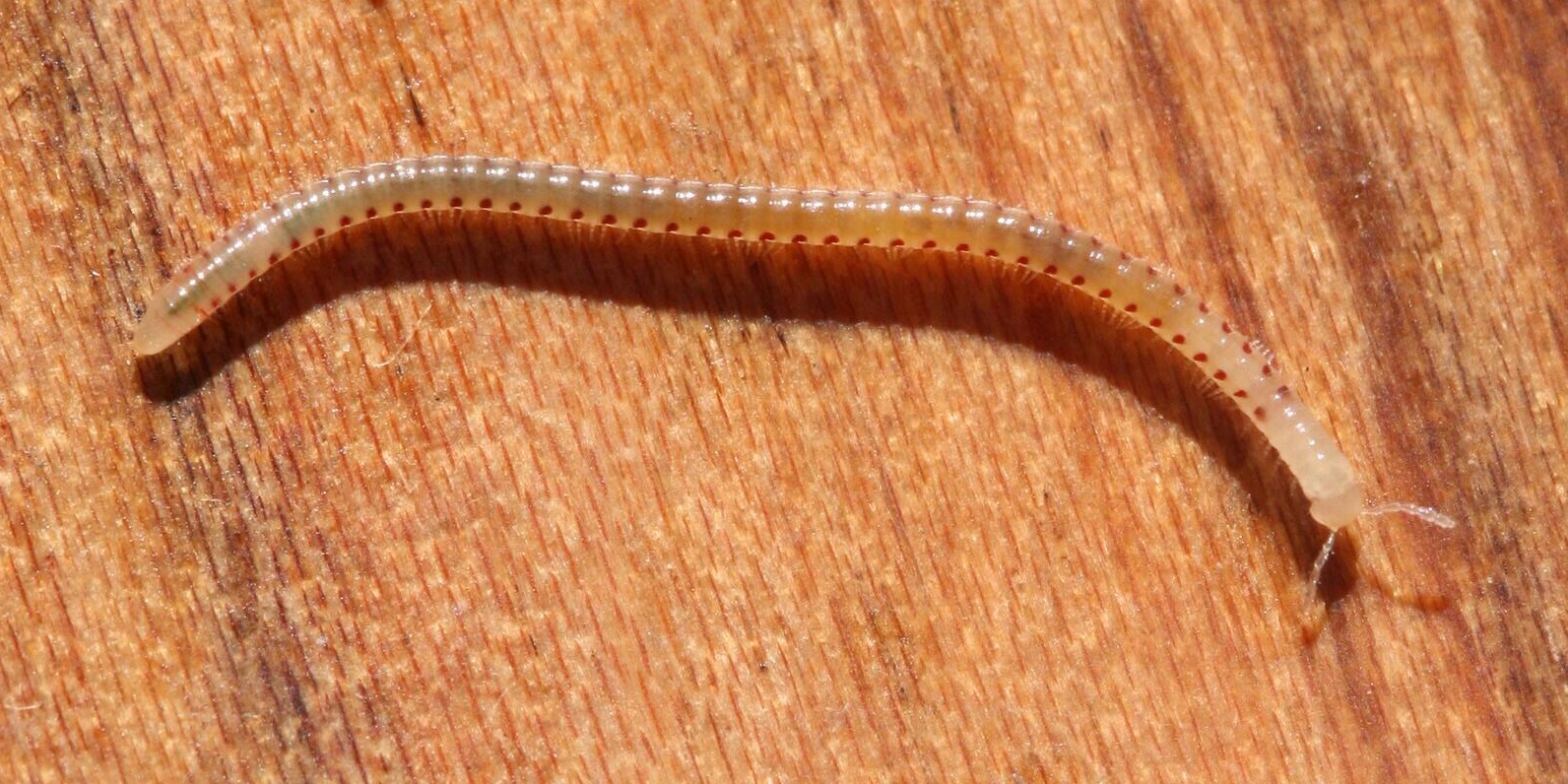
The young hatch after a few weeks, and typically have only three pairs of legs, followed by up to four legless segments. As they grow, they continually moult, adding further segments and legs as they do so, a mode of development known as anamorphosis
Anamorphosis is a distorted projection that requires the viewer to occupy a specific vantage point, use special devices, or both to view a recognizable image. It is used in painting, photography, sculpture and installation, toys, and film speci ...
. Some species moult within specially prepared chambers of soil or silk, and may also shelter in these during wet weather, and most species eat the discarded exoskeleton after moulting. The adult stage, when individuals become reproductively mature, is generally reached in the final moult stage, which varies between species and orders, although some species continue to moult after adulthood. Furthermore, some species alternate between reproductive and non-reproductive stages after maturity, a phenomenon known as periodomorphosis, in which the reproductive structures regress during non-reproductive stages. Millipedes may live from one to ten years, depending on species.
Ecology
Habitat and distribution
Millipedes occur on all continents except Antarctica, and occupy almost all terrestrial habitats, ranging as far north as theArctic Circle
The Arctic Circle is one of the two polar circles, and the northernmost of the five major circle of latitude, circles of latitude as shown on maps of Earth at about 66° 34' N. Its southern counterpart is the Antarctic Circle.
The Arctic Circl ...
in Iceland, Norway, and Central Russia, and as far south as Santa Cruz Province, Argentina. Typically forest floor dwellers, they live in leaf litter, dead wood, or soil, with a preference for humid conditions. In temperate zones, millipedes are most abundant in moist deciduous forests, and may reach densities of over 1,000 individuals per square metre. Other habitats include coniferous forests, caves, and alpine ecosystems. Deserticolous millipedes, species evolved to live in the desert, like '' Orthoporus ornatus'', may show adaptations like a waxy epicuticle and the ability of water uptake from unsaturated air. Some species can survive freshwater floods and live submerged underwater for up to 11 months. A few species occur near the seashore and can survive in somewhat salty conditions.
Burrowing
The diplosegments of millipedes have evolved in conjunction with their burrowing habits, and nearly all millipedes adopt a mainly subterranean lifestyle. They use three main methods of burrowing; bulldozing, wedging and boring. Members of the orders Julida, Spirobolida and Spirostreptida, lower their heads and barge their way into the substrate, the collum leading the way. Flat-backed millipedes in the order Polydesmida tend to insert their front end, like a wedge, into a horizontal crevice, and then widen the crack by pushing upwards with their legs, the paranota in this instance constituting the main lifting surface. Boring is used by members of the order Polyzoniida. These have smaller segments at the front and increasingly large ones further back; they propel themselves forward into a crack with their legs, the wedge-shaped body widening the gap as they go. Some millipedes have adopted an above-ground lifestyle and lost the burrowing habit. This may be because they are too small to have enough leverage to burrow, or because they are too large to make the effort worthwhile, or in some cases because they move relatively fast (for a millipede) and are active predators.
Diet
Most millipedes are detritivores and feed on decomposing vegetation, feces, or organic matter mixed with soil. They often play important roles in the breakdown and decomposition of plant litter: estimates of consumption rates for individual species range from 1 to 11 percent of all leaf litter, depending on species and region, and collectively millipedes may consume nearly all the leaf litter in a region. The leaf litter is fragmented in the millipede gut and excreted as pellets of leaf fragments, algae, fungi, and bacteria, which facilitates decomposition by the microorganisms. Where earthworm populations are low in tropical forests, millipedes play an important role in facilitating microbial decomposition of the leaf litter. Some millipedes are herbivorous, feeding on living plants, and some species can become serious pests of crops. Millipedes in the order Polyxenida graze algae from bark, and Platydesmida feed on fungi. A few species are omnivorous or in Callipodida and Chordeumatida occasionally carnivorous, feeding on insects, centipedes, earthworms, or snails. Some species have piercing mouth parts that allow them to suck up plant juices. Cave dwelling species in Julidae, Blaniulidae, and Polydesmidae have specialized mouthparts and appears to be filter feeders, filtering small particles from running water inside caves.Predators and parasites
 Millipedes are preyed on by a wide range of animals, including various
Millipedes are preyed on by a wide range of animals, including various reptile
Reptiles, as commonly defined, are a group of tetrapods with an ectothermic metabolism and Amniotic egg, amniotic development. Living traditional reptiles comprise four Order (biology), orders: Testudines, Crocodilia, Squamata, and Rhynchocepha ...
s, amphibian
Amphibians are ectothermic, anamniote, anamniotic, tetrapod, four-limbed vertebrate animals that constitute the class (biology), class Amphibia. In its broadest sense, it is a paraphyletic group encompassing all Tetrapod, tetrapods, but excl ...
s, bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class (biology), class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the Oviparity, laying of Eggshell, hard-shelled eggs, a high Metabolism, metabolic rate, a fou ...
s, mammal
A mammal () is a vertebrate animal of the Class (biology), class Mammalia (). Mammals are characterised by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a broad neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three ...
s, and insect
Insects (from Latin ') are Hexapoda, hexapod invertebrates of the class (biology), class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body (Insect morphology#Head, head, ...
s. Mammalian predators such as coatis and meerkat
The meerkat (''Suricata suricatta'') or suricate is a small mongoose found in southern Africa. It is characterised by a broad head, large eyes, a pointed snout, long legs, a thin tapering tail, and a brindled coat pattern. The head-and-body ...
s roll captured millipedes on the ground to deplete and rub off their defensive secretions before consuming their prey, and certain poison dart frogs are believed to incorporate the toxic compounds of millipedes into their own defences. Several invertebrates have specialised behaviours or structures to feed on millipedes, including larval glowworm beetles, '' Probolomyrmex'' ants, chlamydephorid slugs, and predaceous dung beetles of the genera '' Sceliages'' and '' Deltochilum''. A large subfamily of assassin bugs, the Ectrichodiinae with over 600 species, has specialised in preying upon millipedes. Parasites of millipedes include nematode
The nematodes ( or ; ; ), roundworms or eelworms constitute the phylum Nematoda. Species in the phylum inhabit a broad range of environments. Most species are free-living, feeding on microorganisms, but many are parasitic. Parasitic worms (h ...
s, phaeomyiid flies, and acanthocephalans. Nearly 30 fungal species of the order Laboulbeniales have been found growing externally on millipedes, but some species may be commensal rather than parasitic.
Defence mechanisms
Due to their lack of speed and their inability to bite or sting, millipedes' primary defence mechanism is to curl into a tight coil – protecting their delicate legs inside an armoured exoskeleton. Many species also emit various foul-smelling liquid secretions through microscopic holes called ozopores (the openings of "odoriferous" or "repugnatorial glands"), along the sides of their bodies as a secondary defence. Among the many irritant and toxic chemicals found in these secretions arealkaloid
Alkaloids are a broad class of natural product, naturally occurring organic compounds that contain at least one nitrogen atom. Some synthetic compounds of similar structure may also be termed alkaloids.
Alkaloids are produced by a large varie ...
s, benzoquinones, phenols
In organic chemistry, phenols, sometimes called phenolics, are a class of chemical compounds consisting of one or more hydroxyl groups (− O H) bonded directly to an aromatic hydrocarbon group. The simplest is phenol, . Phenolic compounds ar ...
, terpenoid
The terpenoids, also known as isoprenoids, are a class of naturally occurring organic compound, organic chemicals derived from the 5-carbon compound isoprene and its derivatives called terpenes, diterpenes, etc. While sometimes used interchangeabl ...
s, and hydrogen cyanide
Hydrogen cyanide (formerly known as prussic acid) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula, formula HCN and structural formula . It is a highly toxic and flammable liquid that boiling, boils slightly above room temperature, at . HCN is ...
. Some of these substances are caustic and can burn the exoskeleton of ant
Ants are Eusociality, eusocial insects of the Family (biology), family Formicidae and, along with the related wasps and bees, belong to the Taxonomy (biology), order Hymenoptera. Ants evolved from Vespoidea, vespoid wasp ancestors in the Cre ...
s and other insect predators, and the skin and eyes of larger predators. Primates such as capuchin monkeys and lemur
Lemurs ( ; from Latin ) are Strepsirrhini, wet-nosed primates of the Superfamily (biology), superfamily Lemuroidea ( ), divided into 8 Family (biology), families and consisting of 15 genera and around 100 existing species. They are Endemism, ...
s have been observed intentionally irritating millipedes in order to rub the chemicals on themselves to repel mosquito
Mosquitoes, the Culicidae, are a Family (biology), family of small Diptera, flies consisting of 3,600 species. The word ''mosquito'' (formed by ''Musca (fly), mosca'' and diminutive ''-ito'') is Spanish and Portuguese for ''little fly''. Mos ...
es. Some of these defensive compounds also show antifungal activity.
The bristly millipedes (order Polyxenida) lack both an armoured exoskeleton and odiferous glands, and instead are covered in numerous bristles that in at least one species, '' Polyxenus fasciculatus'', detach and entangle ants.
Other inter-species interactions
 Some millipedes form mutualistic relationships with organisms of other species, in which both species benefit from the interaction, or commensal relationships, in which only one species benefits while the other is unaffected. Several species form close relationships with ants, a relationship known as myrmecophily, especially within the family Pyrgodesmidae (Polydesmida), which contains "obligate myrmecophiles", species which have only been found in ant colonies. More species are "facultative myrmecophiles", non-exclusively associated with ants, including many species of Polyxenida that have been found in ant nests around the world.
Many millipede species have commensal relationships with
Some millipedes form mutualistic relationships with organisms of other species, in which both species benefit from the interaction, or commensal relationships, in which only one species benefits while the other is unaffected. Several species form close relationships with ants, a relationship known as myrmecophily, especially within the family Pyrgodesmidae (Polydesmida), which contains "obligate myrmecophiles", species which have only been found in ant colonies. More species are "facultative myrmecophiles", non-exclusively associated with ants, including many species of Polyxenida that have been found in ant nests around the world.
Many millipede species have commensal relationships with mite
Mites are small arachnids (eight-legged arthropods) of two large orders, the Acariformes and the Parasitiformes, which were historically grouped together in the subclass Acari. However, most recent genetic analyses do not recover the two as eac ...
s of the orders Mesostigmata and Astigmata. Many of these mites are believed to be phoretic rather than parasitic, which means that they use the millipede host as a means of dispersal.
A novel interaction between millipedes and mosses was described in 2011, in which individuals of the newly discovered '' Psammodesmus bryophorus'' was found to have up to ten species living on its dorsal surface, in what may provide camouflage
Camouflage is the use of any combination of materials, coloration, or illumination for concealment, either by making animals or objects hard to see, or by disguising them as something else. Examples include the leopard's spotted coat, the b ...
for the millipede and increased dispersal for the mosses.
Interactions with humans
Millipedes generally have little impact on human economic or social well-being, especially in comparison with insects, although locally they can be a nuisance or agricultural pest. Millipedes do not bite, and their defensive secretions are mostly harmless to humans — usually causing only minor discolouration on the skin — but the secretions of some tropical species may cause pain, itching, local erythema, edema, blisters, eczema, and occasionally cracked skin. Eye exposures to these secretions causes general irritation and potentially more severe effects such as conjunctivitis and keratitis. This is called millipede burn. First aid consists of flushing the area thoroughly with water; further treatment is aimed at relieving the local effects. Some millipedes are considered household pests, including '' Xenobolus carnifex'' which can infest thatched roofs in India, and '' Ommatoiulus moreleti'', which periodically invades homes in Australia. Other species exhibit periodical swarming behaviour, which can result in home invasions, crop damage, and train delays when the tracks become slippery with the crushed remains of hundreds of millipedes. Some millipedes can cause significant damage to crops: the spotted snake millipede (''Blaniulus guttulatus'') is a pest of
Some millipedes are considered household pests, including '' Xenobolus carnifex'' which can infest thatched roofs in India, and '' Ommatoiulus moreleti'', which periodically invades homes in Australia. Other species exhibit periodical swarming behaviour, which can result in home invasions, crop damage, and train delays when the tracks become slippery with the crushed remains of hundreds of millipedes. Some millipedes can cause significant damage to crops: the spotted snake millipede (''Blaniulus guttulatus'') is a pest of sugar beet
A sugar beet is a plant whose root contains a high concentration of sucrose and that is grown commercially for sugar production. In plant breeding, it is known as the Altissima cultivar group of the common beet (''Beta vulgaris''). Together with ...
s and other root crops, and as a result is one of the few millipedes with a common name
In biology, a common name of a taxon or organism (also known as a vernacular name, English name, colloquial name, country name, popular name, or farmer's name) is a name that is based on the normal language of everyday life; and is often con ...
.
Some of the larger millipedes in the orders Spirobolida, Spirostreptida, and Sphaerotheriida
Sphaerotheriida is an order (biology), order of millipedes in the infraclass Pentazonia, sometimes known as giant pill millipedes. They inhabit Southern Africa, Madagascar, South and Southeast Asia, Australia and New Zealand. Like the Northern He ...
are popular as pets. Some species commonly sold or kept include species of '' Archispirostreptus'', '' Aphistogoniulus'', '' Narceus'', and '' Orthoporus''.
 Millipedes appear in
Millipedes appear in folklore
Folklore is the body of expressive culture shared by a particular group of people, culture or subculture. This includes oral traditions such as Narrative, tales, myths, legends, proverbs, Poetry, poems, jokes, and other oral traditions. This also ...
and traditional medicine
Traditional medicine (also known as indigenous medicine or folk medicine) refers to the knowledge, skills, and practices rooted in the cultural beliefs of various societies, especially Indigenous groups, used for maintaining health and treatin ...
around the world. Some cultures associate millipede activity with coming rains. In Zambia, smashed millipede pulp is used to treat wounds, and the Bafia people of Cameroon use millipede juice to treat earache. In certain Himalayan Bhotiya tribes, dry millipede smoke is used to treat haemorrhoids. Native people in Malaysia
Malaysia is a country in Southeast Asia. Featuring the Tanjung Piai, southernmost point of continental Eurasia, it is a federation, federal constitutional monarchy consisting of States and federal territories of Malaysia, 13 states and thre ...
use millipede secretions in poison-tipped arrows. The secretions of ''Spirobolus bungii'' have been observed to inhibit division of human cancer cells. The only recorded usage of millipedes as food by humans comes from the Bobo people of Burkina Faso
Burkina Faso is a landlocked country in West Africa, bordered by Mali to the northwest, Niger to the northeast, Benin to the southeast, Togo and Ghana to the south, and Ivory Coast to the southwest. It covers an area of 274,223 km2 (105,87 ...
in West Africa
West Africa, also known as Western Africa, is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations geoscheme for Africa#Western Africa, United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Gha ...
, who consume boiled, dried millipedes belonging to the families Gomphodesmidae and Spirostreptidae to which they add tomato sauce.
Millipedes have also inspired and played roles in scientific research. In 1963, a walking vehicle with 36 legs was designed, said to have been inspired by a study of millipede locomotion.
Experimental robots have had the same inspiration, in particular when heavy loads are needed to be carried in tight areas involving turns and curves. In biology, some authors have advocated millipedes as model organism
A model organism is a non-human species that is extensively studied to understand particular biological phenomena, with the expectation that discoveries made in the model organism will provide insight into the workings of other organisms. Mo ...
s for the study of arthropod physiology and the developmental processes controlling the number and shape of body segments.
Similar to vermicompost, millipedes can be used to convert plant matter into compost in what has been named millicomposting, which improves the quality of the compost./ref>
References
External links
Milli-PEET: The Class Diplopoda
– The Field Museum, Chicago
Diplopoda: Guide to New Zealand Soil Invertebrates
– Massey University
British Myriapod & Isopod Group
{{DEFAULTSORT:Millipede Detritivores Wenlock first appearances Extant Silurian first appearances Myriapods Taxa named by Henri Marie Ducrotay de Blainville