metal halide lighting on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
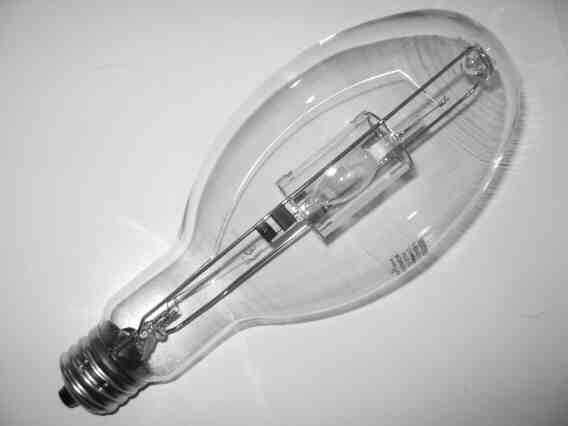



 A metal-halide lamp is an electrical lamp that produces light by an
A metal-halide lamp is an electrical lamp that produces light by an
 The electric arc in metal-halide lamps, as in all gas discharge lamps has a negative resistance property; meaning that as the current through the bulb increases, the
The electric arc in metal-halide lamps, as in all gas discharge lamps has a negative resistance property; meaning that as the current through the bulb increases, the
 Metal halide lamps, usually lose their output or change color due to the loss of halides and arctube blackening. They stop working at the end of a life that is similar to mercury lamps. In rare cases, they can also cycle on/off. Some can exhibit major color shift, and in rare cases, explode.
Metal halide lamps, usually lose their output or change color due to the loss of halides and arctube blackening. They stop working at the end of a life that is similar to mercury lamps. In rare cases, they can also cycle on/off. Some can exhibit major color shift, and in rare cases, explode.High Intensity Discharge Lamps (NASA)
File:MetalHalideHighBay.jpg, A low-bay

 A metal-halide lamp is an electrical lamp that produces light by an
A metal-halide lamp is an electrical lamp that produces light by an electric arc
An electric arc, or arc discharge, is an electrical breakdown of a gas that produces a prolonged electrical discharge. The current through a normally nonconductive medium such as air produces a plasma; the plasma may produce visible light. ...
through a gaseous mixture of vaporized mercury and metal halides
Metal halides are compounds between metals and halogens. Some, such as sodium chloride are ionic, while others are covalently bonded. A few metal halides are discrete molecules, such as uranium hexafluoride, but most adopt polymeric structures, su ...
(compounds of metals with bromine
Bromine is a chemical element with the symbol Br and atomic number 35. It is the third-lightest element in group 17 of the periodic table ( halogens) and is a volatile red-brown liquid at room temperature that evaporates readily to form a simi ...
or iodine
Iodine is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol I and atomic number 53. The heaviest of the stable halogens, it exists as a semi-lustrous, non-metallic solid at standard conditions that melts to form a deep violet liquid at , ...
). It is a type of high-intensity discharge (HID) gas discharge lamp. Developed in the 1960s, they are similar to mercury vapor lamp
A mercury-vapor lamp is a gas-discharge lamp that uses an electric arc through vaporized mercury to produce light. The arc discharge is generally confined to a small fused quartz arc tube mounted within a larger soda lime or borosilicate g ...
s, but contain additional metal halide compounds in the quartz
Quartz is a hard, crystalline mineral composed of silica ( silicon dioxide). The atoms are linked in a continuous framework of SiO4 silicon-oxygen tetrahedra, with each oxygen being shared between two tetrahedra, giving an overall chemical f ...
arc tube, which improve the efficiency and color rendition of the light.
The most common metal halide compound used is sodium iodide
Sodium iodide (chemical formula NaI) is an ionic compound formed from the chemical reaction of sodium metal and iodine. Under standard conditions, it is a white, water-soluble solid comprising a 1:1 mix of sodium cations (Na+) and iodide anions (I ...
. Once the arc tube reaches its running temperature, the sodium dissociates from the iodine, adding orange and reds to the lamp's spectrum from the sodium D line as the metal ionizes.
As a result, metal-halide lamps have high luminous efficacy
Luminous efficacy is a measure of how well a light source produces visible light. It is the ratio of luminous flux to power, measured in lumens per watt in the International System of Units (SI). Depending on context, the power can be either the ...
of around 75–100 lumens per watt, which is about twice that of mercury vapor lights and 3 to 5 times that of incandescent light
An incandescent light bulb, incandescent lamp or incandescent light globe is an electric light with a wire filament heated until it glows. The filament is enclosed in a glass bulb with a vacuum or inert gas to protect the filament from oxidat ...
s and produce an intense white light. Lamp life is 6,000 to 15,000 hours. As one of the most efficient sources of high CRI white light, metal halides were the fastest growing segment of the lighting industry. They are used for wide area overhead lighting of commercial, industrial, and public places, such as parking lots, sports arenas, factories, and retail stores, as well as residential security lighting In the field of physical security, security lighting is lighting that intended to deter or detect intrusions or other criminal activity occurring on a property or site. It can also be used to increase a feeling of safety. Lighting is integral to cr ...
, automotive headlamp
A headlamp is a lamp attached to the front of a vehicle to illuminate the road ahead. Headlamps are also often called headlights, but in the most precise usage, ''headlamp'' is the term for the device itself and ''headlight'' is the term for ...
s (Often generically known as " xenon headlights") and indoor cannabis grow operations.
The lamps consist of a small fused quartz
Fused quartz, fused silica or quartz glass is a glass consisting of almost pure silica (silicon dioxide, SiO2) in amorphous (non-crystalline) form. This differs from all other commercial glasses in which other ingredients are added which change ...
or ceramic
A ceramic is any of the various hard, brittle, heat-resistant and corrosion-resistant materials made by shaping and then firing an inorganic, nonmetallic material, such as clay, at a high temperature. Common examples are earthenware, porcelain, ...
arc tube
An arc lamp or arc light is a lamp that produces light by an electric arc (also called a voltaic arc).
The carbon arc light, which consists of an arc between carbon electrodes in air, invented by Humphry Davy in the first decade of the 1800s, ...
which contains the gases and the arc, enclosed inside a larger glass bulb which has a coating to filter out the ultraviolet light
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 PHz) to 400 nm (750 THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiatio ...
produced. They operate at a pressure between 4 and 20 atmospheres, and require special fixtures to operate safely, as well as an electrical ballast
Ballast is material that is used to provide stability to a vehicle or structure. Ballast, other than cargo, may be placed in a vehicle, often a ship or the gondola of a balloon or airship, to provide stability. A compartment within a boat, ship ...
. Metal atoms produce most of the light output. They require a warm-up period of several minutes to reach full light output.
Uses
Metal-halide lamps are used for general lighting purposes both indoors and outdoors, such as commercial, industrial, and public spaces, parking lots, sports arenas, factories, and retail stores, as well asresidential security
Home security includes both the security hardware placed on a property and individuals' personal security practices. Security hardware includes doors, locks, alarm systems, lighting, motion detectors, and security camera systems. Personal se ...
lighting; automotive and specialty applications are further fields of usage.
Metal-halide lamps are used in automobile headlights
A headlamp is a lamp attached to the front of a vehicle to illuminate the road ahead. Headlamps are also often called headlights, but in the most precise usage, ''headlamp'' is the term for the device itself and ''headlight'' is the term for ...
, where they are commonly generically called "xenon headlamps" due to the use of xenon
Xenon is a chemical element with the symbol Xe and atomic number 54. It is a dense, colorless, odorless noble gas found in Earth's atmosphere in trace amounts. Although generally unreactive, it can undergo a few chemical reactions such as the ...
gas in the bulb, to provide minimal light upon turning on before the lamp warms up, instead of the argon
Argon is a chemical element with the symbol Ar and atomic number 18. It is in group 18 of the periodic table and is a noble gas. Argon is the third-most abundant gas in Earth's atmosphere, at 0.934% (9340 ppmv). It is more than twice a ...
typically used in other halide lamps.
Another widespread use for such lamps is in photographic lighting and stage lighting
Stage lighting is the craft of lighting as it applies to the production of theater, dance, opera, and other performance arts.
fixtures, where they are commonly generically known as MSD or HMI lamps and are generally used in 150, 250, 400, 575 and 1,200 watt
The watt (symbol: W) is the unit of power or radiant flux in the International System of Units (SI), equal to 1 joule per second or 1 kg⋅m2⋅s−3. It is used to quantify the rate of energy transfer. The watt is named after James ...
ratings, especially intelligent lighting
Intelligent lighting refers to lighting that has automated or mechanical abilities beyond those of traditional, stationary illumination. Although the most advanced intelligent lights can produce extraordinarily complex effects, the intelligence l ...
.
Because of their wide spectrum and good efficiency they are used for indoor growing applications, specifically cannabis and are quite popular with reef aquarists who need a high intensity light source for their corals.
Operation
Like othergas-discharge lamp
Gas-discharge lamps are a family of artificial light sources that generate light by sending an electric discharge through an ionized gas, a plasma.
Typically, such lamps use a
noble gas (argon, neon, krypton, and xenon) or a mixture of t ...
s such as the very-similar mercury-vapor lamp
A mercury-vapor lamp is a gas-discharge lamp that uses an electric arc through vaporized mercury to produce light. The arc discharge is generally confined to a small fused quartz arc tube mounted within a larger soda lime or borosilicate gl ...
s, metal-halide lamps produce light by ionizing a mixture of gases in an electric arc
An electric arc, or arc discharge, is an electrical breakdown of a gas that produces a prolonged electrical discharge. The current through a normally nonconductive medium such as air produces a plasma; the plasma may produce visible light. ...
. In a metal-halide lamp, the compact arc tube
An arc lamp or arc light is a lamp that produces light by an electric arc (also called a voltaic arc).
The carbon arc light, which consists of an arc between carbon electrodes in air, invented by Humphry Davy in the first decade of the 1800s, ...
contains a mixture of argon
Argon is a chemical element with the symbol Ar and atomic number 18. It is in group 18 of the periodic table and is a noble gas. Argon is the third-most abundant gas in Earth's atmosphere, at 0.934% (9340 ppmv). It is more than twice a ...
or xenon
Xenon is a chemical element with the symbol Xe and atomic number 54. It is a dense, colorless, odorless noble gas found in Earth's atmosphere in trace amounts. Although generally unreactive, it can undergo a few chemical reactions such as the ...
, mercury, and a variety of metal halide
In chemistry, a halide (rarely halogenide) is a binary chemical compound, of which one part is a halogen atom and the other part is an element or radical that is less electronegative (or more electropositive) than the halogen, to make a flu ...
s, such as sodium iodide and scandium iodide. The particular mixture of metal halides influences the correlated color temperature
Color temperature is the color of light emitted by an idealized opaque, non-reflective body at a particular temperature measured in kelvins. The color temperature scale is used to categorize the color of light emitted by other light sources ...
and intensity (making the light more blue or red, for example). When started, the argon gas in the lamp is ionized first, which helps to maintain the arc across the two electrodes with the applied starting voltage. The heat generated by the arc and electrodes then ionizes the mercury and metal halides into a plasma, which produces an increasingly brighter white light as the temperature and pressure increases to operating conditions.
The arc-tube operates at anywhere from 5–50 atm or more (70–700 psi or 500–5000 kPa) and 1000–3000 °C. Like all other gas-discharge lamps, metal-halide lamps have negative resistance (with the rare exception of self-ballasted lamps with a filament), and so require a ballast
Ballast is material that is used to provide stability to a vehicle or structure. Ballast, other than cargo, may be placed in a vehicle, often a ship or the gondola of a balloon or airship, to provide stability. A compartment within a boat, ship ...
to provide proper starting and operating voltages while regulating the current flow through the lamp. About 24% of the energy used by metal-halide lamps produces light (an efficacy of 65–115 lm/ W), making them substantially more efficient than incandescent bulbs
An incandescent light bulb, incandescent lamp or incandescent light globe is an electric light with a wire filament heated until it glows. The filament is enclosed in a glass bulb with a vacuum or inert gas to protect the filament from oxidat ...
, which typically have efficiencies in the range 2–4%.
Components
Metal-halide lamps consist of an arc tube with electrodes, an outer bulb, and a base.Arc tube
Inside thefused quartz
Fused quartz, fused silica or quartz glass is a glass consisting of almost pure silica (silicon dioxide, SiO2) in amorphous (non-crystalline) form. This differs from all other commercial glasses in which other ingredients are added which change ...
''arc tube'', two tungsten
Tungsten, or wolfram, is a chemical element with the symbol W and atomic number 74. Tungsten is a rare metal found naturally on Earth almost exclusively as compounds with other elements. It was identified as a new element in 1781 and first isol ...
electrodes doped with thorium
Thorium is a weakly radioactive metallic chemical element with the symbol Th and atomic number 90. Thorium is silvery and tarnishes black when it is exposed to air, forming thorium dioxide; it is moderately soft and malleable and has a high ...
are sealed into each end and an AC voltage is applied to them through molybdenum
Molybdenum is a chemical element with the symbol Mo and atomic number 42 which is located in period 5 and group 6. The name is from Neo-Latin ''molybdaenum'', which is based on Ancient Greek ', meaning lead, since its ores were confused with lead ...
foil seals fused in silica. It is the arc between the two electrodes where the light is actually created.
Besides mercury vapor, the lamp contains iodide
An iodide ion is the ion I−. Compounds with iodine in formal oxidation state −1 are called iodides. In everyday life, iodide is most commonly encountered as a component of iodized salt, which many governments mandate. Worldwide, iodine de ...
s or bromide
A bromide ion is the negatively charged form (Br−) of the element bromine, a member of the halogens group on the periodic table. Most bromides are colorless. Bromides have many practical roles, being found in anticonvulsants, flame-retardant ...
s of different metals. Iodine
Iodine is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol I and atomic number 53. The heaviest of the stable halogens, it exists as a semi-lustrous, non-metallic solid at standard conditions that melts to form a deep violet liquid at , ...
and bromine
Bromine is a chemical element with the symbol Br and atomic number 35. It is the third-lightest element in group 17 of the periodic table ( halogens) and is a volatile red-brown liquid at room temperature that evaporates readily to form a simi ...
are of the halogen group of the periodic table, and so are termed "halides" when ionized. Scandium
Scandium is a chemical element with the symbol Sc and atomic number 21. It is a silvery-white metallic d-block element. Historically, it has been classified as a rare-earth element, together with yttrium and the Lanthanides. It was discovered in ...
and sodium
Sodium is a chemical element with the symbol Na (from Latin ''natrium'') and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 of the periodic table. Its only stable ...
are also used in some types, with thallium
Thallium is a chemical element with the symbol Tl and atomic number 81. It is a gray post-transition metal that is not found free in nature. When isolated, thallium resembles tin, but discolors when exposed to air. Chemists William Crookes an ...
, indium
Indium is a chemical element with the symbol In and atomic number 49. Indium is the softest metal that is not an alkali metal. It is a silvery-white metal that resembles tin in appearance. It is a post-transition metal that makes up 0.21 parts ...
, and sodium
Sodium is a chemical element with the symbol Na (from Latin ''natrium'') and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 of the periodic table. Its only stable ...
in European ''Tri-Salt'' models. Dysprosium
Dysprosium is the chemical element with the symbol Dy and atomic number 66. It is a rare-earth element in the lanthanide series with a metallic silver luster. Dysprosium is never found in nature as a free element, though, like other lanthanide ...
used for high color temperature
Color temperature is the color of light emitted by an idealized opaque, non-reflective body at a particular temperature measured in kelvins. The color temperature scale is used to categorize the color of light emitted by other light sources ...
and tin for lower color temperature. Holmium
Holmium is a chemical element with the symbol Ho and atomic number 67. It is a rare-earth element and the eleventh member of the lanthanide series. It is a relatively soft, silvery, fairly corrosion-resistant and malleable metal. Like a lot of oth ...
and thulium
Thulium is a chemical element with the symbol Tm and atomic number 69. It is the thirteenth and third-last element in the lanthanide series. Like the other lanthanides, the most common oxidation state is +3, seen in its oxide, halides and other c ...
are used in very high power movie lighting models and in daylight colored metal halide lamps for area floodlighting, compact low wattage metal halide lamps, as well as stadium lighting in Europe. Gallium
Gallium is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ga and atomic number 31. Discovered by France, French chemist Paul-Émile Lecoq de Boisbaudran in 1875, Gallium is in boron group, group 13 of the periodic table and is similar to ...
or lead
Lead is a chemical element with the symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metal that is denser than most common materials. Lead is soft and malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cut, ...
are used in special high UV-A models for printing purposes. The mixture of the metals used defines the color of the lamp. Some types, for festive or theatrical effect, use almost pure iodides of thallium, for green lamps, and indium, for blue lamps. An alkali metal
The alkali metals consist of the chemical elements lithium (Li), sodium (Na), potassium (K),The symbols Na and K for sodium and potassium are derived from their Latin names, ''natrium'' and ''kalium''; these are still the origins of the names ...
, (sodium or potassium
Potassium is the chemical element with the symbol K (from Neo-Latin '' kalium'') and atomic number19. Potassium is a silvery-white metal that is soft enough to be cut with a knife with little force. Potassium metal reacts rapidly with atmos ...
), is almost always added to reduce the arc impedance, allowing the arc tube to be made sufficiently long and simple electrical ballast
An electrical ballast is a device placed in series with a load to limit the amount of current in an electrical circuit.
A familiar and widely used example is the inductive ballast used in fluorescent lamps to limit the current through the tub ...
s to be used. A noble gas
The noble gases (historically also the inert gases; sometimes referred to as aerogens) make up a class of chemical elements with similar properties; under standard conditions, they are all odorless, colorless, monatomic gases with very low ch ...
, usually argon
Argon is a chemical element with the symbol Ar and atomic number 18. It is in group 18 of the periodic table and is a noble gas. Argon is the third-most abundant gas in Earth's atmosphere, at 0.934% (9340 ppmv). It is more than twice a ...
, is cold filled into the arc tube at a pressure of about 2 kPa to facilitate starting of the discharge. Argon filled lamps are typically quite slow to start up, taking several minutes to reach full light intensity; xenon fill, as used in automotive headlamps, start up relatively faster.
The ends of the arc tube are often externally coated with white infrared
Infrared (IR), sometimes called infrared light, is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than those of Light, visible light. It is therefore invisible to the human eye. IR is generally understood to encompass wavelengths from ...
–reflective zirconium silicate or zirconium oxide
Zirconium dioxide (), sometimes known as zirconia (not to be confused with zircon), is a white crystalline oxide of zirconium. Its most naturally occurring form, with a monoclinic crystalline structure, is the mineral baddeleyite. A dopant stabi ...
to reflect heat back onto the electrodes to keep them hot and thermionically emitting. Some bulbs have a phosphor coating on the inner side of the outer bulb to improve the spectrum and diffuse the light.
In the mid-1980s a new type of metal-halide lamp was developed, which, instead of a quartz (fused silica) arc tube as used in mercury vapor lamps and previous metal-halide lamp designs, use a sintered
Clinker nodules produced by sintering
Sintering or frittage is the process of compacting and forming a solid mass of material by pressure or heat without melting it to the point of liquefaction.
Sintering happens as part of a manufacturing ...
alumina arc tube similar to those used in the high pressure sodium lamp. This development reduces the effects of ion creep that plagues fused silica arc tubes. During their life, sodium and other elements tend to migrate into the quartz tube and because of high UV radiation and gas ionization, will result in erosion of the electrodes therefore causing cycling of the lamp. The sintered alumina arc tube does not allow the ions to creep through, maintaining a more constant colour over the life of the lamp. These are usually referred as ceramic metal-halide lamp
A ceramic metal-halide lamp (CMH), also generically known as a ceramic discharge metal-halide (CDM) lamp, is a type of metal-halide lamp that is 10–20% more efficient than the traditional quartz metal halide and produces a superior color rend ...
s or CMH lamps.
The concept of adding metallic iodides for spectral modification (specifically: sodium - yellow, lithium - red, indium - blue, potassium and rubidium - deep red, and thallium - green) of a mercury arc discharge to create the first metal-halide lamp can be traced to patent US1025932 in 1912 by Charles Proteus Steinmetz
Charles Proteus Steinmetz (born Karl August Rudolph Steinmetz, April 9, 1865 – October 26, 1923) was a German-born American mathematician and electrical engineer and professor at Union College. He fostered the development of alternati ...
, the "Wizard of General Electric".
The amount of mercury used has lessened over years of progress.
Outer bulb
Most types are fitted with an outer glass bulb to protect the inner components and prevent heat loss. The outer bulb can also be used to block some or all of the UV light generated by the mercury vapor discharge, and can be composed of specially doped "UV stop" fused silica. Ultraviolet protection is commonly employed in single ended (single base) models and double ended models that provide illumination for nearby human use. Some high-powered models, particularly the lead-gallium UV printing models and models used for some types of sports stadium lighting do not have an outer bulb. The use of a bare arc tube can allow transmission of UV or precise positioning within the optical system of aluminaire
A light fixture (US English), light fitting (UK English), or luminaire is an electrical device containing an Lamp (electrical component), electric lamp that provides Lighting, illumination. All light fixtures have a fixture body and one or more ...
. The cover glass of the luminaire can be used to block the UV, and can also protect people or equipment if the lamp should fail by exploding.
Base
Some types have anEdison screw
Edison screw (ES) is a standard lightbulb socket for electric light bulbs. It was developed by Thomas Edison (1847–1931), patented in 1881, and was licensed in 1909 under General Electric's Mazda trademark. The bulbs have right-hand threaded ...
metal base, for various power ratings between 10 and 18,000 watts. Other types are double-ended, as depicted above, with R7s-24 bases composed of ceramic, along with metal connections between the interior of the arc tube and the exterior. These are made of various alloys (such as iron-cobalt-nickel) that have a thermal coefficient of expansion that matches that of the arc tube.
Ballasts
voltage
Voltage, also known as electric pressure, electric tension, or (electric) potential difference, is the difference in electric potential between two points. In a static electric field, it corresponds to the work needed per unit of charge to ...
across it decreases. If the bulb is powered from a constant voltage source such as directly from the AC wiring, the current will increase until the bulb destroys itself; therefore, halide bulbs require electrical ballast
An electrical ballast is a device placed in series with a load to limit the amount of current in an electrical circuit.
A familiar and widely used example is the inductive ballast used in fluorescent lamps to limit the current through the tub ...
s to limit the arc's current. There are two types:
#''Inductive ballast'' - Many fixtures use an inductive ballast, also known as a magnetic ballast, similar to those used with fluorescent lamp
A fluorescent lamp, or fluorescent tube, is a low-pressure mercury-vapor gas-discharge lamp that uses fluorescence to produce visible light. An electric current in the gas excites mercury vapor, which produces short-wave ultraviolet, ult ...
s. This consists of an iron-core inductor
An inductor, also called a coil, choke, or reactor, is a passive two-terminal electrical component that stores energy in a magnetic field when electric current flows through it. An inductor typically consists of an insulated wire wound into a c ...
. The inductor presents an impedance to AC current. If the current through the lamp increases, the inductor reduces the voltage to keep the current limited.
#''Electronic ballast'' - These are lighter and more compact. They consist of an electronic oscillator
An electronic oscillator is an electronic circuit that produces a periodic, oscillating electronic signal, often a sine wave or a square wave or a triangle wave. Oscillators convert direct current (DC) from a power supply to an alternating ...
which generates high frequency which is then converted to a low frequency square wave current to drive the lamp. Because they have lower resistive losses than an inductive ballast, they are more energy efficient. However, high-frequency operation does not increase lamp efficiency as for fluorescent lamp
A fluorescent lamp, or fluorescent tube, is a low-pressure mercury-vapor gas-discharge lamp that uses fluorescence to produce visible light. An electric current in the gas excites mercury vapor, which produces short-wave ultraviolet, ult ...
s. It may cause acoustic resonance
Acoustic resonance is a phenomenon in which an acoustic system amplifies sound waves whose frequency matches one of its own natural frequencies of vibration (its ''resonance frequencies'').
The term "acoustic resonance" is sometimes used to nar ...
in the arc, shortening the lamp life.
Pulse-start metal-halide bulbs don't contain a starting electrode which strikes the arc, and require an ignitor to generate a high-voltage (1–5 kV on cold strike, over 30 kV on hot restrike) pulse to start the arc. Electronic ballasts include the igniter circuit in one package. American National Standards Institute
The American National Standards Institute (ANSI ) is a private non-profit organization that oversees the development of voluntary consensus standards for products, services, processes, systems, and personnel in the United States. The orga ...
(ANSI) lamp-ballast system standards establish parameters for all metal-halide components (with the exception of some newer products).
Color temperature
Because of the whiter and more natural light generated, metal-halide lamps were initially preferred to the bluish mercury vapor lamps. With the introduction of specialized metal-halide mixtures, metal-halide lamps are now available with acorrelated color temperature
Color temperature is the color of light emitted by an idealized opaque, non-reflective body at a particular temperature measured in kelvins. The color temperature scale is used to categorize the color of light emitted by other light sources ...
from 3,000 K to over 20,000 K. Color temperature can vary slightly from lamp to lamp, and this effect is noticeable in places where many lamps are used. Because the lamp's color characteristics tend to change during lamp's life, color is measured after the bulb has been burned for 100 hours (seasoned) according to ANSI
The American National Standards Institute (ANSI ) is a private non-profit organization that oversees the development of voluntary consensus standards for products, services, processes, systems, and personnel in the United States. The organi ...
standards. Pulse start metal halide lamps have improved color rendering and provided a more controlled kelvin variance (±100 to 200 kelvins).
The color temperature of a metal-halide lamp can also be affected by the electrical characteristics of the electrical system powering the bulb and manufacturing variances in the bulb itself. If a metal-halide bulb is underpowered, because of the lower operating temperature
An operating temperature is the allowable temperature range of the local ambient environment at which an electrical or mechanical device operates. The device will operate effectively within a specified temperature range which varies based on the de ...
, its light output will be bluish because of the evaporation of mercury alone. This phenomenon can be seen during warmup, when the arc tube has not yet reached full operating temperature and the halides have not fully vaporized. It is also very apparent with dimming ballasts. The inverse is true for an overpowered bulb, but this condition can be hazardous, leading possibly to arc-tube explosion because of overheating and overpressure.
Starting and warm up
A cold metal-halide lamp cannot immediately begin producing its full light capacity because the temperature and pressure in the inner arc chamber require time to reach full operating levels. Starting the initial argon arc (or xenon in automotive) sometimes takes a few seconds, and the warm up period can be as long as five minutes (depending upon lamp type). During this time the lamp exhibits different colors as the various metal halides vaporize in the arc chamber. If power is interrupted, the lamp's arc will extinguish, and the high pressure that exists in the hot arc tube will prevent restriking the arc; with a normal ignitor a cool-down period of 5–10 minutes will be required before the lamp can be restarted, but with special ignitors and specially designed lamps, the arc can be immediately re-established. On fixtures without instant restrike capability, a momentary loss of power can mean no light for several minutes. For safety reasons, many metal-halide fixtures have a backup tungsten-halogen incandescent lamp that operates during cool-down and restrike. Once the metal halide restrikes and warms up, the incandescent safety light is switched off. A warm lamp also tends to take more time to reach its full brightness than a lamp that is started completely cold. Most hanging ceiling lamps tend to be passively cooled, with a combined ballast and lamp fixture.End of life behaviour
 Metal halide lamps, usually lose their output or change color due to the loss of halides and arctube blackening. They stop working at the end of a life that is similar to mercury lamps. In rare cases, they can also cycle on/off. Some can exhibit major color shift, and in rare cases, explode.
Metal halide lamps, usually lose their output or change color due to the loss of halides and arctube blackening. They stop working at the end of a life that is similar to mercury lamps. In rare cases, they can also cycle on/off. Some can exhibit major color shift, and in rare cases, explode.Risk of lamp explosion
All metal halide arc tubes deteriorate in strength over their lifetime due to chemical attack, thermal stress and mechanical vibration. As the lamp ages the arc tube becomes discoloured (often obtaining a dark grey shade), absorbing light and getting hotter. The tube will continue to become weaker until it eventually fails, causing the breakup of the tube. Early failure of the arc tube may occur due to manufacturing defects. Manufacturers may "season" new lamps to check for such defects before sale. Since a metal-halide lamp contains gases at a significant high pressure (up to 3.4 atmospheres), failure of the arc tube is inevitably a violent event. Fragments of arc tube will break the outer bulb, and hot glass fragments may fall on people or objects below. Hot fragments may present a fire hazard. Fixtures are designed to contain hot fragments with a hard glass cover, or may be designed for lamps with a quartz tube surrounding the arc tube to prevent breakage. Shattering of the arc tube may be avoided by replacing the lamp if there is an excessive blackening of the arc tube, the arc tube begins to swell, there is a sudden changing of the light color, or the lamp begins to cycle on and off.Gallery
light fixture
A light fixture (US English), light fitting (UK English), or luminaire is an electrical device containing an electric lamp that provides illumination. All light fixtures have a fixture body and one or more lamps. The lamps may be in sockets for ...
using a high-wattage metal-halide lamp, of the type used in factories and warehouses
File:HK CWB Tung Lo Wan 聖馬利亞堂 Saint Mary's Church electric light lamp May-2013.JPG, Metal halide floodlight
File:150 Watt Metal Halide.jpg, A Philips
Koninklijke Philips N.V. (), commonly shortened to Philips, is a Dutch multinational conglomerate corporation that was founded in Eindhoven in 1891. Since 1997, it has been mostly headquartered in Amsterdam, though the Benelux headquarters is ...
MHN-TD 150W/842 (150 watts, 4200 K) linear/tubular metal-halide lamp
File:Closeup Metal Halide Lamp.jpg, A Philips MHN-TD 150W/842 linear/tubular metal-halide lamp lit up at half power
File:Skybeamer-uniqema-640.jpg, A light source using a broad-spectrum metal-halide lamp pointing upward towards the sky
File:Night-Game.jpg, A metal-halide light bank at a softball field
File:Metal-Halide lamp 70 Watt screw fixture.jpg, A ceramic metal-halide lamp 70 Watt - screw fixture (aquarium)
See also
*Arc lamp
An arc lamp or arc light is a lamp that produces light by an electric arc (also called a voltaic arc).
The carbon arc light, which consists of an arc between carbon electrodes in air, invented by Humphry Davy in the first decade of the 1800s, ...
* Hydrargyrum medium-arc iodide lamp - high power metal-halide lamps as used in cinematography
*Mercury-vapor lamp
A mercury-vapor lamp is a gas-discharge lamp that uses an electric arc through vaporized mercury to produce light. The arc discharge is generally confined to a small fused quartz arc tube mounted within a larger soda lime or borosilicate gl ...
* Sodium-vapor lamp
*Neon lamp
A neon lamp (also neon glow lamp) is a miniature gas discharge lamp. The lamp typically consists of a small glass capsule that contains a mixture of neon and other gases at a low pressure and two electrodes (an anode and a cathode). When suff ...
*Sulfur lamp
The sulfur lamp (also sulphur lamp) is a highly efficient full-spectrum electrodeless lighting system whose light is generated by sulfur plasma that has been excited by microwave radiation. They are a particular type of plasma lamp, and one ...
*Charles Proteus Steinmetz
Charles Proteus Steinmetz (born Karl August Rudolph Steinmetz, April 9, 1865 – October 26, 1923) was a German-born American mathematician and electrical engineer and professor at Union College. He fostered the development of alternati ...
References
Further reading
* * Raymond Kane, Heinz Sell ''Revolution in lamps: a chronicle of 50 years of progress (2nd ed.)'', The Fairmont Press, Inc. 2001 {{DEFAULTSORT:Metal Halide Lamp Gas discharge lamps