Memes on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A meme ( ) is an idea, behavior, or style that spreads by means of imitation from person to person within a culture and often carries symbolic meaning representing a particular phenomenon or theme. A meme acts as a unit for carrying
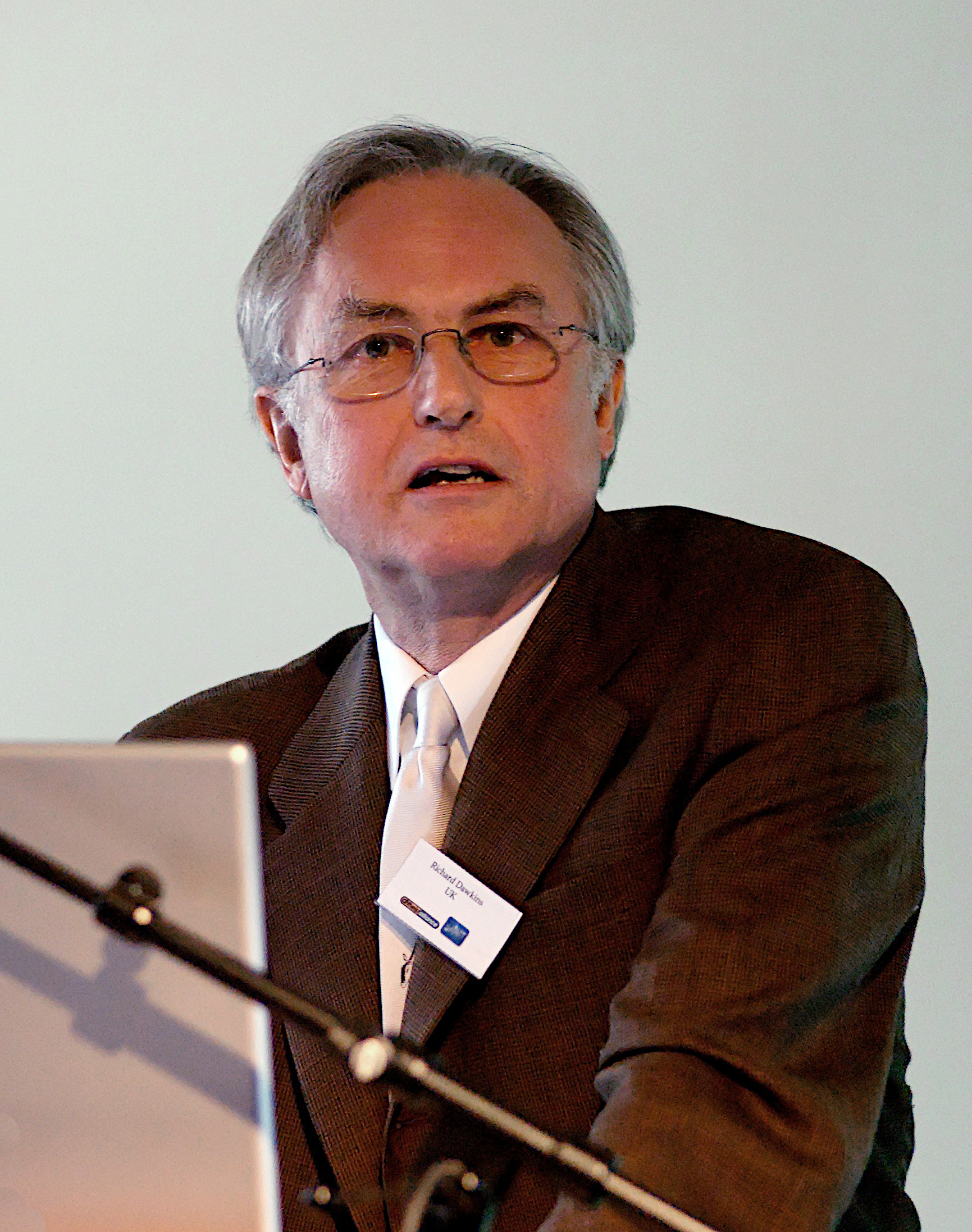

 Dawkins used the term to refer to any cultural entity that an observer might consider a replicator. He hypothesized that one could view many cultural entities as replicators, and pointed to melodies, fashions and learned skills as examples. Memes generally replicate through exposure to humans, who have evolved as efficient copiers of information and behavior. Because humans do not always copy memes perfectly, and because they may refine, combine or otherwise modify them with other memes to create new memes, they can change over time. Dawkins likened the process by which memes survive and change through the evolution of culture to the natural selection of genes in biological
Dawkins used the term to refer to any cultural entity that an observer might consider a replicator. He hypothesized that one could view many cultural entities as replicators, and pointed to melodies, fashions and learned skills as examples. Memes generally replicate through exposure to humans, who have evolved as efficient copiers of information and behavior. Because humans do not always copy memes perfectly, and because they may refine, combine or otherwise modify them with other memes to create new memes, they can change over time. Dawkins likened the process by which memes survive and change through the evolution of culture to the natural selection of genes in biological

 Memes, analogously to genes, vary in their aptitude to replicate; successful memes remain and spread, whereas unfit ones stall and are forgotten. Thus, memes that prove more effective at replicating and surviving are selected in the meme pool.
Memes first need retention. The longer a meme stays in its hosts, the higher its chances of propagation are. When a host uses a meme, the meme's life is extended. The reuse of the neural space hosting a certain meme's copy to host different memes is the greatest threat to that meme's copy. A meme that increases the longevity of its hosts will generally survive longer. On the contrary, a meme that shortens the longevity of its hosts will tend to disappear faster. However, as hosts are mortal, retention is not sufficient to perpetuate a meme in the long term; memes also need transmission.
Life-forms can transmit information both vertically (from parent to child, via replication of genes) and horizontally (through viruses and other means).
Memes can replicate vertically or horizontally within a single biological generation. They may also lie dormant for long periods of time.
Memes reproduce by copying from a nervous system to another one, either by communication or
Memes, analogously to genes, vary in their aptitude to replicate; successful memes remain and spread, whereas unfit ones stall and are forgotten. Thus, memes that prove more effective at replicating and surviving are selected in the meme pool.
Memes first need retention. The longer a meme stays in its hosts, the higher its chances of propagation are. When a host uses a meme, the meme's life is extended. The reuse of the neural space hosting a certain meme's copy to host different memes is the greatest threat to that meme's copy. A meme that increases the longevity of its hosts will generally survive longer. On the contrary, a meme that shortens the longevity of its hosts will tend to disappear faster. However, as hosts are mortal, retention is not sufficient to perpetuate a meme in the long term; memes also need transmission.
Life-forms can transmit information both vertically (from parent to child, via replication of genes) and horizontally (through viruses and other means).
Memes can replicate vertically or horizontally within a single biological generation. They may also lie dormant for long periods of time.
Memes reproduce by copying from a nervous system to another one, either by communication or
Dawkins's speech on the 30th anniversary of the publication of ''The Selfish Gene''
Dawkins 2006
article by
Journal of Memetics
a peer-refereed journal of memetics published from 1997 until 2005.
TED Talks February 2008.
Christopher von Bülow: ''Article Meme''
translated from: Jürgen Mittelstraß (ed.), ''Enzyklopädie Philosophie und Wissenschaftstheorie'', 2nd edn, vol. 5, Stuttgart/Weimar: Metzler 2013.
Richard Dawkins explains the real meaning of the word 'meme'
Richard Dawkins , Memes , Oxford Union
{{Authority control Abstraction Collective intelligence Concepts in epistemology Concepts in the philosophy of mind Concepts in the philosophy of science Cultural anthropology Emergence Evolutionary psychology Metaphysics of mind Philosophical theories Philosophy of language Philosophy of science 1976 neologisms
cultural
Culture () is an umbrella term which encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, customs, capabilities, and habits of the individuals in these groups.T ...
ideas, symbols, or practices, that can be transmitted from one mind to another through writing, speech, gestures, rituals, or other imitable phenomena with a mimicked theme. Supporters of the concept regard memes as cultural analogues to gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a b ...
s in that they self-replicate, mutate, and respond to selective pressures. In popular language, a meme may refer to an Internet meme
An Internet meme, commonly known simply as a meme ( ), is an idea, behavior, style, or image that is spread via the Internet, often through social media platforms. What is considered a meme may vary across different communities on the Internet ...
, typically an image, that is remixed, copied, and circulated in a shared cultural experience online.
Proponents theorize that memes are a viral phenomenon
Viral phenomena or viral sensation are objects or patterns that are able to replicate themselves or convert other objects into copies of themselves when these objects are exposed to them. Analogous to the way in which viruses propagate, the te ...
that may evolve by natural selection in a manner analogous to that of biological evolution
Evolution is change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. These characteristics are the expressions of genes, which are passed on from parent to offspring during reproduction. Variation t ...
. Memes do this through the processes of variation, mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, m ...
, competition
Competition is a rivalry where two or more parties strive for a common goal which cannot be shared: where one's gain is the other's loss (an example of which is a zero-sum game). Competition can arise between entities such as organisms, ind ...
, and inheritance
Inheritance is the practice of receiving private property, titles, debts, entitlements, privileges, rights, and obligations upon the death of an individual. The rules of inheritance differ among societies and have changed over time. Of ...
, each of which influences a meme's reproductive success. Memes spread through the behavior that they generate in their hosts. Memes that propagate
Propagation can refer to:
*Chain propagation in a chemical reaction mechanism
* Crack propagation, the growth of a crack during the fracture of materials
*Propaganda, non-objective information used to further an agenda
*Reproduction, and other form ...
less prolifically may become extinct
Extinction is the termination of a kind of organism or of a group of kinds (taxon), usually a species. The moment of extinction is generally considered to be the death of the last individual of the species, although the capacity to breed and ...
, while others may survive, spread, and (for better or for worse) mutate. Memes that replicate most effectively enjoy more success, and some may replicate effectively even when they prove to be detrimental to the welfare of their hosts. "But if we consider culture as its own self-organizing system—a system with its own agenda and pressure to survive—then the history of humanity gets even more interesting. As Richard Dawkins has shown, systems of self-replicating ideas or memes can quickly accumulate their own agenda and behaviours. I assign no higher motive to a cultural entity than the primitive drive to reproduce itself and modify its environment to aid its spread. One way the self organizing system can do this is by consuming human biological resources."
A field of study called ''memetics
Memetics is a study of information and culture. While memetics originated as an analogy with Darwinian evolution, digital communication, media, and sociology scholars have also adopted the term "memetics" to describe an established empirical stud ...
'' arose in the 1990s to explore the concepts and transmission of memes in terms of an evolutionary model
A number of different Markov models of DNA sequence evolution have been proposed. These substitution models differ in terms of the parameters used to describe the rates at which one nucleotide replaces another during evolution. These models are ...
. Criticism from a variety of fronts has challenged the notion that academic study can examine memes empirical
Empirical evidence for a proposition is evidence, i.e. what supports or counters this proposition, that is constituted by or accessible to sense experience or experimental procedure. Empirical evidence is of central importance to the sciences and ...
ly. However, developments in neuroimaging
Neuroimaging is the use of quantitative (computational) techniques to study the structure and function of the central nervous system, developed as an objective way of scientifically studying the healthy human brain in a non-invasive manner. Incr ...
may make empirical study possible. Some commentators in the social sciences
Social science is one of the branches of science, devoted to the study of societies and the relationships among individuals within those societies. The term was formerly used to refer to the field of sociology, the original "science of so ...
question the idea that one can meaningfully categorize culture in terms of discrete units, and are especially critical of the biological nature of the theory's underpinnings. Others have argued that this use of the term is the result of a misunderstanding of the original proposal.
The word ''meme'' itself is a neologism
A neologism Ancient_Greek.html"_;"title="_from_Ancient_Greek">Greek_νέο-_''néo''(="new")_and_λόγος_/''lógos''_meaning_"speech,_utterance"is_a_relatively_recent_or_isolated_term,_word,_or_phrase_that_may_be_in_the_process_of_entering_com ...
coined by Richard Dawkins
Richard Dawkins (born 26 March 1941) is a British evolutionary biologist and author. He is an emeritus fellow of New College, Oxford and was Professor for Public Understanding of Science in the University of Oxford from 1995 to 2008. An ...
, originating from his 1976 book ''The Selfish Gene
''The Selfish Gene'' is a 1976 book on evolution by the ethologist Richard Dawkins, in which the author builds upon the principal theory of George C. Williams's '' Adaptation and Natural Selection'' (1966). Dawkins uses the term "selfish gen ...
''. "We need a name for the new replicator, a noun that conveys the idea of a unit of cultural transmission, or a unit of ''imitation''. 'Mimeme' comes from a suitable Greek root, but I want a monosyllable that sounds a bit like 'gene'. I hope my classicist friends will forgive me if I abbreviate mimeme to ''meme''. If it is any consolation, it could alternatively be thought of as being related to 'memory', or to the French word ''même''. It should be pronounced to rhyme with 'cream'." Dawkins's own position is somewhat ambiguous. He welcomed N. K. Humphrey's suggestion that "memes should be considered as living structures, not just metaphorically" and proposed to regard memes as "physically residing in the brain." Although Dawkins said his original intentions had been simpler, he approved Humphrey's opinion and he endorsed Susan Blackmore
Susan Jane Blackmore (born 29 July 1951) is a British writer, lecturer, sceptic, broadcaster, and a Visiting Professor at the University of Plymouth. Her fields of research include memetics, parapsychology, consciousness, and she is best known ...
's 1999 project to give a scientific theory of memes, complete with predictions and empirical support.
Etymology
The term ''meme'' is a shortening (modeled on ''gene'') of ''mimeme'', which comes fromAncient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic pe ...
''mīmēma'' (; ), meaning 'imitated thing', itself from ''mimeisthai'' (, 'to imitate'), from ''mimos'' (, 'mime').
The word was coined by British evolutionary biologist Richard Dawkins
Richard Dawkins (born 26 March 1941) is a British evolutionary biologist and author. He is an emeritus fellow of New College, Oxford and was Professor for Public Understanding of Science in the University of Oxford from 1995 to 2008. An ...
in ''The Selfish Gene
''The Selfish Gene'' is a 1976 book on evolution by the ethologist Richard Dawkins, in which the author builds upon the principal theory of George C. Williams's '' Adaptation and Natural Selection'' (1966). Dawkins uses the term "selfish gen ...
'' (1976) as a concept for discussion of evolution
Evolution is change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. These characteristics are the expressions of genes, which are passed on from parent to offspring during reproduction. Variation ...
ary principles in explaining the spread of ideas and cultural phenomena. Examples of memes given in Dawkins' book include melodies
A melody (from Greek μελῳδία, ''melōidía'', "singing, chanting"), also tune, voice or line, is a linear succession of musical tones that the listener perceives as a single entity. In its most literal sense, a melody is a combinati ...
, catchphrase
A catchphrase (alternatively spelled catch phrase) is a phrase or expression recognized by its repeated utterance. Such phrases often originate in popular culture and in the arts, and typically spread through word of mouth and a variety of mass ...
s, fashion, and the technology of building arches. The word 'meme' is autological in nature, meaning it's a word that describes itself; in other words, the word 'meme' is itself a meme.
Origins

Early formulations
Although Richard Dawkins invented the term ''meme'' and developed meme theory, he has not claimed that the idea was entirely novel, and there have been other expressions for similar ideas in the past. For instance, the possibility that ideas were subject to the same pressures of evolution as were biological attributes was discussed in the time of Charles Darwin. T. H. Huxley (1880) claimed that "The struggle for existence holds as much in the intellectual as in the physical world. A theory is a species of thinking, and its right to exist is coextensive with its power of resisting extinction by its rivals." In 1904,Richard Semon
Richard Wolfgang Semon (22 August 1859, in Berlin – 27 December 1918, in Munich) was a German zoologist, explorer, evolutionary biologist, a memory researcher who believed in the inheritance of acquired characteristics and applied this to social ...
published ''Die Mneme'' (which appeared in English in 1924 as ''The Mneme''). The term ''mneme'' was also used in Maurice Maeterlinck
Maurice Polydore Marie Bernard Maeterlinck (29 August 1862 – 6 May 1949), also known as Count (or Comte) Maeterlinck from 1932, was a Belgian playwright, poet, and essayist who was Flemish but wrote in French. He was awarded the Nobel Prize in ...
's ''The Life of the White Ant'' (1926), with some parallels to Dawkins's concept. Kenneth Pike
Kenneth Lee Pike (June 9, 1912 – December 31, 2000) was an American linguist and anthropologist. He was the originator of the theory of tagmemics, the coiner of the terms "emic" and "etic" and the developer of the constructed language ...
had, in 1954, coined the related terms ''emic'' and ''etic'', generalizing the linguistic units of phoneme
In phonology and linguistics, a phoneme () is a unit of sound that can distinguish one word from another in a particular language.
For example, in most dialects of English, with the notable exception of the West Midlands and the north-wes ...
, morpheme
A morpheme is the smallest meaningful Constituent (linguistics), constituent of a linguistic expression. The field of linguistics, linguistic study dedicated to morphemes is called morphology (linguistics), morphology.
In English, morphemes are ...
, grapheme
In linguistics, a grapheme is the smallest functional unit of a writing system.
The word ''grapheme'' is derived and the suffix ''-eme'' by analogy with ''phoneme'' and other names of emic units. The study of graphemes is called '' graphemi ...
, lexeme
A lexeme () is a unit of lexical meaning that underlies a set of words that are related through inflection. It is a basic abstract unit of meaning, a unit of morphological analysis in linguistics that roughly corresponds to a set of forms take ...
, and tagmeme
A tagmeme is the smallest functional element in the grammatical structure of a language. The term was introduced in the 1930s by the linguist Leonard Bloomfield, who defined it as the smallest meaningful unit of grammatical form (analogous to th ...
(as set out by Leonard Bloomfield
Leonard Bloomfield (April 1, 1887 – April 18, 1949) was an American linguist who led the development of structural linguistics in the United States during the 1930s and the 1940s. He is considered to be the father of American distributionalis ...
), distinguishing insider and outside views of communicative behavior.
Dawkins
The word ''meme'' originated withRichard Dawkins
Richard Dawkins (born 26 March 1941) is a British evolutionary biologist and author. He is an emeritus fellow of New College, Oxford and was Professor for Public Understanding of Science in the University of Oxford from 1995 to 2008. An ...
' 1976 book ''The Selfish Gene
''The Selfish Gene'' is a 1976 book on evolution by the ethologist Richard Dawkins, in which the author builds upon the principal theory of George C. Williams's '' Adaptation and Natural Selection'' (1966). Dawkins uses the term "selfish gen ...
''.
Dawkins cites as inspiration the work of geneticist L. L. Cavalli-Sforza, anthropologist F. T. Cloak, and ethologist J. M. Cullen. Dawkins wrote that evolution depended not on the particular chemical basis of genetics, but only on the existence of a self-replicating unit of transmission—in the case of biological evolution, the gene. For Dawkins, the meme exemplified another self-replicating unit with potential significance in explaining human behavior and cultural evolution.
 Dawkins used the term to refer to any cultural entity that an observer might consider a replicator. He hypothesized that one could view many cultural entities as replicators, and pointed to melodies, fashions and learned skills as examples. Memes generally replicate through exposure to humans, who have evolved as efficient copiers of information and behavior. Because humans do not always copy memes perfectly, and because they may refine, combine or otherwise modify them with other memes to create new memes, they can change over time. Dawkins likened the process by which memes survive and change through the evolution of culture to the natural selection of genes in biological
Dawkins used the term to refer to any cultural entity that an observer might consider a replicator. He hypothesized that one could view many cultural entities as replicators, and pointed to melodies, fashions and learned skills as examples. Memes generally replicate through exposure to humans, who have evolved as efficient copiers of information and behavior. Because humans do not always copy memes perfectly, and because they may refine, combine or otherwise modify them with other memes to create new memes, they can change over time. Dawkins likened the process by which memes survive and change through the evolution of culture to the natural selection of genes in biological evolution
Evolution is change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. These characteristics are the expressions of genes, which are passed on from parent to offspring during reproduction. Variation ...
.
Dawkins defined the ''meme'' as a unit of cultural transmission
Cultural learning is the way a group of people or animals within a society or culture tend to learn and pass on information. Learning styles are greatly influenced by how a culture socializes with its children and young people. Cross-cultural res ...
, or a unit of imitation and replication, but later definitions would vary. The lack of a consistent, rigorous, and precise understanding of what typically makes up one unit of cultural transmission remains a problem in debates about memetics
Memetics is a study of information and culture. While memetics originated as an analogy with Darwinian evolution, digital communication, media, and sociology scholars have also adopted the term "memetics" to describe an established empirical stud ...
. In contrast, the concept of genetics gained concrete evidence with the discovery
Discovery may refer to:
* Discovery (observation), observing or finding something unknown
* Discovery (fiction), a character's learning something unknown
* Discovery (law), a process in courts of law relating to evidence
Discovery, The Discove ...
of the biological functions of DNA. Meme transmission requires a physical medium, such as photons, sound waves, touch, taste, or smell because memes can be transmitted only through the senses.
Dawkins noted that in a society with culture a person need not have descendants to remain influential in the actions of individuals thousands of years after their death:
But if you contribute to the world's culture, if you have a good idea...it may live on, intact, long after your genes have dissolved in the common pool.Socrates Socrates (; ; –399 BC) was a Greek philosopher from Athens who is credited as the founder of Western philosophy and among the first moral philosophers of the ethical tradition of thought. An enigmatic figure, Socrates authored no t ...may or may not have a gene or two alive in the world today, as G.C. Williams has remarked, but who cares? The meme-complexes of Socrates,Leonardo Leonardo is a masculine given name, the Italian, Spanish, and Portuguese equivalent of the English, German, and Dutch name, Leonard. People Notable people with the name include: * Leonardo da Vinci (1452–1519), Italian Renaissance scientist ...,Copernicus Nicolaus Copernicus (; pl, Mikołaj Kopernik; gml, Niklas Koppernigk, german: Nikolaus Kopernikus; 19 February 1473 – 24 May 1543) was a Renaissance polymath, active as a mathematician, astronomer, and Catholic canon, who formulat ...and Marconi are still going strong.
Memetic lifecycle: transmission, retention

 Memes, analogously to genes, vary in their aptitude to replicate; successful memes remain and spread, whereas unfit ones stall and are forgotten. Thus, memes that prove more effective at replicating and surviving are selected in the meme pool.
Memes first need retention. The longer a meme stays in its hosts, the higher its chances of propagation are. When a host uses a meme, the meme's life is extended. The reuse of the neural space hosting a certain meme's copy to host different memes is the greatest threat to that meme's copy. A meme that increases the longevity of its hosts will generally survive longer. On the contrary, a meme that shortens the longevity of its hosts will tend to disappear faster. However, as hosts are mortal, retention is not sufficient to perpetuate a meme in the long term; memes also need transmission.
Life-forms can transmit information both vertically (from parent to child, via replication of genes) and horizontally (through viruses and other means).
Memes can replicate vertically or horizontally within a single biological generation. They may also lie dormant for long periods of time.
Memes reproduce by copying from a nervous system to another one, either by communication or
Memes, analogously to genes, vary in their aptitude to replicate; successful memes remain and spread, whereas unfit ones stall and are forgotten. Thus, memes that prove more effective at replicating and surviving are selected in the meme pool.
Memes first need retention. The longer a meme stays in its hosts, the higher its chances of propagation are. When a host uses a meme, the meme's life is extended. The reuse of the neural space hosting a certain meme's copy to host different memes is the greatest threat to that meme's copy. A meme that increases the longevity of its hosts will generally survive longer. On the contrary, a meme that shortens the longevity of its hosts will tend to disappear faster. However, as hosts are mortal, retention is not sufficient to perpetuate a meme in the long term; memes also need transmission.
Life-forms can transmit information both vertically (from parent to child, via replication of genes) and horizontally (through viruses and other means).
Memes can replicate vertically or horizontally within a single biological generation. They may also lie dormant for long periods of time.
Memes reproduce by copying from a nervous system to another one, either by communication or imitation
Imitation (from Latin ''imitatio'', "a copying, imitation") is a behavior whereby an individual observes and replicates another's behavior. Imitation is also a form of that leads to the "development of traditions, and ultimately our culture. I ...
. Imitation often involves the copying of an observed behavior of another individual. Communication may be direct or indirect, where memes transmit from one individual to another through a copy recorded in an inanimate source, such as a book or a musical score. Adam McNamara has suggested that memes can be thereby classified as either internal or external memes (i-memes or e-memes).
Some commentators have likened the transmission of memes to the spread of contagions. Social contagions such as fads, hysteria
Hysteria is a term used colloquially to mean ungovernable emotional excess and can refer to a temporary state of mind or emotion. In the nineteenth century, hysteria was considered a diagnosable physical illness in women. It is assumed that ...
, copycat crime
A copycat crime is a criminal act that is modelled after or inspired by a previous crime. It notably occurs after exposure to media content depicted said crimes, and/or a live criminal model.
Copycat effect
The copycat effect is the alleged tend ...
, and copycat suicide
A copycat suicide is defined as an emulation of another suicide that the person attempting suicide knows about either from local knowledge or due to accounts or depictions of the original suicide on television and in other media. The publicized ...
exemplify memes seen as the contagious imitation of ideas. Observers distinguish the contagious imitation of memes from instinctively contagious phenomena such as yawning and laughing, which they consider innate (rather than socially learned) behaviors.
Aaron Lynch described seven general patterns of meme transmission, or "thought contagion":
# ''Quantity of parenthood'': an idea that influences the number of children one has. Children respond particularly receptively to the ideas of their parents, and thus ideas that directly or indirectly encourage a higher birth rate will replicate themselves at a higher rate than those that discourage higher birth rates.
# ''Efficiency of parenthood'': an idea that increases the proportion of children who will adopt ideas of their parents. Cultural separatism
Separatism is the advocacy of cultural, ethnic, tribal, religious, racial, governmental or gender separation from the larger group. As with secession, separatism conventionally refers to full political separation. Groups simply seeking greate ...
exemplifies one practice in which one can expect a higher rate of meme-replication—because the meme for separation creates a barrier from exposure to competing ideas.
# ''Proselytic'': ideas generally passed to others beyond one's own children. Ideas that encourage the proselytism
Proselytism () is the policy of attempting to convert people's religious or political beliefs. Proselytism is illegal in some countries.
Some draw distinctions between ''evangelism'' or '' Da‘wah'' and proselytism regarding proselytism as invol ...
of a meme, as seen in many religious or political movements, can replicate memes horizontally through a given generation, spreading more rapidly than parent-to-child meme-transmissions do.
# ''Preservational'': ideas that influence those that hold them to continue to hold them for a long time. Ideas that encourage longevity in their hosts, or leave their hosts particularly resistant to abandoning or replacing these ideas, enhance the preservability of memes and afford protection from the competition or proselytism of other memes.
# ''Adversative'': ideas that influence those that hold them to attack or sabotage competing ideas and/or those that hold them. Adversative replication can give an advantage in meme transmission when the meme itself encourages aggression against other memes.
# ''Cognitive'': ideas perceived as cogent by most in the population who encounter them. Cognitively transmitted memes depend heavily on a cluster of other ideas and cognitive traits already widely held in the population, and thus usually spread more passively than other forms of meme transmission. Memes spread in cognitive transmission do not count as self-replicating.
# ''Motivational'': ideas that people adopt because they perceive some self-interest in adopting them. Strictly speaking, motivationally transmitted memes do not self-propagate, but this mode of transmission often occurs in association with memes self-replicated in the efficiency parental, proselytic and preservational modes.
Memes as discrete units
Dawkins initially defined ''meme'' as a noun that "conveys the idea of a unit of cultural transmission, or a unit of ''imitation''." John S. Wilkins retained the notion of meme as a kernel of cultural imitation while emphasizing the meme's evolutionary aspect, defining the meme as "the least unit of sociocultural information relative to a selection process that has favorable or unfavorable selection bias that exceeds its endogenous tendency to change." The meme as a unit provides a convenient means of discussing "a piece of thought copied from person to person," regardless of whether that thought contains others inside it, or forms part of a larger meme. A meme could consist of a single word, or a meme could consist of the entire speech in which that word first occurred. This forms an analogy to the idea of a gene as a single unit of self-replicating information found on the self-replicatingchromosome
A chromosome is a long DNA molecule with part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells the most important of these proteins ar ...
.
While the identification of memes as "units" conveys their nature to replicate as discrete, indivisible entities, it does not imply that thoughts somehow become quantized or that "atom
Every atom is composed of a nucleus and one or more electrons bound to the nucleus. The nucleus is made of one or more protons and a number of neutrons. Only the most common variety of hydrogen has no neutrons.
Every solid, liquid, gas, a ...
ic" ideas exist that cannot be dissected into smaller pieces. A meme has no given size. Susan Blackmore
Susan Jane Blackmore (born 29 July 1951) is a British writer, lecturer, sceptic, broadcaster, and a Visiting Professor at the University of Plymouth. Her fields of research include memetics, parapsychology, consciousness, and she is best known ...
writes that melodies from Beethoven
Ludwig van Beethoven (baptised 17 December 177026 March 1827) was a German composer and pianist. Beethoven remains one of the most admired composers in the history of Western music; his works rank amongst the most performed of the classic ...
's symphonies are commonly used to illustrate the difficulty involved in delimiting memes as discrete units. She notes that while the first four notes of Beethoven's Fifth Symphony
The Symphony No. 5 in C minor of Ludwig van Beethoven, Op. 67, was written between 1804 and 1808. It is one of the best-known compositions in classical music and one of the most frequently played symphonies, and it is widely considered one of ...
() form a meme widely replicated as an independent unit, one can regard the entire symphony as a single meme as well.
The inability to pin an idea or cultural feature to quantifiable key units is widely acknowledged as a problem for memetics. It has been argued however that the traces of memetic processing can be quantified utilizing neuroimaging techniques which measure changes in the connectivity profiles between brain regions." Blackmore meets such criticism by stating that memes compare with genes in this respect: that while a gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a b ...
has no particular size, nor can we ascribe every phenotypic
In genetics, the phenotype () is the set of observable characteristics or traits of an organism. The term covers the organism's morphology or physical form and structure, its developmental processes, its biochemical and physiological pr ...
feature directly to a particular gene, it has value because it encapsulates that key unit of inherited expression subject to evolutionary pressures. To illustrate, she notes evolution selects for the gene for features such as eye color; it does not select for the individual nucleotide in a strand of DNA. Memes play a comparable role in understanding the evolution of imitated behaviors.
''Genes, Mind, and Culture: The Coevolutionary Process'' (1981) by Charles J. Lumsden and E. O. Wilson proposes the theory that genes and culture co-evolve, and that the fundamental biological units of culture must correspond to neuronal networks that function as nodes of semantic memory
Memory is the faculty of the mind by which data or information is encoded, stored, and retrieved when needed. It is the retention of information over time for the purpose of influencing future action. If past events could not be remember ...
. Lumsden and Wilson coined their own word, '' culturgen'', which did not catch on. Coauthor Wilson later acknowledged the term ''meme'' as the best label for the fundamental unit of cultural inheritance in his 1998 book '' Consilience: The Unity of Knowledge'', which elaborates upon the fundamental role of memes in unifying the natural
Nature, in the broadest sense, is the physical world or universe. "Nature" can refer to the phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large, if not the only, part of science. Although humans ar ...
and social sciences
Social science is one of the branches of science, devoted to the study of societies and the relationships among individuals within those societies. The term was formerly used to refer to the field of sociology, the original "science of so ...
.
Evolutionary influences on memes
Dawkins noted the three conditions that must exist for evolution to occur: # variation, or the introduction of new change to existing elements; # heredity or replication, or the capacity to create copies of elements; # differential "fitness", or the opportunity for one element to be more or less suited to the environment than another. Dawkins emphasizes that the process of evolution naturally occurs whenever these conditions co-exist, and that evolution does not apply only to organic elements such as genes. He regards memes as also having the properties necessary for evolution, and thus sees meme evolution as not simply analogous to genetic evolution, but as a real phenomenon subject to the laws ofnatural selection
Natural selection is the differential survival and reproduction of individuals due to differences in phenotype. It is a key mechanism of evolution, the change in the heritable traits characteristic of a population over generations. Cha ...
. Dawkins noted that as various ideas pass from one generation
A generation refers to all of the people born and living at about the same time, regarded collectively. It can also be described as, "the average period, generally considered to be about 20–30 years, during which children are born and gr ...
to the next, they may either enhance or detract from the survival of the people who obtain those ideas, or influence the survival of the ideas themselves. For example, a certain culture may develop unique designs and methods of tool
A tool is an object that can extend an individual's ability to modify features of the surrounding environment or help them accomplish a particular task. Although many animals use simple tools, only human beings, whose use of stone tools dates b ...
-making that give it a competitive advantage over another culture. Each tool-design thus acts somewhat similarly to a biological gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a b ...
in that some populations have it and others do not, and the meme's function directly affects the presence of the design in future generations. In keeping with the thesis that in evolution one can regard organisms simply as suitable "hosts" for reproducing genes, Dawkins argues that one can view people as "hosts" for replicating memes. Consequently, a successful meme may or may not need to provide any benefit to its host.
Unlike genetic evolution, memetic evolution can show both Darwinian
Darwinism is a theory of biological evolution developed by the English naturalist Charles Darwin (1809–1882) and others, stating that all species of organisms arise and develop through the natural selection of small, inherited variations that ...
and Lamarckian
Lamarckism, also known as Lamarckian inheritance or neo-Lamarckism, is the notion that an organism can pass on to its offspring physical characteristics that the parent organism acquired through use or disuse during its lifetime. It is also calle ...
traits. Cultural memes will have the characteristic of Lamarckian inheritance when a host aspires to replicate the given meme through inference rather than by exactly copying it. Take for example the case of the transmission of a simple skill such as hammering a nail, a skill that a learner imitates from watching a demonstration without necessarily imitating every discrete movement modeled by the teacher in the demonstration, stroke for stroke. Susan Blackmore
Susan Jane Blackmore (born 29 July 1951) is a British writer, lecturer, sceptic, broadcaster, and a Visiting Professor at the University of Plymouth. Her fields of research include memetics, parapsychology, consciousness, and she is best known ...
distinguishes the difference between the two modes of inheritance in the evolution of memes, characterizing the Darwinian mode as "copying the instructions" and the Lamarckian as "copying the product."
Clusters of memes, or '' memeplexes'' (also known as ''meme complexes'' or as ''memecomplexes''), such as cultural or political doctrines and systems, may also play a part in the acceptance of new memes. Memeplexes comprise groups of memes that replicate together and coadapt. Memes that fit within a successful memeplex may gain acceptance by "piggybacking" on the success of the memeplex.
As an example, John D. Gottsch discusses the transmission, mutation and selection of religious memeplexes and the theistic memes contained. Theistic memes discussed include the "prohibition of aberrant sexual practices such as incest, adultery, homosexuality, bestiality, castration, and religious prostitution", which may have increased vertical transmission of the parent religious memeplex. Similar memes are thereby included in the majority of religious memeplexes, and harden over time; they become an "inviolable canon" or set of dogma
Dogma is a belief or set of beliefs that is accepted by the members of a group without being questioned or doubted. It may be in the form of an official system of principles or doctrines of a religion, such as Roman Catholicism, Judaism, Islam ...
s, eventually finding their way into secular law
Law is a set of rules that are created and are enforceable by social or governmental institutions to regulate behavior,Robertson, ''Crimes against humanity'', 90. with its precise definition a matter of longstanding debate. It has been vario ...
. This could also be referred to as the propagation of a taboo
A taboo or tabu is a social group's ban, prohibition, or avoidance of something (usually an utterance or behavior) based on the group's sense that it is excessively repulsive, sacred, or allowed only for certain persons.''Encyclopædia Britannica ...
.
Memetics
The discipline of memetics, which dates from the mid-1980s, provides an approach toevolutionary model
A number of different Markov models of DNA sequence evolution have been proposed. These substitution models differ in terms of the parameters used to describe the rates at which one nucleotide replaces another during evolution. These models are ...
s of cultural information transfer
In telecommunications, information transfer is the process of moving messages containing user information from a source to a sink via a communication channel. In this sense, information transfer is equivalent to data transmission which highlights ...
based on the concept of the meme. Memeticists have proposed that just as memes function analogously to gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a b ...
s, memetics functions analogously to genetics
Genetics is the study of genes, genetic variation, and heredity in organisms.Hartl D, Jones E (2005) It is an important branch in biology because heredity is vital to organisms' evolution. Gregor Mendel, a Moravian Augustinian friar work ...
. Memetics attempts to apply conventional scientific methods (such as those used in population genetics
Population genetics is a subfield of genetics that deals with genetic differences within and between populations, and is a part of evolutionary biology. Studies in this branch of biology examine such phenomena as adaptation, speciation, and po ...
and epidemiology
Epidemiology is the study and analysis of the distribution (who, when, and where), patterns and determinants of health and disease conditions in a defined population.
It is a cornerstone of public health, and shapes policy decisions and evi ...
) to explain existing patterns and transmission of cultural
Culture () is an umbrella term which encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, customs, capabilities, and habits of the individuals in these groups.T ...
ideas.
Principal criticisms of memetics include the claim that memetics ignores established advances in other fields of cultural study, such as sociology
Sociology is a social science that focuses on society, human social behavior, patterns of social relationships, social interaction, and aspects of culture associated with everyday life. It uses various methods of empirical investigation an ...
, cultural anthropology
Cultural anthropology is a branch of anthropology focused on the study of cultural variation among humans. It is in contrast to social anthropology, which perceives cultural variation as a subset of a posited anthropological constant. The portma ...
, cognitive psychology
Cognitive psychology is the scientific study of mental processes such as attention, language use, memory, perception, problem solving, creativity, and reasoning.
Cognitive psychology originated in the 1960s in a break from behaviorism, which ...
, and social psychology
Social psychology is the scientific study of how thoughts, feelings, and behaviors are influenced by the real or imagined presence of other people or by social norms. Social psychologists typically explain human behavior as a result of the ...
. Questions remain whether or not the meme concept counts as a validly disprovable scientific theory. This view regards memetics as a theory in its infancy: a protoscience
__NOTOC__
In the philosophy of science, there are several definitions of protoscience. Its simplest meaning (most closely reflecting its roots of '' proto-'' + ''science'') involves the earliest eras of the history of science, when the scientific m ...
to proponents, or a pseudoscience
Pseudoscience consists of statements, beliefs, or practices that claim to be both scientific and factual but are incompatible with the scientific method. Pseudoscience is often characterized by contradictory, exaggerated or unfalsifiable claim ...
to some detractors.
Criticism of meme theory
An objection to the study of the evolution of memes in genetic terms (although not to the existence of memes) involves a perceived gap in the gene/meme analogy: the cumulative evolution of genes depends on biological selection-pressures neither too great nor too small in relation to mutation-rates. There seems no reason to think that the same balance will exist in the selection pressures on memes. Luis Benitez-Bribiesca M.D., a critic of memetics, calls the theory a "pseudoscientific
Pseudoscience consists of statements, beliefs, or practices that claim to be both scientific and factual but are incompatible with the scientific method. Pseudoscience is often characterized by contradictory, exaggerated or unfalsifiable claim ...
dogma
Dogma is a belief or set of beliefs that is accepted by the members of a group without being questioned or doubted. It may be in the form of an official system of principles or doctrines of a religion, such as Roman Catholicism, Judaism, Islam ...
" and "a dangerous idea that poses a threat to the serious study of consciousness
Consciousness, at its simplest, is sentience and awareness of internal and external existence. However, the lack of definitions has led to millennia of analyses, explanations and debates by philosophers, theologians, linguisticians, and scien ...
and cultural evolution
Cultural evolution is an evolutionary theory of social change. It follows from the definition of culture as "information capable of affecting individuals' behavior that they acquire from other members of their species through teaching, imitation ...
". As a factual criticism, Benitez-Bribiesca points to the lack of a "code script" for memes (analogous to the DNA of genes), and to the excessive instability of the meme mutation mechanism (that of an idea going from one brain to another), which would lead to a low replication accuracy and a high mutation rate, rendering the evolutionary process chaotic. In his book ''Darwin's Dangerous Idea
''Darwin's Dangerous Idea: Evolution and the Meanings of Life'' is a 1995 book by the philosopher Daniel Dennett, in which the author looks at some of the repercussions of Darwinian theory. The crux of the argument is that, whether or not Darwin ...
'' Daniel C. Dennett rebuts this claim, pointing to the existence of self-regulating correction mechanisms (vaguely resembling those of gene transcription) enabled by the redundancy and other properties of most meme expression languages which stabilize information transfer. Dennett notes that spiritual narratives, including music and dance forms, can survive in full detail across any number of generations even in cultures with oral tradition only. Memes for which stable copying methods are available will inevitably get selected for survival more often than those which can only have unstable mutations, therefore going extinct.
British political philosopher John Gray has characterized Dawkins's memetic theory of religion as "nonsense" and "not even a theory... the latest in a succession of ill-judged Darwinian metaphors", comparable to Intelligent Design
Intelligent design (ID) is a pseudoscientific argument for the existence of God, presented by its proponents as "an evidence-based scientific theory about life's origins". Numbers 2006, p. 373; " Dcaptured headlines for its bold attempt to ...
in its value as a science.
Another critique comes from semiotic
Semiotics (also called semiotic studies) is the systematic study of sign processes ( semiosis) and meaning making. Semiosis is any activity, conduct, or process that involves signs, where a sign is defined as anything that communicates something ...
theorists such as Terrence Deacon
Terrence William Deacon (born 1950) is an American neuroanthropologist (Ph.D. in Biological Anthropology, Harvard University 1984). He taught at Harvard for eight years, relocated to Boston University in 1992, and is currently Professor of Anth ...
and Kalevi Kull. This view regards the concept of "meme" as a primitivized concept of "sign". The meme is thus described in memetics as a sign lacking a triadic nature. Semioticians can regard a meme as a "degenerate" sign, which includes only its ability of being copied. Accordingly, in the broadest sense, the objects of copying are memes, whereas the objects of translation and interpretation are signs.
Fracchia and Lewontin regard memetics as reductionist
Reductionism is any of several related philosophical ideas regarding the associations between phenomena which can be described in terms of other simpler or more fundamental phenomena. It is also described as an intellectual and philosophical p ...
and inadequate. Evolutionary biologist Ernst Mayr
Ernst Walter Mayr (; 5 July 1904 – 3 February 2005) was one of the 20th century's leading evolutionary biologists. He was also a renowned taxonomist, tropical explorer, ornithologist, philosopher of biology, and historian of science. His ...
disapproved of Dawkins's gene-based view and usage of the term "meme", asserting it to be an "unnecessary synonym" for "concept
Concepts are defined as abstract ideas. They are understood to be the fundamental building blocks of the concept behind principles, thoughts and beliefs.
They play an important role in all aspects of cognition. As such, concepts are studied by ...
", reasoning that concepts are not restricted to an individual or a generation, may persist for long periods of time, and may evolve.
Radim Chvaja, a researcher for Masaryk University states that Memetic theory has failed due to the idea's founders Richard Dawkins and George C. Williams taking on a "strict adoption" of their argument which in turn forced them to dig in to the idea that the replication of a meme is biological in nature.
Elliott Oring calls Dawkins' term "the selfish gene" potentially "dangerous and misleading". According to Oring, Dawkins suggests that genes aren't already selfish in the sense that they will do whatever it takes to survive and replicate as it is. Memes as Dawkins describes them do not behave that way, according to Oring. They do not have strict generational lines, and they do not do whatever it takes to assure their own survival, since memes are not alive. Oring goes on to say that memes are dissimilar from genes in the sense that they do not particularly need to keep their individual biological hosts alive, as they do not rely on any type of genetic code to replicate and reproduce. Oring suggests that the problem with memes as a whole is that they cannot be "precisely specified".
Applications
Opinions differ as to how best to apply the concept of memes within a "proper" disciplinary framework. One view sees memes as providing a useful philosophical perspective with which to examinecultural evolution
Cultural evolution is an evolutionary theory of social change. It follows from the definition of culture as "information capable of affecting individuals' behavior that they acquire from other members of their species through teaching, imitation ...
. Proponents of this view (such as Susan Blackmore
Susan Jane Blackmore (born 29 July 1951) is a British writer, lecturer, sceptic, broadcaster, and a Visiting Professor at the University of Plymouth. Her fields of research include memetics, parapsychology, consciousness, and she is best known ...
and Daniel Dennett
Daniel Clement Dennett III (born March 28, 1942) is an American philosopher, writer, and cognitive scientist whose research centers on the philosophy of mind, philosophy of science, and philosophy of biology, particularly as those fields relat ...
) argue that considering cultural developments from a meme's-eye view—''as if'' memes themselves respond to pressure to maximise their own replication and survival—can lead to useful insights and yield valuable predictions into how culture develops over time. Others such as Bruce Edmonds and Robert Aunger have focused on the need to provide an empirical grounding for memetics to become a useful and respected scientific discipline
The branches of science, also referred to as sciences, scientific fields or scientific disciplines, are commonly divided into three major groups:
* Formal sciences: the study of formal systems, such as those under the branches of logic and ma ...
.
A third approach, described by Joseph Poulshock, as "radical memetics" seeks to place memes at the centre of a materialistic theory of mind
In psychology, theory of mind refers to the capacity to understand other people by ascribing mental states to them (that is, surmising what is happening in their mind). This includes the knowledge that others' mental states may be different fro ...
and of personal identity
Personal identity is the unique numerical identity of a person over time. Discussions regarding personal identity typically aim to determine the necessary and sufficient conditions under which a person at one time and a person at another time ca ...
.
Prominent researchers in evolutionary psychology
Evolutionary psychology is a theoretical approach in psychology that examines cognition and behavior from a modern evolutionary perspective. It seeks to identify human psychological adaptations with regards to the ancestral problems they evo ...
and anthropology
Anthropology is the scientific study of humanity, concerned with human behavior, human biology, cultures, societies, and linguistics, in both the present and past, including past human species. Social anthropology studies patterns of be ...
, including Scott Atran, Dan Sperber
Dan Sperber (born 20 June 1942 in Cagnes-sur-Mer) is a French social and cognitive scientist and philosopher. His most influential work has been in the fields of cognitive anthropology, linguistic pragmatics, psychology of reasoning, and phil ...
, Pascal Boyer
Pascal Robert Boyer is a French-American cognitive anthropologist and evolutionary psychologist, mostly known for his work in the cognitive science of religion. He taught at the University of Cambridge for eight years, before taking up the posit ...
, John Tooby
John Tooby (born 1952) is an American anthropologist, who, together with psychologist wife Leda Cosmides, helped pioneer the field of evolutionary psychology.
Biography
Tooby received his PhD in Biological Anthropology from Harvard Universit ...
and others, argue the possibility of incompatibility between modularity of mind Modularity of mind is the notion that a mind may, at least in part, be composed of innate neural structures or mental modules which have distinct, established, and evolutionarily developed functions. However, different definitions of "module" have b ...
and memetics. In their view, minds structure certain communicable aspects of the ideas produced, and these communicable aspects generally trigger or elicit ideas in other minds through inference (to relatively rich structures generated from often low-fidelity input) and not high-fidelity replication or imitation. Atran discusses communication involving religious beliefs as a case in point. In one set of experiments he asked religious people to write down on a piece of paper the meanings of the Ten Commandments
The Ten Commandments (Biblical Hebrew עשרת הדברים \ עֲשֶׂרֶת הַדְּבָרִים, ''aséret ha-dvarím'', lit. The Decalogue, The Ten Words, cf. Mishnaic Hebrew עשרת הדיברות \ עֲשֶׂרֶת הַדִּבְ ...
. Despite the subjects' own expectations of consensus, interpretations of the commandments showed wide ranges of variation, with little evidence of consensus. In another experiment, subjects with autism and subjects without autism interpreted ideological and religious sayings (for example, "Let a thousand flowers bloom" or "To everything there is a season"). People with autism showed a significant tendency to closely paraphrase and repeat content from the original statement (for example: "Don't cut flowers before they bloom"). Controls tended to infer a wider range of cultural meanings with little replicated content (for example: "Go with the flow" or "Everyone should have equal opportunity"). Only the subjects with autism—who lack the degree of inferential capacity normally associated with aspects of theory of mind
In psychology, theory of mind refers to the capacity to understand other people by ascribing mental states to them (that is, surmising what is happening in their mind). This includes the knowledge that others' mental states may be different fro ...
—came close to functioning as "meme machines."
In his book ''The Robot's Rebellion'', Keith Stanovich
Keith E. Stanovich is a Canadian psychologist. He is an Emeritus Professor of Applied Psychology and Human Development at the University of Toronto and former Canada Research Chair of Applied Cognitive Science. His research areas are the psych ...
uses the memes and memeplex concepts to describe a program of cognitive reform that he refers to as a "rebellion." Specifically, Stanovich argues that the use of memes as a descriptor for cultural units is beneficial because it serves to emphasize transmission and acquisition properties that parallel the study of epidemiology
Epidemiology is the study and analysis of the distribution (who, when, and where), patterns and determinants of health and disease conditions in a defined population.
It is a cornerstone of public health, and shapes policy decisions and evi ...
. These properties make salient the sometimes parasitic nature of acquired memes, and as a result individuals should be motivated to reflectively acquire memes using what he calls a " Neurathian bootstrap" process.
Memetic explanations of racism
In ''Cultural Software: A Theory of Ideology'',Jack Balkin
Jack M. Balkin (born August 13, 1956) is an American legal scholar. He is the Knight Professor of Constitutional Law and the First Amendment at Yale Law School. Balkin is the founder and director of the Yale Information Society Project (ISP), a r ...
argued that memetic processes can explain many of the most familiar features of ideological
An ideology is a set of beliefs or philosophies attributed to a person or group of persons, especially those held for reasons that are not purely epistemic, in which "practical elements are as prominent as theoretical ones." Formerly applied prim ...
thought. His theory of "cultural software" maintained that memes form narrative
A narrative, story, or tale is any account of a series of related events or experiences, whether nonfictional ( memoir, biography, news report, documentary, travelogue, etc.) or fictional ( fairy tale, fable, legend, thriller, novel, etc ...
s, social networks, metaphoric and metonymic
Metonymy () is a figure of speech in which a concept is referred to by the name of something closely associated with that thing or concept.
Etymology
The words ''metonymy'' and ''metonym'' come from grc, μετωνυμία, 'a change of name ...
models, and a variety of different mental structures. Balkin maintains that the same structures used to generate ideas about free speech or free markets also serve to generate racistic beliefs. To Balkin, whether memes become harmful or maladaptive depends on the environmental context in which they exist rather than in any special source or manner to their origination. Balkin describes racist beliefs as "fantasy" memes that become harmful or unjust "ideologies" when diverse peoples come together, as through trade or competition.
Religion
Richard Dawkins called for a re-analysis of religion in terms of the evolution of self-replicatingideas
In common usage and in philosophy, ideas are the results of thought. Also in philosophy, ideas can also be mental representational images of some object. Many philosophers have considered ideas to be a fundamental ontological category of being. ...
''apart from'' any resulting biological advantages they might bestow.
He argued that the role of key replicator in cultural evolution belongs not to genes, but to memes replicating thought from person to person by means of imitation. These replicators respond to selective pressures that may or may not affect biological reproduction or survival.
In her book ''The Meme Machine
''The Meme Machine'' is a popular science book by Susan Blackmore on the subject of memes. Blackmore attempts to constitute memetics as a science by discussing its empirical and analytic potential, as well as some important problems with memeti ...
'', Susan Blackmore
Susan Jane Blackmore (born 29 July 1951) is a British writer, lecturer, sceptic, broadcaster, and a Visiting Professor at the University of Plymouth. Her fields of research include memetics, parapsychology, consciousness, and she is best known ...
regards religions as particularly tenacious memes. Many of the features common to the most widely practiced religions provide built-in advantages in an evolutionary context, she writes. For example, religions that preach of the value of faith
Faith, derived from Latin ''fides'' and Old French ''feid'', is confidence or trust in a person, thing, or In the context of religion, one can define faith as "belief in God or in the doctrines or teachings of religion".
Religious people ofte ...
over evidence
Evidence for a proposition is what supports this proposition. It is usually understood as an indication that the supported proposition is true. What role evidence plays and how it is conceived varies from field to field.
In epistemology, evidenc ...
from everyday experience or reason
Reason is the capacity of consciously applying logic by drawing conclusions from new or existing information, with the aim of seeking the truth. It is closely associated with such characteristically human activities as philosophy, science, lang ...
inoculate societies against many of the most basic tools people commonly use to evaluate their ideas. By linking altruism
Altruism is the principle and moral practice of concern for the welfare and/or happiness of other human beings or animals, resulting in a quality of life both material and spiritual. It is a traditional virtue in many cultures and a cor ...
with religious affiliation, religious memes can proliferate more quickly because people perceive that they can reap societal as well as personal rewards. The longevity of religious memes improves with their documentation in revered religious texts.
Aaron Lynch attributed the robustness of religious memes in human culture to the fact that such memes incorporate multiple modes of meme transmission. Religious memes pass down the generations from parent to child and across a single generation through the meme-exchange of proselytism
Proselytism () is the policy of attempting to convert people's religious or political beliefs. Proselytism is illegal in some countries.
Some draw distinctions between ''evangelism'' or '' Da‘wah'' and proselytism regarding proselytism as invol ...
. Most people will hold the religion taught them by their parents throughout their life. Many religions feature adversarial elements, punishing apostasy
Apostasy (; grc-gre, ἀποστασία , 'a defection or revolt') is the formal disaffiliation from, abandonment of, or renunciation of a religion by a person. It can also be defined within the broader context of embracing an opinion that ...
, for instance, or demonizing infidels. In ''Thought Contagion'' Lynch identifies the memes of transmission in Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global popula ...
as especially powerful in scope. Believers view the conversion of non-believers both as a religious duty and as an act of altruism. The promise of heaven
Heaven or the heavens, is a common religious cosmological or transcendent supernatural place where beings such as deities, angels, souls, saints, or venerated ancestors are said to originate, be enthroned, or reside. According to the belie ...
to believers and threat of hell
In religion and folklore, hell is a location in the afterlife in which evil souls are subjected to punitive suffering, most often through torture, as eternal punishment after death. Religions with a linear divine history often depict hell ...
to non-believers provide a strong incentive for members to retain their belief. Lynch asserts that belief in the Crucifixion of Jesus
The crucifixion and death of Jesus occurred in 1st-century Judea, most likely in AD 30 or AD 33. It is described in the four canonical gospels, referred to in the New Testament epistles, attested to by other ancient sources, and consider ...
in Christianity amplifies each of its other replication advantages through the indebtedness believers have to their Savior
Savior or Saviour may refer to:
*A person who helps people achieve salvation, or saves them from something
Religion
* Mahdi, the prophesied redeemer of Islam who will rule for seven, nine or nineteen years
* Maitreya
* Messiah, a saviour or ...
for sacrifice on the cross. The image of the crucifixion recurs in religious sacrament
A sacrament is a Christian rite that is recognized as being particularly important and significant. There are various views on the existence and meaning of such rites. Many Christians consider the sacraments to be a visible symbol of the rea ...
s, and the proliferation of symbols of the cross
A cross is a geometrical figure consisting of two intersecting lines or bars, usually perpendicular to each other. The lines usually run vertically and horizontally. A cross of oblique lines, in the shape of the Latin letter X, is termed a s ...
in homes and churches potently reinforces the wide array of Christian memes.
Although religious memes have proliferated in human cultures, the modern scientific community has been relatively resistant to religious belief. Robertson (2007) reasoned that if evolution is accelerated in conditions of propagative difficulty, then we would expect to encounter variations of religious memes, established in general populations, addressed to scientific communities. Using a memetic approach, Robertson deconstructed two attempts to privilege religiously held spirituality in scientific discourse. Advantages of a memetic approach as compared to more traditional "modernization" and "supply side" theses in understanding the evolution and propagation of religion were explored.
Architectural memes
In '' A Theory of Architecture'', Nikos Salingaros speaks of memes as "freely propagating clusters of information" which can be beneficial or harmful. He contrasts memes topatterns
A pattern is a regularity in the world, in human-made design, or in abstract ideas. As such, the elements of a pattern repeat in a predictable manner. A geometric pattern is a kind of pattern formed of geometric shapes and typically repeated li ...
and true knowledge, characterizing memes as "greatly simplified versions of patterns" and as "unreasoned matching to some visual or mnemonic prototype." Taking reference to Dawkins, Salingaros emphasizes that they can be transmitted due to their own communicative properties, that "the simpler they are, the faster they can proliferate," and that the most successful memes "come with a great psychological appeal."
Architectural memes, according to Salingaros, can have destructive power: "Images portrayed in architectural magazines representing buildings that could not possibly accommodate everyday uses become fixed in our memory, so we reproduce them unconsciously." He lists various architectural memes that circulated since the 1920s and which, in his view, have led to contemporary architecture becoming quite decoupled from human needs. They lack connection and meaning, thereby preventing "the creation of true connections necessary to our understanding of the world." He sees them as no different from antipattern
An anti-pattern in software engineering, project management, and business processes is a common response to a recurring problem that is usually ineffective and risks being highly counterproductive. The term, coined in 1995 by computer programmer A ...
s in software design—as solutions that are false but are re-utilized nonetheless.
Internet culture
An "Internet meme" is a concept that spreads rapidly from person to person via theInternet
The Internet (or internet) is the global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to communicate between networks and devices. It is a '' network of networks'' that consists of private, p ...
. They can spread from person to person via social network
A social network is a social structure made up of a set of social actors (such as individuals or organizations), sets of dyadic ties, and other social interactions between actors. The social network perspective provides a set of methods fo ...
s, blog
A blog (a Clipping (morphology), truncation of "weblog") is a discussion or informational website published on the World Wide Web consisting of discrete, often informal diary-style text entries (posts). Posts are typically displayed in Reverse ...
s, direct email
Electronic mail (email or e-mail) is a method of exchanging messages ("mail") between people using electronic devices. Email was thus conceived as the electronic ( digital) version of, or counterpart to, mail, at a time when "mail" mean ...
, or news sources.
In 2013, Dawkins characterized an Internet meme as one deliberately altered by human creativity, distinguished from his original idea involving mutation "by random change and a form of Darwinian selection."
Internet memes are an example of Dawkins' meme theory at work in the sense of how they so rapidly mirror current cultural events and become a part of how the time period is defined. Limor Shifman uses the example of the 'Gangnam Style' Music video by South Korean pop-star, Psy
Park Jae-sang (, ; born December 31, 1977), known professionally as Psy (stylized in all caps as PSY) (; ; ), is a South Korean singer, rapper, songwriter, and record producer. Psy is known domestically for his humorous videos and stage per ...
that went viral in 2012. Shifman cites examples of how the meme mutated itself into the cultural sphere, mixing with other things going on at the time such as the 2012 U.S. presidential election
The 2012 United States presidential election was the 57th quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 6, 2012. Incumbent Democratic President Barack Obama and his running mate, incumbent Vice President Joe Biden, were re-el ...
, which led to the creation of Mitt Romney
Willard Mitt Romney (born March 12, 1947) is an American politician, businessman, and lawyer serving as the junior United States senator from Utah since January 2019, succeeding Orrin Hatch. He served as the 70th governor of Massachusetts ...
Style, a parody of the original Gangnam style, intended to be a jab at the 2012 Republican presidential candidate, Mitt Romney.
Meme stocks
Meme stocks, a particular subset of Internet memes in general, are listed companies lauded for the social media buzz they create, rather than their operating performance.r/wallstreetbets
r/wallstreetbets, also known as WallStreetBets or WSB, is a subreddit where participants discuss stock and option trading. It has become notable for its colorful and profane jargon, aggressive trading strategies, and for playing a major role i ...
, a subreddit where participants discuss stock and option trading, and the financial services company Robinhood Markets
Robinhood Markets, Inc. is an American financial services company headquartered in Menlo Park, California, that facilitates commission-free trades of stocks, exchange-traded funds and cryptocurrencies as well as individual retirement accounts ...
, became notable in 2021 for their involvement on the popularization and enhancement of meme stocks.The ‘Roaring Kitty’ Rally: How a Reddit User and His Friends Roiled the Markets (The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid ...
) https://www.nytimes.com/2021/01/29/technology/roaring-kitty-reddit-gamestop-markets.html
See also
* Baldwin effect * ''The Beginning of Infinity
''The Beginning of Infinity: Explanations that Transform the World'' is a popular science book by the physicist David Deutsch first published in 2011.
Synopsis
Deutsch views the Enlightenment of the 18th century as near the beginning of an in ...
''
* Biosemiotics
Biosemiotics (from the Greek βίος ''bios'', "life" and σημειωτικός ''sēmeiōtikos'', "observant of signs") is a field of semiotics and biology that studies the prelinguistic meaning-making, biological interpretation processes, p ...
* Chain letter
A chain letter is a message that attempts to convince the recipient to make a number of copies and pass them on to a certain number of recipients. The "chain" is an exponentially growing pyramid (a tree graph) that cannot be sustained indefinite ...
* Darwin machine A Darwin machine (a 1987 coinage by William H. Calvin, by analogy to a Turing machine) is a machine that, like a Turing machine, involves an iteration process that yields a high-quality result, but, whereas a Turing machine uses logic, the Darwin ...
* Dual inheritance theory
Dual inheritance theory (DIT), also known as gene–culture coevolution or biocultural evolution, was developed in the 1960s through early 1980s to explain how human behavior is a product of two different and interacting evolutionary processes: gen ...
* Evolutionary biology
Evolutionary biology is the subfield of biology that studies the evolutionary processes (natural selection, common descent, speciation) that produced the diversity of life on Earth. It is also defined as the study of the history of life ...
* Framing (social sciences)
In the social sciences, framing comprises a set of concepts and theoretical perspectives on how individuals, groups, and societies organize, perceive, and communicate about reality.
Framing can manifest in thought or interpersonal communica ...
* Internet meme
An Internet meme, commonly known simply as a meme ( ), is an idea, behavior, style, or image that is spread via the Internet, often through social media platforms. What is considered a meme may vary across different communities on the Internet ...
* The Leiden school The Leiden school is a school of thought in linguistics that models languages as memes or benign neurological parasites,http://www.semioticon.com/virtuals/imitation/van_driem_paper.pdf and tries to use rigorous mathematical tools borrowed by analog ...
* Memetic algorithm
A memetic algorithm (MA) in computer science and operations research, is an extension of the traditional genetic algorithm. It may provide a sufficiently good solution to an optimization problem. It uses a local search technique to reduce the like ...
* Memetic engineering
* Phraseme
A phraseme, also called a set phrase, idiomatic phrase, multi-word expression (in computational linguistics), or idiom, is a multi-word or multi-morphemic utterance whose components include at least one that is selectionally constrained or restr ...
* Propaganda
Propaganda is communication that is primarily used to influence or persuade an audience to further an agenda, which may not be objective and may be selectively presenting facts to encourage a particular synthesis or perception, or using loaded ...
* Psycholinguistics
Psycholinguistics or psychology of language is the study of the interrelation between linguistic factors and psychological aspects. The discipline is mainly concerned with the mechanisms by which language is processed and represented in the mind ...
* Snowclone
* Survivals
* Universal Darwinism
Universal Darwinism, also known as generalized Darwinism, universal selection theory, or Darwinian metaphysics, is a variety of approaches that extend the theory of Darwinism beyond its original domain of biological evolution on Earth. Universal ...
* Viral marketing
Viral marketing is a business strategy that uses existing social networks to promote a product mainly on various social media platforms. Its name refers to how consumers spread information about a product with other people, much in the same way tha ...
* Viral video
A viral video is a video that becomes popular through a viral process of Internet sharing, typically through video sharing websites such as YouTube as well as social media and email.Lu Jiang, Yajie Miao, Yi Yang, ZhenZhong Lan, Alexander H ...
Notes
References
* * * * * * * * rade paperback (1999), (2000)* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Moritz, Elan. (1995): "Metasystems, Memes and Cybernetic Immortality," in: Heylighen F., Joslyn C. & Turchin V. (eds.), ''The Quantum of Evolution. Toward a theory of metasystem transitions'', (Gordon and Breach Science Publishers, New York) (special issue of ''World Futures: the journal of general evolution'', vol. 45, pp. 155–171). * * * * * *External links
Dawkins's speech on the 30th anniversary of the publication of ''The Selfish Gene''
Dawkins 2006
article by
Susan Blackmore
Susan Jane Blackmore (born 29 July 1951) is a British writer, lecturer, sceptic, broadcaster, and a Visiting Professor at the University of Plymouth. Her fields of research include memetics, parapsychology, consciousness, and she is best known ...
.
*
Journal of Memetics
a peer-refereed journal of memetics published from 1997 until 2005.
TED Talks February 2008.
Christopher von Bülow: ''Article Meme''
translated from: Jürgen Mittelstraß (ed.), ''Enzyklopädie Philosophie und Wissenschaftstheorie'', 2nd edn, vol. 5, Stuttgart/Weimar: Metzler 2013.
Richard Dawkins explains the real meaning of the word 'meme'
Richard Dawkins , Memes , Oxford Union
{{Authority control Abstraction Collective intelligence Concepts in epistemology Concepts in the philosophy of mind Concepts in the philosophy of science Cultural anthropology Emergence Evolutionary psychology Metaphysics of mind Philosophical theories Philosophy of language Philosophy of science 1976 neologisms