lymphatic vessel on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The lymphatic vessels (or lymph vessels or lymphatics) are thin-walled vessels (tubes), structured like
The lymphatic vessels (or lymph vessels or lymphatics) are thin-walled vessels (tubes), structured like
File:Illu lymphatic system.jpg, Lymphatic system
File:Gray1093.png , Section across portal canal of pig. X 250.
Efferent lymph vessel
- BioWeb at University of Wisconsin System {{Authority control Cardiovascular system anatomy Lymphatic system
 The lymphatic vessels (or lymph vessels or lymphatics) are thin-walled vessels (tubes), structured like
The lymphatic vessels (or lymph vessels or lymphatics) are thin-walled vessels (tubes), structured like blood vessel
Blood vessels are the tubular structures of a circulatory system that transport blood throughout many Animal, animals’ bodies. Blood vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to most of the Tissue (biology), tissues of a Body (bi ...
s, that carry lymph. As part of the lymphatic system
The lymphatic system, or lymphoid system, is an organ system in vertebrates that is part of the immune system and complementary to the circulatory system. It consists of a large network of lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, lymphoid organs, lympha ...
, lymph vessels are complementary to the cardiovascular system
In vertebrates, the circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the body. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, that consists of the heart a ...
. Lymph vessels are lined by endothelial cells, and have a thin layer of smooth muscle
Smooth muscle is one of the three major types of vertebrate muscle tissue, the others being skeletal and cardiac muscle. It can also be found in invertebrates and is controlled by the autonomic nervous system. It is non- striated, so-called bec ...
, and adventitia that binds the lymph vessels to the surrounding tissue. Lymph vessels are devoted to the propulsion
Propulsion is the generation of force by any combination of pushing or pulling to modify the translational motion of an object, which is typically a rigid body (or an articulated rigid body) but may also concern a fluid. The term is derived from ...
of the lymph from the lymph capillaries, which are mainly concerned with the absorption of interstitial fluid from the tissues. Lymph capillaries are slightly bigger than their counterpart capillaries of the vascular system. Lymph vessels that carry lymph to a lymph node are called afferent lymph vessels, and those that carry it from a lymph node are called efferent lymph vessels, from where the lymph may travel to another lymph node, may be returned to a vein, or may travel to a larger lymph duct. Lymph ducts drain the lymph into one of the subclavian veins and thus return it to general circulation.
The vessels that bring lymph away from the tissues and towards the lymph nodes can be classified as afferent vessels. These afferent vessels then drain into the subcapsular sinus.
The efferent vessels that bring lymph from the lymphatic organs to the nodes bringing the lymph to the right lymphatic duct or the thoracic duct, the largest lymph vessel in the body. These vessels drain into the right and left subclavian veins, respectively. There are far more afferent vessels bringing in lymph than efferent vessels taking it out to allow for lymphocytes and macrophages to fulfill their immune support functions. The lymphatic vessels contain valves.
Structure
The general structure of lymphatics is based on that ofblood vessel
Blood vessels are the tubular structures of a circulatory system that transport blood throughout many Animal, animals’ bodies. Blood vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to most of the Tissue (biology), tissues of a Body (bi ...
s. There is an inner lining of single flattened epithelial cells (simple squamous epithelium) composed of a type of epithelium
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is a thin, continuous, protective layer of cells with little extracellular matrix. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. Epithelial ( mesothelial) tissues line the outer surfaces of man ...
that is called the endothelium
The endothelium (: endothelia) is a single layer of squamous endothelial cells that line the interior surface of blood vessels and lymphatic vessels. The endothelium forms an interface between circulating blood or lymph in the lumen and the r ...
, and the cells are called ''endothelial cells''. This layer functions to mechanically transport fluid and since the basement membrane on which it rests is discontinuous; it leaks easily. The next layer is that of smooth muscle
Smooth muscle is one of the three major types of vertebrate muscle tissue, the others being skeletal and cardiac muscle. It can also be found in invertebrates and is controlled by the autonomic nervous system. It is non- striated, so-called bec ...
s that are arranged in a circular fashion around the endothelium, which by shortening (contracting) or relaxing alter the diameter (caliber) of the lumen. The outermost layer is the adventitia which consists of fibrous tissue. The general structure described here is seen only in larger lymphatics; smaller lymphatics have fewer layers. The smallest vessels (''lymphatic'' or '' lymph capillaries'') lack both the muscular layer and the outer adventitia. As they proceed forward and in their course are joined by other capillaries, they grow larger and first take on an adventitia, and then smooth muscles.
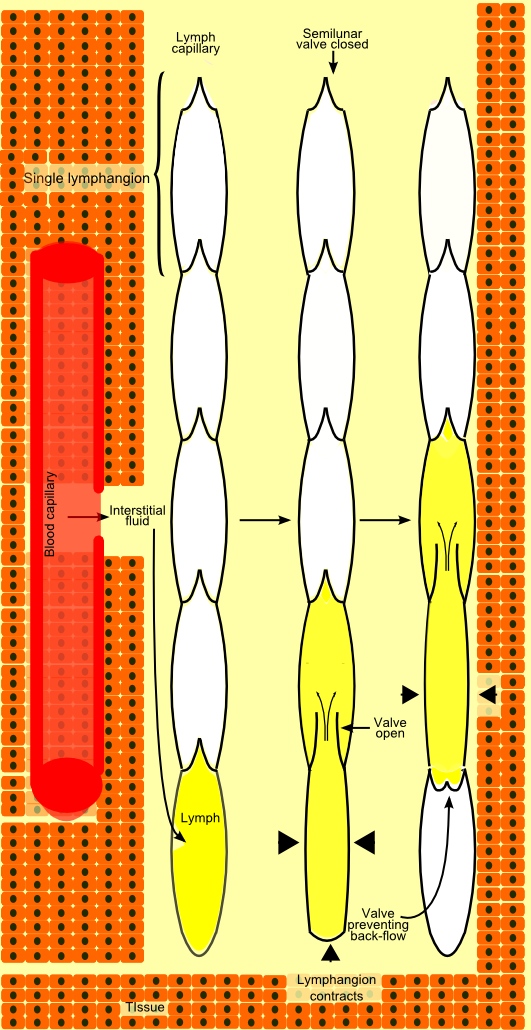
The lymphatic conducting system broadly consists of two types of channels—the ''initial lymphatics'', the ''prelymphatics'' or ''lymph capillaries'' that specialize in collection of the lymph from the interstital fluid, and the larger ''lymph vessels'' that propel the lymph forward.
Unlike the cardiovascular system, the lymphatic system is not closed and has no central pump. Lymph movement occurs despite low pressure due to peristalsis
Peristalsis ( , ) is a type of intestinal motility, characterized by symmetry in biology#Radial symmetry, radially symmetrical contraction and relaxation of muscles that propagate in a wave down a tube, in an wikt:anterograde, anterograde dir ...
(propulsion of the lymph due to alternate contraction and relaxation of smooth muscle
Smooth muscle is one of the three major types of vertebrate muscle tissue, the others being skeletal and cardiac muscle. It can also be found in invertebrates and is controlled by the autonomic nervous system. It is non- striated, so-called bec ...
), valves, and compression during contraction of adjacent skeletal muscle and arterial pulsation.

Lymph capillaries
The lymphatic circulation begins with blind ending (closed at one end) highly permeable superficial lymph capillaries, formed by endothelial cells with button-like junctions between them that allow fluid to pass through them when the interstitial pressure is sufficiently high. These button-like junctions consist of protein filaments like platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1, or PECAM-1. A valve system in place here prevents the absorbed lymph from leaking back into the interstital fluid. This valve system involves collagen fibers attached to lymphatic endothelial cells that respond to increased interstitial fluid pressure by separating the endothelial cells and allowing the flow of lymph into the capillary for circulation. There is another system of semilunar valves that prevents back-flow of lymph along the lumen of the vessel. Lymph capillaries have many interconnections ( anastomoses) between them and form a very fine network. Rhythmic contraction of the vessel walls through movements may also help draw fluid into the smallest lymphatic vessels, capillaries. If tissue fluid builds up the tissue will swell; this is called edema. As the circular path through the body's system continues, the fluid is then transported to progressively larger lymphatic vessels culminating in the right lymphatic duct (for lymph from the right upper body) and the thoracic duct (for the rest of the body); both ducts ''drain'' into the circulatory system at the right and left subclavian veins. The system collaborates with white blood cells in lymph nodes to protect the body from being infected by cancer cells, fungi, viruses or bacteria. This is known as a secondary circulatory system.Lymph vessels
The lymph capillaries drain into larger ''collecting lymphatics''. These are ''contractile lymphatics'' which transport lymph using a combination of smooth muscle walls, which contract to assist in transporting lymph, as well as valves to prevent the lymph from flowing backwards. As the collecting lymph vessel accumulates lymph from more and more lymph capillaries along its length, it becomes larger and eventually becomes an afferent lymph vessel as it enters a lymphs node. The lymph percolates through the lymph node tissue and exits via anefferent lymph vessel
The lymphatic vessels (or lymph vessels or lymphatics) are thin-walled vessels (tubes), structured like blood vessels, that carry lymph. As part of the lymphatic system, lymph vessels are complementary to the cardiovascular system. Lymph vessel ...
. An efferent lymph vessel may directly drain into one of the (right
Rights are law, legal, social, or ethics, ethical principles of freedom or Entitlement (fair division), entitlement; that is, rights are the fundamental normative rules about what is allowed of people or owed to people according to some legal sy ...
or thoracic
The thorax (: thoraces or thoraxes) or chest is a part of the anatomy of mammals and other tetrapod animals located between the neck and the abdomen.
In insects, crustaceans, and the extinct trilobites, the thorax is one of the three main ...
) lymph ducts, or may empty into another lymph node as its afferent lymph vessel. Both the lymph ducts return the lymph to the blood stream by emptying into the subclavian veins
Lymph vessels consist of functional units known as lymphangions which are segments separated by semilunar valves. These segments propel or resist the flow of lymph by the contraction of the encircling smooth muscle depending upon the ratio of its length to its radius.
Function
Lymph vessels act as reservoirs for plasma and other substances including cells that have leaked from the vascular system and transport lymph fluid back from the tissues to the circulatory system. Without functioning lymph vessels, lymph cannot be effectively drained and lymphedema typically results.Afferent vessels
The afferent lymph vessels enter at all parts of the periphery of the lymph node, and after branching and forming a dense plexus in the substance of the capsule, open into the ''lymph sinuses'' of the cortical part. It carries unfiltered lymph into the node. In doing this they lose all their coats except their endothelial lining, which is continuous with a layer of similar cells lining the lymph paths. Afferent lymphatic vessels are only found in lymph nodes. This is in contrast to efferent lymphatic vessel which are also found in thethymus
The thymus (: thymuses or thymi) is a specialized primary lymphoid organ of the immune system. Within the thymus, T cells mature. T cells are critical to the adaptive immune system, where the body adapts to specific foreign invaders. The thymus ...
and spleen
The spleen (, from Ancient Greek '' σπλήν'', splḗn) is an organ (biology), organ found in almost all vertebrates. Similar in structure to a large lymph node, it acts primarily as a blood filter.
The spleen plays important roles in reg ...
.
Efferent vessels
The efferent lymphatic vessel commences from the lymph sinuses of the medullary portion of the lymph nodes and leave the lymph nodes at the hilum, either to veins or greater nodes. It carries filtered lymph out of the node. Efferent lymphatic vessels are also found in association with the thymus andspleen
The spleen (, from Ancient Greek '' σπλήν'', splḗn) is an organ (biology), organ found in almost all vertebrates. Similar in structure to a large lymph node, it acts primarily as a blood filter.
The spleen plays important roles in reg ...
. This is in contrast to afferent lymphatic vessels, which are found only in association with lymph nodes.
Clinical significance
Lymphedema is the swelling of tissues due to insufficient fluid drainage by the lymphatic vessels. It can be the result from absent, underdeveloped or dysfunctional lymphatic vessels. In hereditary (or primary) lymphedema, the lymphatic vessels are absent, underdeveloped or dysfunctional due to genetic causes. In acquired (or secondary) lymphedema, the lymphatic vessels are damaged by injury or infection. Lymphangiomatosis is a disease involving multiple cysts or lesions formed from lymphatic vessels.Additional images
See also
*Lacteal
A lacteal is a Lymph capillary, lymphatic capillary that absorbs dietary fats in the Intestinal villus, villi of the small intestine.
Triglycerides are emulsified by bile and hydrolyzed by the enzyme lipase, resulting in a mixture of fatty acids, ...
* Meningeal lymphatic vessels
References
Further reading
*External links
*Efferent lymph vessel
- BioWeb at University of Wisconsin System {{Authority control Cardiovascular system anatomy Lymphatic system