Lymphatic Tissues on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The lymphatic system, or lymphoid system, is an
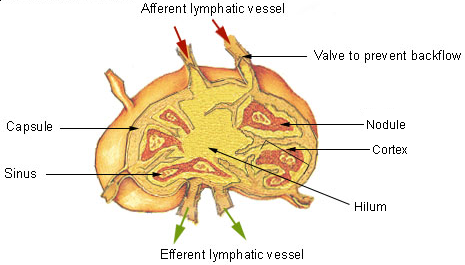 A lymph node is an organized collection of lymphoid tissue, through which the lymph passes on its way back to the blood. Lymph nodes are located at intervals along the lymphatic system. Several
A lymph node is an organized collection of lymphoid tissue, through which the lymph passes on its way back to the blood. Lymph nodes are located at intervals along the lymphatic system. Several
 The
The
 Lymph vessels called
Lymph vessels called

Image:Galen detail.jpg, "Claude Galien". Lithograph by Pierre Roche Vigneron. (Paris: Lith de Gregoire et Deneux, ca. 1865)
Gabriele_Falloppio.jpg,
Lymphatic System
(innerbody.com) {{DEFAULTSORT:Lymphatic System Angiology Animal anatomy
organ system
An organ system is a biological system consisting of a group of organs that work together to perform one or more functions. Each organ has a specialized role in a plant or animal body, and is made up of distinct tissues.
Plants
Plants have ...
in vertebrates that is part of the immune system
The immune system is a network of biological processes that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, as well as cancer cells and objects such as wood splint ...
, and complementary to the circulatory system
The blood circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the entire body of a human or other vertebrate. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, tha ...
. It consists of a large network of lymphatic vessel
The lymphatic vessels (or lymph vessels or lymphatics) are thin-walled vessels (tubes), structured like blood vessels, that carry lymph. As part of the lymphatic system, lymph vessels are complementary to the cardiovascular system. Lymph ve ...
s, lymph nodes, lymphatic or lymphoid organs, and lymphoid tissues. The vessels carry a clear fluid called lymph
Lymph (from Latin, , meaning "water") is the fluid that flows through the lymphatic system, a system composed of lymph vessels (channels) and intervening lymph nodes whose function, like the venous system, is to return fluid from the tissues ...
(the Latin word ''lympha'' refers to the deity of fresh water, "Lympha
The Lympha (plural ''Lymphae'') is an ancient Roman deity of fresh water. She is one of twelve agricultural deities listed by Varro as "leaders" (''duces'') of Roman farmers, because "without water all agriculture is dry and poor." The Lymphae ...
") back towards the heart
The heart is a muscular organ in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as carbon dioxide to t ...
, for re-circulation.
Unlike the circulatory system that is a closed system
A closed system is a natural physical system that does not allow transfer of matter in or out of the system, although — in contexts such as physics, chemistry or engineering — the transfer of energy (''e.g.'' as work or heat) is allowed.
In ...
, the lymphatic system is open. The human circulatory system processes an average of 20 litres of blood
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells. Blood in the cir ...
per day through capillary filtration, which removes plasma from the blood
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells. Blood in the cir ...
. Roughly 17 litres of the filtered blood is reabsorbed directly into the blood vessel
The blood vessels are the components of the circulatory system that transport blood throughout the human body. These vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to the tissues of the body. They also take waste and carbon dioxide away ...
s, while the remaining three litres are left in the interstitial fluid
In cell biology, extracellular fluid (ECF) denotes all body fluid outside the cells of any multicellular organism. Total body water in healthy adults is about 60% (range 45 to 75%) of total body weight; women and the obese typically have a lower ...
. One of the main functions of the lymphatic system is to provide an accessory return route to the blood for the surplus three litres.
The other main function is that of immune defense. Lymph is very similar to blood plasma, in that it contains waste products and cellular debris, together with bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometr ...
and protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, res ...
s. The cells of the lymph are mostly lymphocyte
A lymphocyte is a type of white blood cell (leukocyte) in the immune system of most vertebrates. Lymphocytes include natural killer cells (which function in cell-mediated, cytotoxic innate immunity), T cells (for cell-mediated, cytotoxic ad ...
s. Associated lymphoid organs are composed of lymphoid tissue, and are the sites either of lymphocyte production or of lymphocyte activation. These include the lymph nodes (where the highest lymphocyte concentration is found), the spleen
The spleen is an organ found in almost all vertebrates. Similar in structure to a large lymph node, it acts primarily as a blood filter. The word spleen comes .
, the thymus
The thymus is a specialized primary lymphoid organ of the immune system. Within the thymus, thymus cell lymphocytes or ''T cells'' mature. T cells are critical to the adaptive immune system, where the body adapts to specific foreign invaders. ...
, and the tonsil
The tonsils are a set of lymphoid organs facing into the aerodigestive tract, which is known as Waldeyer's tonsillar ring and consists of the adenoid tonsil, two tubal tonsils, two palatine tonsils, and the lingual tonsils. These organs play ...
s. Lymphocytes are initially generated in the bone marrow. The lymphoid organs also contain other types of cells such as stromal cell
Stromal cells, or mesenchymal stromal cells, are differentiating cells found in abundance within bone marrow but can also be seen all around the body. Stromal cells can become connective tissue cells of any organ, for example in the uterine mucosa ...
s for support. Lymphoid tissue is also associated with mucosas such as mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue
The mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT), also called mucosa-associated lymphatic tissue, is a diffuse system of small concentrations of lymphoid tissue found in various submucosal membrane sites of the body, such as the gastrointestinal tr ...
(MALT).
Fluid from circulating blood leaks into the tissues of the body by capillary action, carrying nutrients to the cells. The fluid bathes the tissues as interstitial fluid, collecting waste products, bacteria, and damaged cells, and then drains as lymph into the lymphatic capillaries and lymphatic vessels. These vessels carry the lymph throughout the body, passing through numerous lymph nodes which filter out unwanted materials such as bacteria and damaged cells. Lymph then passes into much larger lymph vessels known as lymph duct
A lymph duct is a great lymphatic vessel that empties lymph into one of the subclavian veins. There are two lymph ducts in the body—the right lymphatic duct and the thoracic duct. The right lymphatic duct drains lymph from the right upper li ...
s. The right lymphatic duct
The right lymphatic duct is an important lymphatic vessel that drains the right upper quadrant of the body. It forms various combinations with the right subclavian vein and right internal jugular vein.
Structure
The right lymphatic duct course ...
drains the right side of the region and the much larger left lymphatic duct, known as the thoracic duct
In human anatomy, the thoracic duct is the larger of the two lymph ducts of the lymphatic system. It is also known as the ''left lymphatic duct'', ''alimentary duct'', ''chyliferous duct'', and ''Van Hoorne's canal''. The other duct is the righ ...
, drains the left side of the body. The ducts empty into the subclavian veins to return to the blood circulation. Lymph is moved through the system by muscle contractions. In some vertebrates, a lymph heart
A lymph heart is an organ which pumps lymph in lungfishes, amphibians, reptiles, and flightless birds back into the circulatory system. In some amphibian species, lymph hearts are in pairs, and may number as many as 200 in one animal the size of ...
is present that pumps the lymph to the veins.
The lymphatic system was first described in the 17th century independently by Olaus Rudbeck
Olaus Rudbeck (also known as Olof Rudbeck the Elder, to distinguish him from his son, and occasionally with the surname Latinized as ''Olaus Rudbeckius'') (13 September 1630 – 12 December 1702) was a Swedish scientist and writer, professor o ...
and Thomas Bartholin
Thomas Bartholin (; Latinized as ''Thomas Bartholinus''; 20 October 1616 – 4 December 1680) was a Danish physician, mathematician, and theologian. He is best known for his work in the discovery of the lymphatic system in humans and for hi ...
.
Structure
The lymphatic system consists of a conducting network of lymphatic vessels, lymphoid organs, lymphoid tissues, and the circulatinglymph
Lymph (from Latin, , meaning "water") is the fluid that flows through the lymphatic system, a system composed of lymph vessels (channels) and intervening lymph nodes whose function, like the venous system, is to return fluid from the tissues ...
.
Primary lymphoid organs
The primary (or central) lymphoid organs generatelymphocyte
A lymphocyte is a type of white blood cell (leukocyte) in the immune system of most vertebrates. Lymphocytes include natural killer cells (which function in cell-mediated, cytotoxic innate immunity), T cells (for cell-mediated, cytotoxic ad ...
s from immature progenitor cell
A progenitor cell is a biological cell that can differentiate into a specific cell type. Stem cells and progenitor cells have this ability in common. However, stem cells are less specified than progenitor cells. Progenitor cells can only differ ...
s. The thymus
The thymus is a specialized primary lymphoid organ of the immune system. Within the thymus, thymus cell lymphocytes or ''T cells'' mature. T cells are critical to the adaptive immune system, where the body adapts to specific foreign invaders. ...
and the bone marrow constitute the primary lymphoid organs involved in the production and early clonal selection
In immunology, clonal selection theory explains the functions of cells of the immune system (lymphocytes) in response to specific antigens invading the body. The concept was introduced by Australian doctor Frank Macfarlane Burnet in 1957, in an ...
of lymphocyte tissues.
Bone marrow
Bone marrow is responsible for both the creation ofT cell
A T cell is a type of lymphocyte. T cells are one of the important white blood cells of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell r ...
precursors and the production and maturation of B cells, which are important cell types of the immune system. From the bone marrow, B cells immediately join the circulatory system and travel to secondary lymphoid organs in search of pathogens. T cells, on the other hand, travel from the bone marrow to the thymus, where they develop further and mature. Mature T cells then join B cells in search of pathogens. The other 95% of T cells begin a process of apoptosis, a form of programmed cell death
Programmed cell death (PCD; sometimes referred to as cellular suicide) is the death of a cell (biology), cell as a result of events inside of a cell, such as apoptosis or autophagy. PCD is carried out in a biological process, which usually confers ...
.
Thymus
The thymus increases in size from birth in response to postnatal antigen stimulation. It is most active during the neonatal and pre-adolescent periods. The thymus is located between the inferior neck and the superior thorax. At puberty, by the early teens, the thymus begins to atrophy and regress, with adipose tissue mostly replacing the thymic stroma. However, residual T cell lymphopoiesis continues throughout adult life, providing some immune response. The thymus is where the T lymphocytes mature and become immunocompetent. The loss or lack of the thymus results in severe immunodeficiency and subsequent high susceptibility to infection. In most species, the thymus consists of lobules divided by septa which are made up of epithelium which is often considered an epithelial organ. T cells mature from thymocytes, proliferate, and undergo a selection process in the thymic cortex before entering the medulla to interact with epithelial cells. Research on bony fish showed a buildup of T cells in the thymus and spleen of lymphoid tissues insalmon
Salmon () is the common name for several commercially important species of euryhaline ray-finned fish from the family Salmonidae, which are native to tributaries of the North Atlantic (genus ''Salmo'') and North Pacific (genus '' Oncorhy ...
and showed that there are not many T cells in non-lymphoid tissues.
The thymus provides an inductive environment for the development of T cells from hematopoietic progenitor cells. In addition, thymic stromal cells allow for the selection of a functional and self-tolerant T cell repertoire. Therefore, one of the most important roles of the thymus is the induction of central tolerance. However, the thymus is not where the infection is fought, as the T cells have yet to become immunocompetent.
Secondary lymphoid organs
The secondary (or peripheral) lymphoid organs (SLO), which include lymph nodes and thespleen
The spleen is an organ found in almost all vertebrates. Similar in structure to a large lymph node, it acts primarily as a blood filter. The word spleen comes .
, maintain mature naive lymphocytes and initiate an adaptive immune response. The secondary lymphoid organs are the sites of lymphocyte activation by antigen
In immunology, an antigen (Ag) is a molecule or molecular structure or any foreign particulate matter or a pollen grain that can bind to a specific antibody or T-cell receptor. The presence of antigens in the body may trigger an immune respons ...
s. Activation leads to clonal expansion and affinity maturation. Mature lymphocytes recirculate between the blood and the secondary lymphoid organs until they encounter their specific antigen.
Spleen
The main functions of the spleen are: # to produceimmune cell
White blood cells, also called leukocytes or leucocytes, are the cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and foreign invaders. All white blood cells are produced and derived from multi ...
s to fight antigen
In immunology, an antigen (Ag) is a molecule or molecular structure or any foreign particulate matter or a pollen grain that can bind to a specific antibody or T-cell receptor. The presence of antigens in the body may trigger an immune respons ...
s
# to remove particulate matter and aged blood cells, mainly red blood cell
Red blood cells (RBCs), also referred to as red cells, red blood corpuscles (in humans or other animals not having nucleus in red blood cells), haematids, erythroid cells or erythrocytes (from Greek ''erythros'' for "red" and ''kytos'' for "holl ...
s
# to produce blood cells during fetal life.
The spleen synthesizes antibodies in its white pulp
White pulp is a histological designation for regions of the spleen (named because it appears whiter than the surrounding red pulp on gross section), that encompasses approximately 25% of splenic tissue. White pulp consists entirely of lymphoid ti ...
and removes antibody-coated bacteria and antibody-coated blood cells by way of blood and lymph node circulation. The white pulp of the spleen provides immune fucntion due to the lymphocytes that are housed there. The spleen also consists of red pulp which is responsible for getting rid of aged red blood cells, as well as pathogens. This is carried out by macrophages present in the red pulp. A study published in 2009 using mice found that the spleen contains, in its reserve, half of the body's monocyte
Monocytes are a type of leukocyte or white blood cell. They are the largest type of leukocyte in blood and can differentiate into macrophages and conventional dendritic cells. As a part of the vertebrate innate immune system monocytes also ...
s within the red pulp. These monocytes, upon moving to injured tissue (such as the heart), turn into dendritic cells and macrophages while promoting tissue healing. The spleen is a center of activity of the mononuclear phagocyte system
In immunology, the mononuclear phagocyte system or mononuclear phagocytic system (MPS) also known as the reticuloendothelial system or macrophage system is a part of the immune system that consists of the phagocytic cells located in reticular co ...
and can be considered analogous to a large lymph node, as its absence causes a predisposition to certain infection
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable dis ...
s. Notably, the spleen is important for a multitude of functions. The spleen removes pathogens and old erythrocytes from the blood (red pulp) and produces lymphocytes for immune response (white pulp). The spleen also is responsible for recycling some erythrocytes components and discarding others. For example, hemoglobin is broken down into amino acids that are reused.
Research on bony fish has shown that a high concentration of T cells are found in the white pulp of the spleen.ref name="Koppang"/>
Like the thymus
The thymus is a specialized primary lymphoid organ of the immune system. Within the thymus, thymus cell lymphocytes or ''T cells'' mature. T cells are critical to the adaptive immune system, where the body adapts to specific foreign invaders. ...
, the spleen has only efferent lymphatic vessels. Both the short gastric arteries
The short gastric arteries consist of from five to seven small branches, which arise from the end of the splenic artery, and from its terminal divisions.
They pass from left to right, between the layers of the gastrolienal ligament, and are dist ...
and the splenic artery
In human anatomy, the splenic artery or lienal artery is the blood vessel that supplies oxygenated blood to the spleen. It branches from the celiac artery, and follows a course superior to the pancreas. It is known for its tortuous path to the s ...
supply it with blood. The germinal centers
Germinal centers or germinal centres (GCs) are transiently formed structures within B cell zone (follicles) in secondary lymphoid organs – lymph nodes, ileal Peyer's patches, and the spleen – where mature B cells are activated, prolifer ...
are supplied by arteriole
An arteriole is a small-diameter blood vessel in the microcirculation that extends and branches out from an artery and leads to capillaries.
Arterioles have muscular walls (usually only one to two layers of smooth muscle cells) and are the primar ...
s called ''penicilliary radicles''.
In the human until the fifth month of prenatal development, the spleen creates red blood cells; after birth, the bone marrow is solely responsible for hematopoiesis
Haematopoiesis (, from Greek , 'blood' and 'to make'; also hematopoiesis in American English; sometimes also h(a)emopoiesis) is the formation of blood cellular components. All cellular blood components are derived from haematopoietic stem cells ...
. As a major lymphoid organ and a central player in the reticuloendothelial system, the spleen retains the ability to produce lymphocytes. The spleen stores red blood cells and lymphocytes. It can store enough blood cells to help in an emergency. Up to 25% of lymphocytes can be stored at any one time.
Lymph nodes
 A lymph node is an organized collection of lymphoid tissue, through which the lymph passes on its way back to the blood. Lymph nodes are located at intervals along the lymphatic system. Several
A lymph node is an organized collection of lymphoid tissue, through which the lymph passes on its way back to the blood. Lymph nodes are located at intervals along the lymphatic system. Several afferent lymph vessel
The lymphatic vessels (or lymph vessels or lymphatics) are thin-walled vessels (tubes), structured like blood vessels, that carry lymph. As part of the lymphatic system, lymph vessels are complementary to the cardiovascular system. Lymph vessel ...
s bring in lymph, which percolates through the substance of the lymph node, and is then drained out by an efferent lymph vessel
The lymphatic vessels (or lymph vessels or lymphatics) are thin-walled vessels (tubes), structured like blood vessels, that carry lymph. As part of the lymphatic system, lymph vessels are complementary to the cardiovascular system. Lymph vessel ...
. Of the nearly 800 lymph nodes in the human body, about 300 are located in the head and neck. Many are grouped in clusters in different regions, as in the underarm and abdominal areas. Lymph node clusters are commonly found at the proximal ends of limbs (groin, armpits) and in the neck, where lymph is collected from regions of the body likely to sustain pathogen contamination from injuries. Lymph nodes are particularly numerous in the mediastinum in the chest, neck, pelvis, axilla
The axilla (also, armpit, underarm or oxter) is the area on the human body directly under the shoulder joint. It includes the axillary space, an anatomical space within the shoulder girdle between the arm and the thoracic cage, bounded superior ...
, inguinal region, and in association with the blood vessels of the intestines.
The substance of a lymph node consists of lymphoid follicles in an outer portion called the cortex
Cortex or cortical may refer to:
Biology
* Cortex (anatomy), the outermost layer of an organ
** Cerebral cortex, the outer layer of the vertebrate cerebrum, part of which is the ''forebrain''
*** Motor cortex, the regions of the cerebral cortex i ...
. The inner portion of the node is called the medulla
Medulla or Medullary may refer to:
Science
* Medulla oblongata, a part of the brain stem
* Renal medulla, a part of the kidney
* Adrenal medulla, a part of the adrenal gland
* Medulla of ovary, a stroma in the center of the ovary
* Medulla of t ...
, which is surrounded by the cortex on all sides except for a portion known as the hilum. The hilum presents as a depression on the surface of the lymph node, causing the otherwise spherical lymph node to be bean-shaped or ovoid. The efferent lymph vessel directly emerges from the lymph node at the hilum. The arteries and veins supplying the lymph node with blood enter and exit through the hilum. The region of the lymph node called the paracortex immediately surrounds the medulla. Unlike the cortex, which has mostly immature T cells, or thymocytes
A Thymocyte is an immune cell present in the thymus, before it undergoes transformation into a T cell. Thymocytes are produced as stem cells in the bone marrow and reach the thymus via the blood. Thymopoiesis describes the process which turns thym ...
, the paracortex has a mixture of immature and mature T cells. Lymphocytes enter the lymph nodes through specialised high endothelial venules found in the paracortex.
A lymph follicle is a dense collection of lymphocytes, the number, size, and configuration of which change in accordance with the functional state of the lymph node. For example, the follicles expand significantly when encountering a foreign antigen. The selection of B cells, or ''B lymphocytes'', occurs in the germinal centre
Germinal centers or germinal centres (GCs) are transiently formed structures within B cell zone (follicles) in secondary lymphoid organs – lymph nodes, ileal Peyer's patches, and the spleen – where mature B cells are activated, prolifera ...
of the lymph nodes.
Secondary lymphoid tissue provides the environment for the foreign or altered native molecules (antigens) to interact with the lymphocytes. It is exemplified by the lymph nodes, and the lymphoid follicles in tonsil
The tonsils are a set of lymphoid organs facing into the aerodigestive tract, which is known as Waldeyer's tonsillar ring and consists of the adenoid tonsil, two tubal tonsils, two palatine tonsils, and the lingual tonsils. These organs play ...
s, Peyer's patch
Peyer's patches (or aggregated lymphoid nodules) are organized lymphoid follicles, named after the 17th-century Swiss anatomist Johann Conrad Peyer.
* Reprinted as:
* Peyer referred to Peyer's patches as ''plexus'' or ''agmina glandularum'' (c ...
es, spleen
The spleen is an organ found in almost all vertebrates. Similar in structure to a large lymph node, it acts primarily as a blood filter. The word spleen comes .
, adenoid
In anatomy, the adenoid, also known as the pharyngeal tonsil or nasopharyngeal tonsil, is the superior-most of the tonsils. It is a mass of lymphatic tissue located behind the nasal cavity, in the roof of the nasopharynx, where the nose blends ...
s, skin
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation.
Other animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have different de ...
, etc. that are associated with the mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue
The mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT), also called mucosa-associated lymphatic tissue, is a diffuse system of small concentrations of lymphoid tissue found in various submucosal membrane sites of the body, such as the gastrointestinal tr ...
(MALT).
In the gastrointestinal wall, the appendix has mucosa resembling that of the colon, but here it is heavily infiltrated with lymphocytes.
Tertiary lymphoid organs
Tertiary lymphoid organs (TLOs) are abnormal lymph node-like structures that form in peripheral tissues at sites of chronic inflammation, such as chronic infection, transplanted organs undergoinggraft rejection
Transplant rejection occurs when transplanted tissue is rejected by the recipient's immune system, which destroys the transplanted tissue. Transplant rejection can be lessened by determining the molecular similitude between donor and recipient a ...
, some cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ...
s, and autoimmune
In immunology, autoimmunity is the system of immune responses of an organism against its own healthy cells, tissues and other normal body constituents. Any disease resulting from this type of immune response is termed an "autoimmune disease". ...
and autoimmune-related diseases. TLOs are regulated differently from the normal process whereby lymphoid tissues are formed during ontogeny
Ontogeny (also ontogenesis) is the origination and development of an organism (both physical and psychological, e.g., moral development), usually from the time of fertilization of the egg to adult. The term can also be used to refer to the s ...
, being dependent on cytokines and hematopoietic cells, but still drain interstitial fluid
In cell biology, extracellular fluid (ECF) denotes all body fluid outside the cells of any multicellular organism. Total body water in healthy adults is about 60% (range 45 to 75%) of total body weight; women and the obese typically have a lower ...
and transport lymphocytes in response to the same chemical messengers and gradients. TLOs typically contain far fewer lymphocytes, and assume an immune role only when challenged with antigen
In immunology, an antigen (Ag) is a molecule or molecular structure or any foreign particulate matter or a pollen grain that can bind to a specific antibody or T-cell receptor. The presence of antigens in the body may trigger an immune respons ...
s that result in inflammation
Inflammation (from la, inflammatio) is part of the complex biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants, and is a protective response involving immune cells, blood vessels, and molec ...
. They achieve this by importing the lymphocytes from blood and lymph. TLOs often have an active germinal center
Germinal centers or germinal centres (GCs) are transiently formed structures within B cell zone (follicles) in secondary lymphoid organs – lymph nodes, ileal Peyer's patches, and the spleen – where mature B cells are activated, prolifera ...
, surrounded by a network of follicular dendritic cells (FDCs).
TLOs are thought to play an important role in the immune response to cancer and to have possible implications in immunotherapy. They have been observed in a number of cancer types such as melanoma, non-small cell lung cancer and colorectal cancer (reviewed in ) as well as glioma. Patients with TLOs in the vicinity of their tumors tend to have a better prognosis, although the opposite is true for certain cancers. TLOs that contain an active germinal center
Germinal centers or germinal centres (GCs) are transiently formed structures within B cell zone (follicles) in secondary lymphoid organs – lymph nodes, ileal Peyer's patches, and the spleen – where mature B cells are activated, prolifera ...
tend to have a better prognosis than those with TLOs without a germinal center. The reason that these patients tend to live longer is thought to be the immune response against the tumor, which is mediated by the TLOs. TLOs may also promote an anti-tumor response when patients are treated with immunotherapy. TLOs have been referred to in many different ways, including as tertiary lymphoid structures (TLS) and ectopic lymphoid structures (ELS). When associated with colorectal cancer, they are often referred to as a Crohn's-like lymphoid reaction.
Other lymphoid tissue
Lymphoid tissue associated with the lymphatic system is concerned with immune functions in defending the body againstinfection
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable dis ...
s and the spread of tumour
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists ...
s. It consists of connective tissue formed of reticular fiber
Reticular fibers, reticular fibres or reticulin is a type of fiber in connective tissue composed of type III collagen secreted by reticular cells. Reticular fibers crosslink to form a fine meshwork (reticulin). This network acts as a supportin ...
s, with various types of leukocytes (white blood cells), mostly lymphocyte
A lymphocyte is a type of white blood cell (leukocyte) in the immune system of most vertebrates. Lymphocytes include natural killer cells (which function in cell-mediated, cytotoxic innate immunity), T cells (for cell-mediated, cytotoxic ad ...
s enmeshed in it, through which the lymph passes. Regions of the lymphoid tissue that are densely packed with lymphocytes are known as ''lymphoid follicles''. Lymphoid tissue can either be structurally well organized as lymph nodes or may consist of loosely organized lymphoid follicles known as the mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue
The mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT), also called mucosa-associated lymphatic tissue, is a diffuse system of small concentrations of lymphoid tissue found in various submucosal membrane sites of the body, such as the gastrointestinal tr ...
(MALT).
The central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all p ...
also has lymphatic vessels. The search for T cell gateways into and out of the meninges uncovered functional meningeal lymphatic vessels
The meningeal lymphatic vessels (or meningeal lymphatics) are a network of conventional lymphatic vessels located parallel to the dural venous sinuses and middle meningeal arteries of the mammalian central nervous system (CNS). As a part of the ly ...
lining the dural sinuses, anatomically integrated into the membrane surrounding the brain.
*
Lymphatic vessels
 The
The lymphatic vessel
The lymphatic vessels (or lymph vessels or lymphatics) are thin-walled vessels (tubes), structured like blood vessels, that carry lymph. As part of the lymphatic system, lymph vessels are complementary to the cardiovascular system. Lymph ve ...
s, also called lymph vessels, are thin-walled vessels that conduct lymph between different parts of the body. They include the tubular vessels of the lymph capillaries
Lymph capillaries or lymphatic capillaries are tiny, thin-walled microvessels located in the spaces between cells (except in the central nervous system and non-vascular tissues) which serve to drain and process extracellular fluid. Upon enteri ...
, and the larger collecting vessels–the right lymphatic duct
The right lymphatic duct is an important lymphatic vessel that drains the right upper quadrant of the body. It forms various combinations with the right subclavian vein and right internal jugular vein.
Structure
The right lymphatic duct course ...
and the thoracic duct
In human anatomy, the thoracic duct is the larger of the two lymph ducts of the lymphatic system. It is also known as the ''left lymphatic duct'', ''alimentary duct'', ''chyliferous duct'', and ''Van Hoorne's canal''. The other duct is the righ ...
(the left lymphatic duct). The lymph capillaries are mainly responsible for the absorption of interstitial fluid from the tissues, while lymph vessels propel the absorbed fluid forward into the larger collecting ducts, where it ultimately returns to the bloodstream via one of the subclavian veins.
The tissues of the lymphatic system are responsible for maintaining the balance of the body fluid
Body fluids, bodily fluids, or biofluids, sometimes body liquids, are liquids within the human body. In lean healthy adult men, the total body water is about 60% (60–67%) of the total body weight; it is usually slightly lower in women (52-55% ...
s. Its network of capillaries and collecting lymphatic vessels work to efficiently drain and transport extravasated fluid, along with proteins and antigens, back to the circulatory system. Numerous intraluminal valves in the vessels ensure a unidirectional flow of lymph without reflux. Two valve systems, a primary and a secondary valve system, are used to achieve this unidirectional flow. The capillaries are blind-ended, and the valves at the ends of capillaries use specialised junctions together with anchoring filaments to allow a unidirectional flow to the primary vessels. The collecting lymphatics, however, act to propel the lymph by the combined actions of the intraluminal valves and lymphatic muscle cells.
Development
Lymphatic tissues begin to develop by the end of the fifth week of embryonic development. Lymphatic vessels develop from lymph sacs that arise from developing veins, which are derived from mesoderm. The first lymph sacs to appear are the paired jugular lymph sacs at the junction of the internal jugular and subclavian veins. From the jugular lymph sacs, lymphatic capillary plexuses spread to the thorax, upper limbs, neck, and head. Some of the plexuses enlarge and form lymphatic vessels in their respective regions. Each jugular lymph sac retains at least one connection with its jugular vein, the left one developing into the superior portion of the thoracic duct. Thespleen
The spleen is an organ found in almost all vertebrates. Similar in structure to a large lymph node, it acts primarily as a blood filter. The word spleen comes .
develops from mesenchymal cells between layers of the dorsal mesentery of the stomach.
The thymus
The thymus is a specialized primary lymphoid organ of the immune system. Within the thymus, thymus cell lymphocytes or ''T cells'' mature. T cells are critical to the adaptive immune system, where the body adapts to specific foreign invaders. ...
arises as an outgrowth of the third pharyngeal pouch.
Function
The lymphatic system has multiple interrelated functions: * It is responsible for the removal ofinterstitial fluid
In cell biology, extracellular fluid (ECF) denotes all body fluid outside the cells of any multicellular organism. Total body water in healthy adults is about 60% (range 45 to 75%) of total body weight; women and the obese typically have a lower ...
from tissues
* It absorbs and transports fatty acid
In chemistry, particularly in biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with an aliphatic chain, which is either saturated or unsaturated. Most naturally occurring fatty acids have an unbranched chain of an even number of carbon atoms, ...
s and fat
In nutrition, biology, and chemistry, fat usually means any ester of fatty acids, or a mixture of such compounds, most commonly those that occur in living beings or in food.
The term often refers specifically to triglycerides (triple est ...
s as chyle
Chyle (from the Greek word χυλός ''chylos'', "juice") is a milky bodily fluid consisting of lymph and emulsified fats, or free fatty acids (FFAs). It is formed in the small intestine during digestion of fatty foods, and taken up by lymph v ...
from the digestive system
* It transports white blood cells
White blood cells, also called leukocytes or leucocytes, are the cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and foreign invaders. All white blood cells are produced and derived from mult ...
to and from the lymph nodes into the bones
* The lymph transports antigen-presenting cells, such as dendritic cells
Dendritic cells (DCs) are antigen-presenting cells (also known as ''accessory cells'') of the mammalian immune system. Their main function is to process antigen material and present it on the cell surface to the T cells of the immune system. The ...
, to the lymph nodes where an immune response is stimulated.
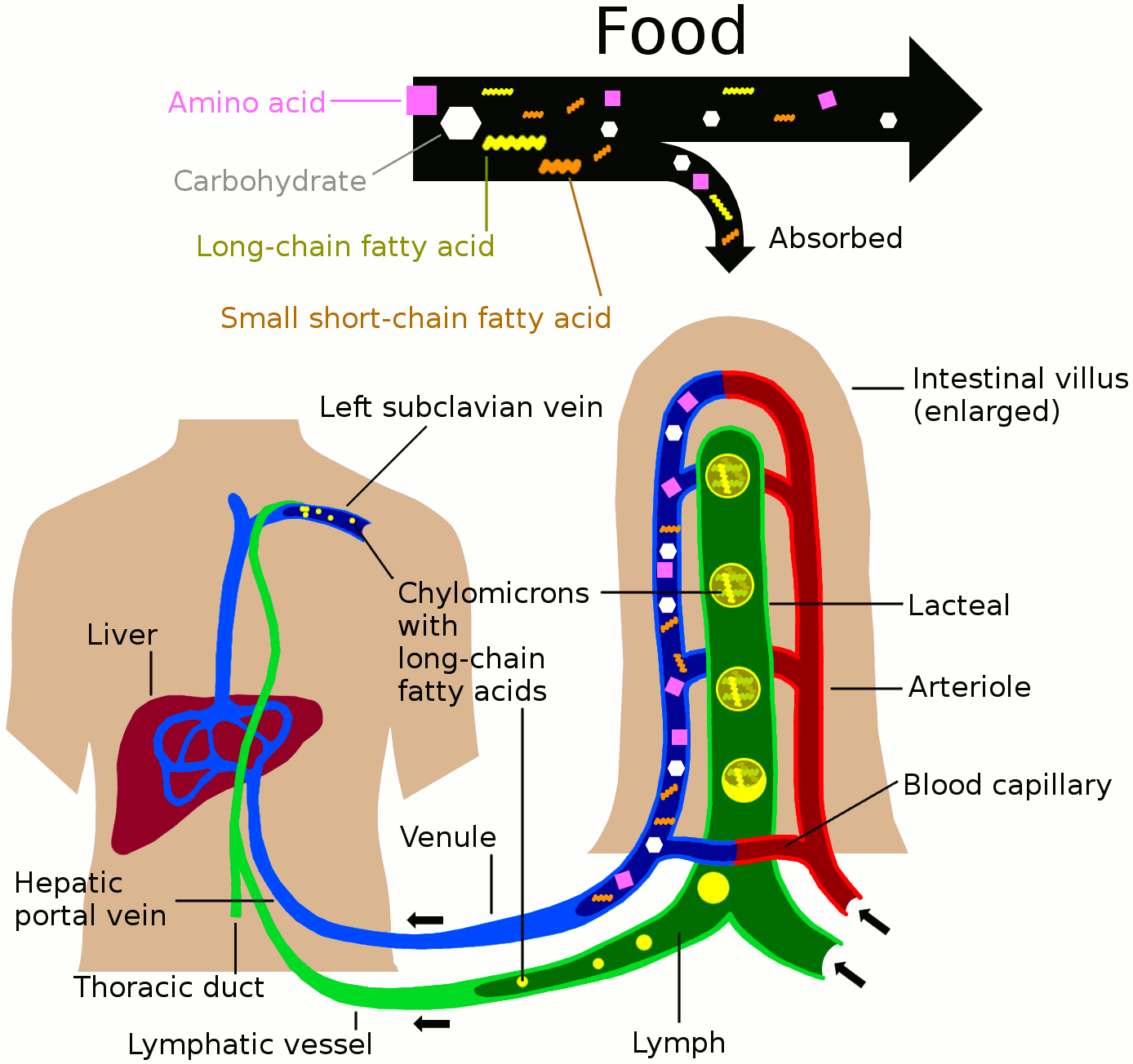
Fat absorption
 Lymph vessels called
Lymph vessels called lacteal
A lacteal is a lymphatic capillary that absorbs dietary fats in the villi of the small intestine.
Triglycerides are emulsified by bile and hydrolyzed by the enzyme lipase, resulting in a mixture of fatty acids, di- and monoglycerides. Thes ...
s are at the beginning of the gastrointestinal tract, predominantly in the small intestine. While most other nutrients absorbed by the small intestine are passed on to the portal venous system
In the circulatory system of animals, a portal venous system occurs when a capillary bed pools into another capillary bed through veins, without first going through the heart. Both capillary beds and the blood vessels that connect them are con ...
to drain via the portal vein into the liver
The liver is a major organ only found in vertebrates which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for digestion and growth. In humans, it ...
for processing, fats (lipids
Lipids are a broad group of naturally-occurring molecules which includes fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids include ...
) are passed on to the lymphatic system to be transported to the blood circulation via the thoracic duct
In human anatomy, the thoracic duct is the larger of the two lymph ducts of the lymphatic system. It is also known as the ''left lymphatic duct'', ''alimentary duct'', ''chyliferous duct'', and ''Van Hoorne's canal''. The other duct is the righ ...
. (There are exceptions, for example medium-chain triglycerides are fatty acid esters of glycerol that passively diffuse from the GI tract to the portal system.) The enriched lymph originating in the lymphatics of the small intestine is called chyle
Chyle (from the Greek word χυλός ''chylos'', "juice") is a milky bodily fluid consisting of lymph and emulsified fats, or free fatty acids (FFAs). It is formed in the small intestine during digestion of fatty foods, and taken up by lymph v ...
. The nutrients that are released into the circulatory system are processed by the liver
The liver is a major organ only found in vertebrates which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for digestion and growth. In humans, it ...
, having passed through the systemic circulation.
Immune function
The lymphatic system plays a major role in the body's immune system, as the primary site for cells relating toadaptive immune system
The adaptive immune system, also known as the acquired immune system, is a subsystem of the immune system that is composed of specialized, systemic cells and processes that eliminate pathogens or prevent their growth. The acquired immune system ...
including T-cell
A T cell is a type of lymphocyte. T cells are one of the important white blood cells of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell r ...
s and B-cells.
Cells in the lymphatic system react to antigens presented or found by the cells directly or by other dendritic cells
Dendritic cells (DCs) are antigen-presenting cells (also known as ''accessory cells'') of the mammalian immune system. Their main function is to process antigen material and present it on the cell surface to the T cells of the immune system. The ...
.
When an antigen is recognized, an immunological cascade begins involving the activation and recruitment of more and more cells, the production of antibodies and cytokines and the recruitment of other immunological cells such as macrophages
Macrophages (abbreviated as M φ, MΦ or MP) ( el, large eaters, from Greek ''μακρός'' (') = large, ''φαγεῖν'' (') = to eat) are a type of white blood cell of the immune system that engulfs and digests pathogens, such as cancer ce ...
.
Clinical significance
The study of lymphatic drainage of various organs is important in the diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment of cancer. The lymphatic system, because of its closeness to many tissues of the body, is responsible for carrying cancerous cells between the various parts of the body in a process calledmetastasis
Metastasis is a pathogenic agent's spread from an initial or primary site to a different or secondary site within the host's body; the term is typically used when referring to metastasis by a cancerous tumor. The newly pathological sites, then ...
. The intervening lymph nodes can trap the cancer cells. If they are not successful in destroying the cancer cells the nodes may become sites of secondary tumours.
Enlarged lymph nodes
Lymphadenopathy refers to one or more enlarged lymph nodes. Small groups or individually enlarged lymph nodes are generally ''reactive'' in response toinfection
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable dis ...
or inflammation
Inflammation (from la, inflammatio) is part of the complex biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants, and is a protective response involving immune cells, blood vessels, and molec ...
. This is called ''local'' lymphadenopathy. When many lymph nodes in different areas of the body are involved, this is called ''generalised'' lymphadenopathy. Generalised lymphadenopathy may be caused by infection
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable dis ...
s such as infectious mononucleosis
Infectious mononucleosis (IM, mono), also known as glandular fever, is an infection usually caused by the Epstein–Barr virus (EBV). Most people are infected by the virus as children, when the disease produces few or no symptoms. In young adult ...
, tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease usually caused by '' Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, i ...
and HIV
The human immunodeficiency viruses (HIV) are two species of ''Lentivirus'' (a subgroup of retrovirus) that infect humans. Over time, they cause acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), a condition in which progressive failure of the immune ...
, connective tissue disease
A connective tissue disease (collagenosis) is any disease that has the connective tissues of the body as a target of pathology. Connective tissue is any type of biological tissue with an extensive extracellular matrix that supports, binds togeth ...
s such as SLE and rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long-term autoimmune disorder that primarily affects joints. It typically results in warm, swollen, and painful joints. Pain and stiffness often worsen following rest. Most commonly, the wrist and hands are invol ...
, and cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ...
s, including both cancers of tissue within lymph nodes, discussed below, and metastasis
Metastasis is a pathogenic agent's spread from an initial or primary site to a different or secondary site within the host's body; the term is typically used when referring to metastasis by a cancerous tumor. The newly pathological sites, then ...
of cancerous cells from other parts of the body, that have arrived via the lymphatic system.
Lymphedema
Lymphedema
Lymphedema, also known as lymphoedema and lymphatic edema, is a condition of localized swelling caused by a compromised lymphatic system. The lymphatic system functions as a critical portion of the body's immune system and returns interstitial fl ...
is the swelling caused by the accumulation of lymph, which may occur if the lymphatic system is damaged or has malformations. It usually affects limbs, though the face, neck and abdomen may also be affected. In an extreme state, called elephantiasis, the edema progresses to the extent that the skin becomes thick with an appearance similar to the skin on elephant
Elephants are the largest existing land animals. Three living species are currently recognised: the African bush elephant, the African forest elephant, and the Asian elephant. They are the only surviving members of the family Elephantidae ...
limbs.
Causes are unknown in most cases, but sometimes there is a previous history of severe infection, usually caused by a parasitic disease
A parasitic disease, also known as parasitosis, is an infectious disease caused by parasites. Parasites are organisms which derive sustenance from its host while causing it harm. The study of parasites and parasitic diseases is known as parasitolo ...
, such as lymphatic filariasis.
Lymphangiomatosis is a disease involving multiple cysts or lesions formed from lymphatic vessels.
Lymphedema can also occur after surgical removal of lymph nodes in the armpit (causing the arm to swell due to poor lymphatic drainage) or groin (causing swelling of the leg). Conventional treatment is by manual lymphatic drainage
Manual lymphatic drainage (MLD) is a type of massage based on the hypothesis that it will encourage the natural drainage of the lymph, which carries waste products away from the tissues back toward the heart. The lymph system depends on intrinsic c ...
and compression garment
Compression garments are pieces of clothing that fit tightly around the skin. In medical contexts, compression garments provide support for people who have to stand for long periods or have poor circulation. These come in varying degrees of co ...
s. Two drugs for the treatment of lymphedema are in clinical trials: Lymfactin and Ubenimex/Bestatin
Ubenimex (INN), also known more commonly as bestatin, is a competitive, reversible protease inhibitor. It is an inhibitor of arginyl aminopeptidase (aminopeptidase B), leukotriene A4 hydrolase (a zinc metalloprotease that displays both epoxi ...
. There is no evidence to suggest that the effects of manual lymphatic drainage are permanent.
Cancer

Cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ...
of the lymphatic system can be primary or secondary. Lymphoma
Lymphoma is a group of blood and lymph tumors that develop from lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell). In current usage the name usually refers to just the cancerous versions rather than all such tumours. Signs and symptoms may include enla ...
refers to cancer that arises from lymphatic tissue
The lymphatic system, or lymphoid system, is an organ system in vertebrates that is part of the immune system, and complementary to the circulatory system. It consists of a large network of lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, lymphatic or lymphoid o ...
. Lymphoid leukaemias and lymphomas are now considered to be tumours of the same type of cell lineage. They are called "leukaemia" when in the blood or marrow and "lymphoma" when in lymphatic tissue. They are grouped together under the name "lymphoid malignancy".
Lymphoma is generally considered as either Hodgkin lymphoma
Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) is a type of lymphoma, in which cancer originates from a specific type of white blood cell called lymphocytes, where multinucleated Reed–Sternberg cells (RS cells) are present in the patient's lymph nodes. The condition w ...
or non-Hodgkin lymphoma
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), also known as non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, is a group of blood cancers that includes all types of lymphomas except Hodgkin lymphomas. Symptoms include enlarged lymph nodes, fever, night sweats, weight loss, and tirednes ...
. Hodgkin lymphoma is characterised by a particular type of cell, called a Reed–Sternberg cell
Reed–Sternberg cells (also known as lacunar histiocytes for certain types) are distinctive, giant cells found with light microscopy in biopsies from individuals with Hodgkin lymphoma. They are usually derived from B lymphocytes, classically con ...
, visible under microscope. It is associated with past infection with the Epstein–Barr virus
The Epstein–Barr virus (EBV), formally called ''Human gammaherpesvirus 4'', is one of the nine known human herpesvirus types in the herpes family, and is one of the most common viruses in humans. EBV is a double-stranded DNA virus.
It is b ...
, and generally causes a painless "rubbery" lymphadenopathy. It is staged, using Ann Arbor staging. Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated to chemo and sometimes CTX or CTx) is a type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs ( chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) as part of a standardized chemotherapy regimen. Chemothe ...
generally involves the ABVD
ABVD is a chemotherapy regimen used in the first-line treatment of Hodgkin lymphoma, replacing the older MOPP protocol. It consists of concurrent treatment with the chemotherapy drugs:
* Adriamycin (also known as doxorubicin/hydroxydaunorubicin, ...
and may also involve radiotherapy. Non-Hodgkin lymphoma is a cancer characterised by increased proliferation of B-cells or T-cells
A T cell is a type of lymphocyte. T cells are one of the important white blood cells of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell r ...
, generally occurs in an older age group than Hodgkin lymphoma. It is treated according to whether it is '' high-grade'' or ''low-grade'', and carries a poorer prognosis than Hodgkin lymphoma.
Lymphangiosarcoma
Lymphangiosarcoma is a rare cancer which occurs in long-standing cases of primary or secondary lymphedema. It involves either the upper or lower lymphedematous extremities but is most common in upper extremities. Although its name implies lymphat ...
is a malignant soft tissue tumour, whereas lymphangioma is a benign tumour occurring frequently in association with Turner syndrome
Turner syndrome (TS), also known as 45,X, or 45,X0, is a genetic condition in which a female is partially or completely missing an X chromosome. Signs and symptoms vary among those affected. Often, a short and webbed neck, low-set ears, low hair ...
. Lymphangioleiomyomatosis
Lymphangioleiomyomatosis (LAM) is a rare, progressive and systemic disease that typically results in cystic lung destruction. It predominantly affects women, especially during childbearing years. The term sporadic LAM is used for patients with LAM ...
is a benign tumour of the smooth muscles of the lymphatics that occurs in the lungs.
Lymphoid leukaemia is another form of cancer where the host is devoid of different lymphatic cells.
Other
*Castleman's disease
Castleman disease (CD) describes a group of rare lymphoproliferative disorders that involve enlarged lymph nodes, and a broad range of inflammatory symptoms and laboratory abnormalities. Whether Castleman disease should be considered an autoimmu ...
* Chylothorax
* Kawasaki disease
Kawasaki disease is a syndrome of unknown cause that results in a fever and mainly affects children under 5 years of age. It is a form of vasculitis, where blood vessels become inflamed throughout the body. The fever typically lasts for more th ...
* Kikuchi disease
* Lipedema
* Lymphangitis
* Lymphatic filariasis
* Lymphocytic choriomeningitis
* Solitary lymphatic nodule
History
Hippocrates
Hippocrates of Kos (; grc-gre, Ἱπποκράτης ὁ Κῷος, Hippokrátēs ho Kôios; ), also known as Hippocrates II, was a Greek physician of the classical period who is considered one of the most outstanding figures in the history o ...
, in the 5th century BC, was one of the first people to mention the lymphatic system. In his work ''On Joints'', he briefly mentioned the lymph nodes in one sentence. Rufus of Ephesus, a Roman physician, identified the axillary, inguinal and mesenteric lymph nodes as well as the thymus during the 1st to 2nd century AD. The first mention of lymphatic vessels was in the 3rd century BC by Herophilos
Herophilos (; grc-gre, Ἡρόφιλος; 335–280 BC), sometimes Latinised Herophilus, was a Greek physician regarded as one of the earliest anatomists. Born in Chalcedon, he spent the majority of his life in Alexandria. He was the first sci ...
, a Greek anatomist living in Alexandria
Alexandria ( or ; ar, ٱلْإِسْكَنْدَرِيَّةُ ; grc-gre, Αλεξάνδρεια, Alexándria) is the second largest city in Egypt, and the largest city on the Mediterranean coast. Founded in by Alexander the Great, Alexandri ...
, who incorrectly concluded that the "absorptive veins of the lymphatics," by which he meant the lacteal
A lacteal is a lymphatic capillary that absorbs dietary fats in the villi of the small intestine.
Triglycerides are emulsified by bile and hydrolyzed by the enzyme lipase, resulting in a mixture of fatty acids, di- and monoglycerides. Thes ...
s (lymph vessels of the intestines), drained into the hepatic portal vein
The portal vein or hepatic portal vein (HPV) is a blood vessel that carries blood from the gastrointestinal tract, gallbladder, pancreas and spleen to the liver. This blood contains nutrients and toxins extracted from digested contents. Approx ...
s, and thus into the liver. The findings of Ruphus and Herophilos were further propagated by the Greek physician Galen
Aelius Galenus or Claudius Galenus ( el, Κλαύδιος Γαληνός; September 129 – c. AD 216), often Anglicized as Galen () or Galen of Pergamon, was a Greek physician, surgeon and philosopher in the Roman Empire. Considered to be one ...
, who described the lacteals and mesenteric lymph nodes which he observed in his dissection of apes and pigs in the 2nd century AD.
In the mid 16th century, Gabriele Falloppio
Gabriele Falloppio (also Gabrielle Falloppia) (1522/23 – 9 October 1562) was an Italian anatomist often known by his Latin name Fallopius. He was one of the most important anatomists and physicians of the sixteenth century, giving his name ...
(discoverer of the fallopian tubes), described what is now known as the lacteals as "coursing over the intestines full of yellow matter." In about 1563 Bartolomeo Eustachi, a professor of anatomy, described the thoracic duct in horses as ''vena alba thoracis.'' The next breakthrough came when in 1622 a physician, Gaspare Aselli, identified lymphatic vessels of the intestines in dogs and termed them ''venae albae et lacteae,'' which are now known as simply the lacteals. The lacteals were termed the fourth kind of vessels (the other three being the artery, vein and nerve, which was then believed to be a type of vessel), and disproved Galen's assertion that chyle was carried by the veins. But, he still believed that the lacteals carried the chyle to the liver (as taught by Galen). He also identified the thoracic duct but failed to notice its connection with the lacteals. This connection was established by Jean Pecquet
Jean Pecquet (9 May 1622, Dieppe, Seine-Maritime – 26 February 1674) was a French scientist. He studied the expansion of air, wrote on psychology, and is also known for investigating the thoracic duct. Furthermore, he studied the nature of visi ...
in 1651, who found a white fluid mixing with blood in a dog's heart. He suspected that fluid to be chyle
Chyle (from the Greek word χυλός ''chylos'', "juice") is a milky bodily fluid consisting of lymph and emulsified fats, or free fatty acids (FFAs). It is formed in the small intestine during digestion of fatty foods, and taken up by lymph v ...
as its flow increased when abdominal pressure was applied. He traced this fluid to the thoracic duct, which he then followed to a chyle-filled sac he called the ''chyli receptaculum,'' which is now known as the cisternae chyli; further investigations led him to find that lacteals' contents enter the venous system via the thoracic duct. Thus, it was proven convincingly that the lacteals did not terminate in the liver
The liver is a major organ only found in vertebrates which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for digestion and growth. In humans, it ...
, thus disproving Galen's second idea: that the chyle flowed to the liver. Johann Veslingius drew the earliest sketches of the lacteals in humans in 1641.
The idea that blood recirculates through the body rather than being produced anew by the liver and the heart was first accepted as a result of works of William Harvey
William Harvey (1 April 1578 – 3 June 1657) was an English physician who made influential contributions in anatomy and physiology. He was the first known physician to describe completely, and in detail, the systemic circulation and propert ...
—a work he published in 1628. In 1652, Olaus Rudbeck
Olaus Rudbeck (also known as Olof Rudbeck the Elder, to distinguish him from his son, and occasionally with the surname Latinized as ''Olaus Rudbeckius'') (13 September 1630 – 12 December 1702) was a Swedish scientist and writer, professor o ...
(1630–1702), a Swede, discovered certain transparent vessels in the liver that contained clear fluid (and not white), and thus named them ''hepatico-aqueous vessels''. He also learned that they emptied into the thoracic duct and that they had valves. He announced his findings in the court of Queen Christina of Sweden, but did not publish his findings for a year, and in the interim similar findings were published by Thomas Bartholin
Thomas Bartholin (; Latinized as ''Thomas Bartholinus''; 20 October 1616 – 4 December 1680) was a Danish physician, mathematician, and theologian. He is best known for his work in the discovery of the lymphatic system in humans and for hi ...
, who additionally published that such vessels are present everywhere in the body, not just in the liver. He is also the one to have named them "lymphatic vessels." This had resulted in a bitter dispute between one of Bartholin's pupils, Martin Bogdan, and Rudbeck, whom he accused of plagiarism.
Galen's ideas prevailed in medicine until the 17th century. It was thought that blood was produced by the liver from chyle contaminated with ailments by the intestine and stomach, to which various spirits were added by other organs, and that this blood was consumed by all the organs of the body. This theory required that the blood be consumed and produced many times over. Even in the 17th century, his ideas were defended by some physicians.
Alexander Monro, of the University of Edinburgh Medical School
The University of Edinburgh Medical School (also known as Edinburgh Medical School) is the medical school of the University of Edinburgh in Scotland and the United Kingdom and part of the University of Edinburgh College of Medicine and Veterinar ...
, was the first to describe the function of the lymphatic system in detail.
Gabriele Falloppio
Gabriele Falloppio (also Gabrielle Falloppia) (1522/23 – 9 October 1562) was an Italian anatomist often known by his Latin name Fallopius. He was one of the most important anatomists and physicians of the sixteenth century, giving his name ...
Image:Bartolomeus Eustachius.jpg, Portrait of Eustachius
File:Olaus Rudbeck Sr (portrait by Martin Mijtens Sr, 1696).jpg, Olaus Rudbeck
Olaus Rudbeck (also known as Olof Rudbeck the Elder, to distinguish him from his son, and occasionally with the surname Latinized as ''Olaus Rudbeckius'') (13 September 1630 – 12 December 1702) was a Swedish scientist and writer, professor o ...
in 1696.
File:Thomas bartholin.jpg, Thomas Bartholin
Thomas Bartholin (; Latinized as ''Thomas Bartholinus''; 20 October 1616 – 4 December 1680) was a Danish physician, mathematician, and theologian. He is best known for his work in the discovery of the lymphatic system in humans and for hi ...
Etymology
''Lymph'' originates in theClassical Latin
Classical Latin is the form of Literary Latin recognized as a literary standard by writers of the late Roman Republic and early Roman Empire. It was used from 75 BC to the 3rd century AD, when it developed into Late Latin. In some later period ...
word ' "water", which is also the source of the English word ''limpid''. The spelling with ''y'' and ''ph'' was influenced by folk etymology with Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
(') "nymph
A nymph ( grc, νύμφη, nýmphē, el, script=Latn, nímfi, label= Modern Greek; , ) in ancient Greek folklore is a minor female nature deity. Different from Greek goddesses, nymphs are generally regarded as personifications of nature, are ...
".
The adjective used for the lymph-transporting system is ''lymphatic''. The adjective used for the tissues where lymphocytes are formed is ''lymphoid''. Lymphatic comes from the Latin word ', meaning "connected to water."
See also
* List of lymphatic vessels of the human body *American Society of Lymphology The Lymphology Association of North America, formerly known as the American Society of Lymphology, is a non-profit organization based in Kansas City, Missouri, Kansas City, Missouri. The society provides current information and resources for profess ...
* Glymphatic system
The glymphatic system (or glymphatic clearance pathway, or paravascular system) was described and named in 2013 as a system for waste clearance in the central nervous system (CNS) of vertebrates. According to this model, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) ...
and Meningeal lymphatic vessels
The meningeal lymphatic vessels (or meningeal lymphatics) are a network of conventional lymphatic vessels located parallel to the dural venous sinuses and middle meningeal arteries of the mammalian central nervous system (CNS). As a part of the ly ...
- equivalent for the central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all p ...
* Innate lymphoid cell
Innate lymphoid cells (ILCs) are the most recently discovered family of innate immune cells, derived from common lymphoid progenitors (CLPs). In response to pathogenic tissue damage, ILCs contribute to immunity via the secretion of signalling mo ...
s
* Lymphangiogenesis
Lymphangiogenesis is the formation of lymphatic vessels from pre-existing lymphatic vessels in a method believed to be similar to angiogenesis (blood vessel development).
Lymphangiogenesis plays an important physiological role in homeostasis, meta ...
* Lymphangion
* Mononuclear phagocyte system
In immunology, the mononuclear phagocyte system or mononuclear phagocytic system (MPS) also known as the reticuloendothelial system or macrophage system is a part of the immune system that consists of the phagocytic cells located in reticular co ...
* Waldemar Olszewski – discovered fundamental processes in human tissues connected with function of the lymphatic system
* Trogocytosis
References
External links
Lymphatic System
(innerbody.com) {{DEFAULTSORT:Lymphatic System Angiology Animal anatomy