lapse rate on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The lapse rate is the rate at which an atmospheric variable, normally
The lapse rate is the rate at which an atmospheric variable, normally
/ref> is: Typically, the lapse rate is the negative of the rate of temperature change with altitude change: : where (sometimes ) is the lapse rate given in units of temperature divided by units of altitude, ''T'' is temperature, and ''z'' is altitude. The ''environmental lapse rate'' (ELR), is the actual rate of decrease of temperature with altitude in the atmosphere at a given time and location. As an average, the
 As convection causes parcels of air to rise or fall, there is little heat transfer between those parcels and the surrounding air. Air has low
As convection causes parcels of air to rise or fall, there is little heat transfer between those parcels and the surrounding air. Air has low
 The following calculations derive the temperature as a function of altitude for a packet of air which is ascending or descending without exchanging heat with its environment.
The following calculations derive the temperature as a function of altitude for a packet of air which is ascending or descending without exchanging heat with its environment.
 The varying environmental lapse rates throughout the Earth's atmosphere are of critical importance in
The varying environmental lapse rates throughout the Earth's atmosphere are of critical importance in
www.air-dispersion.com
*
from the Planetary Data system. * National Science Digital Library glossary: *
Lapse Rate
*
Environmental lapse rate
*
Absolute stable air
* An introduction t
from U. Texas {{DEFAULTSORT:Lapse Rate Atmospheric thermodynamics Climate change feedbacks Fluid mechanics Meteorological quantities Spatial gradient Atmospheric temperature Vertical distributions
 The lapse rate is the rate at which an atmospheric variable, normally
The lapse rate is the rate at which an atmospheric variable, normally temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that quantitatively expresses the attribute of hotness or coldness. Temperature is measurement, measured with a thermometer. It reflects the average kinetic energy of the vibrating and colliding atoms making ...
in Earth's atmosphere
The atmosphere of Earth is composed of a layer of gas mixture that surrounds the Earth's planetary surface (both lands and oceans), known collectively as air, with variable quantities of suspended aerosols and particulates (which create weathe ...
, falls with altitude
Altitude is a distance measurement, usually in the vertical or "up" direction, between a reference datum (geodesy), datum and a point or object. The exact definition and reference datum varies according to the context (e.g., aviation, geometr ...
. ''Lapse rate'' arises from the word ''lapse'' (in its "becoming less" sense, not its "interruption" sense). In dry air, the adiabatic lapse rate (i.e., decrease in temperature of a parcel of air that rises in the atmosphere without exchanging energy with surrounding air) is 9.8 °C/km (5.4 °F per 1,000 ft). The saturated adiabatic lapse rate (SALR), or moist adiabatic lapse rate (MALR), is the decrease in temperature of a parcel of water-saturated air that rises in the atmosphere. It varies with the temperature and pressure of the parcel and is often in the range 3.6 to (2 to ), as obtained from the International Civil Aviation Organization
The International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO ) is a specialized agency of the United Nations that coordinates the principles and techniques of international air navigation, and fosters the planning and development of international sch ...
(ICAO). The environmental lapse rate is the decrease in temperature of air with altitude for a specific time and place (see below). It can be highly variable between circumstances.
Lapse rate corresponds to the vertical component of the spatial gradient of temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that quantitatively expresses the attribute of hotness or coldness. Temperature is measurement, measured with a thermometer. It reflects the average kinetic energy of the vibrating and colliding atoms making ...
. Although this concept is most often applied to the Earth's troposphere
The troposphere is the lowest layer of the atmosphere of Earth. It contains 80% of the total mass of the Atmosphere, planetary atmosphere and 99% of the total mass of water vapor and aerosols, and is where most weather phenomena occur. From the ...
, it can be extended to any gravitationally supported parcel of gas.
Environmental lapse rate
A formal definition from the ''Glossary of Meteorology''(Glossary of Meteorology)/ref> is: Typically, the lapse rate is the negative of the rate of temperature change with altitude change: : where (sometimes ) is the lapse rate given in units of temperature divided by units of altitude, ''T'' is temperature, and ''z'' is altitude. The ''environmental lapse rate'' (ELR), is the actual rate of decrease of temperature with altitude in the atmosphere at a given time and location. As an average, the
International Civil Aviation Organization
The International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO ) is a specialized agency of the United Nations that coordinates the principles and techniques of international air navigation, and fosters the planning and development of international sch ...
(ICAO) defines an international standard atmosphere
The International Standard Atmosphere (ISA) is a static atmospheric model of how the pressure, temperature, density, and viscosity of the Earth's atmosphere change over a wide range of altitudes or elevations. It has been established to provide ...
(ISA) with a temperature lapse rate of or from sea level to 11 km or . From 11 km up to 20 km or , the constant temperature is , which is the lowest assumed temperature in the ISA. The standard atmosphere contains no moisture.
Unlike the idealized ISA, the temperature of the actual atmosphere does not always fall at a uniform rate with height. For example, there can be an inversion layer in which the temperature increases with altitude.
Cause
The temperature profile of the atmosphere is a result of the interaction between radiative heating fromsunlight
Sunlight is the portion of the electromagnetic radiation which is emitted by the Sun (i.e. solar radiation) and received by the Earth, in particular the visible spectrum, visible light perceptible to the human eye as well as invisible infrare ...
, cooling to space via thermal radiation
Thermal radiation is electromagnetic radiation emitted by the thermal motion of particles in matter. All matter with a temperature greater than absolute zero emits thermal radiation. The emission of energy arises from a combination of electro ...
, and upward heat transport via natural convection
Convection is single or multiphase fluid flow that occurs spontaneously through the combined effects of material property heterogeneity and body forces on a fluid, most commonly density and gravity (see buoyancy). When the cause of the conve ...
(which carries hot air and latent heat
Latent heat (also known as latent energy or heat of transformation) is energy released or absorbed, by a body or a thermodynamic system, during a constant-temperature process—usually a first-order phase transition, like melting or condensation. ...
upward). Above the tropopause
The tropopause is the atmospheric boundary that demarcates the lowest two layers of the atmosphere of Earth – the troposphere and stratosphere – which occurs approximately above the equatorial regions, and approximately above the polar regi ...
, convection does not occur and all cooling is radiative.
Within the troposphere
The troposphere is the lowest layer of the atmosphere of Earth. It contains 80% of the total mass of the Atmosphere, planetary atmosphere and 99% of the total mass of water vapor and aerosols, and is where most weather phenomena occur. From the ...
, the lapse rate is essentially the consequence of a balance between (a) radiative cooling of the air, which by itself would lead to a high lapse rate; and (b) convection, which is activated when the lapse rate exceeds a critical value; convection stabilizes the environmental lapse rate.
Sunlight hits the surface of the earth (land and sea) and heats them. The warm surface heats the air above it. In addition, nearly a third of absorbed sunlight is absorbed within the atmosphere, heating the atmosphere directly.
Thermal conduction
Thermal conduction is the diffusion of thermal energy (heat) within one material or between materials in contact. The higher temperature object has molecules with more kinetic energy; collisions between molecules distributes this kinetic energy ...
helps transfer heat from the surface to the air; this conduction occurs within the few millimeters of air closest to the surface. However, above that thin interface layer, thermal conduction plays a negligible role in transferring heat within the atmosphere; this is because the thermal conductivity of air is very low.
The air is radiatively cooled by greenhouse gases
Greenhouse gases (GHGs) are the gases in the atmosphere that raise the surface temperature of planets such as the Earth. Unlike other gases, greenhouse gases absorb the radiations that a planet emits, resulting in the greenhouse effect. T ...
(water vapor, carbon dioxide, etc.) and clouds emitting longwave thermal radiation to space.
If radiation
In physics, radiation is the emission or transmission of energy in the form of waves or particles through space or a material medium. This includes:
* ''electromagnetic radiation'' consisting of photons, such as radio waves, microwaves, infr ...
were the only way to transfer energy within the atmosphere, then the lapse rate near the surface would be roughly 40 °C/km and the greenhouse effect
The greenhouse effect occurs when greenhouse gases in a planet's atmosphere insulate the planet from losing heat to space, raising its surface temperature. Surface heating can happen from an internal heat source (as in the case of Jupiter) or ...
of gases in the atmosphere would keep the ground at roughly .
However, when air gets hot or humid, its density decreases. Thus, air which has been heated by the surface tends to rise and carry internal energy upward, especially if the air has been moistened by evaporation from water surfaces. This is the process of convection
Convection is single or Multiphase flow, multiphase fluid flow that occurs Spontaneous process, spontaneously through the combined effects of material property heterogeneity and body forces on a fluid, most commonly density and gravity (see buoy ...
. Vertical convective motion stops when a parcel of air at a given altitude has the same density as the other air at the same elevation.
Convection carries hot, moist air upward and cold, dry air downward, with a net effect of transferring heat upward. This makes the air below cooler than it would otherwise be and the air above warmer. Because convection is available to transfer heat within the atmosphere, the lapse rate in the troposphere is reduced to around 6.5 °C/km and the greenhouse effect is reduced to a point where Earth has its observed surface temperature of around .
Convection and adiabatic expansion
thermal conductivity
The thermal conductivity of a material is a measure of its ability to heat conduction, conduct heat. It is commonly denoted by k, \lambda, or \kappa and is measured in W·m−1·K−1.
Heat transfer occurs at a lower rate in materials of low ...
, and the bodies of air involved are very large; so transfer of heat by conduction is negligibly small. Also, intra-atmospheric radiative heat transfer is relatively slow and so is negligible for moving air. Thus, when air ascends or descends, there is little exchange of heat with the surrounding air. A process in which no heat is exchanged with the environment is referred to as an adiabatic process
An adiabatic process (''adiabatic'' ) is a type of thermodynamic process that occurs without transferring heat between the thermodynamic system and its Environment (systems), environment. Unlike an isothermal process, an adiabatic process transf ...
.
Air expands as it moves upward, and contracts as it moves downward. The expansion of rising air parcels, and the contraction of descending air parcels, are adiabatic process
An adiabatic process (''adiabatic'' ) is a type of thermodynamic process that occurs without transferring heat between the thermodynamic system and its Environment (systems), environment. Unlike an isothermal process, an adiabatic process transf ...
es, to a good approximation. When a parcel of air expands, it pushes on the air around it, doing thermodynamic work. Since the upward-moving and expanding parcel does work but gains no heat, it loses internal energy
The internal energy of a thermodynamic system is the energy of the system as a state function, measured as the quantity of energy necessary to bring the system from its standard internal state to its present internal state of interest, accoun ...
so that its temperature decreases. Downward-moving and contracting air has work done on it, so it gains internal energy and its temperature increases.
Adiabatic processes for air have a characteristic temperature-pressure curve. As air circulates vertically, the air takes on that characteristic gradient, called the ''adiabatic lapse rate''. When the air contains little water, this lapse rate is known as the dry adiabatic lapse rate: the rate of temperature decrease is ( per 1,000 ft) (3.0 °C/1,000 ft). The reverse occurs for a sinking parcel of air.
When the environmental lapse rate is less than the adiabatic lapse rate the atmosphere is stable and convection will not occur. The environmental lapse is forced towards the adiabatic lapse rate whenever air is convecting vertically.
Only the troposphere
The troposphere is the lowest layer of the atmosphere of Earth. It contains 80% of the total mass of the Atmosphere, planetary atmosphere and 99% of the total mass of water vapor and aerosols, and is where most weather phenomena occur. From the ...
(up to approximately of altitude) in the Earth's atmosphere undergoes convection
Convection is single or Multiphase flow, multiphase fluid flow that occurs Spontaneous process, spontaneously through the combined effects of material property heterogeneity and body forces on a fluid, most commonly density and gravity (see buoy ...
: the stratosphere
The stratosphere () is the second-lowest layer of the atmosphere of Earth, located above the troposphere and below the mesosphere. The stratosphere is composed of stratified temperature zones, with the warmer layers of air located higher ...
does not generally convect. However, some exceptionally energetic convection processes, such as volcanic eruption column
An eruption column or eruption plume is a cloud of super-heated Volcanic ash, ash and tephra suspended in volcanic gas, gases emitted during an explosive eruption, explosive volcanic eruption. The volcanic materials form a vertical column or Plu ...
s and overshooting tops associated with severe supercell thunderstorms, may locally and temporarily inject convection through the tropopause
The tropopause is the atmospheric boundary that demarcates the lowest two layers of the atmosphere of Earth – the troposphere and stratosphere – which occurs approximately above the equatorial regions, and approximately above the polar regi ...
and into the stratosphere.
Energy transport in the atmosphere is more complex than the interaction between radiation and dry convection. The water cycle
The water cycle (or hydrologic cycle or hydrological cycle) is a biogeochemical cycle that involves the continuous movement of water on, above and below the surface of the Earth across different reservoirs. The mass of water on Earth remains fai ...
(including evaporation
Evaporation is a type of vaporization that occurs on the Interface (chemistry), surface of a liquid as it changes into the gas phase. A high concentration of the evaporating substance in the surrounding gas significantly slows down evapora ...
, condensation
Condensation is the change of the state of matter from the gas phase into the liquid phase, and is the reverse of vaporization. The word most often refers to the water cycle. It can also be defined as the change in the state of water vapor ...
, precipitation
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls from clouds due to gravitational pull. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, rain and snow mixed ("sleet" in Commonwe ...
) transports latent heat
Latent heat (also known as latent energy or heat of transformation) is energy released or absorbed, by a body or a thermodynamic system, during a constant-temperature process—usually a first-order phase transition, like melting or condensation. ...
and affects atmospheric humidity levels, significantly influencing the temperature profile, as described below.
Mathematics of the adiabatic lapse rate
Dry adiabatic lapse rate
Thermodynamics defines an adiabatic process as: : thefirst law of thermodynamics
The first law of thermodynamics is a formulation of the law of conservation of energy in the context of thermodynamic processes. For a thermodynamic process affecting a thermodynamic system without transfer of matter, the law distinguishes two ...
can be written as
:
Also, since the density and , we can show that:
:
where is the specific heat
In thermodynamics, the specific heat capacity (symbol ) of a substance is the amount of heat that must be added to one unit of mass of the substance in order to cause an increase of one unit in temperature. It is also referred to as massic heat ...
at constant pressure.
Assuming an atmosphere in hydrostatic equilibrium
In fluid mechanics, hydrostatic equilibrium, also called hydrostatic balance and hydrostasy, is the condition of a fluid or plastic solid at rest, which occurs when external forces, such as gravity, are balanced by a pressure-gradient force. I ...
:Landau and Lifshitz, ''Fluid Mechanics'', Pergamon, 1979
:
where ''g'' is the standard gravity
The standard acceleration of gravity or standard acceleration of free fall, often called simply standard gravity and denoted by or , is the nominal gravitational acceleration of an object in a vacuum near the surface of the Earth. It is a constant ...
. Combining these two equations to eliminate the pressure, one arrives at the result for the ''dry adiabatic lapse rate'' (DALR),
:
The DALR () is the temperature gradient experienced in an ascending or descending packet of air that is not saturated with water vapor, i.e., with less than 100% relative humidity.
Moist adiabatic lapse rate
The presence of water within the atmosphere (usually the troposphere) complicates the process of convection. Water vapor contains latentheat of vaporization
In thermodynamics, the enthalpy of vaporization (symbol ), also known as the (latent) heat of vaporization or heat of evaporation, is the amount of energy (enthalpy) that must be added to a liquid substance to Phase transition, transform a qua ...
. As a parcel of air rises and cools, it eventually becomes saturated; that is, the vapor pressure of water in equilibrium with liquid water has decreased (as temperature has decreased) to the point where it is equal to the actual vapor pressure of water. With further decrease in temperature the water vapor in excess of the equilibrium amount condenses, forming cloud
In meteorology, a cloud is an aerosol consisting of a visible mass of miniature liquid droplets, frozen crystals, or other particles, suspended in the atmosphere of a planetary body or similar space. Water or various other chemicals may ...
, and releasing heat (latent heat of condensation). Before saturation, the rising air follows the dry adiabatic lapse rate. After saturation, the rising air follows the moist (or ''wet'') adiabatic lapse rate. The release of latent heat is an important source of energy in the development of thunderstorms.
While the dry adiabatic lapse rate is a constant ( per 1,000 ft, ), the moist adiabatic lapse rate varies strongly with temperature. A typical value is around , (, , ). The formula for the ''saturated adiabatic lapse rate'' (SALR) or ''moist adiabatic lapse rate'' (MALR) is given by:
:
where:
:
The SALR or MALR () is the temperature gradient experienced in an ascending or descending packet of air that is saturated with water vapor, i.e., with 100% relative humidity.
Effect on weather
 The varying environmental lapse rates throughout the Earth's atmosphere are of critical importance in
The varying environmental lapse rates throughout the Earth's atmosphere are of critical importance in meteorology
Meteorology is the scientific study of the Earth's atmosphere and short-term atmospheric phenomena (i.e. weather), with a focus on weather forecasting. It has applications in the military, aviation, energy production, transport, agricultur ...
, particularly within the troposphere
The troposphere is the lowest layer of the atmosphere of Earth. It contains 80% of the total mass of the Atmosphere, planetary atmosphere and 99% of the total mass of water vapor and aerosols, and is where most weather phenomena occur. From the ...
. They are used to determine if the parcel of rising air will rise high enough for its water to condense to form cloud
In meteorology, a cloud is an aerosol consisting of a visible mass of miniature liquid droplets, frozen crystals, or other particles, suspended in the atmosphere of a planetary body or similar space. Water or various other chemicals may ...
s, and, having formed clouds, whether the air will continue to rise and form bigger shower clouds, and whether these clouds will get even bigger and form cumulonimbus cloud
Cumulonimbus () is a dense, towering, vertical cloud, typically forming from water vapor condensing in the lower troposphere that builds upward carried by powerful buoyant air currents. Above the lower portions of the cumulonimbus the water ...
s (thunder clouds).
As unsaturated air rises, its temperature drops at the dry adiabatic rate. The dew point
The dew point is the temperature the air needs to be cooled to (at constant pressure) in order to produce a relative humidity of 100%. This temperature depends on the pressure and water content of the air. When the air at a temperature above the ...
also drops (as a result of decreasing air pressure) but much more slowly, typically about per 1,000 m. If unsaturated air rises far enough, eventually its temperature will reach its dew point
The dew point is the temperature the air needs to be cooled to (at constant pressure) in order to produce a relative humidity of 100%. This temperature depends on the pressure and water content of the air. When the air at a temperature above the ...
, and condensation will begin to form. This altitude is known as the lifting condensation level (LCL) when mechanical lift is present and the convective condensation level (CCL) when mechanical lift is absent, in which case, the parcel must be heated from below to its convective temperature. The cloud base will be somewhere within the layer bounded by these parameters.
The difference between the dry adiabatic lapse rate and the rate at which the dew point
The dew point is the temperature the air needs to be cooled to (at constant pressure) in order to produce a relative humidity of 100%. This temperature depends on the pressure and water content of the air. When the air at a temperature above the ...
drops is around per 1,000 m. Given a difference in temperature and dew point
The dew point is the temperature the air needs to be cooled to (at constant pressure) in order to produce a relative humidity of 100%. This temperature depends on the pressure and water content of the air. When the air at a temperature above the ...
readings on the ground, one can easily find the LCL by multiplying the difference by 125 m/°C.
If the environmental lapse rate is less than the moist adiabatic lapse rate, the air is absolutely stable — rising air will cool faster than the surrounding air and lose buoyancy
Buoyancy (), or upthrust, is the force exerted by a fluid opposing the weight of a partially or fully immersed object (which may be also be a parcel of fluid). In a column of fluid, pressure increases with depth as a result of the weight of t ...
. This often happens in the early morning, when the air near the ground has cooled overnight. Cloud formation in stable air is unlikely.
If the environmental lapse rate is between the moist and dry adiabatic lapse rates, the air is conditionally unstable — an unsaturated parcel of air does not have sufficient buoyancy to rise to the LCL or CCL, and it is stable to weak vertical displacements in either direction. If the parcel is saturated it is unstable and will rise to the LCL or CCL, and either be halted due to an inversion layer of convective inhibition, or if lifting continues, deep, moist convection (DMC) may ensue, as a parcel rises to the level of free convection
The level of free convection (LFC) is the altitude in the atmosphere where an air parcel lifted adiabatically until saturation becomes warmer than the environment at the same level, so that positive buoyancy can initiate self-sustained convection. ...
(LFC), after which it enters the free convective layer (FCL) and usually rises to the equilibrium level (EL).
If the environmental lapse rate is larger than the dry adiabatic lapse rate, it has a superadiabatic lapse rate, the air is absolutely unstable — a parcel of air will gain buoyancy as it rises both below and above the lifting condensation level or convective condensation level. This often happens in the afternoon mainly over land masses. In these conditions, the likelihood of cumulus cloud
Cumulus clouds are clouds that have flat cloud base, bases and are often described as puffy, cotton-like, or fluffy in appearance. Their name derives from the Latin , meaning "heap" or "pile". Cumulus clouds are low-level clouds, generally less ...
s, showers or even thunderstorm
A thunderstorm, also known as an electrical storm or a lightning storm, is a storm characterized by the presence of lightning and its acoustics, acoustic effect on the Earth's atmosphere, known as thunder. Relatively weak thunderstorm ...
s is increased.
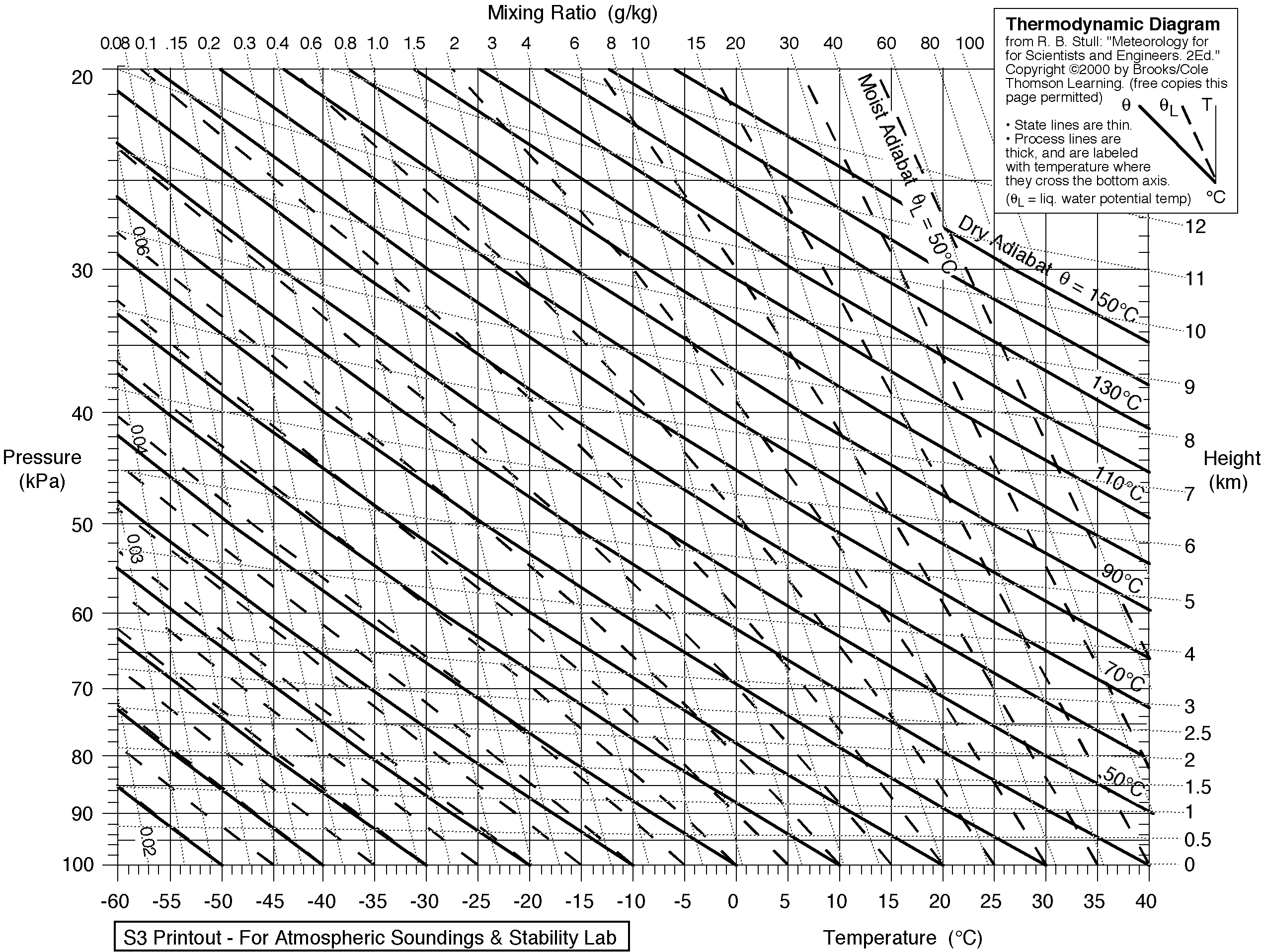
Meteorologists use radiosonde
A radiosonde is a battery-powered telemetry instrument carried into the atmosphere usually by a weather balloon that measures various atmospheric parameters and transmits them by radio to a ground receiver. Modern radiosondes measure or calculat ...
s to measure the environmental lapse rate and compare it to the predicted adiabatic lapse rate to forecast the likelihood that air will rise. Charts of the environmental lapse rate are known as thermodynamic diagrams
Thermodynamic diagrams are diagrams used to represent the thermodynamic states of a material (typically fluid) and the consequences of manipulating this material. For instance, a temperature–entropy diagram (Temperature–entropy diagram, T–s ...
, examples of which include Skew-T log-P diagram
A skew-T log-P diagram is one of four thermodynamic diagrams commonly used in weather analysis and forecasting. In 1947, N. Herlofson proposed a modification to the emagram that allows straight, horizontal isobars and provides for a large angle ...
s and tephigram
A tephigram is one of a number of thermodynamic diagrams commonly used in weather analysis and forecasting. The name evolved from the original name "T-\phi-gram" to describe the axes of temperature (T) and entropy (\phi) used to create the plo ...
s. (See also Thermals
A thermal column (or thermal) is a rising mass of buoyant air, a convective current in the atmosphere, that transfers heat energy vertically. Thermals are created by the uneven heating of Earth's surface from solar radiation, and are an example ...
).
The difference in moist adiabatic lapse rate and the dry rate is the cause of foehn wind
A Foehn, or Föhn (, , , ), is a type of dry, relatively warm downslope wind in the lee of a mountain range. It is a rain shadow wind that results from the subsequent adiabatic warming of air that has dropped most of its moisture on windw ...
phenomenon (also known as "Chinook wind
Chinook winds, or simply Chinooks, are two types of prevailing warm, generally westerly winds in western North America: Coastal Chinooks and interior Chinooks. The coastal Chinooks are persistent seasonal, wet, southwesterly winds blowing in from ...
s" in parts of North America). The phenomenon exists because warm moist air rises through orographic lifting up and over the top of a mountain range or large mountain. The temperature decreases with the dry adiabatic lapse rate, until it hits the dew point, where water vapor in the air begins to condense. Above that altitude, the adiabatic lapse rate decreases to the moist adiabatic lapse rate as the air continues to rise. Condensation is also commonly followed by precipitation
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls from clouds due to gravitational pull. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, rain and snow mixed ("sleet" in Commonwe ...
on the top and windward
In geography and seamanship, windward () and leeward () are directions relative to the wind. Windward is ''upwind'' from the point of reference, i.e., towards the direction from which the wind is coming; leeward is ''downwind'' from the point ...
sides of the mountain. As the air descends on the leeward side, it is warmed by adiabatic compression
An adiabatic process (''adiabatic'' ) is a type of thermodynamic process that occurs without transferring heat between the thermodynamic system and its Environment (systems), environment. Unlike an isothermal process, an adiabatic process transf ...
at the dry adiabatic lapse rate. Thus, the foehn wind at a certain altitude is warmer than the corresponding altitude on the windward side of the mountain range. In addition, because the air has lost much of its original water vapor content, the descending air creates an arid
Aridity is the condition of geographical regions which make up approximately 43% of total global available land area, characterized by low annual precipitation, increased temperatures, and limited water availability.Perez-Aguilar, L. Y., Plata ...
region on the leeward side of the mountain.
Impact on the greenhouse effect
If the environmental lapse rate was zero, so that the atmosphere was the same temperature at all elevations, then there would be nogreenhouse effect
The greenhouse effect occurs when greenhouse gases in a planet's atmosphere insulate the planet from losing heat to space, raising its surface temperature. Surface heating can happen from an internal heat source (as in the case of Jupiter) or ...
. This doesn't mean the lapse rate and the greenhouse effect are the same thing, just that the lapse rate is a prerequisite for the greenhouse effect.
The presence of greenhouse gases on a planet causes radiative cooling of the air, which leads to the formation of a non-zero lapse rate. So, the presence of greenhouse gases leads to there being a greenhouse effect at a global level. However, this need not be the case at a localized level.
The localized greenhouse effect is stronger in locations where the lapse rate is stronger. In Antarctica, thermal inversions in the atmosphere (so that air at higher altitudes is warmer) sometimes cause the localized greenhouse effect to become negative (signifying enhanced radiative cooling to space instead of inhibited radiative cooling as is the case for a positive greenhouse effect).
Lapse rate in an isolated column of gas
A question has sometimes arisen as to whether a temperature gradient will arise in a column of still air in a gravitational field without external energy flows. This issue was addressed byJames Clerk Maxwell
James Clerk Maxwell (13 June 1831 – 5 November 1879) was a Scottish physicist and mathematician who was responsible for the classical theory of electromagnetic radiation, which was the first theory to describe electricity, magnetism an ...
, who established in 1868 that if any temperature gradient forms, then that temperature gradient must be universal (i.e., the gradient must be same for all materials) or the second law of thermodynamics
The second law of thermodynamics is a physical law based on Universal (metaphysics), universal empirical observation concerning heat and Energy transformation, energy interconversions. A simple statement of the law is that heat always flows spont ...
would be violated. Maxwell also concluded that the universal result must be one in which the temperature is uniform, i.e., the lapse rate is zero.
Santiago and Visser (2019) confirm the correctness of Maxwell's conclusion (zero lapse rate) provided relativistic effects are neglected. When relativity is taken into account, gravity gives rise to an extremely small lapse rate, the Tolman gradient (derived by R. C. Tolman in 1930). At Earth's surface, the Tolman gradient would be about m, where is the temperature of the gas at the elevation of Earth's surface. Santiago and Visser remark that "gravity is the only force capable of creating temperature gradients in thermal equilibrium states without violating the laws of thermodynamics" and "the existence of Tolman's temperature gradient is not at all controversial (at least not within the general relativity community)."
See also
*Adiabatic process
An adiabatic process (''adiabatic'' ) is a type of thermodynamic process that occurs without transferring heat between the thermodynamic system and its Environment (systems), environment. Unlike an isothermal process, an adiabatic process transf ...
* Atmospheric thermodynamics Atmospheric thermodynamics is the study of heat-to-Work (physics), work transformations (and their reverse) that take place in the Earth's atmosphere and manifest as weather or climate. Atmospheric thermodynamics use the laws of classical thermodyn ...
* Fluid dynamics
In physics, physical chemistry and engineering, fluid dynamics is a subdiscipline of fluid mechanics that describes the flow of fluids – liquids and gases. It has several subdisciplines, including (the study of air and other gases in motion ...
* Foehn wind
A Foehn, or Föhn (, , , ), is a type of dry, relatively warm downslope wind in the lee of a mountain range. It is a rain shadow wind that results from the subsequent adiabatic warming of air that has dropped most of its moisture on windw ...
* Lapse rate climate feedback
* Scale height
In atmospheric, earth, and planetary sciences, a scale height, usually denoted by the capital letter ''H'', is a distance ( vertical or radial) over which a physical quantity decreases by a factor of e (the base of natural logarithms, approx ...
Notes
References
Further reading
*www.air-dispersion.com
*
External links
from the Planetary Data system. * National Science Digital Library glossary: *
Lapse Rate
*
Environmental lapse rate
*
Absolute stable air
* An introduction t
from U. Texas {{DEFAULTSORT:Lapse Rate Atmospheric thermodynamics Climate change feedbacks Fluid mechanics Meteorological quantities Spatial gradient Atmospheric temperature Vertical distributions