Kingdom Of Scotland on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Kingdom of Scotland (; , ) was a
 In the 16th century, under James V of Scotland and Mary, Queen of Scots, the Crown and court took on many of the attributes of the
In the 16th century, under James V of Scotland and Mary, Queen of Scots, the Crown and court took on many of the attributes of the
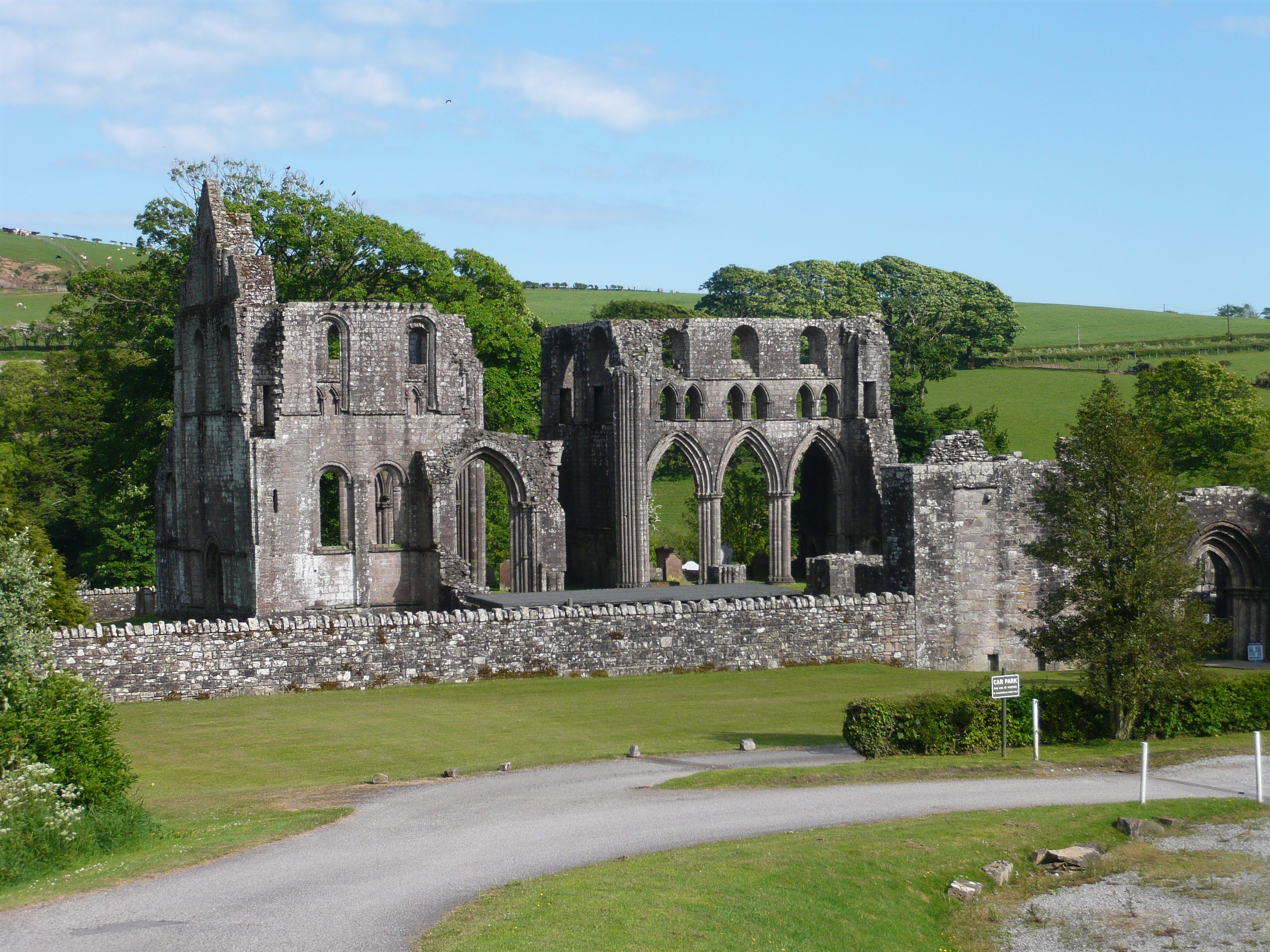
 The unified kingdom of Alba retained some of the ritual aspects of Pictish and Scottish kingship. These can be seen in the elaborate ritual coronation at the Stone of Scone at Scone Abbey..
While the Scottish monarchy in the Middle Ages was a largely itinerant institution, Scone remained one of its most important locations, with royal castles at Stirling and
The unified kingdom of Alba retained some of the ritual aspects of Pictish and Scottish kingship. These can be seen in the elaborate ritual coronation at the Stone of Scone at Scone Abbey..
While the Scottish monarchy in the Middle Ages was a largely itinerant institution, Scone remained one of its most important locations, with royal castles at Stirling and
 Scots law developed into a distinctive system in the Middle Ages and was reformed and codified in the 16th and 17th centuries. Knowledge of the nature of Scots law before the 11th century is largely speculative,. but it was probably a mixture of legal traditions representing the different cultures inhabiting the land at the time, including
Scots law developed into a distinctive system in the Middle Ages and was reformed and codified in the 16th and 17th centuries. Knowledge of the nature of Scots law before the 11th century is largely speculative,. but it was probably a mixture of legal traditions representing the different cultures inhabiting the land at the time, including  During the period of English control over Scotland there is some evidence that
During the period of English control over Scotland there is some evidence that
 David I is the first Scottish king known to have produced his own coinage. There were soon mints at Edinburgh, Berwick and Roxburgh. Early Scottish coins were similar to English ones, but with the king's head in profile instead of full face. The number of coins struck was small and English coins probably remained more significant in this period.. The first gold coin was a noble (6s. 8d.) of David II. Under James I pennies and halfpennies of billon (an alloy of silver with a base metal) were introduced, and copper farthings appeared under James III.. In James V's reign the bawbee ( d) and half-bawbee were issued, and in Mary, Queen of Scot's reign a twopence piece, the hardhead, was issued to help "the common people buy bread, drink, flesh, and fish". The billon coinage was discontinued after 1603, but twopence pieces in copper continued to be issued until the Act of Union in 1707.
David I is the first Scottish king known to have produced his own coinage. There were soon mints at Edinburgh, Berwick and Roxburgh. Early Scottish coins were similar to English ones, but with the king's head in profile instead of full face. The number of coins struck was small and English coins probably remained more significant in this period.. The first gold coin was a noble (6s. 8d.) of David II. Under James I pennies and halfpennies of billon (an alloy of silver with a base metal) were introduced, and copper farthings appeared under James III.. In James V's reign the bawbee ( d) and half-bawbee were issued, and in Mary, Queen of Scot's reign a twopence piece, the hardhead, was issued to help "the common people buy bread, drink, flesh, and fish". The billon coinage was discontinued after 1603, but twopence pieces in copper continued to be issued until the Act of Union in 1707.
 Early Scottish coins were virtually identical in silver content to English ones, but from about 1300 the silver content began to depreciate more rapidly than English. Between then and 1605 they lost value at an average of 12 per cent every ten years, three times the then English rate. The Scottish penny became a base metal coin in about 1484 and virtual disappeared as a separate coin from about 1513.. In 1423, the English government banned the circulation of Scottish coins. At the union of the crowns in 1603, the Scottish pound was fixed at only one-twelfth that of the English pound. The Parliament of Scotland of 1695 enacted proposals to set up the Bank of Scotland. The bank issued pound notes from 1704, which had the face value of £12 Scots. Scottish currency was abolished at the Act of Union, the Scottish coin in circulation was drawn in to be re-minted according to the English standard.
Early Scottish coins were virtually identical in silver content to English ones, but from about 1300 the silver content began to depreciate more rapidly than English. Between then and 1605 they lost value at an average of 12 per cent every ten years, three times the then English rate. The Scottish penny became a base metal coin in about 1484 and virtual disappeared as a separate coin from about 1513.. In 1423, the English government banned the circulation of Scottish coins. At the union of the crowns in 1603, the Scottish pound was fixed at only one-twelfth that of the English pound. The Parliament of Scotland of 1695 enacted proposals to set up the Bank of Scotland. The bank issued pound notes from 1704, which had the face value of £12 Scots. Scottish currency was abolished at the Act of Union, the Scottish coin in circulation was drawn in to be re-minted according to the English standard.
 At its borders in 1707, the Kingdom of Scotland was half the size of England and Wales in area, but with its many inlets, islands and inland lochs, it had roughly the same amount of coastline at . Scotland has over 790 offshore islands, most of which are to be found in four main groups: Shetland, Orkney, and the
At its borders in 1707, the Kingdom of Scotland was half the size of England and Wales in area, but with its many inlets, islands and inland lochs, it had roughly the same amount of coastline at . Scotland has over 790 offshore islands, most of which are to be found in four main groups: Shetland, Orkney, and the
 From the formation of the Kingdom of Alba in the 10th century until before the Black Death arrived in 1349, estimates based on the amount of farmable land suggest that population may have grown from half a million to a million. Although there is no reliable documentation on the impact of the plague, there are many anecdotal references to abandoned land in the following decades. If the pattern followed that in England, then the population may have fallen to as low as half a million by the end of the 15th century.
Compared with the situation after the redistribution of population in the later Highland Clearances and the
From the formation of the Kingdom of Alba in the 10th century until before the Black Death arrived in 1349, estimates based on the amount of farmable land suggest that population may have grown from half a million to a million. Although there is no reliable documentation on the impact of the plague, there are many anecdotal references to abandoned land in the following decades. If the pattern followed that in England, then the population may have fallen to as low as half a million by the end of the 15th century.
Compared with the situation after the redistribution of population in the later Highland Clearances and the
 Historical sources, as well as place name evidence, indicate the ways in which the
Historical sources, as well as place name evidence, indicate the ways in which the
 The Pictish and Scottish kingdoms that would form the basis of the Kingdom of Alba were largely converted by Irish-Scots missions associated with figures such as St Columba, from the 5th to the 7th centuries. These missions tended to found monastic institutions and collegiate churches that served large areas. Partly as a result of these factors, some scholars have identified a distinctive form of Celtic Christianity, in which
The Pictish and Scottish kingdoms that would form the basis of the Kingdom of Alba were largely converted by Irish-Scots missions associated with figures such as St Columba, from the 5th to the 7th centuries. These missions tended to found monastic institutions and collegiate churches that served large areas. Partly as a result of these factors, some scholars have identified a distinctive form of Celtic Christianity, in which  During the 16th century, Scotland underwent a
During the 16th century, Scotland underwent a  In 1635, Charles I authorised a book of canons that made him head of the Church, ordained an unpopular ritual and enforced the use of a new liturgy. When the liturgy emerged in 1637 it was seen as an English-style Prayer Book, resulting in anger and widespread rioting.. Representatives of various sections of Scottish society drew up the National Covenant on 28 February 1638, objecting to the King's liturgical innovations.. The king's supporters were unable to suppress the rebellion and the king refused to compromise. In December of the same year, matters were taken even further, when at a meeting of the General Assembly in Glasgow the Scottish bishops were formally expelled from the Church, which was then established on a full Presbyterian basis. Victory in the resulting Bishops' Wars secured the Presbyterian Kirk and precipitated the outbreak of the civil wars of the 1640s.. Disagreements over collaboration with Royalism created a major conflict between
In 1635, Charles I authorised a book of canons that made him head of the Church, ordained an unpopular ritual and enforced the use of a new liturgy. When the liturgy emerged in 1637 it was seen as an English-style Prayer Book, resulting in anger and widespread rioting.. Representatives of various sections of Scottish society drew up the National Covenant on 28 February 1638, objecting to the King's liturgical innovations.. The king's supporters were unable to suppress the rebellion and the king refused to compromise. In December of the same year, matters were taken even further, when at a meeting of the General Assembly in Glasgow the Scottish bishops were formally expelled from the Church, which was then established on a full Presbyterian basis. Victory in the resulting Bishops' Wars secured the Presbyterian Kirk and precipitated the outbreak of the civil wars of the 1640s.. Disagreements over collaboration with Royalism created a major conflict between
 The establishment of Christianity brought Latin to Scotland as a scholarly and written language. Monasteries served as repositories of knowledge and education, often running schools and providing a small educated elite, who were essential to create and read documents in a largely illiterate society. In the High Middle Ages, new sources of education arose, with
The establishment of Christianity brought Latin to Scotland as a scholarly and written language. Monasteries served as repositories of knowledge and education, often running schools and providing a small educated elite, who were essential to create and read documents in a largely illiterate society. In the High Middle Ages, new sources of education arose, with  The humanist concern with widening education was shared by the Protestant reformers, with a desire for a godly people replacing the aim of having educated citizens. In 1560, the '' First Book of Discipline'' set out a plan for a school in every parish, but this proved financially impossible. In the burghs the old schools were maintained, with the song schools and a number of new foundations becoming reformed grammar schools or ordinary parish schools. Schools were supported by a combination of kirk funds, contributions from local heritors or burgh councils and parents that could pay. They were inspected by kirk sessions, who checked for the quality of teaching and doctrinal purity. There were also large number of unregulated "adventure schools", which sometimes fulfilled a local needs and sometimes took pupils away from the official schools. Outside of the established burgh schools, masters often combined their position with other employment, particularly minor posts within the kirk, such as clerk. At their best, the curriculum included catechism,
The humanist concern with widening education was shared by the Protestant reformers, with a desire for a godly people replacing the aim of having educated citizens. In 1560, the '' First Book of Discipline'' set out a plan for a school in every parish, but this proved financially impossible. In the burghs the old schools were maintained, with the song schools and a number of new foundations becoming reformed grammar schools or ordinary parish schools. Schools were supported by a combination of kirk funds, contributions from local heritors or burgh councils and parents that could pay. They were inspected by kirk sessions, who checked for the quality of teaching and doctrinal purity. There were also large number of unregulated "adventure schools", which sometimes fulfilled a local needs and sometimes took pupils away from the official schools. Outside of the established burgh schools, masters often combined their position with other employment, particularly minor posts within the kirk, such as clerk. At their best, the curriculum included catechism,  The widespread belief in the limited intellectual and moral capacity of women, vied with a desire, intensified after the Reformation, for women to take personal moral responsibility, particularly as wives and mothers. In Protestantism this necessitated an ability to learn and understand the catechism and even to be able to independently read the Bible, but most commentators, even those that tended to encourage the education of girls, thought they should not receive the same academic education as boys. In the lower ranks of society, they benefited from the expansion of the parish schools system that took place after the Reformation, but were usually outnumbered by boys, often taught separately, for a shorter time and to a lower level. They were frequently taught reading, sewing and knitting, but not writing. Female illiteracy rates based on signatures among female servants were around 90 percent, from the late 17th to the early 18th centuries and perhaps 85 percent for women of all ranks by 1750, compared with 35 per cent for men. Among the nobility there were many educated and cultured women, of which Mary, Queen of Scots is the most obvious example.
After the Reformation, Scotland's universities underwent a series of reforms associated with Andrew Melville, who returned from
The widespread belief in the limited intellectual and moral capacity of women, vied with a desire, intensified after the Reformation, for women to take personal moral responsibility, particularly as wives and mothers. In Protestantism this necessitated an ability to learn and understand the catechism and even to be able to independently read the Bible, but most commentators, even those that tended to encourage the education of girls, thought they should not receive the same academic education as boys. In the lower ranks of society, they benefited from the expansion of the parish schools system that took place after the Reformation, but were usually outnumbered by boys, often taught separately, for a shorter time and to a lower level. They were frequently taught reading, sewing and knitting, but not writing. Female illiteracy rates based on signatures among female servants were around 90 percent, from the late 17th to the early 18th centuries and perhaps 85 percent for women of all ranks by 1750, compared with 35 per cent for men. Among the nobility there were many educated and cultured women, of which Mary, Queen of Scots is the most obvious example.
After the Reformation, Scotland's universities underwent a series of reforms associated with Andrew Melville, who returned from
 There are mentions in Medieval records of fleets commanded by Scottish kings including William the Lion. and Alexander II. The latter took personal command of a large naval force which sailed from the
There are mentions in Medieval records of fleets commanded by Scottish kings including William the Lion. and Alexander II. The latter took personal command of a large naval force which sailed from the 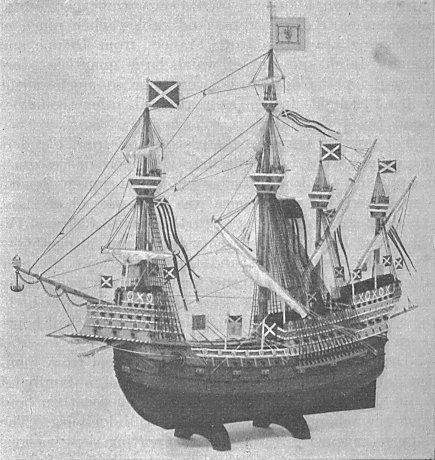 There were various attempts to create royal naval forces in the 15th century. James IV put the enterprise on a new footing, founding a harbour at Newhaven and a dockyard at the Pools of Airth. He acquired a total of 38 ships including the '' Great Michael'',. at that time, the largest ship in Europe.. Scottish ships had some success against privateers, accompanied the king on his expeditions in the islands and intervened in conflicts in Scandinavia and the Baltic, but were sold after the Flodden campaign and after 1516 Scottish naval efforts would rely on privateering captains and hired merchantmen. James V did not share his father's interest in developing a navy and shipbuilding fell behind that of the
There were various attempts to create royal naval forces in the 15th century. James IV put the enterprise on a new footing, founding a harbour at Newhaven and a dockyard at the Pools of Airth. He acquired a total of 38 ships including the '' Great Michael'',. at that time, the largest ship in Europe.. Scottish ships had some success against privateers, accompanied the king on his expeditions in the islands and intervened in conflicts in Scandinavia and the Baltic, but were sold after the Flodden campaign and after 1516 Scottish naval efforts would rely on privateering captains and hired merchantmen. James V did not share his father's interest in developing a navy and shipbuilding fell behind that of the
 Before the
Before the  In the early 17th century, relatively large numbers of Scots took service in foreign armies involved in the Thirty Years War. As armed conflict with Charles I in the Bishop's Wars became likely, hundreds of Scots mercenaries returned home from foreign service, including experienced leaders like Alexander and David Leslie and these veterans played an important role in training recruits.. These systems would form the basis of the Covenanter armies that intervened in the Civil Wars in England and Ireland. Scottish infantry were generally armed, as was almost universal in Western Europe, with a combination of pike and shot. Scottish armies may also have had individuals with a variety of weapons including bows, Lochaber axes, and
In the early 17th century, relatively large numbers of Scots took service in foreign armies involved in the Thirty Years War. As armed conflict with Charles I in the Bishop's Wars became likely, hundreds of Scots mercenaries returned home from foreign service, including experienced leaders like Alexander and David Leslie and these veterans played an important role in training recruits.. These systems would form the basis of the Covenanter armies that intervened in the Civil Wars in England and Ireland. Scottish infantry were generally armed, as was almost universal in Western Europe, with a combination of pike and shot. Scottish armies may also have had individuals with a variety of weapons including bows, Lochaber axes, and
 The earliest recorded use of the
The earliest recorded use of the
sovereign state
A sovereign state or sovereign country, is a political entity represented by one central government that has supreme legitimate authority over territory. International law defines sovereign states as having a permanent population, defined ter ...
in northwest Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
traditionally said to have been founded in 843. Its territories expanded and shrank, but it came to occupy the northern third of the island of Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It ...
, sharing a land border to the south with England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe ...
. It suffered many invasions by the English, but under Robert the Bruce
Robert I (11 July 1274 – 7 June 1329), popularly known as Robert the Bruce (Scottish Gaelic: ''Raibeart an Bruis''), was King of Scots from 1306 to his death in 1329. One of the most renowned warriors of his generation, Robert eventuall ...
it fought a successful War of Independence
This is a list of wars of independence (also called liberation wars). These wars may or may not have been successful in achieving a goal of independence.
List
See also
* Lists of active separatist movements
* List of civil wars
* List of ...
and remained an independent state throughout the late Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
. Following the annexation of the Hebrides
The Hebrides (; gd, Innse Gall, ; non, Suðreyjar, "southern isles") are an archipelago off the west coast of the Scottish mainland. The islands fall into two main groups, based on their proximity to the mainland: the Inner and Outer Hebri ...
and the Northern Isles from Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country in Northern Europe, the mainland territory of which comprises the western and northernmost portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula. The remote Arctic island of ...
in 1266 and 1472 respectively, and the final capture of the Royal Burgh of Berwick by England in 1482, the territory of the Kingdom of Scotland corresponded to that of modern-day Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to ...
, bounded by the North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian ...
to the east, the Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe ...
to the north and west, and the North Channel and Irish Sea
The Irish Sea or , gv, Y Keayn Yernagh, sco, Erse Sie, gd, Muir Èireann , Ulster-Scots: ''Airish Sea'', cy, Môr Iwerddon . is an extensive body of water that separates the islands of Ireland and Great Britain. It is linked to the C ...
to the southwest. In 1603, James VI of Scotland became King of England, joining Scotland with England in a personal union
A personal union is the combination of two or more states that have the same monarch while their boundaries, laws, and interests remain distinct. A real union, by contrast, would involve the constituent states being to some extent interli ...
. In 1707, during the reign of Queen Anne, the two kingdoms were united to form the Kingdom of Great Britain
The Kingdom of Great Britain (officially Great Britain) was a sovereign country in Western Europe from 1 May 1707 to the end of 31 December 1800. The state was created by the 1706 Treaty of Union and ratified by the Acts of Union 1707, wh ...
under the terms of the Acts of Union.
The Crown
The Crown is the state in all its aspects within the jurisprudence of the Commonwealth realms and their subdivisions (such as the Crown Dependencies, overseas territories, provinces, or states). Legally ill-defined, the term has differ ...
was the most important element of government. The Scottish monarchy in the Middle Ages was a largely itinerant institution, before Edinburgh
Edinburgh ( ; gd, Dùn Èideann ) is the capital city of Scotland and one of its 32 Council areas of Scotland, council areas. Historically part of the county of Midlothian (interchangeably Edinburghshire before 1921), it is located in Lothian ...
developed as a capital city
A capital city or capital is the municipality holding primary status in a country, state, province, department, or other subnational entity, usually as its seat of the government. A capital is typically a city that physically encompasses t ...
in the second half of the 15th century. The Crown remained at the centre of political life and in the 16th century emerged as a major centre of display and artistic patronage, until it was effectively dissolved with the 1603 Union of Crowns
The Union of the Crowns ( gd, Aonadh nan Crùintean; sco, Union o the Crouns) was the accession of James VI of Scotland to the throne of the Kingdom of England as James I and the practical unification of some functions (such as overseas dip ...
. The Scottish Crown adopted the conventional offices of western European monarchical states of the time and developed a Privy Council and great offices of state. Parliament also emerged as a major legal institution, gaining an oversight of taxation and policy, but was never as central to the national life. In the early period, the kings of the Scots depended on the great lords—the mormaers and toísechs—but from the reign of David I, sheriffdoms were introduced, which allowed more direct control and gradually limited the power of the major lordships. In the 17th century, the creation of Justices of Peace
A justice of the peace (JP) is a judicial officer of a lower or '' puisne'' court, elected or appointed by means of a commission (letters patent) to keep the peace. In past centuries the term commissioner of the peace was often used with the sam ...
and Commissioners of Supply
Commissioners of Supply were local administrative bodies in Scotland from 1667 to 1930. Originally established in each sheriffdom to collect tax, they later took on much of the responsibility for the local government of the counties of Scotland. ...
helped to increase the effectiveness of local government. The continued existence of courts baron and the introduction of kirk sessions helped consolidate the power of local lairds.
Scots law developed in the Middle Ages and was reformed and codified in the 16th and 17th centuries. Under James IV the legal functions of the council were rationalised, with Court of Session meeting daily in Edinburgh. In 1532, the College of Justice was founded, leading to the training and professionalisation of lawyers. David I is the first Scottish king known to have produced his own coinage. At the 1603 Union the Pound Scots
The pound (Modern and Middle Scots: ''Pund'') was the currency of Scotland prior to the 1707 Treaty of Union between the Kingdom of Scotland and the Kingdom of England, which created the Kingdom of Great Britain. It was introduced by Da ...
was fixed at only one-twelfth the value of the English pound. The Bank of Scotland issued pound notes from 1704. Scottish currency was abolished by the Acts of Union 1707; however to the present day, Scotland retains unique banknotes.
Geographically, Scotland is divided between the Highlands and Islands
The Highlands and Islands is an area of Scotland broadly covering the Scottish Highlands, plus Orkney, Shetland and Outer Hebrides (Western Isles).
The Highlands and Islands are sometimes defined as the area to which the Crofters' Act of 1 ...
and the Lowlands. The Highlands had a relatively short growing season, which was even shorter during the Little Ice Age. Scotland's population at the start of the Black Death was about 1 million; by the end of the plague, it was only half a million. It expanded in the first half of the 16th century, reaching roughly 1.2 million by the 1690s. Significant languages in the medieval kingdom included Gaelic
Gaelic is an adjective that means "pertaining to the Gaels". As a noun it refers to the group of languages spoken by the Gaels, or to any one of the languages individually. Gaelic languages are spoken in Ireland, Scotland, the Isle of Man, an ...
, Old English
Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlers in the mid-5th ...
, Norse and French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
; but by the early modern era Middle Scots had begun to dominate. Christianity was introduced into Scotland from the 6th century. In the Norman period the Scottish church underwent a series of changes that led to new monastic orders and organisation. During the 16th century, Scotland underwent a Protestant Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and i ...
that created a predominately Calvinist
Calvinism (also called the Reformed Tradition, Reformed Protestantism, Reformed Christianity, or simply Reformed) is a major branch of Protestantism that follows the theological tradition and forms of Christian practice set down by John C ...
national kirk. There were a series of religious controversies that resulted in divisions and persecutions. The Scottish Crown developed naval forces at various points in its history, but often relied on privateer
A privateer is a private person or ship that engages in maritime warfare under a commission of war. Since robbery under arms was a common aspect of seaborne trade, until the early 19th century all merchant ships carried arms. A sovereign or deleg ...
s and fought a ''guerre de course
Commerce raiding (french: guerre de course, "war of the chase"; german: Handelskrieg, "trade war") is a form of naval warfare used to destroy or disrupt logistics of the enemy on the open sea by attacking its merchant shipping, rather than enga ...
''. Land forces centred around the large common army, but adopted European innovations from the 16th century; and many Scots took service as mercenaries and as soldiers for the English Crown.
History
Origins: 400–943
From the 5th century on, north Britain was divided into a series of petty kingdoms. Of these, the four most important were those of thePicts
The Picts were a group of peoples who lived in what is now northern and eastern Scotland (north of the Firth of Forth) during Late Antiquity and the Early Middle Ages. Where they lived and what their culture was like can be inferred from ea ...
in the north-east, the Scots of Dál Riata in the west, the Britons of Strathclyde in the south-west and the Anglian kingdom of Bernicia
Bernicia ( ang, Bernice, Bryneich, Beornice; la, Bernicia) was an Anglo-Saxon kingdom established by Anglian settlers of the 6th century in what is now southeastern Scotland and North East England.
The Anglian territory of Bernicia was ap ...
(which united with Deira to form Northumbria
la, Regnum Northanhymbrorum
, conventional_long_name = Kingdom of Northumbria
, common_name = Northumbria
, status = State
, status_text = Unified Anglian kingdom (before 876)North: Anglian kingdom (af ...
in 653) in the south-east, stretching into modern northern England. In 793, ferocious Viking raids began on monasteries such as those at Iona and Lindisfarne, creating fear and confusion across the kingdoms of north Britain. Orkney, Shetland and the Western Isles eventually fell to the Norsemen. These threats may have sped up a long-term process of Gaelicisation of the Pictish kingdoms, which adopted Gaelic
Gaelic is an adjective that means "pertaining to the Gaels". As a noun it refers to the group of languages spoken by the Gaels, or to any one of the languages individually. Gaelic languages are spoken in Ireland, Scotland, the Isle of Man, an ...
language and customs. There was also a merger of the Gaelic and Pictish kingdoms, although historians debate whether it was a Pictish takeover of Dál Riata, or vice-versa. This culminated in the rise of Cínaed mac Ailpín (Kenneth MacAlpin) as "king of the Picts" in the 840s (traditionally dated to 843),. which brought to power the House of Alpin. When he died as king of the combined kingdom in 900, one of his successors, Domnall II (Donald II), was the first man to be called ''rí Alban'' (King of Alba
''Alba'' ( , ) is the Scottish Gaelic name for Scotland. It is also, in English language historiography, used to refer to the polity of Picts and Scots united in the ninth century as the Kingdom of Alba, until it developed into the Kin ...
). The term Scotia would increasingly be used to describe the heartland of these kings, north of the River Forth, and eventually the entire area controlled by its kings would be referred to as Scotland.. The long reign (900–942/3) of Donald's successor Causantín (Constantine II) is often regarded as the key to formation of the Kingdom of Alba/Scotland, and he was later credited with bringing Scottish Christianity into conformity with the Catholic Church.
Expansion: 943–1513
Máel Coluim I (Malcolm I) ( 943–954) is believed to have annexed the Kingdom of Strathclyde, over which the kings of Alba had probably exercised some authority since the later 9th century. His successor, Indulf the Aggressor, was described as the King of Strathclyde before inheriting the throne of Alba; he is credited with later annexing parts of Lothian, including Edinburgh, from the Kingdom of Northumbria. The reign of David I has been characterised as a " Davidian Revolution",. in which he introduced a system of feudal land tenure, established the first royal burghs in Scotland and the first recorded Scottish coinage, and continued a process of religious and legal reforms.. Until the 13th century, the border with England was very fluid, with Northumbria being annexed to Scotland by David I, but lost under his grandson and successor Malcolm IV in 1157. The Treaty of York (1237) fixed the boundaries with England close to the modern border. By the reign of Alexander III, the Scots had annexed the remainder of the, Norwegian held, western seaboard after the stalemate of theBattle of Largs
The Battle of Largs (2 October 1263) was a battle between the kingdoms of Norway and Scotland, on the Firth of Clyde near Largs, Scotland. Through it, Scotland achieved the end of 500 years of Norse Viking depredations and invasions despite bei ...
and the Treaty of Perth in 1266.. The Isle of Man
)
, anthem = " O Land of Our Birth"
, image = Isle of Man by Sentinel-2.jpg
, image_map = Europe-Isle_of_Man.svg
, mapsize =
, map_alt = Location of the Isle of Man in Europe
, map_caption = Location of the Isle of Man (green)
in Europ ...
fell under English control, from Norwegian, in the 14th century, despite several attempts to seize it for Scotland. The English briefly occupied most of Scotland, under Edward I; under Edward III, the English backed Edward Balliol's, son of King John Balliol, attempt to gain his father's throne and restore the lands of the Scottish lords dispossessed by Robert I and his successors in the 14th century in the Wars of Independence (1296–1357). The king of France attempted to thwart the exercise, under the terms of what became known as the Auld Alliance, which provided for mutual aid against the English. In the 15th and early 16th centuries, under the Stewart Dynasty, despite a turbulent political history, the Crown gained greater political control at the expense of independent lords and regained most of its lost territory to around the modern borders of the country.. The dowry of the Orkney and Shetland Islands, by the Norwegian crown, in 1468 was the last great land acquisition for the kingdom. In 1482 the border fortress of Berwick—the largest port in medieval Scotland—fell to the English once again; this was the last time it changed hands. The Auld Alliance with France led to the heavy defeat of a Scottish army at the Battle of Flodden Field in 1513 and the death of the King James IV. A long period of political instability followed.
Consolidation and union: 1513–1707
 In the 16th century, under James V of Scotland and Mary, Queen of Scots, the Crown and court took on many of the attributes of the
In the 16th century, under James V of Scotland and Mary, Queen of Scots, the Crown and court took on many of the attributes of the Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass ide ...
and New Monarchy
The New Monarchs is a concept developed by European historians during the first half of the 20th century to characterize 15th-century European rulers who unified their respective nations, creating stable and centralized governments. This centrali ...
, despite long royal minorities, civil wars and interventions by the English and French. In the mid-16th century, the Scottish Reformation
The Scottish Reformation was the process by which Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland broke with the Pope, Papacy and developed a predominantly Calvinist national Church of Scotland, Kirk (church), which was strongly Presbyterianism, Presbyterian in ...
was strongly influenced by Calvinism
Calvinism (also called the Reformed Tradition, Reformed Protestantism, Reformed Christianity, or simply Reformed) is a major branch of Protestantism that follows the theological tradition and forms of Christian practice set down by John C ...
, leading to widespread iconoclasm
Iconoclasm (from Greek: grc, εἰκών, lit=figure, icon, translit=eikṓn, label=none + grc, κλάω, lit=to break, translit=kláō, label=none)From grc, εἰκών + κλάω, lit=image-breaking. ''Iconoclasm'' may also be consid ...
and the introduction of a Presbyterian
Presbyterianism is a part of the Reformed tradition within Protestantism that broke from the Roman Catholic Church in Scotland by John Knox, who was a priest at St. Giles Cathedral (Church of Scotland). Presbyterian churches derive their n ...
system of organisation and discipline that would have a major impact on Scottish life.
In the late 16th century, James VI emerged as a major intellectual figure with considerable authority over the kingdom. In 1603, he inherited the thrones of England and Ireland, creating a Union of the Crowns that left the three states with their separate identities and institutions. He also moved the centre of royal patronage and power to London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary dow ...
.
When James' son Charles I Charles I may refer to:
Kings and emperors
* Charlemagne (742–814), numbered Charles I in the lists of Holy Roman Emperors and French kings
* Charles I of Anjou (1226–1285), also king of Albania, Jerusalem, Naples and Sicily
* Charles I of ...
attempted to impose elements of the English religious settlement on Scotland, the result was the Bishops' Wars (1637–1640), which ended in defeat for the king and a virtually independent Presbyterian Covenanter state in Scotland.. It also helped precipitate the Wars of the Three Kingdoms
The Wars of the Three Kingdoms were a series of related conflicts fought between 1639 and 1653 in the kingdoms of England, Scotland and Ireland, then separate entities united in a personal union under Charles I. They include the 1639 to 1640 Bi ...
, during which the Scots carried out major military interventions.
After Charles I's defeat, the Scots backed the king in the Second English Civil War
The Second English Civil War took place between February to August 1648 in England and Wales. It forms part of the series of conflicts known collectively as the 1639-1651 Wars of the Three Kingdoms, which include the 1641–1653 Irish Confed ...
; after his execution, they proclaimed his son Charles II of England king, resulting in the Third English Civil War
Third or 3rd may refer to:
Numbers
* 3rd, the ordinal form of the cardinal number 3
* , a fraction of one third
* 1⁄60 of a ''second'', or 1⁄3600 of a ''minute''
Places
* 3rd Street (disambiguation)
* Third Avenue (disambiguation)
* Hi ...
against the emerging republican regime of Parliamentarians in England led by Oliver Cromwell
Oliver Cromwell (25 April 15993 September 1658) was an English politician and military officer who is widely regarded as one of the most important statesmen in English history. He came to prominence during the 1639 to 1651 Wars of the Three ...
. The results were a series of defeats and the short-lived incorporation of Scotland into the Commonwealth of England, Scotland and Ireland (1653–1660).
After the 1660 restoration of the monarchy
Restoration is the act of restoring something to its original state and may refer to:
* Conservation and restoration of cultural heritage
** Audio restoration
** Film restoration
** Image restoration
** Textile restoration
*Restoration ecology
...
, Scotland regained its separate status and institutions, while the centre of political power remained in London.. After the Glorious Revolution of 1688–1689, in which James VII was deposed by his daughter Mary and her husband William of Orange in England, Scotland accepted them under the Claim of Right Act 1689, but the deposed main hereditary line of the Stuarts
The House of Stuart, originally spelt Stewart, was a royal house of Scotland, England, Ireland and later Great Britain. The family name comes from the office of High Steward of Scotland, which had been held by the family progenitor Walter ...
became a focus for political discontent known as Jacobitism, leading to a series of invasions and rebellions mainly focused on the Scottish Highlands.
After severe economic dislocation in the 1690s, there were moves that led to political union with England as the Kingdom of Great Britain
The Kingdom of Great Britain (officially Great Britain) was a sovereign country in Western Europe from 1 May 1707 to the end of 31 December 1800. The state was created by the 1706 Treaty of Union and ratified by the Acts of Union 1707, wh ...
, which came into force on 1 May 1707. The English and Scottish parliaments were replaced by a combined Parliament of Great Britain, but it sat in Westminster
Westminster is an area of Central London, part of the wider City of Westminster.
The area, which extends from the River Thames to Oxford Street, has many visitor attractions and historic landmarks, including the Palace of Westminster, B ...
and largely continued English traditions without interruption. Forty-five Scots were added to the 513 members of the House of Commons and 16 Scots to the 190 members of the House of Lords
The House of Lords, also known as the House of Peers, is the upper house of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Membership is by appointment, heredity or official function. Like the House of Commons, it meets in the Palace of Westminst ...
. It was also a full economic union, replacing the Scottish systems of currency, taxation and laws regulating trade.
Government
Perth
Perth is the capital and largest city of the Australian state of Western Australia. It is the fourth most populous city in Australia and Oceania, with a population of 2.1 million (80% of the state) living in Greater Perth in 2020. Perth is ...
becoming significant in the later Middle Ages before Edinburgh
Edinburgh ( ; gd, Dùn Èideann ) is the capital city of Scotland and one of its 32 Council areas of Scotland, council areas. Historically part of the county of Midlothian (interchangeably Edinburghshire before 1921), it is located in Lothian ...
developed as a capital city in the second half of the 15th century.
The Crown remained the most important element of government, despite the many royal minorities. In the late Middle Ages, it saw much of the aggrandisement associated with the New Monarchs elsewhere in Europe. Theories of constitutional monarchy
A constitutional monarchy, parliamentary monarchy, or democratic monarchy is a form of monarchy in which the monarch exercises their authority in accordance with a constitution and is not alone in decision making. Constitutional monarchies dif ...
and resistance were articulated by Scots, particularly George Buchanan, in the 16th century, but James VI of Scotland advanced the theory of the divine right of kings, and these debates were restated in subsequent reigns and crises. The court remained at the centre of political life, and in the 16th century emerged as a major centre of display and artistic patronage, until it was effectively dissolved with the Union of the Crowns in 1603.
The Scottish Crown adopted the conventional offices of western European courts, including High Steward, Chamberlain, Lord High Constable, Earl Marischal
The title of Earl Marischal was created in the Peerage of Scotland for William Keith, the Great Marischal of Scotland.
History
The office of Marischal of Scotland (or ''Marascallus Scotie'' or ''Marscallus Scotiae'') had been hereditary, held b ...
and Lord Chancellor.. The King's Council emerged as a full-time body in the 15th century, increasingly dominated by laymen and critical to the administration of justice. The Privy Council, which developed in the mid-16th century, and the great offices of state, including the chancellor, secretary and treasurer, remained central to the administration of the government, even after the departure of the Stuart monarchs to rule in England from 1603. However, it was often sidelined and was abolished after the Acts of Union 1707, with rule direct from London.
The Parliament of Scotland
The Parliament of Scotland ( sco, Pairlament o Scotland; gd, Pàrlamaid na h-Alba) was the legislature of the Kingdom of Scotland from the 13th century until 1707. The parliament evolved during the early 13th century from the king's council o ...
also emerged as a major legal institution, gaining an oversight of taxation and policy. By the end of the Middle Ages it was sitting almost every year, partly because of the frequent royal minorities and regencies of the period, which may have prevented it from being sidelined by the monarchy. In the early modern era, Parliament was also vital to the running of the country, providing laws and taxation, but it had fluctuating fortunes and was never as central to the national life as its counterpart in England.
In the early period, the kings of the Scots depended on the great lords of the mormaers (later earl
Earl () is a rank of the nobility in the United Kingdom. The title originates in the Old English word ''eorl'', meaning "a man of noble birth or rank". The word is cognate with the Scandinavian form ''jarl'', and meant " chieftain", particu ...
s) and toísechs (later thanes), but from the reign of David I, sheriffdoms were introduced, which allowed more direct control and gradually limited the power of the major lordships.. In the 17th century, the creation of justices of the peace
A justice of the peace (JP) is a judicial officer of a lower or '' puisne'' court, elected or appointed by means of a commission (letters patent) to keep the peace. In past centuries the term commissioner of the peace was often used with the sam ...
and the Commissioner of Supply helped to increase the effectiveness of local government. The continued existence of courts baron and introduction of kirk sessions helped consolidate the power of local lairds.
Law
 Scots law developed into a distinctive system in the Middle Ages and was reformed and codified in the 16th and 17th centuries. Knowledge of the nature of Scots law before the 11th century is largely speculative,. but it was probably a mixture of legal traditions representing the different cultures inhabiting the land at the time, including
Scots law developed into a distinctive system in the Middle Ages and was reformed and codified in the 16th and 17th centuries. Knowledge of the nature of Scots law before the 11th century is largely speculative,. but it was probably a mixture of legal traditions representing the different cultures inhabiting the land at the time, including Celtic
Celtic, Celtics or Keltic may refer to:
Language and ethnicity
*pertaining to Celts, a collection of Indo-European peoples in Europe and Anatolia
**Celts (modern)
*Celtic languages
**Proto-Celtic language
*Celtic music
*Celtic nations
Sports Foo ...
, Britonnic, Irish and Anglo-Saxon customs. The legal tract, the '' Leges inter Brettos et Scottos'', set out a system of compensation for injury and death based on ranks and the solidarity of kin groups. in . There were popular courts or ''comhdhail
A comhdhail or couthal was a popular court in medieval Scotland. The word derives from Old Gaelic ''comdal'', "tryst" or "assembly".McNeill and MacQueen, ''Atlas of Scottish History'', p. 191 Distinct from courts of the king, mormaers and senior ...
s'', indicated by dozens of place names in eastern Scotland. In Scandinavian-held areas, Udal law formed the basis of the legal system and it is known that the Hebrides were taxed using the Ounceland measure. Althings were open-air governmental assemblies that met in the presence of the ''Jarl
Jarl is a rank of the nobility in Scandinavia. In Old Norse, it meant "chieftain", particularly a chieftain set to rule a territory in a king's stead. ''Jarl'' could also mean a sovereign prince. For example, the rulers of several of the pet ...
'' and the meetings were open to virtually all "free men". At these sessions decisions were made, laws passed and complaints adjudicated.
The introduction of feudalism in the reign of David I of Scotland
David I or Dauíd mac Maíl Choluim (Modern: ''Daibhidh I mac haoilChaluim''; – 24 May 1153) was a 12th-century ruler who was Prince of the Cumbrians from 1113 to 1124 and later King of Scotland from 1124 to 1153. The youngest son of Malco ...
would have a profound impact on the development of Scottish law, establishing feudal land tenure over many parts of the south and east that eventually spread northward. Sheriffs, originally appointed by the King as royal administrators and tax collectors, developed legal functions. Feudal lords also held courts to adjudicate disputes between their tenants.
By the 14th century, some of these feudal courts had developed into "petty kingdoms" where the King's courts did not have authority except for cases of treason. Burghs also had their local laws dealing mostly with commercial and trade matters and may have become similar in function to sheriff's courts. Ecclesiastical courts had exclusive jurisdiction over matters such as marriage, contracts made on oath, inheritance and legitimacy. ''Judices'' were often royal officials who supervised baronial, abbatial and other lower-ranking "courts".. However, the main official of law in the post-Davidian Kingdom of the Scots was the Justiciar who held courts and reported to the king personally. Normally, there were two Justiciarships, organised by linguistic boundaries: the Justiciar of Scotia and the Justiciar of Lothian
The Justiciar of Lothian (in Norman-Latin, ''Justiciarus Laudonie'') was an important legal office in the High Medieval Kingdom of Scotland.
The Justiciars of Lothian were responsible for the administration of royal justice in the province of ...
, but sometimes Galloway
Galloway ( ; sco, Gallowa; la, Gallovidia) is a region in southwestern Scotland comprising the historic counties of Wigtownshire and Kirkcudbrightshire. It is administered as part of the council area of Dumfries and Galloway.
A native or ...
also had its own Justiciar. Scottish common law
In law, common law (also known as judicial precedent, judge-made law, or case law) is the body of law created by judges and similar quasi-judicial tribunals by virtue of being stated in written opinions."The common law is not a brooding omniprese ...
, the '' jus commune'', began to take shape at the end of the period, assimilating Gaelic and Britonnic law with practices from Anglo-Norman England and the Continent.
 During the period of English control over Scotland there is some evidence that
During the period of English control over Scotland there is some evidence that King Edward I of England
Edward I (17/18 June 1239 – 7 July 1307), also known as Edward Longshanks and the Hammer of the Scots, was King of England and Lord of Ireland from 1272 to 1307. Concurrently, he ruled the duchies of Aquitaine and Gascony as a vass ...
, called "Hammer of the Scots", attempted to abolish Scottish laws contrary to English law as he had done in Wales.
Under Robert I in 1318, a parliament at Scone enacted a code of law that drew upon older practices. It codified procedures for criminal trials and protections for vassal
A vassal or liege subject is a person regarded as having a mutual obligation to a lord or monarch, in the context of the feudal system in medieval Europe. While the subordinate party is called a vassal, the dominant party is called a suzerai ...
s from ejection from the land. From the 14th century, there are surviving examples of early Scottish legal literature, such as the '' Regiam Majestatem'' (on procedure at the royal courts) and the ''Quoniam Attachiamenta'' (on procedure at the barons court), which drew on both common and Roman law
Roman law is the legal system of ancient Rome, including the legal developments spanning over a thousand years of jurisprudence, from the Twelve Tables (c. 449 BC), to the '' Corpus Juris Civilis'' (AD 529) ordered by Eastern Roman emperor J ...
.
Customary laws, such as the Law of Clan MacDuff, came under attack from the Stewart Dynasty which consequently extended the reach of Scots common law. From the reign of King James I James I may refer to:
People
*James I of Aragon (1208–1276)
*James I of Sicily or James II of Aragon (1267–1327)
*James I, Count of La Marche (1319–1362), Count of Ponthieu
*James I, Count of Urgell (1321–1347)
*James I of Cyprus (1334–13 ...
a legal profession began to develop and the administration of criminal and civil justice was centralised. The growing activity of the parliament and the centralisation of administration in Scotland called for the better dissemination of Acts of the parliament to the courts and other enforcers of the law. In the late 15th century, unsuccessful attempts were made to form commissions of experts to codify, update or define Scots law. The general practice during this period, as evidenced from records of cases, seems to have been to defer to specific Scottish laws on a matter when available and to fill in any gaps with provisions from the common law embodied in Civil and Canon law
Canon law (from grc, κανών, , a 'straight measuring rod, ruler') is a set of ordinances and regulations made by ecclesiastical authority (church leadership) for the government of a Christian organization or church and its members. It is t ...
, which had the advantage of being written.
Under James IV the legal functions of the council were rationalised, with a royal Court of Session meeting daily in Edinburgh to deal with civil cases. In 1514, the office of justice-general was created for the Earl of Argyll
Earl () is a rank of the nobility in the United Kingdom. The title originates in the Old English word ''eorl'', meaning "a man of noble birth or rank". The word is cognate with the Old Norse, Scandinavian form ''jarl'', and meant "Germanic ch ...
(and held by his family until 1628). In 1532, the Royal College of Justice was founded, leading to the training and professionalisation of an emerging group of career lawyers. The Court of Session placed increasing emphasis on its independence from influence, including from the king, and superior jurisdiction over local justice. Its judges were increasingly able to control entry to their own ranks. In 1672, the High Court of Justiciary was founded from the College of Justice as a supreme court of appeal.
Coinage
 David I is the first Scottish king known to have produced his own coinage. There were soon mints at Edinburgh, Berwick and Roxburgh. Early Scottish coins were similar to English ones, but with the king's head in profile instead of full face. The number of coins struck was small and English coins probably remained more significant in this period.. The first gold coin was a noble (6s. 8d.) of David II. Under James I pennies and halfpennies of billon (an alloy of silver with a base metal) were introduced, and copper farthings appeared under James III.. In James V's reign the bawbee ( d) and half-bawbee were issued, and in Mary, Queen of Scot's reign a twopence piece, the hardhead, was issued to help "the common people buy bread, drink, flesh, and fish". The billon coinage was discontinued after 1603, but twopence pieces in copper continued to be issued until the Act of Union in 1707.
David I is the first Scottish king known to have produced his own coinage. There were soon mints at Edinburgh, Berwick and Roxburgh. Early Scottish coins were similar to English ones, but with the king's head in profile instead of full face. The number of coins struck was small and English coins probably remained more significant in this period.. The first gold coin was a noble (6s. 8d.) of David II. Under James I pennies and halfpennies of billon (an alloy of silver with a base metal) were introduced, and copper farthings appeared under James III.. In James V's reign the bawbee ( d) and half-bawbee were issued, and in Mary, Queen of Scot's reign a twopence piece, the hardhead, was issued to help "the common people buy bread, drink, flesh, and fish". The billon coinage was discontinued after 1603, but twopence pieces in copper continued to be issued until the Act of Union in 1707.
 Early Scottish coins were virtually identical in silver content to English ones, but from about 1300 the silver content began to depreciate more rapidly than English. Between then and 1605 they lost value at an average of 12 per cent every ten years, three times the then English rate. The Scottish penny became a base metal coin in about 1484 and virtual disappeared as a separate coin from about 1513.. In 1423, the English government banned the circulation of Scottish coins. At the union of the crowns in 1603, the Scottish pound was fixed at only one-twelfth that of the English pound. The Parliament of Scotland of 1695 enacted proposals to set up the Bank of Scotland. The bank issued pound notes from 1704, which had the face value of £12 Scots. Scottish currency was abolished at the Act of Union, the Scottish coin in circulation was drawn in to be re-minted according to the English standard.
Early Scottish coins were virtually identical in silver content to English ones, but from about 1300 the silver content began to depreciate more rapidly than English. Between then and 1605 they lost value at an average of 12 per cent every ten years, three times the then English rate. The Scottish penny became a base metal coin in about 1484 and virtual disappeared as a separate coin from about 1513.. In 1423, the English government banned the circulation of Scottish coins. At the union of the crowns in 1603, the Scottish pound was fixed at only one-twelfth that of the English pound. The Parliament of Scotland of 1695 enacted proposals to set up the Bank of Scotland. The bank issued pound notes from 1704, which had the face value of £12 Scots. Scottish currency was abolished at the Act of Union, the Scottish coin in circulation was drawn in to be re-minted according to the English standard.
Geography
 At its borders in 1707, the Kingdom of Scotland was half the size of England and Wales in area, but with its many inlets, islands and inland lochs, it had roughly the same amount of coastline at . Scotland has over 790 offshore islands, most of which are to be found in four main groups: Shetland, Orkney, and the
At its borders in 1707, the Kingdom of Scotland was half the size of England and Wales in area, but with its many inlets, islands and inland lochs, it had roughly the same amount of coastline at . Scotland has over 790 offshore islands, most of which are to be found in four main groups: Shetland, Orkney, and the Hebrides
The Hebrides (; gd, Innse Gall, ; non, Suðreyjar, "southern isles") are an archipelago off the west coast of the Scottish mainland. The islands fall into two main groups, based on their proximity to the mainland: the Inner and Outer Hebri ...
, subdivided into the Inner Hebrides and Outer Hebrides. Only a fifth of Scotland is less than 60 metres above sea level. The defining factor in the geography of Scotland is the distinction between the Highlands and Islands in the north and west and the Lowlands in the south and east. The highlands are further divided into the Northwest Highlands and the Grampian Mountains by the fault line of the Great Glen. The Lowlands are divided into the fertile belt of the Central Lowlands and the higher terrain of the Southern Uplands, which included the Cheviot Hills, over which the border with England ran. The Central Lowland belt averages about in width and, because it contains most of the good quality agricultural land and has easier communications, could support most of the urbanisation and elements of conventional government. However, the Southern Uplands, and particularly the Highlands were economically less productive and much more difficult to govern.
Its east Atlantic position means that Scotland has very heavy rainfall: today about 700 mm per year in the east and over 1000 mm in the west. This encouraged the spread of blanket bog
A bog or bogland is a wetland that accumulates peat as a deposit of dead plant materials often mosses, typically sphagnum moss. It is one of the four main types of wetlands. Other names for bogs include mire, mosses, quagmire, and muskeg; a ...
s, the acidity of which, combined with high level of wind and salt spray, made most of the islands treeless. The existence of hills, mountains, quicksands and marshes made internal communication and conquest extremely difficult and may have contributed to the fragmented nature of political power. The Uplands and Highlands had a relatively short growing season, in the extreme case of the upper Grampians an ice free season of four months or less and for much of the Highlands and Uplands of seven months or less. The early modern era also saw the impact of the Little Ice Age, with 1564 seeing thirty-three days of continual frost, where rivers and lochs froze, leading to a series of subsistence crises until the 1690s.
Demography
 From the formation of the Kingdom of Alba in the 10th century until before the Black Death arrived in 1349, estimates based on the amount of farmable land suggest that population may have grown from half a million to a million. Although there is no reliable documentation on the impact of the plague, there are many anecdotal references to abandoned land in the following decades. If the pattern followed that in England, then the population may have fallen to as low as half a million by the end of the 15th century.
Compared with the situation after the redistribution of population in the later Highland Clearances and the
From the formation of the Kingdom of Alba in the 10th century until before the Black Death arrived in 1349, estimates based on the amount of farmable land suggest that population may have grown from half a million to a million. Although there is no reliable documentation on the impact of the plague, there are many anecdotal references to abandoned land in the following decades. If the pattern followed that in England, then the population may have fallen to as low as half a million by the end of the 15th century.
Compared with the situation after the redistribution of population in the later Highland Clearances and the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going f ...
, these numbers would have been relatively evenly spread over the kingdom, with roughly half living north of the River Tay. Perhaps ten per cent of the population lived in one of many burghs that grew up in the later medieval period, mainly in the east and south. They would have had a mean population of about 2000, but many would have been much smaller than 1000 and the largest, Edinburgh, probably had a population of over 10,000 by the end of the Medieval era.
Price inflation, which generally reflects growing demand for food, suggests that the population probably expanded in the first half of the 16th century, levelling off after the famine of 1595, as prices were relatively stable in the early 17th century. Calculations based on hearth tax
A hearth tax was a property tax in certain countries during the medieval and early modern period, levied on each hearth, thus by proxy on wealth. It was calculated based on the number of hearths, or fireplaces, within a municipal area and is c ...
returns for 1691 indicate a population of 1,234,575, but this figure may have been seriously effected by the subsequent famines of the late 1690s. By 1750, with its suburbs, Edinburgh reached 57,000. The only other towns above 10,000 by the same time were Glasgow
Glasgow ( ; sco, Glesca or ; gd, Glaschu ) is the most populous city in Scotland and the fourth-most populous city in the United Kingdom, as well as being the 27th largest city by population in Europe. In 2020, it had an estimated popu ...
with 32,000, Aberdeen
Aberdeen (; sco, Aiberdeen ; gd, Obar Dheathain ; la, Aberdonia) is a city in North East Scotland, and is the third most populous city in the country. Aberdeen is one of Scotland's 32 local government council areas (as Aberdeen City), a ...
with around 16,000 and Dundee with 12,000.
Language
Pictish language
Pictish is the extinct Brittonic language spoken by the Picts, the people of eastern and northern Scotland from Late Antiquity to the Early Middle Ages. Virtually no direct attestations of Pictish remain, short of a limited number of geograp ...
in the north and Cumbric languages in the south were overlaid and replaced by Gaelic
Gaelic is an adjective that means "pertaining to the Gaels". As a noun it refers to the group of languages spoken by the Gaels, or to any one of the languages individually. Gaelic languages are spoken in Ireland, Scotland, the Isle of Man, an ...
, Old English
Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlers in the mid-5th ...
and later Norse in the Early Middle Ages
The Early Middle Ages (or early medieval period), sometimes controversially referred to as the Dark Ages, is typically regarded by historians as lasting from the late 5th or early 6th century to the 10th century. They marked the start of the Mi ...
. By the High Middle Ages
The High Middle Ages, or High Medieval Period, was the periodization, period of European history that lasted from AD 1000 to 1300. The High Middle Ages were preceded by the Early Middle Ages and were followed by the Late Middle Ages, which ended ...
, the majority of people within Scotland spoke the Gaelic language, then simply called ''Scottish'', or in Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through ...
, ''lingua Scotica''. In the Northern Isles the Norse language brought by Scandinavian occupiers and settlers evolved into the local Norn, which lingered until the end of the 18th century, and Norse may also have survived as a spoken language until the 16th century in the Outer Hebrides. French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
, Flemish
Flemish (''Vlaams'') is a Low Franconian dialect cluster of the Dutch language. It is sometimes referred to as Flemish Dutch (), Belgian Dutch ( ), or Southern Dutch (). Flemish is native to Flanders, a historical region in northern Belgium; ...
and particularly English became the main languages of Scottish burghs, most of which were located in the south and east, an area to which Anglian settlers had already brought a form of Old English. In the later part of the 12th century, the writer Adam of Dryburgh
Adam of Dryburgh ( 1140 – 1212), in later times also known as Adam the Carthusian, Adam Anglicus and Adam Scotus, was an Anglo-Scottish theologian, writer and Premonstratensian and Carthusian monk.
Life
He was born around 1140 in the Anglo ...
described lowland Lothian as "the Land of the English in the Kingdom of the Scots". At least from the accession of David I, Gaelic ceased to be the main language of the royal court and was probably replaced by French, as evidenced by reports from contemporary chronicles, literature and translations of administrative documents into the French language.
In the Late Middle Ages
The Late Middle Ages or Late Medieval Period was the period of European history lasting from AD 1300 to 1500. The Late Middle Ages followed the High Middle Ages and preceded the onset of the early modern period (and in much of Europe, the Ren ...
, Early Scots, then called English, became the dominant spoken language of the kingdom, aside from in the Highlands and Islands
The Highlands and Islands is an area of Scotland broadly covering the Scottish Highlands, plus Orkney, Shetland and Outer Hebrides (Western Isles).
The Highlands and Islands are sometimes defined as the area to which the Crofters' Act of 1 ...
and Galloway
Galloway ( ; sco, Gallowa; la, Gallovidia) is a region in southwestern Scotland comprising the historic counties of Wigtownshire and Kirkcudbrightshire. It is administered as part of the council area of Dumfries and Galloway.
A native or ...
. It was derived largely from Old English, with the addition of elements from Gaelic and French. Although resembling the language spoken in northern England, it became a distinct dialect from the late 14th century onwards.. It began to be adopted by the ruling elite as they gradually abandoned French. By the 15th century, it was the language of government, with acts of parliament, council records and treasurer's accounts almost all using it from the reign of James I onwards. As a result, Gaelic, once dominant north of the Tay, began a steady decline. Lowland writers began to treat Gaelic as a second-class, rustic and even amusing language, helping to frame attitudes towards the Highlands and to create a cultural gulf with the Lowlands.
From the mid-16th century, written Scots was increasingly influenced by the developing Standard English of Southern England due to developments in royal and political interactions with England. With the increasing influence and availability of books printed in England, most writing in Scotland came to be done in the English fashion. Unlike many of his predecessors, James VI generally despised Gaelic culture. Having extolled the virtues of Scots "poesie", after his accession to the English throne, he increasingly favoured the language of southern England. In 1611, the Kirk adopted the 1611 Authorized King James Version of the Bible. In 1617, interpreters were declared no longer necessary in the port of London because as Scots and Englishmen were now "not so far different bot ane understandeth ane uther". Jenny Wormald
Jennifer "Jenny" Wormald HonFSA Scot (18 January 1942 – 9 December 2015) was a Scottish historian who studied late medieval and early modern Scotland.
Life
Jennifer (Jenny) was born in Glasgow on 18 January 1942, and was adopted by Margaret ...
describes James as creating a "three-tier system, with Gaelic at the bottom and English at the top".
Religion
 The Pictish and Scottish kingdoms that would form the basis of the Kingdom of Alba were largely converted by Irish-Scots missions associated with figures such as St Columba, from the 5th to the 7th centuries. These missions tended to found monastic institutions and collegiate churches that served large areas. Partly as a result of these factors, some scholars have identified a distinctive form of Celtic Christianity, in which
The Pictish and Scottish kingdoms that would form the basis of the Kingdom of Alba were largely converted by Irish-Scots missions associated with figures such as St Columba, from the 5th to the 7th centuries. These missions tended to found monastic institutions and collegiate churches that served large areas. Partly as a result of these factors, some scholars have identified a distinctive form of Celtic Christianity, in which abbot
Abbot is an ecclesiastical title given to the male head of a monastery in various Western religious traditions, including Christianity. The office may also be given as an honorary title to a clergyman who is not the head of a monastery. Th ...
s were more significant than bishop
A bishop is an ordained clergy member who is entrusted with a position of authority and oversight in a religious institution.
In Christianity, bishops are normally responsible for the governance of dioceses. The role or office of bishop is ...
s, attitudes to clerical celibacy were more relaxed and there were some significant differences in practice with Roman Christianity, particularly the form of tonsure and the method of calculating Easter. Most of these issues had been resolved by the mid-7th century. After the reconversion of Scandinavian Scotland from the 10th century, Christianity under papal authority was the dominant religion of the kingdom.
In the Norman period, the Scottish church underwent a series of reforms and transformations. With royal and lay patronage, a clearer parochial structure based around local churches was developed. Large numbers of new foundations, which followed continental forms of reformed monasticism, began to predominate and the Scottish church established its independence from England, developed a clearer diocesan structure, becoming a "special daughter of the see of Rome", but lacking leadership in the form of Archbishops. In the late Middle Ages, the problems of schism in the Catholic Church allowed the Scottish Crown to gain greater influence over senior appointments and two archbishoprics had been established by the end of the 15th century.. While some historians have discerned a decline of monasticism in the late Middle Ages, the mendicant orders of friar
A friar is a member of one of the mendicant orders founded in the twelfth or thirteenth century; the term distinguishes the mendicants' itinerant apostolic character, exercised broadly under the jurisdiction of a superior general, from the ...
s grew, particularly in the expanding burghs, to meet the spiritual needs of the population. New saints and cults of devotion also proliferated. Despite problems over the number and quality of clergy after the Black Death in the 14th century, and some evidence of heresy in this period, the Church in Scotland remained relatively stable before the 16th century.
 During the 16th century, Scotland underwent a
During the 16th century, Scotland underwent a Protestant Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and i ...
that created a predominately Calvinist national kirk, which was strongly Presbyterian in outlook, severely reducing the powers of bishops, although not abolishing them. The teachings of first Martin Luther and then John Calvin began to influence Scotland, particularly through Scottish scholars who had visited continental and English universities. Particularly important was the work of the Lutheran Scot Patrick Hamilton. His execution with other Protestant preachers in 1528, and of the Zwingli-influenced George Wishart in 1546, who was burnt at the stake in St Andrews, did nothing to stem the growth of these ideas. Wishart's supporters seized St Andrews Castle, which they held for a year before they were defeated with the help of French forces. The survivors, including chaplain John Knox, were condemned to be galley slaves, helping to create resentment of the French and martyrs for the Protestant cause. Limited toleration and the influence of exiled Scots and Protestants in other countries, led to the expansion of Protestantism, with a group of lairds declaring themselves Lords of the Congregation
The Lords of the Congregation (), originally styling themselves "the Faithful", were a group of Protestant Scottish nobles who in the mid-16th century favoured a reformation of the Catholic church according to Protestant principles and a Scot ...
in 1557. By 1560, a relatively small group of Protestants were in a position to impose reform on the Scottish church. A confession of faith, rejecting papal jurisdiction and the mass, was adopted by Parliament in 1560. The Calvinism of the reformers led by Knox resulted in a settlement that adopted a Presbyterian
Presbyterianism is a part of the Reformed tradition within Protestantism that broke from the Roman Catholic Church in Scotland by John Knox, who was a priest at St. Giles Cathedral (Church of Scotland). Presbyterian churches derive their n ...
system and rejected most of the elaborate trappings of the Medieval church. This gave considerable power within the new Kirk to local lairds, who often had control over the appointment of the clergy, and resulting in widespread, but generally orderly, iconoclasm
Iconoclasm (from Greek: grc, εἰκών, lit=figure, icon, translit=eikṓn, label=none + grc, κλάω, lit=to break, translit=kláō, label=none)From grc, εἰκών + κλάω, lit=image-breaking. ''Iconoclasm'' may also be consid ...
. At this point the majority of the population was probably still Catholic in persuasion and the Kirk would find it difficult to penetrate the Highlands and Islands, but began a gradual process of conversion and consolidation that, compared with reformations elsewhere, was conducted with relatively little persecution.
 In 1635, Charles I authorised a book of canons that made him head of the Church, ordained an unpopular ritual and enforced the use of a new liturgy. When the liturgy emerged in 1637 it was seen as an English-style Prayer Book, resulting in anger and widespread rioting.. Representatives of various sections of Scottish society drew up the National Covenant on 28 February 1638, objecting to the King's liturgical innovations.. The king's supporters were unable to suppress the rebellion and the king refused to compromise. In December of the same year, matters were taken even further, when at a meeting of the General Assembly in Glasgow the Scottish bishops were formally expelled from the Church, which was then established on a full Presbyterian basis. Victory in the resulting Bishops' Wars secured the Presbyterian Kirk and precipitated the outbreak of the civil wars of the 1640s.. Disagreements over collaboration with Royalism created a major conflict between
In 1635, Charles I authorised a book of canons that made him head of the Church, ordained an unpopular ritual and enforced the use of a new liturgy. When the liturgy emerged in 1637 it was seen as an English-style Prayer Book, resulting in anger and widespread rioting.. Representatives of various sections of Scottish society drew up the National Covenant on 28 February 1638, objecting to the King's liturgical innovations.. The king's supporters were unable to suppress the rebellion and the king refused to compromise. In December of the same year, matters were taken even further, when at a meeting of the General Assembly in Glasgow the Scottish bishops were formally expelled from the Church, which was then established on a full Presbyterian basis. Victory in the resulting Bishops' Wars secured the Presbyterian Kirk and precipitated the outbreak of the civil wars of the 1640s.. Disagreements over collaboration with Royalism created a major conflict between Protesters
A protest (also called a demonstration, remonstration or remonstrance) is a public expression of objection, disapproval or dissent towards an idea or action, typically a political one.
Protests can be thought of as acts of coopera ...
and Resolutioners
The Act of Classes was passed by the Parliament of Scotland on 23 January 1649. It was probably drafted by Lord Warriston, a leading member of the Kirk Party, who along with the Marquess of Argyll were leading proponents of its clauses. It bann ...
, which became a long term divide in the Kirk.
At the Restoration of the monarchy in 1660, legislation was revoked back to 1633, removing the Covenanter gains of the Bishops' Wars, but the discipline of kirk sessions, presbyteries and synods were renewed.. The reintroduction of episcopacy was a source of particular trouble in the south-west of the country, an area with strong Presbyterian sympathies. Abandoning the official church, many of the people here began to attend illegal field assemblies led by excluded ministers, known as conventicles. In the early 1680s, a more intense phase of persecution began, in what was later to be known in Protestant historiography as " the Killing Time".. After the Glorious Revolution, Presbyterianism was restored and the bishops, who had generally supported James VII, abolished. However, William, who was more tolerant than the kirk tended to be, passed acts restoring the Episcopalian clergy excluded after the Revolution. The result was a Kirk divided between factions, with significant minorities, particularly in the west and north, of Episcopalians and Catholics.
Education
 The establishment of Christianity brought Latin to Scotland as a scholarly and written language. Monasteries served as repositories of knowledge and education, often running schools and providing a small educated elite, who were essential to create and read documents in a largely illiterate society. In the High Middle Ages, new sources of education arose, with
The establishment of Christianity brought Latin to Scotland as a scholarly and written language. Monasteries served as repositories of knowledge and education, often running schools and providing a small educated elite, who were essential to create and read documents in a largely illiterate society. In the High Middle Ages, new sources of education arose, with song
A song is a musical composition intended to be performed by the human voice. This is often done at distinct and fixed pitches (melodies) using patterns of sound and silence. Songs contain various forms, such as those including the repetiti ...
and grammar school
A grammar school is one of several different types of school in the history of education in the United Kingdom and other English-speaking countries, originally a school teaching Latin, but more recently an academically oriented secondary school ...
s. These were usually attached to cathedrals or a collegiate church and were most common in the developing burghs. By the end of the Middle Ages grammar schools could be found in all the main burghs and some small towns. There were also petty schools, more common in rural areas and providing an elementary education.. Some monasteries, like the Cistercian abbey at Kinloss, opened their doors to a wider range of students. The number and size of these schools seems to have expanded rapidly from the 1380s. They were almost exclusively aimed at boys, but by the end of the 15th century, Edinburgh also had schools for girls, sometimes described as "sewing schools", and probably taught by lay women or nuns. There was also the development of private tuition in the families of lords and wealthy burghers. The growing emphasis on education cumulated with the passing of the Education Act 1496
The Education Act 1496 was an act of the Parliament of Scotland (1496 c. 87) that required landowners to send their eldest sons to school to study Latin, arts and law. This made schooling compulsory for the first time in the world.
The humanis ...
, which decreed that all sons of barons and freeholders of substance should attend grammar schools to learn "perfyct Latyne". All this resulted in an increase in literacy, but which was largely concentrated among a male and wealthy elite,. with perhaps 60 per cent of the nobility being literate by the end of the period..
Until the 15th century, those who wished to attend university had to travel to England or the continent, and just over a 1,000 have been identified as doing so between the 12th century and 1410. Among these the most important intellectual figure was John Duns Scotus, who studied at Oxford
Oxford () is a city in England. It is the county town and only city of Oxfordshire. In 2020, its population was estimated at 151,584. It is north-west of London, south-east of Birmingham and north-east of Bristol. The city is home to the ...
, Cambridge
Cambridge ( ) is a university city and the county town in Cambridgeshire, England. It is located on the River Cam approximately north of London. As of the 2021 United Kingdom census, the population of Cambridge was 145,700. Cambridge bec ...
and Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. Si ...
and probably died at Cologne in 1308, becoming a major influence on late medieval religious thought.. The Wars of Independence largely closed English universities to Scots, and consequently continental universities became more significant.. This situation was transformed by the founding of the University of St Andrews in 1413, the University of Glasgow
, image = UofG Coat of Arms.png
, image_size = 150px
, caption = Coat of arms
Flag
, latin_name = Universitas Glasguensis
, motto = la, Via, Veritas, Vita
, ...
in 1451 and the University of Aberdeen in 1495. Initially these institutions were designed for the training of clerics, but they were increasingly used by laymen who would begin to challenge the clerical monopoly of administrative posts in the government and law. Those wanting to study for second degrees still needed to go abroad. The continued movement to other universities produced a school of Scottish nominalists at Paris in the early 16th century, of which John Mair was probably the most important figure. By 1497, the humanist and historian Hector Boece, born in Dundee, returned from Paris to become the first principal at the new university of Aberdeen. These international contacts helped integrate Scotland into a wider European scholarly world and would be one of the most important ways in which the new ideas of humanism
Humanism is a philosophical stance that emphasizes the individual and social potential and agency of human beings. It considers human beings the starting point for serious moral and philosophical inquiry.
The meaning of the term "human ...
were brought into Scottish intellectual life.
 The humanist concern with widening education was shared by the Protestant reformers, with a desire for a godly people replacing the aim of having educated citizens. In 1560, the '' First Book of Discipline'' set out a plan for a school in every parish, but this proved financially impossible. In the burghs the old schools were maintained, with the song schools and a number of new foundations becoming reformed grammar schools or ordinary parish schools. Schools were supported by a combination of kirk funds, contributions from local heritors or burgh councils and parents that could pay. They were inspected by kirk sessions, who checked for the quality of teaching and doctrinal purity. There were also large number of unregulated "adventure schools", which sometimes fulfilled a local needs and sometimes took pupils away from the official schools. Outside of the established burgh schools, masters often combined their position with other employment, particularly minor posts within the kirk, such as clerk. At their best, the curriculum included catechism,
The humanist concern with widening education was shared by the Protestant reformers, with a desire for a godly people replacing the aim of having educated citizens. In 1560, the '' First Book of Discipline'' set out a plan for a school in every parish, but this proved financially impossible. In the burghs the old schools were maintained, with the song schools and a number of new foundations becoming reformed grammar schools or ordinary parish schools. Schools were supported by a combination of kirk funds, contributions from local heritors or burgh councils and parents that could pay. They were inspected by kirk sessions, who checked for the quality of teaching and doctrinal purity. There were also large number of unregulated "adventure schools", which sometimes fulfilled a local needs and sometimes took pupils away from the official schools. Outside of the established burgh schools, masters often combined their position with other employment, particularly minor posts within the kirk, such as clerk. At their best, the curriculum included catechism, Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through ...
, French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
, Classical literature and sports.
In 1616, an act in Privy council commanded every parish to establish a school "where convenient means may be had", and when the Parliament of Scotland
The Parliament of Scotland ( sco, Pairlament o Scotland; gd, Pàrlamaid na h-Alba) was the legislature of the Kingdom of Scotland from the 13th century until 1707. The parliament evolved during the early 13th century from the king's council o ...
ratified this with the Education Act of 1633, a tax on local landowners was introduced to provide the necessary endowment. A loophole which allowed evasion of this tax was closed in the Education Act of 1646, which established a solid institutional foundation for schools on Covenanter principles. Although the Restoration brought a reversion to the 1633 position, in 1696 new legislation restored the provisions of 1646. An act of the Scottish parliament in 1696 underlined the aim of having a school in every parish. In rural communities these obliged local landowners (heritors) to provide a schoolhouse and pay a schoolmaster, while ministers and local presbyteries oversaw the quality of the education. In many Scottish towns, burgh schools were operated by local councils. By the late 17th century, there was a largely complete network of parish schools in the Lowlands, but in the Highlands basic education was still lacking in many areas..
 The widespread belief in the limited intellectual and moral capacity of women, vied with a desire, intensified after the Reformation, for women to take personal moral responsibility, particularly as wives and mothers. In Protestantism this necessitated an ability to learn and understand the catechism and even to be able to independently read the Bible, but most commentators, even those that tended to encourage the education of girls, thought they should not receive the same academic education as boys. In the lower ranks of society, they benefited from the expansion of the parish schools system that took place after the Reformation, but were usually outnumbered by boys, often taught separately, for a shorter time and to a lower level. They were frequently taught reading, sewing and knitting, but not writing. Female illiteracy rates based on signatures among female servants were around 90 percent, from the late 17th to the early 18th centuries and perhaps 85 percent for women of all ranks by 1750, compared with 35 per cent for men. Among the nobility there were many educated and cultured women, of which Mary, Queen of Scots is the most obvious example.
After the Reformation, Scotland's universities underwent a series of reforms associated with Andrew Melville, who returned from
The widespread belief in the limited intellectual and moral capacity of women, vied with a desire, intensified after the Reformation, for women to take personal moral responsibility, particularly as wives and mothers. In Protestantism this necessitated an ability to learn and understand the catechism and even to be able to independently read the Bible, but most commentators, even those that tended to encourage the education of girls, thought they should not receive the same academic education as boys. In the lower ranks of society, they benefited from the expansion of the parish schools system that took place after the Reformation, but were usually outnumbered by boys, often taught separately, for a shorter time and to a lower level. They were frequently taught reading, sewing and knitting, but not writing. Female illiteracy rates based on signatures among female servants were around 90 percent, from the late 17th to the early 18th centuries and perhaps 85 percent for women of all ranks by 1750, compared with 35 per cent for men. Among the nobility there were many educated and cultured women, of which Mary, Queen of Scots is the most obvious example.
After the Reformation, Scotland's universities underwent a series of reforms associated with Andrew Melville, who returned from Geneva
Geneva ( ; french: Genève ) frp, Genèva ; german: link=no, Genf ; it, Ginevra ; rm, Genevra is the second-most populous city in Switzerland (after Zürich) and the most populous city of Romandy, the French-speaking part of Switzerland. Situa ...
to become principal of the University of Glasgow in 1574. He placed an emphasis on simplified logic and elevated languages and sciences to the same status as philosophy, allowing accepted ideas in all areas to be challenged. He introduced new specialist teaching staff, replacing the system of "regenting", where one tutor took the students through the entire arts curriculum. Metaphysics
Metaphysics is the branch of philosophy that studies the fundamental nature of reality, the first principles of being, identity and change, space and time, causality, necessity, and possibility. It includes questions about the nature of conscio ...
were abandoned and Greek became compulsory in the first year followed by Aramaic
The Aramaic languages, short Aramaic ( syc, ܐܪܡܝܐ, Arāmāyā; oar, 𐤀𐤓𐤌𐤉𐤀; arc, 𐡀𐡓𐡌𐡉𐡀; tmr, אֲרָמִית), are a language family containing many varieties (languages and dialects) that originated i ...
, Syriac and Hebrew
Hebrew (; ; ) is a Northwest Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Historically, it is one of the spoken languages of the Israelites and their longest-surviving descendants, the Jews and Samaritans. It was largely preserved ...
, launching a new fashion for ancient and biblical languages. Glasgow had probably been declining as a university before his arrival, but students now began to arrive in large numbers. He assisted in the reconstruction of Marischal College
Marischal College ( ) is a large granite building on Broad Street in the centre of Aberdeen in north-east Scotland, and since 2011 has acted as the headquarters of Aberdeen City Council. However, the building was constructed for and is on lon ...
, Aberdeen
Aberdeen (; sco, Aiberdeen ; gd, Obar Dheathain ; la, Aberdonia) is a city in North East Scotland, and is the third most populous city in the country. Aberdeen is one of Scotland's 32 local government council areas (as Aberdeen City), a ...
, and in order to do for St Andrews what he had done for Glasgow, he was appointed Principal of St Mary's College, St Andrews, in 1580. The University of Edinburgh
The University of Edinburgh ( sco, University o Edinburgh, gd, Oilthigh Dhùn Èideann; abbreviated as ''Edin.'' in post-nominals) is a public research university based in Edinburgh, Scotland. Granted a royal charter by King James VI in 1 ...
developed out of public lectures were established in the town 1440s on law, Greek, Latin and philosophy, under the patronage of Mary of Guise. These evolved into the "Tounis College", which would become the University of Edinburgh in 1582. The results were a revitalisation of all Scottish universities, which were now producing a quality of education the equal of that offered anywhere in Europe.. Under the Commonwealth, the universities saw an improvement in their funding, as they were given income from deaneries, defunct bishoprics and the excise, allowing the completion of buildings including the college in the High Street in Glasgow. They were still largely seen as a training school for clergy, and came under the control of the hard line Protestors.. After the Restoration there was a purge of the universities, but much of the intellectual advances of the preceding period was preserved. The universities recovered from the upheavals of the mid-century with a lecture-based curriculum that was able to embrace economics and science, offering a high quality liberal education to the sons of the nobility and gentry.
Military
Navy
 There are mentions in Medieval records of fleets commanded by Scottish kings including William the Lion. and Alexander II. The latter took personal command of a large naval force which sailed from the
There are mentions in Medieval records of fleets commanded by Scottish kings including William the Lion. and Alexander II. The latter took personal command of a large naval force which sailed from the Firth of Clyde
The Firth of Clyde is the mouth of the River Clyde. It is located on the west coast of Scotland and constitutes the deepest coastal waters in the British Isles (it is 164 metres deep at its deepest). The firth is sheltered from the Atlantic ...
and anchored off the island of Kerrera
Kerrera (; gd, Cearara or ''Cearrara'') is an island in the Scottish Inner Hebrides, close to the town of Oban. In 2016 it had a population of 45, divided into two communities in the north and south of the island.
Geology
The oldest bedrock ...
in 1249, intended to transport his army in a campaign against the Kingdom of the Isles, but he died before the campaign could begin. Records indicate that Alexander had several large oared ships built at Ayr
Ayr (; sco, Ayr; gd, Inbhir Àir, "Mouth of the River Ayr") is a town situated on the southwest coast of Scotland. It is the administrative centre of the South Ayrshire council area and the historic county town of Ayrshire. With a population ...
, but he avoided a sea battle. Defeat on land at the Battle of Largs
The Battle of Largs (2 October 1263) was a battle between the kingdoms of Norway and Scotland, on the Firth of Clyde near Largs, Scotland. Through it, Scotland achieved the end of 500 years of Norse Viking depredations and invasions despite bei ...
and winter storms forced the Norwegian fleet to return home, leaving the Scottish crown as the major power in the region and leading to the ceding of the Western Isles to Alexander in 1266.
Part of the reason for Robert I's success in the Wars of Independence was his ability to call on naval forces from the Islands. As a result of the expulsion of the Flemings
The Flemish or Flemings ( nl, Vlamingen ) are a Germanic ethnic group native to Flanders, Belgium, who speak Dutch. Flemish people make up the majority of Belgians, at about 60%.
"''Flemish''" was historically a geographical term, as all in ...
from England in 1303, he gained the support of a major naval power in the North Sea.. The development of naval power allowed Robert to successfully defeat English attempts to capture him in the Highlands and Islands and to blockade major English controlled fortresses at Perth and Stirling, the last forcing Edward II to attempt the relief that resulted in English defeat at Bannockburn in 1314. Scottish naval forces allowed invasions of the Isle of Man in 1313 and 1317 and Ireland in 1315. They were also crucial in the blockade of Berwick, which led to its fall in 1318. After the establishment of Scottish independence, Robert I turned his attention to building up a Scottish naval capacity. This was largely focused on the west coast, with the Exchequer Rolls of 1326 recording the feudal duties of his vassals in that region to aid him with their vessels and crews. Towards the end of his reign he supervised the building of at least one royal man-of-war near his palace at Cardross
Cardross (Scottish Gaelic: ''Càrdainn Ros'') is a large village with a population of 2,194 (2011) in Scotland, on the north side of the Firth of Clyde, situated halfway between Dumbarton and Helensburgh. Cardross is in the historic geographical ...
on the River Clyde. In the late 14th century, naval warfare with England was conducted largely by hired Scots, Flemish and French merchantmen and privateers.. James I James I may refer to:
People
*James I of Aragon (1208–1276)
*James I of Sicily or James II of Aragon (1267–1327)
*James I, Count of La Marche (1319–1362), Count of Ponthieu
*James I, Count of Urgell (1321–1347)
*James I of Cyprus (1334–13 ...
took a greater interest in naval power. After his return to Scotland in 1424, he established a shipbuilding yard at Leith
Leith (; gd, Lìte) is a port area in the north of the city of Edinburgh, Scotland, founded at the mouth of the Water of Leith. In 2021, it was ranked by ''Time Out'' as one of the top five neighbourhoods to live in the world.
The earliest ...
, a house for marine stores, and a workshop. King's ships were built and equipped there to be used for trade as well as war, one of which accompanied him on his expedition to the Islands in 1429. The office of Lord High Admiral was probably founded in this period. In his struggles with his nobles in 1488 James III received assistance from his two warships the ''Flower'' and the ''King's Carvel'' also known as the ''Yellow Carvel''.
 There were various attempts to create royal naval forces in the 15th century. James IV put the enterprise on a new footing, founding a harbour at Newhaven and a dockyard at the Pools of Airth. He acquired a total of 38 ships including the '' Great Michael'',. at that time, the largest ship in Europe.. Scottish ships had some success against privateers, accompanied the king on his expeditions in the islands and intervened in conflicts in Scandinavia and the Baltic, but were sold after the Flodden campaign and after 1516 Scottish naval efforts would rely on privateering captains and hired merchantmen. James V did not share his father's interest in developing a navy and shipbuilding fell behind that of the
There were various attempts to create royal naval forces in the 15th century. James IV put the enterprise on a new footing, founding a harbour at Newhaven and a dockyard at the Pools of Airth. He acquired a total of 38 ships including the '' Great Michael'',. at that time, the largest ship in Europe.. Scottish ships had some success against privateers, accompanied the king on his expeditions in the islands and intervened in conflicts in Scandinavia and the Baltic, but were sold after the Flodden campaign and after 1516 Scottish naval efforts would rely on privateering captains and hired merchantmen. James V did not share his father's interest in developing a navy and shipbuilding fell behind that of the Low Countries
The term Low Countries, also known as the Low Lands ( nl, de Lage Landen, french: les Pays-Bas, lb, déi Niddereg Lännereien) and historically called the Netherlands ( nl, de Nederlanden), Flanders, or Belgica, is a coastal lowland region in N ...
. Despite truces between England and Scotland there were periodic outbreaks of a ''guerre de course
Commerce raiding (french: guerre de course, "war of the chase"; german: Handelskrieg, "trade war") is a form of naval warfare used to destroy or disrupt logistics of the enemy on the open sea by attacking its merchant shipping, rather than enga ...
''. James V built a new harbour at Burntisland in 1542. The chief use of naval power in his reign was a series of expeditions to the Isles and France.. After the Union of Crowns
The Union of the Crowns ( gd, Aonadh nan Crùintean; sco, Union o the Crouns) was the accession of James VI of Scotland to the throne of the Kingdom of England as James I and the practical unification of some functions (such as overseas dip ...
in 1603 conflict between Scotland and England ended, but Scotland found itself involved in England's foreign policy, opening up Scottish shipping to attack. In 1626, a squadron of three ships was bought and equipped. There were also several marque fleets of privateers. In 1627, the Royal Scots Navy
The Royal Scots Navy (or Old Scots Navy) was the navy of the Kingdom of Scotland from its origins in the Middle Ages until its merger with the Kingdom of England's Royal Navy per the Acts of Union 1707. There are mentions in Medieval records ...
and accompanying contingents of burgh privateers participated in the major expedition to Biscay. The Scots also returned to the West Indies and in 1629 took part in the capture of Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirte ...
.
During the Bishop's Wars the king attempted to blockade Scotland and planned amphibious assaults from England on the East coast and from Ireland to the West. Scottish privateers took a number of English prizes. After the Covenanters allied with the English Parliament they established two patrol squadrons for the Atlantic and North Sea coasts, known collectively as the "Scotch Guard". The Scottish navy was unable to withstand the English fleet that accompanied the army led by Cromwell that conquered Scotland in 1649–1651 and the Scottish ships and crews were split up among the Commonwealth fleet. Scottish seamen received protection against arbitrary impressment by English men of war, but a fixed quota of conscripts for the Royal Navy was levied from the sea-coast burghs during the second half of the 17th century. Royal Navy patrols were now found in Scottish waters even in peacetime. In the Second (1665–1667) and Third Anglo-Dutch Wars (1672–1674) between 80 and 120 captains, took Scottish letters of marque and privateers played a major part in the naval conflict. In the 1690s, a small fleet of five ships was established by merchants for the Darien Scheme, and a professional navy was established for the protection of commerce in home waters during the Nine Years' War, with three purpose-built warships bought from English shipbuilders in 1696. After the Act of Union in 1707, these vessels were transferred to the Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against Fr ...
.
Army
 Before the
Before the Wars of the Three Kingdoms
The Wars of the Three Kingdoms were a series of related conflicts fought between 1639 and 1653 in the kingdoms of England, Scotland and Ireland, then separate entities united in a personal union under Charles I. They include the 1639 to 1640 Bi ...
in the mid-17th century, there was no standing army in the Kingdom of Scotland. In the Early Middle Ages
The Early Middle Ages (or early medieval period), sometimes controversially referred to as the Dark Ages, is typically regarded by historians as lasting from the late 5th or early 6th century to the 10th century. They marked the start of the Mi ...
, war in Scotland was characterised by the use of small war-bands of household troops often engaging in raids and low level warfare. By the High Middle Ages
The High Middle Ages, or High Medieval Period, was the periodization, period of European history that lasted from AD 1000 to 1300. The High Middle Ages were preceded by the Early Middle Ages and were followed by the Late Middle Ages, which ended ...
, the kings of Scotland could command forces of tens of thousands of men for short periods as part of the "common army", mainly of poorly armoured spear and bowmen. After the " Davidian Revolution" of the 12th century, which introduced elements of feudalism to Scotland, these forces were augmented by small numbers of mounted and heavily armoured knights. These armies rarely managed to stand up to the usually larger and more professional armies produced by England, but they were used to good effect by Robert I at the Battle of Bannockburn in 1314 to secure Scottish independence. After the Wars of Scottish Independence
The Wars of Scottish Independence were a series of military campaigns fought between the Kingdom of Scotland and the Kingdom of England in the late 13th and early 14th centuries.
The First War (1296–1328) began with the English invasion of ...
, the Auld Alliance between Scotland and France played a large part in the country's military activities, especially during the Hundred Years' War. In the Late Middle Ages
The Late Middle Ages or Late Medieval Period was the period of European history lasting from AD 1300 to 1500. The Late Middle Ages followed the High Middle Ages and preceded the onset of the early modern period (and in much of Europe, the Ren ...
, under the Stewart kings forces were further augmented by specialist troops, particularly men-at-arms and archers, hired by bonds of '' manrent'', similar to English indentures
An indenture is a legal contract that reflects or covers a debt or purchase obligation. It specifically refers to two types of practices: in historical usage, an indentured servant status, and in modern usage, it is an instrument used for commercia ...
of the same period. Archers became much sought after as mercenaries in French armies of the 15th century in order to help counter the English superiority in this arm, becoming a major element of the French royal guards as the Garde Écossaise
The Scottish Guards () was a bodyguard unit founded in 1418 by the Valois Charles VII of France, to be personal bodyguards to the French monarchy. They were assimilated into the ''Maison du Roi'' and later formed the first company of the '' Gard ...
. The Stewarts also adopted major innovations in continental warfare, such as longer pikes and the extensive use of artillery. However, in the early 16th century one of the best armed and largest Scottish armies ever assembled still met with defeat at the hands of an English army at the Battle of Flodden Field
The Battle of Flodden, Flodden Field, or occasionally Branxton, (Brainston Moor) was a battle fought on 9 September 1513 during the War of the League of Cambrai between the Kingdom of England and the Kingdom of Scotland, resulting in an English ...
in 1513, which saw the destruction of a large number of ordinary troops, a large section of the nobility and the king, James IV. In the 16th century, the crown took an increasing role in the supply of military equipment. The pike began to replace the spear and the Scots began to convert from the bow to gunpowder firearms. The feudal heavy cavalry had begun to disappear from Scottish armies and the Scots fielded relatively large numbers of light horse, often drawn from the borders. James IV brought in experts from France, Germany and the Netherlands and established a gun foundry in 1511. Gunpowder weaponry fundamentally altered the nature of castle architecture from the mid-15th century.
 In the early 17th century, relatively large numbers of Scots took service in foreign armies involved in the Thirty Years War. As armed conflict with Charles I in the Bishop's Wars became likely, hundreds of Scots mercenaries returned home from foreign service, including experienced leaders like Alexander and David Leslie and these veterans played an important role in training recruits.. These systems would form the basis of the Covenanter armies that intervened in the Civil Wars in England and Ireland. Scottish infantry were generally armed, as was almost universal in Western Europe, with a combination of pike and shot. Scottish armies may also have had individuals with a variety of weapons including bows, Lochaber axes, and
In the early 17th century, relatively large numbers of Scots took service in foreign armies involved in the Thirty Years War. As armed conflict with Charles I in the Bishop's Wars became likely, hundreds of Scots mercenaries returned home from foreign service, including experienced leaders like Alexander and David Leslie and these veterans played an important role in training recruits.. These systems would form the basis of the Covenanter armies that intervened in the Civil Wars in England and Ireland. Scottish infantry were generally armed, as was almost universal in Western Europe, with a combination of pike and shot. Scottish armies may also have had individuals with a variety of weapons including bows, Lochaber axes, and halberd
A halberd (also called halbard, halbert or Swiss voulge) is a two-handed pole weapon that came to prominent use during the 13th, 14th, 15th, and 16th centuries. The word ''halberd'' is cognate with the German word ''Hellebarde'', deriving from ...
s. Most cavalry were probably equipped with pistols and swords, although there is some evidence that they included lancers. Royalist armies, like those led by James Graham, Marquis of Montrose (1643–1644) and in Glencairn's rising (1653–1654) were mainly composed of conventionally armed infantry with pike and shot. Montrose's forces were short of heavy artillery suitable for siege warfare and had only a small force of cavalry.
At the Restoration the Privy Council established a force of several infantry regiments and a few troops of horse and there were attempts to found a national militia on the English model. The standing army was mainly employed in the suppression of Covenanter rebellions and the guerilla war undertaken by the Cameronians in the East.. Pikemen became less important in the late 17th century and after the introduction of the socket bayonet disappeared altogether, while matchlock muskets were replaced by the more reliable flintlock
Flintlock is a general term for any firearm that uses a flint-striking ignition mechanism, the first of which appeared in Western Europe in the early 16th century. The term may also apply to a particular form of the mechanism itself, also know ...
. On the eve of the Glorious Revolution, the standing army in Scotland was about 3,000 men in various regiments and another 268 veterans in the major garrison towns. After the Glorious Revolution the Scots were drawn into King William II's continental wars, beginning with the Nine Years' War in Flanders (1689–1697). By the time of the Act of Union, the Kingdom of Scotland had a standing army of seven units of infantry, two of horse and one troop of Horse Guards, besides varying levels of fortress artillery in the garrison castles of Edinburgh, Dumbarton, and Stirling, which would be incorporated into the British Army
The British Army is the principal land warfare force of the United Kingdom, a part of the British Armed Forces along with the Royal Navy and the Royal Air Force. , the British Army comprises 79,380 regular full-time personnel, 4,090 Gurkha ...
.
Flags
Lion Rampant
The lion is a common charge in heraldry. It traditionally symbolises courage, nobility, royalty, strength, stateliness and valour, because historically the lion has been regarded as the "king of beasts". The lion also carries Judeo-Chris ...
as a royal emblem in Scotland was by Alexander II in 1222.. It is recorded with the additional embellishment
In sewing and crafts, an embellishment is anything that adds design interest to the piece.
Examples in sewing and craft
* appliqué can be made by sewing machine of decorative techniques and or
* embroidery, done either by machine or by hand
* ...
of a double border set with lilies during the reign of Alexander III (1249–1286). This emblem
An emblem is an abstract or representational pictorial image that represents a concept, like a moral truth, or an allegory, or a person, like a king or saint.
Emblems vs. symbols
Although the words ''emblem'' and '' symbol'' are often use ...
occupied the shield of the royal coat of arms which, together with a royal banner
A banner can be a flag or another piece of cloth bearing a symbol, logo, slogan or another message. A flag whose design is the same as the shield in a coat of arms (but usually in a square or rectangular shape) is called a banner of arms. Als ...
displaying the same, was used by the King of Scots until the Union of the Crowns in 1603. Then it was incorporated into both the royal arms and royal banners of successive Scottish then British monarchs in order to symbolise Scotland; as can be seen today in the Royal Standard of the United Kingdom. Although now officially restricted to use by representatives of the Sovereign and at royal residences, the Royal Standard of Scotland continues to be one of Scotland's most recognisable symbols.
According to legend, the apostle and martyr Saint Andrew, the patron saint
A patron saint, patroness saint, patron hallow or heavenly protector is a saint who in Catholicism, Anglicanism, or Eastern Orthodoxy is regarded as the heavenly advocate of a nation, place, craft, activity, class, clan, family, or perso ...
of Scotland, was crucified on an X-shaped cross
A cross is a geometrical figure consisting of two intersecting lines or bars, usually perpendicular to each other. The lines usually run vertically and horizontally. A cross of oblique lines, in the shape of the Latin letter X, is termed a s ...
at Patras (Patrae) in Achaea. Use of the familiar iconography of his martyrdom, showing the apostle bound to an X-shaped cross, first appears in the Kingdom of Scotland in 1180 during the reign of William I. This image was again depicted on seals
Seals may refer to:
* Pinniped, a diverse group of semi-aquatic marine mammals, many of which are commonly called seals, particularly:
** Earless seal, or "true seal"
** Fur seal
* Seal (emblem), a device to impress an emblem, used as a means of a ...
used during the late 13th century; including on one particular example used by the Guardians of Scotland, dated 1286. Use of a simplified symbol associated with Saint Andrew which does not depict his image, namely the saltire, or crux decussata (from the Latin crux, 'cross', and decussis, 'having the shape of the Roman numeral X'), has its origins in the late 14th century; the Parliament of Scotland
The Parliament of Scotland ( sco, Pairlament o Scotland; gd, Pàrlamaid na h-Alba) was the legislature of the Kingdom of Scotland from the 13th century until 1707. The parliament evolved during the early 13th century from the king's council o ...
decreed in 1385 that Scottish soldiers wear a white Saint Andrew's Cross on their person, both in front and behind, for the purpose of identification. The earliest reference to the Saint Andrew's Cross as a flag is to be found in the ''Vienna Book of Hours'', 1503, where a white saltire is depicted with a red background. In the case of Scotland, use of a blue background for the Saint Andrew's Cross is said to date from at least the 15th century, with the first certain illustration of a flag depicting such appearing in Sir David Lyndsay of the Mount's ''Register of Scottish Arms,'' 1542.
Following the Union of the Crowns in 1603, James VI, King of Scots, commissioned new designs for a banner incorporating the flags of the Kingdom of Scotland and Kingdom of England
The Kingdom of England (, ) was a sovereign state on the island of Great Britain from 12 July 927, when it emerged from various Anglo-Saxon kingdoms, until 1 May 1707, when it united with Scotland to form the Kingdom of Great Britain.
On ...
. In 1606, a Union Flag was commissioned, combining the crosses of Saint George
Saint George ( Greek: Γεώργιος (Geórgios), Latin: Georgius, Arabic: القديس جرجس; died 23 April 303), also George of Lydda, was a Christian who is venerated as a saint in Christianity. According to tradition he was a soldie ...
(the Flag of England), with that of Saint Andrew. There was also a ''Scottish'' version of this flag, in which the cross of Saint Andrew overlaid the cross of St George. This design may have seen limited, unofficial use in Scotland until 1707, when the ''English'' variant of the same, whereby the cross of St George overlaid that of St Andrew, was adopted as the flag of the unified Kingdom of Great Britain
The Kingdom of Great Britain (officially Great Britain) was a sovereign country in Western Europe from 1 May 1707 to the end of 31 December 1800. The state was created by the 1706 Treaty of Union and ratified by the Acts of Union 1707, wh ...
.; ; ;
See also
*Falkland Palace
Falkland Palace, in Falkland, Fife, Scotland, is a royal palace of the Scottish Kings. It was one of the favourite places of Mary, Queen of Scots, providing an escape from political and religious turmoil. Today it is under the stewardship of ...
* Linlithgow Palace
* List of monarchs of Scotland
* Obsolete Scottish units of measurement
* Royal Consorts of Scotland
The consorts of the monarchs of Scotland bore titles derived from their marriage. The Kingdom of Scotland was first unified as a state by Kenneth I of Scotland in 843, and ceased to exist as an independent kingdom after the Act of Union 1707 ...
* Scottish monarchs family tree This is a family tree for the kings of Scotland, since the unification under the House of Alpin in 834, to the personal union with England in 1603 under James VI of Scotland. It includes also the Houses of Dunkeld, Balliol, Bruce, and Stewart.
...
* Scottish Term Day
Notes
References
Cited works
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * . * * Cannon, J., ''The Oxford Companion to British History'' (Oxford University Press, 1997), . * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * in . * * * * * * * * * * * * * in . * * in * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * in * in . * * in . * * * * * * * in * * * in * * in . * * * * * * * * * in . {{DEFAULTSORT:Scotland, Kingdom Of 1707 disestablishments in Scotland Scottish monarchy States and territories established in the 840s States and territories disestablished in 1707 States and territories disestablished in 1654 States and territories established in 1660Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to ...
Former monarchies of Europe
Former countries in the British Isles
843 establishments
9th-century establishments in Scotland
Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to ...