ionising radiation on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Ionizing (ionising) radiation, including nuclear radiation, consists of
Ionizing (ionising) radiation, including nuclear radiation, consists of
 Ionizing radiation may be grouped as directly or indirectly ionizing.
Any charged particle with mass can ionize
Ionizing radiation may be grouped as directly or indirectly ionizing.
Any charged particle with mass can ionize
 Even though photons are electrically neutral, they can ionize
Even though photons are electrically neutral, they can ionize



 There are three standard ways to limit exposure:
# Time: For people exposed to radiation in addition to natural background radiation, limiting or minimizing the exposure time will reduce the dose from the source of radiation.
# Distance: Radiation intensity decreases sharply with distance, according to an inverse-square law (in an absolute vacuum).Camphausen KA, Lawrence RC
There are three standard ways to limit exposure:
# Time: For people exposed to radiation in addition to natural background radiation, limiting or minimizing the exposure time will reduce the dose from the source of radiation.
# Distance: Radiation intensity decreases sharply with distance, according to an inverse-square law (in an absolute vacuum).Camphausen KA, Lawrence RC
"Principles of Radiation Therapy"
in Pazdur R, Wagman LD, Camphausen KA, Hoskins WJ (Eds
Cancer Management: A Multidisciplinary Approach
. 11 ed. 2008. # Shielding: Air or skin can be sufficient to substantially attenuate alpha radiation, while sheet metal or plastic is often sufficient to stop beta radiation. Barriers of
File:Radioactive.svg, Ionizing radiation
The Nuclear Regulatory Commission
regulates most commercial radiation sources and non-medical exposures in the US:
NLM Hazardous Substances Databank – Ionizing Radiation
* United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation 2000 Repor
Volume 1: Sources
Beginners Guide to Ionising Radiation Measurement
* (from CT scans and xrays).
Health Physics Society Public Education Website
Basic Radiation Facts {{DEFAULTSORT:Ionizing Radiation Carcinogens Mutagens Radioactivity Radiobiology Radiation health effects Radiation protection
subatomic particle
In physics, a subatomic particle is a particle smaller than an atom. According to the Standard Model of particle physics, a subatomic particle can be either a composite particle, which is composed of other particles (for example, a baryon, lik ...
s or electromagnetic wave
In physics, electromagnetic radiation (EMR) is a self-propagating wave of the electromagnetic field that carries momentum and radiant energy through space. It encompasses a broad spectrum, classified by frequency or its inverse, wavelength, ...
s that have enough energy
Energy () is the physical quantity, quantitative physical property, property that is transferred to a physical body, body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of Work (thermodynamics), work and in the form of heat and l ...
per individual photon or particle to ionize
Ionization or ionisation is the process by which an atom or a molecule acquires a negative or positive charge by gaining or losing electrons, often in conjunction with other chemical changes. The resulting electrically charged atom or molecule i ...
atom
Atoms are the basic particles of the chemical elements. An atom consists of a atomic nucleus, nucleus of protons and generally neutrons, surrounded by an electromagnetically bound swarm of electrons. The chemical elements are distinguished fr ...
s or molecule
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms that are held together by Force, attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions that satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemi ...
s by detaching electron
The electron (, or in nuclear reactions) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary charge, elementary electric charge. It is a fundamental particle that comprises the ordinary matter that makes up the universe, along with up qua ...
s from them. Some particles can travel up to 99% of the speed of light
The speed of light in vacuum, commonly denoted , is a universal physical constant exactly equal to ). It is exact because, by international agreement, a metre is defined as the length of the path travelled by light in vacuum during a time i ...
, and the electromagnetic waves are on the high-energy portion of the electromagnetic spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum is the full range of electromagnetic radiation, organized by frequency or wavelength. The spectrum is divided into separate bands, with different names for the electromagnetic waves within each band. From low to high ...
.
Gamma ray
A gamma ray, also known as gamma radiation (symbol ), is a penetrating form of electromagnetic radiation arising from high energy interactions like the radioactive decay of atomic nuclei or astronomical events like solar flares. It consists o ...
s, X-rays
An X-ray (also known in many languages as Röntgen radiation) is a form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than those of ultraviolet rays and longer than those of gamma rays. Roughly, X-rays have a wavelength ran ...
, and the higher energy ultraviolet
Ultraviolet radiation, also known as simply UV, is electromagnetic radiation of wavelengths of 10–400 nanometers, shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight and constitutes about 10% of ...
part of the electromagnetic spectrum are ionizing radiation; whereas the lower energy ultraviolet
Ultraviolet radiation, also known as simply UV, is electromagnetic radiation of wavelengths of 10–400 nanometers, shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight and constitutes about 10% of ...
, visible light
Light, visible light, or visible radiation is electromagnetic radiation that can be visual perception, perceived by the human eye. Visible light spans the visible spectrum and is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400– ...
, infrared
Infrared (IR; sometimes called infrared light) is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than that of visible light but shorter than microwaves. The infrared spectral band begins with the waves that are just longer than those ...
, microwave
Microwave is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths shorter than other radio waves but longer than infrared waves. Its wavelength ranges from about one meter to one millimeter, corresponding to frequency, frequencies between 300&n ...
s, and radio wave
Radio waves (formerly called Hertzian waves) are a type of electromagnetic radiation with the lowest frequencies and the longest wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum, typically with frequencies below 300 gigahertz (GHz) and wavelengths g ...
s are non-ionizing radiation. Nearly all types of laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word ''laser'' originated as an acronym for light amplification by stimulated emission of radi ...
light are non-ionizing radiation. The boundary between ionizing and non-ionizing radiation in the ultraviolet area cannot be sharply defined, as different molecules and atoms ionize at different energies. The energy of ionizing radiation starts between 10 electronvolt
In physics, an electronvolt (symbol eV), also written electron-volt and electron volt, is the measure of an amount of kinetic energy gained by a single electron accelerating through an Voltage, electric potential difference of one volt in vacuum ...
s (eV) and 33 eV.
Ionizing subatomic particles include alpha particle
Alpha particles, also called alpha rays or alpha radiation, consist of two protons and two neutrons bound together into a particle identical to a helium-4 nucleus. They are generally produced in the process of alpha decay but may also be produce ...
s, beta particle
A beta particle, also called beta ray or beta radiation (symbol β), is a high-energy, high-speed electron or positron emitted by the radioactive decay of an atomic nucleus, known as beta decay. There are two forms of beta decay, β− decay and � ...
s, and neutron
The neutron is a subatomic particle, symbol or , that has no electric charge, and a mass slightly greater than that of a proton. The Discovery of the neutron, neutron was discovered by James Chadwick in 1932, leading to the discovery of nucle ...
s. These particles are created by radioactive decay
Radioactive decay (also known as nuclear decay, radioactivity, radioactive disintegration, or nuclear disintegration) is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by radiation. A material containing unstable nuclei is conside ...
, and almost all are energetic enough to ionize. There are also secondary cosmic particle
Cosmic rays or astroparticles are high-energy particles or clusters of particles (primarily represented by protons or atomic nuclei) that move through space at nearly the speed of light. They originate from the Sun, from outside of the Sol ...
s produced after cosmic rays
Cosmic rays or astroparticles are high-energy particles or clusters of particles (primarily represented by protons or atomic nuclei) that move through space at nearly the speed of light. They originate from the Sun, from outside of the Solar ...
interact with Earth's atmosphere, including muon
A muon ( ; from the Greek letter mu (μ) used to represent it) is an elementary particle similar to the electron, with an electric charge of −1 '' e'' and a spin of ''ħ'', but with a much greater mass. It is classified as a ...
s, meson
In particle physics, a meson () is a type of hadronic subatomic particle composed of an equal number of quarks and antiquarks, usually one of each, bound together by the strong interaction. Because mesons are composed of quark subparticles, the ...
s, and positron
The positron or antielectron is the particle with an electric charge of +1''elementary charge, e'', a Spin (physics), spin of 1/2 (the same as the electron), and the same Electron rest mass, mass as an electron. It is the antiparticle (antimatt ...
s. Cosmic rays
Cosmic rays or astroparticles are high-energy particles or clusters of particles (primarily represented by protons or atomic nuclei) that move through space at nearly the speed of light. They originate from the Sun, from outside of the Solar ...
may also produce radioisotope
A radionuclide (radioactive nuclide, radioisotope or radioactive isotope) is a nuclide that has excess numbers of either neutrons or protons, giving it excess nuclear energy, and making it unstable. This excess energy can be used in one of three ...
s on Earth (for example, carbon-14
Carbon-14, C-14, C or radiocarbon, is a radioactive isotope of carbon with an atomic nucleus containing 6 protons and 8 neutrons. Its presence in organic matter is the basis of the radiocarbon dating method pioneered by Willard Libby and coll ...
), which in turn decay and emit ionizing radiation. Cosmic rays and the decay of radioactive isotopes
Isotopes are distinct nuclear species (or ''nuclides'') of the same chemical element. They have the same atomic number (number of protons in their nuclei) and position in the periodic table (and hence belong to the same chemical element), but ...
are the primary sources of natural ionizing radiation on Earth, contributing to background radiation. Ionizing radiation is also generated artificially by X-ray tubes, particle accelerators
A particle accelerator is a machine that uses electromagnetic fields to propel electric charge, charged particles to very high speeds and energies to contain them in well-defined particle beam, beams. Small accelerators are used for fundamental ...
, and nuclear fission
Nuclear fission is a reaction in which the nucleus of an atom splits into two or more smaller nuclei. The fission process often produces gamma photons, and releases a very large amount of energy even by the energetic standards of radioactiv ...
.
Ionizing radiation is not immediately detectable by human senses, so instruments such as Geiger counters are used to detect and measure it. However, very high energy particles can produce visible effects on both organic and inorganic matter (e.g. water lighting in Cherenkov radiation) or humans (e.g. acute radiation syndrome
Acute radiation syndrome (ARS), also known as radiation sickness or radiation poisoning, is a collection of health effects that are caused by being exposed to high amounts of ionizing radiation in a short period of time. Symptoms can start wit ...
).
Ionizing radiation is used in a wide variety of fields such as medicine
Medicine is the science and Praxis (process), practice of caring for patients, managing the Medical diagnosis, diagnosis, prognosis, Preventive medicine, prevention, therapy, treatment, Palliative care, palliation of their injury or disease, ...
, nuclear power
Nuclear power is the use of nuclear reactions to produce electricity. Nuclear power can be obtained from nuclear fission, nuclear decay and nuclear fusion reactions. Presently, the vast majority of electricity from nuclear power is produced by ...
, research, and industrial manufacturing, but is a health hazard if proper measures against excessive exposure are not taken. Exposure to ionizing radiation causes cell damage to living tissue and organ damage. In high acute doses, it will result in radiation burns and radiation sickness
Acute radiation syndrome (ARS), also known as radiation sickness or radiation poisoning, is a collection of health effects that are caused by being exposed to high amounts of ionizing radiation in a short period of time. Symptoms can start wit ...
, and lower level doses over a protracted time can cause cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Po ...
. The International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP) issues guidance on ionizing radiation protection, and the effects of dose uptake on human health.
Directly ionizing radiation
atom
Atoms are the basic particles of the chemical elements. An atom consists of a atomic nucleus, nucleus of protons and generally neutrons, surrounded by an electromagnetically bound swarm of electrons. The chemical elements are distinguished fr ...
s directly by fundamental interaction
In physics, the fundamental interactions or fundamental forces are interactions in nature that appear not to be reducible to more basic interactions. There are four fundamental interactions known to exist:
* gravity
* electromagnetism
* weak int ...
through the Coulomb force if it has enough kinetic energy. Such particles include atomic nuclei
The atomic nucleus is the small, dense region consisting of protons and neutrons at the center of an atom, discovered in 1911 by Ernest Rutherford at the University of Manchester based on the 1909 Geiger–Marsden gold foil experiment. Aft ...
, electron
The electron (, or in nuclear reactions) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary charge, elementary electric charge. It is a fundamental particle that comprises the ordinary matter that makes up the universe, along with up qua ...
s, muon
A muon ( ; from the Greek letter mu (μ) used to represent it) is an elementary particle similar to the electron, with an electric charge of −1 '' e'' and a spin of ''ħ'', but with a much greater mass. It is classified as a ...
s, charged pion
In particle physics, a pion (, ) or pi meson, denoted with the Greek alphabet, Greek letter pi (letter), pi (), is any of three subatomic particles: , , and . Each pion consists of a quark and an antiquark and is therefore a meson. Pions are the ...
s, proton
A proton is a stable subatomic particle, symbol , Hydron (chemistry), H+, or 1H+ with a positive electric charge of +1 ''e'' (elementary charge). Its mass is slightly less than the mass of a neutron and approximately times the mass of an e ...
s, and energetic charged nuclei stripped of their electrons. When moving at relativistic speeds (near the speed of light
The speed of light in vacuum, commonly denoted , is a universal physical constant exactly equal to ). It is exact because, by international agreement, a metre is defined as the length of the path travelled by light in vacuum during a time i ...
, c) these particles have enough kinetic energy to be ionizing, but there is considerable speed variation. For example, a typical alpha particle moves at about 5% of c, but an electron with 33 eV (just enough to ionize) moves at about 1% of c.
Two of the first types of directly ionizing radiation to be discovered are alpha particles which are helium nuclei ejected from the nucleus of an atom during radioactive decay, and energetic electrons, which are called beta particle
A beta particle, also called beta ray or beta radiation (symbol β), is a high-energy, high-speed electron or positron emitted by the radioactive decay of an atomic nucleus, known as beta decay. There are two forms of beta decay, β− decay and � ...
s.
Natural cosmic ray
Cosmic rays or astroparticles are high-energy particles or clusters of particles (primarily represented by protons or atomic nuclei) that move through space at nearly the speed of light. They originate from the Sun, from outside of the ...
s are made up primarily of relativistic protons but also include heavier atomic nuclei like helium
Helium (from ) is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol He and atomic number 2. It is a colorless, odorless, non-toxic, inert gas, inert, monatomic gas and the first in the noble gas group in the periodic table. Its boiling point is ...
ions and HZE ions. In the atmosphere such particles are often stopped by air molecules, and this produces short-lived charged pions, which soon decay to muons, a primary type of cosmic ray radiation that reaches the surface of the earth. Pions can also be produced in large amounts in particle accelerator
A particle accelerator is a machine that uses electromagnetic fields to propel electric charge, charged particles to very high speeds and energies to contain them in well-defined particle beam, beams. Small accelerators are used for fundamental ...
s.
Alpha particles
Alpha (α) particles consist of twoproton
A proton is a stable subatomic particle, symbol , Hydron (chemistry), H+, or 1H+ with a positive electric charge of +1 ''e'' (elementary charge). Its mass is slightly less than the mass of a neutron and approximately times the mass of an e ...
s and two neutron
The neutron is a subatomic particle, symbol or , that has no electric charge, and a mass slightly greater than that of a proton. The Discovery of the neutron, neutron was discovered by James Chadwick in 1932, leading to the discovery of nucle ...
s bound together into a particle: a helium
Helium (from ) is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol He and atomic number 2. It is a colorless, odorless, non-toxic, inert gas, inert, monatomic gas and the first in the noble gas group in the periodic table. Its boiling point is ...
-4 nucleus. Alpha particle emissions are generally produced in the process of alpha decay
Alpha decay or α-decay is a type of radioactive decay in which an atomic nucleus emits an alpha particle (helium nucleus). The parent nucleus transforms or "decays" into a daughter product, with a mass number that is reduced by four and an a ...
.
Alpha particles are a strongly ionizing form of radiation, but when emitted by radioactive decay they have low penetration power and can be absorbed by a few centimeters of air, or by the top layer of human skin. More powerful alpha particles from ternary fission
Ternary fission is a comparatively rare (0.2 to 0.4% of events) type of nuclear fission in which three charged products are produced rather than two. As in other nuclear fission processes, other uncharged particles such as multiple neutrons and ...
are three times as energetic, and penetrate proportionately farther in air. The helium nuclei that form 10–12% of cosmic rays, are also usually of much higher energy than those from radioactive decay and pose shielding problems in space. However, this type of radiation is significantly absorbed by Earth's atmosphere, which is a radiation shield equivalent to about 10 meters of water.
The alpha particle was named by Ernest Rutherford
Ernest Rutherford, 1st Baron Rutherford of Nelson (30 August 1871 – 19 October 1937) was a New Zealand physicist who was a pioneering researcher in both Atomic physics, atomic and nuclear physics. He has been described as "the father of nu ...
after the first letter in the Greek alphabet
The Greek alphabet has been used to write the Greek language since the late 9th or early 8th century BC. It was derived from the earlier Phoenician alphabet, and is the earliest known alphabetic script to systematically write vowels as wel ...
, α, when he ranked the known radioactive emissions in descending order of ionizing effect in 1899. The symbol is α or α. Because they are identical to helium nuclei, they are also called He or indicating helium with a +2 charge (missing its two electrons). If the ion gains electrons from its environment, the α particle can be written as a normal (electrically neutral) helium atom .
Beta particles
Beta (β) particles are high-energy, high-speedelectron
The electron (, or in nuclear reactions) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary charge, elementary electric charge. It is a fundamental particle that comprises the ordinary matter that makes up the universe, along with up qua ...
s or positron
The positron or antielectron is the particle with an electric charge of +1''elementary charge, e'', a Spin (physics), spin of 1/2 (the same as the electron), and the same Electron rest mass, mass as an electron. It is the antiparticle (antimatt ...
s emitted by certain types of radioactive
Radioactive decay (also known as nuclear decay, radioactivity, radioactive disintegration, or nuclear disintegration) is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by radiation. A material containing unstable nuclei is conside ...
nuclei, such as potassium-40
Potassium-40 (K) is a long lived and the main naturally occurring radioactive isotope of potassium. Its half-life is 1.25 billion years. It makes up about 0.012% (120 parts-per notation, ppm) of natural potassium.
Potassium-40 undergoes four dif ...
. The production of β particles is termed beta decay
In nuclear physics, beta decay (β-decay) is a type of radioactive decay in which an atomic nucleus emits a beta particle (fast energetic electron or positron), transforming into an isobar of that nuclide. For example, beta decay of a neutron ...
. There are two forms of β decay, β and β, which respectively give rise to the electron and the positron. Beta particles are much less penetrating than gamma radiation, but more penetrating than alpha particles.
High-energy beta particles may produce X-rays known as bremsstrahlung ("braking radiation") or secondary electrons ( delta ray) as they pass through matter. Both of these can cause an indirect ionization effect. Bremsstrahlung is of concern when shielding beta emitters, as the interaction of beta particles with some shielding materials produces bremsstrahlung. The effect is greater with material having high atomic numbers, so material with low atomic numbers is used for beta source shielding.
Positrons and other types of antimatter
The positron or antielectron is theantiparticle
In particle physics, every type of particle of "ordinary" matter (as opposed to antimatter) is associated with an antiparticle with the same mass but with opposite physical charges (such as electric charge). For example, the antiparticle of the ...
or the antimatter
In modern physics, antimatter is defined as matter composed of the antiparticles (or "partners") of the corresponding subatomic particle, particles in "ordinary" matter, and can be thought of as matter with reversed charge and parity, or go ...
counterpart of the electron
The electron (, or in nuclear reactions) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary charge, elementary electric charge. It is a fundamental particle that comprises the ordinary matter that makes up the universe, along with up qua ...
. When a low-energy positron collides with a low-energy electron, annihilation
In particle physics, annihilation is the process that occurs when a subatomic particle collides with its respective antiparticle to produce other particles, such as an electron colliding with a positron to produce two photons. The total energy a ...
occurs, resulting in their conversion into the energy of two or more gamma ray
A gamma ray, also known as gamma radiation (symbol ), is a penetrating form of electromagnetic radiation arising from high energy interactions like the radioactive decay of atomic nuclei or astronomical events like solar flares. It consists o ...
photon
A photon () is an elementary particle that is a quantum of the electromagnetic field, including electromagnetic radiation such as light and radio waves, and the force carrier for the electromagnetic force. Photons are massless particles that can ...
s (see electron–positron annihilation). As positrons are positively charged particles they can directly ionize an atom through Coulomb interactions.
Positrons can be generated by positron emission
Positron emission, beta plus decay, or β+ decay is a subtype of radioactive decay called beta decay, in which a proton inside a radionuclide nucleus is converted into a neutron while releasing a positron and an electron neutrino (). Positron emi ...
nuclear decay (through weak interaction
In nuclear physics and particle physics, the weak interaction, weak force or the weak nuclear force, is one of the four known fundamental interactions, with the others being electromagnetism, the strong interaction, and gravitation. It is th ...
s), or by pair production
Pair production is the creation of a subatomic particle and its antiparticle from a neutral boson. Examples include creating an electron and a positron, a muon and an antimuon, or a proton and an antiproton. Pair production often refers ...
from a sufficiently energetic photon
A photon () is an elementary particle that is a quantum of the electromagnetic field, including electromagnetic radiation such as light and radio waves, and the force carrier for the electromagnetic force. Photons are massless particles that can ...
. Positrons are common artificial sources of ionizing radiation used in medical positron emission tomography
Positron emission tomography (PET) is a functional imaging technique that uses radioactive substances known as radiotracers to visualize and measure changes in metabolic processes, and in other physiological activities including blood flow, r ...
(PET) scans.
Charged nuclei
Charged nuclei are characteristic of galactic cosmic rays and solar particle events and except for alpha particles (charged helium nuclei) have no natural sources on Earth. In space, however, very high energy protons, helium nuclei, and HZE ions can be initially stopped by relatively thin layers of shielding, clothes, or skin. However, the resulting interaction will generate secondary radiation and cause cascading biological effects. If just one atom of tissue is displaced by an energetic proton, for example, the collision will cause further interactions in the body. This is called "linear energy transfer
In dosimetry, linear energy transfer (LET) is the amount of energy that an ionizing particle transfers to the material traversed per unit distance. It describes the action of radiation into matter.
It is identical to the retarding force acting o ...
" (LET), which utilizes elastic scattering
Elastic scattering is a form of particle scattering in scattering theory, nuclear physics and particle physics. In this process, the internal states of the Elementary particle, particles involved stay the same. In the non-relativistic case, where ...
.
LET can be visualized as a billiard ball hitting another in the manner of the conservation of momentum
In Newtonian mechanics, momentum (: momenta or momentums; more specifically linear momentum or translational momentum) is the product of the mass and velocity of an object. It is a vector quantity, possessing a magnitude and a direction. ...
, sending both away with the energy of the first ball divided between the two unequally. When a charged nucleus strikes a relatively slow-moving nucleus of an object in space, LET occurs and neutrons, alpha particles, low-energy protons, and other nuclei will be released by the collisions and contribute to the total absorbed dose of tissue. Contribution of High Charge and Energy (HZE) Ions During Solar-Particle Event of September 29, 1989 Kim, Myung-Hee Y.; Wilson, John W.; Cucinotta, Francis A.; Simonsen, Lisa C.; Atwell, William; Badavi, Francis F.; Miller, Jack, NASA Johnson Space Center; Langley Research Center, May 1999.
Indirectly ionizing radiation
Indirectly ionizing radiation is electrically neutral and does not interact strongly with matter, therefore the bulk of the ionization effects are due to secondary ionization.Photon radiation
atom
Atoms are the basic particles of the chemical elements. An atom consists of a atomic nucleus, nucleus of protons and generally neutrons, surrounded by an electromagnetically bound swarm of electrons. The chemical elements are distinguished fr ...
s indirectly through the photoelectric effect
The photoelectric effect is the emission of electrons from a material caused by electromagnetic radiation such as ultraviolet light. Electrons emitted in this manner are called photoelectrons. The phenomenon is studied in condensed matter physi ...
and the Compton effect. Either of those interactions cause the ejection of an electron from an atom at relativistic speeds, turning that electron into a (secondary) beta particle that will ionize other atoms. Since most of the ionized atoms are due to the secondary beta particles, photons are indirectly ionizing radiation.
Radiated photons are called gamma ray
A gamma ray, also known as gamma radiation (symbol ), is a penetrating form of electromagnetic radiation arising from high energy interactions like the radioactive decay of atomic nuclei or astronomical events like solar flares. It consists o ...
s if they are produced by a nuclear reaction
In nuclear physics and nuclear chemistry, a nuclear reaction is a process in which two atomic nucleus, nuclei, or a nucleus and an external subatomic particle, collide to produce one or more new nuclides. Thus, a nuclear reaction must cause a t ...
, subatomic particle
In physics, a subatomic particle is a particle smaller than an atom. According to the Standard Model of particle physics, a subatomic particle can be either a composite particle, which is composed of other particles (for example, a baryon, lik ...
decay, or radioactive decay
Radioactive decay (also known as nuclear decay, radioactivity, radioactive disintegration, or nuclear disintegration) is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by radiation. A material containing unstable nuclei is conside ...
within the nucleus. They are called x-ray
An X-ray (also known in many languages as Röntgen radiation) is a form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than those of ultraviolet rays and longer than those of gamma rays. Roughly, X-rays have a wavelength ran ...
s if produced outside the nucleus. The generic term "photon" is used to describe both.
X-rays normally have a lower energy than gamma rays, and an older convention was to define the boundary as a wavelength of 10−11 m (or a photon energy of 100 keV). That threshold was driven by historic limitations of older X-ray tubes and low awareness of isomeric transition
A nuclear isomer is a metastable state of an atomic nucleus, in which one or more nucleons (protons or neutrons) occupy excited state levels (higher energy levels). "Metastable" describes nuclei whose excited states have half-lives of 10−9 s ...
s. Modern technologies and discoveries have shown an overlap between X-ray and gamma energies. In many fields they are functionally identical, differing for terrestrial studies only in origin of the radiation. In astronomy, however, where radiation origin often cannot be reliably determined, the old energy division has been preserved, with X-rays defined as being between about 120 eV and 120 keV, and gamma rays as being of any energy above 100 to 120 keV, regardless of source. Most astronomical " gamma-rays" are known ''not'' to originate from radioactivity but, rather, result from processes like those that produce astronomical X-rays, except driven by much more energetic electrons.
Photoelectric absorption is the dominant mechanism in organic materials for photon energies below 100 keV, typical of classical X-ray tube originated X-ray
An X-ray (also known in many languages as Röntgen radiation) is a form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than those of ultraviolet rays and longer than those of gamma rays. Roughly, X-rays have a wavelength ran ...
s. At energies beyond 100 keV, photons ionize matter increasingly through the Compton effect, and then indirectly through pair production
Pair production is the creation of a subatomic particle and its antiparticle from a neutral boson. Examples include creating an electron and a positron, a muon and an antimuon, or a proton and an antiproton. Pair production often refers ...
at energies beyond 5 MeV. The accompanying interaction diagram shows two Compton scatterings happening sequentially. In every scattering event, the gamma ray transfers energy to an electron, and it continues on its path in a different direction and with reduced energy.
Definition boundary for lower-energy photons
The lowest ionization energy of any element is 3.89 eV, forcaesium
Caesium (IUPAC spelling; also spelled cesium in American English) is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Cs and atomic number 55. It is a soft, silvery-golden alkali metal with a melting point of , which makes it one of only f ...
. However, US Federal Communications Commission material defines ionizing radiation as that with a photon energy greater than 10 eV (equivalent to a far ultraviolet
Ultraviolet radiation, also known as simply UV, is electromagnetic radiation of wavelengths of 10–400 nanometers, shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight and constitutes about 10% of ...
wavelength of 124 nanometers). Roughly, this corresponds to both the first ionization energy
In physics and chemistry, ionization energy (IE) is the minimum energy required to remove the most loosely bound electron of an isolated gaseous atom, Ion, positive ion, or molecule. The first ionization energy is quantitatively expressed as
: ...
of oxygen, and the ionization energy of hydrogen, both about 14 eV. In some Environmental Protection Agency references, the ionization of a typical water molecule at an energy of 33 eV is referenced as the appropriate biological threshold for ionizing radiation: this value represents the so-called ''W-value'', the colloquial name for the ICRU's mean energy expended in a gas per ion pair formed, which combines ionization energy plus the energy lost to other processes such as excitation. At 38 nanometers wavelength for electromagnetic radiation
In physics, electromagnetic radiation (EMR) is a self-propagating wave of the electromagnetic field that carries momentum and radiant energy through space. It encompasses a broad spectrum, classified by frequency or its inverse, wavelength ...
, 33 eV is close to the energy at the conventional 10 nm wavelength transition between extreme ultraviolet and X-ray radiation, which occurs at about 125 eV. Thus, X-ray radiation is always ionizing, but only extreme-ultraviolet radiation can be considered ionizing under all definitions.
Neutrons
Neutron
The neutron is a subatomic particle, symbol or , that has no electric charge, and a mass slightly greater than that of a proton. The Discovery of the neutron, neutron was discovered by James Chadwick in 1932, leading to the discovery of nucle ...
s have a neutral electrical charge often misunderstood as zero electrical charge and thus often do not ''directly'' cause ionization in a single step or interaction with matter. However, fast neutrons will interact with the protons in hydrogen via linear energy transfer
In dosimetry, linear energy transfer (LET) is the amount of energy that an ionizing particle transfers to the material traversed per unit distance. It describes the action of radiation into matter.
It is identical to the retarding force acting o ...
, energy that a particle transfers to the material it is moving through. This mechanism scatters the nuclei of the materials in the target area, causing direct ionization of the hydrogen atoms. When neutrons strike the hydrogen nuclei, proton radiation (fast protons) results. These protons are themselves ionizing because they are of high energy, are charged, and interact with electrons.
Neutrons that strike other nuclei besides hydrogen, transfer less energy to the other particle if linear energy transfer does occur. But, for many nuclei struck by neutrons, inelastic scattering occurs. Whether elastic or inelastic scatter occurs is dependent on the speed of the neutron, whether fast or thermal or somewhere in between. It is also dependent on the nuclei it strikes and its neutron cross section.
In inelastic scattering, neutrons are readily absorbed in a type of nuclear reaction
In nuclear physics and nuclear chemistry, a nuclear reaction is a process in which two atomic nucleus, nuclei, or a nucleus and an external subatomic particle, collide to produce one or more new nuclides. Thus, a nuclear reaction must cause a t ...
called neutron capture
Neutron capture is a nuclear reaction in which an atomic nucleus and one or more neutrons collide and merge to form a heavier nucleus. Since neutrons have no electric charge, they can enter a nucleus more easily than positively charged protons, wh ...
and attributes to the neutron activation of the nucleus. Neutron interactions with most types of matter in this manner usually produce radioactive
Radioactive decay (also known as nuclear decay, radioactivity, radioactive disintegration, or nuclear disintegration) is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by radiation. A material containing unstable nuclei is conside ...
nuclei. Oxygen-16, for example, undergoes neutron activation, rapidly decays by a proton emission forming nitrogen-16, which decays to oxygen-16. The short-lived nitrogen-16 decay emits a powerful beta ray. This process can be written as:
O (n,p) N (fast neutron capture possible with >11 MeV neutron) N → O + β (Decay t = 7.13 s) This high-energy β further interacts rapidly with other nuclei, emitting high-energy γ via BremsstrahlungWhile not a favorable reaction, the O (n,p) N reaction is a major source of X-rays emitted from the cooling water of a
pressurized water reactor
A pressurized water reactor (PWR) is a type of light-water nuclear reactor. PWRs constitute the large majority of the world's nuclear power plants (with notable exceptions being the UK, Japan, India and Canada).
In a PWR, water is used both as ...
and contributes enormously to the radiation generated by a water-cooled nuclear reactor
A nuclear reactor is a device used to initiate and control a Nuclear fission, fission nuclear chain reaction. They are used for Nuclear power, commercial electricity, nuclear marine propulsion, marine propulsion, Weapons-grade plutonium, weapons ...
while operating.
For the best shielding of neutrons, hydrocarbons that have an abundance of hydrogen
Hydrogen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol H and atomic number 1. It is the lightest and abundance of the chemical elements, most abundant chemical element in the universe, constituting about 75% of all baryon, normal matter ...
are used.
In fissile
In nuclear engineering, fissile material is material that can undergo nuclear fission when struck by a neutron of low energy. A self-sustaining thermal Nuclear chain reaction#Fission chain reaction, chain reaction can only be achieved with fissil ...
materials, secondary neutrons may produce nuclear chain reactions, causing a larger amount of ionization from the daughter products of fission.
Outside the nucleus, free neutrons are unstable and have a mean lifetime of 14 minutes, 42 seconds. Free neutrons decay by emission of an electron and an electron antineutrino to become a proton, a process known as beta decay
In nuclear physics, beta decay (β-decay) is a type of radioactive decay in which an atomic nucleus emits a beta particle (fast energetic electron or positron), transforming into an isobar of that nuclide. For example, beta decay of a neutron ...
:
In the adjacent diagram, a neutron collides with a proton of the target material, and then becomes a fast recoil proton that ionizes in turn. At the end of its path, the neutron is captured by a nucleus in an (n,γ)-reaction that leads to the emission of a neutron capture
Neutron capture is a nuclear reaction in which an atomic nucleus and one or more neutrons collide and merge to form a heavier nucleus. Since neutrons have no electric charge, they can enter a nucleus more easily than positively charged protons, wh ...
photon. Such photons always have enough energy to qualify as ionizing radiation.
Physical effects

Nuclear effects
Neutron radiation, alpha radiation, and extremely energetic gamma (> ~20 MeV) can cause nuclear transmutation and induced radioactivity. The relevant mechanisms are neutron activation, alpha absorption, andphotodisintegration
Photodisintegration (also called phototransmutation, or a photonuclear reaction) is a nuclear process in which an atomic nucleus absorbs a high-energy gamma ray, enters an excited state, and immediately decays by emitting a subatomic particle. The ...
. A large enough number of transmutations can change macroscopic properties and cause targets to become radioactive themselves, even after the original source is removed.
Chemical effects
Ionization of molecules can lead to radiolysis (breaking chemical bonds), and formation of highly reactive free radicals. These free radicals may then react chemically with neighbouring materials even after the original radiation has stopped (e.g. ozone cracking of polymers by ozone formed by ionization of air). Ionizing radiation can also accelerate existing chemical reactions such as polymerization and corrosion, by contributing to the activation energy required for the reaction. Optical materials deteriorate under the effect of ionizing radiation. High-intensity ionizing radiation in air can produce a visible ionized air glow of telltale bluish-purple color. The glow can be observed, e.g., during criticality accidents, aroundmushroom cloud
A mushroom cloud is a distinctive mushroom-shaped flammagenitus cloud of debris, smoke, and usually condensed water vapour resulting from a large explosion. The effect is most commonly associated with a nuclear explosion, but any sufficiently e ...
s shortly after a nuclear explosion, or the inside of a damaged nuclear reactor like during the Chernobyl disaster
On 26 April 1986, the no. 4 reactor of the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant, located near Pripyat, Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic, Ukrainian SSR, Soviet Union (now Ukraine), exploded. With dozens of direct casualties, it is one of only ...
.
Monatomic fluids, e.g. molten sodium
Sodium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Na (from Neo-Latin ) and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 element, group 1 of the peri ...
, have no chemical bonds to break and no crystal lattice to disturb, so they are immune to the chemical effects of ionizing radiation. Simple diatomic compounds with very negative enthalpy of formation, such as hydrogen fluoride
Hydrogen fluoride (fluorane) is an Inorganic chemistry, inorganic compound with chemical formula . It is a very poisonous, colorless gas or liquid that dissolves in water to yield hydrofluoric acid. It is the principal industrial source of fluori ...
will reform rapidly and spontaneously after ionization.
Electrical effects
The ionization of materials temporarily increases their conductivity, potentially permitting damaging current levels. This is a particular hazard insemiconductor
A semiconductor is a material with electrical conductivity between that of a conductor and an insulator. Its conductivity can be modified by adding impurities (" doping") to its crystal structure. When two regions with different doping level ...
microelectronics used in electronic equipment; subsequent currents introduce operation errors or even permanently damage the devices. Devices intended for high-radiation environments such as the nuclear industry or outer space, may be made ''radiation hard'' to resist such effects through design, material selection, and fabrication methods.
Ionizing radiation can cause an increase in the density of interface traps by reactivating passivated dangling bonds at interfaces between two materials, such as the Si/SiO2 interface in CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS, pronounced "sea-moss
", , ) is a type of MOSFET, metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) semiconductor device fabrication, fabrication process that uses complementary an ...
devices. These traps can capture charge carriers, resulting in parasitic effects including mobility degradation, increased noise
Noise is sound, chiefly unwanted, unintentional, or harmful sound considered unpleasant, loud, or disruptive to mental or hearing faculties. From a physics standpoint, there is no distinction between noise and desired sound, as both are vibrat ...
, and threshold voltage shifts.
Proton radiation found in space can also cause single-event upsets in digital circuits. The electrical effects of ionizing radiation are exploited in gas-filled radiation detectors, e.g. the Geiger counter or the ion chamber.
Health effects
Most adverse health effects of exposure to ionizing radiation may be grouped in two general categories: * deterministic effects (harmful tissue reactions) due in large part to killing or malfunction of cells following high doses from radiation burns. * stochastic effects, i.e.,cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Po ...
and heritable effects involving either cancer development in exposed individuals owing to mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, ...
of somatic cells or heritable disease in their offspring owing to mutation of reproductive (germ) cells.
The most common impact is stochastic radiation-induced cancer with a latent period of years or decades after exposure. For example, ionizing radiation is one cause of chronic myelogenous leukemia, although most people with CML have not been exposed to radiation. The mechanism by which this occurs is well understood, but quantitative models predicting the level of risk remain controversial.
The most widely accepted model, the Linear no-threshold model (LNT), holds that the incidence of cancers due to ionizing radiation increases linearly with effective radiation dose at a rate of 5.5% per sievert
The sievert (symbol: SvPlease note there are two non-SI units that use the same Sv abbreviation: the sverdrup and svedberg.) is a derived unit in the International System of Units (SI) intended to represent the stochastic health risk of ionizin ...
. If this is correct, then natural background radiation is the most hazardous source of radiation to general public health, followed by medical imaging as a close second. Other stochastic effects of ionizing radiation are teratogenesis, cognitive decline, and heart disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is any disease involving the heart or blood vessels. CVDs constitute a class of diseases that includes: coronary artery diseases (e.g. angina pectoris, angina, myocardial infarction, heart attack), heart failure, ...
.
Though DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid (; DNA) is a polymer composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix. The polymer carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of al ...
is always susceptible to damage by ionizing radiation, the DNA molecule may also be damaged by radiation with enough energy to excite certain molecular bonds to form pyrimidine dimers. This energy may be less than ionizing, but near to it. A good example is ultraviolet spectrum energy which begins at about 3.1 eV (400 nm) at close to the same energy level which can cause sunburn
Sunburn is a form of radiation burn that affects living tissue, such as skin, that results from an overexposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation, usually from the Sun. Common symptoms in humans and other animals include red or reddish skin tha ...
to unprotected skin, as a result of photoreactions in collagen
Collagen () is the main structural protein in the extracellular matrix of the connective tissues of many animals. It is the most abundant protein in mammals, making up 25% to 35% of protein content. Amino acids are bound together to form a trip ...
and (in the UV-B range) also damage in DNA (for example, pyrimidine dimers). Thus, the mid and lower ultraviolet electromagnetic spectrum is damaging to biological tissues as a result of electronic excitation in molecules which falls short of ionization, but produces similar non-thermal effects. To some extent, visible light and also ultraviolet A (UVA) which is closest to visible energies, have been proven to result in formation of reactive oxygen species
In chemistry and biology, reactive oxygen species (ROS) are highly Reactivity (chemistry), reactive chemicals formed from diatomic oxygen (), water, and hydrogen peroxide. Some prominent ROS are hydroperoxide (H2O2), superoxide (O2−), hydroxyl ...
in skin, which cause indirect damage since these are electronically excited molecules which can inflict reactive damage, although they do not cause sunburn (erythema). Like ionization-damage, all these effects in skin are beyond those produced by simple thermal effects.
Measurement of radiation
The table below shows radiation and dose quantities in SI and non-SI units.
Uses of radiation
Ionizing radiation has many industrial, military, and medical uses. Its usefulness must be balanced with its hazards, a compromise that has shifted over time. For example, at one time, assistants in shoe shops in the US used X-rays to check a child's shoe size, but this practice was halted when the risks of ionizing radiation were better understood. Neutron radiation is essential to the working ofnuclear reactor
A nuclear reactor is a device used to initiate and control a Nuclear fission, fission nuclear chain reaction. They are used for Nuclear power, commercial electricity, nuclear marine propulsion, marine propulsion, Weapons-grade plutonium, weapons ...
s and nuclear weapon
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission (fission or atomic bomb) or a combination of fission and fusion reactions (thermonuclear weapon), producing a nuclear exp ...
s. The penetrating power of x-ray, gamma, beta, and positron radiation is used for medical imaging
Medical imaging is the technique and process of imaging the interior of a body for clinical analysis and medical intervention, as well as visual representation of the function of some organs or tissues (physiology). Medical imaging seeks to revea ...
, nondestructive testing
Nondestructive testing (NDT) is any of a wide group of analysis techniques used in science and technology industry to evaluate the properties of a material, component or system without causing damage.
The terms nondestructive examination (NDE), n ...
, and a variety of industrial gauges. Radioactive tracers are used in medical and industrial applications, as well as biological and radiation chemistry. Alpha radiation is used in static eliminators and smoke detectors. The sterilizing effects of ionizing radiation are useful for cleaning medical instruments, food irradiation, and the sterile insect technique. Measurements of carbon-14
Carbon-14, C-14, C or radiocarbon, is a radioactive isotope of carbon with an atomic nucleus containing 6 protons and 8 neutrons. Its presence in organic matter is the basis of the radiocarbon dating method pioneered by Willard Libby and coll ...
, is used for radiocarbon dating
Radiocarbon dating (also referred to as carbon dating or carbon-14 dating) is a method for Chronological dating, determining the age of an object containing organic material by using the properties of carbon-14, radiocarbon, a radioactive Isotop ...
.
Sources of radiation
Ionizing radiation is generated through nuclear reactions, nuclear decay, by very high temperature, or via acceleration of charged particles in electromagnetic fields. Natural sources include the Sun, lightning and supernova explosions. Artificial sources include nuclear reactors, particle accelerators, and x-ray tubes. The United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation (UNSCEAR) itemized types of human exposures. The International Commission on Radiological Protection manages the International System of Radiological Protection, which sets recommended limits for dose uptake.Background radiation
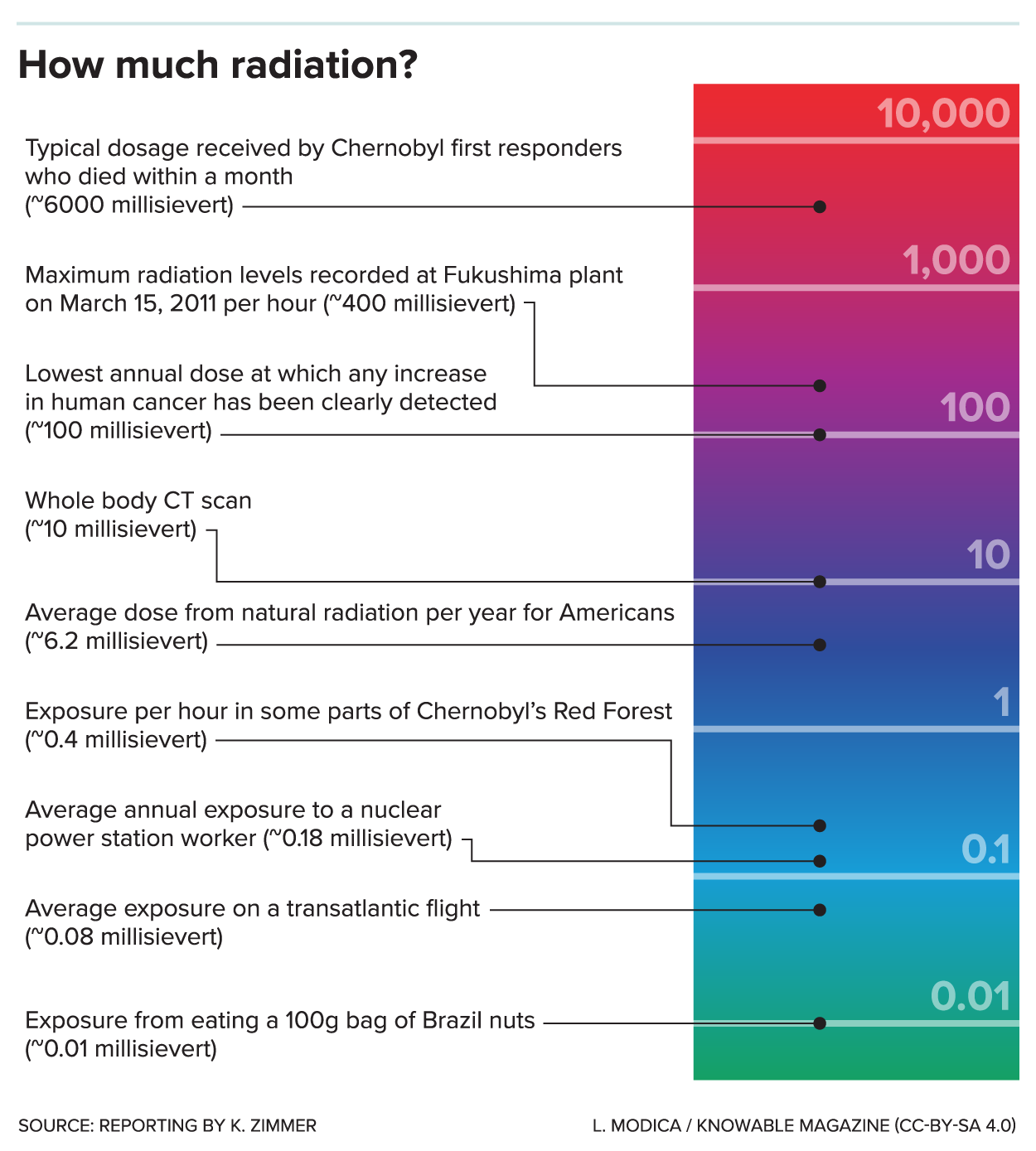
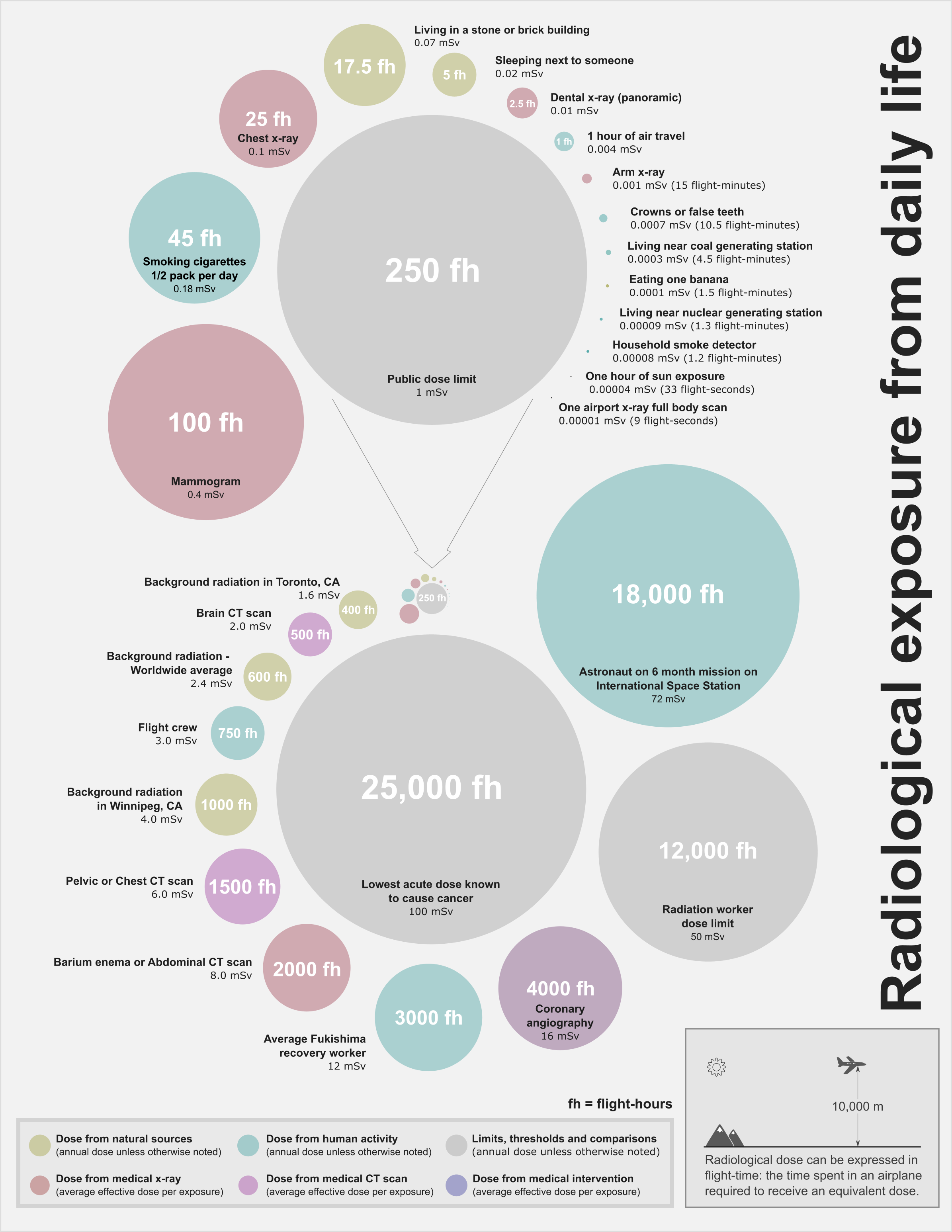
Background radiation comes from both natural and human-made sources. The global average exposure of humans to ionizing radiation is about 3 mSv (0.3 rem) per year, 80% of which comes from nature. The remaining 20% results from exposure to human-made radiation sources, mainlymedical imaging
Medical imaging is the technique and process of imaging the interior of a body for clinical analysis and medical intervention, as well as visual representation of the function of some organs or tissues (physiology). Medical imaging seeks to revea ...
. Average human-made exposure is much higher in developed countries, mostly due to CT scans and nuclear medicine
Nuclear medicine (nuclear radiology, nucleology), is a medical specialty involving the application of radioactivity, radioactive substances in the diagnosis and treatment of disease. Nuclear imaging is, in a sense, ''radiology done inside out'', ...
.
Natural background radiation comes from five primary sources: cosmic radiation, solar radiation, external terrestrial sources, radiation in the human body, and radon
Radon is a chemical element; it has symbol Rn and atomic number 86. It is a radioactive noble gas and is colorless and odorless. Of the three naturally occurring radon isotopes, only Rn has a sufficiently long half-life (3.825 days) for it to b ...
.
The background rate for natural radiation varies considerably with location, being as low as 1.5 mSv/a (1.5 mSv per year) in some areas and over 100 mSv/a in others. The highest level of purely natural radiation recorded on the Earth's surface is 90 μGy/h (0.8 Gy/a) on a Brazilian black beach composed of monazite. The highest background radiation in an inhabited area is found in Ramsar, mainly due to naturally radioactive limestone used as a building material. Some 2000 of the most exposed residents receive an average radiation dose
Ionizing (ionising) radiation, including nuclear radiation, consists of subatomic particles or electromagnetic waves that have enough energy per individual photon or particle to ionize atoms or molecules by detaching electrons from them. Some pa ...
of 10 mGy per year, (1 rad/yr) ten times more than the ICRP recommended limit for exposure to the public from artificial sources. Record levels were found in a house where the effective radiation dose due to external radiation was 135 mSv/a, (13.5 rem/yr) and the committed dose from radon
Radon is a chemical element; it has symbol Rn and atomic number 86. It is a radioactive noble gas and is colorless and odorless. Of the three naturally occurring radon isotopes, only Rn has a sufficiently long half-life (3.825 days) for it to b ...
was 640 mSv/a (64.0 rem/yr). This unique case is over 200 times higher than the world average background radiation. Despite the high levels of background radiation that the residents of Ramsar receive there is no compelling evidence that they experience a greater health risk. The ICRP recommendations are conservative limits and may represent an over representation of the actual health risk. Generally radiation safety organization recommend the most conservative limits assuming it is best to err on the side of caution. This level of caution is appropriate but should not be used to create fear about background radiation danger. Radiation danger from background radiation may be a serious threat but is more likely a small overall risk compared to all other factors in the environment.
Cosmic radiation
The Earth, and all living things on it, are constantly bombarded by radiation from outside theSolar System
The Solar SystemCapitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Sola ...
. This cosmic radiation consists of relativistic particles: positively charged nuclei (ions) from 1 amu proton
A proton is a stable subatomic particle, symbol , Hydron (chemistry), H+, or 1H+ with a positive electric charge of +1 ''e'' (elementary charge). Its mass is slightly less than the mass of a neutron and approximately times the mass of an e ...
s (about 85% of it) to ~56 amu iron
Iron is a chemical element; it has symbol Fe () and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, forming much of Earth's o ...
nuclei and even beyond. (The high-atomic number particles are called HZE ions.) The energy of this radiation can far exceed that which humans can create, even in the largest particle accelerator
A particle accelerator is a machine that uses electromagnetic fields to propel electric charge, charged particles to very high speeds and energies to contain them in well-defined particle beam, beams. Small accelerators are used for fundamental ...
s (see ultra-high-energy cosmic ray). This radiation interacts in the atmosphere to create secondary radiation that rains down, including x-rays
An X-ray (also known in many languages as Röntgen radiation) is a form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than those of ultraviolet rays and longer than those of gamma rays. Roughly, X-rays have a wavelength ran ...
, muon
A muon ( ; from the Greek letter mu (μ) used to represent it) is an elementary particle similar to the electron, with an electric charge of −1 '' e'' and a spin of ''ħ'', but with a much greater mass. It is classified as a ...
s, proton
A proton is a stable subatomic particle, symbol , Hydron (chemistry), H+, or 1H+ with a positive electric charge of +1 ''e'' (elementary charge). Its mass is slightly less than the mass of a neutron and approximately times the mass of an e ...
s, antiproton
The antiproton, , (pronounced ''p-bar'') is the antiparticle of the proton. Antiprotons are stable, but they are typically short-lived, since any collision with a proton will cause both particles to be annihilated in a burst of energy.
The exis ...
s, alpha particle
Alpha particles, also called alpha rays or alpha radiation, consist of two protons and two neutrons bound together into a particle identical to a helium-4 nucleus. They are generally produced in the process of alpha decay but may also be produce ...
s, pion
In particle physics, a pion (, ) or pi meson, denoted with the Greek alphabet, Greek letter pi (letter), pi (), is any of three subatomic particles: , , and . Each pion consists of a quark and an antiquark and is therefore a meson. Pions are the ...
s, electron
The electron (, or in nuclear reactions) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary charge, elementary electric charge. It is a fundamental particle that comprises the ordinary matter that makes up the universe, along with up qua ...
s, positron
The positron or antielectron is the particle with an electric charge of +1''elementary charge, e'', a Spin (physics), spin of 1/2 (the same as the electron), and the same Electron rest mass, mass as an electron. It is the antiparticle (antimatt ...
s, and neutron
The neutron is a subatomic particle, symbol or , that has no electric charge, and a mass slightly greater than that of a proton. The Discovery of the neutron, neutron was discovered by James Chadwick in 1932, leading to the discovery of nucle ...
s.
The dose from cosmic radiation is largely from muons, neutrons, and electrons, with a dose rate that varies in different parts of the world and based largely on the geomagnetic field, altitude, and solar cycle. The cosmic-radiation dose rate on airplanes is so high that, according to the United Nations UNSCEAR 2000 Report (see links at bottom), airline flight crew workers receive more dose on average than any other worker, including those in nuclear power plants. Airline crews receive more cosmic rays if they routinely work flight routes that take them close to the North or South pole at high altitudes, where this type of radiation is maximal.
Cosmic rays also include high-energy gamma rays, which are far beyond the energies produced by solar or human sources.
External terrestrial sources
Most materials on Earth contain some radioactiveatom
Atoms are the basic particles of the chemical elements. An atom consists of a atomic nucleus, nucleus of protons and generally neutrons, surrounded by an electromagnetically bound swarm of electrons. The chemical elements are distinguished fr ...
s, even if in small quantities. Most of the dose received from these sources is from gamma-ray emitters in building materials, or rocks and soil when outside. The major radionuclide
A radionuclide (radioactive nuclide, radioisotope or radioactive isotope) is a nuclide that has excess numbers of either neutrons or protons, giving it excess nuclear energy, and making it unstable. This excess energy can be used in one of three ...
s of concern for terrestrial radiation are isotopes of potassium
Potassium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol K (from Neo-Latin ) and atomic number19. It is a silvery white metal that is soft enough to easily cut with a knife. Potassium metal reacts rapidly with atmospheric oxygen to ...
, uranium
Uranium is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol U and atomic number 92. It is a silvery-grey metal in the actinide series of the periodic table. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons. Ura ...
, and thorium
Thorium is a chemical element; it has symbol Th and atomic number 90. Thorium is a weakly radioactive light silver metal which tarnishes olive grey when it is exposed to air, forming thorium dioxide; it is moderately soft, malleable, and ha ...
. Each of these sources has been decreasing in activity since the formation of the Earth.
Internal radiation sources
All earthly materials that are the building blocks of life contain a radioactive component. As organisms consume food, air, and water, an inventory of radioisotopes builds up within the organism (seebanana equivalent dose
Banana equivalent dose (BED) is an informal unit of measurement of ionizing radiation exposure, intended as a general educational example to compare a dose of radioactivity to the dose one is exposed to by eating one average-sized banana. Bananas ...
). Some radionuclides, like potassium-40
Potassium-40 (K) is a long lived and the main naturally occurring radioactive isotope of potassium. Its half-life is 1.25 billion years. It makes up about 0.012% (120 parts-per notation, ppm) of natural potassium.
Potassium-40 undergoes four dif ...
, emit a high-energy gamma ray that can be measured by sensitive electronic radiation measurement systems. These internal radiation sources contribute to an individual's total radiation dose from natural background radiation.
Radon
An important source of natural radiation isradon
Radon is a chemical element; it has symbol Rn and atomic number 86. It is a radioactive noble gas and is colorless and odorless. Of the three naturally occurring radon isotopes, only Rn has a sufficiently long half-life (3.825 days) for it to b ...
gas, which seeps continuously from bedrock but can, because of its high density, accumulate in poorly ventilated houses.
Radon-222 is a gas produced by the α-decay of radium
Radium is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Ra and atomic number 88. It is the sixth element in alkaline earth metal, group 2 of the periodic table, also known as the alkaline earth metals. Pure radium is silvery-white, ...
-226. Both are a part of the natural uranium
Uranium is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol U and atomic number 92. It is a silvery-grey metal in the actinide series of the periodic table. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons. Ura ...
decay chain. Uranium is found in soil throughout the world in varying concentrations. Radon is the largest cause of lung cancer among non-smokers and the second-leading cause overall.
Radiation exposure

 There are three standard ways to limit exposure:
# Time: For people exposed to radiation in addition to natural background radiation, limiting or minimizing the exposure time will reduce the dose from the source of radiation.
# Distance: Radiation intensity decreases sharply with distance, according to an inverse-square law (in an absolute vacuum).Camphausen KA, Lawrence RC
There are three standard ways to limit exposure:
# Time: For people exposed to radiation in addition to natural background radiation, limiting or minimizing the exposure time will reduce the dose from the source of radiation.
# Distance: Radiation intensity decreases sharply with distance, according to an inverse-square law (in an absolute vacuum).Camphausen KA, Lawrence RC"Principles of Radiation Therapy"
in Pazdur R, Wagman LD, Camphausen KA, Hoskins WJ (Eds
Cancer Management: A Multidisciplinary Approach
. 11 ed. 2008. # Shielding: Air or skin can be sufficient to substantially attenuate alpha radiation, while sheet metal or plastic is often sufficient to stop beta radiation. Barriers of
lead
Lead () is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol Pb (from Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a Heavy metal (elements), heavy metal that is density, denser than most common materials. Lead is Mohs scale, soft and Ductility, malleabl ...
, concrete
Concrete is a composite material composed of aggregate bound together with a fluid cement that cures to a solid over time. It is the second-most-used substance (after water), the most–widely used building material, and the most-manufactur ...
, or water are often used to give effective protection from more penetrating forms of ionizing radiation such as gamma rays and neutrons. Some radioactive materials are stored or handled underwater or by remote control
A remote control, also known colloquially as a remote or clicker, is an consumer electronics, electronic device used to operate another device from a distance, usually wirelessly. In consumer electronics, a remote control can be used to operat ...
in rooms constructed of thick concrete or lined with lead. There are special plastic
Plastics are a wide range of synthetic polymers, synthetic or Semisynthesis, semisynthetic materials composed primarily of Polymer, polymers. Their defining characteristic, Plasticity (physics), plasticity, allows them to be Injection moulding ...
shields that stop beta particles, and air will stop most alpha particles. The effectiveness of a material in shielding radiation is determined by its half-value thicknesses, the thickness of material that reduces the radiation by half. This value is a function of the material itself and of the type and energy of ionizing radiation. Some generally accepted thicknesses of attenuating material are 5 mm of aluminum for most beta particles, and 3 inches of lead for gamma radiation.
These can all be applied to natural and human-made sources. For human-made sources the use of Containment is a major tool in reducing dose uptake and is effectively a combination of shielding and isolation from the open environment. Radioactive materials are confined in the smallest possible space and kept out of the environment such as in a hot cell (for radiation) or glove box (for contamination). Radioactive isotope
A radionuclide (radioactive nuclide, radioisotope or radioactive isotope) is a nuclide that has excess numbers of either neutrons or protons, giving it excess nuclear energy, and making it unstable. This excess energy can be used in one of three ...
s for medical use, for example, are dispensed in closed handling facilities, usually gloveboxes, while nuclear reactor
A nuclear reactor is a device used to initiate and control a Nuclear fission, fission nuclear chain reaction. They are used for Nuclear power, commercial electricity, nuclear marine propulsion, marine propulsion, Weapons-grade plutonium, weapons ...
s operate within closed systems with multiple barriers that keep the radioactive materials contained. Work rooms, hot cells and gloveboxes have slightly reduced air pressures to prevent escape of airborne material to the open environment.
In nuclear conflicts or civil nuclear releases civil defense
Civil defense or civil protection is an effort to protect the citizens of a state (generally non-combatants) from human-made and natural disasters. It uses the principles of emergency management: Risk management, prevention, mitigation, prepara ...
measures can help reduce exposure of populations by reducing ingestion of isotopes and occupational exposure. One is the issue of potassium iodide (KI) tablets, which blocks the uptake of radioactive iodine
There are 40 known isotopes of iodine (53I) from 108I to 147I; all undergo radioactive decay except 127I, which is stable. Iodine is thus a monoisotopic element.
Its longest-lived radioactive isotope, 129I, has a half-life of 16.14 million year ...
(one of the major radioisotope products of nuclear fission
Nuclear fission is a reaction in which the nucleus of an atom splits into two or more smaller nuclei. The fission process often produces gamma photons, and releases a very large amount of energy even by the energetic standards of radioactiv ...
) into the human thyroid gland.
Occupational exposure
Occupationally exposed individuals are controlled within the regulatory framework of the country they work in, and in accordance with any local nuclear licence constraints. These are usually based on the recommendations of the International Commission on Radiological Protection. The ICRP recommends limiting artificial irradiation. For occupational exposure, the limit is 50 mSv in a single year with a maximum of 100 mSv in a consecutive five-year period. The radiation exposure of these individuals is carefully monitored with the use ofdosimeter
A radiation dosimeter is a device that measures the equivalent dose, dose uptake of external ionizing radiation. It is worn by the person being monitored when used as a personal dosimeter, and is a record of the radiation dose received. Modern el ...
s and other radiological protection instruments which will measure radioactive particulate concentrations, area gamma dose readings and radioactive contamination
Radioactive contamination, also called radiological pollution, is the deposition of, or presence of Radioactive decay, radioactive substances on surfaces or within solids, liquids, or gases (including the human body), where their presence is uni ...
. A legal record of dose is kept.
Examples of activities where occupational exposure is a concern include:
* Airline crew (the most exposed population)
* Industrial radiography
Industrial radiography is a modality of non-destructive testing that uses ionizing radiation to inspect materials and components with the objective of locating and quantifying defects and degradation in material properties that would lead to the ...
* Medical radiology
Radiology ( ) is the medical specialty that uses medical imaging to diagnose diseases and guide treatment within the bodies of humans and other animals. It began with radiography (which is why its name has a root referring to radiation), but tod ...
and nuclear medicine
Nuclear medicine (nuclear radiology, nucleology), is a medical specialty involving the application of radioactivity, radioactive substances in the diagnosis and treatment of disease. Nuclear imaging is, in a sense, ''radiology done inside out'', ...
* Uranium mining
* Nuclear power plant
A nuclear power plant (NPP), also known as a nuclear power station (NPS), nuclear generating station (NGS) or atomic power station (APS) is a thermal power station in which the heat source is a nuclear reactor. As is typical of thermal power st ...
and nuclear fuel reprocessing plant workers
* Research laboratories (government, university and private)
Some human-made radiation sources affect the body through direct radiation, known as effective dose (radiation) while others take the form of radioactive contamination
Radioactive contamination, also called radiological pollution, is the deposition of, or presence of Radioactive decay, radioactive substances on surfaces or within solids, liquids, or gases (including the human body), where their presence is uni ...
and irradiate the body from within. The latter is known as committed dose.
Public exposure
Medical procedures, such as diagnosticX-ray
An X-ray (also known in many languages as Röntgen radiation) is a form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than those of ultraviolet rays and longer than those of gamma rays. Roughly, X-rays have a wavelength ran ...
s, nuclear medicine
Nuclear medicine (nuclear radiology, nucleology), is a medical specialty involving the application of radioactivity, radioactive substances in the diagnosis and treatment of disease. Nuclear imaging is, in a sense, ''radiology done inside out'', ...
, and radiation therapy
Radiation therapy or radiotherapy (RT, RTx, or XRT) is a therapy, treatment using ionizing radiation, generally provided as part of treatment of cancer, cancer therapy to either kill or control the growth of malignancy, malignant cell (biology), ...
are by far the most significant source of human-made radiation exposure to the general public. Some of the major radionuclide
A radionuclide (radioactive nuclide, radioisotope or radioactive isotope) is a nuclide that has excess numbers of either neutrons or protons, giving it excess nuclear energy, and making it unstable. This excess energy can be used in one of three ...
s used are I-131, Tc-99m, Co-60, Ir-192, and Cs-137. The public is also exposed to radiation from consumer products, such as tobacco
Tobacco is the common name of several plants in the genus '' Nicotiana'' of the family Solanaceae, and the general term for any product prepared from the cured leaves of these plants. More than 70 species of tobacco are known, but the ...
( polonium-210), combustible fuels (gas, coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other Chemical element, elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen.
Coal i ...
, etc.), television
Television (TV) is a telecommunication medium for transmitting moving images and sound. Additionally, the term can refer to a physical television set rather than the medium of transmission. Television is a mass medium for advertising, ...
s, luminous watch
A watch is a timepiece carried or worn by a person. It is designed to maintain a consistent movement despite the motions caused by the person's activities. A wristwatch is worn around the wrist, attached by a watch strap or another type of ...
es and dials (tritium
Tritium () or hydrogen-3 (symbol T or H) is a rare and radioactive isotope of hydrogen with a half-life of ~12.33 years. The tritium nucleus (t, sometimes called a ''triton'') contains one proton and two neutrons, whereas the nucleus of the ...
), airport X-ray
An X-ray (also known in many languages as Röntgen radiation) is a form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than those of ultraviolet rays and longer than those of gamma rays. Roughly, X-rays have a wavelength ran ...
systems, smoke detectors (americium
Americium is a synthetic element, synthetic chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol Am and atomic number 95. It is radioactive and a transuranic member of the actinide series in the periodic table, located under the lanthanide element e ...
), electron tubes, and gas lantern mantles (thorium
Thorium is a chemical element; it has symbol Th and atomic number 90. Thorium is a weakly radioactive light silver metal which tarnishes olive grey when it is exposed to air, forming thorium dioxide; it is moderately soft, malleable, and ha ...
).
Of lesser magnitude, members of the public are exposed to radiation from the nuclear fuel
Nuclear fuel refers to any substance, typically fissile material, which is used by nuclear power stations or other atomic nucleus, nuclear devices to generate energy.
Oxide fuel
For fission reactors, the fuel (typically based on uranium) is ...
cycle, which includes the entire sequence from processing uranium
Uranium is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol U and atomic number 92. It is a silvery-grey metal in the actinide series of the periodic table. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons. Ura ...
to the disposal of the spent fuel. The effects of such exposure have not been reliably measured due to the extremely low doses involved. Opponents use a cancer per dose model to assert that such activities cause several hundred cases of cancer per year, an application of the widely accepted Linear no-threshold model (LNT).
The International Commission on Radiological Protection recommends limiting artificial irradiation to the public to an average of 1 mSv (0.001 Sv) of effective dose per year, not including medical and occupational exposures.
In a nuclear war
Nuclear warfare, also known as atomic warfare, is a War, military conflict or prepared Policy, political strategy that deploys nuclear weaponry. Nuclear weapons are Weapon of mass destruction, weapons of mass destruction; in contrast to conven ...
, gamma rays from both the initial weapon explosion and fallout would be sources of radiation exposure.
Spaceflight
Massive particles are a concern for astronauts outside theEarth's magnetic field
Earth's magnetic field, also known as the geomagnetic field, is the magnetic field that extends from structure of Earth, Earth's interior out into space, where it interacts with the solar wind, a stream of charged particles emanating from ...
who would receive solar particles from solar proton events (SPE) and galactic cosmic rays from cosmic sources. These high-energy charged nuclei are blocked by Earth's magnetic field but pose a major health concern for astronauts traveling to the Moon and to any distant location beyond Earth orbit. Highly charged HZE ions in particular are known to be extremely damaging, though protons make up the vast majority of galactic cosmic rays. Evidence indicates past SPE radiation levels that would have been lethal for unprotected astronauts.
Air travel
Air travel exposes people on aircraft to increased radiation from space as compared to sea level, includingcosmic rays
Cosmic rays or astroparticles are high-energy particles or clusters of particles (primarily represented by protons or atomic nuclei) that move through space at nearly the speed of light. They originate from the Sun, from outside of the Solar ...
and from solar flare
A solar flare is a relatively intense, localized emission of electromagnetic radiation in the Sun's atmosphere. Flares occur in active regions and are often, but not always, accompanied by coronal mass ejections, solar particle events, and ot ...
events. Software programs such as Epcard, CARI, SIEVERT, PCAIRE are attempts to simulate exposure by aircrews and passengers. An example of a measured dose (not simulated dose) is 6 μSv per hour from London Heathrow to Tokyo Narita on a polar route. However, dosages can vary, such as during periods of high solar activity. The United States FAA requires airlines to provide flight crew with information about cosmic radiation, and an International Commission on Radiological Protection recommendation for the general public is no more than 1 mSv per year. Also, many airlines do not allow pregnant
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring gestation, gestates inside a woman's uterus. A multiple birth, multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Conception (biology), Conception usually occurs ...
flightcrew members, to comply with a European Directive. The FAA has a recommended limit of 1 mSv total for a pregnancy, and no more than 0.5 mSv per month. Information originally based on ''Fundamentals of Aerospace Medicine'' published in 2008.
Radiation hazard warning signs
Hazardous levels of ionizing radiation are signified by the trefoil sign on a yellow background. These are usually posted at the boundary of a radiation controlled area or in any place where radiation levels are significantly above background due to human intervention. The red ionizing radiation warning symbol (ISO 21482) was launched in 2007, and is intended for IAEA Category 1, 2 and 3 sources defined as dangerous sources capable of death or serious injury, including food irradiators, teletherapy machines for cancer treatment and industrial radiography units. The symbol is to be placed on the device housing the source, as a warning not to dismantle the device or to get any closer. It will not be visible under normal use, only if someone attempts to disassemble the device. The symbol will not be located on building access doors, transportation packages or containers.hazard symbol
Hazard symbols are universally recognized Symbol, symbols designed to alert individuals to the presence of Hazard, hazardous or dangerous materials, locations, or conditions. These include risks associated with Electromagnetic field, electromag ...
File:Logo iso radiation.svg, 2007 ISO radioactivity
Radioactive decay (also known as nuclear decay, radioactivity, radioactive disintegration, or nuclear disintegration) is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by radiation. A material containing unstable nuclei is conside ...
danger symbol intended for IAEA Category 1, 2 and 3 sources defined as dangerous sources capable of death or serious injury.
See also
* European Committee on Radiation Risk * International Commission on Radiological Protection – manages the International System of Radiological Protection * Ionometer * Irradiated mail * National Council on Radiation Protection and Measurements – US national organisation *Nuclear safety
Nuclear safety is defined by the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) as "The achievement of proper operating conditions, prevention of accidents or mitigation of accident consequences, resulting in protection of workers, the public and the ...
* Nuclear semiotics
* Radiant energy
In physics, and in particular as measured by radiometry, radiant energy is the energy of electromagnetic radiation, electromagnetic and gravitational radiation. As energy, its SI unit is the joule (J). The quantity of radiant energy may be calcul ...
* Exposure (radiation)
* Radiation hormesis
* Radiation physics
* Radiation protection
Radiation protection, also known as radiological protection, is defined by the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) as "The protection of people from harmful effects of exposure to ionizing radiation, and the means for achieving this". Exposu ...
* Radiation Protection Convention, 1960
* Radiation protection of patients
* Sievert
The sievert (symbol: SvPlease note there are two non-SI units that use the same Sv abbreviation: the sverdrup and svedberg.) is a derived unit in the International System of Units (SI) intended to represent the stochastic health risk of ionizin ...
* Treatment of infections after accidental or hostile exposure to ionizing radiation
References
Literature
*External links
The Nuclear Regulatory Commission
regulates most commercial radiation sources and non-medical exposures in the US:
NLM Hazardous Substances Databank – Ionizing Radiation
* United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation 2000 Repor
Volume 1: Sources
Beginners Guide to Ionising Radiation Measurement
* (from CT scans and xrays).
Health Physics Society Public Education Website
Basic Radiation Facts {{DEFAULTSORT:Ionizing Radiation Carcinogens Mutagens Radioactivity Radiobiology Radiation health effects Radiation protection