Infinite Dimensional Lie Group on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In mathematics, a Lie group (pronounced ) is a
 Lie groups are
Lie groups are
 The group can, however, be given a different topology, in which the distance between two points is defined as the length of the shortest path ''in the group '' joining to . In this topology, is identified homeomorphically with the real line by identifying each element with the number in the definition of . With this topology, is just the group of real numbers under addition and is therefore a Lie group.
The group is an example of a " Lie subgroup" of a Lie group that is not closed. See the discussion below of Lie subgroups in the section on basic concepts.
The group can, however, be given a different topology, in which the distance between two points is defined as the length of the shortest path ''in the group '' joining to . In this topology, is identified homeomorphically with the real line by identifying each element with the number in the definition of . With this topology, is just the group of real numbers under addition and is therefore a Lie group.
The group is an example of a " Lie subgroup" of a Lie group that is not closed. See the discussion below of Lie subgroups in the section on basic concepts.
'A'', ''B''= 0.
(In general the Lie bracket of a connected Lie group is always 0 if and only if the Lie group is abelian.) * The Lie algebra of the
'A'', ''B''= ''AB'' − ''BA''. *If ''G'' is a closed subgroup of GL(''n'', C) then the Lie algebra of ''G'' can be thought of informally as the matrices ''m'' of M(''n'', C) such that 1 + ε''m'' is in ''G'', where ε is an infinitesimal positive number with ε2 = 0 (of course, no such real number ε exists). For example, the orthogonal group O(''n'', R) consists of matrices ''A'' with ''AA''T = 1, so the Lie algebra consists of the matrices ''m'' with (1 + ε''m'')(1 + ε''m'')T = 1, which is equivalent to ''m'' + ''m''T = 0 because ε2 = 0. *The preceding description can be made more rigorous as follows. The Lie algebra of a closed subgroup ''G'' of GL(''n'', C), may be computed as : where exp(''tX'') is defined using the
 (In short, exp is a natural transformation from the functor Lie to the identity functor on the category of Lie groups.)
The exponential map from the Lie algebra to the Lie group is not always Surjective function, onto, even if the group is connected (though it does map onto the Lie group for connected groups that are either compact or nilpotent). For example, the exponential map of is not surjective. Also, the exponential map is neither surjective nor injective for infinite-dimensional (see below) Lie groups modelled on ''C''∞
(In short, exp is a natural transformation from the functor Lie to the identity functor on the category of Lie groups.)
The exponential map from the Lie algebra to the Lie group is not always Surjective function, onto, even if the group is connected (though it does map onto the Lie group for connected groups that are either compact or nilpotent). For example, the exponential map of is not surjective. Also, the exponential map is neither surjective nor injective for infinite-dimensional (see below) Lie groups modelled on ''C''∞
Borel's review
* * . * . * * * . The 2003 reprint corrects several typographical mistakes. * * . * * Heldermann Verla
* * .
Lie Groups. Representation Theory and Symmetric Spaces
Wolfgang Ziller, Vorlesung 2010
group
A group is a number of persons or things that are located, gathered, or classed together.
Groups of people
* Cultural group, a group whose members share the same cultural identity
* Ethnic group, a group whose members share the same ethnic ide ...
that is also a differentiable manifold. A manifold is a space that locally resembles Euclidean space
Euclidean space is the fundamental space of geometry, intended to represent physical space. Originally, that is, in Euclid's ''Elements'', it was the three-dimensional space of Euclidean geometry, but in modern mathematics there are Euclidean ...
, whereas groups define the abstract concept of a binary operation along with the additional properties it must have to be thought of as a "transformation" in the abstract sense, for instance multiplication and the taking of inverses (division), or equivalently, the concept of addition and the taking of inverses (subtraction). Combining these two ideas, one obtains a continuous group
In mathematics, topological groups are logically the combination of Group (mathematics), groups and Topological space, topological spaces, i.e. they are groups and topological spaces at the same time, such that the Continuous function, continui ...
where multiplying points and their inverses are continuous. If the multiplication and taking of inverses are smooth
Smooth may refer to:
Mathematics
* Smooth function, a function that is infinitely differentiable; used in calculus and topology
* Smooth manifold, a differentiable manifold for which all the transition maps are smooth functions
* Smooth algebrai ...
(differentiable) as well, one obtains a Lie group.
Lie groups provide a natural model for the concept of continuous symmetry
In mathematics, continuous symmetry is an intuitive idea corresponding to the concept of viewing some symmetries as motions, as opposed to discrete symmetry, e.g. reflection symmetry, which is invariant under a kind of flip from one state to ano ...
, a celebrated example of which is the rotational symmetry in three dimensions (given by the special orthogonal group ). Lie groups are widely used in many parts of modern mathematics and physics
Physics is the natural science that studies matter, its fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge which r ...
.
Lie groups were first found by studying matrix subgroups contained in or , the groups of invertible matrices over or . These are now called the classical group
In mathematics, the classical groups are defined as the special linear groups over the reals , the complex numbers and the quaternions together with special automorphism groups of symmetric or skew-symmetric bilinear forms and Hermitian or s ...
s, as the concept has been extended far beyond these origins. Lie groups are named after Norwegian mathematician Sophus Lie
Marius Sophus Lie ( ; ; 17 December 1842 – 18 February 1899) was a Norwegian mathematician. He largely created the theory of continuous symmetry and applied it to the study of geometry and differential equations.
Life and career
Marius Soph ...
(1842–1899), who laid the foundations of the theory of continuous transformation group
In mathematics, the automorphism group of an object ''X'' is the group consisting of automorphisms of ''X'' under composition of morphisms. For example, if ''X'' is a finite-dimensional vector space, then the automorphism group of ''X'' is the gr ...
s. Lie's original motivation for introducing Lie groups was to model the continuous symmetries of differential equations, in much the same way that finite groups are used in Galois theory
In mathematics, Galois theory, originally introduced by Évariste Galois, provides a connection between field theory and group theory. This connection, the fundamental theorem of Galois theory, allows reducing certain problems in field theory to ...
to model the discrete symmetries of algebraic equation
In mathematics, an algebraic equation or polynomial equation is an equation of the form
:P = 0
where ''P'' is a polynomial with coefficients in some field, often the field of the rational numbers. For many authors, the term ''algebraic equation'' ...
s.
History
According to the most authoritative source on the early history of Lie groups (Hawkins, p. 1),Sophus Lie
Marius Sophus Lie ( ; ; 17 December 1842 – 18 February 1899) was a Norwegian mathematician. He largely created the theory of continuous symmetry and applied it to the study of geometry and differential equations.
Life and career
Marius Soph ...
himself considered the winter of 1873–1874 as the birth date of his theory of continuous groups. Hawkins, however, suggests that it was "Lie's prodigious research activity during the four-year period from the fall of 1869 to the fall of 1873" that led to the theory's creation (''ibid''). Some of Lie's early ideas were developed in close collaboration with Felix Klein
Christian Felix Klein (; 25 April 1849 – 22 June 1925) was a German mathematician and mathematics educator, known for his work with group theory, complex analysis, non-Euclidean geometry, and on the associations between geometry and grou ...
. Lie met with Klein every day from October 1869 through 1872: in Berlin from the end of October 1869 to the end of February 1870, and in Paris, Göttingen and Erlangen in the subsequent two years (''ibid'', p. 2). Lie stated that all of the principal results were obtained by 1884. But during the 1870s all his papers (except the very first note) were published in Norwegian journals, which impeded recognition of the work throughout the rest of Europe (''ibid'', p. 76). In 1884 a young German mathematician, Friedrich Engel, came to work with Lie on a systematic treatise to expose his theory of continuous groups. From this effort resulted the three-volume ''Theorie der Transformationsgruppen'', published in 1888, 1890, and 1893. The term ''groupes de Lie'' first appeared in French in 1893 in the thesis of Lie's student Arthur Tresse.
Lie's ideas did not stand in isolation from the rest of mathematics. In fact, his interest in the geometry of differential equations was first motivated by the work of Carl Gustav Jacobi
Carl Gustav Jacob Jacobi (; ; 10 December 1804 – 18 February 1851) was a German mathematician who made fundamental contributions to elliptic functions, dynamics, differential equations, determinants, and number theory. His name is occas ...
, on the theory of partial differential equations of first order and on the equations of classical mechanics
Classical mechanics is a physical theory describing the motion of macroscopic objects, from projectiles to parts of machinery, and astronomical objects, such as spacecraft, planets, stars, and galaxies. For objects governed by classi ...
. Much of Jacobi's work was published posthumously in the 1860s, generating enormous interest in France and Germany (Hawkins, p. 43). Lie's ''idée fixe'' was to develop a theory of symmetries of differential equations that would accomplish for them what Évariste Galois
Évariste Galois (; ; 25 October 1811 – 31 May 1832) was a French mathematician and political activist. While still in his teens, he was able to determine a necessary and sufficient condition for a polynomial to be solvable by radicals, ...
had done for algebraic equations: namely, to classify them in terms of group theory. Lie and other mathematicians showed that the most important equations for special function
Special functions are particular mathematical functions that have more or less established names and notations due to their importance in mathematical analysis, functional analysis, geometry, physics, or other applications.
The term is defined b ...
s and orthogonal polynomials
In mathematics, an orthogonal polynomial sequence is a family of polynomials such that any two different polynomials in the sequence are orthogonal to each other under some inner product.
The most widely used orthogonal polynomials are the class ...
tend to arise from group theoretical symmetries. In Lie's early work, the idea was to construct a theory of ''continuous groups'', to complement the theory of discrete group
In mathematics, a topological group ''G'' is called a discrete group if there is no limit point in it (i.e., for each element in ''G'', there is a neighborhood which only contains that element). Equivalently, the group ''G'' is discrete if and o ...
s that had developed in the theory of modular forms, in the hands of Felix Klein
Christian Felix Klein (; 25 April 1849 – 22 June 1925) was a German mathematician and mathematics educator, known for his work with group theory, complex analysis, non-Euclidean geometry, and on the associations between geometry and grou ...
and Henri Poincaré. The initial application that Lie had in mind was to the theory of differential equation
In mathematics, a differential equation is an equation that relates one or more unknown functions and their derivatives. In applications, the functions generally represent physical quantities, the derivatives represent their rates of change, an ...
s. On the model of Galois theory
In mathematics, Galois theory, originally introduced by Évariste Galois, provides a connection between field theory and group theory. This connection, the fundamental theorem of Galois theory, allows reducing certain problems in field theory to ...
and polynomial equation
In mathematics, an algebraic equation or polynomial equation is an equation of the form
:P = 0
where ''P'' is a polynomial with coefficients in some field (mathematics), field, often the field of the rational numbers. For many authors, the term '' ...
s, the driving conception was of a theory capable of unifying, by the study of symmetry, the whole area of ordinary differential equation
In mathematics, an ordinary differential equation (ODE) is a differential equation whose unknown(s) consists of one (or more) function(s) of one variable and involves the derivatives of those functions. The term ''ordinary'' is used in contrast ...
s. However, the hope that Lie Theory would unify the entire field of ordinary differential equations was not fulfilled. Symmetry methods for ODEs continue to be studied, but do not dominate the subject. There is a differential Galois theory
In mathematics, differential Galois theory studies the Galois groups of differential equations.
Overview
Whereas algebraic Galois theory studies extensions of algebraic fields, differential Galois theory studies extensions of differential field ...
, but it was developed by others, such as Picard and Vessiot, and it provides a theory of quadratures, the indefinite integral
In calculus, an antiderivative, inverse derivative, primitive function, primitive integral or indefinite integral of a function is a differentiable function whose derivative is equal to the original function . This can be stated symbolicall ...
s required to express solutions.
Additional impetus to consider continuous groups came from ideas of Bernhard Riemann, on the foundations of geometry, and their further development in the hands of Klein. Thus three major themes in 19th century mathematics were combined by Lie in creating his new theory: the idea of symmetry, as exemplified by Galois through the algebraic notion of a group
A group is a number of persons or things that are located, gathered, or classed together.
Groups of people
* Cultural group, a group whose members share the same cultural identity
* Ethnic group, a group whose members share the same ethnic ide ...
; geometric theory and the explicit solutions of differential equation
In mathematics, a differential equation is an equation that relates one or more unknown functions and their derivatives. In applications, the functions generally represent physical quantities, the derivatives represent their rates of change, an ...
s of mechanics, worked out by Poisson and Jacobi; and the new understanding of geometry
Geometry (; ) is, with arithmetic, one of the oldest branches of mathematics. It is concerned with properties of space such as the distance, shape, size, and relative position of figures. A mathematician who works in the field of geometry is ...
that emerged in the works of Plücker, Möbius, Grassmann
Hermann Günther Grassmann (german: link=no, Graßmann, ; 15 April 1809 – 26 September 1877) was a German polymath known in his day as a linguist and now also as a mathematician. He was also a physicist, general scholar, and publisher. His mat ...
and others, and culminated in Riemann's revolutionary vision of the subject.
Although today Sophus Lie is rightfully recognized as the creator of the theory of continuous groups, a major stride in the development of their structure theory, which was to have a profound influence on subsequent development of mathematics, was made by Wilhelm Killing
Wilhelm Karl Joseph Killing (10 May 1847 – 11 February 1923) was a German mathematician who made important contributions to the theories of Lie algebras, Lie groups, and non-Euclidean geometry.
Life
Killing studied at the University of Mü ...
, who in 1888 published the first paper in a series entitled ''Die Zusammensetzung der stetigen endlichen Transformationsgruppen'' (''The composition of continuous finite transformation groups'') (Hawkins, p. 100). The work of Killing, later refined and generalized by Élie Cartan
Élie Joseph Cartan (; 9 April 1869 – 6 May 1951) was an influential French mathematician who did fundamental work in the theory of Lie groups, differential systems (coordinate-free geometric formulation of PDEs), and differential geometr ...
, led to classification of semisimple Lie algebra
In mathematics, a Lie algebra is semisimple if it is a direct sum of simple Lie algebras. (A simple Lie algebra is a non-abelian Lie algebra without any non-zero proper ideals).
Throughout the article, unless otherwise stated, a Lie algebra is ...
s, Cartan's theory of symmetric spaces, and Hermann Weyl's description of representations
''Representations'' is an interdisciplinary journal in the humanities published quarterly by the University of California Press. The journal was established in 1983 and is the founding publication of the New Historicism movement of the 1980s. It ...
of compact and semisimple Lie groups using highest weights.
In 1900 David Hilbert challenged Lie theorists with his Fifth Problem presented at the International Congress of Mathematicians in Paris.
Weyl brought the early period of the development of the theory of Lie groups to fruition, for not only did he classify irreducible representations of semisimple Lie groups and connect the theory of groups with quantum mechanics, but he also put Lie's theory itself on firmer footing by clearly enunciating the distinction between Lie's ''infinitesimal groups'' (i.e., Lie algebras) and the Lie groups proper, and began investigations of topology of Lie groups. The theory of Lie groups was systematically reworked in modern mathematical language in a monograph by Claude Chevalley
Claude Chevalley (; 11 February 1909 – 28 June 1984) was a French mathematician who made important contributions to number theory, algebraic geometry, class field theory, finite group theory and the theory of algebraic groups. He was a foun ...
.
Overview
smooth
Smooth may refer to:
Mathematics
* Smooth function, a function that is infinitely differentiable; used in calculus and topology
* Smooth manifold, a differentiable manifold for which all the transition maps are smooth functions
* Smooth algebrai ...
differentiable manifolds and as such can be studied using differential calculus, in contrast with the case of more general topological group
In mathematics, topological groups are logically the combination of groups and topological spaces, i.e. they are groups and topological spaces at the same time, such that the continuity condition for the group operations connects these two st ...
s. One of the key ideas in the theory of Lie groups is to replace the ''global'' object, the group, with its ''local'' or linearized version, which Lie himself called its "infinitesimal group" and which has since become known as its Lie algebra.
Lie groups play an enormous role in modern geometry
Geometry (; ) is, with arithmetic, one of the oldest branches of mathematics. It is concerned with properties of space such as the distance, shape, size, and relative position of figures. A mathematician who works in the field of geometry is ...
, on several different levels. Felix Klein
Christian Felix Klein (; 25 April 1849 – 22 June 1925) was a German mathematician and mathematics educator, known for his work with group theory, complex analysis, non-Euclidean geometry, and on the associations between geometry and grou ...
argued in his Erlangen program
In mathematics, the Erlangen program is a method of characterizing geometries based on group theory and projective geometry. It was published by Felix Klein in 1872 as ''Vergleichende Betrachtungen über neuere geometrische Forschungen.'' It is nam ...
that one can consider various "geometries" by specifying an appropriate transformation group that leaves certain geometric properties invariant. Thus Euclidean geometry
Euclidean geometry is a mathematical system attributed to ancient Greek mathematician Euclid, which he described in his textbook on geometry: the '' Elements''. Euclid's approach consists in assuming a small set of intuitively appealing axioms ...
corresponds to the choice of the group E(3) of distance-preserving transformations of the Euclidean space R3, conformal geometry
In mathematics, conformal geometry is the study of the set of angle-preserving ( conformal) transformations on a space.
In a real two dimensional space, conformal geometry is precisely the geometry of Riemann surfaces. In space higher than two di ...
corresponds to enlarging the group to the conformal group
In mathematics, the conformal group of an inner product space is the group of transformations from the space to itself that preserve angles. More formally, it is the group of transformations that preserve the conformal geometry of the space.
Se ...
, whereas in projective geometry
In mathematics, projective geometry is the study of geometric properties that are invariant with respect to projective transformations. This means that, compared to elementary Euclidean geometry, projective geometry has a different setting, ...
one is interested in the properties invariant under the projective group. This idea later led to the notion of a G-structure, where ''G'' is a Lie group of "local" symmetries of a manifold.
Lie groups (and their associated Lie algebras) play a major role in modern physics, with the Lie group typically playing the role of a symmetry of a physical system. Here, the representations
''Representations'' is an interdisciplinary journal in the humanities published quarterly by the University of California Press. The journal was established in 1983 and is the founding publication of the New Historicism movement of the 1980s. It ...
of the Lie group (or of its Lie algebra) are especially important. Representation theory is used extensively in particle physics. Groups whose representations are of particular importance include the rotation group SO(3) (or its double cover SU(2)), the special unitary group SU(3) and the Poincaré group
The Poincaré group, named after Henri Poincaré (1906), was first defined by Hermann Minkowski (1908) as the group of Minkowski spacetime isometries. It is a ten-dimensional non-abelian Lie group that is of importance as a model in our und ...
.
On a "global" level, whenever a Lie group acts
The Acts of the Apostles ( grc-koi, Πράξεις Ἀποστόλων, ''Práxeis Apostólōn''; la, Actūs Apostolōrum) is the fifth book of the New Testament; it tells of the founding of the Christian Church and the spread of its message ...
on a geometric object, such as a Riemannian or a symplectic manifold, this action provides a measure of rigidity and yields a rich algebraic structure. The presence of continuous symmetries expressed via a Lie group action on a manifold places strong constraints on its geometry and facilitates analysis
Analysis ( : analyses) is the process of breaking a complex topic or substance into smaller parts in order to gain a better understanding of it. The technique has been applied in the study of mathematics and logic since before Aristotle (3 ...
on the manifold. Linear actions of Lie groups are especially important, and are studied in representation theory
Representation theory is a branch of mathematics that studies abstract algebraic structures by ''representing'' their elements as linear transformations of vector spaces, and studies modules over these abstract algebraic structures. In essen ...
.
In the 1940s–1950s, Ellis Kolchin
Ellis Robert Kolchin (April 18, 1916 – October 30, 1991) was an American mathematician at Columbia University. Kolchin earned a doctorate in mathematics from Columbia University in 1941 under supervision of Joseph Ritt. He was awarded a Gugg ...
, Armand Borel
Armand Borel (21 May 1923 – 11 August 2003) was a Swiss mathematician, born in La Chaux-de-Fonds, and was a permanent professor at the Institute for Advanced Study in Princeton, New Jersey, United States from 1957 to 1993. He worked in alg ...
, and Claude Chevalley
Claude Chevalley (; 11 February 1909 – 28 June 1984) was a French mathematician who made important contributions to number theory, algebraic geometry, class field theory, finite group theory and the theory of algebraic groups. He was a foun ...
realised that many foundational results concerning Lie groups can be developed completely algebraically, giving rise to the theory of algebraic group
In mathematics, an algebraic group is an algebraic variety endowed with a group structure which is compatible with its structure as an algebraic variety. Thus the study of algebraic groups belongs both to algebraic geometry and group theory.
Ma ...
s defined over an arbitrary field
Field may refer to:
Expanses of open ground
* Field (agriculture), an area of land used for agricultural purposes
* Airfield, an aerodrome that lacks the infrastructure of an airport
* Battlefield
* Lawn, an area of mowed grass
* Meadow, a grass ...
. This insight opened new possibilities in pure algebra, by providing a uniform construction for most finite simple group
Finite is the opposite of infinite. It may refer to:
* Finite number (disambiguation)
* Finite set, a set whose cardinality (number of elements) is some natural number
* Finite verb, a verb form that has a subject, usually being inflected or marked ...
s, as well as in algebraic geometry. The theory of automorphic forms, an important branch of modern number theory
Number theory (or arithmetic or higher arithmetic in older usage) is a branch of pure mathematics devoted primarily to the study of the integers and integer-valued functions. German mathematician Carl Friedrich Gauss (1777–1855) said, "Mat ...
, deals extensively with analogues of Lie groups over adele ring
Adele Laurie Blue Adkins (, ; born 5 May 1988), professionally known by the mononym Adele, is an English singer and songwriter. After graduating in arts from the BRIT School in 2006, Adele signed a reco ...
s; ''p''-adic Lie groups play an important role, via their connections with Galois representations in number theory.
Definitions and examples
A real Lie group is agroup
A group is a number of persons or things that are located, gathered, or classed together.
Groups of people
* Cultural group, a group whose members share the same cultural identity
* Ethnic group, a group whose members share the same ethnic ide ...
that is also a finite-dimensional real smooth manifold
In mathematics, a differentiable manifold (also differential manifold) is a type of manifold that is locally similar enough to a vector space to allow one to apply calculus. Any manifold can be described by a collection of charts (atlas). One ma ...
, in which the group operations of multiplication and inversion are smooth map
In mathematical analysis, the smoothness of a function is a property measured by the number of continuous derivatives it has over some domain, called ''differentiability class''. At the very minimum, a function could be considered smooth if ...
s. Smoothness of the group multiplication
:
means that ''μ'' is a smooth mapping of the product manifold into ''G''. The two requirements can be combined to the single requirement that the mapping
:
be a smooth mapping of the product manifold into ''G''.
First examples
* The 2×2real
Real may refer to:
Currencies
* Brazilian real (R$)
* Central American Republic real
* Mexican real
* Portuguese real
* Spanish real
* Spanish colonial real
Music Albums
* ''Real'' (L'Arc-en-Ciel album) (2000)
* ''Real'' (Bright album) (2010) ...
invertible matrices
In linear algebra, an -by- square matrix is called invertible (also nonsingular or nondegenerate), if there exists an -by- square matrix such that
:\mathbf = \mathbf = \mathbf_n \
where denotes the -by- identity matrix and the multiplicati ...
form a group under multiplication, denoted by or by GL2(R):
::
: This is a four-dimensional noncompact real Lie group; it is an open subset of . This group is disconnected; it has two connected components corresponding to the positive and negative values of the determinant
In mathematics, the determinant is a scalar value that is a function of the entries of a square matrix. It characterizes some properties of the matrix and the linear map represented by the matrix. In particular, the determinant is nonzero if a ...
.
* The rotation matrices form a subgroup
In group theory, a branch of mathematics, given a group ''G'' under a binary operation ∗, a subset ''H'' of ''G'' is called a subgroup of ''G'' if ''H'' also forms a group under the operation ∗. More precisely, ''H'' is a subgroup ...
of , denoted by . It is a Lie group in its own right: specifically, a one-dimensional compact connected Lie group which is diffeomorphic
In mathematics, a diffeomorphism is an isomorphism of smooth manifolds. It is an invertible function that maps one differentiable manifold to another such that both the function and its inverse are differentiable.
Definition
Given two man ...
to the circle
A circle is a shape consisting of all points in a plane that are at a given distance from a given point, the centre. Equivalently, it is the curve traced out by a point that moves in a plane so that its distance from a given point is con ...
. Using the rotation angle as a parameter, this group can be parametrized as follows:
::
:Addition of the angles corresponds to multiplication of the elements of , and taking the opposite angle corresponds to inversion. Thus both multiplication and inversion are differentiable maps.
* The affine group of one dimension is a two-dimensional matrix Lie group, consisting of real, upper-triangular matrices, with the first diagonal entry being positive and the second diagonal entry being 1. Thus, the group consists of matrices of the form
::
Non-example
We now present an example of a group with anuncountable
In mathematics, an uncountable set (or uncountably infinite set) is an infinite set that contains too many elements to be countable. The uncountability of a set is closely related to its cardinal number: a set is uncountable if its cardinal num ...
number of elements that is not a Lie group under a certain topology. The group given by
:
with a ''fixed'' irrational number
In mathematics, the irrational numbers (from in- prefix assimilated to ir- (negative prefix, privative) + rational) are all the real numbers that are not rational numbers. That is, irrational numbers cannot be expressed as the ratio of two inte ...
, is a subgroup of the torus
In geometry, a torus (plural tori, colloquially donut or doughnut) is a surface of revolution generated by revolving a circle in three-dimensional space about an axis that is coplanar with the circle.
If the axis of revolution does not tou ...
that is not a Lie group when given the subspace topology
In topology and related areas of mathematics, a subspace of a topological space ''X'' is a subset ''S'' of ''X'' which is equipped with a topology induced from that of ''X'' called the subspace topology (or the relative topology, or the induced to ...
. If we take any small neighborhood of a point in , for example, the portion of in is disconnected. The group winds repeatedly around the torus without ever reaching a previous point of the spiral and thus forms a dense
Density (volumetric mass density or specific mass) is the substance's mass per unit of volume. The symbol most often used for density is ''ρ'' (the lower case Greek letter rho), although the Latin letter ''D'' can also be used. Mathematically ...
subgroup of .
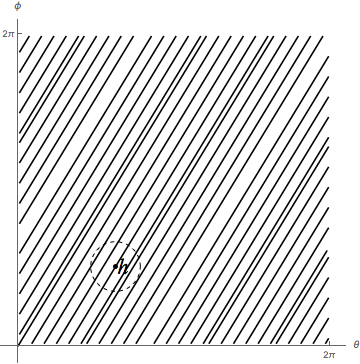
 The group can, however, be given a different topology, in which the distance between two points is defined as the length of the shortest path ''in the group '' joining to . In this topology, is identified homeomorphically with the real line by identifying each element with the number in the definition of . With this topology, is just the group of real numbers under addition and is therefore a Lie group.
The group is an example of a " Lie subgroup" of a Lie group that is not closed. See the discussion below of Lie subgroups in the section on basic concepts.
The group can, however, be given a different topology, in which the distance between two points is defined as the length of the shortest path ''in the group '' joining to . In this topology, is identified homeomorphically with the real line by identifying each element with the number in the definition of . With this topology, is just the group of real numbers under addition and is therefore a Lie group.
The group is an example of a " Lie subgroup" of a Lie group that is not closed. See the discussion below of Lie subgroups in the section on basic concepts.
Matrix Lie groups
Let denote the group of invertible matrices with entries in . Anyclosed subgroup
In mathematics, topological groups are logically the combination of groups and topological spaces, i.e. they are groups and topological spaces at the same time, such that the continuity condition for the group operations connects these two ...
of is a Lie group; Lie groups of this sort are called matrix Lie groups. Since most of the interesting examples of Lie groups can be realized as matrix Lie groups, some textbooks restrict attention to this class, including those of Hall, Rossmann, and Stillwell.
Restricting attention to matrix Lie groups simplifies the definition of the Lie algebra and the exponential map. The following are standard examples of matrix Lie groups.
*The special linear group
In mathematics, the special linear group of degree ''n'' over a field ''F'' is the set of matrices with determinant 1, with the group operations of ordinary matrix multiplication and matrix inversion. This is the normal subgroup of the ge ...
s over and , and , consisting of matrices with determinant one and entries in or
*The unitary group
In mathematics, the unitary group of degree ''n'', denoted U(''n''), is the group of unitary matrices, with the group operation of matrix multiplication. The unitary group is a subgroup of the general linear group . Hyperorthogonal group is ...
s and special unitary groups, and , consisting of complex matrices satisfying (and also in the case of )
*The orthogonal groups and special orthogonal groups, and , consisting of real matrices satisfying (and also in the case of )
All of the preceding examples fall under the heading of the classical group
In mathematics, the classical groups are defined as the special linear groups over the reals , the complex numbers and the quaternions together with special automorphism groups of symmetric or skew-symmetric bilinear forms and Hermitian or s ...
s.
Related concepts
A complex Lie group is defined in the same way using complex manifolds rather than real ones (example: ), and holomorphic maps. Similarly, using an alternate metric completion of , one can define a ''p''-adic Lie group over the ''p''-adic numbers, a topological group which is also an analytic ''p''-adic manifold, such that the group operations are analytic. In particular, each point has a ''p''-adic neighborhood.Hilbert's fifth problem
Hilbert's fifth problem is the fifth mathematical problem from the problem list publicized in 1900 by mathematician David Hilbert, and concerns the characterization of Lie groups.
The theory of Lie groups describes continuous symmetry in mathem ...
asked whether replacing differentiable manifolds with topological or analytic ones can yield new examples. The answer to this question turned out to be negative: in 1952, Gleason, Montgomery and Zippin showed that if ''G'' is a topological manifold with continuous group operations, then there exists exactly one analytic structure on ''G'' which turns it into a Lie group (see also Hilbert–Smith conjecture). If the underlying manifold is allowed to be infinite-dimensional (for example, a Hilbert manifold), then one arrives at the notion of an infinite-dimensional Lie group. It is possible to define analogues of many Lie groups over finite fields, and these give most of the examples of finite simple group
Finite is the opposite of infinite. It may refer to:
* Finite number (disambiguation)
* Finite set, a set whose cardinality (number of elements) is some natural number
* Finite verb, a verb form that has a subject, usually being inflected or marked ...
s.
The language of category theory provides a concise definition for Lie groups: a Lie group is a group object in the category
Category, plural categories, may refer to:
Philosophy and general uses
*Categorization, categories in cognitive science, information science and generally
* Category of being
* ''Categories'' (Aristotle)
* Category (Kant)
* Categories (Peirce) ...
of smooth manifolds. This is important, because it allows generalization of the notion of a Lie group to Lie supergroups. This categorical point of view leads also to a different generalization of Lie groups, namely Lie groupoids, which are groupoid objects in the category of smooth manifolds with a further requirement.
Topological definition
A Lie group can be defined as a ( Hausdorff)topological group
In mathematics, topological groups are logically the combination of groups and topological spaces, i.e. they are groups and topological spaces at the same time, such that the continuity condition for the group operations connects these two st ...
that, near the identity element, looks like a transformation group, with no reference to differentiable manifolds. First, we define an immersely linear Lie group to be a subgroup ''G'' of the general linear group such that
# for some neighborhood ''V'' of the identity element ''e'' in ''G'', the topology on ''V'' is the subspace topology of and ''V'' is closed in .
# ''G'' has at most countably many connected components.
(For example, a closed subgroup of ; that is, a matrix Lie group satisfies the above conditions.)
Then a ''Lie group'' is defined as a topological group that (1) is locally isomorphic near the identities to an immersely linear Lie group and (2) has at most countably many connected components. Showing the topological definition is equivalent to the usual one is technical (and the beginning readers should skip the following) but is done roughly as follows:
# Given a Lie group ''G'' in the usual manifold sense, the Lie group–Lie algebra correspondence In mathematics, Lie group–Lie algebra correspondence allows one to correspond a Lie group to a Lie algebra or vice versa, and study the conditions for such a relationship. Lie groups that are isomorphic to each other have Lie algebras that are ...
(or a version of Lie's third theorem) constructs an immersed Lie subgroup such that share the same Lie algebra; thus, they are locally isomorphic. Hence, ''G'' satisfies the above topological definition.
# Conversely, let ''G'' be a topological group that is a Lie group in the above topological sense and choose an immersely linear Lie group that is locally isomorphic to ''G''. Then, by a version of the closed subgroup theorem, is a real-analytic manifold and then, through the local isomorphism, ''G'' acquires a structure of a manifold near the identity element. One then shows that the group law on ''G'' can be given by formal power series; so the group operations are real-analytic and ''G'' itself is a real-analytic manifold.
The topological definition implies the statement that if two Lie groups are isomorphic as topological groups, then they are isomorphic as Lie groups. In fact, it states the general principle that, to a large extent, ''the topology of a Lie group'' together with the group law determines the geometry of the group.
More examples of Lie groups
Lie groups occur in abundance throughout mathematics and physics.Matrix group In mathematics, a matrix group is a group ''G'' consisting of invertible matrices over a specified field ''K'', with the operation of matrix multiplication. A linear group is a group that is isomorphic to a matrix group (that is, admitting a fa ...
s or algebraic group
In mathematics, an algebraic group is an algebraic variety endowed with a group structure which is compatible with its structure as an algebraic variety. Thus the study of algebraic groups belongs both to algebraic geometry and group theory.
Ma ...
s are (roughly) groups of matrices (for example, orthogonal and symplectic group
In mathematics, the name symplectic group can refer to two different, but closely related, collections of mathematical groups, denoted and for positive integer ''n'' and field F (usually C or R). The latter is called the compact symplectic gro ...
s), and these give most of the more common examples of Lie groups.
Dimensions one and two
The only connected Lie groups with dimension one are the real line (with the group operation being addition) and the circle group of complex numbers with absolute value one (with the group operation being multiplication). The group is often denoted as , the group of unitary matrices. In two dimensions, if we restrict attention to simply connected groups, then they are classified by their Lie algebras. There are (up to isomorphism) only two Lie algebras of dimension two. The associated simply connected Lie groups are (with the group operation being vector addition) and the affine group in dimension one, described in the previous subsection under "first examples".Additional examples
*The group SU(2) is the group of unitary matrices with determinant . Topologically, is the -sphere ; as a group, it may be identified with the group of unit quaternions. *TheHeisenberg group
In mathematics, the Heisenberg group H, named after Werner Heisenberg, is the group of 3×3 upper triangular matrices of the form
::\begin
1 & a & c\\
0 & 1 & b\\
0 & 0 & 1\\
\end
under the operation of matrix multiplication. Elements ...
is a connected nilpotent
In mathematics, an element x of a ring R is called nilpotent if there exists some positive integer n, called the index (or sometimes the degree), such that x^n=0.
The term was introduced by Benjamin Peirce in the context of his work on the cla ...
Lie group of dimension , playing a key role in quantum mechanics
Quantum mechanics is a fundamental theory in physics that provides a description of the physical properties of nature at the scale of atoms and subatomic particles. It is the foundation of all quantum physics including quantum chemistr ...
.
*The Lorentz group
In physics and mathematics, the Lorentz group is the group of all Lorentz transformations of Minkowski spacetime, the classical and quantum setting for all (non-gravitational) physical phenomena. The Lorentz group is named for the Dutch physicis ...
is a 6-dimensional Lie group of linear isometries
In mathematics, an isometry (or congruence, or congruent transformation) is a distance-preserving transformation between metric spaces, usually assumed to be bijective. The word isometry is derived from the Ancient Greek: ἴσος ''isos'' mea ...
of the Minkowski space
In mathematical physics, Minkowski space (or Minkowski spacetime) () is a combination of three-dimensional Euclidean space and time into a four-dimensional manifold where the spacetime interval between any two events is independent of the iner ...
.
*The Poincaré group
The Poincaré group, named after Henri Poincaré (1906), was first defined by Hermann Minkowski (1908) as the group of Minkowski spacetime isometries. It is a ten-dimensional non-abelian Lie group that is of importance as a model in our und ...
is a 10-dimensional Lie group of affine
Affine may describe any of various topics concerned with connections or affinities.
It may refer to:
* Affine, a relative by marriage in law and anthropology
* Affine cipher, a special case of the more general substitution cipher
* Affine comb ...
isometries of the Minkowski space.
*The exceptional Lie groups of types ''G''2, ''F''4, ''E''6, ''E''7, ''E''8 have dimensions 14, 52, 78, 133, and 248. Along with the A-B-C-D series of simple Lie group
In mathematics, a simple Lie group is a connected non-abelian Lie group ''G'' which does not have nontrivial connected normal subgroups. The list of simple Lie groups can be used to read off the list of simple Lie algebras and Riemannian symm ...
s, the exceptional groups complete the list of simple Lie groups.
*The symplectic group
In mathematics, the name symplectic group can refer to two different, but closely related, collections of mathematical groups, denoted and for positive integer ''n'' and field F (usually C or R). The latter is called the compact symplectic gro ...
consists of all matrices preserving a ''symplectic form In mathematics, a symplectic vector space is a vector space ''V'' over a field ''F'' (for example the real numbers R) equipped with a symplectic bilinear form.
A symplectic bilinear form is a mapping that is
; Bilinear: Linear in each argument ...
'' on . It is a connected Lie group of dimension .
Constructions
There are several standard ways to form new Lie groups from old ones: *The product of two Lie groups is a Lie group. *Any topologically closed subgroup of a Lie group is a Lie group. This is known as the Closed subgroup theorem or Cartan's theorem. *The quotient of a Lie group by a closed normal subgroup is a Lie group. *Theuniversal cover A covering of a topological space X is a continuous map \pi : E \rightarrow X with special properties.
Definition
Let X be a topological space. A covering of X is a continuous map
: \pi : E \rightarrow X
such that there exists a discrete spa ...
of a connected Lie group is a Lie group. For example, the group is the universal cover of the circle group . In fact any covering of a differentiable manifold is also a differentiable manifold, but by specifying ''universal'' cover, one guarantees a group structure (compatible with its other structures).
Related notions
Some examples of groups that are ''not'' Lie groups (except in the trivial sense that any group having at most countably many elements can be viewed as a 0-dimensional Lie group, with thediscrete topology
In topology, a discrete space is a particularly simple example of a topological space or similar structure, one in which the points form a , meaning they are ''isolated'' from each other in a certain sense. The discrete topology is the finest top ...
), are:
*Infinite-dimensional groups, such as the additive group of an infinite-dimensional real vector space, or the space of smooth functions from a manifold to a Lie group , . These are not Lie groups as they are not ''finite-dimensional'' manifolds.
*Some totally disconnected groups, such as the Galois group
In mathematics, in the area of abstract algebra known as Galois theory, the Galois group of a certain type of field extension is a specific group associated with the field extension. The study of field extensions and their relationship to the po ...
of an infinite extension of fields, or the additive group of the ''p''-adic numbers. These are not Lie groups because their underlying spaces are not real manifolds. (Some of these groups are "''p''-adic Lie groups".) In general, only topological groups having similar local properties to R''n'' for some positive integer ''n'' can be Lie groups (of course they must also have a differentiable structure).
Basic concepts
The Lie algebra associated with a Lie group
To every Lie group we can associate a Lie algebra whose underlying vector space is the tangent space of the Lie group at the identity element and which completely captures the local structure of the group. Informally we can think of elements of the Lie algebra as elements of the group that are " infinitesimally close" to the identity, and the Lie bracket of the Lie algebra is related to the commutator of two such infinitesimal elements. Before giving the abstract definition we give a few examples: * The Lie algebra of the vector space R''n'' is just R''n'' with the Lie bracket given by'A'', ''B''= 0.
(In general the Lie bracket of a connected Lie group is always 0 if and only if the Lie group is abelian.) * The Lie algebra of the
general linear group
In mathematics, the general linear group of degree ''n'' is the set of invertible matrices, together with the operation of ordinary matrix multiplication. This forms a group, because the product of two invertible matrices is again invertible, ...
GL(''n'', C) of invertible matrices is the vector space M(''n'', C) of square matrices with the Lie bracket given by 'A'', ''B''= ''AB'' − ''BA''. *If ''G'' is a closed subgroup of GL(''n'', C) then the Lie algebra of ''G'' can be thought of informally as the matrices ''m'' of M(''n'', C) such that 1 + ε''m'' is in ''G'', where ε is an infinitesimal positive number with ε2 = 0 (of course, no such real number ε exists). For example, the orthogonal group O(''n'', R) consists of matrices ''A'' with ''AA''T = 1, so the Lie algebra consists of the matrices ''m'' with (1 + ε''m'')(1 + ε''m'')T = 1, which is equivalent to ''m'' + ''m''T = 0 because ε2 = 0. *The preceding description can be made more rigorous as follows. The Lie algebra of a closed subgroup ''G'' of GL(''n'', C), may be computed as : where exp(''tX'') is defined using the
matrix exponential
In mathematics, the matrix exponential is a matrix function on square matrices analogous to the ordinary exponential function. It is used to solve systems of linear differential equations. In the theory of Lie groups, the matrix exponential give ...
. It can then be shown that the Lie algebra of ''G'' is a real vector space that is closed under the bracket operation, .
The concrete definition given above for matrix groups is easy to work with, but has some minor problems: to use it we first need to represent a Lie group as a group of matrices, but not all Lie groups can be represented in this way, and it is not even obvious that the Lie algebra is independent of the representation we use. To get around these problems we give
the general definition of the Lie algebra of a Lie group (in 4 steps):
#Vector fields on any smooth manifold ''M'' can be thought of as derivations
Derivation may refer to:
Language
* Morphological derivation, a word-formation process
* Parse tree or concrete syntax tree, representing a string's syntax in formal grammars
Law
* Derivative work, in copyright law
* Derivation proceeding, a proc ...
''X'' of the ring of smooth functions on the manifold, and therefore form a Lie algebra under the Lie bracket 'X'', ''Y''nbsp;= ''XY'' − ''YX'', because the Lie bracket
In mathematics, a Lie algebra (pronounced ) is a vector space \mathfrak g together with an operation called the Lie bracket, an alternating bilinear map \mathfrak g \times \mathfrak g \rightarrow \mathfrak g, that satisfies the Jacobi identi ...
of any two derivations is a derivation.
#If ''G'' is any group acting smoothly on the manifold ''M'', then it acts on the vector fields, and the vector space of vector fields fixed by the group is closed under the Lie bracket and therefore also forms a Lie algebra.
#We apply this construction to the case when the manifold ''M'' is the underlying space of a Lie group ''G'', with ''G'' acting on ''G'' = ''M'' by left translations ''Lg''(''h'') = ''gh''. This shows that the space of left invariant vector fields (vector fields satisfying ''Lg''*''Xh'' = ''Xgh'' for every ''h'' in ''G'', where ''Lg''* denotes the differential of ''Lg'') on a Lie group is a Lie algebra under the Lie bracket of vector fields.
#Any tangent vector at the identity of a Lie group can be extended to a left invariant vector field by left translating the tangent vector to other points of the manifold. Specifically, the left invariant extension of an element ''v'' of the tangent space at the identity is the vector field defined by ''v''^''g'' = ''Lg''*''v''. This identifies the tangent space
In mathematics, the tangent space of a manifold generalizes to higher dimensions the notion of '' tangent planes'' to surfaces in three dimensions and ''tangent lines'' to curves in two dimensions. In the context of physics the tangent space to a ...
''TeG'' at the identity with the space of left invariant vector fields, and therefore makes the tangent space at the identity into a Lie algebra, called the Lie algebra of ''G'', usually denoted by a Fraktur
Fraktur () is a calligraphic hand of the Latin alphabet and any of several blackletter typefaces derived from this hand. The blackletter lines are broken up; that is, their forms contain many angles when compared to the curves of the Antiqu ...
Thus the Lie bracket on is given explicitly by 'v'', ''w''nbsp;= 'v''^, ''w''^sub>''e''.
This Lie algebra is finite-dimensional and it has the same dimension as the manifold ''G''. The Lie algebra of ''G'' determines ''G'' up to "local isomorphism", where two Lie groups are called locally isomorphic if they look the same near the identity element.
Problems about Lie groups are often solved by first solving the corresponding problem for the Lie algebras, and the result for groups then usually follows easily.
For example, simple Lie groups are usually classified by first classifying the corresponding Lie algebras.
We could also define a Lie algebra structure on ''Te'' using right invariant vector fields instead of left invariant vector fields. This leads to the same Lie algebra, because the inverse map on ''G'' can be used to identify left invariant vector fields with right invariant vector fields, and acts as −1 on the tangent space ''Te''.
The Lie algebra structure on ''Te'' can also be described as follows:
the commutator operation
: (''x'', ''y'') → ''xyx''−1''y''−1
on ''G'' × ''G'' sends (''e'', ''e'') to ''e'', so its derivative yields a bilinear operation on ''TeG''. This bilinear operation is actually the zero map, but the second derivative, under the proper identification of tangent spaces, yields an operation that satisfies the axioms of a Lie bracket
In mathematics, a Lie algebra (pronounced ) is a vector space \mathfrak g together with an operation called the Lie bracket, an alternating bilinear map \mathfrak g \times \mathfrak g \rightarrow \mathfrak g, that satisfies the Jacobi identi ...
, and it is equal to twice the one defined through left-invariant vector fields.
Homomorphisms and isomorphisms
If ''G'' and ''H'' are Lie groups, then a Lie group homomorphism ''f'' : ''G'' → ''H'' is a smoothgroup homomorphism
In mathematics, given two groups, (''G'', ∗) and (''H'', ·), a group homomorphism from (''G'', ∗) to (''H'', ·) is a function ''h'' : ''G'' → ''H'' such that for all ''u'' and ''v'' in ''G'' it holds that
: h(u*v) = h(u) \cdot h(v)
w ...
. In the case of complex Lie groups, such a homomorphism is required to be a holomorphic map
In mathematics, a holomorphic function is a complex-valued function of one or more complex variables that is complex differentiable in a neighbourhood of each point in a domain in complex coordinate space . The existence of a complex derivat ...
. However, these requirements are a bit stringent; every continuous homomorphism between real Lie groups turns out to be (real) analytic.
The composition of two Lie homomorphisms is again a homomorphism, and the class of all Lie groups, together with these morphisms, forms a category
Category, plural categories, may refer to:
Philosophy and general uses
*Categorization, categories in cognitive science, information science and generally
* Category of being
* ''Categories'' (Aristotle)
* Category (Kant)
* Categories (Peirce) ...
. Moreover, every Lie group homomorphism induces a homomorphism between the corresponding Lie algebras. Let be a Lie group homomorphism and let be its derivative
In mathematics, the derivative of a function of a real variable measures the sensitivity to change of the function value (output value) with respect to a change in its argument (input value). Derivatives are a fundamental tool of calculus. ...
at the identity. If we identify the Lie algebras of ''G'' and ''H'' with their tangent space
In mathematics, the tangent space of a manifold generalizes to higher dimensions the notion of '' tangent planes'' to surfaces in three dimensions and ''tangent lines'' to curves in two dimensions. In the context of physics the tangent space to a ...
s at the identity elements, then is a map between the corresponding Lie algebras:
:
which turns out to be a Lie algebra homomorphism
In mathematics, a Lie algebra (pronounced ) is a vector space \mathfrak g together with an operation called the Lie bracket, an alternating bilinear map \mathfrak g \times \mathfrak g \rightarrow \mathfrak g, that satisfies the Jacobi ident ...
(meaning that it is a linear map
In mathematics, and more specifically in linear algebra, a linear map (also called a linear mapping, linear transformation, vector space homomorphism, or in some contexts linear function) is a mapping V \to W between two vector spaces that pr ...
which preserves the Lie bracket
In mathematics, a Lie algebra (pronounced ) is a vector space \mathfrak g together with an operation called the Lie bracket, an alternating bilinear map \mathfrak g \times \mathfrak g \rightarrow \mathfrak g, that satisfies the Jacobi identi ...
). In the language of category theory, we then have a covariant functor
In mathematics, specifically category theory, a functor is a mapping between categories. Functors were first considered in algebraic topology, where algebraic objects (such as the fundamental group) are associated to topological spaces, and m ...
from the category of Lie groups to the category of Lie algebras which sends a Lie group to its Lie algebra and a Lie group homomorphism to its derivative at the identity.
Two Lie groups are called ''isomorphic'' if there exists a bijective
In mathematics, a bijection, also known as a bijective function, one-to-one correspondence, or invertible function, is a function between the elements of two sets, where each element of one set is paired with exactly one element of the other ...
homomorphism between them whose inverse is also a Lie group homomorphism. Equivalently, it is a diffeomorphism
In mathematics, a diffeomorphism is an isomorphism of smooth manifolds. It is an invertible function that maps one differentiable manifold to another such that both the function and its inverse are differentiable.
Definition
Given two ...
which is also a group homomorphism. Observe that, by the above, a continuous homomorphism from a Lie group to a Lie group is an isomorphism of Lie groups if and only if it is bijective.
Lie group versus Lie algebra isomorphisms
Isomorphic Lie groups necessarily have isomorphic Lie algebras; it is then reasonable to ask how isomorphism classes of Lie groups relate to isomorphism classes of Lie algebras. The first result in this direction is Lie's third theorem, which states that every finite-dimensional, real Lie algebra is the Lie algebra of some (linear) Lie group. One way to prove Lie's third theorem is to useAdo's theorem In abstract algebra, Ado's theorem is a theorem characterizing finite-dimensional Lie algebras.
Statement
Ado's theorem states that every finite-dimensional Lie algebra ''L'' over a field ''K'' of characteristic zero can be viewed as a Lie algebr ...
, which says every finite-dimensional real Lie algebra is isomorphic to a matrix Lie algebra. Meanwhile, for every finite-dimensional matrix Lie algebra, there is a linear group (matrix Lie group) with this algebra as its Lie algebra.
On the other hand, Lie groups with isomorphic Lie algebras need not be isomorphic. Furthermore, this result remains true even if we assume the groups are connected. To put it differently, the ''global'' structure of a Lie group is not determined by its Lie algebra; for example, if ''Z'' is any discrete subgroup of the center of ''G'' then ''G'' and ''G''/''Z'' have the same Lie algebra (see the table of Lie groups for examples). An example of importance in physics are the groups SU(2)
In mathematics, the special unitary group of degree , denoted , is the Lie group of unitary matrices with determinant 1.
The more general unitary matrices may have complex determinants with absolute value 1, rather than real 1 in the special ...
and SO(3)
In mechanics and geometry, the 3D rotation group, often denoted SO(3), is the group of all rotations about the origin of three-dimensional Euclidean space \R^3 under the operation of composition.
By definition, a rotation about the origin is a tr ...
. These two groups have isomorphic Lie algebras, but the groups themselves are not isomorphic, because SU(2) is simply connected but SO(3) is not.
On the other hand, if we require that the Lie group be simply connected, then the global structure is determined by its Lie algebra: two simply connected Lie groups with isomorphic Lie algebras are isomorphic. (See the next subsection for more information about simply connected Lie groups.) In light of Lie's third theorem, we may therefore say that there is a one-to-one correspondence between isomorphism classes of finite-dimensional real Lie algebras and isomorphism classes of simply connected Lie groups.
Simply connected Lie groups
A Lie group is said to be simply connected if every loop in can be shrunk continuously to a point in . This notion is important because of the following result that has simple connectedness as a hypothesis: :Theorem: Suppose and are Lie groups with Lie algebras and and that is a Lie algebra homomorphism. If is simply connected, then there is a unique Lie group homomorphism such that , where is the differential of at the identity. Lie's third theorem says that every finite-dimensional real Lie algebra is the Lie algebra of a Lie group. It follows from Lie's third theorem and the preceding result that every finite-dimensional real Lie algebra is the Lie algebra of a ''unique'' simply connected Lie group. An example of a simply connected group is the special unitary groupSU(2)
In mathematics, the special unitary group of degree , denoted , is the Lie group of unitary matrices with determinant 1.
The more general unitary matrices may have complex determinants with absolute value 1, rather than real 1 in the special ...
, which as a manifold is the 3-sphere. The rotation group SO(3)
In mechanics and geometry, the 3D rotation group, often denoted SO(3), is the group of all rotations about the origin of three-dimensional Euclidean space \R^3 under the operation of composition.
By definition, a rotation about the origin is a ...
, on the other hand, is not simply connected. (See Topology of SO(3).) The failure of SO(3) to be simply connected is intimately connected to the distinction between integer spin
In particle physics, a boson ( ) is a subatomic particle whose spin quantum number has an integer value (0,1,2 ...). Bosons form one of the two fundamental classes of subatomic particle, the other being fermions, which have odd half-integer spi ...
and half-integer spin in quantum mechanics. Other examples of simply connected Lie groups include the special unitary group SU(n), the spin group (double cover of rotation group) Spin(n) for , and the compact symplectic group Sp(n).
Methods for determining whether a Lie group is simply connected or not are discussed in the article on fundamental groups of Lie groups.
The exponential map
The exponential map from the Lie algebra of thegeneral linear group
In mathematics, the general linear group of degree ''n'' is the set of invertible matrices, together with the operation of ordinary matrix multiplication. This forms a group, because the product of two invertible matrices is again invertible, ...
to is defined by the matrix exponential
In mathematics, the matrix exponential is a matrix function on square matrices analogous to the ordinary exponential function. It is used to solve systems of linear differential equations. In the theory of Lie groups, the matrix exponential give ...
, given by the usual power series:
:
for matrices . If is a closed subgroup of , then the exponential map takes the Lie algebra of into ; thus, we have an exponential map for all matrix groups. Every element of that is sufficiently close to the identity is the exponential of a matrix in the Lie algebra.
The definition above is easy to use, but it is not defined for Lie groups that are not matrix groups, and it is not clear that the exponential map of a Lie group does not depend on its representation as a matrix group. We can solve both problems using a more abstract definition of the exponential map that works for all Lie groups, as follows.
For each vector in the Lie algebra of (i.e., the tangent space to at the identity), one proves that there is a unique one-parameter subgroup such that . Saying that is a one-parameter subgroup means simply that is a smooth map into and that
:
for all and . The operation on the right hand side is the group multiplication in . The formal similarity of this formula with the one valid for the exponential function
The exponential function is a mathematical function denoted by f(x)=\exp(x) or e^x (where the argument is written as an exponent). Unless otherwise specified, the term generally refers to the positive-valued function of a real variable, ...
justifies the definition
:
This is called the exponential map, and it maps the Lie algebra into the Lie group . It provides a diffeomorphism
In mathematics, a diffeomorphism is an isomorphism of smooth manifolds. It is an invertible function that maps one differentiable manifold to another such that both the function and its inverse are differentiable.
Definition
Given two ...
between a neighborhood of 0 in and a neighborhood of in . This exponential map is a generalization of the exponential function for real numbers (because is the Lie algebra of the Lie group of positive real numbers
In mathematics, the set of positive real numbers, \R_ = \left\, is the subset of those real numbers that are greater than zero. The non-negative real numbers, \R_ = \left\, also include zero. Although the symbols \R_ and \R^ are ambiguously used fo ...
with multiplication), for complex numbers (because is the Lie algebra of the Lie group of non-zero complex numbers with multiplication) and for matrices
Matrix most commonly refers to:
* ''The Matrix'' (franchise), an American media franchise
** ''The Matrix'', a 1999 science-fiction action film
** "The Matrix", a fictional setting, a virtual reality environment, within ''The Matrix'' (franchis ...
(because with the regular commutator is the Lie algebra of the Lie group of all invertible matrices).
Because the exponential map is surjective on some neighbourhood of , it is common to call elements of the Lie algebra infinitesimal generators of the group . The subgroup of generated by is the identity component of .
The exponential map and the Lie algebra determine the ''local group structure'' of every connected Lie group, because of the Baker–Campbell–Hausdorff formula: there exists a neighborhood of the zero element of , such that for we have
:
where_the_omitted_terms_are_known_and_involve_Lie_brackets_of_four_or_more_elements._In_case__and__commute,_this_formula_reduces_to_the_familiar_exponential_law_
The_exponential_map_relates_Lie_group_homomorphisms._That_is,_if__is_a_Lie_group_homomorphism_and__the_induced_map_on_the_corresponding_Lie_algebras,_then_for_all__we_have
:
In_other_words,_the_following_diagram_commutative_diagram.html" ;"title=",Y.html"_;"title=",[X,Y">,[X,YX.html" ;"title=",Y">,[X,YY.html" ;"title=",Y.html" ;"title=",[X,Y">,[X,YY">,Y.html" ;"title=",[X,Y">,[X,YY- \tfrac ,[X,YX">,Y">,[X,YY.html" ;"title=",Y.html" ;"title=",[X,Y">,[X,YY">,Y.html" ;"title=",[X,Y">,[X,YY- \tfrac ,[X,YX- \cdots \right),
where the omitted terms are known and involve Lie brackets of four or more elements. In case and commute, this formula reduces to the familiar exponential law
The exponential map relates Lie group homomorphisms. That is, if is a Lie group homomorphism and the induced map on the corresponding Lie algebras, then for all we have
:
In other words, the following diagram commutative diagram">commutes,
 (In short, exp is a natural transformation from the functor Lie to the identity functor on the category of Lie groups.)
The exponential map from the Lie algebra to the Lie group is not always Surjective function, onto, even if the group is connected (though it does map onto the Lie group for connected groups that are either compact or nilpotent). For example, the exponential map of is not surjective. Also, the exponential map is neither surjective nor injective for infinite-dimensional (see below) Lie groups modelled on ''C''∞
(In short, exp is a natural transformation from the functor Lie to the identity functor on the category of Lie groups.)
The exponential map from the Lie algebra to the Lie group is not always Surjective function, onto, even if the group is connected (though it does map onto the Lie group for connected groups that are either compact or nilpotent). For example, the exponential map of is not surjective. Also, the exponential map is neither surjective nor injective for infinite-dimensional (see below) Lie groups modelled on ''C''∞ Fréchet space
In functional analysis and related areas of mathematics, Fréchet spaces, named after Maurice Fréchet, are special topological vector spaces.
They are generalizations of Banach spaces ( normed vector spaces that are complete with respect to th ...
, even from arbitrary small neighborhood of 0 to corresponding neighborhood of 1.
Lie subgroup
A Lie subgroup of a Lie group is a Lie group that is a subset of and such that theinclusion map
In mathematics, if A is a subset of B, then the inclusion map (also inclusion function, insertion, or canonical injection) is the function \iota that sends each element x of A to x, treated as an element of B:
\iota : A\rightarrow B, \qquad \iota ...
from to is an injective immersion
Immersion may refer to:
The arts
* "Immersion", a 2012 story by Aliette de Bodard
* ''Immersion'', a French comic book series by Léo Quievreux#Immersion, Léo Quievreux
* Immersion (album), ''Immersion'' (album), the third album by Australian gro ...
and group homomorphism
In mathematics, given two groups, (''G'', ∗) and (''H'', ·), a group homomorphism from (''G'', ∗) to (''H'', ·) is a function ''h'' : ''G'' → ''H'' such that for all ''u'' and ''v'' in ''G'' it holds that
: h(u*v) = h(u) \cdot h(v)
w ...
. According to Cartan's theorem, a closed subgroup
In group theory, a branch of mathematics, given a group ''G'' under a binary operation ∗, a subset ''H'' of ''G'' is called a subgroup of ''G'' if ''H'' also forms a group under the operation ∗. More precisely, ''H'' is a subgroup ...
of admits a unique smooth structure which makes it an embedded Lie subgroup of —i.e. a Lie subgroup such that the inclusion map is a smooth embedding.
Examples of non-closed subgroups are plentiful; for example take to be a torus of dimension 2 or greater, and let be a one-parameter subgroup of ''irrational slope'', i.e. one that winds around in ''G''. Then there is a Lie group homomorphism
In algebra, a homomorphism is a structure-preserving map between two algebraic structures of the same type (such as two groups, two rings, or two vector spaces). The word ''homomorphism'' comes from the Ancient Greek language: () meaning "same" ...
with . The closure of will be a sub-torus in .
The exponential map gives a one-to-one correspondence
In mathematics, a bijection, also known as a bijective function, one-to-one correspondence, or invertible function, is a function between the elements of two sets, where each element of one set is paired with exactly one element of the other ...
between the connected Lie subgroups of a connected Lie group and the subalgebras of the Lie algebra of . Typically, the subgroup corresponding to a subalgebra is not a closed subgroup. There is no criterion solely based on the structure of which determines which subalgebras correspond to closed subgroups.
Representations
One important aspect of the study of Lie groups is their representations, that is, the way they can act (linearly) on vector spaces. In physics, Lie groups often encode the symmetries of a physical system. The way one makes use of this symmetry to help analyze the system is often through representation theory. Consider, for example, the time-independentSchrödinger equation
The Schrödinger equation is a linear partial differential equation that governs the wave function of a quantum-mechanical system. It is a key result in quantum mechanics, and its discovery was a significant landmark in the development of th ...
in quantum mechanics, . Assume the system in question has the rotation group SO(3)
In mechanics and geometry, the 3D rotation group, often denoted SO(3), is the group of all rotations about the origin of three-dimensional Euclidean space \R^3 under the operation of composition.
By definition, a rotation about the origin is a ...
as a symmetry, meaning that the Hamiltonian operator commutes with the action of SO(3) on the wave function . (One important example of such a system is the Hydrogen atom, which has a single spherical orbital.) This assumption does not necessarily mean that the solutions are rotationally invariant functions. Rather, it means that the ''space'' of solutions to is invariant under rotations (for each fixed value of ). This space, therefore, constitutes a representation of SO(3). These representations have been classified and the classification leads to a substantial simplification of the problem, essentially converting a three-dimensional partial differential equation to a one-dimensional ordinary differential equation.
The case of a connected compact Lie group ''K'' (including the just-mentioned case of SO(3)) is particularly tractable. In that case, every finite-dimensional representation of ''K'' decomposes as a direct sum of irreducible representations. The irreducible representations, in turn, were classified by Hermann Weyl. The classification is in terms of the "highest weight" of the representation. The classification is closely related to the classification of representations of a semisimple Lie algebra.
One can also study (in general infinite-dimensional) unitary representations of an arbitrary Lie group (not necessarily compact). For example, it is possible to give a relatively simple explicit description of the representations of the group SL(2,R) and the representations of the Poincaré group.
Classification
Lie groups may be thought of as smoothly varying families of symmetries. Examples of symmetries include rotation about an axis. What must be understood is the nature of 'small' transformations, for example, rotations through tiny angles, that link nearby transformations. The mathematical object capturing this structure is called a Lie algebra ( Lie himself called them "infinitesimal groups"). It can be defined because Lie groups are smooth manifolds, so havetangent space
In mathematics, the tangent space of a manifold generalizes to higher dimensions the notion of '' tangent planes'' to surfaces in three dimensions and ''tangent lines'' to curves in two dimensions. In the context of physics the tangent space to a ...
s at each point.
The Lie algebra of any compact Lie group (very roughly: one for which the symmetries form a bounded set) can be decomposed as a direct sum of an abelian Lie algebra and some number of simple
Simple or SIMPLE may refer to:
*Simplicity, the state or quality of being simple
Arts and entertainment
* ''Simple'' (album), by Andy Yorke, 2008, and its title track
* "Simple" (Florida Georgia Line song), 2018
* "Simple", a song by Johnn ...
ones. The structure of an abelian Lie algebra is mathematically uninteresting (since the Lie bracket is identically zero); the interest is in the simple summands. Hence the question arises: what are the simple Lie algebras of compact groups? It turns out that they mostly fall into four infinite families, the "classical Lie algebras" A''n'', B''n'', C''n'' and D''n'', which have simple descriptions in terms of symmetries of Euclidean space. But there are also just five "exceptional Lie algebras" that do not fall into any of these families. E8 is the largest of these.
Lie groups are classified according to their algebraic properties (simple
Simple or SIMPLE may refer to:
*Simplicity, the state or quality of being simple
Arts and entertainment
* ''Simple'' (album), by Andy Yorke, 2008, and its title track
* "Simple" (Florida Georgia Line song), 2018
* "Simple", a song by Johnn ...
, semisimple
In mathematics, semi-simplicity is a widespread concept in disciplines such as linear algebra, abstract algebra, representation theory, category theory, and algebraic geometry. A semi-simple object is one that can be decomposed into a sum of ''sim ...
, solvable, nilpotent
In mathematics, an element x of a ring R is called nilpotent if there exists some positive integer n, called the index (or sometimes the degree), such that x^n=0.
The term was introduced by Benjamin Peirce in the context of his work on the cla ...
, abelian), their connectedness
In mathematics, connectedness is used to refer to various properties meaning, in some sense, "all one piece". When a mathematical object has such a property, we say it is connected; otherwise it is disconnected. When a disconnected object can be s ...
(connected
Connected may refer to:
Film and television
* ''Connected'' (2008 film), a Hong Kong remake of the American movie ''Cellular''
* '' Connected: An Autoblogography About Love, Death & Technology'', a 2011 documentary film
* ''Connected'' (2015 TV ...
or simply connected) and their compactness.
A first key result is the Levi decomposition, which says that every simply connected Lie group is the semidirect product of a solvable normal subgroup and a semisimple subgroup.
*Connected compact Lie group
In mathematics, a compact (topological) group is a topological group whose topology realizes it as a compact topological space (when an element of the group is operated on, the result is also within the group). Compact groups are a natural gen ...
s are all known: they are finite central quotients of a product of copies of the circle group S1 and simple compact Lie groups (which correspond to connected Dynkin diagram
In the Mathematics, mathematical field of Lie theory, a Dynkin diagram, named for Eugene Dynkin, is a type of Graph (discrete mathematics), graph with some edges doubled or tripled (drawn as a double or triple line). Dynkin diagrams arise in the ...
s).
*Any simply connected solvable Lie group is isomorphic to a closed subgroup of the group of invertible upper triangular matrices of some rank, and any finite-dimensional irreducible representation of such a group is 1-dimensional. Solvable groups are too messy to classify except in a few small dimensions.
*Any simply connected nilpotent Lie group is isomorphic to a closed subgroup of the group of invertible upper triangular matrices with 1's on the diagonal of some rank, and any finite-dimensional irreducible representation of such a group is 1-dimensional. Like solvable groups, nilpotent groups are too messy to classify except in a few small dimensions.
*Simple Lie group
In mathematics, a simple Lie group is a connected non-abelian Lie group ''G'' which does not have nontrivial connected normal subgroups. The list of simple Lie groups can be used to read off the list of simple Lie algebras and Riemannian symm ...
s are sometimes defined to be those that are simple as abstract groups, and sometimes defined to be connected Lie groups with a simple Lie algebra. For example, SL(2, R) is simple according to the second definition but not according to the first. They have all been classified (for either definition).
*Semisimple
In mathematics, semi-simplicity is a widespread concept in disciplines such as linear algebra, abstract algebra, representation theory, category theory, and algebraic geometry. A semi-simple object is one that can be decomposed into a sum of ''sim ...
Lie groups are Lie groups whose Lie algebra is a product of simple Lie algebras. They are central extensions of products of simple Lie groups.
The identity component
In mathematics, specifically group theory, the identity component of a group ''G'' refers to several closely related notions of the largest connected subgroup of ''G'' containing the identity element.
In point set topology, the identity compo ...
of any Lie group is an open normal subgroup, and the quotient group is a discrete group
In mathematics, a topological group ''G'' is called a discrete group if there is no limit point in it (i.e., for each element in ''G'', there is a neighborhood which only contains that element). Equivalently, the group ''G'' is discrete if and o ...
. The universal cover of any connected Lie group is a simply connected Lie group, and conversely any connected Lie group is a quotient of a simply connected Lie group by a discrete normal subgroup of the center. Any Lie group ''G'' can be decomposed into discrete, simple, and abelian groups in a canonical way as follows. Write
:''G''con for the connected component of the identity
:''G''sol for the largest connected normal solvable subgroup
:''G''nil for the largest connected normal nilpotent subgroup
so that we have a sequence of normal subgroups
:1 ⊆ ''G''nil ⊆ ''G''sol ⊆ ''G''con ⊆ ''G''.
Then
:''G''/''G''con is discrete
:''G''con/''G''sol is a central extension of a product of simple connected Lie groups.
:''G''sol/''G''nil is abelian. A connected abelian Lie group is isomorphic to a product of copies of R and the circle group ''S''1.
:''G''nil/1 is nilpotent, and therefore its ascending central series has all quotients abelian.
This can be used to reduce some problems about Lie groups (such as finding their unitary representations) to the same problems for connected simple groups and nilpotent and solvable subgroups of smaller dimension.
* The diffeomorphism group
In mathematics, a diffeomorphism is an isomorphism of smooth manifolds. It is an Inverse function, invertible Function (mathematics), function that maps one differentiable manifold to another such that both the function and its inverse function ...
of a Lie group acts transitively on the Lie group
* Every Lie group is parallelizable
In mathematics, a differentiable manifold M of dimension ''n'' is called parallelizable if there exist smooth vector fields
\
on the manifold, such that at every point p of M the tangent vectors
\
provide a basis of the tangent space at p. Equi ...
, and hence an orientable manifold
In mathematics, orientability is a property of some topological spaces such as real vector spaces, Euclidean spaces, surfaces, and more generally manifolds that allows a consistent definition of "clockwise" and "counterclockwise". A space is ...
(there is a bundle isomorphism
In mathematics, a bundle map (or bundle morphism) is a morphism in the category of fiber bundles. There are two distinct, but closely related, notions of bundle map, depending on whether the fiber bundles in question have a common base space. There ...
between its tangent bundle
In differential geometry, the tangent bundle of a differentiable manifold M is a manifold TM which assembles all the tangent vectors in M . As a set, it is given by the disjoint unionThe disjoint union ensures that for any two points and of ...
and the product of itself with the tangent space
In mathematics, the tangent space of a manifold generalizes to higher dimensions the notion of '' tangent planes'' to surfaces in three dimensions and ''tangent lines'' to curves in two dimensions. In the context of physics the tangent space to a ...
at the identity)
Infinite-dimensional Lie groups
Lie groups are often defined to be finite-dimensional, but there are many groups that resemble Lie groups, except for being infinite-dimensional. The simplest way to define infinite-dimensional Lie groups is to model them locally on Banach spaces (as opposed toEuclidean space
Euclidean space is the fundamental space of geometry, intended to represent physical space. Originally, that is, in Euclid's ''Elements'', it was the three-dimensional space of Euclidean geometry, but in modern mathematics there are Euclidean ...
in the finite-dimensional case), and in this case much of the basic theory is similar to that of finite-dimensional Lie groups. However this is inadequate for many applications, because many natural examples of infinite-dimensional Lie groups are not Banach manifold
In mathematics, a Banach manifold is a manifold modeled on Banach spaces. Thus it is a topological space in which each point has a neighbourhood homeomorphic to an open set in a Banach space (a more involved and formal definition is given below) ...
s. Instead one needs to define Lie groups modeled on more general locally convex topological vector spaces. In this case the relation between the Lie algebra and the Lie group becomes rather subtle, and several results about finite-dimensional Lie groups no longer hold.
The literature is not entirely uniform in its terminology as to exactly which properties of infinite-dimensional groups qualify the group for the prefix ''Lie'' in ''Lie group''. On the Lie algebra side of affairs, things are simpler since the qualifying criteria for the prefix ''Lie'' in ''Lie algebra'' are purely algebraic. For example, an infinite-dimensional Lie algebra may or may not have a corresponding Lie group. That is, there may be a group corresponding to the Lie algebra, but it might not be nice enough to be called a Lie group, or the connection between the group and the Lie algebra might not be nice enough (for example, failure of the exponential map to be onto a neighborhood of the identity). It is the "nice enough" that is not universally defined.
Some of the examples that have been studied include:
*The group of diffeomorphism
In mathematics, a diffeomorphism is an isomorphism of smooth manifolds. It is an invertible function that maps one differentiable manifold to another such that both the function and its inverse are differentiable.
Definition
Given two ...
s of a manifold. Quite a lot is known about the group of diffeomorphisms of the circle. Its Lie algebra is (more or less) the Witt algebra, whose central extension the Virasoro algebra
In mathematics, the Virasoro algebra (named after the physicist Miguel Ángel Virasoro) is a complex Lie algebra and the unique central extension of the Witt algebra. It is widely used in two-dimensional conformal field theory and in string the ...
(see Virasoro algebra from Witt algebra for a derivation of this fact) is the symmetry algebra of two-dimensional conformal field theory
A two-dimensional conformal field theory is a quantum field theory on a Euclidean two-dimensional space, that is invariant under local conformal transformations.
In contrast to other types of conformal field theories, two-dimensional conformal fi ...
. Diffeomorphism groups of compact manifolds of larger dimension are regular Fréchet Lie groups; very little about their structure is known.
*The diffeomorphism group of spacetime sometimes appears in attempts to quantize gravity.
*The group of smooth maps from a manifold to a finite-dimensional Lie group is an example of a gauge group
In physics, a gauge theory is a type of field theory in which the Lagrangian (and hence the dynamics of the system itself) does not change (is invariant) under local transformations according to certain smooth families of operations (Lie group ...
(with operation of pointwise multiplication
In mathematics, the pointwise product of two functions is another function, obtained by multiplying the images of the two functions at each value in the domain. If and are both functions with domain and codomain , and elements of can be mul ...
), and is used in quantum field theory and Donaldson theory
In mathematics, and especially gauge theory, Donaldson theory is the study of the topology of smooth 4-manifolds using moduli spaces of anti-self-dual instantons. It was started by Simon Donaldson (1983) who proved Donaldson's theorem restricti ...
. If the manifold is a circle these are called loop group
In mathematics, a loop group is a group of loops in a topological group ''G'' with multiplication defined pointwise.
Definition
In its most general form a loop group is a group of continuous mappings from a manifold to a topological group .
...
s, and have central extensions whose Lie algebras are (more or less) Kac–Moody algebras.
*There are infinite-dimensional analogues of general linear groups, orthogonal groups, and so on. One important aspect is that these may have ''simpler'' topological properties: see for example Kuiper's theorem. In M-theory
M-theory is a theory in physics that unifies all consistent versions of superstring theory. Edward Witten first conjectured the existence of such a theory at a string theory conference at the University of Southern California in 1995. Witten's ...
, for example, a 10-dimensional SU(''N'') gauge theory becomes an 11-dimensional theory when ''N'' becomes infinite.
See also
*Adjoint representation of a Lie group
In mathematics, the adjoint representation (or adjoint action) of a Lie group ''G'' is a way of representing the elements of the group as linear transformations of the group's Lie algebra, considered as a vector space. For example, if ''G'' is GL( ...
* Haar measure
* Homogeneous space
* List of Lie group topics
*Representations of Lie groups
In mathematics and theoretical physics, a representation of a Lie group is a linear action of a Lie group on a vector space. Equivalently, a representation is a smooth homomorphism of the group into the group of invertible operators on the vecto ...
*Symmetry in quantum mechanics
Symmetries in quantum mechanics describe features of spacetime and particles which are unchanged under some transformation, in the context of quantum mechanics, relativistic quantum mechanics and quantum field theory, and with applications in the ...
* Lie point symmetry, about the application of Lie groups to the study of differential equations.
Notes
Explanatory notes
Citations
References
* . * * * . Chapters 1–3 , Chapters 4–6 , Chapters 7–9 * . * P. M. Cohn (1957) ''Lie Groups'', Cambridge Tracts in Mathematical Physics. * J. L. Coolidge (1940) ''A History of Geometrical Methods'', pp 304–17,Oxford University Press
Oxford University Press (OUP) is the university press of the University of Oxford. It is the largest university press in the world, and its printing history dates back to the 1480s. Having been officially granted the legal right to print books ...
(Dover Publications
Dover Publications, also known as Dover Books, is an American book publisher founded in 1941 by Hayward and Blanche Cirker. It primarily reissues books that are out of print from their original publishers. These are often, but not always, book ...
2003).
*
* Robert Gilmore (2008) ''Lie groups, physics, and geometry: an introduction for physicists, engineers and chemists'', Cambridge University Press
Cambridge University Press is the university press of the University of Cambridge. Granted letters patent by King Henry VIII in 1534, it is the oldest university press in the world. It is also the King's Printer.
Cambridge University Pre ...
.
* .
* F. Reese Harvey (1990) ''Spinors and calibrations'', Academic Press
Academic Press (AP) is an academic book publisher founded in 1941. It was acquired by Harcourt, Brace & World in 1969. Reed Elsevier bought Harcourt in 2000, and Academic Press is now an imprint of Elsevier.
Academic Press publishes referen ...
, .
Borel's review
* * . * . * * * . The 2003 reprint corrects several typographical mistakes. * * . * * Heldermann Verla
* * .
Lie Groups. Representation Theory and Symmetric Spaces
Wolfgang Ziller, Vorlesung 2010
External links
* {{Authority control Manifolds Symmetry