hot dark matter on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Hot dark matter (HDM) is a theoretical form of
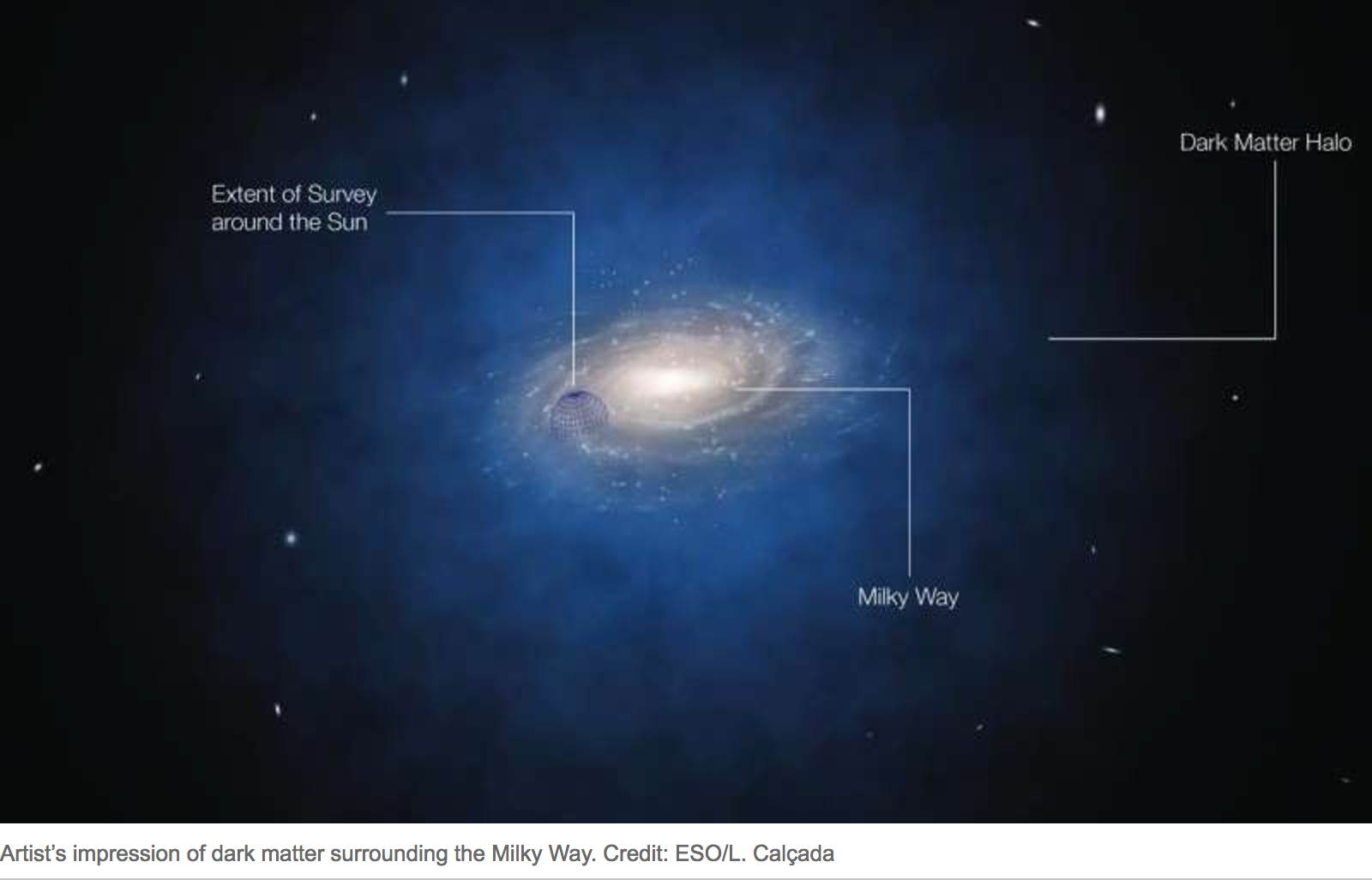 In terms of its application, the distribution of hot dark matter could also help explain how clusters and
In terms of its application, the distribution of hot dark matter could also help explain how clusters and
Hot dark matter by Berkeley
{{Dark matter Dark matter Physical cosmological concepts
dark matter
In astronomy, dark matter is an invisible and hypothetical form of matter that does not interact with light or other electromagnetic radiation. Dark matter is implied by gravity, gravitational effects that cannot be explained by general relat ...
which consists of particles that travel with ultrarelativistic velocities.
Description
Dark matter
In astronomy, dark matter is an invisible and hypothetical form of matter that does not interact with light or other electromagnetic radiation. Dark matter is implied by gravity, gravitational effects that cannot be explained by general relat ...
is a form of matter that neither emits nor absorbs light. Within physics, this behavior is characterized by dark matter not interacting with electromagnetic radiation
In physics, electromagnetic radiation (EMR) is a self-propagating wave of the electromagnetic field that carries momentum and radiant energy through space. It encompasses a broad spectrum, classified by frequency or its inverse, wavelength ...
, hence making it ''dark'' and rendering it undetectable via conventional instruments in physics.
Data from galaxy rotation curves indicate that approximately 80% of the mass of a galaxy cannot be seen, forcing researchers to innovate ways that ''indirectly'' detect it through dark matter's effects on gravitational fluctuations.
As we shall see below, it is useful to differentiate dark matter into "hot" (HDM) and "cold
Cold is the presence of low temperature, especially in the atmosphere. In common usage, cold is often a subjectivity, subjective perception. A lower bound to temperature is absolute zero, defined as 0.00K on the Kelvin scale, an absolute t ...
" (CDM) types–some even suggesting a middle-ground of "warm" dark matter (WDM). The terminology refers to the mass of the dark matter particles (which dictates the speed at which they travel): HDM travels faster than CDM because the HDM particles are theorized to be of lower mass.
Role in galaxy formation
 In terms of its application, the distribution of hot dark matter could also help explain how clusters and
In terms of its application, the distribution of hot dark matter could also help explain how clusters and supercluster
A supercluster is a large group of smaller galaxy clusters or galaxy groups; they are among the largest known structures in the universe. The Milky Way is part of the Local Group galaxy group (which contains more than 54 galaxies), which in tu ...
s of galaxies
A galaxy is a system of stars, stellar remnants, interstellar gas, dust, and dark matter bound together by gravity. The word is derived from the Greek ' (), literally 'milky', a reference to the Milky Way galaxy that contains the Solar Sys ...
formed after the Big Bang
The Big Bang is a physical theory that describes how the universe expanded from an initial state of high density and temperature. Various cosmological models based on the Big Bang concept explain a broad range of phenomena, including th ...
. Theorists claim that there exist two classes of dark matter:
1) those that "congregate around individual members of a cluster of visible galaxies" and
2) those that encompass "the clusters as a whole." Because cold dark matter possesses a lower velocity, it could be the source of "smaller, galaxy-sized lumps," as shown in the image.
Hot dark matter, then, should correspond to the formation of larger mass aggregates that surround whole galaxy clusters. However, data from the cosmic microwave background
The cosmic microwave background (CMB, CMBR), or relic radiation, is microwave radiation that fills all space in the observable universe. With a standard optical telescope, the background space between stars and galaxies is almost completely dar ...
radiation, as measured by the COBE satellite, is highly uniform, and such high-velocity hot dark matter particles cannot form clumps as small as galaxies beginning from such a smooth initial state, highlighting a discrepancy in what dark matter theory and the actual data are saying. Theoretically, in order to explain relatively small-scale structures in the observable Universe
The observable universe is a Ball (mathematics), spherical region of the universe consisting of all matter that can be observation, observed from Earth; the electromagnetic radiation from these astronomical object, objects has had time to reach t ...
, it is necessary to invoke cold dark matter or WDM. In other words, hot dark matter being the sole substance in explaining cosmic galaxy formation is no longer viable, placing hot dark matter under the larger umbrella of mixed dark matter (MDM) theory.
Neutrinos
An example of a hot dark matter particle is theneutrino
A neutrino ( ; denoted by the Greek letter ) is an elementary particle that interacts via the weak interaction and gravity. The neutrino is so named because it is electrically neutral and because its rest mass is so small ('' -ino'') that i ...
. Neutrinos have very small masses, and do not take part in two of the four fundamental forces, the electromagnetic interaction and the strong interaction
In nuclear physics and particle physics, the strong interaction, also called the strong force or strong nuclear force, is one of the four known fundamental interaction, fundamental interactions. It confines Quark, quarks into proton, protons, n ...
. They interact by the weak interaction
In nuclear physics and particle physics, the weak interaction, weak force or the weak nuclear force, is one of the four known fundamental interactions, with the others being electromagnetism, the strong interaction, and gravitation. It is th ...
, and most probably gravity
In physics, gravity (), also known as gravitation or a gravitational interaction, is a fundamental interaction, a mutual attraction between all massive particles. On Earth, gravity takes a slightly different meaning: the observed force b ...
, but due to the feeble strength of these forces, they are difficult to detect. A number of projects, such as the Super-Kamiokande
Super-Kamiokande (abbreviation of Super-Kamioka Neutrino Detection Experiment, also abbreviated to Super-K or SK; ) is a neutrino detector, neutrino observatory located Kamioka Observatory, under Mount Ikeno near the city of Hida, Gifu, Hida, ...
neutrino observatory, in Gifu
is a Cities of Japan, city located in the south-central portion of Gifu Prefecture, Japan, and serves as the prefectural capital. The city has played an important role in Japan's history because of its location in the middle of the country. Durin ...
, Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
are currently studying these neutrinos.
See also
* * * Weakly interacting slender particle (WISP)References
Further reading
*External links
Hot dark matter by Berkeley
{{Dark matter Dark matter Physical cosmological concepts