guanacos on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The guanaco (; ''Lama guanicoe'') is a
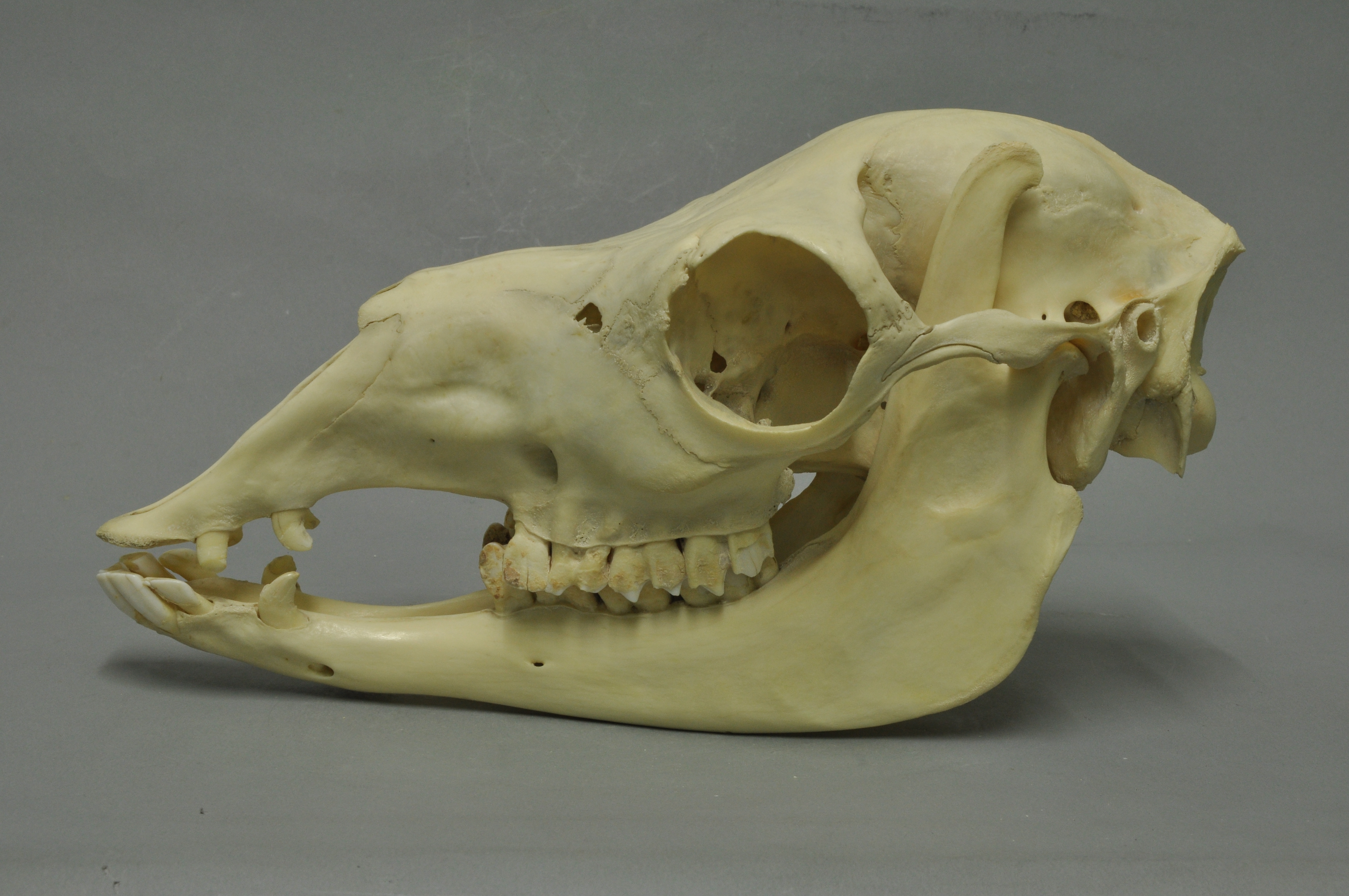 Guanacos stand between at the shoulder, body length of , and weigh . Their color varies very little (unlike the domestic
Guanacos stand between at the shoulder, body length of , and weigh . Their color varies very little (unlike the domestic
Other terrestrial mammalian

 Guanacos inhabit the steppes, scrublands and mountainous regions of South America. They are found in the
Guanacos inhabit the steppes, scrublands and mountainous regions of South America. They are found in the
camelid
Camelids are members of the biological family Camelidae, the only currently living family in the suborder Tylopoda. The seven extant members of this group are: dromedary camels, Bactrian camels, wild Bactrian camels, llamas, alpacas, vicuñas, ...
native to South America, closely related to the llama
The llama (; ) (''Lama glama'') is a domesticated South American camelid, widely used as a List of meat animals, meat and pack animal by Inca empire, Andean cultures since the Pre-Columbian era.
Llamas are social animals and live with othe ...
. Guanacos are one of two wild South American camelids, the other being the vicuña, which lives at higher elevations.
Etymology
The guanaco gets its name from theQuechua
Quechua may refer to:
*Quechua people, several indigenous ethnic groups in South America, especially in Peru
*Quechuan languages, a Native South American language family spoken primarily in the Andes, derived from a common ancestral language
**So ...
word ''huanaco'' (modern spelling ''wanaku''). Young guanacos are called ''chulengos''.
Characteristics
 Guanacos stand between at the shoulder, body length of , and weigh . Their color varies very little (unlike the domestic
Guanacos stand between at the shoulder, body length of , and weigh . Their color varies very little (unlike the domestic llama
The llama (; ) (''Lama glama'') is a domesticated South American camelid, widely used as a List of meat animals, meat and pack animal by Inca empire, Andean cultures since the Pre-Columbian era.
Llamas are social animals and live with othe ...
), ranging from a light brown to dark cinnamon and shading to white underneath. Guanacos have grey faces and small, straight ears. The lifespan of a guanaco can be as long as 28 years.
Guanacos are one of the largest terrestrial mammals native to South America today.San Diego Zoo's Animal BytesOther terrestrial mammalian
megafauna
In terrestrial zoology, the megafauna (from Greek μέγας ''megas'' "large" and New Latin ''fauna'' "animal life") comprises the large or giant animals of an area, habitat, or geological period, extinct and/or extant. The most common threshold ...
weighing as much or more than the guanaco include the tapir
Tapirs ( ) are large, herbivorous mammals belonging to the family Tapiridae. They are similar in shape to a pig, with a short, prehensile nose trunk. Tapirs inhabit jungle and forest regions of South and Central America, with one species inh ...
s, the marsh deer
The marsh deer (''Blastocerus dichotomus'') is the largest deer species from South America reaching a length of and a shoulder height of . It is found in Argentina, Bolivia, Peru, Brazil, Uruguay and Paraguay. Formerly found in much of tropical ...
, the white-tailed deer
The white-tailed deer (''Odocoileus virginianus''), also known as the whitetail or Virginia deer, is a medium-sized deer native to North America, Central America, and South America as far south as Peru and Bolivia. It has also been introduced t ...
, the spectacled bear, and the jaguar.
Guanacos have thick skin on their necks, a trait also found in their domestic counterparts, the llama
The llama (; ) (''Lama glama'') is a domesticated South American camelid, widely used as a List of meat animals, meat and pack animal by Inca empire, Andean cultures since the Pre-Columbian era.
Llamas are social animals and live with othe ...
, and their relatives, the wild vicuña and domesticated alpaca
The alpaca (''Lama pacos'') is a species of South American camelid mammal. It is similar to, and often confused with, the llama. However, alpacas are often noticeably smaller than llamas. The two animals are closely related and can successf ...
. This protects their necks from predator attacks. Bolivians use the neck skin of these animals to make shoes, flattening and pounding the skin to be used for the soles. In Chile, hunting is allowed only in Tierra del Fuego, where the only population not classified as endangered in the country resides. Between 2007 and 2012, 13,200 guanacos were legally hunted in Tierra del Fuego.
Food
Like all camels, Guanacos are herbivores, grazing on grasses, shrubs, herbs, lichens, fungi, cacti and flowers. The food is swallowed with little chewing and first enters the forestomach to be digested finally after rumination. This process is similar to that of ruminants, to which camels are not zoologically classified. The camels' digestive system is likely to have developed independently of ruminants, which is shown by the fact that the forestomachs are equipped with glands.Hemoglobin levels
Guanacos are often found at high altitudes, up to 4,000 meters above sea level, except in Patagonia, where the southerly latitude means ice covers the vegetation at these altitudes. For guanacos to survive in the low oxygen levels found at these high altitudes, their blood is rich in red blood cells. A teaspoon of guanaco blood contains about 68 million red blood cells; four times that of a human.Guanaco fiber
Guanaco fiber is particularly prized for its soft, warm feel and is found inluxury
Luxury may refer to:
*Luxury goods, an economic good or service for which demand increases more than proportionally as income rises
*Luxury tax, tax on products not considered essential, such as expensive cars
**Luxury tax (sports), surcharge put ...
fabric
Textile is an umbrella term that includes various fiber-based materials, including fibers, yarns, filaments, threads, different fabric types, etc. At first, the word "textiles" only referred to woven fabrics. However, weaving is not t ...
. In South America, the guanaco's soft wool is valued second only to that of vicuña wool
Vicuña wool refers to the hair of the South American vicuña, an animal of the family of ''camelidae''. The wool has, after shahtoosh, the second smallest fiber diameter of all animal hair and is the most expensive legal wool.
Properties
The ...
. The pelts, particularly from the calves, are sometimes used as a substitute for red fox pelts, because the texture is difficult to differentiate. Like their domestic descendant, the llama, the guanaco is double-coated with coarse guard hairs and a soft undercoat, the hairs of which are about 16–18 µ in diameter and comparable to cashmere.
Subspecies
*''Lama guanicoe guanicoe'' *''Lama guanicoe cacsilensis'' *''Lama guanicoe voglii'' *''Lama guanicoe huanacus''Population and distribution

 Guanacos inhabit the steppes, scrublands and mountainous regions of South America. They are found in the
Guanacos inhabit the steppes, scrublands and mountainous regions of South America. They are found in the altiplano
The Altiplano (Spanish for "high plain"), Collao (Quechua and Aymara: Qullaw, meaning "place of the Qulla") or Andean Plateau, in west-central South America, is the most extensive high plateau on Earth outside Tibet. The plateau is located at t ...
of Peru, Bolivia
, image_flag = Bandera de Bolivia (Estado).svg
, flag_alt = Horizontal tricolor (red, yellow, and green from top to bottom) with the coat of arms of Bolivia in the center
, flag_alt2 = 7 × 7 square p ...
and Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of land between the Andes to the east a ...
, and in Patagonia, with a small population in Paraguay. In Argentina
Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the second-largest country in South America after Brazil, th ...
they are more numerous in Patagonian regions, as well as in places such as Isla Grande de Tierra del Fuego
Isla Grande de Tierra del Fuego (English: ''Big Island of the Land of Fire'') also formerly ''Isla de Xátiva'' A small population introduced by John Hamilton exists on
File:Guanacos, Torres del Paine.jpg, Guanacos in
Puma takes on Guanaco 3 Times Her Weight
, Seven Worlds, One Planet ,
Staats Island
Staats Island is an uninhabited island of the Beaver Island Group in the Falkland Islands. It lies between Beaver Island and Weddell Island, parallel to Tea Island and is in area.
Wildlife
The island is known for its Patagonian foxes and gu ...
in the Falkland Islands (Malvinas), with a population of around 400 as of 2003. In Torres del Paine National Park, the numbers of Guanacos increased from 175 in 1975 to 3,000 in 1993.
Guanacos live in herds composed of females, their young, and a dominant male. Bachelor males form separate herds. While reproductive groups tend to remain small, often containing no more than 10 adults, bachelor herds may contain as many as 50 males. When they feel threatened, guanacos alert the herd to flee with a high-pitched, bleating call. The male usually runs behind the herd to defend them. They can run at 56 km (35 mi) per hour, often over steep and rocky terrain. They are also excellent swimmers. A guanaco's typical lifespan is 20 to 25 years.
In Bolivia, the habitat of Guanacos is found to be threatened by woody plant encroachment.
Atacama Desert
Some guanacos live in theAtacama Desert
The Atacama Desert ( es, Desierto de Atacama) is a desert plateau in South America covering a 1,600 km (990 mi) strip of land on the Pacific coast, west of the Andes Mountains. The Atacama Desert is the driest nonpolar desert in the w ...
, where in some areas it has not rained for over 50 years. A mountainous coastline running parallel to the desert enables them to survive in what are called "fog oases" or lomas
Lomas (Spanish for "hills"), also called fog oases and mist oases, are areas of fog-watered vegetation in the coastal desert of Peru and northern Chile. About 100 lomas near the Pacific Ocean are identified between 5°S and 30°S latitude, a nort ...
. Where the cool water touches the hotter land, the air above the desert is cooled, creating a fog and thus, water vapor. Winds carry the fog across the desert, where cacti
A cactus (, or less commonly, cactus) is a member of the plant family Cactaceae, a family comprising about 127 genera with some 1750 known species of the order Caryophyllales. The word ''cactus'' derives, through Latin, from the Ancient Gree ...
catch the water droplets and lichens that cling to the cacti soak it in like a sponge. Guanacos then eat the cacti flowers and the lichens.
Torres del Paine National Park
Torres del Paine National Park ( es, Parque Nacional Torres del Paine) is a national park encompassing mountains, glaciers, lakes, and rivers in southern Chilean Patagonia. The Cordillera del Paine is the centerpiece of the park. It lies in a tr ...
in Patagonia
File:The Guanacos of Atacama.jpg, Guanacos near the La Silla Observatory
La Silla Observatory is an astronomical observatory in Chile with three telescopes built and operated by the European Southern Observatory (ESO). Several other telescopes are located at the site and are partly maintained by ESO. The observatory i ...
, 2400 meters above sea level.
File:GuanacoBonesInAtacama.jpg, The remains of a guanaco scattered in the Atacama Desert, southwest of Cerro Paranal
Cerro Paranal is a mountain in the Atacama Desert of northern Chile and is the home of the Paranal Observatory. Prior to the construction of the observatory, the summit was a horizontal control point with an elevation of ; now it is above sea ...
: The only intact section of skin is the thicker skin around the neck
File:Lama guanicoe in Parque Nacional Torres del Paine in Patagonia, Chile.jpg, Guanacos near Torres del Paine
The Cordillera Paine is a mountain group in Torres del Paine National Park in Chilean Patagonia. The cordillera is located north of Punta Arenas, and about south of the Chilean capital Santiago. It belongs to the Commune of Torres del Paine i ...
, Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of land between the Andes to the east a ...
Ecology
The guanaco is a diurnal animal. It lives in small herds consisting of one male and several females with their young. When the male detects danger, he warns the group by bleating. The guanaco can run up to 64 km/h. This speed is important for the survival of guanacos because they cannot easily hide in the open grasslands of the Altiplano. Natural predators of the guanaco include pumas and the culpeo or Andean fox. Fox predation was unknown until 2007 when predators began to be observed in the Karukinka Reserve in Tierra del Fuego. Scientists attribute the reason for the alleged new predation to the unfavourable climatic conditions on the island, which are causing food to become scarce, weakening the animals. The absence of pumas on Tierra del Fuego is also believed to be a factor that allows the fox to occupy its ecological niche. Finally, it is believed that this behaviour is not new, as the fox is nocturnal, which allows it to capture most of its prey, but makes it challenging to observe. Faced with the threat of the red fox, guanacos resort to cooperative strategies to protect their young with a shield formation, a circle around the vulnerable. If they are successful, they chase the fox away, which would be impossible with a puma. When threatened, the guanaco alerts the rest of the herd with a high-pitched bleating sound, which sounds similar to a short, sharp laugh. Though typically mild-mannered, guanacos often spit when threatened, and can do so up to a distance of six feet.Mating season
Mating season occurs between November and February, during which males often fight violently to establish dominance and breeding rights. Eleven-and-a-half months later, a single chulengo is born. Chulengos are able to walk immediately after birth. Male chulengos are chased off from the herd by the dominant male around one year of age.Domestication
Although the species is still considered wild, around 300 guanacos are in U.S. zoos, and around 200 are registered in private herds. Guanacos have long been thought to be the parent species of the domesticatedllama
The llama (; ) (''Lama glama'') is a domesticated South American camelid, widely used as a List of meat animals, meat and pack animal by Inca empire, Andean cultures since the Pre-Columbian era.
Llamas are social animals and live with othe ...
, which was confirmed via molecular phylogenetic
Molecular phylogenetics () is the branch of phylogeny that analyzes genetic, hereditary molecular differences, predominantly in DNA sequences, to gain information on an organism's evolutionary relationships. From these analyses, it is possible to ...
analysis in 2001, although the analysis also found that domestic llamas had experienced considerable cross-hybridization with alpaca
The alpaca (''Lama pacos'') is a species of South American camelid mammal. It is similar to, and often confused with, the llama. However, alpacas are often noticeably smaller than llamas. The two animals are closely related and can successf ...
s, which are descended from the wild vicuña.
The guanaco was independently domesticated by the Mapuche
The Mapuche ( (Mapuche & Spanish: )) are a group of indigenous inhabitants of south-central Chile and southwestern Argentina, including parts of Patagonia. The collective term refers to a wide-ranging ethnicity composed of various groups who sh ...
of Mocha Island in southern Chile
Southern Chile is an informal geographic term for any place south of the capital city, Santiago, or south of Biobío River, the mouth of which is Concepción, about {{convert, 200, mi, km, sigfig=1, order=flip south of Santiago. Generally cities ...
, producing the "chilihueque
The chilihueque or hueque was a South American camelid variety or species that existed in central and south-central Chile in Pre-Hispanic and colonial times. There are two main hypotheses on their status among South American camelids: the f ...
" which was bred for its wool and to pull the plough. This animal disappeared in the 17th century when it was replaced by Old World
The "Old World" is a term for Afro-Eurasia that originated in Europe , after Europeans became aware of the existence of the Americas. It is used to contrast the continents of Africa, Europe, and Asia, which were previously thought of by th ...
sheep and draft animal
A working animal is an animal, usually domesticated, that is kept by humans and trained to perform tasks instead of being slaughtered to harvest animal products. Some are used for their physical strength (e.g. oxen and draft horses) or for tr ...
s.Westbury, M., Prost, S., Seelenfreund, A., Ramírez, J. M., Matisoo-Smith, E. A., & Knapp, M. (2016). First complete mitochondrial genome data from ancient South American camelids-the mystery of the chilihueques from Isla Mocha (Chile). ''Scientific reports'', 6(1), 1-7.
References
Further reading
* *External links
Puma takes on Guanaco 3 Times Her Weight
, Seven Worlds, One Planet ,
BBC Earth
BBC Earth is a brand used by BBC Studios since 2009 to market and distribute the BBC's natural history content to countries other than the United Kingdom. BBC Studios is the commercial arm of the public service broadcaster.
BBC Earth commerci ...
{{Authority control
Mammals of the Andes
Mammals of Patagonia
Mammals of Chile
Mammals of Argentina
Mammals of Peru
Mammals of Bolivia
Camelids
Quechua words and phrases
Mammals described in 1776
Taxa named by Philipp Ludwig Statius Müller
Animal hair products
Wool animals