grid storage on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 Grid energy storage (also called large-scale energy storage) is a collection of methods used for
Grid energy storage (also called large-scale energy storage) is a collection of methods used for
 The demand side can also store electricity from the grid, for example charging a
The demand side can also store electricity from the grid, for example charging a

 Battery storage was used in the early days of
Battery storage was used in the early days of
 Companies are researching the possible use of electric vehicles to meet peak demand. A parked and plugged-in electric vehicle could sell the electricity from the battery during peak loads and charge either during night (at home) or during off-peak.
Companies are researching the possible use of electric vehicles to meet peak demand. A parked and plugged-in electric vehicle could sell the electricity from the battery during peak loads and charge either during night (at home) or during off-peak.
"PG&E's Battery Power Plans Could Jump Start Electric Car Market."
(Blog). ''Green Wombat'', 2007-06-12. Retrieved on 2007-08-19 However, a large disadvantage of using vehicle to grid energy storage would be if each storage cycle stressed the battery with one complete charge-discharge cycle. However, one major study showed that used intelligently, vehicle-to-grid storage actually improved the batteries longevity. Conventional (cobalt-based) lithium-ion batteries break down with the number of cycles – newer li-ion batteries do not break down significantly with each cycle, and so have much longer lives. One approach is to reuse unreliable vehicle batteries in dedicated grid storage as they are expected to be good in this role for ten years. If such storage is done on a large scale it becomes much easier to guarantee replacement of a vehicle battery degraded in mobile use, as the old battery has value and immediate use.
 Mechanical inertia is the basis of this storage method. When the electric power flows into the device, an
Mechanical inertia is the basis of this storage method. When the electric power flows into the device, an
 In 2008, world pumped storage generating capacity was 104 GW, while other sources claim 127 GW, which comprises the vast majority of all types of grid electric storage – all other types combined are some hundreds of MW.
In many places, pumped storage hydroelectricity is used to even out the daily generating load, by pumping water to a high storage reservoir during off-peak hours and weekends, using the excess base-load capacity from coal or nuclear sources. During peak hours, this water can be used for
In 2008, world pumped storage generating capacity was 104 GW, while other sources claim 127 GW, which comprises the vast majority of all types of grid electric storage – all other types combined are some hundreds of MW.
In many places, pumped storage hydroelectricity is used to even out the daily generating load, by pumping water to a high storage reservoir during off-peak hours and weekends, using the excess base-load capacity from coal or nuclear sources. During peak hours, this water can be used for
 Hydroelectric dams with large reservoirs can also be operated to provide peak generation at times of peak demand. Water is stored in the reservoir during periods of low demand and released through the plant when demand is higher. The net effect is the same as pumped storage, but without the pumping loss. Depending on the reservoir capacity the plant can provide daily, weekly, or seasonal load following.
Many existing hydroelectric dams are fairly old (for example, the
Hydroelectric dams with large reservoirs can also be operated to provide peak generation at times of peak demand. Water is stored in the reservoir during periods of low demand and released through the plant when demand is higher. The net effect is the same as pumped storage, but without the pumping loss. Depending on the reservoir capacity the plant can provide daily, weekly, or seasonal load following.
Many existing hydroelectric dams are fairly old (for example, the
Energy Storage Hits the Rails Out West: In California and Nevada, projects store electricity in the form of heavy rail cars pulled up a hill
, '' ScientificAmerican.com'' website, 25 March 2014. Retrieved 28 March 2014. In disused oil-well potential energy storage, weights are raised or lowered in a deep, decommissioned oil well.
Saving For a Windless day
by Sean Davies in The E&T Magazine Vol 5 Issue 9 from th
www.IET.org
UK Government report on the Benefits of long-duration electricity storage (Aug 2022)
A large grid-connected nickel-cadmium battery
Stationary Energy Storage…Key to the Renewable Grid
Electricity Storage FactBook
{{emerging technologies, energy=yes Power engineering

 Grid energy storage (also called large-scale energy storage) is a collection of methods used for
Grid energy storage (also called large-scale energy storage) is a collection of methods used for energy storage
Energy storage is the capture of energy produced at one time for use at a later time to reduce imbalances between energy demand and energy production.
A device that stores energy is generally called an accumulator or battery.
Energy comes in ...
on a large scale within an electrical power grid
An electrical grid is an interconnected network for electricity delivery from producers to consumers. Electrical grids vary in size and can cover whole countries or continents. It consists of:Kaplan, S. M. (2009). Smart Grid. Electrical Power ...
. Electrical energy is stored during times when electricity is plentiful and inexpensive (especially from intermittent power sources such as renewable electricity
Renewable energy is energy that is collected from renewable resources that are naturally replenished on a human timescale. It includes sources such as sunlight, wind, the movement of water, and geothermal heat. Although most renewable energy ...
from wind power
Wind power or wind energy is mostly the use of wind turbines to generate electricity. Wind power is a popular, sustainable, renewable energy source that has a much smaller impact on the environment than burning fossil fuels. Historically, w ...
, tidal power
Tidal power or tidal energy is harnessed by converting energy from tides into useful forms of power, mainly electricity using various methods.
Although not yet widely used, tidal energy has the potential for future electricity generation. Ti ...
and solar power
Solar power is the conversion of energy from sunlight into electricity, either directly using photovoltaics (PV) or indirectly using concentrated solar power. Photovoltaic cells convert light into an electric current using the photovoltaic e ...
) or when demand is low, and later returned to the grid when demand is high, and electricity prices tend to be higher.
, the largest form of grid energy storage is dammed hydroelectricity
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies one sixth of the world's electricity, almost 4500 TWh in 2020, which is more than all other renewable sources combined and ...
, with both conventional hydroelectric generation as well as pumped storage hydroelectricity
Pumped-storage hydroelectricity (PSH), or pumped hydroelectric energy storage (PHES), is a type of hydroelectric energy storage used by electric power systems for load balancing. The method stores energy in the form of gravitational potential ...
.
Developments in battery storage have enabled commercially viable projects to store energy during peak production and release during peak demand, and for use when production unexpectedly falls giving time for slower responding resources to be brought online.
Two alternatives to grid storage are the use of peaking power plant
Peaking power plants, also known as peaker plants, and occasionally just "peakers", are power plants that generally run only when there is a high demand, known as peak demand, for electricity. Because they supply power only occasionally, the power ...
s to fill in supply gaps and demand response
Demand response is a change in the power consumption of an electric utility customer to better match the demand for power with the supply. Until the 21st century decrease in the cost of pumped storage and batteries electric energy could not be ...
to shift load to other times.
Benefits
Anyelectrical power grid
An electrical grid is an interconnected network for electricity delivery from producers to consumers. Electrical grids vary in size and can cover whole countries or continents. It consists of:Kaplan, S. M. (2009). Smart Grid. Electrical Power ...
must match electricity production to consumption, both of which vary drastically over time. Any combination of energy storage and demand response has these advantages:
*fuel-based power plants (i.e. coal, oil, gas, nuclear) can be more efficiently and easily operated at constant production levels
*electricity generated by intermittent sources can be stored and used later, whereas it would otherwise have to be transmitted for sale elsewhere, or shut down
*peak generating or transmission capacity can be reduced by the total potential of all storage plus deferrable loads (see demand side management
Energy demand management, also known as demand-side management (DSM) or demand-side response (DSR), is the modification of consumer demand for energy through various methods such as financial incentives and behavioral change through education.
Us ...
), saving the expense of this capacity
*more stable pricing – the cost of the storage or demand management is included in pricing so there is less variation in power rates charged to customers, or alternatively (if rates are kept stable by law) less loss to the utility from expensive on-peak wholesale power rates when peak demand must be met by imported wholesale power
*emergency preparedness – vital needs can be met reliably even with no transmission or generation going on while non-essential needs are deferred
Energy derived from solar, tidal and wind sources inherently varies on time scales ranging from minutes to weeks or longer – the amount of electricity produced varies with time of day, moon phase, season, and random factors such as the weather. Thus, renewables in the absence of storage present special challenges to electric utilities. While hooking up many separate wind sources can reduce the overall variability, solar is reliably not available at night, and tidal power shifts with the moon, so slack tides occur four times a day.
How much this affects any given utility varies significantly. In a summer peak utility, more solar can generally be absorbed and matched to demand. In winter peak utilities, to a lesser degree, wind correlates to heating demand and can be used to meet that demand. Depending on these factors, beyond about 20–40% of total generation, grid-connected intermittent sources such as solar power
Solar power is the conversion of energy from sunlight into electricity, either directly using photovoltaics (PV) or indirectly using concentrated solar power. Photovoltaic cells convert light into an electric current using the photovoltaic e ...
and wind power
Wind power or wind energy is mostly the use of wind turbines to generate electricity. Wind power is a popular, sustainable, renewable energy source that has a much smaller impact on the environment than burning fossil fuels. Historically, w ...
tend to require investment in grid interconnections, grid energy storage or demand-side management.
In an electrical grid
An electrical grid is an interconnected network for electricity delivery from producers to consumers. Electrical grids vary in size and can cover whole countries or continents. It consists of:Kaplan, S. M. (2009). Smart Grid. Electrical Power ...
without energy storage, generation that relies on energy stored within fuels (coal, biomass, natural gas, nuclear) must be scaled up and down to match the rise and fall of electrical production from intermittent sources (see load following power plant
A load-following power plant, regarded as producing mid-merit or mid-priced electricity, is a power plant that adjusts its power output as demand for electricity fluctuates throughout the day. Load-following plants are typically in between base lo ...
). While hydroelectric and natural gas plants can be quickly scaled up or down to follow the wind, coal and nuclear plants take considerable time to respond to load. Utilities with less natural gas or hydroelectric generation are thus more reliant on demand management, grid interconnections or costly pumped storage.
The French consulting firm Yole Développement estimates the "stationary storage" market could be a $13.5 billion opportunity by 2023, compared with less than $1 billion in 2015.
Demand side management and grid storage
 The demand side can also store electricity from the grid, for example charging a
The demand side can also store electricity from the grid, for example charging a battery electric vehicle
A battery electric vehicle (BEV), pure electric vehicle, only-electric vehicle, fully electric vehicle or all-electric vehicle is a type of electric vehicle (EV) that exclusively uses chemical energy stored in rechargeable battery packs, wi ...
stores energy for a vehicle and storage heater
A storage heater or heat bank (Australia) is an electrical heater which stores thermal energy during the evening, or at night when electricity is available at lower cost, and releases the heat during the day as required. Alternatively, solar s ...
s, district heating storage or ice storage provide thermal storage for buildings. At present this storage serves only to shift consumption to the off-peak time of day, no electricity is returned to the grid.
The need for grid storage to provide peak power is reduced by demand side time of use pricing, one of the benefits of smart meter
A smart meter is an electronic device that records information such as consumption of electric energy, voltage levels, current, and power factor. Smart meters communicate the information to the consumer for greater clarity of consumption beh ...
s. At the household level, consumers may choose less expensive off-peak times to wash and dry clothes, use dishwashers, take showers and cook. As well, commercial and industrial users will take advantage of cost savings by deferring some processes to off-peak times.
Regional impacts from the unpredictable operation of wind power has created a new need for interactive demand response
Demand response is a change in the power consumption of an electric utility customer to better match the demand for power with the supply. Until the 21st century decrease in the cost of pumped storage and batteries electric energy could not be ...
, where the utility communicates with the demand. Historically this was only done in cooperation with large industrial consumers, but now may be expanded to entire grids. For instance, a few large-scale projects in Europe link variations in wind power to change industrial food freezer loads, causing small variations in temperature. If communicated on a grid-wide scale, small changes to heating/cooling temperatures would instantly change consumption across the grid.
A report released in December 2013 by the United States Department of Energy
The United States Department of Energy (DOE) is an executive department of the U.S. federal government that oversees U.S. national energy policy and manages the research and development of nuclear power and nuclear weapons in the United States ...
further describes the potential benefits of energy storage and demand side technologies to the electric grid: "Modernizing the electric system will help the nation meet the challenge of handling projected energy needs—including addressing climate change by integrating more energy from renewable sources and enhancing efficiency from non-renewable energy processes. Advances to the electric grid must maintain a robust and resilient electricity delivery system, and energy storage can play a significant role in meeting these challenges by improving the operating capabilities of the grid, lowering cost and ensuring high reliability, as well as deferring and reducing infrastructure investments. Finally, energy storage can be instrumental for emergency preparedness because of its ability to provide backup power as well as grid stabilization services". The report was written by a core group of developers representing Office of Electricity Delivery and Energy Reliability
The Office of Electricity (OE) is a program office within the United States Department of Energy. The mission of OE is "to lead national efforts to modernize the electric grid; enhance security and reliability of the energy infrastructure; and faci ...
, ARPA-E
ARPA-E, or Advanced Research Projects Agency–Energy is a United States government agency tasked with promoting and funding research and development of advanced energy technologies. It is modeled after the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agenc ...
, Office of Science
The Office of Science is a component of the United States Department of Energy (DOE). The Office of Science is the lead federal agency supporting fundamental scientific research for energy and the Nation’s largest supporter of basic research in t ...
, Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy
The Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy (EERE) is an office within the United States Department of Energy. Formed from other energy agencies after the 1973 energy crisis, EERE is led by the Assistant Secretary of Energy Efficiency and ...
, Sandia National Laboratories
Sandia National Laboratories (SNL), also known as Sandia, is one of three research and development laboratories of the United States Department of Energy's National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA). Headquartered in Kirtland Air Force Bas ...
, and Pacific Northwest National Laboratory
Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (PNNL) is one of the United States Department of Energy national laboratories, managed by the United States Department of Energy, Department of Energy's (DOE) Office of Science. The main campus of the labor ...
; all of whom are engaged in the development of grid energy storage.
Energy storage for grid applications
Energy storage assets are a valuable asset for theelectrical grid
An electrical grid is an interconnected network for electricity delivery from producers to consumers. Electrical grids vary in size and can cover whole countries or continents. It consists of:Kaplan, S. M. (2009). Smart Grid. Electrical Power ...
. They can provide benefits and services such as load management
Load management, also known as demand-side management (DSM), is the process of balancing the supply of electricity on the network with the electrical load by adjusting or controlling the load rather than the power station output. This can be ach ...
, power quality Electric power quality is the degree to which the voltage, frequency, and waveform of a power supply system conform to established specifications. Good power quality can be defined as a steady supply voltage that stays within the prescribed range, ...
and uninterruptable power supply
An uninterruptible power supply or uninterruptible power source (UPS) is an electrical apparatus that provides emergency power to a load when the input power source or mains power fails. A UPS differs from an auxiliary or emergency power system ...
to increase the efficiency and supply security. This becomes more and more important in regard to the energy transition
The energy transition is the process of downshifting fossil fuels and re-developing whole systems to operate on low carbon energy sources. More generally, an energy transition is a significant structural change in an energy system regarding ...
and the need for a more efficient and sustainable energy system.
Numerous energy storage technologies (pumped-storage hydroelectricity
Pumped-storage hydroelectricity (PSH), or pumped hydroelectric energy storage (PHES), is a type of hydroelectric energy storage used by electric power systems for load balancing. The method stores energy in the form of gravitational potential ...
, electric battery
An electric battery is a source of electric power consisting of one or more electrochemical cells with external connections for powering electrical devices.
When a battery is supplying power, its positive terminal is the cathode and its negati ...
, flow battery
A flow battery, or redox flow battery (after reduction–oxidation), is a type of electrochemical cell where chemical energy is provided by two chemical components dissolved in liquids that are pumped through the system on separate sides of a ...
, flywheel energy storage
Flywheel energy storage (FES) works by accelerating a rotor (flywheel) to a very high speed and maintaining the energy in the system as rotational energy. When energy is extracted from the system, the flywheel's rotational speed is reduced as a c ...
, supercapacitor
A supercapacitor (SC), also called an ultracapacitor, is a high-capacity capacitor, with a capacitance value much higher than other capacitors but with lower voltage limits. It bridges the gap between electrolytic capacitors and Rechargeable ba ...
etc.) are suitable for grid-scale applications, however their characteristics differ. For example, a pumped-hydro station is well suited for bulk load management applications due to their large capacities and power capabilities. However, suitable locations are limited and their usefulness fades when dealing with localized power quality Electric power quality is the degree to which the voltage, frequency, and waveform of a power supply system conform to established specifications. Good power quality can be defined as a steady supply voltage that stays within the prescribed range, ...
issues. On the other hand, flywheels and capacitors are most effective in maintaining power quality Electric power quality is the degree to which the voltage, frequency, and waveform of a power supply system conform to established specifications. Good power quality can be defined as a steady supply voltage that stays within the prescribed range, ...
but lack storage capacities to be used in larger applications. These constraints are a natural limitation to the storage's applicability.
Several studies have developed interest and investigated the suitability or selection of the optimal energy storage for certain applications. Literature surveys comprise the available information of the state-of-the-art and compare the storage's uses based on current existing projects. Other studies take a step further in evaluating energy storage with each other and rank their fitness based on multiple-criteria decision analysis
Multiple-criteria decision-making (MCDM) or multiple-criteria decision analysis (MCDA) is a sub-discipline of operations research that explicitly evaluates multiple conflicting criteria in decision making (both in daily life and in settings ...
. Another paper proposed an evaluation scheme through the investigation and modelling of storage as equivalent circuits. An indexing approach has also been suggested in a few studies, but is still in the novel stages. In order to gain increased economic potential of grid connected energy storage systems, it is of interest to consider a portfolio with several services for one or more applications for an energy storage system. By doing so, several revenue streams can be achieved by a single storage and thereby also increasing the degree of utilization. To mention two examples, a combination of frequency response
In signal processing and electronics, the frequency response of a system is the quantitative measure of the magnitude and phase of the output as a function of input frequency. The frequency response is widely used in the design and analysis of sy ...
and reserve services is examined in, meanwhile load peak shaving together with power smoothing is considered in.
Forms
Air
Compressed air
One grid energy storage method is to use off-peak or renewably generated electricity to compress air, which is usually stored in an old mine or some other kind of geological feature. When electricity demand is high, the compressed air is heated with a small amount ofnatural gas
Natural gas (also called fossil gas or simply gas) is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane in addition to various smaller amounts of other higher alkanes. Low levels of trace gases like carbon di ...
and then goes through turboexpander
A turboexpander, also referred to as a turbo-expander or an expansion turbine, is a centrifugal or axial-flow turbine, through which a high-pressure gas is expanded to produce work that is often used to drive a compressor or generator.
Because w ...
s to generate electricity.
Compressed air storage is typically around 60–90% efficient.
Liquid air
Another electricity storage method is to compress and cool air, turning it into liquid air, which can be stored, and expanded when needed, turning a turbine, generating electricity, with a storage efficiency of up to 70%. A commercial liquid-air energy storage plant is under construction in the North of England, with commercial operation planned for 2022. The energy storage capacity of 250MWh of the plant will be nearly twice the capacity of the world's largest existing lithium-ion battery, theHornsdale Power Reserve
Hornsdale Power Reserve is a 150 MW (194 MWh) grid-connected energy storage system owned by Neoen co-located with the Hornsdale Wind Farm in the Mid North region of South Australia, also owned by Neoen.
The original installation in 2017 was th ...
in South Australia.
Since 2022 the Italian Company Energy Dome has run an almost similar pilot of 4 MWh on Corsica
Corsica ( , Upper , Southern ; it, Corsica; ; french: Corse ; lij, Còrsega; sc, Còssiga) is an island in the Mediterranean Sea and one of the 18 regions of France. It is the fourth-largest island in the Mediterranean and lies southeast o ...
with not the use of (liquid) air but only . While discharging, the is stored in a dome.
Batteries

 Battery storage was used in the early days of
Battery storage was used in the early days of direct current
Direct current (DC) is one-directional flow of electric charge. An electrochemical cell is a prime example of DC power. Direct current may flow through a conductor such as a wire, but can also flow through semiconductors, insulators, or even ...
electric power. Where AC grid power was not readily available, isolated lighting plants run by wind turbine
A wind turbine is a device that converts the kinetic energy of wind into electrical energy. Hundreds of thousands of large turbines, in installations known as wind farms, now generate over 650 gigawatts of power, with 60 GW added each year. W ...
s or internal combustion engines provided lighting and power to small motors. The battery system could be used to run the load without starting the engine or when the wind was calm. A bank of lead–acid batteries in glass jars both supplied power to illuminate lamps, as well as to start an engine to recharge the batteries. Battery storage technology is typically around 80% to more than 90% efficient for newer lithium-ion devices.
Battery systems connected to large solid-state converters have been used to stabilize power distribution networks. Some grid batteries are co-located with renewable energy plants, either to smooth the power supplied by the intermittent wind or solar output, or to shift the power output into other hours of the day when the renewable plant cannot produce power directly (see Installation examples). These hybrid systems (generation and storage) can either alleviate the pressure on the grid when connecting renewable sources or be used to reach self-sufficiency and work "off-the-grid" (see Stand-alone power system
A stand-alone power system (SAPS or SPS), also known as remote area power supply (RAPS), is an off-the-grid electricity system for locations that are not fitted with an electricity distribution system. Typical SAPS include one or more methods of e ...
).
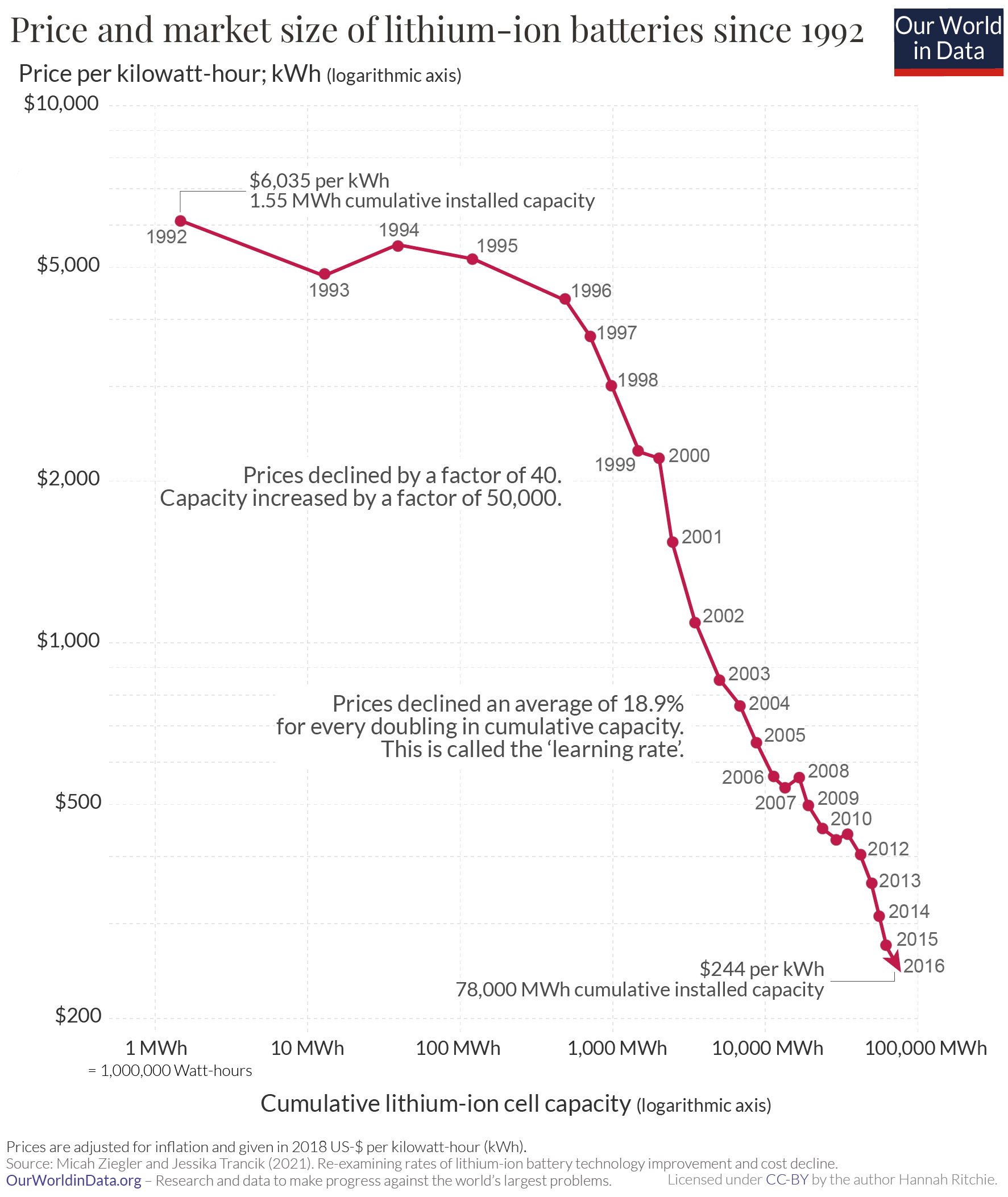
Contrary to electric vehicle applications, batteries for stationary storage do not suffer from mass or volume constraints. However, due to the large amounts of energy and power implied, the cost per power or energy unit is crucial. The relevant metrics to assess the interest of a technology for grid-scale storage is the $/Wh (or $/W) rather than the Wh/kg (or W/kg). The electrochemical grid storage was made possible thanks to the development of the electric vehicle, that induced a fast decrease in the production costs of batteries below $300/kWh. By optimizing the production chain, major industrials aimed to reach $150/kWh by the end of 2020, but actually achieved $140/kWh. The rate of decline in battery prices has consistently outpaced most estimates, reaching $132/kWh in 2021. These batteries rely on a lithium-ion
A lithium-ion or Li-ion battery is a type of rechargeable battery which uses the reversible reduction of lithium ions to store energy. It is the predominant battery type used in portable consumer electronics and electric vehicles. It also see ...
technology, which is suited for mobile applications (high cost, high density). Technologies optimized for the grid should focus on low cost per kWh. Lithium iron phosphate batteries are increasingly being used in both vehicles and grid storage because of their low cost, scale and acceptable energy density for many applications.
Grid-oriented battery technologies
Sodium-ion batteries are a cheap and sustainable alternative to lithium-ion, because sodium is far more abundant and cheaper than lithium, but it has a lower power density. However, they are still on the early stages of their development. Automotive-oriented technologies rely on solid electrodes, which feature a high energy density but require an expensive manufacturing process. Liquid electrodes represent a cheaper and less dense alternative as they do not need any processing.= Molten-salt/liquid-metal batteries
= These batteries are composed of two molten metal alloys separated by an electrolyte. They are simple to manufacture but require a temperature of several hundred degree Celsius to keep the alloys in a liquid state. This technology includesZEBRA
Zebras (, ) (subgenus ''Hippotigris'') are African equines with distinctive black-and-white striped coats. There are three living species: the Grévy's zebra (''Equus grevyi''), plains zebra (''E. quagga''), and the mountain zebra (''E. z ...
, sodium-sulfur batteries and liquid metal
A liquid metal is a metal or a metal alloy which is liquid at or near room temperature.
The only stable liquid elemental metal at room temperature is mercury (Hg), which is molten above −38.8 °C (234.3 K, −37.9 °F). Three more ...
. Sodium sulphur batteries are being used for grid storage in Japan and in the United States. The electrolyte is composed of solid beta alumina. The liquid metal battery, developed by the group of Pr. Donald Sadoway, uses molten alloys of magnesium and antimony separated by an electrically insulating molten salt. It is being brought to market by MIT spinoff company Ambri, which is currently contracted to install a first 250MWh system for TerraScale data centre company near Reno, Nevada.
= Flow batteries
= In rechargeableflow batteries
A flow battery, or redox flow battery (after reduction–oxidation), is a type of electrochemical cell where chemical energy is provided by two chemical components dissolved in liquids that are pumped through the system on separate sides of a ...
, the liquid electrodes are composed of transition metals in water at room temperature. They can be used as a rapid-response storage medium. Vanadium redox batteries are a type of flow battery. Various flow batteries are installed at different sites including; Huxley Hill wind farm (Australia), Tomari Wind Hills at Hokkaidō
is Japan's second largest island and comprises the largest and northernmost prefecture, making up its own region. The Tsugaru Strait separates Hokkaidō from Honshu; the two islands are connected by the undersea railway Seikan Tunnel.
The lar ...
(Japan), as well as in non-wind farm applications. A 12 MW·h flow battery was to be installed at the Sorne Hill wind farm (Ireland
Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean, in north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel, the Irish Sea, and St George's Channel. Ireland is the s ...
). These storage systems are designed to smooth out transient wind fluctuations. Hydrogen Bromide has been proposed for use in a utility-scale flow-type battery.
Examples
In Puerto Rico a system with a capacity of 20 megawatts for 15 minutes (5 megawatt hour) stabilizes the frequency of electric power produced on the island. A 27 megawatt 15-minute (6.75 megawatt hour) nickel-cadmium battery bank was installed at Fairbanks Alaska in 2003 to stabilize voltage at the end of a long transmission line. In 2014, the Tehachapi Energy Storage Project was commissioned bySouthern California Edison
Southern California Edison (or SCE Corp), the largest subsidiary of Edison International, is the primary electricity supply company for much of Southern California. It provides 15 million people with electricity across a service territory of app ...
.
In 2016, a zinc-ion battery was proposed for use in grid storage applications.
In 2017, the California Public Utilities Commission
The California Public Utilities Commission (CPUC or PUC) is a regulatory agency that regulates privately owned public utilities in the state of California, including electric power, telecommunications, natural gas and water companies. In additio ...
installed 396 refrigerator-sized stacks of Tesla batteries at the Mira Loma substation in Ontario, California
Ontario is a city in southwestern San Bernardino County in the U.S. state of California, east of downtown Los Angeles and west of downtown San Bernardino, the county seat. Located in the western part of the Inland Empire metropolitan area, ...
. The stacks are deployed in two modules of 10 MW each (20 MW in total), each capable of running for 4 hours, thus adding up to 80 MWh of storage. The array is capable of powering 15,000 homes for over four hours.
BYD proposes to use conventional consumer battery technologies such as lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) battery, connecting many batteries in parallel.
The largest grid storage batteries in the United States include the 31.5 MW battery at Grand Ridge Power plant in Illinois and the 31.5 MW battery at Beech Ridge, West Virginia. Two batteries under construction in 2015 include the 400 MWh (100 MW for 4 hours) Southern California Edison
Southern California Edison (or SCE Corp), the largest subsidiary of Edison International, is the primary electricity supply company for much of Southern California. It provides 15 million people with electricity across a service territory of app ...
project and the 52 MWh project on Kauai, Hawaii to entirely time shift a 13MW solar farm's output to the evening. Two batteries are in Fairbanks, Alaska
Fairbanks is a home rule city and the borough seat of the Fairbanks North Star Borough in the U.S. state of Alaska. Fairbanks is the largest city in the Interior region of Alaska and the second largest in the state. The 2020 Census put the p ...
(40 MW for 7 minutes using Ni-Cd cells), and in Notrees, Texas
Notrees is an unincorporated community in west-central Ector County, Texas, United States. It is located on State Highway 302, about 20 miles northwest of Odessa. The community is part of the Odessa metropolitan statistical area.
The area began ...
(36 MW for 40 minutes using lead–acid batteries). A 13 MWh battery made of used batteries from Daimler's Smart electric drive cars is being constructed in Lünen
Lünen is a town in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is located north of Dortmund, on both banks of the River Lippe. It is the largest town of the Unna district and part of the Ruhr Area.
In 2009 a biogas plant was built to provide electric ...
, Germany, with an expected second life of 10 years.
In 2015, a 221 MW battery storage was installed in the US, with total capacity expected to reach 1.7 GW in 2020.
The UK had a 50 MW lithium-ion grid-battery installed in Hertfordshire in 2018. In February 2021, construction began on a 50 MW battery storage development in Burwell, Cambridgeshire and a 40 MW site in Barnsley, South Yorkshire.
In November 2017 Tesla installed a 100 MW, 129 MWh battery system in South Australia. The Australian Energy Market Operator stated that this "is both rapid and precise, compared to the service typically provided by a conventional synchronous generation unit".
Electric vehicles
 Companies are researching the possible use of electric vehicles to meet peak demand. A parked and plugged-in electric vehicle could sell the electricity from the battery during peak loads and charge either during night (at home) or during off-peak.
Companies are researching the possible use of electric vehicles to meet peak demand. A parked and plugged-in electric vehicle could sell the electricity from the battery during peak loads and charge either during night (at home) or during off-peak.
Plug-in hybrid
A plug-in hybrid electric vehicle (PHEV) is a hybrid electric vehicle whose battery pack can be recharged by plugging a charging cable into an external electric power source, in addition to internally by its on-board internal combustion engin ...
or electric car
An electric car, battery electric car, or all-electric car is an automobile that is propelled by one or more electric motors, using only energy stored in batteries. Compared to internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles, electric cars are qui ...
s could be used for their energy storage capabilities. Vehicle-to-grid
Vehicle-to-grid (V2G), also known as Vehicle-to-home (V2H) or Vehicle-to-load (V2L) describes a system in which plug-in electric vehicles (PEV) sell demand response services to the grid. Demand services are either delivering electricity or by red ...
technology can be employed, turning each vehicle with its 20 to 50 kWh battery pack
A battery pack is a set of any number of (preferably) identical batteries or individual battery cells. They may be configured in a series, parallel or a mixture of both to deliver the desired voltage, capacity, or power density. The term battery ...
into a distributed load-balancing device or emergency power source. This represents two to five days per vehicle of average household requirements of 10 kWh per day, assuming annual consumption of 3,650 kWh. This quantity of energy is equivalent to between of range in such vehicles consuming . These figures can be achieved even in home-made electric vehicle conversion
In automobile engineering, electric vehicle conversion is the replacement of a car's combustion engine and connected components with an electric motor and batteries, to create an all-electric vehicle (AEV).
There are two main aims for convertin ...
s. Some electric utilities plan to use old plug-in vehicle batteries (sometimes resulting in a giant battery) to store electricityWoody, Todd"PG&E's Battery Power Plans Could Jump Start Electric Car Market."
(Blog). ''Green Wombat'', 2007-06-12. Retrieved on 2007-08-19 However, a large disadvantage of using vehicle to grid energy storage would be if each storage cycle stressed the battery with one complete charge-discharge cycle. However, one major study showed that used intelligently, vehicle-to-grid storage actually improved the batteries longevity. Conventional (cobalt-based) lithium-ion batteries break down with the number of cycles – newer li-ion batteries do not break down significantly with each cycle, and so have much longer lives. One approach is to reuse unreliable vehicle batteries in dedicated grid storage as they are expected to be good in this role for ten years. If such storage is done on a large scale it becomes much easier to guarantee replacement of a vehicle battery degraded in mobile use, as the old battery has value and immediate use.
Flywheel
 Mechanical inertia is the basis of this storage method. When the electric power flows into the device, an
Mechanical inertia is the basis of this storage method. When the electric power flows into the device, an electric motor
An electric motor is an electrical machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Most electric motors operate through the interaction between the motor's magnetic field and electric current in a wire winding to generate force ...
accelerates a heavy rotating disc. The motor acts as a generator when the flow of power is reversed, slowing down the disc and producing electricity. Electricity is stored as the kinetic energy
In physics, the kinetic energy of an object is the energy that it possesses due to its motion.
It is defined as the work needed to accelerate a body of a given mass from rest to its stated velocity. Having gained this energy during its accel ...
of the disc. Friction
Friction is the force resisting the relative motion of solid surfaces, fluid layers, and material elements sliding against each other. There are several types of friction:
*Dry friction is a force that opposes the relative lateral motion of t ...
must be kept to a minimum to prolong the storage time. This is often achieved by placing the flywheel in a vacuum and using magnetic bearing
A magnetic bearing is a type of bearing that supports a load using magnetic levitation. Magnetic bearings support moving parts without physical contact. For instance, they are able to levitate a rotating shaft and permit relative motion with ve ...
s, tending to make the method expensive. Greater flywheel speeds allow greater storage capacity but require strong materials such as steel
Steel is an alloy made up of iron with added carbon to improve its strength and fracture resistance compared to other forms of iron. Many other elements may be present or added. Stainless steels that are corrosion- and oxidation-resistant t ...
or composite materials to resist the centrifugal force
In Newtonian mechanics, the centrifugal force is an inertial force (also called a "fictitious" or "pseudo" force) that appears to act on all objects when viewed in a rotating frame of reference. It is directed away from an axis which is parallel ...
s. The ranges of power and energy storage technology that make this method economic, however, tends to make flywheels unsuitable for general power system application; they are probably best suited to load-leveling applications on railway power systems and for improving power quality Electric power quality is the degree to which the voltage, frequency, and waveform of a power supply system conform to established specifications. Good power quality can be defined as a steady supply voltage that stays within the prescribed range, ...
in renewable energy
Renewable energy is energy that is collected from renewable resources that are naturally replenished on a human timescale. It includes sources such as sunlight, wind, the movement of water, and geothermal heat. Although most renewable energy ...
systems such as the 20MW system in Ireland.
Applications that use flywheel storage are those that require very high bursts of power for very short durations such as tokamak
A tokamak (; russian: токамáк; otk, 𐱃𐰸𐰢𐰴, Toḳamaḳ) is a device which uses a powerful magnetic field to confine plasma in the shape of a torus. The tokamak is one of several types of magnetic confinement devices being d ...
and laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word "laser" is an acronym for "light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation". The firs ...
experiments where a motor generator is spun up to operating speed and is partially slowed down during discharge.
Flywheel storage is also currently used in the form of the Diesel rotary uninterruptible power supply
Most forms of uninterruptible power supply (UPS) can be either powered by battery or flywheel energy. These are ready for immediate use at the instant that the mains electricity fails, but the relatively small and finite amount of stored energy t ...
to provide uninterruptible power supply
An uninterruptible power supply or uninterruptible power source (UPS) is an electrical apparatus that provides emergency power to a load when the input power source or mains power fails. A UPS differs from an auxiliary or emergency power system ...
systems (such as those in large datacenters) for ride-through power necessary during transfer – that is, the relatively brief amount of time between a loss of power to the mains and the warm-up of an alternate source, such as a diesel generator
A diesel generator (DG) (also known as a diesel Genset) is the combination of a diesel engine with an electric generator (often an alternator) to generate electrical energy. This is a specific case of engine generator. A diesel compression-ig ...
.
This potential solution has been implemented by EDA in the Azores
)
, motto =( en, "Rather die free than subjected in peace")
, anthem= ( en, "Anthem of the Azores")
, image_map=Locator_map_of_Azores_in_EU.svg
, map_alt=Location of the Azores within the European Union
, map_caption=Location of the Azores wi ...
on the islands of Graciosa
Graciosa Island () (literally "graceful" or "enchanting" in Portuguese) is referred to as the ''White Island'', the northernmost of the Central Group of islands in the Azores. The ovular Portuguese island has an area of , a length of and a width ...
and Flores
Flores is one of the Lesser Sunda Islands, a group of islands in the eastern half of Indonesia. Including the Komodo Islands off its west coast (but excluding the Solor Archipelago to the east of Flores), the land area is 15,530.58 km2, and the ...
. This system uses an 18 megawatt-second flywheel to improve power quality Electric power quality is the degree to which the voltage, frequency, and waveform of a power supply system conform to established specifications. Good power quality can be defined as a steady supply voltage that stays within the prescribed range, ...
and thus allow increased renewable energy usage. As the description suggests, these systems are again designed to smooth out transient fluctuations in supply, and could never be used to cope with an outage exceeding a couple of days.
Powercorp in Australia have been developing applications using wind turbines, flywheels and low load diesel (LLD) technology to maximize the wind input to small grids. A system installed in Coral Bay, Western Australia, uses wind turbines coupled with a flywheel based control system and LLDs. The flywheel technology enables the wind turbines to supply up to 95 percent of Coral Bay's energy supply at times, with a total annual wind penetration of 45 percent.
Hydrogen
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxi ...
is being developed as an electrical energy storage medium. Hydrogen is produced, then compressed or liquefied, cryogenically stored at −252.882 °C, and then converted back to electrical energy or heat. Hydrogen can be used as a fuel for portable (vehicles) or stationary energy generation. Compared to pumped water storage and batteries, hydrogen has the advantage that it is a high energy density fuel.
Hydrogen can be produced either by reforming natural gas with steam or by the electrolysis of water
Electrolysis of water, also known as electrochemical water splitting, is the process of using electricity to decompose water into oxygen and hydrogen gas by electrolysis. Hydrogen gas released in this way can be used as hydrogen fuel, or rem ...
into hydrogen and oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as well ...
(see hydrogen production
Hydrogen production is the family of industrial methods for generating hydrogen gas. As of 2020, the majority of hydrogen (∼95%) is produced from fossil fuels by steam reforming of natural gas and other light hydrocarbons, partial oxidation of h ...
). Reforming natural gas produces carbon dioxide as a by-product. High temperature electrolysis and high pressure electrolysis
High-pressure electrolysis (HPE) is the electrolysis of water by decomposition of water (H2O) into oxygen (O2) and hydrogen gas (H2) due to the passing of an electric current through the water. The difference with a standard proton exchange me ...
are two techniques by which the efficiency of hydrogen production may be able to be increased. Hydrogen is then converted back to electricity in an internal combustion engine
An internal combustion engine (ICE or IC engine) is a heat engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer (usually air) in a combustion chamber that is an integral part of the working fluid flow circuit. In an internal combust ...
, or a fuel cell
A fuel cell is an electrochemical cell that converts the chemical energy of a fuel (often hydrogen) and an oxidizing agent (often oxygen) into electricity through a pair of redox reactions. Fuel cells are different from most batteries in requ ...
.
The AC-to-AC efficiency of hydrogen storage has been shown to be on the order of 20 to 45%, which imposes economic constraints. The price ratio between purchase and sale of electricity must be at least proportional to the efficiency in order for the system to be economic. Hydrogen fuel cells can respond quickly enough to correct rapid fluctuations in electricity demand or supply and regulate frequency. Whether hydrogen can use natural gas infrastructure depends on the network construction materials, standards in joints, and storage pressure.
The equipment necessary for hydrogen energy storage includes an electrolysis plant, hydrogen compressor
A hydrogen compressor is a device that increases the pressure of hydrogen by reducing its volume resulting in compressed hydrogen or liquid hydrogen.
Traditionally, applications for hydrogen compressors included Chlorine electrolyser and many chem ...
s or liquifiers, and storage tanks.
Biohydrogen
Biohydrogen is H2 that is produced biologically. Interest is high in this technology because H2 is a clean fuel and can be readily produced from certain kinds of biomass.
Many challenges characterize this technology, including those intrinsic to ...
is a process being investigated for producing hydrogen using biomass.
Micro combined heat and power
Micro combined heat and power, micro-CHP, µCHP or mCHP is an extension of the idea of cogeneration to the single/multi family home or small office building in the range of up to 50 kW. Usual technologies for the production of heat and power in ...
(microCHP) can use hydrogen as a fuel.
Some nuclear power plants may be able to benefit from a symbiosis with hydrogen production. High temperature (950 to 1,000 °C) gas cooled nuclear generation IV reactor
Generation IV reactors (Gen IV) are six nuclear reactor designs recognized by the Generation IV International Forum. The designs target improved safety, sustainability, efficiency, and cost.
The most developed Gen IV reactor design is the sodium ...
s have the potential to electrolyze hydrogen from water by thermochemical means using nuclear heat as in the sulfur-iodine cycle. The first commercial reactors are expected in 2030.
A community based pilot program using wind turbines and hydrogen generators was started in 2007 in the remote community of Ramea, Newfoundland and Labrador. A similar project has been going on since 2004 in Utsira
Utsira () is the smallest municipality in Norway. The island municipality is located in northwestern Rogaland county, just off the western coast of Norway. Utsira is part of the traditional district of Haugaland.
The municipality consists of t ...
, a small Norwegian island municipality.
Underground hydrogen storage
Underground hydrogen storage is the practice ofhydrogen storage
Hydrogen storage can be accomplished by several existing methods of holding hydrogen for later use. These include mechanical approaches such as using high pressures and low temperatures, or employing chemical compounds that release H2 upon deman ...
in cave
A cave or cavern is a natural void in the ground, specifically a space large enough for a human to enter. Caves often form by the weathering of rock and often extend deep underground. The word ''cave'' can refer to smaller openings such as se ...
rns, salt domes and depleted oil and gas fields. Large quantities of gaseous hydrogen have been stored in caverns by Imperial Chemical Industries
Imperial Chemical Industries (ICI) was a British chemical company. It was, for much of its history, the largest manufacturer in Britain.
It was formed by the merger of four leading British chemical companies in 1926.
Its headquarters were at Mi ...
(ICI) for many years without any difficulties. The European project Hyunder indicated in 2013 that for the storage of wind and solar energy an additional 85 caverns are required as it cannot be covered by PHES and CAES systems.
Power to gas
Power to gas
Power-to-gas (often abbreviated P2G) is a technology that uses electric power to produce a gaseous fuel. When using surplus power from wind generation, the concept is sometimes called windgas.
Most P2G systems use electrolysis to produce hydrogen ...
is a technology which converts electrical
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter that has a property of electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described ...
power to a gas fuel
A fuel is any material that can be made to react with other substances so that it releases energy as thermal energy or to be used for work. The concept was originally applied solely to those materials capable of releasing chemical energy but ...
. There are 2 methods, the first is to use the electricity for water splitting
Water splitting is the chemical reaction in which water is broken down into oxygen and hydrogen:
:2 H2O → 2 H2 + O2
Efficient and economical water splitting would be a technological breakthrough that could underpin a hydrogen economy, base ...
and inject the resulting hydrogen into the natural gas grid. The second less efficient method is used to convert carbon dioxide and water to methane
Methane ( , ) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms). It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The relative abundance of methane on ...
, (see natural gas
Natural gas (also called fossil gas or simply gas) is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane in addition to various smaller amounts of other higher alkanes. Low levels of trace gases like carbon di ...
) using electrolysis
In chemistry and manufacturing, electrolysis is a technique that uses direct electric current (DC) to drive an otherwise non-spontaneous chemical reaction. Electrolysis is commercially important as a stage in the separation of elements from na ...
and the Sabatier reaction
The Sabatier reaction or Sabatier process produces methane and water from a reaction of hydrogen with carbon dioxide at elevated temperatures (optimally 300–400 °C) and pressures (perhaps 3 MPa ) in the presence of a nickel catalyst. ...
. The excess power or off peak power generated by wind generators or solar arrays is then used for load balancing in the energy grid. Using the existing natural gas system for hydrogen, fuel cell maker Hydrogenics
Hydrogenics is a developer and manufacturer of hydrogen generation and fuel cell products based on water electrolysis and proton exchange membrane (PEM) technology. Hydrogenics is divided into two business units: OnSite Generation and Power Syst ...
and natural gas distributor Enbridge
Enbridge Inc. is a multinational pipeline and energy company headquartered in Calgary, Alberta, Canada. Enbridge owns and operates pipelines throughout Canada and the United States, transporting crude oil, natural gas, and natural gas liquids. ...
have teamed up to develop such a power to gas
Power-to-gas (often abbreviated P2G) is a technology that uses electric power to produce a gaseous fuel. When using surplus power from wind generation, the concept is sometimes called windgas.
Most P2G systems use electrolysis to produce hydrogen ...
system in Canada.
Pipeline storage of hydrogen where a natural gas network is used for the storage of hydrogen. Before switching to natural gas
Natural gas (also called fossil gas or simply gas) is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane in addition to various smaller amounts of other higher alkanes. Low levels of trace gases like carbon di ...
, the German gas networks were operated using towngas, which for the most part consisted of hydrogen. The storage capacity of the German natural gas network is more than 200,000 GW·h which is enough for several months of energy requirement. By comparison, the capacity of all German pumped storage power plants amounts to only about 40 GW·h. The transport of energy through a gas network is done with much less loss (<0.1%) than in a power network (8%). The use of the existing natural gas pipelines for hydrogen was studied by NaturalHy
The power-to-ammonia concept
The power-to-ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . A stable binary hydride, and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinct pungent smell. Biologically, it is a common nitrogenous wa ...
concept offers a carbon-free energy storage route with a diversified application palette. At times when there is surplus low-carbon power
Low-carbon power is electricity produced with substantially lower greenhouse gas emissions than conventional fossil fuel power generation. The energy transition to low-carbon power is one of the most important actions required to limit climate ...
, it can be used to create ammonia fuel. Ammonia may be produced by splitting water into hydrogen and oxygen with electricity, then high temperature and pressure are used to combine nitrogen from the air with the hydrogen, creating ammonia. As a liquid it is similar to propane, unlike hydrogen alone, which is difficult to store as a gas under pressure or to cryogenically liquefy and store at −253 °C.
Just like natural gas, the stored ammonia can be used as a thermal fuel for transportation and electricity generation or used in a fuel cell. A standard 60,000 m³ tank of liquid ammonia contains about 211 GWh of energy, equivalent to the annual production of roughly 30 wind turbines. Ammonia can be burned cleanly: water and nitrogen are released, but no CO2 and little or no nitrogen oxides. Ammonia has multiple uses besides being an energy carrier, it is the basis for the production of many chemicals, the most common use is for fertilizer. Given this flexibility of usage, and given that the infrastructure for the safe transport, distribution and usage of ammonia is already in place, it makes ammonia a good candidate to be a large-scale, non-carbon, energy carrier of the future.
Hydroelectricity
Pumped water
hydroelectric
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies one sixth of the world's electricity, almost 4500 TWh in 2020, which is more than all other renewable sources combined and ...
generation, often as a high value rapid-response reserve to cover transient peaks in demand. Pumped storage recovers about 70% to 85% of the energy consumed, and is currently the most cost effective form of mass power storage. The chief problem with pumped storage is that it usually requires two nearby reservoirs at considerably different heights, and often requires considerable capital expenditure.
Pumped water systems have high dispatchability, meaning they can come on-line very quickly, typically within 15 seconds, which makes these systems very efficient at soaking up variability in electrical ''demand'' from consumers. There is over 90 GW of pumped storage in operation around the world, which is about 3% of ''instantaneous'' global generation capacity. Pumped water storage systems, such as the Dinorwig storage system in Britain, hold five or six hours of generating capacity, and are used to smooth out demand variations.
Another example is the 1836 MW Tianhuangping Pumped-Storage Hydro Plant in China, which has a reservoir capacity of eight million cubic meters (2.1 billion U.S. gallons or the volume of water over Niagara Falls
Niagara Falls () is a group of three waterfalls at the southern end of Niagara Gorge, spanning the border between the province of Ontario in Canada and the state of New York in the United States. The largest of the three is Horseshoe Fall ...
in 25 minutes) with a vertical distance of 600 m (1970 feet). The reservoir can provide about 13 GW·h of stored gravitational potential energy
Gravitational energy or gravitational potential energy is the potential energy a massive object has in relation to another massive object due to gravity. It is the potential energy associated with the gravitational field, which is released (conver ...
(convertible to electricity at about 80% efficiency), or about 2% of China's daily electricity consumption.
A new concept in pumped-storage is utilizing wind energy
Wind power or wind energy is mostly the use of wind turbines to generate electricity. Wind power is a popular, sustainable, renewable energy source that has a much smaller impact on the environment than burning fossil fuels. Historically, w ...
or solar power
Solar power is the conversion of energy from sunlight into electricity, either directly using photovoltaics (PV) or indirectly using concentrated solar power. Photovoltaic cells convert light into an electric current using the photovoltaic e ...
to pump water. Wind turbines or solar cells that direct drive water pump
A pump is a device that moves fluids (liquids or gases), or sometimes slurries, by mechanical action, typically converted from electrical energy into hydraulic energy. Pumps can be classified into three major groups according to the method they ...
s for an energy storing wind or solar dam
A dam is a barrier that stops or restricts the flow of surface water or underground streams. Reservoirs created by dams not only suppress floods but also provide water for activities such as irrigation, human consumption, industrial use, a ...
can make this a more efficient process but are limited. Such systems can only increase kinetic water volume during windy and daylight periods. A study published in 2013 showed rooftop solar, coupled to existing pumped-storage, could replace the reactors lost at Fukushima with an equivalent capacity factor.
Hydroelectric dams
 Hydroelectric dams with large reservoirs can also be operated to provide peak generation at times of peak demand. Water is stored in the reservoir during periods of low demand and released through the plant when demand is higher. The net effect is the same as pumped storage, but without the pumping loss. Depending on the reservoir capacity the plant can provide daily, weekly, or seasonal load following.
Many existing hydroelectric dams are fairly old (for example, the
Hydroelectric dams with large reservoirs can also be operated to provide peak generation at times of peak demand. Water is stored in the reservoir during periods of low demand and released through the plant when demand is higher. The net effect is the same as pumped storage, but without the pumping loss. Depending on the reservoir capacity the plant can provide daily, weekly, or seasonal load following.
Many existing hydroelectric dams are fairly old (for example, the Hoover Dam
Hoover Dam is a concrete arch-gravity dam in the Black Canyon of the Colorado River, on the border between the U.S. states of Nevada and Arizona. It was constructed between 1931 and 1936 during the Great Depression and was dedicated on S ...
was built in the 1930s), and their original design predated the newer intermittent power sources such as wind and solar by decades. A hydroelectric dam originally built to provide baseload power
The base load (also baseload) is the minimum level of demand on an electrical grid over a span of time, for example, one week. This demand can be met by unvarying power plants, dispatchable generation, or by a collection of smaller intermittent ...
will have its generators sized according to the average flow of water into the reservoir. Uprating such a dam with additional generators increases its peak power output capacity, thereby increasing its capacity to operate as a virtual grid energy storage unit. The United States Bureau of Reclamation
The Bureau of Reclamation, and formerly the United States Reclamation Service, is a federal agency under the U.S. Department of the Interior, which oversees water resource management, specifically as it applies to the oversight and opera ...
reports an investment cost of $69 per kilowatt capacity to uprate an existing dam, compared to more than $400 per kilowatt for oil-fired peaking generators. While an uprated hydroelectric dam does not directly store excess energy from other generating units, it behaves equivalently by accumulating its own fuel – incoming river water – during periods of high output from other generating units. Functioning as a virtual grid storage unit in this way, the uprated dam is one of the most efficient forms of energy storage, because it has no pumping losses to fill its reservoir, only increased losses to evaporation and leakage.
A dam which impounds a large reservoir can store and release a correspondingly large amount of energy, by controlling river outflow and raising or lowering its reservoir level a few meters. Limitations do apply to dam operation, their releases are commonly subject to government regulated water rights to limit downstream effect on rivers. For example, there are grid situations where baseload thermal plants, nuclear or wind turbines are already producing excess power at night, dams are still required to release enough water to maintain adequate river levels, whether electricity is generated or not. Conversely there's a limit to peak capacity, which if excessive could cause a river to flood for a few hours each day.
Superconducting magnetic energy
Superconducting magnetic energy storage (SMES) systems store energy in themagnetic field
A magnetic field is a vector field that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents, and magnetic materials. A moving charge in a magnetic field experiences a force perpendicular to its own velocity and to ...
created by the flow of direct current
Direct current (DC) is one-directional flow of electric charge. An electrochemical cell is a prime example of DC power. Direct current may flow through a conductor such as a wire, but can also flow through semiconductors, insulators, or even ...
in a superconducting
Superconductivity is a set of physical properties observed in certain materials where electrical resistance vanishes and magnetic flux fields are expelled from the material. Any material exhibiting these properties is a superconductor. Unlike ...
coil which has been cryogenically
In physics, cryogenics is the production and behaviour of materials at very low temperatures.
The 13th IIR International Congress of Refrigeration (held in Washington DC in 1971) endorsed a universal definition of “cryogenics” and “ ...
cooled to a temperature below its superconducting critical temperature. A typical SMES system includes three parts: superconducting coil, power conditioning system and cryogenically cooled refrigerator. Once the superconducting coil is charged, the current will not decay and the magnetic energy can be stored indefinitely. The stored energy can be released back to the network by discharging the coil. The power conditioning system uses an inverter
A power inverter, inverter or invertor is a power electronic device or circuitry that changes direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC). The resulting AC frequency obtained depends on the particular device employed. Inverters do the opp ...
/rectifier
A rectifier is an electrical device that converts alternating current (AC), which periodically reverses direction, to direct current (DC), which flows in only one direction. The reverse operation (converting DC to AC) is performed by an inver ...
to transform alternating current
Alternating current (AC) is an electric current which periodically reverses direction and changes its magnitude continuously with time in contrast to direct current (DC) which flows only in one direction. Alternating current is the form in which ...
(AC) power to direct current or convert DC back to AC power. The inverter/rectifier accounts for about 2–3% energy loss in each direction. SMES loses the least amount of electricity
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter that has a property of electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described ...
in the energy storage process compared to other methods of storing energy. SMES systems are highly efficient; the round-trip efficiency is greater than 95%. The high cost of superconductors is the primary limitation for commercial use of this energy storage method.
Due to the energy requirements of refrigeration
The term refrigeration refers to the process of removing heat from an enclosed space or substance for the purpose of lowering the temperature.International Dictionary of Refrigeration, http://dictionary.iifiir.org/search.phpASHRAE Terminology, ht ...
, and the limits in the total energy able to be stored, SMES is currently used for short duration energy storage. Therefore, SMES is most commonly devoted to improving power quality Electric power quality is the degree to which the voltage, frequency, and waveform of a power supply system conform to established specifications. Good power quality can be defined as a steady supply voltage that stays within the prescribed range, ...
. If SMES were to be used for utilities
A public utility company (usually just utility) is an organization that maintains the infrastructure for a public service (often also providing a service using that infrastructure). Public utilities are subject to forms of public control and r ...
it would be a diurnal storage device, charged from base load
The base load (also baseload) is the minimum level of demand on an electrical grid over a span of time, for example, one week. This demand can be met by unvarying power plants, dispatchable generation, or by a collection of smaller intermittent en ...
power at night and meeting peak loads during the day.
Superconducting magnetic energy storage technical challenges are yet to be solved for it to become practical.
Thermal
In Denmark the direct storage of electricity is perceived as too expensive for very large scale usage, albeit significant usage is made of existing Norwegian Hydro. Instead, the use of existing hot water storage tanks connected to district heating schemes, heated by either electrode boilers or heat pumps, is seen as a preferable approach. The stored heat is then transmitted to dwellings usingdistrict heating
District heating (also known as heat networks or teleheating) is a system for distributing heat generated in a centralized location through a system of insulated pipes for residential and commercial heating requirements such as space heating ...
pipes.
Molten salt
Molten salt is salt which is solid at standard temperature and pressure but enters the liquid phase due to elevated temperature. Regular table salt has a melting point of 801 °C (1474°F) and a heat of fusion of 520 J/g.Journal of Chemical Th ...
is used to store heat collected by a solar power tower
A solar power tower, also known as 'central tower' power plant or 'heliostat' power plant, is a type of solar furnace using a tower to receive focused sunlight. It uses an array of flat, movable mirrors (called heliostats) to focus the sun's ra ...
so that it can be used to generate electricity in bad weather or at night.
Building heating and cooling systems can be controlled to store thermal energy in either the building's mass or dedicated thermal storage tanks. This thermal storage can provide load-shifting or even more complex ancillary services Ancillary services are the services necessary to support the transmission of electric power from generators to consumers given the obligations of control areas and transmission utilities within those control areas to maintain reliable operations of ...
by increasing power consumption (charging the storage) during off-peak times and lowering power consumption (discharging the storage) during higher-priced peak times. For example, off-peak electricity can be used to make ice
Ice is water frozen into a solid state, typically forming at or below temperatures of 0 degrees Celsius or Depending on the presence of impurities such as particles of soil or bubbles of air, it can appear transparent or a more or less opaq ...
from water, and the ice can be stored. The stored ice can be used to cool the air in a large building which would have normally used electric AC, thereby shifting the electric load to off-peak hours. On other systems stored ice is used to cool the intake air of a gas turbine
A gas turbine, also called a combustion turbine, is a type of continuous flow internal combustion engine. The main parts common to all gas turbine engines form the power-producing part (known as the gas generator or core) and are, in the directi ...
generator, thus increasing the on-peak generation capacity and the on-peak efficiency.
A pumped-heat electricity storage system uses a highly reversible heat engine/heat pump to pump heat between two storage vessels, heating one and cooling the other. The UK-based engineering company Isentropic that is developing the system claims a potential electricity-in to electricity-out round-trip efficiency of 72–80%.
A Carnot battery
A Carnot battery is a type of energy storage system that stores electricity in thermal energy storage. During the charging process, electricity is converted into heat and kept in heat storage. During the discharging process, the stored heat is con ...
is a type of energy storage systems that stores electricity in heat storage and converts the stored heat back to electricity via thermodynamics cycles. This concept has been investigated and developed by many research projects recently. One of the advantage of this type of system is that the cost at large-scale and long-duration of thermal storage could be much lower than other storage technologies.
Gravitational potential energy storage with solid masses
Alternatives include storing energy by moving large solid masses upward against gravity. This can be achieved inside old mine shafts or in specially constructed towers where heavy weights arewinch
A winch is a mechanical device that is used to pull in (wind up) or let out (wind out) or otherwise adjust the tension of a rope or wire rope (also called "cable" or "wire cable").
In its simplest form, it consists of a spool (or drum) attach ...
ed up to store energy and allowed a controlled descent to release it. In rail energy storage, rail cars carrying large weights are moved up or down a section of inclined rail track, storing or releasing energy as a result;Massey, Nathanael and ClimateWireEnergy Storage Hits the Rails Out West: In California and Nevada, projects store electricity in the form of heavy rail cars pulled up a hill
, '' ScientificAmerican.com'' website, 25 March 2014. Retrieved 28 March 2014. In disused oil-well potential energy storage, weights are raised or lowered in a deep, decommissioned oil well.
Economics
The levelized cost of storing electricity depends highly on storage type and purpose; as subsecond-scalefrequency regulation Ancillary services are the services necessary to support the transmission of electric power from generators to consumers given the obligations of control areas and transmission utilities within those control areas to maintain reliable operations of ...
, minute/hour-scale peaker plants, or day/week-scale season storage.
Using battery storage is said to have a levelized cost of $120 to $170 per MWh. This compares with open cycle gas turbines which, as of 2020, have a cost of around $151–198 per MWh.
Generally speaking, energy storage is economical when the marginal cost of electricity varies more than the costs of storing and retrieving the energy plus the price of energy lost in the process. For instance, assume a pumped-storage reservoir can pump to its upper reservoir a volume of water capable of producing 1,200 MW·h
A kilowatt-hour ( unit symbol: kW⋅h or kW h; commonly written as kWh) is a unit of energy: one kilowatt of power for one hour. In terms of SI derived units with special names, it equals 3.6 megajoules (MJ). Kilowatt-hours are a common bil ...
after all losses are factored in (evaporation and seeping in the reservoir, efficiency losses, etc.). If the marginal cost of electricity during off-peak times is $15 per MW·h, and the reservoir operates at 75% efficiency (i.e., 1,600 MW·h are consumed and 1,200 MW·h of energy are retrieved), then the total cost of filling the reservoir is $24,000. If all of the stored energy is sold the following day during peak hours for an average $40 per MW·h, then the reservoir will see revenues of $48,000 for the day, for a gross profit of $24,000.
However, the marginal cost of electricity varies because of the varying operational and fuel costs of different classes of generators. At one extreme, base load power plant
The base load (also baseload) is the minimum level of demand on an electrical grid over a span of time, for example, one week. This demand can be met by unvarying power plants, dispatchable generation, or by a collection of smaller intermittent e ...
s such as coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen.
Coal is formed when dead ...
-fired power plants and nuclear power
Nuclear power is the use of nuclear reactions to produce electricity. Nuclear power can be obtained from nuclear fission, nuclear decay and nuclear fusion reactions. Presently, the vast majority of electricity from nuclear power is produced ...
plants are low marginal cost generators, as they have high capital and maintenance costs but low fuel costs. At the other extreme, peaking power plant
Peaking power plants, also known as peaker plants, and occasionally just "peakers", are power plants that generally run only when there is a high demand, known as peak demand, for electricity. Because they supply power only occasionally, the power ...
s such as gas turbine
A gas turbine, also called a combustion turbine, is a type of continuous flow internal combustion engine. The main parts common to all gas turbine engines form the power-producing part (known as the gas generator or core) and are, in the directi ...
natural gas
Natural gas (also called fossil gas or simply gas) is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane in addition to various smaller amounts of other higher alkanes. Low levels of trace gases like carbon di ...
plants burn expensive fuel but are cheaper to build, operate and maintain. To minimize the total operational cost of generating power, base load generators are dispatched most of the time, while peak power generators are dispatched only when necessary, generally when energy demand peaks. This is called "economic dispatch".
Demand for electricity
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter that has a property of electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described ...
from the world's various grids varies over the course of the day and from season to season. For the most part, variation in electric demand is met by varying the amount of electrical energy supplied from primary sources. Increasingly, however, operators are storing lower-cost energy produced at night, then releasing it to the grid during the peak periods of the day when it is more valuable. In areas where hydroelectric dams exist, release can be delayed until demand is greater; this form of storage is common and can make use of existing reservoirs. This is not storing "surplus" energy produced elsewhere, but the net effect is the same – although without the efficiency losses. Renewable supplies with variable production, like wind
Wind is the natural movement of air or other gases relative to a planet's surface. Winds occur on a range of scales, from thunderstorm flows lasting tens of minutes, to local breezes generated by heating of land surfaces and lasting a few hou ...
and solar power
Solar power is the conversion of energy from sunlight into electricity, either directly using photovoltaics (PV) or indirectly using concentrated solar power. Photovoltaic cells convert light into an electric current using the photovoltaic e ...
, tend to increase the net variation in electric load, increasing the opportunity for grid energy storage.
It may be more economical to find an alternative market for unused electricity, rather than try and store it. High Voltage Direct Current
A high-voltage direct current (HVDC) electric power transmission system (also called a power superhighway or an electrical superhighway) uses direct current (DC) for electric power transmission, in contrast with the more common alternating curren ...
allows for transmission of electricity, losing only 3% per 1000 km.
The United States Department of Energy's International Energy Storage Database provides a free list of grid energy storage projects, many of which show funding sources and amounts.
Load leveling
The demand for electricity from consumers and industry is constantly changing, broadly within the following categories: *Seasonal (during dark winters more electric lighting and heating is required, while in other climates hot weather boosts the requirement for air conditioning) *Weekly (most industry closes at the weekend, lowering demand) *Daily (such as the morning peak as offices open and air conditioners get switched on) *Hourly (one method for estimating television viewing figures in the United Kingdom is to measure the power spikes during advertisement breaks or after programmes when viewers go to switch a kettle on) *Transient (fluctuations due to individual's actions, differences in power transmission efficiency and other small factors that need to be accounted for) There are currently three main methods for dealing with changing demand: *Electrical devices generally having a workingvoltage
Voltage, also known as electric pressure, electric tension, or (electric) potential difference, is the difference in electric potential between two points. In a static electric field, it corresponds to the work needed per unit of charge to mo ...
range that they require, commonly 110–120 V or 220–240 V. Minor variations in load are automatically smoothed by slight variations in the voltage available across the system.
*Power plants can be run below their normal output, with the facility to increase the amount they generate almost instantaneously. This is termed 'spinning reserve'.
*Additional generation can be brought online. Typically, these would be hydroelectric or gas turbines, which can be started in a matter of minutes.
The problem with standby gas turbines is higher costs; expensive generating equipment is unused much of the time. Spinning reserve also comes at a cost; plants running below maximum output are usually less efficient. Grid energy storage is used to shift generation from times of peak load to off-peak hours. Power plants are able to run at their peak efficiency during nights and weekends.
Supply-demand leveling strategies may be intended to reduce the cost of supplying peak power or to compensate for the intermittent generation of wind and solar power.
Portability
This is the area of greatest success for current energy storage technologies. Single-use and rechargeable batteries are ubiquitous, and provide power for devices with demands as varied as digital watches and cars. Advances in battery technology have generally been slow, however, with much of the advance in battery life that consumers see being attributable to efficient power management rather than increased storage capacity. Portableconsumer electronics
Consumer electronics or home electronics are electronic ( analog or digital) equipment intended for everyday use, typically in private homes. Consumer electronics include devices used for entertainment, communications and recreation. Usually ...
have benefited greatly from size and power reductions associated with Moore's law
Moore's law is the observation that the number of transistors in a dense integrated circuit (IC) doubles about every two years. Moore's law is an observation and projection of a historical trend. Rather than a law of physics, it is an empir ...
. Unfortunately, Moore's law does not apply to hauling people and freight; the underlying energy requirements for transportation remain much higher than for information and entertainment applications. Battery capacity has become an issue as pressure grows for alternatives to internal combustion engine
An internal combustion engine (ICE or IC engine) is a heat engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer (usually air) in a combustion chamber that is an integral part of the working fluid flow circuit. In an internal combust ...
s in cars, trucks, buses, trains, ships, and aeroplanes. These uses require far more energy density
In physics, energy density is the amount of energy stored in a given system or region of space per unit volume. It is sometimes confused with energy per unit mass which is properly called specific energy or .
Often only the ''useful'' or extract ...
(the amount of energy stored in a given volume or weight) than current battery technology can deliver. Liquid hydrocarbon
In organic chemistry, a hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon. Hydrocarbons are examples of group 14 hydrides. Hydrocarbons are generally colourless and hydrophobic, and their odors are usually weak or ...
fuel (such as gasoline
Gasoline (; ) or petrol (; ) (see ) is a transparent, petroleum-derived flammable liquid that is used primarily as a fuel in most spark-ignited internal combustion engines (also known as petrol engines). It consists mostly of organic com ...
/petrol
Gasoline (; ) or petrol (; ) (see ) is a transparent, petroleum-derived flammable liquid that is used primarily as a fuel in most spark-ignited internal combustion engines (also known as petrol engines). It consists mostly of organic c ...
and diesel), as well as alcohols (methanol
Methanol (also called methyl alcohol and wood spirit, amongst other names) is an organic chemical and the simplest aliphatic alcohol, with the formula C H3 O H (a methyl group linked to a hydroxyl group, often abbreviated as MeOH). It is a lig ...
, ethanol
Ethanol (abbr. EtOH; also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound. It is an alcohol with the chemical formula . Its formula can be also written as or (an ethyl group linked to a hyd ...
, and butanol) and lipids
Lipids are a broad group of naturally-occurring molecules which includes fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids include ...
(straight vegetable oil
Vegetable oil can be used as an alternative fuel in diesel engines and in heating oil burners. When vegetable oil is used directly as a fuel, in either modified or unmodified equipment, it is referred to as straight vegetable oil (SVO) or pure p ...
, biodiesel
Biodiesel is a form of diesel fuel derived from plants or animals and consisting of long-chain fatty acid esters. It is typically made by chemically reacting lipids such as animal fat (tallow), soybean oil, or some other vegetable oil wit ...
) have much higher energy densities.
There are synthetic pathways for using electricity to reduce carbon dioxide and water to liquid hydrocarbon or alcohol fuels. These pathways begin with electrolysis of water to generate hydrogen, and then reducing carbon dioxide with excess hydrogen in variations of the reverse water gas shift reaction
Water (chemical formula ) is an inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living organisms (in which it acts as a ...
. Non-fossil sources of carbon dioxide include fermentation
Fermentation is a metabolic process that produces chemical changes in organic substrates through the action of enzymes. In biochemistry, it is narrowly defined as the extraction of energy from carbohydrates in the absence of oxygen. In food ...
plants and sewage treatment
Sewage treatment (or domestic wastewater treatment, municipal wastewater treatment) is a type of wastewater treatment which aims to remove contaminants from sewage to produce an effluent that is suitable for discharge to the surrounding envi ...
plants. Converting electrical energy to carbon-based liquid fuel has potential to provide portable energy storage usable by the large existing stock of motor vehicles and other engine-driven equipment, without the difficulties of dealing with hydrogen or another exotic energy carrier. These synthetic pathways may attract attention in connection with attempts to improve energy security
Energy security is the association between national security and the availability of natural resources for energy consumption. Access to (relatively) cheap energy has become essential to the functioning of modern economies. However, the uneven ...
in nations that rely on imported petroleum, but have or can develop large sources of renewable or nuclear electricity, as well as to deal with possible future declines in the amount of petroleum available to import.
Because the transport sector uses the energy from petroleum very inefficiently, replacing petroleum with electricity for mobile energy will not require very large investments over many years.
Reliability
Virtually all devices that operate on electricity are adversely affected by the sudden removal of their power supply. Solutions such as UPS (uninterruptible power supplies
An uninterruptible power supply or uninterruptible power source (UPS) is an electrical apparatus that provides emergency power to a load when the input power source or mains power fails. A UPS differs from an auxiliary or emergency power system ...
) or backup generators are available, but these are expensive. Efficient methods of power storage would allow for devices to have a built-in backup for power cuts, and also reduce the impact of a failure in a generating station. Examples of this are currently available using fuel cell
A fuel cell is an electrochemical cell that converts the chemical energy of a fuel (often hydrogen) and an oxidizing agent (often oxygen) into electricity through a pair of redox reactions. Fuel cells are different from most batteries in requ ...
s and flywheels.
See also
* Battery electric vehicles * Battery-to-grid *Cost of electricity by source
Different methods of electricity generation can incur a variety of different costs, which can be divided into three general categories: 1) wholesale costs, or all costs paid by utilities associated with acquiring and distributing electricity to ...
* Distributed generation
Distributed generation, also distributed energy, on-site generation (OSG), or district/decentralized energy, is electrical generation and storage performed by a variety of small, grid-connected or distribution system-connected devices referred to ...
* Energy demand management
Energy demand management, also known as demand-side management (DSM) or demand-side response (DSR), is the modification of consumer demand for energy through various methods such as financial incentives and behavioral change through education.
Us ...
* Energy storage
Energy storage is the capture of energy produced at one time for use at a later time to reduce imbalances between energy demand and energy production.
A device that stores energy is generally called an accumulator or battery.
Energy comes in ...
* Energy storage as a service Energy storage as a service (ESaaS) allows a facility to benefit from the advantages of an energy storage system by entering into a service agreement without purchasing the system. Energy storage systems provide a range of services to generate reven ...
(ESaaS)
* Fuel-cell vehicle
A fuel cell vehicle (FCV) or fuel cell electric vehicle (FCEV) is an electric vehicle that uses a fuel cell, sometimes in combination with a small battery or supercapacitor, to power its onboard electric motor. Fuel cells in vehicles generate elec ...
* Grid-tied electrical system
A grid-tied electrical system, also called ''tied to grid'' or ''grid tie system'', is a semi-autonomous electrical generation or grid energy storage system which links to the mains to feed excess capacity back to the local mains electrical grid. ...
* Hybrid electric vehicle
A hybrid electric vehicle (HEV) is a type of hybrid vehicle that combines a conventional internal combustion engine (ICE) system with an electric propulsion system (hybrid vehicle drivetrain). The presence of the electric powertrain is intended ...
* Hydrogen economy
The hydrogen economy is using hydrogen to decarbonize economic sectors which are hard to electrify, essentially, the "hard-to-abate" sectors such as cement, steel, long-haul transport etc. In order to phase out fossil fuels and limit climate ch ...
* List of energy storage projects
This is a list of energy storage power plants worldwide, other than pumped hydro storage.
Many individual energy storage plants augment electrical grids by capturing excess electrical energy during periods of low demand and storing it in oth ...
* Off-peak
Peak demand on an electrical grid is simply the highest electrical power demand that has occurred over a specified time period (Gönen 2008). Peak demand is typically characterized as annual, daily or seasonal and has the unit of power.
Peak dem ...
* Power-to-X
Power-to-X (also P2X and P2Y and P2Z) is a number of electricity conversion, energy storage, and reconversion pathways that use surplus electric power, typically during periods where fluctuating renewable energy generation exceeds load.
Power ...
* Rechargeable battery
A rechargeable battery, storage battery, or secondary cell (formally a type of energy accumulator), is a type of electrical battery which can be charged, discharged into a load, and recharged many times, as opposed to a disposable or prima ...
* Solar vehicle
A solar vehicle or solar electric vehicle is an electric vehicle powered completely or significantly by direct solar energy. Usually, photovoltaic (PV) cells contained in solar panels convert the sun's energy directly into electric energy. The ...
* Solar-powered boats
* U.S. Department of Energy International Energy Storage Database, a list of grid energy storage projects
* Vanadium redox battery
The vanadium redox battery (VRB), also known as the vanadium flow battery (VFB) or vanadium redox flow battery (VRFB), is a type of rechargeable flow battery. It employs vanadium ions as charge carriers. The battery uses vanadium's ability t ...
, dispatchable grid energy storage
* Vehicle-to-grid
Vehicle-to-grid (V2G), also known as Vehicle-to-home (V2H) or Vehicle-to-load (V2L) describes a system in which plug-in electric vehicles (PEV) sell demand response services to the grid. Demand services are either delivering electricity or by red ...
* Virtual power plant
A virtual power plant (VPP) is a cloud-based distributed power plant that aggregates the capacities of heterogeneous distributed energy resources (DER) for the purposes of enhancing power generation, trading or selling power on the electricity mark ...
* Wind farm
A wind farm or wind park, also called a wind power station or wind power plant, is a group of wind turbines in the same location used to produce electricity. Wind farms vary in size from a small number of turbines to several hundred wind turb ...
References
Saving For a Windless day
by Sean Davies in The E&T Magazine Vol 5 Issue 9 from th
www.IET.org
Further reading
*External links
UK Government report on the Benefits of long-duration electricity storage (Aug 2022)
A large grid-connected nickel-cadmium battery
Stationary Energy Storage…Key to the Renewable Grid
Electricity Storage FactBook
{{emerging technologies, energy=yes Power engineering