gravitational physics on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In physics, gravity () is a
In physics, gravity () is a

 In 1684, Newton sent a manuscript to
In 1684, Newton sent a manuscript to
 A major area of research is the discovery of exact solutions to the Einstein field equations. Solving these equations amounts to calculating a precise value for the metric tensor (which defines the curvature and geometry of spacetime) under certain physical conditions. There is no formal definition for what constitutes such solutions, but most scientists agree that they should be expressable using elementary functions or linear differential equations. Some of the most notable solutions of the equations include:
* The Schwarzschild solution, which describes spacetime surrounding a spherically symmetric non-
A major area of research is the discovery of exact solutions to the Einstein field equations. Solving these equations amounts to calculating a precise value for the metric tensor (which defines the curvature and geometry of spacetime) under certain physical conditions. There is no formal definition for what constitutes such solutions, but most scientists agree that they should be expressable using elementary functions or linear differential equations. Some of the most notable solutions of the equations include:
* The Schwarzschild solution, which describes spacetime surrounding a spherically symmetric non-
 * In 1919, the British astrophysicist
* In 1919, the British astrophysicist
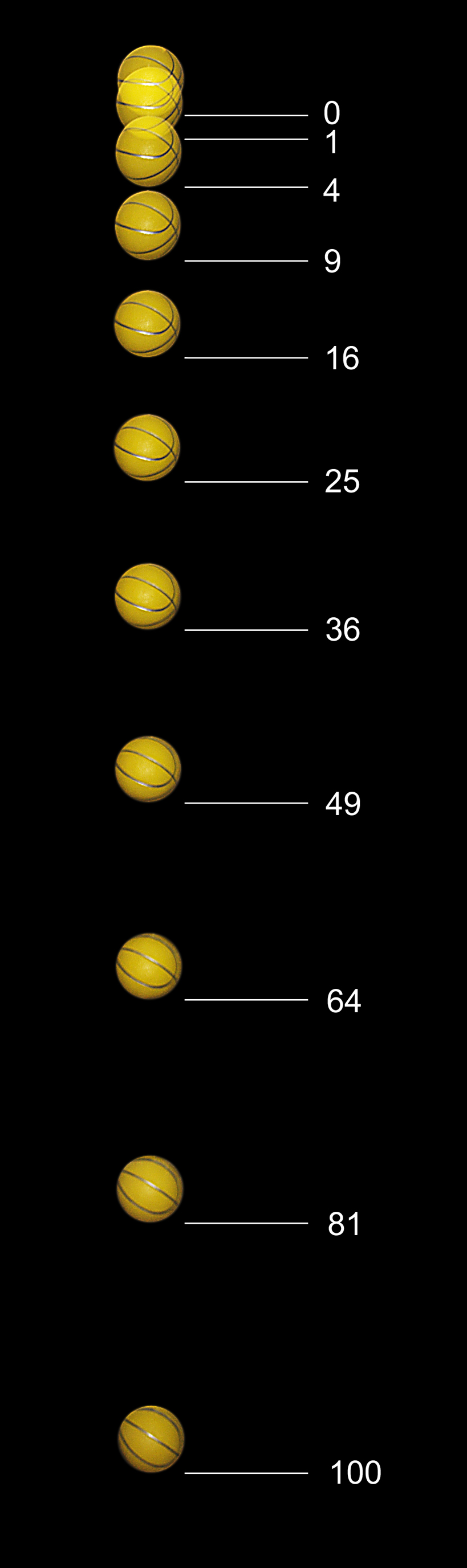 Every planetary body (including the Earth) is surrounded by its own gravitational field, which can be conceptualized with Newtonian physics as exerting an attractive force on all objects. Assuming a spherically symmetrical planet, the strength of this field at any given point above the surface is proportional to the planetary body's mass and inversely proportional to the square of the distance from the center of the body.
Every planetary body (including the Earth) is surrounded by its own gravitational field, which can be conceptualized with Newtonian physics as exerting an attractive force on all objects. Assuming a spherically symmetrical planet, the strength of this field at any given point above the surface is proportional to the planetary body's mass and inversely proportional to the square of the distance from the center of the body.
 The strength of the gravitational field is numerically equal to the acceleration of objects under its influence. The rate of acceleration of falling objects near the Earth's surface varies very slightly depending on latitude, surface features such as mountains and ridges, and perhaps unusually high or low sub-surface densities. For purposes of weights and measures, a standard gravity value is defined by the
The strength of the gravitational field is numerically equal to the acceleration of objects under its influence. The rate of acceleration of falling objects near the Earth's surface varies very slightly depending on latitude, surface features such as mountains and ridges, and perhaps unusually high or low sub-surface densities. For purposes of weights and measures, a standard gravity value is defined by the
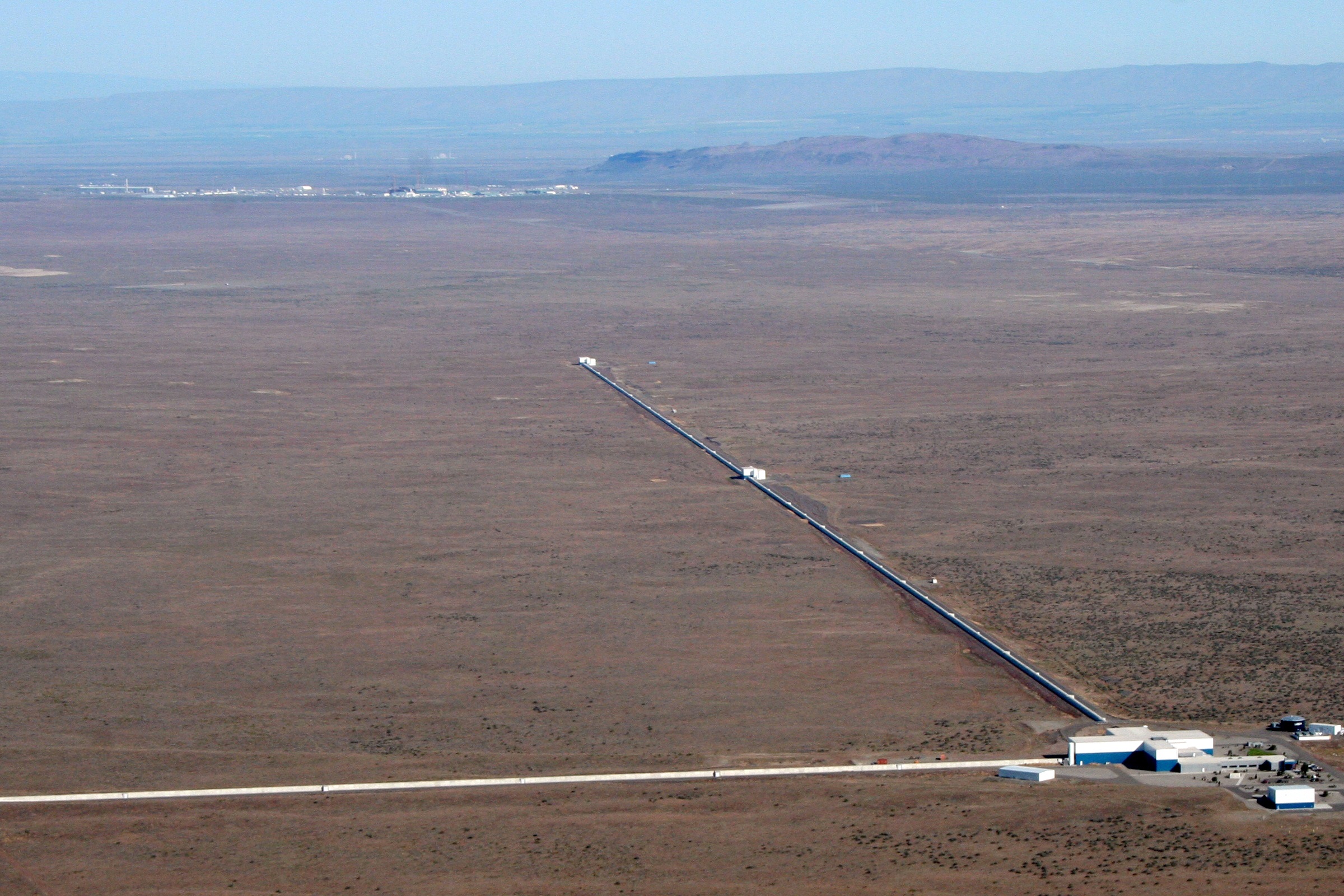 General relativity predicts that energy can be transported out of a system through gravitational radiation. The first indirect evidence for gravitational radiation was through measurements of the
General relativity predicts that energy can be transported out of a system through gravitational radiation. The first indirect evidence for gravitational radiation was through measurements of the
 * Extra-fast stars: Stars in galaxies follow a distribution of velocities where stars on the outskirts are moving faster than they should according to the observed distributions of normal matter. Galaxies within galaxy clusters show a similar pattern.
* Extra-fast stars: Stars in galaxies follow a distribution of velocities where stars on the outskirts are moving faster than they should according to the observed distributions of normal matter. Galaxies within galaxy clusters show a similar pattern.
The Feynman Lectures on Physics Vol. I Ch. 7: The Theory of Gravitation
* * {{Authority control Fundamental interactions Acceleration Articles containing video clips Empirical laws
 In physics, gravity () is a
In physics, gravity () is a fundamental interaction
In physics, the fundamental interactions, also known as fundamental forces, are the interactions that do not appear to be reducible to more basic interactions. There are four fundamental interactions known to exist: the gravitational and electr ...
which causes mutual attraction between all things with mass
Mass is an intrinsic property of a body. It was traditionally believed to be related to the quantity of matter in a physical body, until the discovery of the atom and particle physics. It was found that different atoms and different eleme ...
or energy
In physics, energy (from Ancient Greek: ἐνέργεια, ''enérgeia'', “activity”) is the quantitative property that is transferred to a body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of work and in the form of h ...
. Gravity is, by far, the weakest of the four fundamental interactions, approximately 1038 times weaker than the strong interaction
The strong interaction or strong force is a fundamental interaction that confines quarks into proton, neutron, and other hadron particles. The strong interaction also binds neutrons and protons to create atomic nuclei, where it is called t ...
, 1036 times weaker than the electromagnetic force
In physics, electromagnetism is an interaction that occurs between particles with electric charge. It is the second-strongest of the four fundamental interactions, after the strong force, and it is the dominant force in the interactions of ...
and 1029 times weaker than the weak interaction
In nuclear physics and particle physics, the weak interaction, which is also often called the weak force or weak nuclear force, is one of the four known fundamental interactions, with the others being electromagnetism, the strong interactio ...
. As a result, it has no significant influence at the level of subatomic particles. However, gravity is the most significant interaction between objects at the macroscopic scale
The macroscopic scale is the length scale on which objects or phenomena are large enough to be visible with the naked eye, without magnifying optical instruments. It is the opposite of microscopic.
Overview
When applied to physical phenomena a ...
, and it determines the motion of planets
A planet is a large, rounded astronomical body that is neither a star nor its remnant. The best available theory of planet formation is the nebular hypothesis, which posits that an interstellar cloud collapses out of a nebula to create a yo ...
, stars
A star is an astronomical object comprising a luminous spheroid of plasma held together by its gravity. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked eye at night, but their immense distances from Earth ...
, galaxies
A galaxy is a system of stars, stellar remnants, interstellar gas, dust, dark matter, bound together by gravity. The word is derived from the Greek ' (), literally 'milky', a reference to the Milky Way galaxy that contains the Solar System ...
, and even light
Light or visible light is electromagnetic radiation that can be perceived by the human eye. Visible light is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400–700 nanometres (nm), corresponding to frequencies of 750–420 t ...
.
On Earth, gravity gives weight
In science and engineering, the weight of an object is the force acting on the object due to gravity.
Some standard textbooks define weight as a vector quantity, the gravitational force acting on the object. Others define weight as a scalar quan ...
to physical object
In common usage and classical mechanics, a physical object or physical body (or simply an object or body) is a collection of matter within a defined contiguous boundary in three-dimensional space. The boundary must be defined and identified by t ...
s, and the Moon's gravity is responsible for sublunar tide
Tides are the rise and fall of sea levels caused by the combined effects of the gravitational forces exerted by the Moon (and to a much lesser extent, the Sun) and are also caused by the Earth and Moon orbiting one another.
Tide tables can ...
s in the oceans (the corresponding antipodal tide is caused by the inertia of the Earth and Moon orbiting one another). Gravity also has many important biological functions, helping to guide the growth of plants through the process of gravitropism
Gravitropism (also known as geotropism) is a coordinated process of differential growth by a plant in response to gravity pulling on it. It also occurs in fungi. Gravity can be either "artificial gravity" or natural gravity. It is a general featu ...
and influencing the circulation of fluids in multicellular organisms
A multicellular organism is an organism that consists of more than one cell, in contrast to unicellular organism.
All species of animals, land plants and most fungi are multicellular, as are many algae, whereas a few organisms are partially un ...
. Investigation into the effects of weightlessness
Weightlessness is the complete or near-complete absence of the sensation of weight. It is also termed zero gravity, zero G-force, or zero-G.
Weight is a measurement of the force on an object at rest in a relatively strong gravitational fie ...
has shown that gravity may play a role in immune system
The immune system is a network of biological processes that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, as well as cancer cells and objects such as wood splint ...
function and cell differentiation
Cellular differentiation is the process in which a stem cell alters from one type to a differentiated one. Usually, the cell changes to a more specialized type. Differentiation happens multiple times during the development of a multicellular ...
within the human body.
The gravitational attraction between the original gaseous matter in the Universe
The universe is all of space and time and their contents, including planets, stars, galaxies, and all other forms of matter and energy. The Big Bang theory is the prevailing cosmological description of the development of the universe. A ...
allowed it to coalesce and form stars which eventually condensed into galaxies, so gravity is responsible for many of the large-scale structures in the Universe. Gravity has an infinite range, although its effects become weaker as objects get farther away.
Gravity is most accurately described by the general theory of relativity
General relativity, also known as the general theory of relativity and Einstein's theory of gravity, is the geometric theory of gravitation published by Albert Einstein in 1915 and is the current description of gravitation in modern physic ...
(proposed by Albert Einstein
Albert Einstein ( ; ; 14 March 1879 – 18 April 1955) was a German-born theoretical physicist, widely acknowledged to be one of the greatest and most influential physicists of all time. Einstein is best known for developing the theory ...
in 1915), which describes gravity not as a force, but as the curvature
In mathematics, curvature is any of several strongly related concepts in geometry. Intuitively, the curvature is the amount by which a curve deviates from being a straight line, or a surface deviates from being a plane.
For curves, the cano ...
of spacetime
In physics, spacetime is a mathematical model that combines the three dimensions of space and one dimension of time into a single four-dimensional manifold. Spacetime diagrams can be used to visualize relativistic effects, such as why differ ...
, caused by the uneven distribution of mass, and causing masses to move along geodesic
In geometry, a geodesic () is a curve representing in some sense the shortest path ( arc) between two points in a surface, or more generally in a Riemannian manifold. The term also has meaning in any differentiable manifold with a connection ...
lines. The most extreme example of this curvature of spacetime is a black hole
A black hole is a region of spacetime where gravity is so strong that nothing, including light or other electromagnetic waves, has enough energy to escape it. The theory of general relativity predicts that a sufficiently compact mass can defo ...
, from which nothing—not even light—can escape once past the black hole's event horizon
In astrophysics, an event horizon is a boundary beyond which events cannot affect an observer. Wolfgang Rindler coined the term in the 1950s.
In 1784, John Michell proposed that gravity can be strong enough in the vicinity of massive compact obj ...
. However, for most applications, gravity is well approximated by Newton's law of universal gravitation
Newton's law of universal gravitation is usually stated as that every particle attracts every other particle in the universe with a force that is proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distan ...
, which describes gravity as a force
In physics, a force is an influence that can change the motion of an object. A force can cause an object with mass to change its velocity (e.g. moving from a state of rest), i.e., to accelerate. Force can also be described intuitively as a ...
causing any two bodies to be attracted toward each other, with magnitude proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional
In mathematics, two sequences of numbers, often experimental data, are proportional or directly proportional if their corresponding elements have a constant ratio, which is called the coefficient of proportionality or proportionality constant ...
to the square
In Euclidean geometry, a square is a regular quadrilateral, which means that it has four equal sides and four equal angles (90- degree angles, π/2 radian angles, or right angles). It can also be defined as a rectangle with two equal-lengt ...
of the distance
Distance is a numerical or occasionally qualitative measurement of how far apart objects or points are. In physics or everyday usage, distance may refer to a physical length or an estimation based on other criteria (e.g. "two counties over") ...
between them:
where is the force, and are the masses of the objects interacting, is the distance between the centers of the masses and is the gravitational constant
The gravitational constant (also known as the universal gravitational constant, the Newtonian constant of gravitation, or the Cavendish gravitational constant), denoted by the capital letter , is an empirical physical constant involved in th ...
.
Current models of particle physics
Particle physics or high energy physics is the study of fundamental particles and forces that constitute matter and radiation. The fundamental particles in the universe are classified in the Standard Model as fermions (matter particles) an ...
imply that the earliest instance of gravity in the Universe, possibly in the form of quantum gravity
Quantum gravity (QG) is a field of theoretical physics that seeks to describe gravity according to the principles of quantum mechanics; it deals with environments in which neither gravitational nor quantum effects can be ignored, such as in the ...
, supergravity
In theoretical physics, supergravity (supergravity theory; SUGRA for short) is a modern field theory that combines the principles of supersymmetry and general relativity; this is in contrast to non-gravitational supersymmetric theories such ...
or a gravitational singularity
A gravitational singularity, spacetime singularity or simply singularity is a condition in which gravity is so intense that spacetime itself breaks down catastrophically. As such, a singularity is by definition no longer part of the regular sp ...
, along with ordinary space
Space is the boundless three-dimensional extent in which objects and events have relative position and direction. In classical physics, physical space is often conceived in three linear dimensions, although modern physicists usually con ...
and time
Time is the continued sequence of existence and events that occurs in an apparently irreversible succession from the past, through the present, into the future. It is a component quantity of various measurements used to sequence events, t ...
, developed during the Planck epoch
The chronology of the universe describes the history and future of the universe according to Big Bang cosmology.
Research published in 2015 estimates the earliest stages of the universe's existence as taking place 13.8 billion years ago, wit ...
(up to 10−43 seconds after the birth
Birth is the act or process of bearing or bringing forth offspring, also referred to in technical contexts as parturition. In mammals, the process is initiated by hormones which cause the muscular walls of the uterus to contract, expelling the ...
of the Universe), possibly from a primeval state, such as a false vacuum
In quantum field theory, a false vacuum is a hypothetical vacuum that is relatively stable, but not in the most stable state possible. This condition is known as metastable. It may last for a very long time in that state, but could eventually d ...
, quantum vacuum
In quantum field theory, the quantum vacuum state (also called the quantum vacuum or vacuum state) is the quantum state with the lowest possible energy. Generally, it contains no physical particles. The word zero-point field is sometimes used ...
or virtual particle
A virtual particle is a theoretical transient particle that exhibits some of the characteristics of an ordinary particle, while having its existence limited by the uncertainty principle. The concept of virtual particles arises in the perturba ...
, in a currently unknown manner. – discusses " Planck time" and "Planck era
The chronology of the universe describes the history and future of the universe according to Big Bang cosmology.
Research published in 2015 estimates the earliest stages of the universe's existence as taking place 13.8 billion years ago, wit ...
" at the very beginning of the Universe Scientists are currently working to develop a theory of gravity consistent with quantum mechanics
Quantum mechanics is a fundamental theory in physics that provides a description of the physical properties of nature at the scale of atoms and subatomic particles. It is the foundation of all quantum physics including quantum chemistry, ...
, a quantum gravity
Quantum gravity (QG) is a field of theoretical physics that seeks to describe gravity according to the principles of quantum mechanics; it deals with environments in which neither gravitational nor quantum effects can be ignored, such as in the ...
theory, which would allow gravity to be united in a common mathematical framework (a theory of everything
A theory of everything (TOE or TOE/ToE), final theory, ultimate theory, unified field theory or master theory is a hypothetical, singular, all-encompassing, coherent theoretical framework of physics that fully explains and links together all asp ...
) with the other three fundamental interactions of physics.
History
Ancient world
The nature and mechanism of gravity was explored by a wide range of ancient scholars. InGreece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders with ...
, Aristotle
Aristotle (; grc-gre, Ἀριστοτέλης ''Aristotélēs'', ; 384–322 BC) was a Greek philosopher and polymath during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. Taught by Plato, he was the founder of the Peripatetic school of ...
believed that objects fell towards the Earth because the Earth was the center of the Universe and attracted all of the mass in the Universe towards it. He also thought that the speed of a falling object should increase with its weight, a conclusion which was later shown to be false. While Aristotle's view was widely accepted throughout Ancient Greece, there were other thinkers such as Plutarch
Plutarch (; grc-gre, Πλούταρχος, ''Ploútarchos''; ; – after AD 119) was a Greek Middle Platonist philosopher, historian, biographer, essayist, and priest at the Temple of Apollo in Delphi. He is known primarily for h ...
who correctly predicted that the attraction of gravity was not unique to the Earth.
Although he didn't understand gravity as a force, the ancient Greek philosopher Archimedes
Archimedes of Syracuse (;; ) was a Greek mathematician, physicist, engineer, astronomer, and inventor from the ancient city of Syracuse in Sicily. Although few details of his life are known, he is regarded as one of the leading scientists ...
discovered the center of gravity
In physics, the center of mass of a distribution of mass in space (sometimes referred to as the balance point) is the unique point where the weighted relative position of the distributed mass sums to zero. This is the point to which a force ma ...
of a triangle. He also postulated that if two equal weights did not have the same center of gravity, the center of gravity of the two weights together would be in the middle of the line that joins their centers of gravity.
In India
India, officially the Republic of India ( Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the ...
, the mathematician-astronomer Aryabhata
Aryabhata ( ISO: ) or Aryabhata I (476–550 CE) was an Indian mathematician and astronomer of the classical age of Indian mathematics and Indian astronomy. He flourished in the Gupta Era and produced works such as the ''Aryabhatiya'' (whic ...
first identified gravity to explain why objects are not driven away from the Earth by the centrifugal force
In Newtonian mechanics, the centrifugal force is an inertial force (also called a "fictitious" or "pseudo" force) that appears to act on all objects when viewed in a rotating frame of reference. It is directed away from an axis which is paralle ...
of the planet's rotation. Later, in the seventh century CE, Brahmagupta
Brahmagupta ( – ) was an Indian mathematician and astronomer. He is the author of two early works on mathematics and astronomy: the ''Brāhmasphuṭasiddhānta'' (BSS, "correctly established doctrine of Brahma", dated 628), a theoretical trea ...
proposed the idea that gravity is an attractive force which draws objects to the Earth and used the term '' gurutvākarṣaṇ'' to describe it.
In the ancient Middle East
The Middle East ( ar, الشرق الأوسط, ISO 233: ) is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabia (including the Arabian Peninsula and Bahrain), Asia Minor (Asian part of Turkey except Hatay Province), East Thrace (Europ ...
, gravity was a topic of fierce debate. The Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
intellectual Al-Biruni
Abu Rayhan Muhammad ibn Ahmad al-Biruni (973 – after 1050) commonly known as al-Biruni, was a Khwarazmian Iranian in scholar and polymath during the Islamic Golden Age. He has been called variously the "founder of Indology", "Father of ...
believed that the force of gravity was not unique to the Earth, and he correctly assumed that other heavenly bodies should exert a gravitational attraction as well. In contrast, Al-Khazini
Abū al-Fath Abd al-Rahman Mansūr al-Khāzini or simply al-Khāzini (, flourished 1115–1130) was an Iranian astronomer of Greek origin from Seljuk Persia. His astronomical tables written under the patronage of Sultan Sanjar (', 1115) is con ...
held the same position as Aristotle that all matter in the Universe is attracted to the center of the Earth.

Scientific revolution
In the mid-16th century, various European scientists experimentally disproved the Aristotelian notion that heavier objects fall at a faster rate. In particular, the Spanish Dominican priest Domingo de Soto wrote in 1551 that bodies in free fall uniformly accelerate. De Soto may have been influenced by earlier experiments conducted by other Dominican priests in Italy, including those byBenedetto Varchi
Benedetto Varchi (; 1502/15031565) was an Italian humanist, historian, and poet.
Biography
Born in Florence to a family that had originated at Montevarchi, he frequented the neoplatonic academy that Bernardo Rucellai organized in his garden, the ...
, Francesco Beato, Luca Ghini
Luca Ghini (Casalfiumanese, 1490 – Bologna, 4 May 1556) was an Italian physician and botanist, notable as the creator of the first recorded herbarium, as well as the first botanical garden in Europe.
Biography
Ghini was born in Casalfiumanese, ...
, and Giovan Bellaso which contradicted Aristotle's teachings on the fall of bodies. The mid-16th century Italian physicist Giambattista Benedetti published papers claiming that, due to specific gravity, objects made of the same material but with different masses would fall at the same speed. With the 1586 Delft tower experiment, the Flemish physicist Simon Stevin observed that two cannonballs of differing sizes and weights fell at the same rate when dropped from a tower. Finally, in the late 16th century, Galileo Galilei's careful measurements of balls rolling down inclines allowed him to firmly establish that gravitational acceleration is the same for all objects. Galileo postulated that air resistance
In fluid dynamics, drag (sometimes called air resistance, a type of friction, or fluid resistance, another type of friction or fluid friction) is a force acting opposite to the relative motion of any object moving with respect to a surrounding flu ...
is the reason that objects with a low density and high surface area fall more slowly in an atmosphere.
In 1604, Galileo correctly hypothesized that the distance of a falling object is proportional to the square of the time elapsed. This was later confirmed by Italian scientists Jesuits Grimaldi and Riccioli
Giovanni Battista Riccioli, SJ (17 April 1598 – 25 June 1671) was an Italian astronomer and a Catholic priest in the Jesuit order. He is known, among other things, for his experiments with pendulums and with falling bodies, for his discussion ...
between 1640 and 1650. They also calculated the magnitude of the Earth's gravity by measuring the oscillations of a pendulum.
Newton's theory of gravitation
 In 1684, Newton sent a manuscript to
In 1684, Newton sent a manuscript to Edmond Halley
Edmond (or Edmund) Halley (; – ) was an English astronomer, mathematician and physicist. He was the second Astronomer Royal in Britain, succeeding John Flamsteed in 1720.
From an observatory he constructed on Saint Helena in 1676–77, Hal ...
titled ''De motu corporum in gyrum
(from Latin: "On the motion of bodies in an orbit"; abbreviated ) is the presumed title of a manuscript by Isaac Newton sent to Edmond Halley in November 1684. The manuscript was prompted by a visit from Halley earlier that year when he had qu ...
('On the motion of bodies in an orbit')'', which provided a physical justification for Kepler's laws of planetary motion
In astronomy, Kepler's laws of planetary motion, published by Johannes Kepler between 1609 and 1619, describe the orbits of planets around the Sun. The laws modified the heliocentric theory of Nicolaus Copernicus, replacing its circular orbit ...
. Halley was impressed by the manuscript and urged Newton to expand on it, and a few years later Newton published a groundbreaking book called '' Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica'' (''Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy''). In this book, Newton described gravitation as a universal force, and claimed that "the forces which keep the planets in their orbs must ereciprocally as the squares of their distances from the centers about which they revolve." This statement was later condensed into the following inverse-square law:
where is the force, and are the masses of the objects interacting, is the distance between the centers of the masses and is the gravitational constant
The gravitational constant (also known as the universal gravitational constant, the Newtonian constant of gravitation, or the Cavendish gravitational constant), denoted by the capital letter , is an empirical physical constant involved in th ...
.
Newton's ''Principia'' was well-received by the scientific community, and his law of gravitation quickly spread across the European world. More than a century later, in 1821, his theory of gravitation rose to even greater prominence when it was used to predict the existence of Neptune. In that year, the French astronomer Alexis Bouvard used this theory to create a table modeling the orbit of Uranus, which was shown to differ significantly from the planet's actual trajectory. In order to explain this discrepancy, many astronomers speculated that there might be a large object beyond the orbit of Uranus which was disrupting its orbit. In 1846, the astronomers John Couch Adams and Urbain Le Verrier
Urbain Jean Joseph Le Verrier FRS (FOR) HFRSE (; 11 March 1811 – 23 September 1877) was a French astronomer and mathematician who specialized in celestial mechanics and is best known for predicting the existence and position of Neptune using ...
independently used Newton's law to predict Neptune's location in the night sky, and the planet was discovered there within a day.
General relativity
Eventually, astronomers noticed an eccentricity in the orbit of the planet Mercury which could not be explained by Newton's theory: the perihelion of the orbit was increasing by about 42.98 arcseconds per century. The most obvious explanation for this discrepancy was an as-yet-undiscovered celestial body (such as a planet orbiting the Sun even closer than Mercury), but all efforts to find such a body turned out to be fruitless. Finally, in 1915,Albert Einstein
Albert Einstein ( ; ; 14 March 1879 – 18 April 1955) was a German-born theoretical physicist, widely acknowledged to be one of the greatest and most influential physicists of all time. Einstein is best known for developing the theory ...
developed a theory of general relativity which was able to accurately model Mercury's orbit.
In general relativity, the effects of gravitation are ascribed to spacetime
In physics, spacetime is a mathematical model that combines the three dimensions of space and one dimension of time into a single four-dimensional manifold. Spacetime diagrams can be used to visualize relativistic effects, such as why differ ...
curvature
In mathematics, curvature is any of several strongly related concepts in geometry. Intuitively, the curvature is the amount by which a curve deviates from being a straight line, or a surface deviates from being a plane.
For curves, the cano ...
instead of a force. Einstein began to toy with this idea in the form of the equivalence principle, a discovery which he later described as "the happiest thought of my life." In this theory, free fall is considered to be equivalent to inertial motion, meaning that free-falling inertial objects are accelerated relative to non-inertial observers on the ground. In contrast to Newtonian physics
Classical mechanics is a physical theory describing the motion of macroscopic objects, from projectiles to parts of machinery, and astronomical objects, such as spacecraft, planets, stars, and galaxies. For objects governed by classical m ...
, Einstein believed that it was possible for this acceleration to occur without any force being applied to the object.
Einstein proposed that spacetime is curved by matter, and that free-falling objects are moving along locally straight paths in curved spacetime. These straight paths are called geodesics
In geometry, a geodesic () is a curve representing in some sense the shortest path ( arc) between two points in a surface, or more generally in a Riemannian manifold. The term also has meaning in any differentiable manifold with a connection. ...
. As in Newton's first law of motion, Einstein believed that a force applied to an object would cause it to deviate from a geodesic. For instance, people standing on the surface of the Earth are prevented from following a geodesic path because the mechanical resistance of the Earth exerts an upward force on them. This explains why moving along the geodesics in spacetime is considered inertial.
Einstein's description of gravity was quickly accepted by the majority of physicists, as it was able to explain a wide variety of previously baffling experimental results. In the coming years, a wide range of experiments provided additional support for the idea of general relativity. Today, Einstein's theory of relativity is used for all gravitational calculations where absolute precision is desired, although Newton's inverse-square law continues to be a useful and fairly accurate approximation.
Modern research
Inmodern physics
Modern physics is a branch of physics that developed in the early 20th century and onward or branches greatly influenced by early 20th century physics. Notable branches of modern physics include quantum mechanics, special relativity and general ...
, general relativity remains the framework for the understanding of gravity. Physicists continue to work to find solutions to the Einstein field equations that form the basis of general relativity, while some scientists have speculated that general relativity may not be applicable at all in certain scenarios.
Einstein field equations
The Einstein field equations are a system of 10 partial differential equations which describe how matter affects the curvature of spacetime. The system is often expressed in the form where is theEinstein tensor
In differential geometry, the Einstein tensor (named after Albert Einstein; also known as the trace-reversed Ricci tensor) is used to express the curvature of a pseudo-Riemannian manifold. In general relativity, it occurs in the Einstein fie ...
, is the metric tensor
In the mathematical field of differential geometry, a metric tensor (or simply metric) is an additional structure on a manifold (such as a surface) that allows defining distances and angles, just as the inner product on a Euclidean space allows ...
, is the stress–energy tensor, is the cosmological constant
In cosmology, the cosmological constant (usually denoted by the Greek capital letter lambda: ), alternatively called Einstein's cosmological constant,
is the constant coefficient of a term that Albert Einstein temporarily added to his field equ ...
, is the Newtonian constant of gravitation and is the speed of light. The constant is referred to as the Einstein gravitational constant.
 A major area of research is the discovery of exact solutions to the Einstein field equations. Solving these equations amounts to calculating a precise value for the metric tensor (which defines the curvature and geometry of spacetime) under certain physical conditions. There is no formal definition for what constitutes such solutions, but most scientists agree that they should be expressable using elementary functions or linear differential equations. Some of the most notable solutions of the equations include:
* The Schwarzschild solution, which describes spacetime surrounding a spherically symmetric non-
A major area of research is the discovery of exact solutions to the Einstein field equations. Solving these equations amounts to calculating a precise value for the metric tensor (which defines the curvature and geometry of spacetime) under certain physical conditions. There is no formal definition for what constitutes such solutions, but most scientists agree that they should be expressable using elementary functions or linear differential equations. Some of the most notable solutions of the equations include:
* The Schwarzschild solution, which describes spacetime surrounding a spherically symmetric non-rotating
Rotation, or spin, is the circular movement of an object around a '' central axis''. A two-dimensional rotating object has only one possible central axis and can rotate in either a clockwise or counterclockwise direction. A three-dimensional ...
uncharged massive object. For compact enough objects, this solution generated a black hole
A black hole is a region of spacetime where gravity is so strong that nothing, including light or other electromagnetic waves, has enough energy to escape it. The theory of general relativity predicts that a sufficiently compact mass can defo ...
with a central singularity. At points far away from the central mass, the accelerations predicted by the Schwarzschild solution are practically identical to those predicted by Newton's theory of gravity.
* The Reissner–Nordström solution, which analyzes a non-rotating spherically symmetric object with charge and was independently discovered by several different researchers between 1916 and 1921. In some cases, this solution can predict the existence of black holes with double event horizons.
* The Kerr solution
The Kerr metric or Kerr geometry describes the geometry of empty spacetime around a rotating uncharged axially symmetric black hole with a quasispherical event horizon. The Kerr metric tensor, metric is an Exact solutions in general relativity, e ...
, which generalizes the Schwarzchild solution to rotating massive objects. Because of the difficulty of factoring in the effects of rotation into the Einstein field equations, this solution was not discovered until 1963.
* The Kerr–Newman solution for charged, rotating massive objects. This solution was derived in 1964, using the same technique of complex coordinate transformation that was used for the Kerr solution.
* The cosmological
Cosmology () is a branch of physics and metaphysics dealing with the nature of the universe. The term ''cosmology'' was first used in English in 1656 in Thomas Blount's ''Glossographia'', and in 1731 taken up in Latin by German philosopher ...
Friedmann–Lemaître–Robertson–Walker solution, discovered in 1922 by Alexander Friedmann
Alexander Alexandrovich Friedmann (also spelled Friedman or Fridman ; russian: Алекса́ндр Алекса́ндрович Фри́дман) (June 16 .S. 4 1888 – September 16, 1925) was a Russian and Soviet physicist and mathematicia ...
and then confirmed in 1927 by Georges Lemaître. This solution was revolutionary for predicting the expansion of the Universe
The expansion of the universe is the increase in distance between any two given gravitationally unbound parts of the observable universe with time. It is an intrinsic expansion whereby the scale of space itself changes. The universe does not e ...
, which was confirmed seven years later after a series of measurements by Edwin Hubble
Edwin Powell Hubble (November 20, 1889 – September 28, 1953) was an American astronomer. He played a crucial role in establishing the fields of extragalactic astronomy and observational cosmology.
Hubble proved that many objects previousl ...
. It even showed that general relativity was incompatible with a static universe, and Einstein later conceded that he had been wrong to design his field equations to account for a Universe that was not expanding.
Today, there remain many important situations in which the Einstein field equations have not been solved. Chief among these is the two-body problem
In classical mechanics, the two-body problem is to predict the motion of two massive objects which are abstractly viewed as point particles. The problem assumes that the two objects interact only with one another; the only force affecting each ...
, which concerns the geometry of spacetime around two mutually interacting massive objects (such as the Sun and the Earth, or the two stars in a binary star system). The situation gets even more complicated when considering the interactions of three or more massive bodies (the "''n''-body problem"), and some scientists suspect that the Einstein field equations will never be solved in this context. However, it is still possible to construct an approximate solution to the field equations in the ''n''-body problem by using the technique of post-Newtonian expansion. In general, the extreme nonlinearity of the Einstein field equations makes it difficult to solve them in all but the most specific cases.
Gravity and quantum mechanics
Despite its success in predicting the effects of gravity at large scales, general relativity is ultimately incompatible withquantum mechanics
Quantum mechanics is a fundamental theory in physics that provides a description of the physical properties of nature at the scale of atoms and subatomic particles. It is the foundation of all quantum physics including quantum chemistry, ...
. This is because general relativity describes gravity as a smooth, continuous distortion of spacetime, while quantum mechanics holds that all forces arise from the exchange of discrete particles known as quanta. This contradiction is especially vexing to physicists because the other three fundamental forces (strong force, weak force and electromagnetism) were reconciled with a quantum framework decades ago. As a result, modern researchers have begun to search for a theory that could unite both gravity and quantum mechanics under a more general framework.
One path is to describe gravity in the framework of quantum field theory, which has been successful to accurately describe the other fundamental interaction
In physics, the fundamental interactions, also known as fundamental forces, are the interactions that do not appear to be reducible to more basic interactions. There are four fundamental interactions known to exist: the gravitational and electr ...
s. The electromagnetic force arises from an exchange of virtual photons, where the QFT description of gravity is that there is an exchange of virtual gravitons. This description reproduces general relativity in the classical limit
The classical limit or correspondence limit is the ability of a physical theory to approximate or "recover" classical mechanics when considered over special values of its parameters. The classical limit is used with physical theories that predict n ...
. However, this approach fails at short distances of the order of the Planck length, where a more complete theory of quantum gravity
Quantum gravity (QG) is a field of theoretical physics that seeks to describe gravity according to the principles of quantum mechanics; it deals with environments in which neither gravitational nor quantum effects can be ignored, such as in the ...
(or a new approach to quantum mechanics) is required.
Tests of general relativity
Testing the predictions of general relativity has historically been difficult, because they are almost identical to the predictions of Newtonian gravity for small energies and masses. Still, since its development, an ongoing series of experimental results have provided support for the theory: * In 1919, the British astrophysicist
* In 1919, the British astrophysicist Arthur Eddington
Sir Arthur Stanley Eddington (28 December 1882 – 22 November 1944) was an English astronomer, physicist, and mathematician. He was also a philosopher of science and a populariser of science. The Eddington limit, the natural limit to the lumi ...
was able to confirm the predicted gravitational lensing of light during that year's solar eclipse. Eddington measured starlight deflections twice those predicted by Newtonian corpuscular theory, in accordance with the predictions of general relativity. Although Eddington's analysis was later disputed, this experiment made Einstein famous almost overnight and caused general relativity to become widely accepted in the scientific community.
* In 1959, American physicists Robert Pound and Glen Rebka performed an experiment in which they used gamma rays
A gamma ray, also known as gamma radiation (symbol γ or \gamma), is a penetrating form of electromagnetic radiation arising from the radioactive decay of atomic nuclei. It consists of the shortest wavelength electromagnetic waves, typically sh ...
to confirm the prediction of gravitational time dilation. By sending the rays down a 74-foot tower and measuring their frequency at the bottom, the scientists confirmed that light is redshifted as it moves towards a source of gravity. The observed redshift also supported the idea that time runs more slowly in the presence of a gravitational field.
* The time delay of light passing close to a massive object was first identified by Irwin I. Shapiro in 1964 in interplanetary spacecraft signals.
*In 1971, scientists discovered the first-ever black hole in the galaxy Cygnus. The black hole was detected because it was emitting bursts of x-rays
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30 ...
as it consumed a smaller star, and it came to be known as Cygnus X-1. This discovery confirmed yet another prediction of general relativity, because Einstein's equations implied that light could not escape from a sufficiently large and compact object.
*General relativity states that gravity acts on light and matter equally, meaning that a sufficiently massive object could warp light around it and create a gravitational lens. This phenomenon was first confirmed by observation in 1979 using the 2.1 meter telescope at Kitt Peak National Observatory in Arizona, which saw two mirror images of the same quasar whose light had been bent around the galaxy YGKOW G1.
*Frame dragging
Frame-dragging is an effect on spacetime, predicted by Albert Einstein's general theory of relativity, that is due to non-static stationary distributions of mass–energy. A stationary field is one that is in a steady state, but the masses cau ...
, the idea that a rotating massive object should twist spacetime around it, was confirmed by Gravity Probe B results in 2011.
*In 2015, the LIGO observatory detected faint gravitational waves
Gravitational waves are waves of the intensity of gravity generated by the accelerated masses of an orbital binary system that propagate as waves outward from their source at the speed of light. They were first proposed by Oliver Heaviside i ...
, the existence of which had been predicted by general relativity. Scientists believe that the waves emanated from a black hole merger that occurred 1.5 billion light-years away.
Specifics
Earth's gravity
 Every planetary body (including the Earth) is surrounded by its own gravitational field, which can be conceptualized with Newtonian physics as exerting an attractive force on all objects. Assuming a spherically symmetrical planet, the strength of this field at any given point above the surface is proportional to the planetary body's mass and inversely proportional to the square of the distance from the center of the body.
Every planetary body (including the Earth) is surrounded by its own gravitational field, which can be conceptualized with Newtonian physics as exerting an attractive force on all objects. Assuming a spherically symmetrical planet, the strength of this field at any given point above the surface is proportional to the planetary body's mass and inversely proportional to the square of the distance from the center of the body.
 The strength of the gravitational field is numerically equal to the acceleration of objects under its influence. The rate of acceleration of falling objects near the Earth's surface varies very slightly depending on latitude, surface features such as mountains and ridges, and perhaps unusually high or low sub-surface densities. For purposes of weights and measures, a standard gravity value is defined by the
The strength of the gravitational field is numerically equal to the acceleration of objects under its influence. The rate of acceleration of falling objects near the Earth's surface varies very slightly depending on latitude, surface features such as mountains and ridges, and perhaps unusually high or low sub-surface densities. For purposes of weights and measures, a standard gravity value is defined by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures
The International Bureau of Weights and Measures (french: Bureau international des poids et mesures, BIPM) is an intergovernmental organisation, through which its 59 member-states act together on measurement standards in four areas: chemistry, ...
, under the International System of Units (SI).
The force of gravity on Earth is the resultant (vector sum) of two forces: (a) The gravitational attraction in accordance with Newton's universal law of gravitation, and (b) the centrifugal force, which results from the choice of an earthbound, rotating frame of reference. The force of gravity is weakest at the equator because of the centrifugal force
In Newtonian mechanics, the centrifugal force is an inertial force (also called a "fictitious" or "pseudo" force) that appears to act on all objects when viewed in a rotating frame of reference. It is directed away from an axis which is paralle ...
caused by the Earth's rotation and because points on the equator are furthest from the center of the Earth. The force of gravity varies with latitude and increases from about 9.780 m/s2 at the Equator to about 9.832 m/s2 at the poles. Canada's Hudson Bay has less gravity than any place on Earth.
Origin
The earliest gravity (possibly in the form of quantum gravity,supergravity
In theoretical physics, supergravity (supergravity theory; SUGRA for short) is a modern field theory that combines the principles of supersymmetry and general relativity; this is in contrast to non-gravitational supersymmetric theories such ...
or a gravitational singularity
A gravitational singularity, spacetime singularity or simply singularity is a condition in which gravity is so intense that spacetime itself breaks down catastrophically. As such, a singularity is by definition no longer part of the regular sp ...
), along with ordinary space and time, developed during the Planck epoch
The chronology of the universe describes the history and future of the universe according to Big Bang cosmology.
Research published in 2015 estimates the earliest stages of the universe's existence as taking place 13.8 billion years ago, wit ...
(up to 10−43 seconds after the birth
Birth is the act or process of bearing or bringing forth offspring, also referred to in technical contexts as parturition. In mammals, the process is initiated by hormones which cause the muscular walls of the uterus to contract, expelling the ...
of the Universe), possibly from a primeval state (such as a false vacuum
In quantum field theory, a false vacuum is a hypothetical vacuum that is relatively stable, but not in the most stable state possible. This condition is known as metastable. It may last for a very long time in that state, but could eventually d ...
, quantum vacuum
In quantum field theory, the quantum vacuum state (also called the quantum vacuum or vacuum state) is the quantum state with the lowest possible energy. Generally, it contains no physical particles. The word zero-point field is sometimes used ...
or virtual particle
A virtual particle is a theoretical transient particle that exhibits some of the characteristics of an ordinary particle, while having its existence limited by the uncertainty principle. The concept of virtual particles arises in the perturba ...
), in a currently unknown manner.
Gravitational radiation
 General relativity predicts that energy can be transported out of a system through gravitational radiation. The first indirect evidence for gravitational radiation was through measurements of the
General relativity predicts that energy can be transported out of a system through gravitational radiation. The first indirect evidence for gravitational radiation was through measurements of the Hulse–Taylor binary
The Hulse–Taylor binary is a binary star system composed of a neutron star and a pulsar (known as PSR B1913+16, PSR J1915+1606 or PSR 1913+16) which orbit around their common center of mass. It is the first binary pulsar ever discovere ...
in 1973. This system consists of a pulsar and neutron star in orbit around one another. Its orbital period has decreased since its initial discovery due to a loss of energy, which is consistent for the amount of energy loss due to gravitational radiation. This research was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1993.
The first direct evidence for gravitational radiation was measured on 14 September 2015 by the LIGO detectors. The gravitational waves emitted during the collision of two black holes 1.3 billion light years from Earth were measured. This observation confirms the theoretical predictions of Einstein and others that such waves exist. It also opens the way for practical observation and understanding of the nature of gravity and events in the Universe including the Big Bang. Neutron star and black hole
A black hole is a region of spacetime where gravity is so strong that nothing, including light or other electromagnetic waves, has enough energy to escape it. The theory of general relativity predicts that a sufficiently compact mass can defo ...
formation also create detectable amounts of gravitational radiation. This research was awarded the Nobel Prize in physics in 2017.
Speed of gravity
In December 2012, a research team in China announced that it had produced measurements of the phase lag of Earth tides during full and new moons which seem to prove that the speed of gravity is equal to the speed of light. This means that if the Sun suddenly disappeared, the Earth would keep orbiting the vacant point normally for 8 minutes, which is the time light takes to travel that distance. The team's findings were released in theChinese Science Bulletin
''Science Bulletin'' () is a multidisciplinary scientific journal co-sponsored by the Chinese Academy of Sciences and the National Natural Science Foundation of China. It is published by Elsevier on behalf of Science in China Press and focuses on ...
in February 2013.
In October 2017, the LIGO and Virgo detectors received gravitational wave signals within 2 seconds of gamma ray satellites and optical telescopes seeing signals from the same direction. This confirmed that the speed of gravitational waves was the same as the speed of light.
Anomalies and discrepancies
There are some observations that are not adequately accounted for, which may point to the need for better theories of gravity or perhaps be explained in other ways.Dark matter
Dark matter is a hypothetical form of matter thought to account for approximately 85% of the matter in the universe. Dark matter is called "dark" because it does not appear to interact with the electromagnetic field, which means it does not a ...
, which would interact through gravitation but not electromagnetically, would account for the discrepancy. Various modifications to Newtonian dynamics have also been proposed.
* Flyby anomaly: Various spacecraft have experienced greater acceleration than expected during gravity assist maneuvers.
* Accelerating expansion: The metric expansion of space
The expansion of the universe is the increase in distance between any two given gravitationally unbound parts of the observable universe with time. It is an intrinsic expansion whereby the scale of space itself changes. The universe does not ex ...
seems to be speeding up. Dark energy
In physical cosmology and astronomy, dark energy is an unknown form of energy that affects the universe on the largest scales. The first observational evidence for its existence came from measurements of supernovas, which showed that the univer ...
has been proposed to explain this. A recent alternative explanation is that the geometry of space is not homogeneous (due to clusters of galaxies) and that when the data are reinterpreted to take this into account, the expansion is not speeding up after all, however this conclusion is disputed.
* Anomalous increase of the astronomical unit
The astronomical unit (symbol: au, or or AU) is a unit of length, roughly the distance from Earth to the Sun and approximately equal to or 8.3 light-minutes. The actual distance from Earth to the Sun varies by about 3% as Earth orbits ...
: Recent measurements indicate that planetary orbits are widening faster than if this were solely through the Sun losing mass by radiating energy.
* Extra energetic photons: Photons travelling through galaxy clusters should gain energy and then lose it again on the way out. The accelerating expansion of the Universe should stop the photons returning all the energy, but even taking this into account photons from the cosmic microwave background radiation
In Big Bang cosmology the cosmic microwave background (CMB, CMBR) is electromagnetic radiation that is a remnant from an early stage of the universe, also known as "relic radiation". The CMB is faint cosmic background radiation filling all space ...
gain twice as much energy as expected. This may indicate that gravity falls off faster than inverse-squared at certain distance scales.
* Extra massive hydrogen clouds: The spectral lines of the Lyman-alpha forest
The Lyman-alpha line, typically denoted by Ly-α, is a spectral line of hydrogen (or, more generally, of any one-electron atom) in the Lyman series. It is emitted when the atomic electron transitions from an ''n'' = 2 orbital to the gro ...
suggest that hydrogen clouds are more clumped together at certain scales than expected and, like dark flow, may indicate that gravity falls off slower than inverse-squared at certain distance scales.
Alternative theories
Historical alternative theories
* Aristotelian theory of gravity * Le Sage's theory of gravitation (1784) also called LeSage gravity but originally proposed by Fatio and further elaborated by Georges-Louis Le Sage, based on a fluid-based explanation where a light gas fills the entire Universe. * Ritz's theory of gravitation, ''Ann. Chem. Phys.'' 13, 145, (1908) pp. 267–271, Weber–Gauss electrodynamics applied to gravitation. Classical advancement of perihelia. * Nordström's theory of gravitation (1912, 1913), an early competitor of general relativity. * Kaluza Klein theory (1921) * Whitehead's theory of gravitation (1922), another early competitor of general relativity.Modern alternative theories
* Brans–Dicke theory of gravity (1961) * Induced gravity (1967), a proposal byAndrei Sakharov
Andrei Dmitrievich Sakharov ( rus, Андрей Дмитриевич Сахаров, p=ɐnˈdrʲej ˈdmʲitrʲɪjevʲɪtɕ ˈsaxərəf; 21 May 192114 December 1989) was a Soviet nuclear physicist, dissident, nobel laureate and activist for n ...
according to which general relativity might arise from quantum field theories of matter
* String theory (late 1960s)
* ƒ(R) gravity (1970)
* Horndeski theory (1974)
* Supergravity
In theoretical physics, supergravity (supergravity theory; SUGRA for short) is a modern field theory that combines the principles of supersymmetry and general relativity; this is in contrast to non-gravitational supersymmetric theories such as ...
(1976)
* In the modified Newtonian dynamics (MOND) (1981), Mordehai Milgrom proposes a modification of Newton's second law
Newton's laws of motion are three basic laws of classical mechanics that describe the relationship between the motion of an object and the forces acting on it. These laws can be paraphrased as follows:
# A body remains at rest, or in motion ...
of motion for small accelerations
* The self-creation cosmology theory of gravity (1982) by G.A. Barber in which the Brans–Dicke theory is modified to allow mass creation
* Loop quantum gravity
Loop quantum gravity (LQG) is a theory of quantum gravity, which aims to merge quantum mechanics and general relativity, incorporating matter of the Standard Model into the framework established for the pure quantum gravity case. It is an attem ...
(1988) by Carlo Rovelli
Carlo Rovelli (born May 3, 1956) is an Italian theoretical physicist and writer who has worked in Italy, the United States and, since 2000, in France. He is also currently a Distinguished Visiting Research Chair at the Perimeter Institute, and ...
, Lee Smolin, and Abhay Ashtekar
* Nonsymmetric gravitational theory (NGT) (1994) by John Moffat
* Tensor–vector–scalar gravity (TeVeS) (2004), a relativistic modification of MOND by Jacob Bekenstein
* Chameleon theory (2004) by Justin Khoury and Amanda Weltman.
* Pressuron theory (2013) by Olivier Minazzoli and Aurélien Hees.
*Conformal gravity
Conformal gravity refers to gravity theories that are invariant under conformal transformations in the Riemannian geometry sense; more accurately, they are invariant under Weyl transformations g_\rightarrow\Omega^2(x)g_ where g_ is the metric te ...
* Gravity as an entropic force, gravity arising as an emergent phenomenon from the thermodynamic concept of entropy.
*In the superfluid vacuum theory
Superfluid vacuum theory (SVT), sometimes known as the BEC vacuum theory, is an approach in theoretical physics and quantum mechanics where the fundamental physical vacuum (non-removable background) is viewed as superfluid or as a Bose–Einstei ...
the gravity and curved spacetime arise as a collective excitation mode of non-relativistic background superfluid
Superfluidity is the characteristic property of a fluid with zero viscosity which therefore flows without any loss of kinetic energy. When stirred, a superfluid forms vortices that continue to rotate indefinitely. Superfluidity occurs in two i ...
.
* Massive gravity, a theory where gravitons and gravitational waves have a non-zero mass
See also
*Anti-gravity
Anti-gravity (also known as non-gravitational field) is a hypothetical phenomenon of creating a place or object that is free from the force of gravity. It does not refer to the lack of weight under gravity experienced in free fall or orbit, or to ...
, the idea of neutralizing or repelling gravity
* Artificial gravity
Artificial gravity is the creation of an inertial force that mimics the effects of a gravitational force, usually by rotation.
Artificial gravity, or rotational gravity, is thus the appearance of a centrifugal force in a rotating frame of ref ...
* Equations for a falling body
*Escape velocity
In celestial mechanics, escape velocity or escape speed is the minimum speed needed for a free, non- propelled object to escape from the gravitational influence of a primary body, thus reaching an infinite distance from it. It is typically s ...
**Atmospheric escape
Atmospheric escape is the loss of planetary atmospheric gases to outer space. A number of different mechanisms can be responsible for atmospheric escape; these processes can be divided into thermal escape, non-thermal (or suprathermal) escape, and ...
* Gauss's law for gravity
* Gravitational potential
In classical mechanics, the gravitational potential at a location is equal to the work (energy transferred) per unit mass that would be needed to move an object to that location from a fixed reference location. It is analogous to the electric p ...
* Micro-g environment, also called microgravity
* Newton's laws of motion
* Standard gravitational parameter
* Weightlessness
Footnotes
References
* * *Further reading
* *External links
The Feynman Lectures on Physics Vol. I Ch. 7: The Theory of Gravitation
* * {{Authority control Fundamental interactions Acceleration Articles containing video clips Empirical laws