Grating on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A grating is any regularly spaced collection of essentially identical,
File:Vindobona Hoher Markt-71.JPG, Grating - drain cover,
File:Grating at the historic John Street Roundhouse, Toronto.jpg, Close up view of
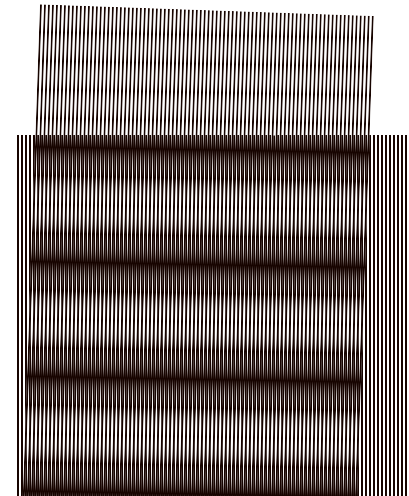
 As optical elements, gratings are images having the characteristic pattern of a grating, that is a pattern comprising several alternating, parallel lines. The lines alternate between high and low
As optical elements, gratings are images having the characteristic pattern of a grating, that is a pattern comprising several alternating, parallel lines. The lines alternate between high and low
parallel
Parallel is a geometric term of location which may refer to:
Computing
* Parallel algorithm
* Parallel computing
* Parallel metaheuristic
* Parallel (software), a UNIX utility for running programs in parallel
* Parallel Sysplex, a cluster o ...
, elongated elements. Gratings usually consist of a single set of elongated elements, but can consist of two sets, in which case the second set is usually perpendicular
In elementary geometry, two geometric objects are perpendicular if they intersect at a right angle (90 degrees or π/2 radians). The condition of perpendicularity may be represented graphically using the '' perpendicular symbol'', ⟂. It c ...
to the first (as illustrated). When the two sets are perpendicular, this is also known as a wikt:grid (as in grid paper) or a mesh
A mesh is a barrier made of connected strands of metal, fiber, or other flexible or ductile materials. A mesh is similar to a web or a net in that it has many attached or woven strands.
Types
* A plastic mesh may be extruded, oriented, exp ...
.
As filters
A grating covering a drain (as illustrated) can be a collection of iron bars (the identical, elongated elements) held together (to ensure the bars are parallel and regularly spaced) by a lighter iron frame. Gratings over drains andair vent
Ventilation is the intentional introduction of outdoor air into a space. Ventilation is mainly used to control indoor air quality by diluting and displacing indoor pollutants; it can also be used to control indoor temperature, humidity, and air m ...
s are used as filters, to block movement of large solids (e.g. people) and to allow movement of liquids. A register
Register or registration may refer to:
Arts entertainment, and media Music
* Register (music), the relative "height" or range of a note, melody, part, instrument, etc.
* ''Register'', a 2017 album by Travis Miller
* Registration (organ), th ...
is a type of grating used in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning
Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) is the use of various technologies to control the temperature, humidity, and purity of the air in an enclosed space. Its goal is to provide thermal comfort and acceptable indoor air quality ...
, which transmits air, while stopping solid objects.
ancient Roman architecture
Ancient Roman architecture adopted the external language of classical Greek architecture for the purposes of the ancient Romans, but was different from Greek buildings, becoming a new architectural style. The two styles are often considered one ...
at Vindobona
Vindobona (from Gaulish ''windo-'' "white" and ''bona'' "base/bottom") was a Roman military camp on the site of the modern city of Vienna in Austria. The settlement area took on a new name in the 13th century, being changed to Berghof, or now si ...
, Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
.
File:Montreal Sewer Cover.jpg, Sewer grating (manhole cover
A manhole cover or maintenance hole cover is a removable plate forming the lid over the opening of a manhole, an opening large enough for a person to pass through that is used as an access point for an underground vault or pipe. It is designed t ...
) that can be driven on despite letting water pass through
File:Tree grating, Washington, D. C. (3678939694).jpg, Tree grating that can be walked on despite letting water pass through
As decking
Grating can also come inpanel
Panel may refer to:
Arts and media Visual arts
*Panel (comics), a single image in a comic book, comic strip or cartoon; also, a comic strip containing one such image
*Panel painting, in art, either one element of a multi-element piece of art, ...
s that are often used for decks on bridge
A bridge is a structure built to span a physical obstacle (such as a body of water, valley, road, or rail) without blocking the way underneath. It is constructed for the purpose of providing passage over the obstacle, which is usually someth ...
s, footbridge
A footbridge (also a pedestrian bridge, pedestrian overpass, or pedestrian overcrossing) is a bridge designed solely for pedestrians.''Oxford English Dictionary'' While the primary meaning for a bridge is a structure which links "two points at ...
s and catwalks. Grating can be made of materials such as steel
Steel is an alloy made up of iron with added carbon to improve its strength and fracture resistance compared to other forms of iron. Many other elements may be present or added. Stainless steels that are corrosion- and oxidation-resistan ...
, aluminum
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. It ha ...
, fiberglass
Fiberglass ( American English) or fibreglass (Commonwealth English) is a common type of fiber-reinforced plastic using glass fiber. The fibers may be randomly arranged, flattened into a sheet called a chopped strand mat, or woven into glass cl ...
. Fiberglass grating is also known as FRP grating Fiberglass reinforced plastic grating (also known as FRP grating, glass reinforced plastic grating or fiberglass grating) is a composite material manufactured by combining a matrix of resin and fiberglass. Fiberglass grating does not corrode like s ...
. They are used to optimize bending stiffness while minimizing weight.
anti-slip grating
Anti-slip steel grating (also known as slip-resistant grating) is a type of bar grating designed to prevent slippage. Steel
Steel is an alloy made up of iron with added carbon to improve its strength and fracture resistance compared to ...
File:Puente rejilla.jpg, Bridge showing deck grating driving surface
File:Stahlbau mit Gitterrosten.JPG, Grating at a power plant
As optical elements

reflectance
The reflectance of the surface of a material is its effectiveness in reflecting radiant energy. It is the fraction of incident electromagnetic power that is reflected at the boundary. Reflectance is a component of the response of the electronic ...
(black-white gratings) or high and low transmittance
Transmittance of the surface of a material is its effectiveness in transmitting radiant energy. It is the fraction of incident electromagnetic power that is transmitted through a sample, in contrast to the transmission coefficient, which is t ...
(transparent-opaque gratings). The grating profile is the function of the reflectance or transmittance perpendicular to the lines. This function is generally a square wave
A square wave is a non-sinusoidal periodic waveform in which the amplitude alternates at a steady frequency between fixed minimum and maximum values, with the same duration at minimum and maximum. In an ideal square wave, the transitions b ...
, in that every transition between lines is abrupt.
A grating can be defined by six parameters:
* ''Spatial frequency
In mathematics, physics, and engineering, spatial frequency is a characteristic of any structure that is periodic across position in space. The spatial frequency is a measure of how often sinusoidal components (as determined by the Fourier tra ...
'' is the number of cycles occupying a particular distance (e.g. 10 line pairs per millimeter). The period of the grating is the inverse of the spatial frequency, measured in distance (e.g. 0.1 mm).
* ''Duty Cycle
A duty cycle or power cycle is the fraction of one period in which a signal or system is active. Duty cycle is commonly expressed as a percentage or a ratio. A period is the time it takes for a signal to complete an on-and-off cycle. As a form ...
'' is the relative thickness of high and low lines. The duty cycle is the ratio of the width of the low line (black or opaque) to one whole grating period.
* '' Profile'' is the shape of the repeating pattern, which is typically a square wave but can also be any periodic pattern (sine wave
A sine wave, sinusoidal wave, or just sinusoid is a mathematical curve defined in terms of the '' sine'' trigonometric function, of which it is the graph. It is a type of continuous wave and also a smooth periodic function. It occurs often in ...
, triangle wave
A triangular wave or triangle wave is a non-sinusoidal waveform named for its triangular shape. It is a periodic, piecewise linear, continuous real function.
Like a square wave, the triangle wave contains only odd harmonics. However, ...
, sawtooth wave
The sawtooth wave (or saw wave) is a kind of non-sinusoidal waveform. It is so named based on its resemblance to the teeth of a plain-toothed saw with a zero rake angle. A single sawtooth, or an intermittently triggered sawtooth, is called ...
, etc.).
* '' Contrast'' is a measure of the difference in luminance between the high lines of the grating and the low lines. It is usually expressed as Michelson contrast: the difference between maximum and minimum luminance divided their sum.
* '' Orientation'' is the angle
In Euclidean geometry, an angle is the figure formed by two rays, called the '' sides'' of the angle, sharing a common endpoint, called the ''vertex'' of the angle.
Angles formed by two rays lie in the plane that contains the rays. Angles ...
the grating makes with some reference orientation (such as the y-axis in a picture or of another grating). It is usually measured in degree or in radians.
* '' Phase'' is the position of the grating profile relative to some reference position. It is usually measured in degrees (from 0 to 360 for one complete cycle) or in radian
The radian, denoted by the symbol rad, is the unit of angle in the International System of Units (SI) and is the standard unit of angular measure used in many areas of mathematics. The unit was formerly an SI supplementary unit (before that ...
s (2π for one complete cycle). For example, two identical transparent gratings of 50% duty cycle and the same orientation will appear fully opaque only if the relative phase is π (180 degrees).
Gratings with sine wave profiles are used extensively in optics
Optics is the branch of physics that studies the behaviour and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behaviour of visible, ultrav ...
to determine the transfer function
In engineering, a transfer function (also known as system function or network function) of a system, sub-system, or component is a mathematical function that theoretically models the system's output for each possible input. They are widely used ...
s of lenses. A lens will form an image of a sine wave grating that is still sinusoidal, but with some reduction in its contrast depending on the spatial frequency and possibly some change in phase. The branch of mathematics dealing with this part of optics is Fourier analysis
In mathematics, Fourier analysis () is the study of the way general functions may be represented or approximated by sums of simpler trigonometric functions. Fourier analysis grew from the study of Fourier series, and is named after Joseph ...
while the associated branch of study is Fourier optics. Gratings are also used extensively in research into visual perception
Visual perception is the ability to interpret the surrounding environment through photopic vision (daytime vision), color vision, scotopic vision (night vision), and mesopic vision (twilight vision), using light in the visible spectrum ref ...
. Campbell and Robson promoted using sine-wave gratings by arguing that the human visual performs a Fourier analysis on retinal images.Campbell, F. W., & Robson, J. G. (1968). Application of Fourier analysis to the visibility of gratings. Journal of Physiology, 197, 551-566.
Diffraction gratings
Grating can also refer to adiffraction grating
In optics, a diffraction grating is an optical component with a periodic structure that diffracts light into several beams travelling in different directions (i.e., different diffraction angles). The emerging coloration is a form of structur ...
: a reflecting or transparent optical component on which there are many fine, parallel
Parallel is a geometric term of location which may refer to:
Computing
* Parallel algorithm
* Parallel computing
* Parallel metaheuristic
* Parallel (software), a UNIX utility for running programs in parallel
* Parallel Sysplex, a cluster o ...
, equally spaced grooves. They disperse light, so are one of the main functional components in many kinds of spectrometer
A spectrometer () is a scientific instrument used to separate and measure spectral components of a physical phenomenon. Spectrometer is a broad term often used to describe instruments that measure a continuous variable of a phenomenon where the ...
s, which decompose a light source into its constituent wavelength components.
See also
* Grate (disambiguation) *Grille (architecture)
A grille or grill ( French word from Latin ''craticula'', small grill) is an opening of several slits side-by-side in a wall, metal sheet or another barrier, usually to allow air or water to enter and/or leave and prevent larger objects ( ...
* Manhole cover
A manhole cover or maintenance hole cover is a removable plate forming the lid over the opening of a manhole, an opening large enough for a person to pass through that is used as an access point for an underground vault or pipe. It is designed t ...
* Pedestrian infrastructure
A pedestrian is a person traveling on foot, whether walking or running. In modern times, the term usually refers to someone walking on a road or pavement, but this was not the case historically.
The meaning of pedestrian is displayed with ...
References
* Palmer, Christopher, ''Diffraction Grating Handbook'', 8th edition, MKS Newport (2020)