Gonopod on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Gonopods are specialized
Gonopods are specialized
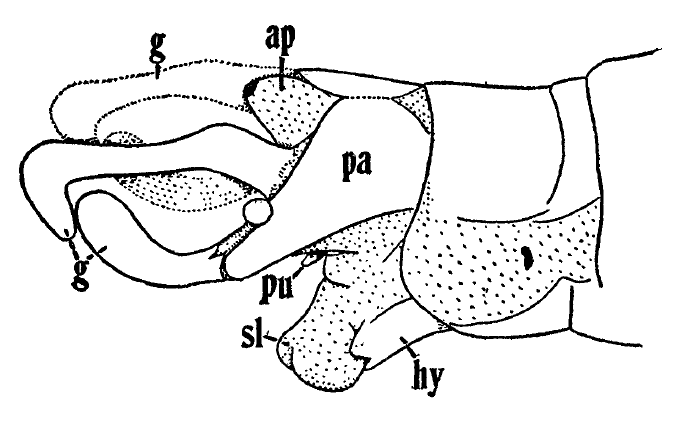 In insects, gonopods are appendages of the genital segment that may be used in insemination, or that comprise the egg-laying apparatus.
In insects, gonopods are appendages of the genital segment that may be used in insemination, or that comprise the egg-laying apparatus.
 In millipedes, gonopods consist of one or two pairs of often highly modified walking legs in mature males, and are primarily found in members of the subgroup
In millipedes, gonopods consist of one or two pairs of often highly modified walking legs in mature males, and are primarily found in members of the subgroup 
 Gonopods are specialized
Gonopods are specialized appendage
An appendage (or outgrowth) is an external body part, or natural prolongation, that protrudes from an organism's body.
In arthropods, an appendage refers to any of the homologous body parts that may extend from a body segment, including ante ...
s of various arthropod
Arthropods (, (gen. ποδός)) are invertebrate animals with an exoskeleton, a segmented body, and paired jointed appendages. Arthropods form the phylum Arthropoda. They are distinguished by their jointed limbs and cuticle made of chiti ...
s used in reproduction or egg-laying. In males, they facilitate the transfer of sperm
Sperm is the male reproductive cell, or gamete, in anisogamous forms of sexual reproduction (forms in which there is a larger, female reproductive cell and a smaller, male one). Animals produce motile sperm with a tail known as a flagellum, ...
from male to female during mating, and thus are a type of intromittent organ
An intromittent organ is any external organ of a male organism that is specialized to deliver sperm during copulation. Intromittent organs are found most often in terrestrial species, as most non-mammalian aquatic species fertilize their eggs e ...
. In crustaceans
Crustaceans (Crustacea, ) form a large, diverse arthropod taxon which includes such animals as decapods, seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean g ...
and millipedes, gonopods are modified walking or swimming legs. Gonopods may be highly decorated with elaborate structures which may play roles in sperm competition, and can be used to differentiate and identify closely related species. Gonopods generally occur in one or more pairs, as opposed to the single (un-paired) reproductive organs such as the aedeagus
An aedeagus (plural aedeagi) is a reproductive organ of male arthropods through which they secrete sperm from the testes during copulation with a female. It can be thought of as the insect equivalent of a mammal's penis, though the comparison i ...
of insects or the penis of harvestmen.
Insects
 In insects, gonopods are appendages of the genital segment that may be used in insemination, or that comprise the egg-laying apparatus.
In insects, gonopods are appendages of the genital segment that may be used in insemination, or that comprise the egg-laying apparatus.
Crustaceans
In male decapodcrustacean
Crustaceans (Crustacea, ) form a large, diverse arthropod taxon which includes such animals as decapoda, decapods, ostracoda, seed shrimp, branchiopoda, branchiopods, argulidae, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopoda, isopods, barnacles, copepods, ...
s, gonopods are modified swimming appendages (pleopod
The decapod ( crustaceans such as a crab, lobster, shrimp or prawn) is made up of 20 body segments grouped into two main body parts: the cephalothorax and the pleon (abdomen). Each segment may possess one pair of appendages, although in variou ...
s). The anterior two pair of pleopods in males are modified for sperm transferring, with differing degree of morphological diversification.
Millipedes
 In millipedes, gonopods consist of one or two pairs of often highly modified walking legs in mature males, and are primarily found in members of the subgroup
In millipedes, gonopods consist of one or two pairs of often highly modified walking legs in mature males, and are primarily found in members of the subgroup Helminthomorpha
Chilognatha is a subclass of the class Diplopoda, which includes the vast majority of extant millipedes, about 12,000 species.
Taxonomy
The classification of Chilognatha presented below is based on Shear, 2011, and Shear & Edgecombe, 2010 (exti ...
—containing most orders and the vast majority of species—where they are located on the seventh body segment consisting of leg pairs 8 and/or 9. Males of the subgroup Pentazonia
Pentazonia is a taxonomic infraclass of millipedes containing the pill-millipedes (Oniscomorpha) which can roll into a ball and the order Glomeridesmida which cannot. Defining traits (apomorphies) include divided sternites, a labrum with single ...
(which includes the Oniscomorpha
Pill millipedes are any members of two living (and one extinct) orders of millipedes, often grouped together into a single superorder, Oniscomorpha. The name Oniscomorpha refers to the millipedes' resemblance to certain woodlice (Oniscidea), also ...
(pill millipedes) and Glomeridesmida) lack gonopods but possess enlarged appendages known as ''telopods'' at the rear of the body used to firmly hold females during mating. The complex structure of gonopods is a primary method of distinguishing closely related species of millipede, although the terminology used to describe the same structures may vary between authors. The complex morphology of millipede gonopods may be driven by sperm competition or other forms of sexual selection
Sexual selection is a mode of natural selection in which members of one biological sex choose mates of the other sex to mate with (intersexual selection), and compete with members of the same sex for access to members of the opposite sex (in ...
, with some structures serving to scoop out or displace sperm of other males, and others acting to stimulate females into becoming sexually receptive.
Millipede gonopods do not produce sperm directly, but rather gather sperm produced from a gonopore on the base of the third body segment.
Gonopods develop gradually during the growth of an individual. In early developmental stages, all legs are of the walking type, and cannot be used to determine sex. Through successive molts, the walking legs metamorphose into mature gonopods.

See also
* Gonopodium, a modified fin for sperm transfer found in some fish * Claspers, pelvic fins modified for copulation incartilaginous fish
Chondrichthyes (; ) is a class that contains the cartilaginous fishes that have skeletons primarily composed of cartilage. They can be contrasted with the Osteichthyes or ''bony fishes'', which have skeletons primarily composed of bone tissue. ...
* Pedipalps, appendages of arachnids involved in sperm-transfer
References
{{reflist Arthropod anatomy Sex organs