Glucokinase on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Glucokinase () is an
Nevertheless, glucokinase remains the name preferred in the contexts of
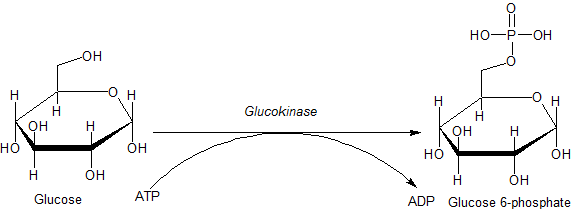 ATP participates in the reaction in a form complexed to
ATP participates in the reaction in a form complexed to
enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. ...
that facilitates phosphorylation
In chemistry, phosphorylation is the attachment of a phosphate group to a molecule or an ion. This process and its inverse, dephosphorylation, are common in biology and could be driven by natural selection. Text was copied from this source, wh ...
of glucose
Glucose is a simple sugar with the molecular formula . Glucose is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. Glucose is mainly made by plants and most algae during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, using ...
to glucose-6-phosphate
Glucose 6-phosphate (G6P, sometimes called the Robison ester) is a glucose sugar phosphorylated at the hydroxy group on carbon 6. This dianion is very common in cells as the majority of glucose entering a cell will become phosphorylated in this wa ...
. Glucokinase occurs in cells
Cell most often refers to:
* Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life
Cell may also refer to:
Locations
* Monastic cell, a small room, hut, or cave in which a religious recluse lives, alternatively the small precursor of a monastery w ...
in the liver
The liver is a major organ only found in vertebrates which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for digestion and growth. In humans, it i ...
and pancreas
The pancreas is an organ of the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdomen behind the stomach and functions as a gland. The pancreas is a mixed or heterocrine gland, i.e. it has both an ...
of humans and most other vertebrate
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxon, taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () (chordates with vertebral column, backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the ...
s. In each of these organs it plays an important role in the regulation of carbohydrate metabolism
Metabolism (, from el, μεταβολή ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cel ...
by acting as a glucose sensor, triggering shifts in metabolism or cell function in response to rising or falling levels of glucose, such as occur after a meal or when fasting
Fasting is the abstention from eating and sometimes drinking. From a purely physiological context, "fasting" may refer to the metabolic status of a person who has not eaten overnight (see "Breakfast"), or to the metabolic state achieved after com ...
. Mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, mitos ...
s of the gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a ba ...
for this enzyme can cause unusual forms of diabetes
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level (hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased ap ...
or hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia, also called low blood sugar, is a fall in blood sugar to levels below normal, typically below 70 mg/dL (3.9 mmol/L). Whipple's triad is used to properly identify hypoglycemic episodes. It is defined as blood glucose belo ...
.
Glucokinase (GK) is a hexokinase
A hexokinase is an enzyme that phosphorylates hexoses (six-carbon sugars), forming hexose phosphate. In most organisms, glucose is the most important substrate for hexokinases, and glucose-6-phosphate is the most important product. Hexoki ...
isozyme In biochemistry, isozymes (also known as isoenzymes or more generally as multiple forms of enzymes) are enzymes that differ in amino acid sequence but catalyze the same chemical reaction. Isozymes usually have different kinetic parameters (e.g. dif ...
, related homologously to at least three other hexokinases. All of the hexokinases can mediate phosphorylation of glucose to glucose-6-phosphate (G6P), which is the first step of both glycogen
Glycogen is a multibranched polysaccharide of glucose that serves as a form of energy storage in animals, fungi, and bacteria. The polysaccharide structure represents the main storage form of glucose in the body.
Glycogen functions as one of ...
synthesis and glycolysis
Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose () into pyruvate (). The free energy released in this process is used to form the high-energy molecules adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH) ...
. However, glucokinase is coded by a separate gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a ba ...
and its distinctive kinetic properties allow it to serve a different set of functions. Glucokinase has a lower affinity for glucose than the other hexokinases do, and its activity is localized to a few cell types, leaving the other three hexokinases as more important preparers of glucose for glycolysis and glycogen synthesis for most tissues and organs. Because of this reduced affinity, the activity of glucokinase, under usual physiological conditions, varies substantially according to the concentration of glucose.
Nomenclature
Alternative names for this enzyme are: human hexokinase IV, hexokinase D, and ATP:D-hexose 6-phosphotransferase, EC 2.7.1.1 (previously 2.7.1.2). The common name, glucokinase, is derived from its relative specificity for glucose under physiologic conditions. Somebiochemist
Biochemists are scientists who are trained in biochemistry. They study chemical processes and chemical transformations in living organisms. Biochemists study DNA, proteins and cell parts. The word "biochemist" is a portmanteau of "biological ch ...
s have argued that the name glucokinase should be abandoned as misleading, as this enzyme can phosphorylate other hexoses in the right conditions, and there are distantly related enzymes in bacteria with more absolute specificity for glucose that better deserve the name and the ECbr>2.7.1.2Nevertheless, glucokinase remains the name preferred in the contexts of
medicine
Medicine is the science and practice of caring for a patient, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, treatment, palliation of their injury or disease, and promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care practice ...
and mammalian physiology
Physiology (; ) is the scientific study of functions and mechanisms in a living system. As a sub-discipline of biology, physiology focuses on how organisms, organ systems, individual organs, cells, and biomolecules carry out the chemica ...
.
Another mammalian glucose kinase, ADP-specific glucokinase
In enzymology, an ADP-specific glucokinase () also known as ADP-dependent glucokinase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
:ADP + D-glucose \rightleftharpoons AMP + D-glucose 6-phosphate
Thus, the two substrates of this enzyme are ...
, was discovered in 2004. The gene is distinct and similar to that of primitive organisms. It is dependent on ADP rather than ATP (suggesting the possibility of more effective function during hypoxia), and the metabolic role and importance remain to be elucidated.
Catalysis
Substrates and products
The principal substrate of physiologic importance of glucokinase isglucose
Glucose is a simple sugar with the molecular formula . Glucose is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. Glucose is mainly made by plants and most algae during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, using ...
, and the most important product
Product may refer to:
Business
* Product (business), an item that serves as a solution to a specific consumer problem.
* Product (project management), a deliverable or set of deliverables that contribute to a business solution
Mathematics
* Produ ...
is glucose-6-phosphate
Glucose 6-phosphate (G6P, sometimes called the Robison ester) is a glucose sugar phosphorylated at the hydroxy group on carbon 6. This dianion is very common in cells as the majority of glucose entering a cell will become phosphorylated in this wa ...
(G6P). The other necessary substrate, from which the phosphate is derived, is adenosine triphosphate
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is an organic compound that provides energy to drive many processes in living cells, such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, condensate dissolution, and chemical synthesis. Found in all known forms of ...
(ATP), which is converted to adenosine diphosphate
Adenosine diphosphate (ADP), also known as adenosine pyrophosphate (APP), is an important organic compound in metabolism and is essential to the flow of energy in living cells. ADP consists of three important structural components: a sugar backbon ...
(ADP) when the phosphate is removed. The reaction catalyzed by glucokinase is:
 ATP participates in the reaction in a form complexed to
ATP participates in the reaction in a form complexed to magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 of the periodic ...
(Mg) as a cofactor. Furthermore, under certain conditions, glucokinase, like other hexokinases, can induce phosphorylation of other hexose
In chemistry, a hexose is a monosaccharide (simple sugar) with six carbon atoms. The chemical formula for all hexoses is C6H12O6, and their molecular weight is 180.156 g/mol.
Hexoses exist in two forms, open-chain or cyclic, that easily conver ...
s (6 carbon sugar
Sugar is the generic name for sweet-tasting, soluble carbohydrates, many of which are used in food. Simple sugars, also called monosaccharides, include glucose, fructose, and galactose. Compound sugars, also called disaccharides or double s ...
s) and similar molecules. Therefore, the general glucokinase reaction is more accurately described as:
::Hexose + → hexose- + +
Among the hexose substrates are mannose
Mannose is a sugar monomer of the aldohexose series of carbohydrates. It is a C-2 epimer of glucose. Mannose is important in human metabolism, especially in the glycosylation of certain proteins. Several congenital disorders of glycosylation ar ...
, fructose
Fructose, or fruit sugar, is a ketonic simple sugar found in many plants, where it is often bonded to glucose to form the disaccharide sucrose. It is one of the three dietary monosaccharides, along with glucose and galactose, that are absorbe ...
, and glucosamine
Glucosamine (C6H13NO5) is an amino sugar and a prominent precursor in the biochemical synthesis of glycosylated proteins and lipids. Glucosamine is part of the structure of two polysaccharides, chitosan and chitin. Glucosamine is one of the most ...
, but the affinity of glucokinase for these requires concentrations not found in cells for significant activity.
Kinetics
Two important kinetic properties distinguish glucokinase from the other hexokinases, allowing it to function in a special role as glucose sensor. # Glucokinase has a lower affinity for glucose than the other hexokinases. Glucokinase changes conformation and/or function in parallel with rising glucose concentrations in the physiologically important range of 4–10mmol/L
Molar concentration (also called molarity, amount concentration or substance concentration) is a measure of the concentration of a chemical species, in particular of a solute in a solution, in terms of amount of substance per unit volume of sol ...
(72–180 mg/ dL). It is half-saturated at a glucose concentration of about 8 mmol/L (144 mg/dL).
# Glucokinase is not inhibited by its product, glucose-6-phosphate. This allows continued signal output (e.g., to trigger insulin
Insulin (, from Latin ''insula'', 'island') is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets encoded in humans by the ''INS'' gene. It is considered to be the main anabolic hormone of the body. It regulates the metabolism ...
release) amid significant amounts of its product
These two features allow it to regulate a "supply-driven" metabolic pathway. That is, the rate of reaction is driven by the supply of glucose, not by the demand for end products.
Another distinctive property of glucokinase is its moderate cooperativity
Cooperativity is a phenomenon displayed by systems involving identical or near-identical elements, which act dependently of each other, relative to a hypothetical standard non-interacting system in which the individual elements are acting indepen ...
with glucose, with a Hill coefficient
In biochemistry and pharmacology, the Hill equation refers to two closely related equations that reflect the binding of ligands to macromolecules, as a function of the ligand concentration. A ligand is "a substance that forms a complex with a bio ...
(''n''H) of about 1.7. Glucokinase has only a single binding site for glucose and is the only monomeric regulatory enzyme known to display substrate cooperativity. The nature of the cooperativity has been postulated to involve a "slow transition" between two different enzyme states with different rates of activity. If the dominant state depends upon glucose concentration, it would produce an apparent cooperativity similar to that observed.
Because of this cooperativity, the kinetic interaction of glucokinase with glucose does not follow classical Michaelis-Menten kinetics. Rather than a ''K''m for glucose, it is more accurate to describe a half-saturation level ''S''0.5, which is the concentration at which the enzyme is 50% saturated and active.
The ''S''0.5 and nH extrapolate to an ''"inflection point"'' of the curve describing enzyme activity as a function of glucose concentration at about 4 mmol/L. In other words, at a glucose concentration of about 72 mg/dL, which is near the low end of the normal range, glucokinase activity is most sensitive to small changes in glucose concentration.
The kinetic relationship with the other substrate, MgATP, can be described by classical Michaelis-Menten kinetics, with an affinity at about 0.3–0.4 mmol/L, well below a typical intracellular concentration of 2.5 mmol/L. The fact that there is nearly always an excess of ATP available implies that ATP concentration rarely influences glucokinase activity.
The maximum specific activity (''k''cat, also known as the turnover rate) of glucokinase when saturated with both substrates is 62/s.
The pH optimum of human glucokinase was identified only recently and is surprisingly high, at pH 8.5–8.7.
A ''"minimal mathematical model"'' has been devised based on the above kinetic information to predict the beta cell glucose phosphorylation rate (BGPR) of normal ("wild type") glucokinase and the known mutations. The BGPR for wild type glucokinase is about 28% at a glucose concentration of 5 mmol/L, indicating that the enzyme is running at 28% of capacity at the usual threshold glucose for triggering insulin release.
Mechanism
Thesulfhydryl
In organic chemistry, a thiol (; ), or thiol derivative, is any organosulfur compound of the form , where R represents an alkyl or other organic substituent. The functional group itself is referred to as either a thiol group or a sulfhydryl grou ...
groups of several cysteines surround the glucose binding site. All except cys 230 are essential for the catalytic process, forming multiple disulfide bridge
In biochemistry, a disulfide (or disulphide in British English) refers to a functional group with the structure . The linkage is also called an SS-bond or sometimes a disulfide bridge and is usually derived by the coupling of two thiol groups. In ...
s during interaction with the substrates and regulators. At least in the beta cells, the ratio of active to inactive glucokinase molecules is at least partly determined by the balance of oxidation
Redox (reduction–oxidation, , ) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of substrate change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is the gain of electrons or a d ...
of sulfhydryl groups or reduction of disulfide bridges.
These sulfhydryl groups are quite sensitive to the oxidation status of the cells, making glucokinase one of the components most vulnerable to oxidative stress, especially in the beta cells.
Interactive pathway map
Structure
Glucokinase is amonomer
In chemistry, a monomer ( ; ''mono-'', "one" + ''-mer'', "part") is a molecule that can react together with other monomer molecules to form a larger polymer chain or three-dimensional network in a process called polymerization.
Classification
M ...
ic protein of 465 amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha am ...
s and a molecular weight
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions which satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and bioche ...
of about 50 kD. There are at least two clefts, one for the active site
In biology and biochemistry, the active site is the region of an enzyme where substrate molecules bind and undergo a chemical reaction. The active site consists of amino acid residues that form temporary bonds with the substrate (binding site) ...
, binding glucose and MgATP, and the other for a putative allosteric
In biochemistry, allosteric regulation (or allosteric control) is the regulation of an enzyme by binding an effector molecule at a site other than the enzyme's active site.
The site to which the effector binds is termed the ''allosteric site ...
activator that has not yet been identified.
This is about half the size of the other mammalian hexokinases, which retain a degree of dimeric structure. Several sequences and the three-dimensional structure of the key active sites. The ATP binding domain, for example, are shared with hexokinases, bacterial glucokinases, and other proteins, and the common structure is termed an ''actin fold''.
Genetics
Human glucokinase is coded for by the ''GCK''gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a ba ...
on chromosome 7
Chromosome 7 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans, who normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 7 spans about 159 million base pairs (the building material of DNA) and represents between 5 and 5.5 percent of the total DN ...
. This single autosomal
An autosome is any chromosome that is not a sex chromosome. The members of an autosome pair in a diploid cell have the same morphology, unlike those in allosomal (sex chromosome) pairs, which may have different structures. The DNA in autosomes ...
gene has 10 exon
An exon is any part of a gene that will form a part of the final mature RNA produced by that gene after introns have been removed by RNA splicing. The term ''exon'' refers to both the DNA sequence within a gene and to the corresponding sequence ...
s.
Genes for glucokinase in other animals are homologous to human ''GCK''.
A distinctive feature of the gene is that it begins with two promoter regions. The first exon
An exon is any part of a gene that will form a part of the final mature RNA produced by that gene after introns have been removed by RNA splicing. The term ''exon'' refers to both the DNA sequence within a gene and to the corresponding sequence ...
from the 5' end contains two tissue-specific promoter regions. Transcription
Transcription refers to the process of converting sounds (voice, music etc.) into letters or musical notes, or producing a copy of something in another medium, including:
Genetics
* Transcription (biology), the copying of DNA into RNA, the fir ...
can begin at either promoter (depending on the tissue) so that the same gene can produce a slightly different molecule in liver and in other tissues. The two isoform
A protein isoform, or "protein variant", is a member of a set of highly similar proteins that originate from a single gene or gene family and are the result of genetic differences. While many perform the same or similar biological roles, some isof ...
s of glucokinase differ only by 13–15 amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha am ...
s at the N-terminal end
The N-terminus (also known as the amino-terminus, NH2-terminus, N-terminal end or amine-terminus) is the start of a protein or polypeptide, referring to the free amine group (-NH2) located at the end of a polypeptide. Within a peptide, the amin ...
of the molecule, which produces only a minimal difference in structure. The two isoforms have the same kinetic and functional characteristics.
The first promoter from the 5' end, referred to as the "upstream" or neuroendocrine promoter, is active in pancreatic islet cells, neural tissue, and enterocytes (small intestine
The small intestine or small bowel is an organ in the gastrointestinal tract where most of the absorption of nutrients from food takes place. It lies between the stomach and large intestine, and receives bile and pancreatic juice through the ...
cells) to produce the "neuroendocrine isoform" of glucokinase. The second promoter, the "downstream" or liver promoter, is active in hepatocyte
A hepatocyte is a cell of the main parenchymal tissue of the liver. Hepatocytes make up 80% of the liver's mass.
These cells are involved in:
* Protein synthesis
* Protein storage
* Transformation of carbohydrates
* Synthesis of cholesterol, ...
s and directs production of the "liver isoform." The two promoters have little or no sequence homology and are separated by a 30 k bp sequence which has not yet been shown to incur any functional differences between isoforms. The two promoters are functionally exclusive and governed by distinct sets of regulatory factors, so that glucokinase expression can be regulated separately in different tissue types. The two promoters correspond to two broad categories of glucokinase function: In liver, glucokinase acts as the gateway for the "bulk processing" of available glucose, while, in the neuroendocrine cells, it acts as a sensor, triggering cell responses that affect body-wide carbohydrate metabolism.
Distribution among organ systems
Glucokinase has been discovered in specific cells in four types of mammalian tissue: liver, pancreas,small intestine
The small intestine or small bowel is an organ in the gastrointestinal tract where most of the absorption of nutrients from food takes place. It lies between the stomach and large intestine, and receives bile and pancreatic juice through the ...
, and brain. All play crucial roles in responding to rising or falling levels of blood glucose
Glycaemia, also known as blood sugar level, blood sugar concentration, or blood glucose level is the measure of glucose concentrated in the blood of humans or other animals. Approximately 4 grams of glucose, a simple sugar, is present in the blo ...
.
*The predominant cells of the liver are the hepatocyte
A hepatocyte is a cell of the main parenchymal tissue of the liver. Hepatocytes make up 80% of the liver's mass.
These cells are involved in:
* Protein synthesis
* Protein storage
* Transformation of carbohydrates
* Synthesis of cholesterol, ...
s, and GK is found exclusively in these cells. During digestion
Digestion is the breakdown of large insoluble food molecules into small water-soluble food molecules so that they can be absorbed into the watery blood plasma. In certain organisms, these smaller substances are absorbed through the small intes ...
of a carbohydrate meal, when blood glucose is plentiful and insulin
Insulin (, from Latin ''insula'', 'island') is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets encoded in humans by the ''INS'' gene. It is considered to be the main anabolic hormone of the body. It regulates the metabolism ...
levels are high, hepatocytes remove glucose from the blood and store it as glycogen
Glycogen is a multibranched polysaccharide of glucose that serves as a form of energy storage in animals, fungi, and bacteria. The polysaccharide structure represents the main storage form of glucose in the body.
Glycogen functions as one of ...
. After completion of digestion and absorption, the liver manufactures glucose from both non-glucose substrates (gluconeogenesis
Gluconeogenesis (GNG) is a metabolic pathway that results in the generation of glucose from certain non- carbohydrate carbon substrates. It is a ubiquitous process, present in plants, animals, fungi, bacteria, and other microorganisms. In vertebra ...
) and glycogen (glycogenolysis
Glycogenolysis is the breakdown of glycogen (n) to glucose-1-phosphate and glycogen (n-1). Glycogen branches are catabolized by the sequential removal of glucose monomers via phosphorolysis, by the enzyme glycogen phosphorylase.
Mechanism
The ...
), and exports it into the blood, to maintain adequate blood glucose levels during fasting. Because GK activity rises rapidly as the glucose concentration rises, it serves as a central metabolic switch to shift hepatic carbohydrate metabolism between fed and fasting states. Phosphorylation of glucose to glucose-6-phosphate by GK facilitates storage of glucose as glycogen and disposal by glycolysis. The separate liver promoter allows glucokinase to be regulated differently in hepatocytes than in the neuroendocrine cells.
*Neuroendocrine cells of the pancreas, gut, and brain share some common aspects of glucokinase production, regulation, and function. These tissues are collectively referred to as "neuroendocrine" cells in this context.
**Beta cell
Beta cells (β-cells) are a type of cell found in pancreatic islets that synthesize and secrete insulin and amylin. Beta cells make up 50–70% of the cells in human islets. In patients with Type 1 diabetes, beta-cell mass and function are dimini ...
s and alpha cells of the pancreatic islet
An islet is a very small, often unnamed island. Most definitions are not precise, but some suggest that an islet has little or no vegetation and cannot support human habitation. It may be made of rock, sand and/or hard coral; may be permanen ...
s
***Beta cells release insulin
Insulin (, from Latin ''insula'', 'island') is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets encoded in humans by the ''INS'' gene. It is considered to be the main anabolic hormone of the body. It regulates the metabolism ...
in response to rising levels of glucose. Insulin enables many types of cells to import and use glucose, and signals the liver to synthesize glycogen. Alpha cells produce less glucagon
Glucagon is a peptide hormone, produced by alpha cells of the pancreas. It raises concentration of glucose and fatty acids in the bloodstream, and is considered to be the main catabolic hormone of the body. It is also used as a medication to tre ...
in response to rising glucose levels, and more glucagon if blood glucose is low. Glucagon serves as a signal to the liver to break down glycogen and release glucose into the blood. Glucokinase in beta cells serves as a glucose sensor, amplifying insulin secretion as blood glucose rises.
***In the pancreatic beta-cell, glucokinase is a key regulator enzyme. Glucokinase is very important in the regulation of insulin secretion and has been known as the pancreatic beta-cell sensor. Mutations in the gene encoding glucokinase can cause both hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia because of its central role in the regulation of insulin release.
**Glucose-sensitive neuron
A neuron, neurone, or nerve cell is an electrically excitable cell that communicates with other cells via specialized connections called synapses. The neuron is the main component of nervous tissue in all animals except sponges and placozoa. ...
s of the hypothalamus
The hypothalamus () is a part of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland. The hypothalamus ...
***In response to rising or falling levels of glucose, cells in the hypothalamus polarize or depolarize. Among the neuroendocrine reactions of the central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all par ...
to hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia, also called low blood sugar, is a fall in blood sugar to levels below normal, typically below 70 mg/dL (3.9 mmol/L). Whipple's triad is used to properly identify hypoglycemic episodes. It is defined as blood glucose belo ...
is activation of the adrenergic
Adrenergic means "working on adrenaline (epinephrine) or noradrenaline (norepinephrine)" (or on their receptors). When not further qualified, it is usually used in the sense of enhancing or mimicking the effects of epinephrine and norepinephrine in ...
responses of the autonomic nervous system
The autonomic nervous system (ANS), formerly referred to as the vegetative nervous system, is a division of the peripheral nervous system that supplies internal organs, smooth muscle and glands. The autonomic nervous system is a control system t ...
. Glucokinase likely serves as a glucose signal here as well. Glucokinase has also been found in cells of the anterior pituitary
In vertebrate anatomy, the pituitary gland, or hypophysis, is an endocrine gland, about the size of a chickpea and weighing, on average, in humans. It is a protrusion off the bottom of the hypothalamus at the base of the brain. The hypo ...
.
**Enterocyte
Enterocytes, or intestinal absorptive cells, are simple columnar epithelial cells which line the inner surface of the small and large intestines. A glycocalyx surface coat contains digestive enzymes. Microvilli on the apical surface increase its ...
s of the small intestine
***This is the least-understood of the glucokinase sensor systems. It seems likely that responses to incoming glucose during digestion play a role in the incretin
Incretins are a group of metabolic hormones that stimulate a decrease in blood glucose levels. Incretins are released after eating and augment the secretion of insulin released from pancreatic beta cells of the islets of Langerhans by a blood-gl ...
amplification of insulin secretion during a meal, or in the generation of satiety signals from gut to brain.
Distribution among species
Liver glucokinase occurs widely but not universally throughout vertebrate species. The gene structure and amino acid sequence are highly conserved among most mammals (e.g., rat and human glucokinase is more than 80% homologous). However, there are some unusual exceptions: For example, it has not been discovered incat
The cat (''Felis catus'') is a domestic species of small carnivorous mammal. It is the only domesticated species in the family Felidae and is commonly referred to as the domestic cat or house cat to distinguish it from the wild members of ...
s and bat
Bats are mammals of the order Chiroptera.''cheir'', "hand" and πτερόν''pteron'', "wing". With their forelimbs adapted as wings, they are the only mammals capable of true and sustained flight. Bats are more agile in flight than most bi ...
s, though some reptile
Reptiles, as most commonly defined are the animals in the class Reptilia ( ), a paraphyletic grouping comprising all sauropsids except birds. Living reptiles comprise turtles, crocodilians, squamates ( lizards and snakes) and rhynchoce ...
s, birds, amphibia
Amphibians are four-limbed and ectothermic vertebrates of the class Amphibia. All living amphibians belong to the group Lissamphibia. They inhabit a wide variety of habitats, with most species living within terrestrial, fossorial, arbore ...
ns, and fish
Fish are aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish as well as various extinct related groups. Approximately 95% of li ...
have it. Whether glucokinase occurs similarly in the pancreas and other organs has not yet been determined. It has been postulated that the presence of glucokinase in liver reflects the ease with which carbohydrates can be included in the animals' diet
Diet may refer to:
Food
* Diet (nutrition), the sum of the food consumed by an organism or group
* Dieting, the deliberate selection of food to control body weight or nutrient intake
** Diet food, foods that aid in creating a diet for weight loss ...
s.
Function and regulation
Most of the glucokinase in a mammal is found in the liver, and glucokinase provides approximately 95% of the hexokinase activity in hepatocytes. Phosphorylation of glucose toglucose-6-phosphate
Glucose 6-phosphate (G6P, sometimes called the Robison ester) is a glucose sugar phosphorylated at the hydroxy group on carbon 6. This dianion is very common in cells as the majority of glucose entering a cell will become phosphorylated in this wa ...
(G6P) by glucokinase is the first step of both glycogen
Glycogen is a multibranched polysaccharide of glucose that serves as a form of energy storage in animals, fungi, and bacteria. The polysaccharide structure represents the main storage form of glucose in the body.
Glycogen functions as one of ...
synthesis and glycolysis
Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose () into pyruvate (). The free energy released in this process is used to form the high-energy molecules adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH) ...
in the liver.
When ample glucose is available, glycogen synthesis proceeds at the periphery of the hepatocytes until the cells are replete with glycogen. Excess glucose is then increasingly converted into triglyceride
A triglyceride (TG, triacylglycerol, TAG, or triacylglyceride) is an ester derived from glycerol and three fatty acids (from ''tri-'' and ''glyceride'').
Triglycerides are the main constituents of body fat in humans and other vertebrates, as w ...
s for export and storage in adipose
Adipose tissue, body fat, or simply fat is a loose connective tissue composed mostly of adipocytes. In addition to adipocytes, adipose tissue contains the stromal vascular fraction (SVF) of cells including preadipocytes, fibroblasts, vascular e ...
tissue. Glucokinase activity in the cytoplasm rises and falls with available glucose.
G6P, the product of glucokinase, is the principal substrate of glycogen synthesis, and glucokinase has a close functional and regulatory association with glycogen synthesis. When maximally active, GK and glycogen synthase
Glycogen synthase (UDP-glucose-glycogen glucosyltransferase) is a key enzyme in glycogenesis, the conversion of glucose into glycogen. It is a glycosyltransferase () that catalyses the reaction of UDP-glucose and (1,4--D-glucosyl)n to yield UDP ...
appears to be located in the same peripheral areas of hepatocyte cytoplasm in which glycogen synthesis occurs. The supply of G6P affects the rate of glycogen synthesis not only as the primary substrate, but by direct stimulation of glycogen synthase and inhibition of glycogen phosphorylase
Glycogen phosphorylase is one of the phosphorylase enzymes (). Glycogen phosphorylase catalyzes the rate-limiting step in glycogenolysis in animals by releasing glucose-1-phosphate from the terminal alpha-1,4-glycosidic bond. Glycogen phosphoryl ...
.
Glucokinase activity can be rapidly amplified or damped in response to changes in the glucose supply, typically resulting from eating and fasting. Regulation occurs at several levels and speeds, and is influenced by many factors that affect mainly two general mechanisms:
#Glucokinase activity can be amplified or reduced in minutes by actions of the glucokinase regulatory protein (GKRP). The actions of this protein are influenced by small molecules such as glucose and fructose.
#The amount of glucokinase can be increased by synthesis of new protein. Insulin is the principal signal for increased transcription, operating mainly by way of a transcription factor called sterol regulatory element binding protein
Sterol regulatory element-binding proteins (SREBPs) are transcription factors that bind to the sterol regulatory element DNA sequence TCACNCCAC. Mammalian SREBPs are encoded by the genes ''SREBF1'' and ''SREBF2''. SREBPs belong to the basic- ...
-1c (SREBP1c) in the liver. This occurs within an hour after a rise in insulin levels, as after a carbohydrate meal.
Transcriptional
Insulin acting via thesterol regulatory element binding protein
Sterol regulatory element-binding proteins (SREBPs) are transcription factors that bind to the sterol regulatory element DNA sequence TCACNCCAC. Mammalian SREBPs are encoded by the genes ''SREBF1'' and ''SREBF2''. SREBPs belong to the basic- ...
-1c (SREBP1c) is thought to be the most important direct activator of glucokinase gene transcription in hepatocytes. SREBP1c is a basic helix-loop-helix zipper (bHLHZ) transactivator. This class of transactivators bind to the "E box" sequence of genes for a number of regulatory enzymes. The liver promoter in the first exon of the glucokinase gene includes such an E box, which appears to be the principal insulin-response element of the gene in hepatocytes. It was previously thought that SREBP1c must be present for transcription of glucokinase in hepatocytes however, it was recently shown that glucokinase transcription was carried out normally in SREBP1c knock out mice. SREBP1c increases in response to a high-carbohydrate diet, presumed as a direct effect of frequent insulin elevation. Increased transcription can be detected in less than an hour after hepatocytes are exposed to rising insulin levels.
Fructose-2,6-bisphosphate () also stimulates GK transcription, it seems by way of Akt2 rather than SREBP1c. It is not known whether this effect is one of the downstream effects of activation of insulin receptors or independent of insulin action. Levels of play other amplifying roles in glycolysis in hepatocytes.
Other transacting factors suspected of playing a role in liver cell transcription regulation include:
# Hepatic nuclear factor-4-alpha ( HNF4α) is an orphan nuclear receptor important in the transcription of many genes for enzymes of carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. It activates ''GCK'' transcription.
# Upstream stimulatory factor 1 (USF1
Upstream stimulatory factor 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''USF1'' gene.
Function
This gene encodes a member of the basic helix-loop-helix leucine zipper family and can function as a cellular transcription factor. The enco ...
) is another basic helix-loop-helix zipper (bHLHZ) transactivator.
# Hepatic nuclear factor 6 ( HNF6) is a homeodomain transcriptional regulator of the "one-cut class." HNF6 is also involved in regulation of transcription of gluconeogenic enzymes such as glucose-6-phosphatase
The enzyme glucose 6-phosphatase (EC 3.1.3.9, G6Pase; systematic name D-glucose-6-phosphate phosphohydrolase) catalyzes the hydrolysis of glucose 6-phosphate, resulting in the creation of a phosphate group and free glucose:
: D-glucose 6-phos ...
and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase
Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (, PEPCK) is an enzyme in the lyase family used in the metabolic pathway of gluconeogenesis. It converts oxaloacetate into phosphoenolpyruvate and carbon dioxide.
It is found in two forms, cytosolic and mitoch ...
.
Hormonal and dietary
Insulin
Insulin (, from Latin ''insula'', 'island') is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets encoded in humans by the ''INS'' gene. It is considered to be the main anabolic hormone of the body. It regulates the metabolism ...
is by far the most important of the hormones that have direct or indirect effects on glucokinase expression and activity in the liver. Insulin appears to affect both glucokinase transcription and activity through multiple direct and indirect pathways. While rising portal vein
The portal vein or hepatic portal vein (HPV) is a blood vessel that carries blood from the gastrointestinal tract, gallbladder, pancreas and spleen to the liver. This blood contains nutrients and toxins extracted from digested contents. Approx ...
glucose levels increase glucokinase activity, the concomitant rise of insulin amplifies this effect by induction of glucokinase synthesis. Glucokinase transcription begins to rise within an hour of rising insulin levels. Glucokinase transcription becomes nearly undetectable in prolonged starvation, severe carbohydrate deprivation, or untreated insulin-deficient diabetes.
The mechanisms by which insulin induces glucokinase may involve both of the major intracellular pathways of insulin action, the extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK 1/2) cascade, and the phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3-K) cascade. The latter may operate via the FOXO1 transactivator.
However, as would be expected given its antagonistic effect on glycogen synthesis, glucagon
Glucagon is a peptide hormone, produced by alpha cells of the pancreas. It raises concentration of glucose and fatty acids in the bloodstream, and is considered to be the main catabolic hormone of the body. It is also used as a medication to tre ...
and its intracellular second messenger cAMP suppresses glucokinase transcription and activity, even in the presence of insulin.
Other hormones such as triiodothyronine
Triiodothyronine, also known as T3, is a thyroid hormone. It affects almost every physiological process in the body, including growth and development, metabolism, body temperature, and heart rate.
Production of T3 and its prohormone thyroxine ...
() and glucocorticoid
Glucocorticoids (or, less commonly, glucocorticosteroids) are a class of corticosteroids, which are a class of steroid hormones. Glucocorticoids are corticosteroids that bind to the glucocorticoid receptor that is present in almost every vertebr ...
s provide permissive or stimulatory effects on glucokinase in certain circumstances. Biotin
Biotin (or vitamin B7) is one of the B vitamins. It is involved in a wide range of metabolic processes, both in humans and in other organisms, primarily related to the utilization of fats, carbohydrates, and amino acids. The name ''biotin'', bor ...
and retinoic acid
Retinoic acid (used simplified here for all-''trans''-retinoic acid) is a metabolite of vitamin A1 (all-''trans''-retinol) that mediates the functions of vitamin A1 required for growth and development. All-''trans''-retinoic acid is required in ...
increase GCK mRNA transcription as well as GK activity. Fatty acid
In chemistry, particularly in biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with an aliphatic chain, which is either saturated or unsaturated. Most naturally occurring fatty acids have an unbranched chain of an even number of carbon atoms, fr ...
s in significant amounts amplify GK activity in the liver, while long chain acyl CoA inhibits it.
Hepatic
Glucokinase can be rapidly activated and inactivated in hepatocytes by a novel regulatory protein ( glucokinase regulatory protein), which operates to maintain an inactive reserve of GK, which can be made quickly available in response to rising levels of portal vein glucose. GKRP moves betweennucleus
Nucleus ( : nuclei) is a Latin word for the seed inside a fruit. It most often refers to:
*Atomic nucleus, the very dense central region of an atom
*Cell nucleus, a central organelle of a eukaryotic cell, containing most of the cell's DNA
Nucle ...
and cytoplasm
In cell biology, the cytoplasm is all of the material within a eukaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, except for the cell nucleus. The material inside the nucleus and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. Th ...
of the hepatocytes and may be tethered to the microfilament cytoskeleton. It forms reversible 1:1 complexes with GK, and can move it from the cytoplasm into the nucleus. It acts as a competitive inhibitor with glucose, such that the enzyme activity is reduced to near-zero while bound. GK:GKRP complexes are sequestered in the nucleus while glucose and fructose levels are low. Nuclear sequestration may serve to protect GK from degradation by cytoplasmic protease
A protease (also called a peptidase, proteinase, or proteolytic enzyme) is an enzyme that catalyzes (increases reaction rate or "speeds up") proteolysis, breaking down proteins into smaller polypeptides or single amino acids, and spurring the form ...
s. GK can be rapidly released from GKRP in response to rising levels of glucose. Unlike GK in beta cells, GK in hepatocytes is not associated with mitochondria.
Fructose
Fructose, or fruit sugar, is a ketonic simple sugar found in many plants, where it is often bonded to glucose to form the disaccharide sucrose. It is one of the three dietary monosaccharides, along with glucose and galactose, that are absorbe ...
in tiny (micromolar) amounts (after phosphorylation by ketohexokinase to fructose-1-phosphate (F1P)) accelerates release of GK from GKRP. This sensitivity to the presence of small amounts of fructose allows GKRP, GK, and ketohexokinase to act as a "fructose sensing system," which signals that a mixed carbohydrate meal is being digested, and accelerates the utilization of glucose. However, fructose 6-phosphate
Fructose 6-phosphate (sometimes called the Neuberg ester) is a derivative of fructose, which has been phosphorylated at the 6-hydroxy group. It is one of several possible fructosephosphates. The β-D-form of this compound is very common in cells. ...
(F6P) potentiates binding of GK by GKRP. F6P decreases phosphorylation of glucose by GK when glycogenolysis
Glycogenolysis is the breakdown of glycogen (n) to glucose-1-phosphate and glycogen (n-1). Glycogen branches are catabolized by the sequential removal of glucose monomers via phosphorolysis, by the enzyme glycogen phosphorylase.
Mechanism
The ...
or gluconeogenesis
Gluconeogenesis (GNG) is a metabolic pathway that results in the generation of glucose from certain non- carbohydrate carbon substrates. It is a ubiquitous process, present in plants, animals, fungi, bacteria, and other microorganisms. In vertebra ...
are underway. F1P and F6P both bind to the same site on GKRP. It is postulated that they produce 2 different conformations of GKRP, one able to bind GK and the other not.
Pancreatic
Although most of the glucokinase in the body is in the liver, smaller amounts in the beta and alpha cells of the pancreas, certain hypothalamic neurons, and specific cells (enterocytes) of the gut play an increasingly appreciated role in regulation of carbohydrate metabolism. In the context of glucokinase function, these cell types are collectively referred to as neuroendocrine tissues, and they share some aspects of glucokinase regulation and function, especially the common neuroendocrine promoter. Of the neuroendocrine cells, the beta cells of the pancreatic islets are the most-studied and best-understood. It is likely that many of the regulatory relationships discovered in the beta cells will also exist in the other neuroendocrine tissues with glucokinase.A signal for insulin
In isletbeta cell
Beta cells (β-cells) are a type of cell found in pancreatic islets that synthesize and secrete insulin and amylin. Beta cells make up 50–70% of the cells in human islets. In patients with Type 1 diabetes, beta-cell mass and function are dimini ...
s, glucokinase activity serves as a principal control for the secretion of insulin
Insulin (, from Latin ''insula'', 'island') is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets encoded in humans by the ''INS'' gene. It is considered to be the main anabolic hormone of the body. It regulates the metabolism ...
in response to rising levels of blood glucose. As G6P is consumed, increasing amounts of ATP initiate a series of processes that result in release of insulin. One of the immediate consequences of increased cellular respiration is a rise in the NADH
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) is a coenzyme central to metabolism. Found in all living cells, NAD is called a dinucleotide because it consists of two nucleotides joined through their phosphate groups. One nucleotide contains an aden ...
and NADPH
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, abbreviated NADP or, in older notation, TPN (triphosphopyridine nucleotide), is a cofactor used in anabolic reactions, such as the Calvin cycle and lipid and nucleic acid syntheses, which require NAD ...
concentrations (collectively referred to as NAD(P)H). This shift in the redox status of the beta cells results in rising intracellular calcium
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar ...
levels, closing of the KATP channels, depolarization of the cell membrane, merging of the insulin secretory granules with the membrane, and release of insulin into the blood.
It is as a signal for insulin release that glucokinase exerts the largest effect on blood sugar levels and overall direction of carbohydrate metabolism. Glucose, in turn, influences both the immediate activity and the amount of glucokinase produced in the beta cells.
Regulation in beta cells
Glucose immediately amplifies glucokinase activity by the cooperativity effect. A second important rapid regulator of glucokinase activity in beta cells occurs by direct protein-protein interaction between glucokinase and the "bifunctional enzyme" (phosphofructokinase-2/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase), which also plays a role in the regulation of glycolysis. This physical association stabilizes glucokinase in a catalytically favorable conformation (somewhat opposite the effect of GKRP binding) that enhances its activity. In as little as 15 minutes, glucose can stimulate ''GCK'' transcription and glucokinase synthesis by way of insulin. Insulin is produced by the beta cells, but some of it acts on beta cell B-typeinsulin receptor
The insulin receptor (IR) is a transmembrane receptor that is activated by insulin, IGF-I, IGF-II and belongs to the large class of receptor tyrosine kinase. Metabolically, the insulin receptor plays a key role in the regulation of glucose ho ...
s, providing an autocrine Autocrine signaling is a form of cell signaling in which a cell secretes a hormone or chemical messenger (called the autocrine agent) that binds to autocrine receptors on that same cell, leading to changes in the cell. This can be contrasted with pa ...
positive-feedback amplification of glucokinase activity. Further amplification occurs by insulin action (via A-type receptors) to stimulate its own transcription.
Transcription of the ''GCK'' gene is initiated through the "upstream," or neuroendocrine, promoter. This promoter, in contrast to the liver promoter, has elements homologous to other insulin-induced gene promoters. Among the probable transacting factors are Pdx-1 and PPARγ
Peroxisome proliferator- activated receptor gamma (PPAR-γ or PPARG), also known as the glitazone reverse insulin resistance
receptor, or NR1C3 (nuclear receptor subfamily 1, group C, member 3) is a type II nuclear receptor functioning as a tran ...
. Pdx-1 is a homeodomain transcription factor involved in the differentiation of the pancreas. PPARγ is a nuclear receptor that responds to glitazone drugs by enhancing insulin sensitivity.
Association with insulin secretory granules
Much, but not all, of the glucokinase found in the cytoplasm of beta cells is associated with insulin secretory granules and with mitochondria. The proportion thus "bound" falls rapidly in response to rising glucose and insulin secretion. It has been suggested that binding serves a purpose similar to the hepatic glucokinase regulatory protein—protecting glucokinase from degradation so that it is rapidly available as the glucose rises. The effect is to amplify the glucokinase response to glucose more rapidly than transcription could do so.Suppression of glucagon in alpha cells
It has also been proposed that glucokinase plays a role in the glucose sensing of the pancreatic alpha cells, but the evidence is less consistent, and some researchers have found no evidence of glucokinase activity in these cells. Alpha cells occur in pancreatic islets, mixed with beta and other cells. While beta cells respond to rising glucose levels by secreting insulin, alpha cells respond by reducingglucagon
Glucagon is a peptide hormone, produced by alpha cells of the pancreas. It raises concentration of glucose and fatty acids in the bloodstream, and is considered to be the main catabolic hormone of the body. It is also used as a medication to tre ...
secretion. When blood glucose concentration falls to hypoglycemic
Hypoglycemia, also called low blood sugar, is a fall in blood sugar to levels below normal, typically below 70 mg/dL (3.9 mmol/L). Whipple's triad is used to properly identify hypoglycemic episodes. It is defined as blood glucose belo ...
levels, alpha cells release glucagon. Glucagon is a protein hormone that blocks the effect of insulin on hepatocytes, inducing glycogenolysis, gluconeogenesis, and reduced glucokinase activity in hepatocytes. The degree to which glucose suppression of glucagon is a direct effect of glucose via glucokinase in alpha cells, or an indirect effect mediated by insulin or other signals from beta cells, is still uncertain.
Hypothalamic
While allneuron
A neuron, neurone, or nerve cell is an electrically excitable cell that communicates with other cells via specialized connections called synapses. The neuron is the main component of nervous tissue in all animals except sponges and placozoa. ...
s use glucose for fuel, certain ''glucose-sensing neurons'' alter their firing rates in response to rising or falling levels of glucose. These glucose-sensing neurons are concentrated primarily in the ventromedial nucleus
The ventromedial nucleus of the hypothalamus (VMN, also sometimes referred to as the ventromedial hypothalamus, VMH) is a nucleus of the hypothalamus. "The ventromedial hypothalamus (VMH) is a distinct morphological nucleus involved in terminatin ...
and arcuate nucleus
The arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus (also known as ARH, ARC, or infundibular nucleus) is an aggregation of neurons in the mediobasal hypothalamus, adjacent to the third ventricle and the median eminence. The arcuate nucleus includes several ...
of the hypothalamus
The hypothalamus () is a part of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland. The hypothalamus ...
, which regulate many aspects of glucose homeostasis (especially the response to hypoglycemia), fuel utilization, satiety
Satiety ( ) is a state or condition of fullness gratified beyond the point of satisfaction, the opposite of hunger. It is a state which induces meal termination.Hetherington, M.Sensory-specific satiety and its importance in meal termination ''Neur ...
and appetite
Appetite is the desire to eat food items, usually due to hunger. Appealing foods can stimulate appetite even when hunger is absent, although appetite can be greatly reduced by satiety. Appetite exists in all higher life-forms, and serves to regul ...
, and weight
In science and engineering, the weight of an object is the force acting on the object due to gravity.
Some standard textbooks define weight as a vector quantity, the gravitational force acting on the object. Others define weight as a scalar quan ...
maintenance. These neurons are most sensitive to glucose changes in the 0.5–3.5 mmol/L glucose range.
Glucokinase has been found in the brain in largely the same areas that contain glucose-sensing neurons, including both of the hypothalamic nuclei. Inhibition of glucokinase abolishes the ventromedial nucleus response to a meal. However, brain glucose levels are lower than plasma levels, typically 0.5–3.5 mmol/L. Although this range is matches the sensitivity of the glucose-sensing neurons, it is below the optimal inflection sensitivity for glucokinase. The presumption, based on indirect evidence and speculation, is that neuronal glucokinase is somehow exposed to plasma glucose levels even in the neurons.
Enterocytes and incretin
While glucokinase has been shown to occur in certain cells (enterocytes) of thesmall intestine
The small intestine or small bowel is an organ in the gastrointestinal tract where most of the absorption of nutrients from food takes place. It lies between the stomach and large intestine, and receives bile and pancreatic juice through the ...
and stomach, its function and regulation have not been worked out. It has been suggested that here, also, glucokinase serves as a glucose sensor, allowing these cells to provide one of the earliest metabolic responses to incoming carbohydrates. It is suspected that these cells are involved in incretin
Incretins are a group of metabolic hormones that stimulate a decrease in blood glucose levels. Incretins are released after eating and augment the secretion of insulin released from pancreatic beta cells of the islets of Langerhans by a blood-gl ...
functions.
Clinical significance
Because insulin is one of, if not the most important, regulators of glucokinase synthesis,diabetes mellitus
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level (hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased ap ...
of all types diminishes glucokinase synthesis and activity by a variety of mechanisms. Glucokinase activity is sensitive to the oxidative stress of cells, especially the beta cells.
At least 497 mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, mitos ...
s of the human glucokinase gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a ba ...
''GCK'' have been discovered, that can change the efficiency of glucose binding and phosphorylation, increasing or decreasing the sensitivity of beta cell insulin secretion in response to glucose, and producing clinically significant hyperglycemia
Hyperglycemia is a condition in which an excessive amount of glucose circulates in the blood plasma. This is generally a blood sugar level higher than 11.1 mmol/L (200 mg/dL), but symptoms may not start to become noticeable until even ...
or hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia, also called low blood sugar, is a fall in blood sugar to levels below normal, typically below 70 mg/dL (3.9 mmol/L). Whipple's triad is used to properly identify hypoglycemic episodes. It is defined as blood glucose belo ...
.
Diabetes mellitus
''GCK'' mutations reduce the functional efficiency of the glucokinase molecule.Heterozygosity
Zygosity (the noun, zygote, is from the Greek "yoked," from "yoke") () is the degree to which both copies of a chromosome or gene have the same genetic sequence. In other words, it is the degree of similarity of the alleles in an organism.
...
for alleles with reduced enzyme activity results in a higher threshold for insulin release and persistent, mild hyperglycemia. This condition is referred to as maturity onset diabetes of the young, type 2 (MODY2). The most recent overview of ''GCK'' mutation that were observed in patients claims 791 mutations, of which 489 are thought to cause the MODY diabetes and therefore reduce the functional efficiency of the glucokinase molecule.
Homozygosity
Zygosity (the noun, zygote, is from the Greek "yoked," from "yoke") () is the degree to which both copies of a chromosome or gene have the same genetic sequence. In other words, it is the degree of similarity of the alleles in an organism.
Mo ...
for ''GCK'' alleles with reduced function can cause severe congenital insulin deficiency, resulting in persistent neonatal diabetes.
Hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia
Some mutations have been found to enhance insulin secretion. Heterozygosity for gain of function mutations reduces the threshold glucose that triggers insulin release. This creates hypoglycemia of varying patterns, including transient or persistentcongenital hyperinsulinism
Congenital hyperinsulinism is a medical term referring to a variety of congenital disorders in which hypoglycemia is caused by excessive insulin secretion.update 2013 Congenital forms of hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia can be transient or persist ...
, or fasting or reactive hypoglycemia
Reactive hypoglycemia, postprandial hypoglycemia, or sugar crash is a term describing recurrent episodes of symptomatic hypoglycemia occurring within four hours"Hypoglycemia." It can also be referred to as "sugar crash" or "glucose crash." Nati ...
appearing at an older age. The most recent overview of ''GCK'' mutation that were observed in patients claimed 17 ''GCK'' mutations to cause hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia.
Homozygosity for gain of function mutations has not been found.
Research
Severalpharmaceutical companies
The pharmaceutical industry discovers, develops, produces, and markets drugs or pharmaceutical drugs for use as medications to be administered to patients (or self-administered), with the aim to cure them, vaccinate them, or alleviate symptoms. ...
are researching molecules that activate glucokinase in hope that it will be useful in the treatment of both type 1 and type 2 diabetes
Type 2 diabetes, formerly known as adult-onset diabetes, is a form of diabetes mellitus that is characterized by high blood sugar, insulin resistance, and relative lack of insulin. Common symptoms include increased thirst, frequent urination, ...
.
References
External links
* *External links
* {{Portal bar, Biology, border=no EC 2.7.1 Protein families