gas thermometer on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A gas thermometer is a
A gas thermometer is a
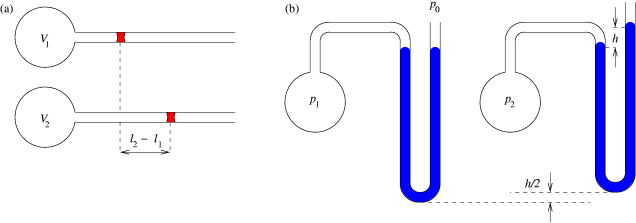
 The constant volume gas thermometer plays a crucial role in understanding how
The constant volume gas thermometer plays a crucial role in understanding how
 A gas thermometer is a
A gas thermometer is a thermometer
A thermometer is a device that temperature measurement, measures temperature or a temperature gradient (the degree of hotness or coldness of an object). A thermometer has two important elements: (1) a temperature sensor (e.g. the bulb of a merc ...
that measures temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that expresses quantitatively the perceptions of hotness and coldness. Temperature is measurement, measured with a thermometer.
Thermometers are calibrated in various Conversion of units of temperature, temp ...
by the variation in volume or pressure of a gas.
Volume Thermometer
This thermometer functions byCharles's Law
Charles's law (also known as the law of volumes) is an experimental gas law that describes how gases tend to expand when heated. A modern statement of Charles's law is:
When the pressure on a sample of a dry gas is held constant, the Kelvin ...
. Charles's Law
Charles's law (also known as the law of volumes) is an experimental gas law that describes how gases tend to expand when heated. A modern statement of Charles's law is:
When the pressure on a sample of a dry gas is held constant, the Kelvin ...
states that when the temperature of a gas increases, so does the volume.
Using Charles's Law
Charles's law (also known as the law of volumes) is an experimental gas law that describes how gases tend to expand when heated. A modern statement of Charles's law is:
When the pressure on a sample of a dry gas is held constant, the Kelvin ...
, the temperature can be measured by knowing the volume of gas at a certain temperature by using the formula, written below. Translating it to the correct levels of the device that is holding the gas. This works on the same principle as mercury thermometers.
:
or
:
is the volume,
is the thermodynamic temperature
Thermodynamic temperature is a quantity defined in thermodynamics as distinct from kinetic theory or statistical mechanics.
Historically, thermodynamic temperature was defined by Kelvin in terms of a macroscopic relation between thermodynamic w ...
,
is the constant for the system.
is not a fixed constant across all systems and therefore needs to be found experimentally for a given system through testing with known temperature values.
Pressure Thermometer and Absolute Zero
 The constant volume gas thermometer plays a crucial role in understanding how
The constant volume gas thermometer plays a crucial role in understanding how absolute zero
Absolute zero is the lowest limit of the thermodynamic temperature scale, a state at which the enthalpy and entropy of a cooled ideal gas reach their minimum value, taken as zero kelvin. The fundamental particles of nature have minimum vibratio ...
could be discovered long before the advent of cryogenics
In physics, cryogenics is the production and behaviour of materials at very low temperatures.
The 13th IIR International Congress of Refrigeration (held in Washington DC in 1971) endorsed a universal definition of “cryogenics” and “cr ...
. Consider a graph of pressure versus temperature made not far from standard conditions (well above absolute zero) for three different samples of any ideal gas ''(a, b, c)''. To the extent that the gas is ideal, the pressure depends linearly on temperature, and the extrapolation to zero pressure occurs at absolute zero. Note that data could have been collected with three different amounts of the same gas, which would have rendered this experiment easy to do in the eighteenth century.
History
See also
* Thermodynamic instruments *Boyle's law
Boyle's law, also referred to as the Boyle–Mariotte law, or Mariotte's law (especially in France), is an experimental gas law that describes the relationship between pressure and volume of a confined gas. Boyle's law has been stated as:
The a ...
* Combined gas law
The ideal gas law, also called the general gas equation, is the equation of state of a hypothetical ideal gas. It is a good approximation of the behavior of many gases under many conditions, although it has several limitations. It was first stat ...
* Gay-Lussac's law
Gay-Lussac's law usually refers to Joseph-Louis Gay-Lussac's law of combining volumes of gases, discovered in 1808 and published in 1809. It sometimes refers to the proportionality of the volume of a gas to its absolute temperature at constant p ...
* Avogadro's law
Avogadro's law (sometimes referred to as Avogadro's hypothesis or Avogadro's principle) or Avogadro-Ampère's hypothesis is an experimental gas law relating the volume of a gas to the amount of substance of gas present. The law is a specific cas ...
* Ideal gas law
The ideal gas law, also called the general gas equation, is the equation of state of a hypothetical ideal gas. It is a good approximation of the behavior of many gases under many conditions, although it has several limitations. It was first stat ...
References