gabbro on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
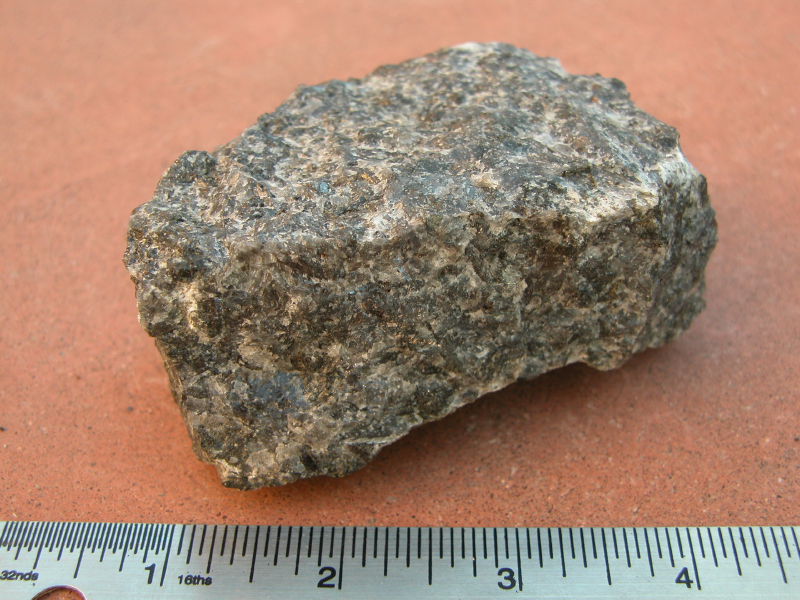

 Gabbro ( ) is a phaneritic (coarse-grained and magnesium- and iron-rich), mafic intrusive
Gabbro ( ) is a phaneritic (coarse-grained and magnesium- and iron-rich), mafic intrusive
 Gabbro is a coarse-grained ( phaneritic)
Gabbro is a coarse-grained ( phaneritic) 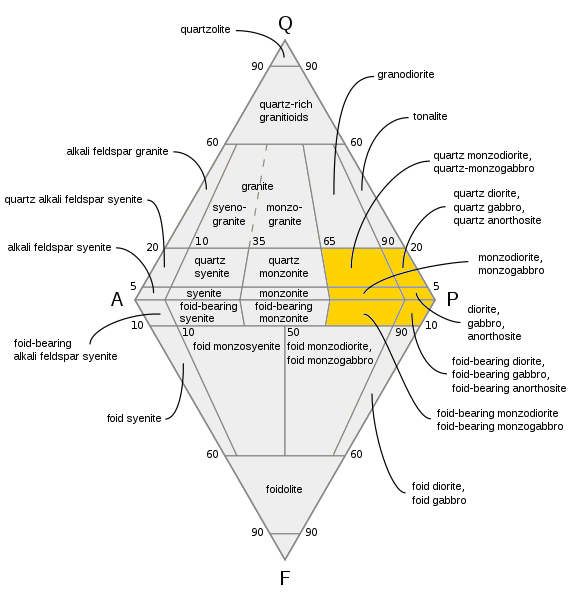 Geologists use rigorous quantitative definitions to classify coarse-grained igneous rocks, based on the mineral content of the rock. For igneous rocks composed mostly of silicate minerals, and in which at least 10% of the mineral content consists of
Geologists use rigorous quantitative definitions to classify coarse-grained igneous rocks, based on the mineral content of the rock. For igneous rocks composed mostly of silicate minerals, and in which at least 10% of the mineral content consists of
 Gabbros are also sometimes classified as alkali or tholleiitic gabbros, by analogy with alkali or tholeiitic basalts, of which they are considered the intrusive equivalents. Alkali gabbro usually contains olivine, nepheline, or analcime, up to 10% of the mineral content, while tholeiitic gabbro contains both clinopyroxene and orthopyroxene, making it a gabbronorite.
Gabbros are also sometimes classified as alkali or tholleiitic gabbros, by analogy with alkali or tholeiitic basalts, of which they are considered the intrusive equivalents. Alkali gabbro usually contains olivine, nepheline, or analcime, up to 10% of the mineral content, while tholeiitic gabbro contains both clinopyroxene and orthopyroxene, making it a gabbronorite.
 Nearly all gabbros are found in plutonic bodies, and the term (as the
Nearly all gabbros are found in plutonic bodies, and the term (as the
Ocean drilling program gabbro petrology
{{Authority control Mafic rocks Plutonic rocks Phaneritic rocks

 Gabbro ( ) is a phaneritic (coarse-grained and magnesium- and iron-rich), mafic intrusive
Gabbro ( ) is a phaneritic (coarse-grained and magnesium- and iron-rich), mafic intrusive igneous rock
Igneous rock ( ), or magmatic rock, is one of the three main rock types, the others being sedimentary and metamorphic. Igneous rocks are formed through the cooling and solidification of magma or lava.
The magma can be derived from partial ...
formed from the slow cooling magma
Magma () is the molten or semi-molten natural material from which all igneous rocks are formed. Magma (sometimes colloquially but incorrectly referred to as ''lava'') is found beneath the surface of the Earth, and evidence of magmatism has also ...
into a holocrystalline mass deep beneath the Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to Planetary habitability, harbor life. This is enabled by Earth being an ocean world, the only one in the Solar System sustaining liquid surface water. Almost all ...
's surface. Slow-cooling, coarse-grained gabbro is chemically equivalent to rapid-cooling, fine-grained basalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanite, aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the planetary surface, surface of a terrestrial ...
. Much of the Earth's oceanic crust
Oceanic crust is the uppermost layer of the oceanic portion of the tectonic plates. It is composed of the upper oceanic crust, with pillow lavas and a dike complex, and the lower oceanic crust, composed of troctolite, gabbro and ultramaf ...
is made of gabbro, formed at mid-ocean ridge
A mid-ocean ridge (MOR) is a undersea mountain range, seafloor mountain system formed by plate tectonics. It typically has a depth of about and rises about above the deepest portion of an ocean basin. This feature is where seafloor spreading ...
s. Gabbro is also found as plutons associated with continental volcanism. Due to its variant nature, the term ''gabbro'' may be applied loosely to a wide range of intrusive rocks, many of which are merely "gabbroic". By rough analogy, gabbro is to basalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanite, aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the planetary surface, surface of a terrestrial ...
as granite
Granite ( ) is a coarse-grained (phanerite, phaneritic) intrusive rock, intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly coo ...
is to rhyolite
Rhyolite ( ) is the most silica-rich of volcanic rocks. It is generally glassy or fine-grained (aphanitic) in texture (geology), texture, but may be porphyritic, containing larger mineral crystals (phenocrysts) in an otherwise fine-grained matri ...
.
Etymology
The term "gabbro" was used in the 1760s to name a set of rock types that were found in theophiolite
An ophiolite is a section of Earth's oceanic crust and the underlying upper mantle (Earth), upper mantle that has been uplifted and exposed, and often emplaced onto continental crustal rocks.
The Greek word ὄφις, ''ophis'' (''snake'') is ...
s of the Apennine Mountains
The Apennines or Apennine Mountains ( ; or Ἀπέννινον ὄρος; or – a singular with plural meaning; )Latin ''Apenninus'' (Greek or ) has the form of an adjective, which would be segmented ''Apenn-inus'', often used with nouns s ...
in Italy. It was named after Gabbro, a hamlet near Rosignano Marittimo in Tuscany
Tuscany ( ; ) is a Regions of Italy, region in central Italy with an area of about and a population of 3,660,834 inhabitants as of 2025. The capital city is Florence.
Tuscany is known for its landscapes, history, artistic legacy, and its in ...
. Then, in 1809, the German geologist Christian Leopold von Buch
Christian Leopold von Buch (26 April 1774 – 4 March 1853), usually cited as Leopold von Buch, was a German geologist and paleontologist born in Stolpe an der Oder (now a part of Angermünde, Brandenburg) and is remembered as one of the mos ...
used the term more restrictively in his description of these Italian ophiolitic rocks. He assigned the name "gabbro" to rocks that geologists nowadays would more strictly call "metagabbro" ( metamorphosed gabbro).
Petrology
igneous rock
Igneous rock ( ), or magmatic rock, is one of the three main rock types, the others being sedimentary and metamorphic. Igneous rocks are formed through the cooling and solidification of magma or lava.
The magma can be derived from partial ...
that is relatively low in silica
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , commonly found in nature as quartz. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is one of the most complex and abundant f ...
and rich in iron, magnesium, and calcium. Such rock is described as '' mafic''. Gabbro is composed of pyroxene (mostly clinopyroxene) and calcium-rich plagioclase, with minor amounts of hornblende
Hornblende is a complex silicate minerals#Inosilicates, inosilicate series of minerals. It is not a recognized mineral in its own right, but the name is used as a general or field term, to refer to a dark amphibole. Hornblende minerals are common ...
, olivine
The mineral olivine () is a magnesium iron Silicate minerals, silicate with the chemical formula . It is a type of Nesosilicates, nesosilicate or orthosilicate. The primary component of the Earth's upper mantle (Earth), upper mantle, it is a com ...
, orthopyroxene and accessory minerals. With significant (>10%) olivine or orthopyroxene it is classified as olivine gabbro or gabbronorite respectively. Where present, hornblende is typically found as a rim around augite crystals or as large grains enclosing smaller grains of other minerals ('' poikilitic'' grains).
 Geologists use rigorous quantitative definitions to classify coarse-grained igneous rocks, based on the mineral content of the rock. For igneous rocks composed mostly of silicate minerals, and in which at least 10% of the mineral content consists of
Geologists use rigorous quantitative definitions to classify coarse-grained igneous rocks, based on the mineral content of the rock. For igneous rocks composed mostly of silicate minerals, and in which at least 10% of the mineral content consists of quartz
Quartz is a hard, crystalline mineral composed of silica (silicon dioxide). The Atom, atoms are linked in a continuous framework of SiO4 silicon–oxygen Tetrahedral molecular geometry, tetrahedra, with each oxygen being shared between two tet ...
, feldspar
Feldspar ( ; sometimes spelled felspar) is a group of rock-forming aluminium tectosilicate minerals, also containing other cations such as sodium, calcium, potassium, or barium. The most common members of the feldspar group are the ''plagiocl ...
, or feldspathoid
The feldspathoids are a group of tectosilicate minerals which resemble feldspar
Feldspar ( ; sometimes spelled felspar) is a group of rock-forming aluminium tectosilicate minerals, also containing other cations such as sodium, calcium, pota ...
minerals, classification begins with the QAPF diagram. The relative abundances of quartz (Q), alkali feldspar (A), plagioclase (P), and feldspathoid (F), are used to plot the position of the rock on the diagram. The rock will be classified as either a gabbroid or a dioritoid if quartz makes up less than 20% of the QAPF content, feldspathoid makes up less than 10% of the QAPF content, and plagioclase makes up more than 65% of the total feldspar content. Gabbroids are distinguished from dioritoids by an anorthite (calcium plagioclase) fraction of their total plagioclase of greater than 50%.
The composition of the plagioclase cannot easily be determined in the field, and then a preliminary distinction is made between dioritoid and gabbroid based on the content of mafic minerals. A gabbroid typically has over 35% mafic minerals, mostly pyroxenes or olivine, while a dioritoid typically has less than 35% mafic minerals, which typically includes hornblende.
Gabbroids form a family of rock types similar to gabbro, such as monzogabbro, quartz gabbro, or nepheline-bearing gabbro. Gabbro itself is more narrowly defined, as a gabbroid in which quartz makes up less than 5% of the QAPF content, feldspathoids are not present, and plagioclase makes up more than 90% of the feldspar content. Gabbro is distinct from anorthosite
Anorthosite () is a phaneritic, intrusive rock, intrusive igneous rock characterized by its composition: mostly plagioclase feldspar (90–100%), with a minimal mafic component (0–10%). Pyroxene, ilmenite, magnetite, and olivine are the mafic ...
, which contains less than 10% mafic minerals.
Coarse-grained gabbroids are produced by slow crystallization of magma
Magma () is the molten or semi-molten natural material from which all igneous rocks are formed. Magma (sometimes colloquially but incorrectly referred to as ''lava'') is found beneath the surface of the Earth, and evidence of magmatism has also ...
having the same composition as the lava
Lava is molten or partially molten rock (magma) that has been expelled from the interior of a terrestrial planet (such as Earth) or a Natural satellite, moon onto its surface. Lava may be erupted at a volcano or through a Fissure vent, fractu ...
that solidifies rapidly to form fine-grained (aphanitic
Aphanites (adj. ''aphanitic''; ) are igneous rocks that are so fine-grained that their component mineral crystals are not visible to the naked eye (in contrast to phanerites, in which the crystals are visible to the unaided eye). This geo ...
) basalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanite, aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the planetary surface, surface of a terrestrial ...
.
Subtypes
There are a number of subtypes of gabbro recognized by geologists. Gabbros can be broadly divided into leucogabbros, with less than 35% mafic mineral content; mesogabbros, with 35% to 65% mafic mineral content; and melagabbros with more than 65% mafic mineral content. A rock with over 90% mafic mineral content will be classified instead as an ultramafic rock. A gabbroic rock with less than 10% mafic mineral content will be classified as an anorthosite. A more detailed classification is based on the relative percentages of plagioclase, pyroxene, hornblende, and olivine. The end members are: * Normal gabbro (gabbro ''sensu stricto'') is composed almost entirely of plagioclase and clinopyroxene (typically augite), with less than 5% each of hornblende, olivine, or orthopyroxene. * Norite is composed almost entirely of plagioclase and orthopyroxene, with less than 5% each of hornblende, clinopyroxene, or olivine. * Troctolite is composed almost entirely of plagioclase and olivine, with less than 5% each of pyroxene or hornblende. * Hornblende gabbro is composed almost entirely of plagioclase and hornblende, with less than 5% each of pyroxene or olivine. Gabbros intermediate between these compositions are given names such as gabbronorite (for a gabbro intermediate between normal gabbro and norite, with almost equal amounts of clinopyroxene and orthopyroxene) or olivine gabbro (for a gabbro containing significant olivine, but almost no clinopyroxene or hornblende). A rock similar to normal gabbro but containing more orthopyroxene is called an orthopyroxene gabbro, while a rock similar to norite but containing more clinopyroxene is called a clinopyroxene norite. Gabbros are also sometimes classified as alkali or tholleiitic gabbros, by analogy with alkali or tholeiitic basalts, of which they are considered the intrusive equivalents. Alkali gabbro usually contains olivine, nepheline, or analcime, up to 10% of the mineral content, while tholeiitic gabbro contains both clinopyroxene and orthopyroxene, making it a gabbronorite.
Gabbros are also sometimes classified as alkali or tholleiitic gabbros, by analogy with alkali or tholeiitic basalts, of which they are considered the intrusive equivalents. Alkali gabbro usually contains olivine, nepheline, or analcime, up to 10% of the mineral content, while tholeiitic gabbro contains both clinopyroxene and orthopyroxene, making it a gabbronorite.
Gabbroids
Gabbroids (also known as gabbroic-rocks) are a family of coarse-grained igneous rocks similar to gabbro: * Quartz gabbro contains 5% to 20% quartz in its QAPF fraction. One example is the ''cizlakite'' at Pohorje in northeastern Slovenia, * Monzogabbro contains 65% to 90% plagioclase out of its total feldspar content. * Quartz monzogabbro combines the features of quartz gabbro and monzogabbro. It contains 5% to 20% quartz in its QAPF fraction, and 65% to 90% of its feldspar is plagioclase. * Foid-bearing gabbro contains up to 10% feldspathoids rather than quartz. "Foid" in the name is usually replaced by the specific feldspathoid that is most abundant in the rock. For example, a nepheline-bearing gabbro is a foid-bearing gabbro in which the most abundant feldspathoid is nepheline. * Foid-bearing monzogabbro resembles monzogabbro, but containing up to 10% feldspathoids in place of quartz. The same naming conventions apply as for foid-bearing gabbro, so that a gabbroid might be classified as a leucite-bearing monzogabbro. Gabbroids contain minor amounts, typically a few percent, of iron-titanium oxides such asmagnetite
Magnetite is a mineral and one of the main iron ores, with the chemical formula . It is one of the iron oxide, oxides of iron, and is ferrimagnetism, ferrimagnetic; it is attracted to a magnet and can be magnetization, magnetized to become a ...
, ilmenite, and ulvospinel. Apatite
Apatite is a group of phosphate minerals, usually hydroxyapatite, fluorapatite and chlorapatite, with high concentrations of Hydroxide, OH−, Fluoride, F− and Chloride, Cl− ion, respectively, in the crystal. The formula of the admixture of ...
, zircon, and biotite may also be present as accessory minerals.
Gabbro is generally coarse-grained, with crystals in the size range of 1 mm or larger. Finer-grained equivalents of gabbro are called diabase (also known as dolerite), although the term ''microgabbro'' is often used when extra descriptiveness is desired. Gabbro may be extremely coarse-grained to pegmatitic. Some pyroxene-plagioclase cumulates are essentially coarse-grained gabbro, and may exhibit acicular crystal habits.
Gabbro is usually equigranular in texture, although it may also show ophitic texture (with laths of plagioclase enclosed in pyroxene).
Distribution
 Nearly all gabbros are found in plutonic bodies, and the term (as the
Nearly all gabbros are found in plutonic bodies, and the term (as the International Union of Geological Sciences
The International Union of Geological Sciences (IUGS) is an international non-governmental organization devoted to global cooperation in the field of geology. As of 2023, it represents more than 1 million geoscientists around the world.
About
Fo ...
recommends) is normally restricted just to plutonic rocks, although gabbro may be found as a coarse-grained interior facies of certain thick lavas. Gabbro can be formed as a massive, uniform intrusion via in-situ crystallisation of pyroxene and plagioclase, or as part of a layered intrusion
A layered intrusion is a large sill-like body of igneous rock which exhibits vertical layering or differences in composition and texture. These intrusions can be many kilometres in area covering from around to over and several hundred metres t ...
as a cumulate formed by settling of pyroxene and plagioclase.
An alternative name for gabbros formed by crystal settling is ''pyroxene-plagioclase adcumulate''.
Gabbro is much less common than more silica-rich intrusive rocks in the continental crust
Continental crust is the layer of igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary rocks that forms the geological continents and the areas of shallow seabed close to their shores, known as '' continental shelves''. This layer is sometimes called '' si ...
of the Earth. Gabbro and gabbroids occur in some batholiths but these rocks are relatively minor components of these very large intrusions because their iron and calcium content usually makes gabbro and gabbroid magmas too dense to have the necessary buoyancy. However, gabbro is an essential part of the oceanic crust, and can be found in many ophiolite
An ophiolite is a section of Earth's oceanic crust and the underlying upper mantle (Earth), upper mantle that has been uplifted and exposed, and often emplaced onto continental crustal rocks.
The Greek word ὄφις, ''ophis'' (''snake'') is ...
complexes as layered gabbro underling sheeted dike complexes and overlying ultramafic rock derived from the Earth's mantle. These layered gabbros may have formed from relatively small but long-lived magma chambers underlying mid-ocean ridge
A mid-ocean ridge (MOR) is a undersea mountain range, seafloor mountain system formed by plate tectonics. It typically has a depth of about and rises about above the deepest portion of an ocean basin. This feature is where seafloor spreading ...
s.
Layered gabbros are also characteristic of lopoliths, which are large, saucer-shaped intrusions that are primarily Precambrian
The Precambrian ( ; or pre-Cambrian, sometimes abbreviated pC, or Cryptozoic) is the earliest part of Earth's history, set before the current Phanerozoic Eon. The Precambrian is so named because it preceded the Cambrian, the first period of t ...
in age. Prominent examples of lopoliths include the Bushveld Complex of South Africa, the Muskox intrusion of the Northwest Territories
The Northwest Territories is a federal Provinces and territories of Canada, territory of Canada. At a land area of approximately and a 2021 census population of 41,070, it is the second-largest and the most populous of Provinces and territorie ...
of Canada, the Rum layered intrusion of Scotland, the Stillwater complex of Montana, and the layered gabbros near Stavanger
Stavanger, officially the Stavanger Municipality, is a city and municipalities of Norway, municipality in Norway. It is the third largest city and third largest metropolitan area in Norway (through conurbation with neighboring Sandnes) and the ...
, Norway. Gabbros are also present in stock
Stocks (also capital stock, or sometimes interchangeably, shares) consist of all the Share (finance), shares by which ownership of a corporation or company is divided. A single share of the stock means fractional ownership of the corporatio ...
s associated with alkaline volcanism of continental rifting
In geology, a rift is a linear zone where the lithosphere is being pulled apart and is an example of extensional tectonics. Typical rift features are a central linear downfaulted depression, called a graben, or more commonly a half-graben ...
.
Uses
Gabbro often contains valuable amounts of chromium, nickel,cobalt
Cobalt is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Co and atomic number 27. As with nickel, cobalt is found in the Earth's crust only in a chemically combined form, save for small deposits found in alloys of natural meteoric iron. ...
, gold
Gold is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol Au (from Latin ) and atomic number 79. In its pure form, it is a brightness, bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile metal. Chemically, gold is a transition metal ...
, silver
Silver is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag () and atomic number 47. A soft, whitish-gray, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and reflectivity of any metal. ...
, platinum
Platinum is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Pt and atomic number 78. It is a density, dense, malleable, ductility, ductile, highly unreactive, precious metal, precious, silverish-white transition metal. Its name origina ...
, and copper
Copper is a chemical element; it has symbol Cu (from Latin ) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orang ...
sulfide
Sulfide (also sulphide in British English) is an inorganic anion of sulfur with the chemical formula S2− or a compound containing one or more S2− ions. Solutions of sulfide salts are corrosive. ''Sulfide'' also refers to large families o ...
s. For example, the Merensky Reef is the world's most important source of platinum.
Gabbro is known in the construction industry by the trade name of ''black granite''. However, gabbro is hard and difficult to work, which limits its use.
The term "indigo gabbro" is used as a common name for a mineralogically complex rock type often found in mottled tones of black and lilac-grey. It is mined in central Madagascar for use as a semi-precious stone. Indigo Gabbro can contain numerous minerals, including quartz and feldspar. Reports state that the dark matrix of the rock is composed of a mafic igneous rock, but whether this is basalt or gabbro is unclear.
See also
* * *References
External links
Ocean drilling program gabbro petrology
{{Authority control Mafic rocks Plutonic rocks Phaneritic rocks