Furanose on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A furanose is a collective term for
A furanose is a collective term for
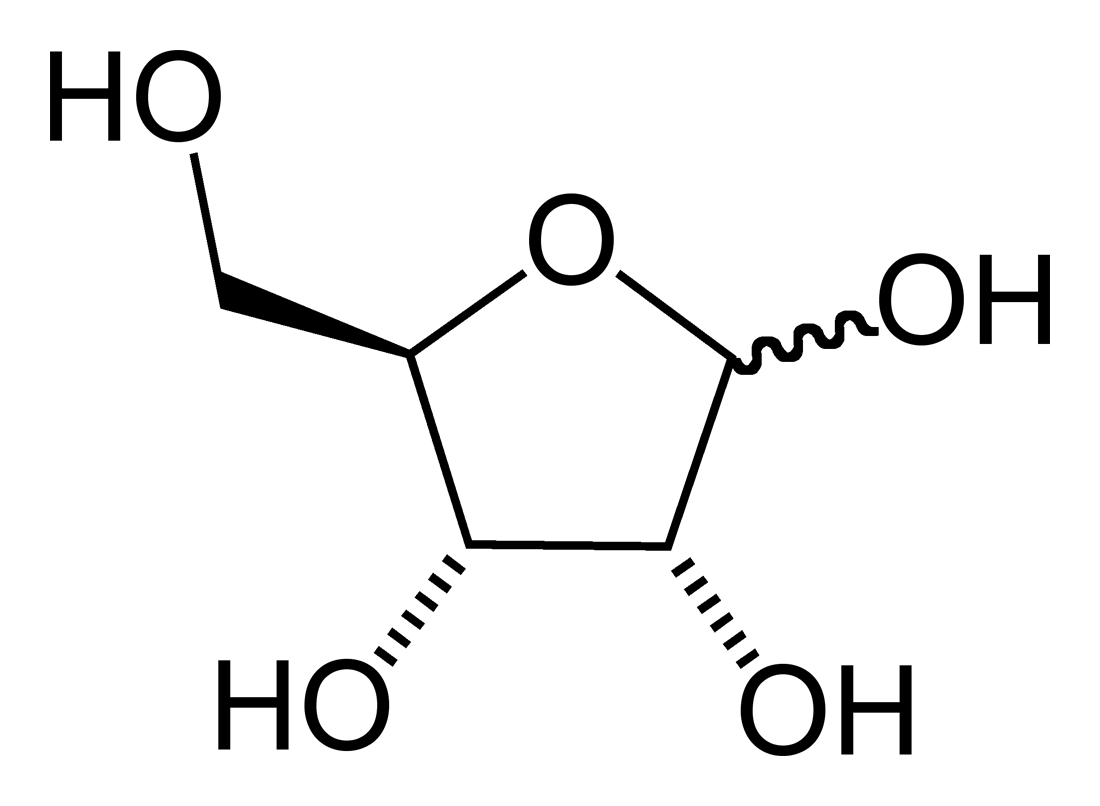 The furanose ring is a cyclic
The furanose ring is a cyclic
carbohydrates
In organic chemistry, a carbohydrate () is a biomolecule consisting of carbon (C), hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O) atoms, usually with a hydrogen–oxygen atom ratio of 2:1 (as in water) and thus with the empirical formula (where ''m'' may or m ...
that have a chemical structure that includes a five-membered ring system consisting of four carbon atoms and one oxygen atom. The name derives from its similarity to the oxygen heterocycle furan
Furan is a heterocyclic organic compound, consisting of a five-membered aromatic ring with four carbon atoms and one oxygen atom. Chemical compounds containing such rings are also referred to as furans.
Furan is a colorless, flammable, highl ...
, but the furanose ring does not have double bond
In chemistry, a double bond is a covalent bond between two atoms involving four bonding electrons as opposed to two in a single bond. Double bonds occur most commonly between two carbon atoms, for example in alkenes. Many double bonds exist betwee ...
s.
Structural properties
 The furanose ring is a cyclic
The furanose ring is a cyclic hemiacetal
A hemiacetal or a hemiketal has the general formula R1R2C(OH)OR, where R1 or R2 is hydrogen or an organic substituent. They generally result from the addition of an alcohol to an aldehyde or a ketone, although the latter are sometimes called hemi ...
of an aldopentose
In chemistry, a pentose is a monosaccharide (simple sugar) with five carbon atoms. The chemical formula of many pentoses is , and their molecular weight is 150.13 g/mol.hemiketal
A hemiacetal or a hemiketal has the general formula R1R2C(OH)OR, where R1 or R2 is hydrogen or an organic substituent. They generally result from the addition of an alcohol to an aldehyde or a ketone, although the latter are sometimes called hemike ...
of a ketohexose.
A furanose ring structure consists of four carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent—its atom making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds. It belongs to group 14 of the periodic table. Carbon ma ...
and one oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements ...
atom with the anomer
In carbohydrate chemistry, a pair of anomers () is a pair of near-identical stereoisomers that differ at only the anomeric carbon, the carbon that bears the aldehyde or ketone functional group in the sugar's open-chain form. However, in order f ...
ic carbon to the right of the oxygen. The highest numbered chiral
Chirality is a property of asymmetry important in several branches of science. The word ''chirality'' is derived from the Greek (''kheir''), "hand", a familiar chiral object.
An object or a system is ''chiral'' if it is distinguishable from i ...
carbon (typically to the left of the oxygen in a Haworth projection
In chemistry, a Haworth projection is a common way of writing a structural formula to represent the cyclic structure of monosaccharides with a simple three-dimensional perspective. Haworth projection approximate the shapes of the actual molec ...
) determines whether or not the structure has a -configuration or L-configuration. In an -configuration furanose, the substituent on the highest numbered chiral carbon is pointed downwards out of the plane, and in a D-configuration furanose, the highest numbered chiral carbon is facing upwards.
The furanose ring will have either alpha or beta configuration, depending on which direction the anomeric hydroxy group is pointing. In a -configuration furanose, alpha configuration has the hydroxy pointing down, and beta has the hydroxy pointing up. It is the opposite in an -configuration furanose. Typically, the anomeric carbon undergoes mutarotation Mutarotation is the change in the '' optical rotation'' because of the change in the equilibrium between two anomers, when the corresponding stereocenters interconvert. Cyclic sugars show mutarotation as α and β anomeric forms interconvert.
The ...
in solution, and the result is an equilibrium mixture of α and β configurations.
See also
*Pyranose Pyranose is a collective term for saccharides that have a chemical structure that includes a six-membered ring consisting of five carbon atoms and one oxygen atom. There may be other carbons external to the ring. The name derives from its similarit ...
References
{{Carbohydrates Carbohydrate chemistry Carbohydrates Tetrahydrofurans Hexoses