fruit on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In
 Many common language terms used for fruit and seeds differ from botanical classifications. For example, in botany, a ''fruit'' is a ripened
Many common language terms used for fruit and seeds differ from botanical classifications. For example, in botany, a ''fruit'' is a ripened  Examples of botanically classified fruit that are typically called vegetables include cucumber, pumpkin, and squash (all are cucurbits); beans, peanuts, and peas (all legumes); and corn, eggplant,
Examples of botanically classified fruit that are typically called vegetables include cucumber, pumpkin, and squash (all are cucurbits); beans, peanuts, and peas (all legumes); and corn, eggplant,

 The outer layer, often edible, of most fruits is called the ''pericarp''. Typically formed from the ovary, it surrounds the seeds; in some species, however, other structural tissues contribute to or form the edible portion. The pericarp may be described in three layers from outer to inner, i.e., the ''epicarp'', ''mesocarp'' and ''endocarp''.
Fruit that bears a prominent pointed terminal projection is said to be ''beaked''.
The outer layer, often edible, of most fruits is called the ''pericarp''. Typically formed from the ovary, it surrounds the seeds; in some species, however, other structural tissues contribute to or form the edible portion. The pericarp may be described in three layers from outer to inner, i.e., the ''epicarp'', ''mesocarp'' and ''endocarp''.
Fruit that bears a prominent pointed terminal projection is said to be ''beaked''.
File:Nectarine Fruit Development.jpg, The development sequence of a typical drupe, the nectarine (''Prunus persica'') over a 7.5-month period, from bud formation in early winter to fruit ripening in midsummer
File:Mature flower diagram.svg, The parts of a flower, showing the stigma-style-ovary system.
File:Pome apples text.jpg, An apple is a simple, fleshy fruit. Key parts are the epicarp, or exocarp, or outer skin (not labelled); and the mesocarp and endocarp (labelled).
image:Ovary position.svg, upright 1.5, Insertion point: There are three positions of insertion of the ovary at the base of a flower: I superior; II half-inferior; III inferior. The 'insertion point' is where the
 Consistent with the three modes of fruit development, plant scientists have classified fruits into three main groups: simple fruits, aggregate fruits, and multiple (or composite) fruits. The groupings reflect how the ovary and other flower organs are arranged and how the fruits develop, but they are not evolutionarily relevant as diverse plant taxa may be in the same group.
While the section of a
Consistent with the three modes of fruit development, plant scientists have classified fruits into three main groups: simple fruits, aggregate fruits, and multiple (or composite) fruits. The groupings reflect how the ovary and other flower organs are arranged and how the fruits develop, but they are not evolutionarily relevant as diverse plant taxa may be in the same group.
While the section of a


 Berries are a type of simple fleshy fruit that issue from a single ovary. (The ovary itself may be compound, with several carpels.) The botanical term ''true berry'' includes grapes, currants, cucumbers, eggplants (aubergines), tomatoes, chili peppers, and bananas, but excludes certain fruits that are called "-berry" by culinary custom or by common usage of the term – such as strawberries and raspberries. Berries may be formed from one or more carpels (i.e., from the simple or compound ovary) from the same, single flower. Seeds typically are embedded in the fleshy interior of the ovary.
Examples include:
*
Berries are a type of simple fleshy fruit that issue from a single ovary. (The ovary itself may be compound, with several carpels.) The botanical term ''true berry'' includes grapes, currants, cucumbers, eggplants (aubergines), tomatoes, chili peppers, and bananas, but excludes certain fruits that are called "-berry" by culinary custom or by common usage of the term – such as strawberries and raspberries. Berries may be formed from one or more carpels (i.e., from the simple or compound ovary) from the same, single flower. Seeds typically are embedded in the fleshy interior of the ovary.
Examples include:
*
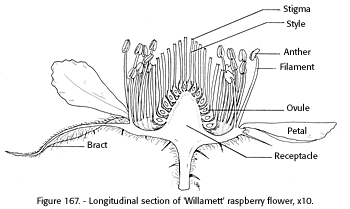 An aggregate fruit is also called an aggregation, or '' etaerio''; it develops from a single flower that presents numerous simple pistils. Each pistil contains one carpel; together, they form a fruitlet. The ultimate (fruiting) development of the aggregation of pistils is called an ''aggregate fruit'', ''etaerio fruit'', or simply an ''etaerio''.
Different types of aggregate fruits can produce different etaerios, such as achenes, drupelets, follicles, and berries.
* For example, the Ranunculaceae species, including '' Clematis'' and '' Ranunculus'', produces an etaerio of achenes;
* '' Rubus'' species, including raspberry: an etaerio of drupelets;
* '' Calotropis'' species: an etaerio of follicles fruit;
* '' Annona'' species: an etaerio of berries.
Some other broadly recognized species and their etaerios (or aggregations) are:
* Teasel; fruit is an aggregation of cypselas.
* Tuliptree; fruit is an aggregation of samaras.
* Magnolia and peony; fruit is an aggregation of follicles.
* American sweet gum; fruit is an aggregation of capsules.
* Sycamore; fruit is an aggregation of achenes.
The pistils of the
An aggregate fruit is also called an aggregation, or '' etaerio''; it develops from a single flower that presents numerous simple pistils. Each pistil contains one carpel; together, they form a fruitlet. The ultimate (fruiting) development of the aggregation of pistils is called an ''aggregate fruit'', ''etaerio fruit'', or simply an ''etaerio''.
Different types of aggregate fruits can produce different etaerios, such as achenes, drupelets, follicles, and berries.
* For example, the Ranunculaceae species, including '' Clematis'' and '' Ranunculus'', produces an etaerio of achenes;
* '' Rubus'' species, including raspberry: an etaerio of drupelets;
* '' Calotropis'' species: an etaerio of follicles fruit;
* '' Annona'' species: an etaerio of berries.
Some other broadly recognized species and their etaerios (or aggregations) are:
* Teasel; fruit is an aggregation of cypselas.
* Tuliptree; fruit is an aggregation of samaras.
* Magnolia and peony; fruit is an aggregation of follicles.
* American sweet gum; fruit is an aggregation of capsules.
* Sycamore; fruit is an aggregation of achenes.
The pistils of the
 Hybrid fruits are created through the controlled speciation of fruits that creates new varieties and cross-breeds. Hybrids are grown using plant propagation to create new cultivars. This may introduce an entirely new type of fruit or improve the properties of an existing fruit.
Hybrid fruits are created through the controlled speciation of fruits that creates new varieties and cross-breeds. Hybrids are grown using plant propagation to create new cultivars. This may introduce an entirely new type of fruit or improve the properties of an existing fruit.

 A large variety of fruits – fleshy (simple) fruits from apples to berries to watermelon; dry (simple) fruits including beans and rice and coconuts; aggregate fruits including strawberries, raspberries, blackberries, pawpaw; and multiple fruits such as pineapple, fig, mulberries – are commercially valuable as human food. They are eaten both fresh and as jams, marmalade and other fruit preserves. They are used extensively in manufactured and processed foods (cakes, cookies, baked goods, flavorings, ice cream, yogurt, canned vegetables, frozen vegetables and meals) and beverages such as fruit juices and alcoholic beverages (brandy, fruit beer, wine). Spices like vanilla, black pepper, paprika, and allspice are derived from berries. Olive fruit is pressed for
A large variety of fruits – fleshy (simple) fruits from apples to berries to watermelon; dry (simple) fruits including beans and rice and coconuts; aggregate fruits including strawberries, raspberries, blackberries, pawpaw; and multiple fruits such as pineapple, fig, mulberries – are commercially valuable as human food. They are eaten both fresh and as jams, marmalade and other fruit preserves. They are used extensively in manufactured and processed foods (cakes, cookies, baked goods, flavorings, ice cream, yogurt, canned vegetables, frozen vegetables and meals) and beverages such as fruit juices and alcoholic beverages (brandy, fruit beer, wine). Spices like vanilla, black pepper, paprika, and allspice are derived from berries. Olive fruit is pressed for
 A meta-analysis of 83 studies showed fruit or vegetable consumption is associated with reduced markers of inflammation (reduced tumor necrosis factor and C-reactive protein) and enhanced immune cell profile (increased gamma delta T cells).
Various culinary fruits provide significant amounts of
A meta-analysis of 83 studies showed fruit or vegetable consumption is associated with reduced markers of inflammation (reduced tumor necrosis factor and C-reactive protein) and enhanced immune cell profile (increased gamma delta T cells).
Various culinary fruits provide significant amounts of
 Because fruits have been such a major part of the human diet, various cultures have developed many different uses for fruits they do not depend on for food. For example:
* Bayberry fruits provide a wax often used to make candles;
* Many dry fruits are used as decorations or in dried flower arrangements (e.g., annual honesty, cotoneaster, lotus, milkweed, unicorn plant, and
Because fruits have been such a major part of the human diet, various cultures have developed many different uses for fruits they do not depend on for food. For example:
* Bayberry fruits provide a wax often used to make candles;
* Many dry fruits are used as decorations or in dried flower arrangements (e.g., annual honesty, cotoneaster, lotus, milkweed, unicorn plant, and
Images of fruit development from flowers
at bioimages.Vanderbilt.edu (archived 18 February 2007)
at bioimages.Vanderbilt.edu (archived 25 April 2017)
( from California Rare Fruit Growers, Inc.)
Photo ID of Fruits
( by Capt. Pawanexh Kohli) * {{Authority control Pollination Types of food
botany
Botany, also called plant science, is the branch of natural science and biology studying plants, especially Plant anatomy, their anatomy, Plant taxonomy, taxonomy, and Plant ecology, ecology. A botanist or plant scientist is a scientist who s ...
, a fruit is the seed
In botany, a seed is a plant structure containing an embryo and stored nutrients in a protective coat called a ''testa''. More generally, the term "seed" means anything that can be Sowing, sown, which may include seed and husk or tuber. Seeds ...
-bearing structure in flowering plant
Flowering plants are plants that bear flowers and fruits, and form the clade Angiospermae (). The term angiosperm is derived from the Ancient Greek, Greek words (; 'container, vessel') and (; 'seed'), meaning that the seeds are enclosed with ...
s (angiosperms) that is formed from the ovary
The ovary () is a gonad in the female reproductive system that produces ova; when released, an ovum travels through the fallopian tube/ oviduct into the uterus. There is an ovary on the left and the right side of the body. The ovaries are end ...
after flowering.
Fruits are the means by which angiosperms disseminate their seeds. Edible fruits in particular have long propagated using the movements of humans and other animals in a symbiotic relationship that is the means for seed dispersal for the one group and nutrition
Nutrition is the biochemistry, biochemical and physiology, physiological process by which an organism uses food and water to support its life. The intake of these substances provides organisms with nutrients (divided into Macronutrient, macro- ...
for the other; humans, and many other animals, have become dependent on fruits as a source of food. Consequently, fruits account for a substantial fraction of the world's agricultural output, and some (such as the apple
An apple is a round, edible fruit produced by an apple tree (''Malus'' spp.). Fruit trees of the orchard or domestic apple (''Malus domestica''), the most widely grown in the genus, are agriculture, cultivated worldwide. The tree originated ...
and the pomegranate) have acquired extensive cultural and symbolic meanings.
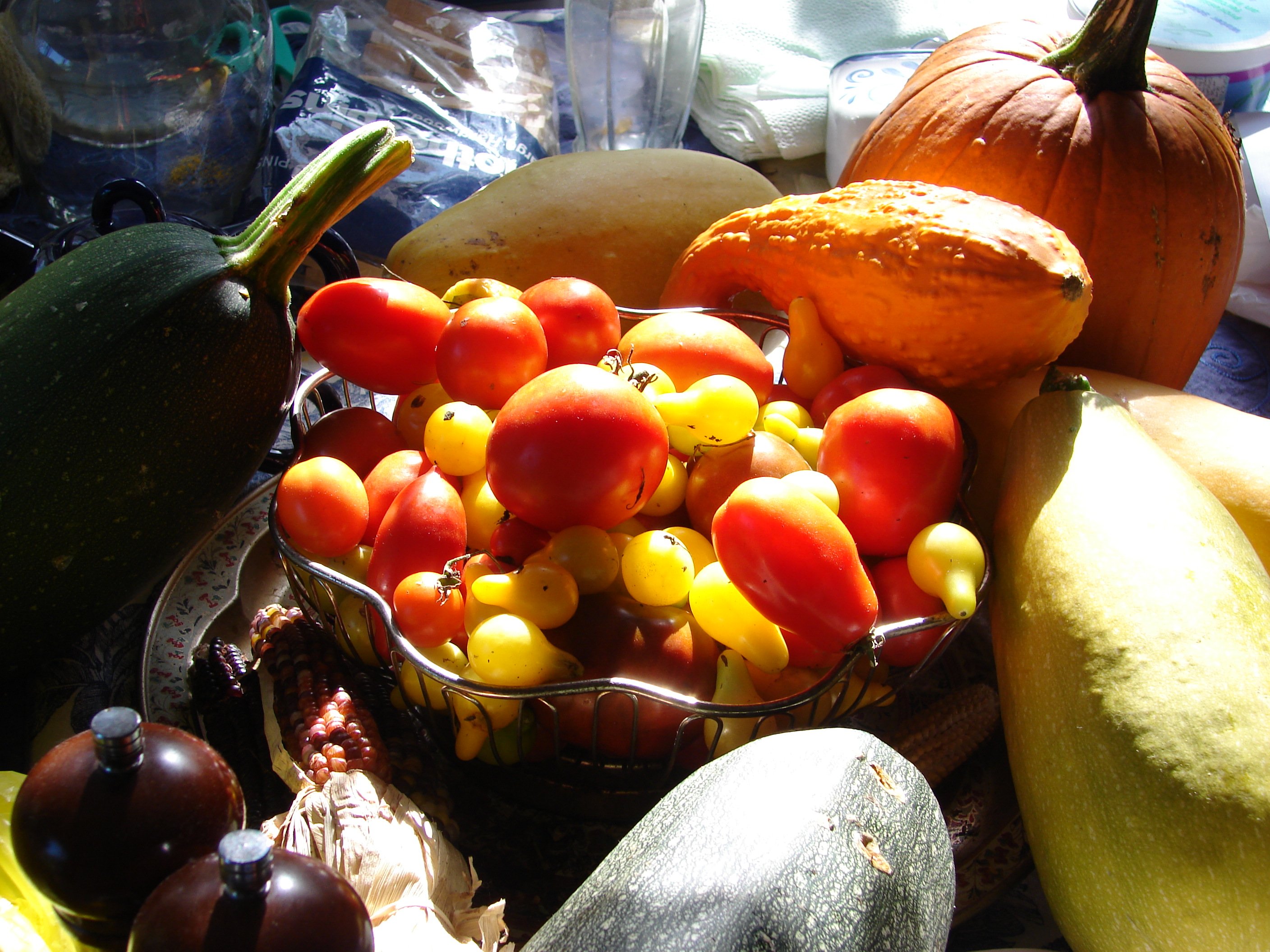
In common language and culinary usage, ''fruit'' normally means the seed-associated fleshy structures (or produce) of plants that typically are sweet (or sour) and edible in the raw state, such as apples, bananas, grapes, lemons, oranges, and strawberries. In botanical usage, the term ''fruit'' also includes many structures that are not commonly called as such in everyday language, such as nuts, bean pods, corn kernels, tomatoes, and wheat grains.
Botanical vs. culinary
 Many common language terms used for fruit and seeds differ from botanical classifications. For example, in botany, a ''fruit'' is a ripened
Many common language terms used for fruit and seeds differ from botanical classifications. For example, in botany, a ''fruit'' is a ripened ovary
The ovary () is a gonad in the female reproductive system that produces ova; when released, an ovum travels through the fallopian tube/ oviduct into the uterus. There is an ovary on the left and the right side of the body. The ovaries are end ...
or carpel that contains seeds, e.g., an orange, pomegranate, tomato or a pumpkin. A '' nut'' is a type of fruit (and not a seed), and a ''seed'' is a ripened ovule.
In culinary language, a ''fruit'' is the sweet- or not sweet- (even sour-) tasting produce of a specific plant (e.g., a peach, pear or lemon); ''nuts'' are hard, oily, non-sweet plant produce in shells ( hazelnut, acorn
The acorn is the nut (fruit), nut of the oaks and their close relatives (genera ''Quercus'', ''Notholithocarpus'' and ''Lithocarpus'', in the family Fagaceae). It usually contains a seedling surrounded by two cotyledons (seedling leaves), en ...
). '' Vegetables'', so-called, typically are savory or non-sweet produce ( zucchini, lettuce, broccoli, and tomato). but some may be sweet-tasting (sweet potato).
 Examples of botanically classified fruit that are typically called vegetables include cucumber, pumpkin, and squash (all are cucurbits); beans, peanuts, and peas (all legumes); and corn, eggplant,
Examples of botanically classified fruit that are typically called vegetables include cucumber, pumpkin, and squash (all are cucurbits); beans, peanuts, and peas (all legumes); and corn, eggplant, bell pepper
The bell pepper (also known as sweet pepper, paprika, pepper, capsicum or, in some parts of the US midwest, mango) is the fruit of plants in the Grossum Group of the species ''Capsicum annuum''. Cultivars of the plant produce fruits in diff ...
(or sweet pepper), and tomato
The tomato (, ), ''Solanum lycopersicum'', is a plant whose fruit is an edible Berry (botany), berry that is eaten as a vegetable. The tomato is a member of the nightshade family that includes tobacco, potato, and chili peppers. It originate ...
. Many spices are fruits, botanically speaking, including black pepper, chili pepper
Chili peppers, also spelled chile or chilli ( ), are varieties of fruit#Berries, berry-fruit plants from the genus ''Capsicum'', which are members of the nightshade family Solanaceae, cultivated for their pungency. They are used as a spice to ...
, cumin and allspice. In contrast, rhubarb is often called a fruit when used in making pies, but the edible produce of rhubarb is actually the leaf stalk or petiole of the plant. Edible gymnosperm seeds are often given fruit names, e.g., ginkgo nuts and pine nuts.
Botanically, a cereal grain, such as corn, rice
Rice is a cereal grain and in its Domestication, domesticated form is the staple food of over half of the world's population, particularly in Asia and Africa. Rice is the seed of the grass species ''Oryza sativa'' (Asian rice)—or, much l ...
, or wheat
Wheat is a group of wild and crop domestication, domesticated Poaceae, grasses of the genus ''Triticum'' (). They are Agriculture, cultivated for their cereal grains, which are staple foods around the world. Well-known Taxonomy of wheat, whe ...
is a kind of fruit (termed a caryopsis). However, the fruit wall is thin and fused to the seed coat, so almost all the edible grain-fruit is actually a seed.
Structure

 The outer layer, often edible, of most fruits is called the ''pericarp''. Typically formed from the ovary, it surrounds the seeds; in some species, however, other structural tissues contribute to or form the edible portion. The pericarp may be described in three layers from outer to inner, i.e., the ''epicarp'', ''mesocarp'' and ''endocarp''.
Fruit that bears a prominent pointed terminal projection is said to be ''beaked''.
The outer layer, often edible, of most fruits is called the ''pericarp''. Typically formed from the ovary, it surrounds the seeds; in some species, however, other structural tissues contribute to or form the edible portion. The pericarp may be described in three layers from outer to inner, i.e., the ''epicarp'', ''mesocarp'' and ''endocarp''.
Fruit that bears a prominent pointed terminal projection is said to be ''beaked''.
Development
A fruit results from the fertilizing and maturing of one or more flowers. Thegynoecium
Gynoecium (; ; : gynoecia) is most commonly used as a collective term for the parts of a flower that produce ovules and ultimately develop into the fruit and seeds. The gynoecium is the innermost whorl (botany), whorl of a flower; it consists ...
, which contains the '' stigma-style-ovary'' system, is centered in the flower-head, and it forms all or part of the fruit. Inside the ovary(ies) are one or more ovules. Here begins a complex sequence called '' double fertilization'': a female gametophyte produces an egg cell for the purpose of fertilization. (A female gametophyte is called a '' megagametophyte'', and also called the '' embryo sac''.) After double fertilization, the ovules will become seeds.
Ovules are fertilized in a process that starts with pollination, which is the movement of pollen from the stamens to the stigma-style-ovary system within the flower-head. After pollination, a pollen tube grows from the (deposited) pollen through the stigma down the style into the ovary to the ovule. Two sperm are transferred from the pollen to a megagametophyte. Within the megagametophyte, one sperm unites with the egg, forming a zygote
A zygote (; , ) is a eukaryote, eukaryotic cell (biology), cell formed by a fertilization event between two gametes.
The zygote's genome is a combination of the DNA in each gamete, and contains all of the genetic information of a new individ ...
, while the second sperm enters the central cell forming the endosperm mother cell, which completes the double fertilization process. Later, the zygote will give rise to the embryo of the seed, and the endosperm mother cell will give rise to endosperm
The endosperm is a tissue produced inside the seeds of most of the flowering plants following double fertilization. It is triploid (meaning three chromosome sets per nucleus) in most species, which may be auxin-driven. It surrounds the Embryo#Pla ...
, a nutritive tissue used by the embryo.
Fruit formation is associated with meiosis, a central aspect of sexual reproduction in flowering plants. During meiosis homologous chromosomes replicate, recombine and randomly segregate, and then undergo segregation of sister chromatids to produce haploid cells. Union of haploid nuclei from pollen
Pollen is a powdery substance produced by most types of flowers of seed plants for the purpose of sexual reproduction. It consists of pollen grains (highly reduced Gametophyte#Heterospory, microgametophytes), which produce male gametes (sperm ...
and ovule ( fertilisation), occurring either by self- or cross- pollination, leads to the formation of a diploid zygote
A zygote (; , ) is a eukaryote, eukaryotic cell (biology), cell formed by a fertilization event between two gametes.
The zygote's genome is a combination of the DNA in each gamete, and contains all of the genetic information of a new individ ...
that can then develop into an embryo within the emerging seed. Repeated fertilisations within the ovary
The ovary () is a gonad in the female reproductive system that produces ova; when released, an ovum travels through the fallopian tube/ oviduct into the uterus. There is an ovary on the left and the right side of the body. The ovaries are end ...
are accompanied by maturation of the ovary to form the fruit.
As the ovules develop into seeds, the ovary begins to ripen and the ovary wall, the ''pericarp'', may become fleshy (as in berries or drupes), or it may form a hard outer covering (as in nuts). In some multi-seeded fruits, the extent to which a fleshy structure develops is proportional to the number of fertilized ovules. The pericarp typically is differentiated into two or three distinct layers; these are called the ''exocarp'' (outer layer, also called epicarp), ''mesocarp'' (middle layer), and ''endocarp'' (inner layer).
In some fruits, the sepal
A sepal () is a part of the flower of angiosperms (flowering plants). Usually green, sepals typically function as protection for the flower in bud, and often as support for the petals when in bloom., p. 106
Etymology
The term ''sepalum'' ...
s, petals, stamen
The stamen (: stamina or stamens) is a part consisting of the male reproductive organs of a flower. Collectively, the stamens form the androecium., p. 10
Morphology and terminology
A stamen typically consists of a stalk called the filament ...
s or the style of the flower fall away as the fleshy fruit ripens. However, for simple fruits derived from an '' inferior ovary'' – i.e., one that lies the attachment of other floral parts – there are parts (including petals, sepals, and stamens) that fuse with the ovary and ripen with it. For such a case, when floral parts other than the ovary form a significant part of the fruit that develops, it is called an accessory fruit. Examples of accessory fruits include apple, rose hip, strawberry, and pineapple.
Because several parts of the flower besides the ovary may contribute to the structure of a fruit, it is important to understand how a particular fruit forms. There are three general modes of fruit development:
* Apocarpous fruits develop from a ''single flower'' (while having one or more separate, unfused, carpels); they are the simple fruits.
* Syncarpous fruits develop from a ''single gynoecium
Gynoecium (; ; : gynoecia) is most commonly used as a collective term for the parts of a flower that produce ovules and ultimately develop into the fruit and seeds. The gynoecium is the innermost whorl (botany), whorl of a flower; it consists ...
'' (having two or more carpels fused together).
* Multiple fruits form from many flowers – i.e., an inflorescence of flowers.
androecium
The stamen (: stamina or stamens) is a part consisting of the male reproductive organs of a flower. Collectively, the stamens form the androecium., p. 10
Morphology and terminology
A stamen typically consists of a stalk called the filament ...
parts (a), the petals (p), and the sepals (s) all converge and attach to the receptacle (r). (Ovary=gynoecium (g).)
File:Noni fruit dev.jpg, upright 1.5, In the noni, flowers are produced in time-sequence along the stem. It is possible to see a progression of flowering, fruit development, and fruit ripening.
Tweelinggroei appels.jpg, Twin apples
Classification of fruits
 Consistent with the three modes of fruit development, plant scientists have classified fruits into three main groups: simple fruits, aggregate fruits, and multiple (or composite) fruits. The groupings reflect how the ovary and other flower organs are arranged and how the fruits develop, but they are not evolutionarily relevant as diverse plant taxa may be in the same group.
While the section of a
Consistent with the three modes of fruit development, plant scientists have classified fruits into three main groups: simple fruits, aggregate fruits, and multiple (or composite) fruits. The groupings reflect how the ovary and other flower organs are arranged and how the fruits develop, but they are not evolutionarily relevant as diverse plant taxa may be in the same group.
While the section of a fungus
A fungus (: fungi , , , or ; or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as one ...
that produces spore
In biology, a spore is a unit of sexual reproduction, sexual (in fungi) or asexual reproduction that may be adapted for biological dispersal, dispersal and for survival, often for extended periods of time, in unfavourable conditions. Spores fo ...
s is called a ''fruiting'' body, fungi are members of the fungi kingdom and not of the plant kingdom.
Simple fruits
Simple fruits are the result of the ripening-to-fruit of a simple or compound ovary in a ''single flower'' with a ''single pistil''. In contrast, a single flower with numerous pistils typically produces an aggregate fruit; and the merging of several flowers, or a 'multiple' of flowers, results in a 'multiple' fruit. A simple fruit is further classified as either dry or fleshy. To distribute their seeds, dry fruits may split open and discharge their seeds to the winds, which is called dehiscence. Or the distribution process may rely upon the decay and degradation of the fruit to expose the seeds; or it may rely upon the eating of fruit and excreting of seeds by frugivores – both are called indehiscence. Fleshy fruits do not split open, but they also are indehiscent and they may also rely on frugivores for distribution of their seeds. Typically, the entire outer layer of the ovary wall ripens into a potentially edible pericarp. Types of dry simple fruits, (with examples) include: * Achene – most commonly seen in aggregate fruits (e.g.,strawberry
The garden strawberry (or simply strawberry; ''Fragaria × ananassa'') is a widely grown Hybrid (biology), hybrid plant cultivated worldwide for its fruit. The genus ''Fragaria'', the strawberries, is in the rose family, Rosaceae. The fruit ...
, see below).
* Capsule – ( Brazil nut: botanically, it is not a nut).
* Caryopsis – (cereal grains, including wheat
Wheat is a group of wild and crop domestication, domesticated Poaceae, grasses of the genus ''Triticum'' (). They are Agriculture, cultivated for their cereal grains, which are staple foods around the world. Well-known Taxonomy of wheat, whe ...
, rice
Rice is a cereal grain and in its Domestication, domesticated form is the staple food of over half of the world's population, particularly in Asia and Africa. Rice is the seed of the grass species ''Oryza sativa'' (Asian rice)—or, much l ...
, oats, barley).
* Cypsela – an achene-like fruit derived from the individual florets in a capitulum: ( dandelion).
* Fibrous drupe – (coconut
The coconut tree (''Cocos nucifera'') is a member of the palm tree family (biology), family (Arecaceae) and the only living species of the genus ''Cocos''. The term "coconut" (or the archaic "cocoanut") can refer to the whole coconut palm, ...
, walnut: botanically, neither is a true nut.).
* Follicle – follicles are formed from a single carpel, and opens by one suture: ( milkweed); also commonly seen in aggregate fruits: ( magnolia, peony).
* Legume – ( bean, pea, peanut: botanically, the peanut is the seed of a legume, not a nut).
* Loment – a type of indehiscent legume: ( sweet vetch or wild potato).
* Nut – ( beechnut, hazelnut, acorn
The acorn is the nut (fruit), nut of the oaks and their close relatives (genera ''Quercus'', ''Notholithocarpus'' and ''Lithocarpus'', in the family Fagaceae). It usually contains a seedling surrounded by two cotyledons (seedling leaves), en ...
(of the oak): botanically, these are true nuts).
* Samara – ( ash, elm, maple key).
* Schizocarp, see below – ( carrot seed).
* Silique – ( radish seed).
* Silicle – ( shepherd's purse).
* Utricle – ( beet, '' Rumex'').
Fruits in which part or all of the ''pericarp'' (fruit wall) is fleshy at maturity are termed ''fleshy simple fruits''.
Types of fleshy simple fruits, (with examples) include:
* Berry – the berry is the most common type of fleshy fruit. The entire outer layer of the ovary wall ripens into a potentially edible "pericarp", (see below).
* Stone fruit or drupe – the definitive characteristic of a drupe is the hard, "lignified" stone (sometimes called the "pit"). It is derived from the ovary wall of the flower: apricot, cherry, olive
The olive, botanical name ''Olea europaea'' ("European olive"), is a species of Subtropics, subtropical evergreen tree in the Family (biology), family Oleaceae. Originating in Anatolia, Asia Minor, it is abundant throughout the Mediterranean ...
, peach
The peach (''Prunus persica'') is a deciduous tree first domesticated and Agriculture, cultivated in China. It bears edible juicy fruits with various characteristics, most called peaches and the glossy-skinned, non-fuzzy varieties called necta ...
, plum, mango.
* Pome – the pome fruits: apple
An apple is a round, edible fruit produced by an apple tree (''Malus'' spp.). Fruit trees of the orchard or domestic apple (''Malus domestica''), the most widely grown in the genus, are agriculture, cultivated worldwide. The tree originated ...
s, pears, rosehips, saskatoon berry, etc., are a syncarpous (fused) fleshy fruit, a simple fruit, developing from a half-inferior ovary. Pomes are of the family Rosaceae.
Berries


 Berries are a type of simple fleshy fruit that issue from a single ovary. (The ovary itself may be compound, with several carpels.) The botanical term ''true berry'' includes grapes, currants, cucumbers, eggplants (aubergines), tomatoes, chili peppers, and bananas, but excludes certain fruits that are called "-berry" by culinary custom or by common usage of the term – such as strawberries and raspberries. Berries may be formed from one or more carpels (i.e., from the simple or compound ovary) from the same, single flower. Seeds typically are embedded in the fleshy interior of the ovary.
Examples include:
*
Berries are a type of simple fleshy fruit that issue from a single ovary. (The ovary itself may be compound, with several carpels.) The botanical term ''true berry'' includes grapes, currants, cucumbers, eggplants (aubergines), tomatoes, chili peppers, and bananas, but excludes certain fruits that are called "-berry" by culinary custom or by common usage of the term – such as strawberries and raspberries. Berries may be formed from one or more carpels (i.e., from the simple or compound ovary) from the same, single flower. Seeds typically are embedded in the fleshy interior of the ovary.
Examples include:
* Tomato
The tomato (, ), ''Solanum lycopersicum'', is a plant whose fruit is an edible Berry (botany), berry that is eaten as a vegetable. The tomato is a member of the nightshade family that includes tobacco, potato, and chili peppers. It originate ...
– in culinary terms, the tomato is regarded as a vegetable, but it is botanically classified as a fruit and a berry.
* Banana – the fruit has been described as a "leathery berry". In cultivated varieties, the seeds are diminished nearly to non-existence.
* Pepo – berries with skin that is hardened: cucurbits, including gourds, squash, melons.
* Hesperidium – berries with a rind and a juicy interior: most citrus
''Citrus'' is a genus of flowering trees and shrubs in the family Rutaceae. Plants in the genus produce citrus fruits, including important crops such as oranges, mandarins, lemons, grapefruits, pomelos, and limes.
''Citrus'' is nativ ...
fruit.
* Cranberry, gooseberry, redcurrant, grape.
The strawberry, regardless of its appearance, is classified as a dry, not a fleshy fruit. Botanically, it is not a berry; it is an aggregate-accessory fruit, the latter term meaning the fleshy part is derived not from the plant's ovaries but from the receptacle that holds the ovaries
The ovary () is a gonad in the female reproductive system that produces ova; when released, an ovum travels through the fallopian tube/oviduct into the uterus. There is an ovary on the left and the right side of the body. The ovaries are endocr ...
.Esau, K. (1977). ''Anatomy of seed plants''. John Wiley and Sons, New York. Numerous dry achenes are attached to the outside of the fruit-flesh; they appear to be seeds but each is actually an ovary of a flower, with a seed inside.
Schizocarps are dry fruits, though some appear to be fleshy. They originate from syncarpous ovaries but do not actually dehisce; rather, they split into segments with one or more seeds. They include a number of different forms from a wide range of families, including carrot, parsnip, parsley, cumin.
Aggregate fruits
 An aggregate fruit is also called an aggregation, or '' etaerio''; it develops from a single flower that presents numerous simple pistils. Each pistil contains one carpel; together, they form a fruitlet. The ultimate (fruiting) development of the aggregation of pistils is called an ''aggregate fruit'', ''etaerio fruit'', or simply an ''etaerio''.
Different types of aggregate fruits can produce different etaerios, such as achenes, drupelets, follicles, and berries.
* For example, the Ranunculaceae species, including '' Clematis'' and '' Ranunculus'', produces an etaerio of achenes;
* '' Rubus'' species, including raspberry: an etaerio of drupelets;
* '' Calotropis'' species: an etaerio of follicles fruit;
* '' Annona'' species: an etaerio of berries.
Some other broadly recognized species and their etaerios (or aggregations) are:
* Teasel; fruit is an aggregation of cypselas.
* Tuliptree; fruit is an aggregation of samaras.
* Magnolia and peony; fruit is an aggregation of follicles.
* American sweet gum; fruit is an aggregation of capsules.
* Sycamore; fruit is an aggregation of achenes.
The pistils of the
An aggregate fruit is also called an aggregation, or '' etaerio''; it develops from a single flower that presents numerous simple pistils. Each pistil contains one carpel; together, they form a fruitlet. The ultimate (fruiting) development of the aggregation of pistils is called an ''aggregate fruit'', ''etaerio fruit'', or simply an ''etaerio''.
Different types of aggregate fruits can produce different etaerios, such as achenes, drupelets, follicles, and berries.
* For example, the Ranunculaceae species, including '' Clematis'' and '' Ranunculus'', produces an etaerio of achenes;
* '' Rubus'' species, including raspberry: an etaerio of drupelets;
* '' Calotropis'' species: an etaerio of follicles fruit;
* '' Annona'' species: an etaerio of berries.
Some other broadly recognized species and their etaerios (or aggregations) are:
* Teasel; fruit is an aggregation of cypselas.
* Tuliptree; fruit is an aggregation of samaras.
* Magnolia and peony; fruit is an aggregation of follicles.
* American sweet gum; fruit is an aggregation of capsules.
* Sycamore; fruit is an aggregation of achenes.
The pistils of the raspberry
The raspberry is the edible fruit of several plant species in the genus ''Rubus'' of the Rosaceae, rose family, most of which are in the subgenus ''Rubus#Modern classification, Idaeobatus''. The name also applies to these plants themselves. Ras ...
are called ''drupelets'' because each pistil is like a small drupe attached to the receptacle. In some bramble fruits, such as blackberry, the receptacle, an accessory part, elongates and then develops as part of the fruit, making the blackberry an aggregate-accessory fruit. The strawberry is also an aggregate-accessory fruit, of which the seeds are contained in the achenes. Notably in all these examples, the fruit develops from a single flower, with numerous pistils.
Hybrid fruits
 Hybrid fruits are created through the controlled speciation of fruits that creates new varieties and cross-breeds. Hybrids are grown using plant propagation to create new cultivars. This may introduce an entirely new type of fruit or improve the properties of an existing fruit.
Hybrid fruits are created through the controlled speciation of fruits that creates new varieties and cross-breeds. Hybrids are grown using plant propagation to create new cultivars. This may introduce an entirely new type of fruit or improve the properties of an existing fruit.
Examples
* Nectaplum * Pluot * Tangelo * Orangequat * Garden strawberry * Plumcot * Rangpur * Blood lime * Ugli fruit * TayberryMultiple fruits
A multiple fruit is formed from a cluster of flowers, (a 'multiple' of flowers) – also called an ''inflorescence
In botany, an inflorescence is a group or cluster of flowers arranged on a plant's Plant stem, stem that is composed of a main branch or a system of branches. An inflorescence is categorized on the basis of the arrangement of flowers on a mai ...
''. Each ('smallish') flower produces a single fruitlet, which, as all develop, all merge into one mass of fruit. Examples include pineapple, fig, mulberry, Osage orange
''Maclura pomifera'', commonly known as the Osage orange ( ), is a small deciduous tree or large shrub, native to the south-central United States. It typically grows about tall. The distinctive fruit, a multiple fruit that resembles an immatur ...
, and breadfruit
Breadfruit (''Artocarpus altilis'') is a species of flowering tree in the mulberry and jackfruit family ( Moraceae) believed to have been selectively bred in Polynesia from the breadnut ('' Artocarpus camansi''). Breadfruit was spread into ...
. An inflorescence (a cluster) of white flowers, called a head, is produced first. After fertilization, each flower in the cluster develops into a drupe; as the drupes expand, they develop as a '' connate'' organ, merging into a multiple fleshy fruit called a ''syncarp''.
Progressive stages of multiple flowering and fruit development can be observed on a single branch of the Indian mulberry, or '' noni''. During the sequence of development, a progression of second, third, and more inflorescences are initiated in turn at the head of the branch or stem.
Accessory fruit forms
Fruits may incorporate tissues derived from other floral parts besides the ovary, including the receptacle, hypanthium, petals, or sepals. Accessory fruits occur in all three classes of fruit development – simple, aggregate, and multiple. Accessory fruits are frequently designated by the hyphenated term showing both characters. For example, a pineapple is a multiple-accessory fruit, a blackberry is an aggregate-accessory fruit, and an apple is a simple-accessory fruit.Table of fleshy fruit examples
Seedless fruits
Seedlessness is an important feature of some fruits of commerce. Commercial cultivars of bananas and pineapples are examples of seedless fruits. Some cultivars ofcitrus
''Citrus'' is a genus of flowering trees and shrubs in the family Rutaceae. Plants in the genus produce citrus fruits, including important crops such as oranges, mandarins, lemons, grapefruits, pomelos, and limes.
''Citrus'' is nativ ...
fruits (especially grapefruit, mandarin oranges, navel oranges, satsumas), table grapes, and of watermelons are valued for their seedlessness. In some species, seedlessness is the result of '' parthenocarpy'', where fruits set without fertilization. Parthenocarpic fruit-set may (or may not) require pollination, but most seedless citrus fruits require a stimulus from pollination to produce fruit. Seedless bananas and grapes are triploids, and seedlessness results from the abortion of the embryonic plant that is produced by fertilization, a phenomenon known as '' stenospermocarpy'', which requires normal pollination and fertilization.
Seed dispersal
Variations in fruit structures largely depend on the modes of dispersal applied to their seeds. Dispersal is achieved by wind or water, by explosive dehiscence, and by interactions with animals. Some fruits present their outer skins or shells coated with spikes or hooked burrs; these evolved either to deter would-be foragers from feeding on them or to serve to attach themselves to the hair, feathers, legs, or clothing of animals, thereby using them as dispersal agents. These plants are termed zoochorous; common examples include cocklebur, unicorn plant, and beggarticks (or Spanish needle). By developments of mutual evolution, the fleshy produce of fruits typically appeals to hungry animals, such that the seeds contained within are taken in, carried away, and later deposited (i.e., defecated) at a distance from the parent plant. Likewise, the nutritious, oily kernels of nuts typically motivate birds and squirrels to hoard them, burying them in soil to retrieve later during the winter of scarcity; thereby, uneaten seeds are sown effectively under natural conditions to germinate and grow a new plant some distance away from the parent. Other fruits have evolved flattened and elongated wings or helicopter-like blades, e.g., elm, maple, and tuliptree. This mechanism increases dispersal distance away from the parent via wind. Other wind-dispersed fruit have tiny " parachutes", e.g., dandelion, milkweed, salsify.Coconut
The coconut tree (''Cocos nucifera'') is a member of the palm tree family (biology), family (Arecaceae) and the only living species of the genus ''Cocos''. The term "coconut" (or the archaic "cocoanut") can refer to the whole coconut palm, ...
fruits can float thousands of miles in the ocean, thereby spreading their seeds. Other fruits that can disperse via water are nipa palm and screw pine.
Some fruits have evolved propulsive mechanisms that fling seeds substantial distances – perhaps up to in the case of the sandbox tree – via explosive dehiscence or other such mechanisms (see impatiens and squirting cucumber).
Food uses

 A large variety of fruits – fleshy (simple) fruits from apples to berries to watermelon; dry (simple) fruits including beans and rice and coconuts; aggregate fruits including strawberries, raspberries, blackberries, pawpaw; and multiple fruits such as pineapple, fig, mulberries – are commercially valuable as human food. They are eaten both fresh and as jams, marmalade and other fruit preserves. They are used extensively in manufactured and processed foods (cakes, cookies, baked goods, flavorings, ice cream, yogurt, canned vegetables, frozen vegetables and meals) and beverages such as fruit juices and alcoholic beverages (brandy, fruit beer, wine). Spices like vanilla, black pepper, paprika, and allspice are derived from berries. Olive fruit is pressed for
A large variety of fruits – fleshy (simple) fruits from apples to berries to watermelon; dry (simple) fruits including beans and rice and coconuts; aggregate fruits including strawberries, raspberries, blackberries, pawpaw; and multiple fruits such as pineapple, fig, mulberries – are commercially valuable as human food. They are eaten both fresh and as jams, marmalade and other fruit preserves. They are used extensively in manufactured and processed foods (cakes, cookies, baked goods, flavorings, ice cream, yogurt, canned vegetables, frozen vegetables and meals) and beverages such as fruit juices and alcoholic beverages (brandy, fruit beer, wine). Spices like vanilla, black pepper, paprika, and allspice are derived from berries. Olive fruit is pressed for olive oil
Olive oil is a vegetable oil obtained by pressing whole olives (the fruit of ''Olea europaea'', a traditional Tree fruit, tree crop of the Mediterranean Basin) and extracting the oil.
It is commonly used in cooking for frying foods, as a cond ...
and similar processing is applied to other oil-bearing fruits and vegetables. Some fruits are available all year round, while others (such as blackberries and apricots in the UK) are subject to seasonal availability.
Fruits are also used for socializing and gift-giving in the form of fruit baskets and fruit bouquets.
Typically, many botanical fruits – "vegetables" in culinary parlance – (including tomato, green beans, leaf greens, bell pepper, cucumber, eggplant, okra, pumpkin, squash, zucchini) are bought and sold daily in fresh produce markets and greengroceries and carried back to kitchens, at home or restaurant, for preparation of meals.
Storage
All fruits benefit from proper post-harvest care, and in many fruits, the plant hormone ethylene causes ripening. Therefore, maintaining most fruits in an efficient cold chain is optimal for post-harvest storage, with the aim of extending and ensuring shelf life.Why Cold Chain for Fruits:Nutritional value
 A meta-analysis of 83 studies showed fruit or vegetable consumption is associated with reduced markers of inflammation (reduced tumor necrosis factor and C-reactive protein) and enhanced immune cell profile (increased gamma delta T cells).
Various culinary fruits provide significant amounts of
A meta-analysis of 83 studies showed fruit or vegetable consumption is associated with reduced markers of inflammation (reduced tumor necrosis factor and C-reactive protein) and enhanced immune cell profile (increased gamma delta T cells).
Various culinary fruits provide significant amounts of fiber
Fiber (spelled fibre in British English; from ) is a natural or artificial substance that is significantly longer than it is wide. Fibers are often used in the manufacture of other materials. The strongest engineering materials often inco ...
and water, and many are generally high in vitamin C. An overview of numerous studies showed that fruits (e.g., whole apples or whole oranges) are satisfying (filling) by simply eating and chewing them.
The dietary fiber consumed in eating fruit promotes satiety, and may help to control body weight and aid reduction of blood cholesterol, a risk factor for cardiovascular diseases. Fruit consumption is under preliminary research for the potential to improve nutrition and affect chronic diseases. Regular consumption of fruit is generally associated with reduced risks of several diseases and functional declines associated with aging.
Food safety
For food safety, the CDC recommends proper fruit handling and preparation to reduce the risk of food contamination and foodborne illness. Fresh fruits and vegetables should be carefully selected; at the store, they should not be damaged or bruised; and precut pieces should be refrigerated or surrounded by ice. All fruits and vegetables should be rinsed before eating. This recommendation also applies to produce with rinds or skins that are not eaten. It should be done just before preparing or eating to avoid premature spoilage. Fruits and vegetables should be kept separate from raw foods like meat, poultry, and seafood, as well as from utensils that have come in contact with raw foods. Fruits and vegetables that are not going to be cooked should be thrown away if they have touched raw meat, poultry, seafood, or eggs. All cut, peeled, or cooked fruits and vegetables should be refrigerated within two hours. After a certain time, harmful bacteria may grow on them and increase the risk of foodborne illness.Allergies
Fruit allergies make up about 10 percent of all food-related allergies.Nonfood uses
wheat
Wheat is a group of wild and crop domestication, domesticated Poaceae, grasses of the genus ''Triticum'' (). They are Agriculture, cultivated for their cereal grains, which are staple foods around the world. Well-known Taxonomy of wheat, whe ...
). Ornamental trees and shrubs are often cultivated for their colorful fruits, including beautyberry, cotoneaster, holly, pyracantha, skimmia, and viburnum.
* Fruits of opium poppy are the source of opium
Opium (also known as poppy tears, or Lachryma papaveris) is the dried latex obtained from the seed Capsule (fruit), capsules of the opium poppy ''Papaver somniferum''. Approximately 12 percent of opium is made up of the analgesic alkaloid mor ...
, which contains the drugs codeine and morphine, as well as the biologically inactive chemical theabaine from which the drug oxycodone is synthesized.
* Osage orange
''Maclura pomifera'', commonly known as the Osage orange ( ), is a small deciduous tree or large shrub, native to the south-central United States. It typically grows about tall. The distinctive fruit, a multiple fruit that resembles an immatur ...
fruits are used to repel cockroaches.
* Many fruits provide natural dyes (e.g., cherry, mulberry, sumac, and walnut).
* Dried gourds are used as bird houses, cups, decorations, dishes, musical instruments, and water jugs.
* Pumpkins are carved into Jack-o'-lanterns for Halloween
Halloween, or Hallowe'en (less commonly known as Allhalloween, All Hallows' Eve, or All Saints' Eve), is a celebration geography of Halloween, observed in many countries on 31 October, the eve of the Western Christianity, Western Christian f ...
.
* The fibrous core of the mature and dry Luffa fruit is used as a sponge.
* The spiny fruit of burdock or cocklebur inspired the invention of Velcro
Velcro IP Holdings LLC, trading as Velcro Companies and commonly referred to as Velcro (pronounced ), is a British privately held company, founded by Swiss electrical engineer George de Mestral in the 1950s. It is the original manufacturer of ho ...
.
* Coir fiber from coconut
The coconut tree (''Cocos nucifera'') is a member of the palm tree family (biology), family (Arecaceae) and the only living species of the genus ''Cocos''. The term "coconut" (or the archaic "cocoanut") can refer to the whole coconut palm, ...
shells is used for brushes, doormats, floor tiles, insulation, mattresses, sacking, and as a growing medium for container plants. The shell of the coconut fruit is used to make bird houses, bowls, cups, musical instruments, and souvenir heads.
* The hard and colorful grain fruits of Job's tears are used as decorative beads for jewelry, garments, and ritual objects.
* Fruit is often a subject of still life paintings.
See also
* Fruit tree * Fruitarianism * List of countries by fruit production * List of culinary fruits * List of foods * List of fruit dishesReferences
Further reading
* Gollner, Adam J. (2010). ''The Fruit Hunters: A Story of Nature, Adventure, Commerce, and Obsession''. Scribner. . * Watson, R. R., and Preedy, V.R. (2010, eds.). ''Bioactive Foods in Promoting Health: Fruits and Vegetables''. Academic Press. .External links
Images of fruit development from flowers
at bioimages.Vanderbilt.edu (archived 18 February 2007)
at bioimages.Vanderbilt.edu (archived 25 April 2017)
( from California Rare Fruit Growers, Inc.)
Photo ID of Fruits
( by Capt. Pawanexh Kohli) * {{Authority control Pollination Types of food