fjords and channels of Chile on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The southern coast of
Consecuencias de la tala maderera colonial en los bosques de alece de Chiloé, sur de Chile (Siglos XVI-XIX)*
''
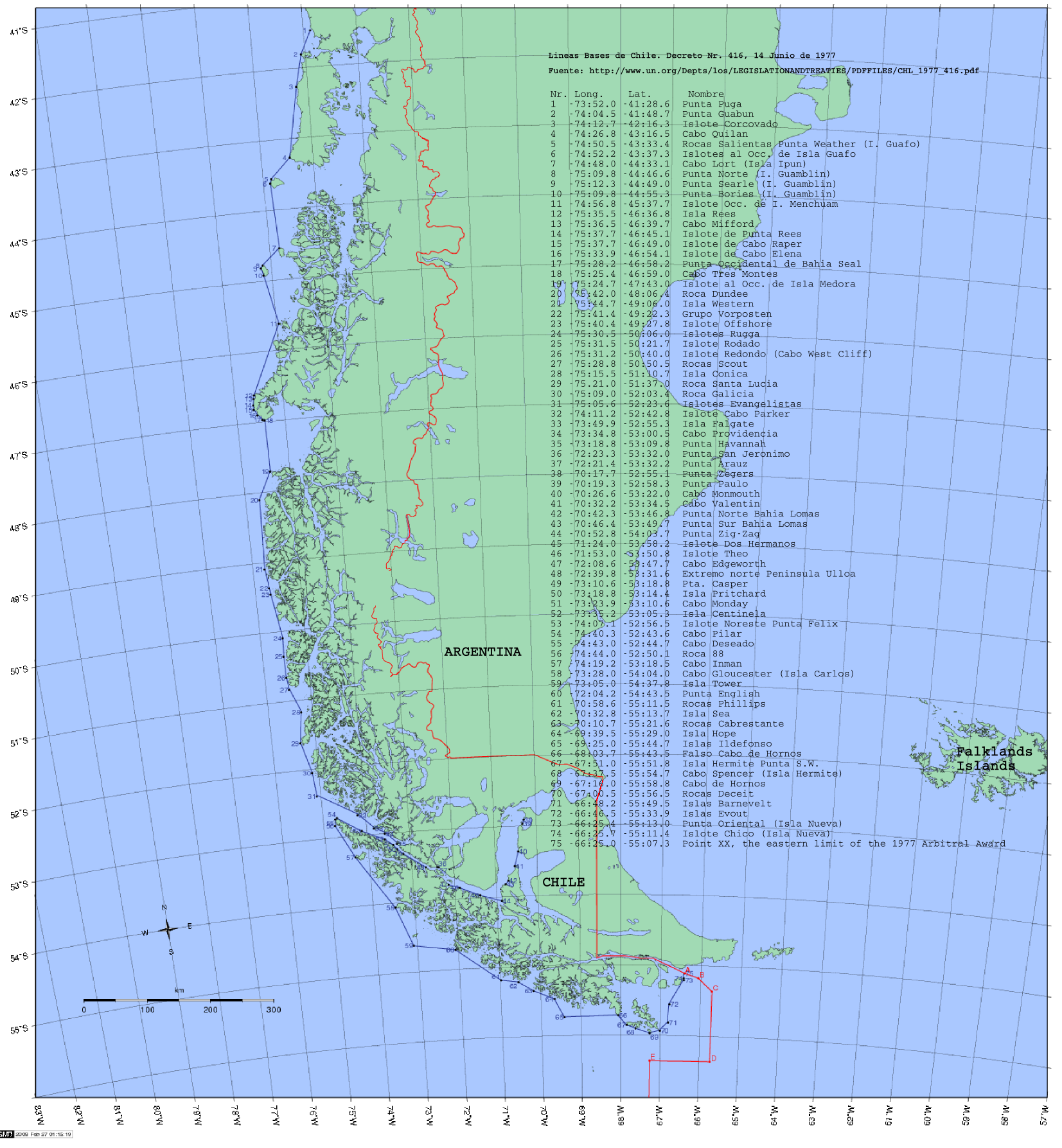 All waters between the Chilean baselines and the continental shoreline are
All waters between the Chilean baselines and the continental shoreline are
 In order to carry significant quantities of persons, vehicles, and cargo directly onto an unimproved shore to supply the islands and coastal region including settlements, the
In order to carry significant quantities of persons, vehicles, and cargo directly onto an unimproved shore to supply the islands and coastal region including settlements, the
 In order to open a direct passage from the Moraleda Channel to the Messier Channel without to go out into the open Pacific Ocean to round the Taitao Peninsula, the Chilean Government ordered in 1937 the construction of a
In order to open a direct passage from the Moraleda Channel to the Messier Channel without to go out into the open Pacific Ocean to round the Taitao Peninsula, the Chilean Government ordered in 1937 the construction of a
 *
*
File:0 125 2574 Puerto Edén (Villa Puerto Edén) - Chilenische Fjorde.jpg, Puerto Edén - Messier-Canal
Image:Fiordo Comau.jpg, Comau Fjord in Pumalín Park
Image:BeagleChannelGlacier.jpg, Romanche Glacier at Beagle Channel
File:0 125 2589 Puerto Edén (Villa Puerto Edén) - Chilenische Fjorde.jpg, Puerto Edén - Messier-Canal
Image:Beagle Channel 2006.JPG, Beagle Channel, January 2006
File:00 2605 Ship wreck in Chile (Patagonia).jpg, Messier-Canal
File:00 0597 Puerto Edén - a place in the fjords in Chilean Patagonia.jpg, Puerto Edén - Messier-Canal
Image:MV Logos.jpg, Shipwreck ''Logos'' in the Beagle Channel
Image:Chili-Puerto Edén.jpg,
Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of land between the Andes to the eas ...
presents a large number of fjord
In physical geography, a fjord or fiord () is a long, narrow inlet with steep sides or cliffs, created by a glacier. Fjords exist on the coasts of Alaska, Antarctica, British Columbia, Chile, Denmark, Germany, Greenland, the Faroe Islands, Icel ...
s and fjord-like channels from the latitudes of Cape Horn
Cape Horn ( es, Cabo de Hornos, ) is the southernmost headland of the Tierra del Fuego archipelago of southern Chile, and is located on the small Hornos Island. Although not the most southerly point of South America (which are the Diego Ramí ...
(55° S) to Reloncaví Estuary
Reloncaví Estuary (Spanish: Esturario de Reloncaví, archaic: Sin Fondo) is a fjord off Reloncaví Sound, located in the Los Lagos Region of Chile. Several National Parks and Wilderness Areas are situated in the vicinity of this fjord. Among t ...
(42° S). Some fjords and channels are important navigable channels providing access to ports like Punta Arenas
Punta Arenas (; historically Sandy Point in English) is the capital city of Chile's southernmost region, Magallanes and Antarctica Chilena. The city was officially renamed as Magallanes in 1927, but in 1938 it was changed back to "Punta Are ...
, Puerto Chacabuco
Puerto Chacabuco is a Chilean town in Aisén commune. Administratively it belongs to Aysén Province in Aysén del General Carlos Ibáñez del Campo Region and is located at the head of Aisén Fjord. It is the main port of the region, a port o ...
and Puerto Natales
Puerto Natales is a city in Chilean Patagonia. It is the capital of both the commune of Natales and the province of Última Esperanza, one of the four provinces that make up the Magallanes and Antartica Chilena Region in the southernmost part ...
.
History
Indigenous peoples
The earliest known inhabitants of the fjords and channels were, from north to south, the Chono, Alacalufe andYaghan Yaghan, Yagán or Yahgan may refer to:
* Yahgan people, an ethnic group of Argentina and Chile
* Yahgan language, their language
* Yaghan (dog), an extinct domesticated fox
See also
* Yagan (disambiguation)
* Yagha, a province of Burkina Faso ...
, all of whom shared a life style as canoe-faring hunter-gatherers. They also shared physical traits such as being of low stature, long-headed (''Dolichocephalic''), and having a "low face".Trivero Rivera 2005, p. 42. Despite similarities their languages were completely different.Trivero Rivera 2005, p. 33. The Chono moved around in the area from Chiloé Archipelago
The Chiloé Archipelago ( es, Archipiélago de Chiloé, , ) is a group of islands lying off the coast of Chile, in the Los Lagos Region. It is separated from mainland Chile by the Chacao Channel in the north, the Sea of Chiloé in the east and t ...
to 50° S and the Alacalufe from 46° S to the Strait of Magellan
The Strait of Magellan (), also called the Straits of Magellan, is a navigable sea route in southern Chile separating mainland South America to the north and Tierra del Fuego to the south. The strait is considered the most important natural ...
. Thus both groups overlapped in Gulf of Penas, Guayaneco Archipelago and other islands. Yaghans inhabited a reduced area south of Tierra del Fuego
Tierra del Fuego (, ; Spanish for "Land of the Fire", rarely also Fireland in English) is an archipelago off the southernmost tip of the South American mainland, across the Strait of Magellan. The archipelago consists of the main island, Isla ...
.
It is often assumed that Chonos were the people who left behind most of the abundant Pre-Historic shell middens (chonchales) of Chiloé Archipelago
The Chiloé Archipelago ( es, Archipiélago de Chiloé, , ) is a group of islands lying off the coast of Chile, in the Los Lagos Region. It is separated from mainland Chile by the Chacao Channel in the north, the Sea of Chiloé in the east and t ...
, yet this claim is unverified.Trivero Rivera 2005, p. 39. Guaitecas Archipelago made up the southern limit of Pre-Hispanic agriculture as noted by the mention of the cultivation of potatoes
The potato is a starchy food, a tuber of the plant ''Solanum tuberosum'' and is a root vegetable native to the Americas. The plant is a perennial in the nightshade family Solanaceae.
Wild potato species can be found from the southern United ...
by a Spanish expedition in 1557.
Both Chonos and Alacalufes used '' Pilgerodendron uviferum'' as firewood as well as wood for rows, boats and houses.
Colonial expeditions and decline of the Chono
Pedro de Valdivia
Pedro Gutiérrez de Valdivia or Valdiva (; April 17, 1497 – December 25, 1553) was a Spanish conquistador and the first royal governor of Chile. After serving with the Spanish army in Italy and Flanders, he was sent to South America in 1534, wh ...
sought originally to conquer all of southern South America to the Straits of Magellan
The Strait of Magellan (), also called the Straits of Magellan, is a navigable sea route in southern Chile separating mainland South America to the north and Tierra del Fuego to the south. The strait is considered the most important natural pas ...
(53° S). He did however only reach Reloncaví Sound
Reloncaví Sound or ''Seno de Reloncaví'' is a body of water immediately south of Puerto Montt, a port city in the Los Lagos Region of Chile. It is the place where the Chilean Central Valley meets the Pacific Ocean.
The Calbuco Archipelago comp ...
(41°45' S). Later in 1567 Chiloé Archipelago
The Chiloé Archipelago ( es, Archipiélago de Chiloé, , ) is a group of islands lying off the coast of Chile, in the Los Lagos Region. It is separated from mainland Chile by the Chacao Channel in the north, the Sea of Chiloé in the east and t ...
(42°30' S) was conquered, from there on southern expansion of the Spanish Empire halted. The Spanish are thought to have lacked incentives for further conquests south. The indigenous populations were scarce and had ways of life that differed from the sedentary agricultural life the Spanish were accustomed to. The harsh climate in the fjords and channels of Patagonia may also have deterred further expansion. Indeed, even in Chiloé did the Spanish encounter difficulties to adapt as their attempts to base the economy on gold extraction and a "hispanic-mediterranean" agricultural model failed.Torrejón, Fernando; Cisternas, Marco; Alvial, Ingrid and Torres, Laura. 2011Consecuencias de la tala maderera colonial en los bosques de alece de Chiloé, sur de Chile (Siglos XVI-XIX)*
''
Magallania
''Magallania'' is an academic journal published by the University of Magallanes. It publishes articles on social sciences and humanities regarding Patagonia, Tierra del Fuego, and Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and lea ...
''. Vol. 39(2):75–95.
During colonial times, the fjords and channels of Patagonia
Patagonia () refers to a geographical region that encompasses the southern end of South America, governed by Argentina and Chile. The region comprises the southern section of the Andes Mountains with lakes, fjords, temperate rainforests, and g ...
were first explored by the Spaniards
Spaniards, or Spanish people, are a Romance ethnic group native to Spain. Within Spain, there are a number of national and regional ethnic identities that reflect the country's complex history, including a number of different languages, both ...
. There were a number of motivations for their explorations, including a desire to Christianize indigenous peoples, to prevent intrusions of foreign powers into territory claimed by Spain, to increase geographic knowledge of the zone, and finally, to search for a mythical city called City of the Caesars
The City of the Caesars (Spanish Ciudad de los Césares), also variously known as ''City of Patagonia'', ''the Wandering City'', ''Trapalanda'' or ''Trapananda'', ''Lin Lin'' or ''Elelín'', is a mythical city of South America. It was supposedly ...
. False rumors of European settlements near the Straits of Magellan led the Spanish to organize the Antonio de Vea expedition of 1675–1676, the largest expedition to the date. In 1792, the viceroy of Peru ordered the exploration of the Patagonian channels in order to find an entrance to the interior of Patagonia. The said order was carried of by José de Moraleda who led an expedition that visited many of the main channels of the zone.
Following the decline of the Chono populations in the archipelago in the 18th century, the area gained a reputation of "emptiness" among Chileans akin to the description of eastern Patagonia as a "desert." However, the islands were often visited and traversed in the 19th century by fishermen, lumberjack
Lumberjacks are mostly North American workers in the logging industry who perform the initial harvesting and transport of trees for ultimate processing into forest products. The term usually refers to loggers in the era (before 1945 in the Unite ...
s, and hunters from Chiloé. This makes it clear that many areas that were traversed by explorers were already known to the inhabitants of southern Chiloé who visited these areas for wood, fish or hunting.
Over-all the physical infrastructure of the Spanish in the fjords and channels during the colonial period was negligible and consisted of a few chapels built in the 1610s and 1620s and a wooden fortress built in 1750. All these buildings were abandoned after a few years.
19th century: Explorations and first settlements
Chilean and European exploration
In the early to mid 19th century, explorations by hydrographers like Robert FitzRoy and Francisco Hudson increased knowledge on the channels. With Hudson's death in 1859 Francisco Vidal Gormaz continued the explorations, a duty thatEnrique Simpson
Enrique Simpson Baeza (Valparaíso, 1835–Valparaíso, May 17, 1901) was a Chilean Navy officer and explorer. Simpson mapped the archipelagoes and coast of Aysén Region onboard of the corvette '' Chacabuco'' in the 1870s. Among his feats is the r ...
assumed in the 1870s. The channels south of the Isthmus of Ofqui were explored in detail by Chilean government agent Hans Steffen in the late 19th century.
During his explorations and charting in the second half of the 19th century Vidal Gormaz became critical of the work of Robert FitzRoy and Charles Darwin
Charles Robert Darwin ( ; 12 February 1809 – 19 April 1882) was an English naturalist, geologist, and biologist, widely known for his contributions to evolutionary biology. His proposition that all species of life have descended ...
whom according to him had failed acknowledge the importance of the Patagonian islands.
''Pilgerodendron'' boom
Felipe Westhoff Felipe Arnold Westhoff Rodhius was a 19th-century entrepreneur known for his role in the logging of ''Pilgerodendron uviferum'' and the founding of Melinka in Guaitecas Archipelago in 1860. Westhoff was an ethnic German who migrated to South Americ ...
, a German-Lithuanian immigrant who operated a '' Pilgerodendron uviferum'' logging business from Ancud, founded Melinka
Melinka is a Chilean town in Aysén Province, Aysén Region. It is located on Ascención Island and is the administrative center of the commune of Guaitecas since 1979.
The town is on a small peninsula off the main island, and shelters a smal ...
in Guaitecas Archipelago in 1860. This was the first permanent settlement in the archipelago. Chilean authorities granted Westhoff exclusive rights on ''Pilgerodendron'' extraction in the archipelago and bestowed him the title of '' subdelegado marítimo'' which gave him some duties and authority over the archipelago, in reality it meant little since he did no had the means to enforce the law or his rights. After Westhoff's retirement in the 1870s Ciriaco Álvarez Ciriaco Álvarez was a businessman from Chonchi, Chiloé who rose to prominence in the exploitation of ''Pilgerodendron uviferum'' ( es, ciprés de las Guaitecas) in the southern Chilean archipelagoes. His dominance of the industry led him being du ...
rose to prominence as the foremost ''Pilgerodendron'' businessman. The chief export products of Álvarez were poles
Poles,, ; singular masculine: ''Polak'', singular feminine: ''Polka'' or Polish people, are a West Slavic nation and ethnic group, who share a common history, culture, the Polish language and are identified with the country of Poland in ...
and vine training stacks that went to northern Chile and Peru
, image_flag = Flag of Peru.svg
, image_coat = Escudo nacional del Perú.svg
, other_symbol = Great Seal of the State
, other_symbol_type = National seal
, national_motto = "Firm and Happy f ...
. Álvarez business owned him the nickname of "The King of Pilgerodendron" ( es, El Rey del Ciprés) and had great effects on the incipient economic development
In the economics study of the public sector, economic and social development is the process by which the economic well-being and quality of life of a nation, region, local community, or an individual are improved according to targeted goals and ...
that came to link the archipelagoes of Chiloé, Guaitecas and Chonos.
Climate and geography
This route is mostly used by vessels desiring to avoid the heavy seas and bad weather so often experienced on passing into thePacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the conti ...
from the western end of the Strait of Magellan
The Strait of Magellan (), also called the Straits of Magellan, is a navigable sea route in southern Chile separating mainland South America to the north and Tierra del Fuego to the south. The strait is considered the most important natural ...
. The large full-powered mail steamers generally at once gain the open sea at Cape Pillar (at the west entrance of the Strait of Magellan), as experience has shown that time is thus saved to them; but vessels of less engine power, to which punctuality and dispatch is not so much an object as avoiding possible danger, will find the Patagonian Channels the best route.
The general features of these channels are high, abrupt shores, with innumerable peaks and headlands remarkably alike in character, their bold, rugged heads giving an appearance of gloomy grandeur rarely seen elsewhere. The shores are generally steep-to and the channels, for the most part, open and free, while the few dangers that exist are usually marked by kelp. The tides are regular and not strong, except in the English Narrows
English Narrows (Spanish ''Angostura Inglesa'') is a contracted passage in Messier Channel in the southwestern coast of Chile. Here it is only wide, but it presents no great difficulty or danger (excepting to very long vessels) unless a vessel go ...
.
In the case of the two above mentioned and some other fjords, these waterways proved of value as transport lanes when western Patagonia was settled and incorporated into Chile. On the other hand, the fjords have served as a natural barrier preventing north-south land travel in Chilean Patagonia.
Legal status of the waterways
 All waters between the Chilean baselines and the continental shoreline are
All waters between the Chilean baselines and the continental shoreline are internal waters
According to the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea, a nation's internal waters include waters on the side of the baseline of a nation's territorial waters that is facing toward the land, except in archipelagic states. It includes wat ...
, according to the Chilean decree 416 of 14 June 1977 based in the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea
The United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS), also called the Law of the Sea Convention or the Law of the Sea Treaty, is an international agreement that establishes a legal framework for all marine and maritime activities. , 167 ...
, that is, the coastal nation is free to set laws, regulate any use, and use any resource. Foreign vessels have no right of passage within internal waters, and this lack of right to innocent passage is the key difference between internal waters and territorial waters
The term territorial waters is sometimes used informally to refer to any area of water over which a sovereign state has jurisdiction, including internal waters, the territorial sea, the contiguous zone, the exclusive economic zone, and potent ...
. Chile allows the use of the main waterways under maritime authority dispositions for the following navigation lanes (all names in Spanish):
a) throughout the Strait of Magellan:
Punta Dúngenes - Primera Angostura - Segunda Angostura, Paso Nuevo -Paso Inglés - Paso Tortuoso - Paso Largo - Paso del Mar - Cabo Pilar (and back).
b) from Cabo Tamar to isla San Pedro :
Cabo Tamar - Canal Smyth - Canal Mayne or Canal Gray - Paso Victoria - Estrecho Collingwood - Paso Farquhar - Canal Sarmiento - Angostura Guías - Canal Inocentes - Canal Concepción - Paso Caffin - Canal Trinidad - either Pacific Ocean, (and back) or to continue Canal Wide - either (east route) Canal Icy - Canal Grappler or (west route) Canal Escape - Paso del Abismo or Paso Piloto Pardo - Canal Escape; then Paso del Indio - Angostura Inglesa - Canal Messier to Isla San Pedro, (and back) or from Cabo Ladrillero to Canal Concepción to inner channels (and back)
c) From Strait of Magellan to Puerto Natales or Puerto Bories:
from Isla Brinkley - Seno Unión - Canal Morla Vicuña - Canal y angostura Kirke - Canal Valdés, Golfo Almirante Montt - Canal Señoret - Seno Última Esperanza - Puerto Natales - Puerto Bories (and back)
d) from Strait of Magellan to Puerto Williams:
from islote Anxious - Canal Magdalena - Canal Cockburn - Paso Brecknock or Canal Ocasión - Canal Unión - Paso Occidental - Paso Norte - Canal Ballenero- Canal O'Brien - Paso Timbales - Brazo noroeste del Canal Beagle - Canal Beagle - Puerto Williams (and back).(Chilean ships can use Paso Aguirre)
e) from Puerto Williams to Cabo de Hornos:
Canal Beagle - Paso Picton - Paso Richmond - to Cabo de Hornos (and back)
f) to the east Beagle Channel:
Ships coming from east can access through the eastern mouth, northeast of Isla Nueva or through the Pasos Richmond and Picton.
g) to Seno Otway and Seno Skyring:
from Isla Carlos III - Canal Jerónimo - Seno Otway - Canal Fitz-Roy - Seno Skyring to Bahía Mina Elena (and back).
h) to Isla Guarello:
from Isla Inocentes - Canal Concepción - Canal Oeste - Seno Contreras - Bahía Corbeta Papudo in Isla Guarello, (and back), or from Bahía Corbeta Papudo in Isla Guarello - Seno Contreras - Paso Metalero (and back).
i) throughout Chonos Archipelago:
*from isla Inchemó - Bahía Anna Pink - Boca Wickham - Canal Pulluche - Canal Chacabuco - Canal Errázuriz - Canal Moraleda until Gulf of Corcovado and Boca del Guafo (and back) or
*from isla Inchemó - Bahía Anna Pink - Boca Wickham - Canal Pulluche - Canal Utarupa - Canal Darwin -Canal Moraleda to Gulf of Corcovado and Boca del Guafo (and back) or
*from isla Auchilú, - Bahía Darwin - Canal Darwin - Canal Moraleda to Gulf of Corcovado and Boca del Guafo (and back) or
*from Bahía Adventure - Isla Liebre - Canal Niñualac - Canal Moraleda to Gulf of Corcovado and Boca del Guafo (and back).
j) to bahía Chacabuco:
from Canal Moraleda - Paso del Medio or Canal Pilcomayo or Canal Ferronave - Seno Aysén to Bahía Chacabuco (and back).
k) to Laguna San Rafael:
*from Canal Moraleda - Paso Casma - Canal Costa - Estero Elefante - Paso Quesahuén - Golfo Elefantes and Río Témpanos - Laguna San Rafael (and back) or
*from Canal Moraleda - Canal Errázuriz - Paso Tres Cruces - Estero Elefantes - Paso Quesahuén - Golfo Elefantes and Río Témpanos - Laguna San Rafael (and back).
l) through the inner channels of Chiloé:
from Boca del Guafo or Golfo Corcovado to Puerto Montt or to Golfo de Coronados, (and back) throughout the inner Channels heading to ports and bays
m) to Puerto Montt through Canal de Chacao:
from golfo Coronados - Canal de Chacao - Golfo de Ancud - Canal Calbuco or Paso Queullín - Seno de Reloncaví - Paso Guar - Puerto Montt (and back).
Transportation
Since it is impossible to reach all the region by road through Chile, the transport of persons and cargo must be done by ship or airplanes according to the public infrastructure provision.Ferry lanes
ferry
A ferry is a ship, watercraft or amphibious vehicle used to carry passengers, and sometimes vehicles and cargo, across a body of water. A passenger ferry with many stops, such as in Venice, Italy, is sometimes called a water bus or water ta ...
is the best suited ship type and most of them are basically a cargo boat with no fancy, cruiser-type accommodation, even though they have managed to improve their customer service. There are 150 major ships sailing in the southern regions of Chile.
Cruise ship
Cruise ships are large passenger ships used mainly for vacationing. Unlike ocean liners, which are used for transport, cruise ships typically embark on round-trip voyages to various ports-of-call, where passengers may go on tours known as ...
s also operate between the main ports of the region and offer a journey that is considered an experience in itself, due to the slow way of entering this magnificent landscape of narrow channels and solitary islands.
The Carretera Austral requires the use of three ferries: a 30-minute crossing about south of the start of the highway in Puerto Montt
Puerto Montt (Mapuche: Meli Pulli) is a port city and commune in southern Chile, located at the northern end of the Reloncaví Sound in the Llanquihue Province, Los Lagos Region, 1,055 km to the south of the capital, Santiago. The commune ...
, a 5-hour crossing from Hornopirén
Hornopirén is a town ( es, pueblo) in the commune of Hualaihué in Palena Province, southern Chile. It lies along the northern portion of Carretera Austral
The Carretera Austral (CH-7, ''in English: Southern Way'') is the name given to Chil ...
( south of Puerto Montt) to Caleta Gonzalo and a 50-minute crossing from Puerto Yungay to Rio Bravo, connecting to the final of the highway.
With the exception of Chiloé Island
Chiloé Island ( es, Isla de Chiloé, , ) also known as Greater Island of Chiloé (''Isla Grande de Chiloé''), is the largest island of the Chiloé Archipelago off the west coast of Chile, in the Pacific Ocean. The island is located in southern ...
, the region is sparsely inhabited. The main ports are: Puerto Montt, Quellón, Chaitén, Melinka
Melinka is a Chilean town in Aysén Province, Aysén Region. It is located on Ascención Island and is the administrative center of the commune of Guaitecas since 1979.
The town is on a small peninsula off the main island, and shelters a smal ...
, Puerto Chacabuco
Puerto Chacabuco is a Chilean town in Aisén commune. Administratively it belongs to Aysén Province in Aysén del General Carlos Ibáñez del Campo Region and is located at the head of Aisén Fjord. It is the main port of the region, a port o ...
, Puyuguapi, Puerto Natales
Puerto Natales is a city in Chilean Patagonia. It is the capital of both the commune of Natales and the province of Última Esperanza, one of the four provinces that make up the Magallanes and Antartica Chilena Region in the southernmost part ...
, Punta Arenas
Punta Arenas (; historically Sandy Point in English) is the capital city of Chile's southernmost region, Magallanes and Antarctica Chilena. The city was officially renamed as Magallanes in 1927, but in 1938 it was changed back to "Punta Are ...
, Porvenir and Puerto Williams.
South of Chiloé, there are also small ports like Villa Puerto Edén
Villa Puerto Edén is a Chilean hamlet and minor port located in Wellington Island, in Natales commune, Última Esperanza Province, Magallanes Region. It is considered one of Chile's most isolated inhabited places together with Easter Island and ...
, Bahía Corbeta Papudo on Guarello Island
Guarello Island (Spanish: ''Isla Guarello'') is an island in Madre de Dios Archipelago in Magallanes Region. Guarello Island is in a limestone area that also includes Madre de Dios Island. The island has the world's southernmost limestone mine a ...
, Puerto Bories, Puerto Navarino, Puerto Toro, and Caleta Eugenia.This list doesn't include the lakes. Despite the name, Puerto Aisen is not a port.
The Isthmus of Ofqui canal project
canal
Canals or artificial waterways are waterways or engineered channels built for drainage management (e.g. flood control and irrigation) or for conveyancing water transport vehicles (e.g. water taxi). They carry free, calm surface f ...
from the San Rafael Lagoon through the isthmus (2,200 m long, 17 m wide, 5 m depth) to the Negro River, that later should be dredged . 1937 began the work on the ground, under the management of the railways department of the Ministry of Public Works. Work continued until May 1943 when funds ran out. The map on the right shows the ''Laguna San Rafael'' and the ''Golfo Elefantes'', they are the southernmost part of the Moraleda Channel. The ''Golfo San Esteban'' can be seen as the northernmost part of the Messier Channel.
Chacao Channel bridge
The Chacao Channel bridge, also known as Chiloé Bicentennial Bridge, is a planned bridge that is to link the island of Chiloé with mainlandChile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of land between the Andes to the eas ...
crossing the Chacao Channel
The Chacao Channel ( es, Canal de Chacao) is located in Los Lagos Region, Chile and separates Chiloé Island from mainland Chile. The channel was created during the Quaternary glaciations by successive glaciers that flowed down from the Andes ...
. It was one of the several projects that were planned to commemorate the Chile's bicentennial in 2010. If completed as a suspension bridge
A suspension bridge is a type of bridge in which the deck is hung below suspension cables on vertical suspenders. The first modern examples of this type of bridge were built in the early 1800s. Simple suspension bridges, which lack vertical ...
, it would be the largest such bridge in South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the sou ...
.
Main fjords and channels
Chacao to Guafo
Chacao Channel
The Chacao Channel ( es, Canal de Chacao) is located in Los Lagos Region, Chile and separates Chiloé Island from mainland Chile. The channel was created during the Quaternary glaciations by successive glaciers that flowed down from the Andes ...
::Access to the Sea of Chiloé
250px, Map of the Sea of Chiloé, located between Continental Chiloé ">Palena_Province.html" ;"title="Chiloé Island and Palena Province">Continental Chiloé
The sea of Chiloé (Spanish: ''Mar de Chiloé'' or ''Mar Chilote'') is a marginal sea ...
and Reloncaví Sound
Reloncaví Sound or ''Seno de Reloncaví'' is a body of water immediately south of Puerto Montt, a port city in the Los Lagos Region of Chile. It is the place where the Chilean Central Valley meets the Pacific Ocean.
The Calbuco Archipelago comp ...
::Settlements: Chacao
* Calbuco Channel
::Access to
::Settlements:
* Comau Fjord
::Access to
::Settlements:
* Dalcahue Channel
::Access to
::Settlements:
* Hornopirén Channel
::Access to Hornopirén area
::Settlements: Hornopirén
Hornopirén is a town ( es, pueblo) in the commune of Hualaihué in Palena Province, southern Chile. It lies along the northern portion of Carretera Austral
The Carretera Austral (CH-7, ''in English: Southern Way'') is the name given to Chil ...
* Piti Palena Fjord
Piti may refer to:
* Pīti, a mental factor in Buddhism
* PITI, the principal, interest, taxes, and insurance sum of a mortgage payment
* Piti (food), a soup dish of Central Asia
* Piti (footballer) (born 1981), Spanish footballer
* Piti, Guam
* Pi ...
::Access to
::Settlements: Raúl Marin
* Apiao Channel
::Access to
::Settlements:
* Paso Desertores
Paso or PASO may refer to:
People
* Fernando del Paso (born 1935), Mexican novelist
* Juan José Paso, (1758–1833), Argentine politician
Other uses
* Paso (float), an elaborate float made for religious processions
* Paso (theatre), a seventeen ...
::Access to
::Settlements:
*Reloncaví Estuary
Reloncaví Estuary (Spanish: Esturario de Reloncaví, archaic: Sin Fondo) is a fjord off Reloncaví Sound, located in the Los Lagos Region of Chile. Several National Parks and Wilderness Areas are situated in the vicinity of this fjord. Among t ...
::Access to Puelo River, Todos los Santos Lake
Lake Todos los Santos (Spanish for "All Saints Lake") is a lake located in the Los Lagos Region of southern Chile, 96 km northeast of the regional capital Puerto Montt and 76 km east of Puerto Varas, within the boundaries of the Vicent ...
and Vuriloche Pass
::Settlements: Canutillar, Cochamó
* Reñihué Fjord
::Access to Carretera Austral
::Settlements: Caleta Gonzalo
Guaitecas to the Gulf of Penas
* Aysén Fjord ::Access to Coyhaique area ::Settlements:Puerto Chacabuco
Puerto Chacabuco is a Chilean town in Aisén commune. Administratively it belongs to Aysén Province in Aysén del General Carlos Ibáñez del Campo Region and is located at the head of Aisén Fjord. It is the main port of the region, a port o ...
* Baker Channel
Baker Channel, also known as Calen Inlet, is a channel of Chile located in the Tortel, Aysén del General Carlos Ibáñez del Campo Region. The Baker River discharges into Martinez Inlet, the northern part of this large estuary. It penetrates t ...
::Access to Baker
A baker is a tradesperson who baking, bakes and sometimes Sales, sells breads and other products made of flour by using an oven or other concentrated heat source. The place where a baker works is called a bakery.
History
Ancient history
Si ...
and Pascua River
The Pascua River is a river located in the Aysén del General Carlos Ibáñez del Campo Region of Chile. In spite of being a short river, its drainage basin is the seventh-largest in the country due to the great size of the O'Higgins/San Martí ...
area
::Settlements: Caleta Tortel
* Estero Capquelan
::Access to
::Settlements:
* Mitchell Fjord
Mitchell Fjord is a 30- to 50-km long fjord in Aysén Region, Chile, stretching southeast from the vicinities of Baker Channel into the valley of Bravo River. Through a ferry based on Puerto Yungay, the channel provides access to the southernmos ...
::Access to Villa O'Higgins
__NOTOC__
Villa O'Higgins is a small town in the Aysén Region of southern Chile, located 220 km south of Cochrane and 550 km south of Coyhaique. Founded in 1966 and named after the Chilean independence hero Bernardo O'Higgins, it is the capital o ...
and O'Higgins Lake O’Higgins may refer to:
People
*O'Higgins (surname), lists notable people with the surname
*O'Higgins family
Places
*O'Higgins Region, Chile
* O'Higgins, Chile, commune in the Capitán Prat Province, Aysén Region, Chile
* Villa O'Higgins, the ...
::Settlements: Puerto Yungay
* Darwin Channel (not to be confused with Darwin Sound)
::Access to
::Settlements:
* Moraleda Channel
::Access to northern Aysén Region
The Aysén del General Carlos Ibáñez del Campo Region ( es, Región de Aysén, , '), often shortened to Aysén Region or Aisén,Examples of name usage1, official regional government site refers to the region as "Región de Aysén"., Chile's of ...
::Settlements:
* Puyuhuapi Channel
::Access to Villa La Tapera
::Settlements: Puerto Cisnes
Puerto Cisnes (Spanish for: "port swans") is a town and seaport in Cisnes commune, Aysén Province, Aysén del General Carlos Ibáñez del Campo Region in the Chilean Patagonia. The town is on the Puyuhuapi Channel at the outflow of Cisnes Rive ...
* Ventisquero Sound
::Access to
::Settlements:
Gulf of Penas to Straits of Magellan
* Messier Channel **English Narrows
English Narrows (Spanish ''Angostura Inglesa'') is a contracted passage in Messier Channel in the southwestern coast of Chile. Here it is only wide, but it presents no great difficulty or danger (excepting to very long vessels) unless a vessel go ...
** Guía Narrows
::Safe sea-lane from Central Chile to Punta Arenas
Punta Arenas (; historically Sandy Point in English) is the capital city of Chile's southernmost region, Magallanes and Antarctica Chilena. The city was officially renamed as Magallanes in 1927, but in 1938 it was changed back to "Punta Are ...
, Puerto Natales
Puerto Natales is a city in Chilean Patagonia. It is the capital of both the commune of Natales and the province of Última Esperanza, one of the four provinces that make up the Magallanes and Antartica Chilena Region in the southernmost part ...
and Tierra del Fuego
Tierra del Fuego (, ; Spanish for "Land of the Fire", rarely also Fireland in English) is an archipelago off the southernmost tip of the South American mainland, across the Strait of Magellan. The archipelago consists of the main island, Isla ...
::Settlements: Villa Puerto Edén
Villa Puerto Edén is a Chilean hamlet and minor port located in Wellington Island, in Natales commune, Última Esperanza Province, Magallanes Region. It is considered one of Chile's most isolated inhabited places together with Easter Island and ...
* Concepción Channel
Concepción Channel is an inside passage of the Chilean Patagonia. It extends from the point where Wide Channel and Trinidad Channel meet to the open sea. It is located at Earth Info, ''earth-info.nga.mil'' webpage: . and separates Madre de Dios ...
::Access to
::Settlements:
* Wide Channel
Wide Channel is an inside passage of the Chilean Patagonia. It is long, extending northward from the junction of Concepción Channel and Trinidad Channel, to Saumarez Island. The channel is located at .Earth Info, ''earth-info.nga.mil'' webpage: ...
::Access to
::Settlements:
* Inocentes Channel
Inocentes Channel (Spanish ''Canal Inocentes'') is a strait in Chile that reaches from the Guía Narrows (''Angostura Guías'') 18 miles to the northern extreme of Inocentes Island, where it joins the Concepción Channel. The south side of the str ...
::Access to
::Settlements:
* Sarmiento Channel
Sarmiento Channel is a principal Patagonia channel, which extends in a north–south direction. It begins with the Guia Narrows ('' Angostura Guía'') and is located in Magallanes y Antártica Chilena Region. The kawésqar people sailed its wat ...
::Safe sea-lane from Central Chile to Punta Arenas
Punta Arenas (; historically Sandy Point in English) is the capital city of Chile's southernmost region, Magallanes and Antarctica Chilena. The city was officially renamed as Magallanes in 1927, but in 1938 it was changed back to "Punta Are ...
, Puerto Natales
Puerto Natales is a city in Chilean Patagonia. It is the capital of both the commune of Natales and the province of Última Esperanza, one of the four provinces that make up the Magallanes and Antartica Chilena Region in the southernmost part ...
and Tierra del Fuego
Tierra del Fuego (, ; Spanish for "Land of the Fire", rarely also Fireland in English) is an archipelago off the southernmost tip of the South American mainland, across the Strait of Magellan. The archipelago consists of the main island, Isla ...
::Settlements:
* Señoret Channel
::Access to
::Settlements:
* Peel Fjord
::Access to
::Settlements:
*Eyre Fjord
Eyre Fjord is a fjord in Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of l ...
::Access to
::Settlements:
*Fallos Channel
''Fallos Channel'' (Spanish: ''Canal Fallos'') is a waterway in the Aisen Region of Chile that runs north of Ladrillero Channel between the Little Wellington Island and Prat Island at the east and Campana Island at the west.
It forms with the ...
::Access to
::Settlements:
*Trinidad Channel
Trinidad Channel is a channel in Chile that leads to seaward from the northern end of Concepción Channel, is exceedingly useful to pass out to the Pacific ocean from the Patagonian Channels in case it is desirable to avoid the possible delay occa ...
::Access to
::Settlements:
*Ladrillero Channel
The Ladrillero Channel is a strait between Angamos Island and Stosch Island in the Magallanes Region of Chile. It forms, with the Picton Channel and the Fallos Channel, an optional route to the Messier Channel-Grappler Channel-Wide Channel. It h ...
::Access to
::Settlements:
*Picton Channel
''Picton Channel'' (Spanish: ''Canal Picton'') is a waterway in the Magallanes Region of Chile that continues southward the Ladrillero Channel, and it runs between the Chipana Island (east) and Mornington Island (Chile) (west).
With the Ladril ...
::Access to
::Settlements:
* Covadonga Channel
::Access to
::Settlements:
* Albatros Channel
::Access to
::Settlements:
* Adalbert Channel
::Access to
::Settlements:
*Esteban Channel Esteban () is a Spanish male given name, derived from Greek Στέφανος (Stéphanos) and related to the English names Steven and Stephen. Although in its original pronunciation the accent is on the penultimate syllable, English-speakers tend ...
::Access to
::Settlements:
Tierra del Fuego and Puerto Natales
*Nelson Strait (Chile)
Nelson Strait is a channel in the Chilean Archipelago. It is located in Magallanes y Antártica Chilena Region of Chilean Patagonia.
The Strait opens in the west to the Pacific Ocean, at , between the Diego de Almagro Island to the north and Ra ...
::Access to
::Settlements:
* Fjord of the Mountains Fjord of the Mountains, also known as "Channel of the Mountains" (Spanish Canal de las Montañas), is located to the west of Puerto Natales, Chile and inside the boundaries of the Alacalufes National Reserve. It stretches 66 km from north to ...
::Access to
::Settlements:
* Smyth Channel
Smyth Channel () is a principal Patagonia channel. Its south arm is the southward continuation of the Sarmiento Channel and is located in Magallanes y Antártica Chilena Region. The Kawésqar people lived along its coast for thousands of year ...
::Safe sea-lane from Central Chile to Punta Arenas
Punta Arenas (; historically Sandy Point in English) is the capital city of Chile's southernmost region, Magallanes and Antarctica Chilena. The city was officially renamed as Magallanes in 1927, but in 1938 it was changed back to "Punta Are ...
, Puerto Natales
Puerto Natales is a city in Chilean Patagonia. It is the capital of both the commune of Natales and the province of Última Esperanza, one of the four provinces that make up the Magallanes and Antartica Chilena Region in the southernmost part ...
and Tierra del Fuego
Tierra del Fuego (, ; Spanish for "Land of the Fire", rarely also Fireland in English) is an archipelago off the southernmost tip of the South American mainland, across the Strait of Magellan. The archipelago consists of the main island, Isla ...
::Settlements:
* Seno Última Esperanza
::Access to
::Settlements:
* Eberhard Fjord
::Access to
::Settlements:
* Agostini Fjord
::Access to
::Settlements:
* Almirantazgo Fjord
Almirantazgo Fjord ( es, Fiordo Almirantazgo), also known as Almirantazgo Sound ( es, Seno Almirantazgo) or Admiralty Sound, is a Chilean fjord located in the far south of the country at .Earth Info, ''earth-info.nga.mil'' webpage: . The fjor ...
::Access to Cami Lake
Fagnano Lake ( es, Lago Fagnano), also called ''Lake Cami'' (), is a lake located on the Isla Grande de Tierra del Fuego, main island of the Tierra del Fuego archipelago, and shared by Argentina and Chile. The 645 km2 lake runs east–west f ...
in Tierra del Fuego
Tierra del Fuego (, ; Spanish for "Land of the Fire", rarely also Fireland in English) is an archipelago off the southernmost tip of the South American mainland, across the Strait of Magellan. The archipelago consists of the main island, Isla ...
::Settlements:
* Canal Whiteside
::Access to
::Settlements:
* Inútil Bay
300px, Satellite image of Inútil Bay and the Strait of Magellan. Selected settlements are marked with yellow dots.
Inútil Bay (Spanish: ''Bahía Inútil'') or Useless Bay is a bay in the western and Chilean part of Tierra del Fuego Island. Loc ...
::Access to
::Settlements:
* Seno Otway
Seno Otway is a large inland sound lying between Brunswick Peninsula and Riesco Island in southern Chile. Alternatively called Otway Sound, this natural waterway occupies a valley blocked by a large terminal moraine left by the retreat of a glacie ...
::Access to
::Settlements:
* Seno Skyring
Seno Skyring is a large inland sound lying north of Riesco Island and south of mainland South America in southern Chile. Alternatively called Skyring Sound, this natural waterway occupies a valley blocked by a large terminal moraine left by the re ...
::Access to
::Settlements:
* Beagle Channel
::Safe sea-lane between the South Atlantic
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the "Old World" of Africa, Europe a ...
and the South Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the continen ...
::Settlements: Puerto Navarino, Puerto Williams, Puerto Toro.
* Darwin Sound (not to be confused with Darwin Channel)
::Access to Beagle Channel from the Pacific and the Strait of Magellan
The Strait of Magellan (), also called the Straits of Magellan, is a navigable sea route in southern Chile separating mainland South America to the north and Tierra del Fuego to the south. The strait is considered the most important natural ...
::Settlements:
* Abra Channel
Abra Channel (Spanish ''Canal Abra'', formerly ''Sea Shell Channel'') is one of the three channels which connects Magellan Strait with the Pacific Ocean (Others are Bárbara Channel and Magdalena Channel). It is located between the Santa Inés Isl ...
:: Access to the Strait of Magellan
The Strait of Magellan (), also called the Straits of Magellan, is a navigable sea route in southern Chile separating mainland South America to the north and Tierra del Fuego to the south. The strait is considered the most important natural ...
from Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the conti ...
::Settlements:
* Magdalena Channel
350px, The channel is visible in the lower left corner.
Magdalena Channel () is a Chilean channel joining the Strait of Magellan with the Cockburn Channel and is part of a major navigation route which ultimately connects with the Beagle Channe ...
::Access to the Strait of Magellan
The Strait of Magellan (), also called the Straits of Magellan, is a navigable sea route in southern Chile separating mainland South America to the north and Tierra del Fuego to the south. The strait is considered the most important natural ...
from Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the conti ...
::Settlements:
* Cockburn Channel
The Cockburn Channel () is a channel that separates the Brecknock Peninsula, which is the westernmost projection of the Isla Grande de Tierra del Fuego, from Clarence Island, Capitán Aracena Island and other minor islands in Chile. It is located ...
::Access to the Strait of Magellan
The Strait of Magellan (), also called the Straits of Magellan, is a navigable sea route in southern Chile separating mainland South America to the north and Tierra del Fuego to the south. The strait is considered the most important natural ...
from Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the conti ...
, route from Beagle Channel to Strait of Magellan
::Settlements:
* Ballenero Channel
::Route from Beagle Channel to Strait of Magellan
::Settlements:
* Strait of Magellan
The Strait of Magellan (), also called the Straits of Magellan, is a navigable sea route in southern Chile separating mainland South America to the north and Tierra del Fuego to the south. The strait is considered the most important natural ...
** Punta Dúngenes
** Bahia Possession
** Primera Angostura
** Segunda Angostura
Segunda Angostura is a sound of the Strait of Magellan between the Patagonian mainland and Tierra del Fuego. It is located southwest of Primera Angostura, the narrowest part of the Strait between the island and the continent. The sound was named ...
** Cape Froward
** Evangelistas Lighthouse
The Evangelistas Lighthouse () is one of the most exposed, isolated and least accessible in the world. Sited on the Evangelistas Islets on Chile's continental shelf in the south-eastern Pacific Ocean, it is the landfall light for ships crossing ...
::Safe sea-lane between the South Atlantic
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the "Old World" of Africa, Europe a ...
and the South Pacific
::Settlements: Porvenir, Punta Arenas
Punta Arenas (; historically Sandy Point in English) is the capital city of Chile's southernmost region, Magallanes and Antarctica Chilena. The city was officially renamed as Magallanes in 1927, but in 1938 it was changed back to "Punta Are ...
, Camerón
* Murray Channel
::Connects Beagle Channel with Cape Horn
Cape Horn ( es, Cabo de Hornos, ) is the southernmost headland of the Tierra del Fuego archipelago of southern Chile, and is located on the small Hornos Island. Although not the most southerly point of South America (which are the Diego Ramí ...
through Bahía Nassau
:: Puerto Navarino
* Pitt Channel
::Access to
::Settlements:
Gallery
Villa Puerto Edén
Villa Puerto Edén is a Chilean hamlet and minor port located in Wellington Island, in Natales commune, Última Esperanza Province, Magallanes Region. It is considered one of Chile's most isolated inhabited places together with Easter Island and ...
in ''Paso del Indio''
Image:Caleta Tortel, Chile.jpg, Caleta Tortel in Baker Channel
Baker Channel, also known as Calen Inlet, is a channel of Chile located in the Tortel, Aysén del General Carlos Ibáñez del Campo Region. The Baker River discharges into Martinez Inlet, the northern part of this large estuary. It penetrates t ...
Image:Estuario de Reloncaví.jpg, Reloncaví Estuary
Reloncaví Estuary (Spanish: Esturario de Reloncaví, archaic: Sin Fondo) is a fjord off Reloncaví Sound, located in the Los Lagos Region of Chile. Several National Parks and Wilderness Areas are situated in the vicinity of this fjord. Among t ...
, Chilé's northernmost fjord
Image:090111-6 Above ビーグル水道.jpg, Aerial view of Beagle Channel
Image:Chile12.JPG, shipwreck in the Smyth Channel
Smyth Channel () is a principal Patagonia channel. Its south arm is the southward continuation of the Sarmiento Channel and is located in Magallanes y Antártica Chilena Region. The Kawésqar people lived along its coast for thousands of year ...
Image:2007-12-21 English-Narrows-Patagonian-Channels.JPG, MV ''Evangelistas'' passes English Narrows
English Narrows (Spanish ''Angostura Inglesa'') is a contracted passage in Messier Channel in the southwestern coast of Chile. Here it is only wide, but it presents no great difficulty or danger (excepting to very long vessels) unless a vessel go ...
early in the morning, in journey from Puerto Natales to its destination, Puerto Montt.
Image: 2019-03-14 CAPITÁIN LEONIDAS - IMO 5542705.jpg, Wreck of the ''Capitan Leonidas'' serves as a warning for the submerged Bajo Cotopaxi (Cotopaxi Bank) in the Messier Channel.
Image:Melinka.jpg, Aerial view of the Ascención Island, known as Melinka
Melinka is a Chilean town in Aysén Province, Aysén Region. It is located on Ascención Island and is the administrative center of the commune of Guaitecas since 1979.
The town is on a small peninsula off the main island, and shelters a smal ...
See also
* Archipelagoes of Patagonia * Geography of Chile *Islands of Chile The islands of Chile encompass the various islands that the government of Chile has sovereignty over. By far the majority of these are the islands in the south of the country. Chile has one of the world's longest coastlines, and one of the most dang ...
* List of Antarctic and subantarctic islands
* List of fjords, channels, sounds and straits of Chile
The information regarding fjords, channels, sound and straits of Chile on this page is compiled from the data supplied by the National Geospatial-Intelligence AgencyCountry Files (GNS)The NGA country data of Chile data was retrieved on 19 January ...
* List of islands of Chile
* List of lighthouses and lightvessels in Chile
In order to mark dangerous coastlines, hazardous shoals, reefs, safe entries to harbors the Chilean authorities maintain 650 lighthouses from the boundary to Peru until the Atlantic Ocean. Information on these lighthouses is presented in the follow ...
Notes
References
* * * * *United States Hydrographic Office
The United States Hydrographic Office prepared and published maps, charts, and nautical books required in navigation.
The office was established by an act of 21 June 1866 as part of the Bureau of Navigation, Department of the Navy.
It was trans ...
, South America Pilot (1916)
*
{{Authority control
Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of land between the Andes to the eas ...
Fjords
Straits of Chile
Temperate South America