Fibrosis on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Fibrosis, also known as fibrotic scarring, is a pathological wound healing in which
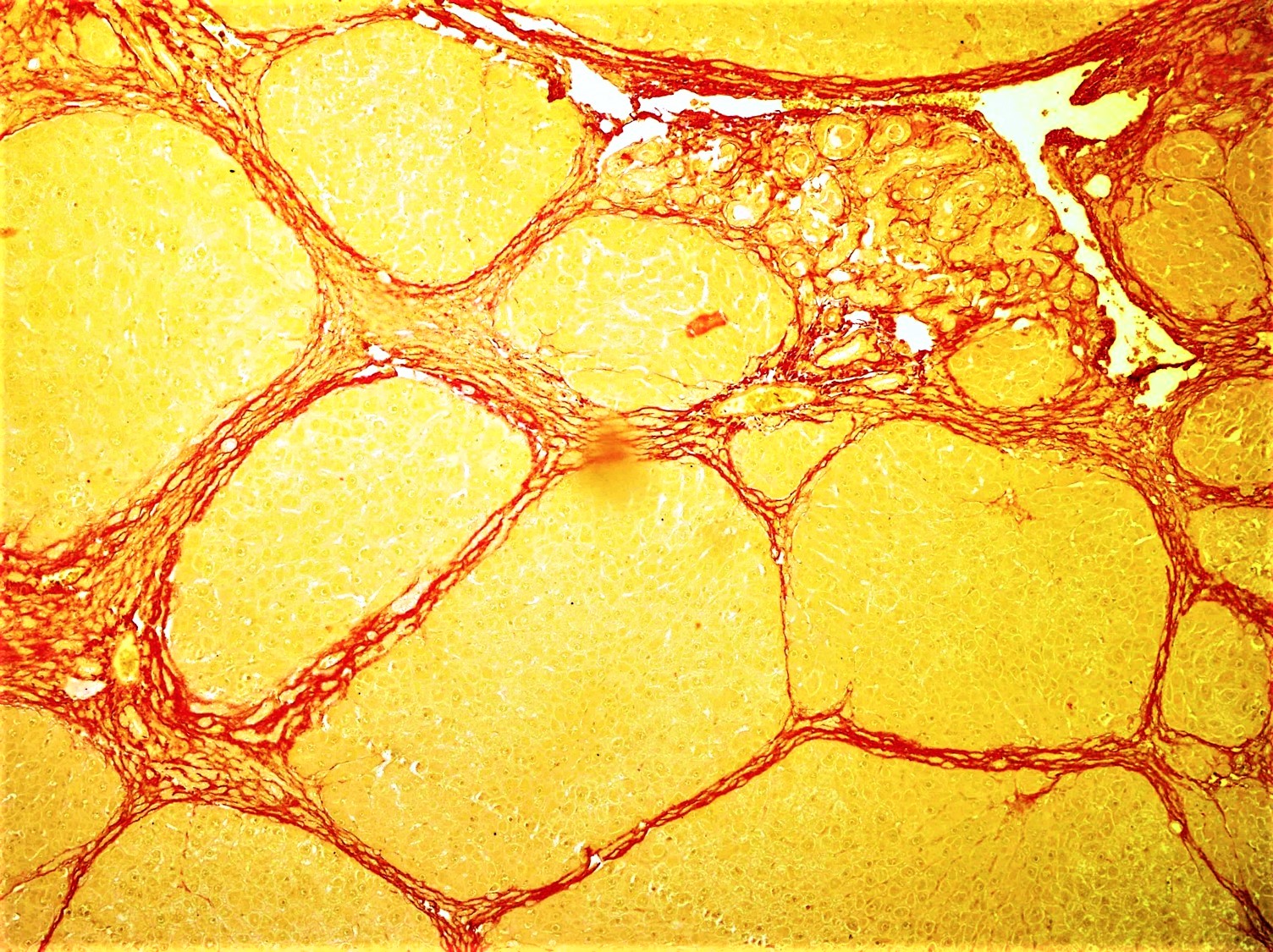 *
*
File:Histopathology of interstitial fibrosis in dilated cardiomyopathy.jpg, Healthy myocardium versus interstitial fibrosis in dilated cardiomyopathy. Alcian blue stain.
File:Histopathology of dense fibrous scar replacing myocyte loss in myocardial infarction.jpg, Replacement fibrosis in myocardial infarction, being boundless and dense.
connective tissue
Connective tissue is one of the four primary types of animal tissue, along with epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. It develops from the mesenchyme derived from the mesoderm the middle embryonic germ layer. Connective tiss ...
replaces normal parenchymal tissue to the extent that it goes unchecked, leading to considerable tissue remodelling and the formation of permanent scar tissue.
Repeated injuries, chronic inflammation and repair are susceptible to fibrosis where an accidental excessive accumulation of extracellular matrix components, such as the collagen is produced by fibroblasts, leading to the formation of a permanent fibrotic scar.
In response to injury, this is called scar
A scar (or scar tissue) is an area of fibrous tissue that replaces normal skin after an injury. Scars result from the biological process of wound repair in the skin, as well as in other organs, and tissues of the body. Thus, scarring is a ...
ring, and if fibrosis arises from a single cell line, this is called a fibroma
Fibromas are benign tumors that are composed of fibrous or connective tissue. They can grow in all organs, arising from mesenchyme tissue. The term "fibroblastic" or "fibromatous" is used to describe tumors of the fibrous connective tissue. Whe ...
. Physiologically, fibrosis acts to deposit connective tissue, which can interfere with or totally inhibit the normal architecture and function of the underlying organ or tissue. Fibrosis can be used to describe the pathological state of excess deposition of fibrous tissue, as well as the process of connective tissue deposition in healing. Defined by the pathological accumulation of extracellular matrix
In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM), also called intercellular matrix, is a three-dimensional network consisting of extracellular macromolecules and minerals, such as collagen, enzymes, glycoproteins and hydroxyapatite that provide s ...
(ECM) proteins, fibrosis results in scarring and thickening of the affected it is in essence an exaggerated wound healing response which interferes with normal organ function.
Physiology
Fibrosis is similar to the process of scarring, in that both involve stimulatedfibroblast
A fibroblast is a type of biological cell that synthesizes the extracellular matrix and collagen, produces the structural framework ( stroma) for animal tissues, and plays a critical role in wound healing. Fibroblasts are the most common cells ...
s laying down connective tissue
Connective tissue is one of the four primary types of animal tissue, along with epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. It develops from the mesenchyme derived from the mesoderm the middle embryonic germ layer. Connective tiss ...
, including collagen
Collagen () is the main structural protein in the extracellular matrix found in the body's various connective tissues. As the main component of connective tissue, it is the most abundant protein in mammals, making up from 25% to 35% of the whol ...
and glycosaminoglycan
Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) or mucopolysaccharides are long, linear polysaccharides consisting of repeating disaccharide units (i.e. two-sugar units). The repeating two-sugar unit consists of a uronic sugar and an amino sugar, except in the case ...
s. The process is initiated when immune cells such as macrophage
Macrophages (abbreviated as M φ, MΦ or MP) ( el, large eaters, from Greek ''μακρός'' (') = large, ''φαγεῖν'' (') = to eat) are a type of white blood cell of the immune system that engulfs and digests pathogens, such as cancer ce ...
s release soluble factors that stimulate fibroblasts. The most well characterized pro-fibrotic mediator is TGF beta, which is released by macrophages as well as any damaged tissue between surfaces called interstitium
The interstitium is a contiguous fluid-filled space existing between a structural barrier, such as a cell membrane or the skin, and internal structures, such as organs, including muscles and the circulatory system. The fluid in this space is ...
. Other soluble mediators of fibrosis include CTGF, platelet-derived growth factor
Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) is one among numerous growth factors that regulate cell growth and division. In particular, PDGF plays a significant role in blood vessel formation, the growth of blood vessels from already-existing blood v ...
(PDGF), and interleukin 10
Interleukin 10 (IL-10), also known as human cytokine synthesis inhibitory factor (CSIF), is an anti- inflammatory cytokine. In humans, interleukin 10 is encoded by the ''IL10'' gene. IL-10 signals through a receptor complex consisting of two IL-10 ...
(IL-10). These initiate signal transduction pathways such as the AKT/mTOR and SMAD pathways that ultimately lead to the proliferation and activation of fibroblasts, which deposit extracellular matrix into the surrounding connective tissue. This process of tissue repair is a complex one, with tight regulation of extracellular matrix
In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM), also called intercellular matrix, is a three-dimensional network consisting of extracellular macromolecules and minerals, such as collagen, enzymes, glycoproteins and hydroxyapatite that provide s ...
(ECM) synthesis and degradation ensuring maintenance of normal tissue architecture. However, the entire process, although necessary, can lead to a progressive irreversible fibrotic response if tissue injury is severe or repetitive, or if the wound healing response itself becomes deregulated.
Anatomical location
Fibrosis can occur in many tissues within the body, typically as a result of inflammation or damage, and examples include:Lungs
* Fibrothorax * Pulmonary fibrosis **Cystic fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a rare genetic disorder that affects mostly the lungs, but also the pancreas, liver, kidneys, and intestine. Long-term issues include difficulty breathing and coughing up mucus as a result of frequent lung infections. Ot ...
** Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (idiopathic meaning the cause is unknown)
* Radiation-induced lung injury (following treatment for cancer)
Liver
* Bridging fibrosis An advanced stage of liver fibrosis seen in the progressive form of chronic liver diseases. The term “bridging” means ‘the formation of “bridge” (by the band of mature & thick fibrous tissue) obliterating portal area to central vein’, leads to the formation of pseudolobules. Long-term exposure to hepatotoxin (e.g. thioacetamide, carbon tetrachloride, diethylnitrosamine) results in the bridging fibrosis in experimental animal models. * Senescence of hepatic stellate cells could prevent progression of liver fibrosis, although this has not been implemented as a therapy, and would carry the risk of hepatic dysfunction. *
* Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis, also known as liver cirrhosis or hepatic cirrhosis, and end-stage liver disease, is the impaired liver function caused by the formation of scar tissue known as fibrosis due to damage caused by liver disease. Damage causes tissue rep ...
Kidney
* CYR61 induction ofcellular senescence
Cellular senescence is a phenomenon characterized by the cessation of cell division. In their experiments during the early 1960s, Leonard Hayflick and Paul Moorhead found that normal human fetal fibroblasts in culture reach a maximum of approxim ...
in the kidney is a potential therapy to limit fibrosis.
Brain
* Glial scarHeart
Myocardial fibrosis has mainly two forms: * ''Interstitial fibrosis'', which has been described in congestive heart failure, hypertension, and normal aging. * ''Replacement fibrosis'', which indicates an oldermyocardial infarction
A myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when blood flow decreases or stops to the coronary artery of the heart, causing damage to the heart muscle. The most common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which ma ...
.
Other
*Arterial stiffness
Arterial stiffness occurs as a consequence of biological aging and arteriosclerosis. Inflammation plays a major role in arteriosclerosis development, and consequently it is a major contributor in large arteries stiffening. Increased arterial stiff ...
* Arthrofibrosis Arthrofibrosis (from Greek: ''arthro-'' joint, ''fibrosis'' – scar tissue formation) has been described in most joints like knee, hip, ankle, foot joints, shoulder (frozen shoulder, adhesive capsulitis), elbow (stiff elbow), wrist, hand joints as ...
(knee, shoulder, other joints)
* Chronic kidney disease
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a type of kidney disease in which a gradual loss of kidney function occurs over a period of months to years. Initially generally no symptoms are seen, but later symptoms may include leg swelling, feeling tired, vo ...
* Crohn's disease
Crohn's disease is a type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that may affect any segment of the gastrointestinal tract. Symptoms often include abdominal pain, diarrhea (which may be bloody if inflammation is severe), fever, abdominal distensi ...
(intestine)
* Dupuytren's contracture (hands, fingers)
* Keloid
Keloid, also known as keloid disorder and keloidal scar,
is the formation of a type of scar which, depending on its maturity, is composed mainly of either type III (early) or type I (late) collagen. It is a result of an overgrowth of granulation ...
(skin)
* Mediastinal fibrosis
Mediastinal fibrosis most common cause is idiopathic mediastinal fibrosis; less commonly histoplasmosis tuberculosis or unknown. It is characterized by invasive, calcified fibrosis centered on lymph nodes that block major vessels and airways. In ...
(soft tissue of the mediastinum)
* Myelofibrosis (bone marrow)
* Peyronie's disease (penis)
* Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis (skin)
* Progressive massive fibrosis Progressive massive fibrosis (PMF), characterized by the development of large conglomerate masses of dense fibrosis (usually in the upper lung zones), can complicate silicosis and coal worker's pneumoconiosis. Conglomerate masses may also occur in ...
(lungs); a complication of coal workers' pneumoconiosis
Pneumoconiosis is the general term for a class of interstitial lung disease where inhalation of dust ( for example, ash dust, lead particles, pollen grains etc) has caused interstitial fibrosis. The three most common types are asbestosis, silico ...
* Retroperitoneal fibrosis (soft tissue of the retroperitoneum)
* Scleroderma/ systemic sclerosis (skin, lungs)
* Some forms of adhesive capsulitis (shoulder)
References
External links
* {{Connective tissue Symptoms and signs Medical terminology Rheumatology