Factory (trading post) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Factory was the common name during the
Factory was the common name during the

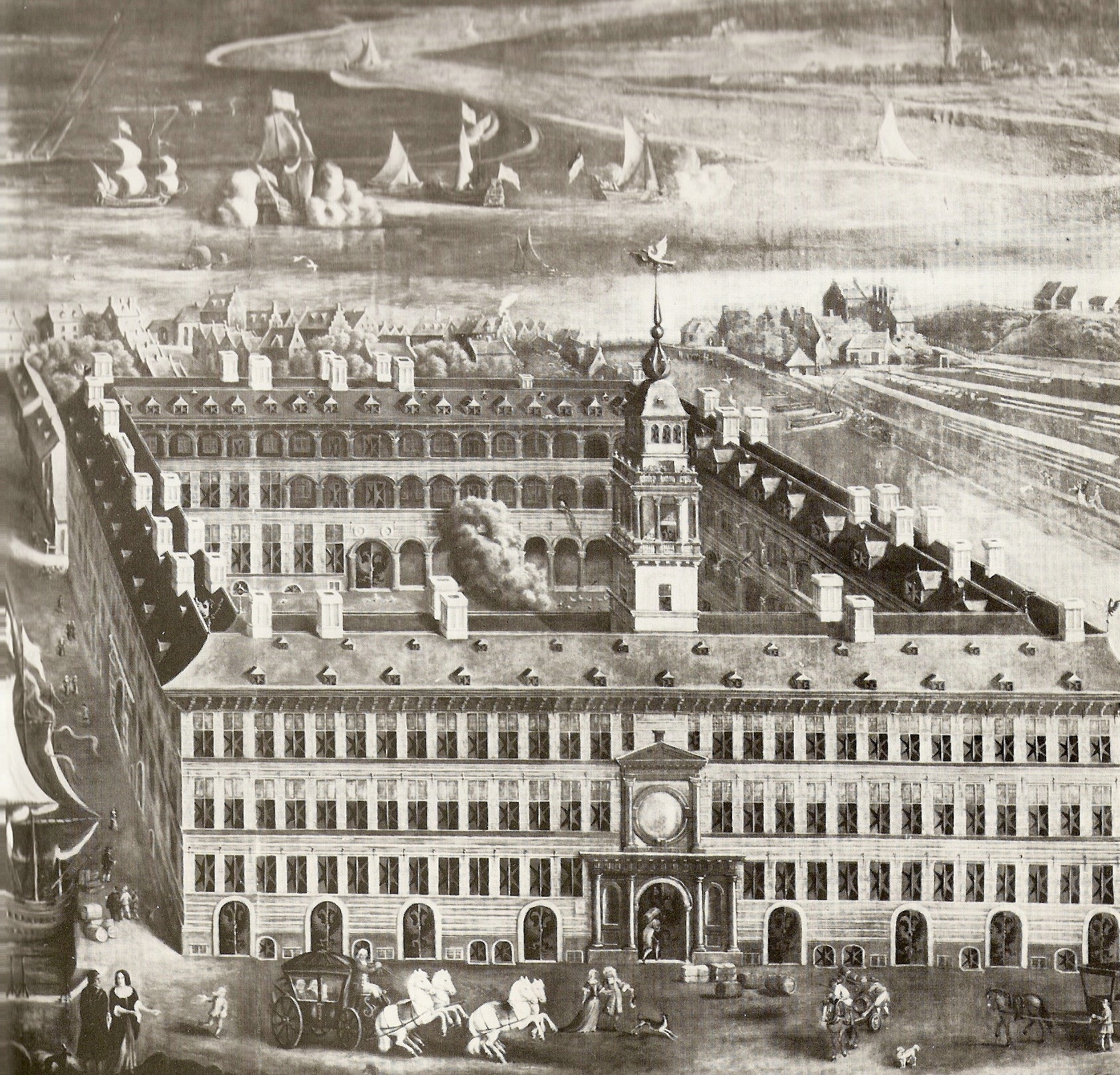 Although European
Although European
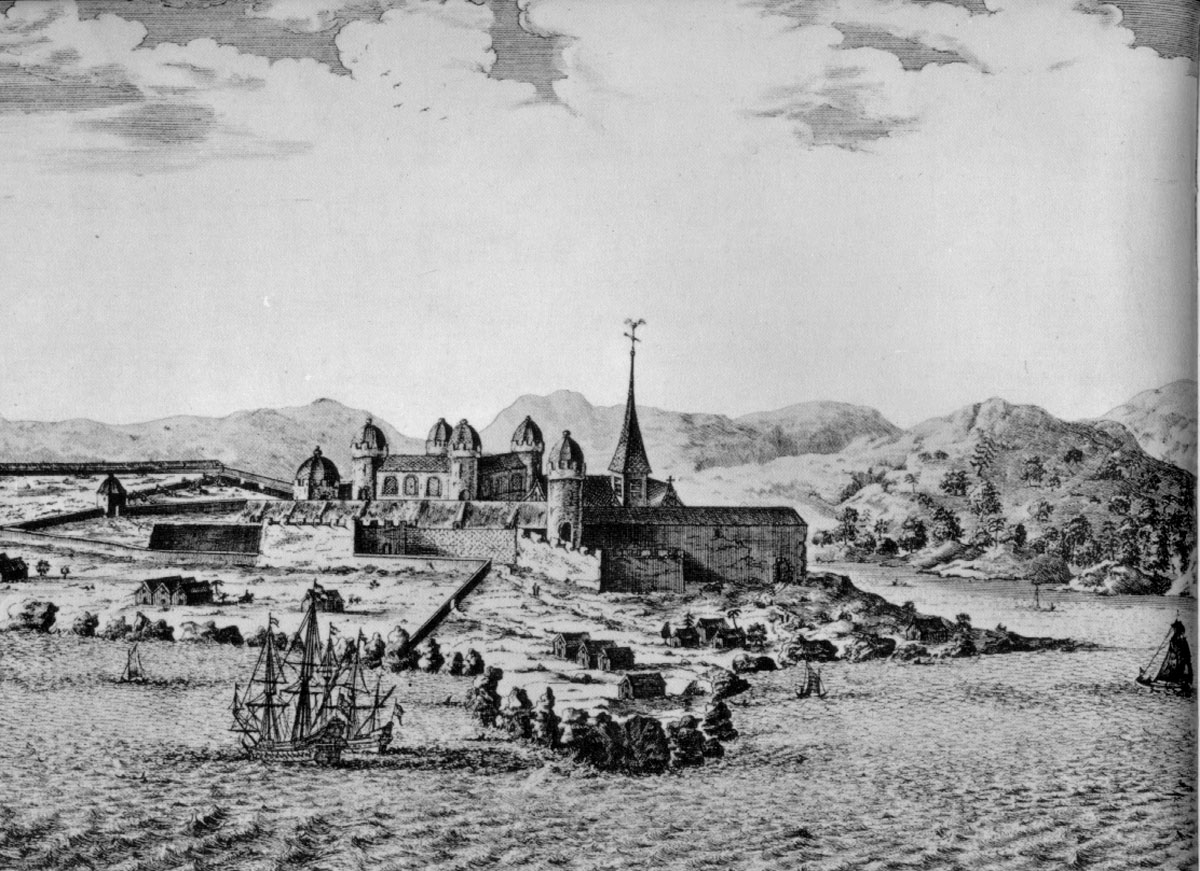 The first Portuguese ''feitoria'' overseas was established by Henry the Navigator in 1445 on the island of
The first Portuguese ''feitoria'' overseas was established by Henry the Navigator in 1445 on the island of
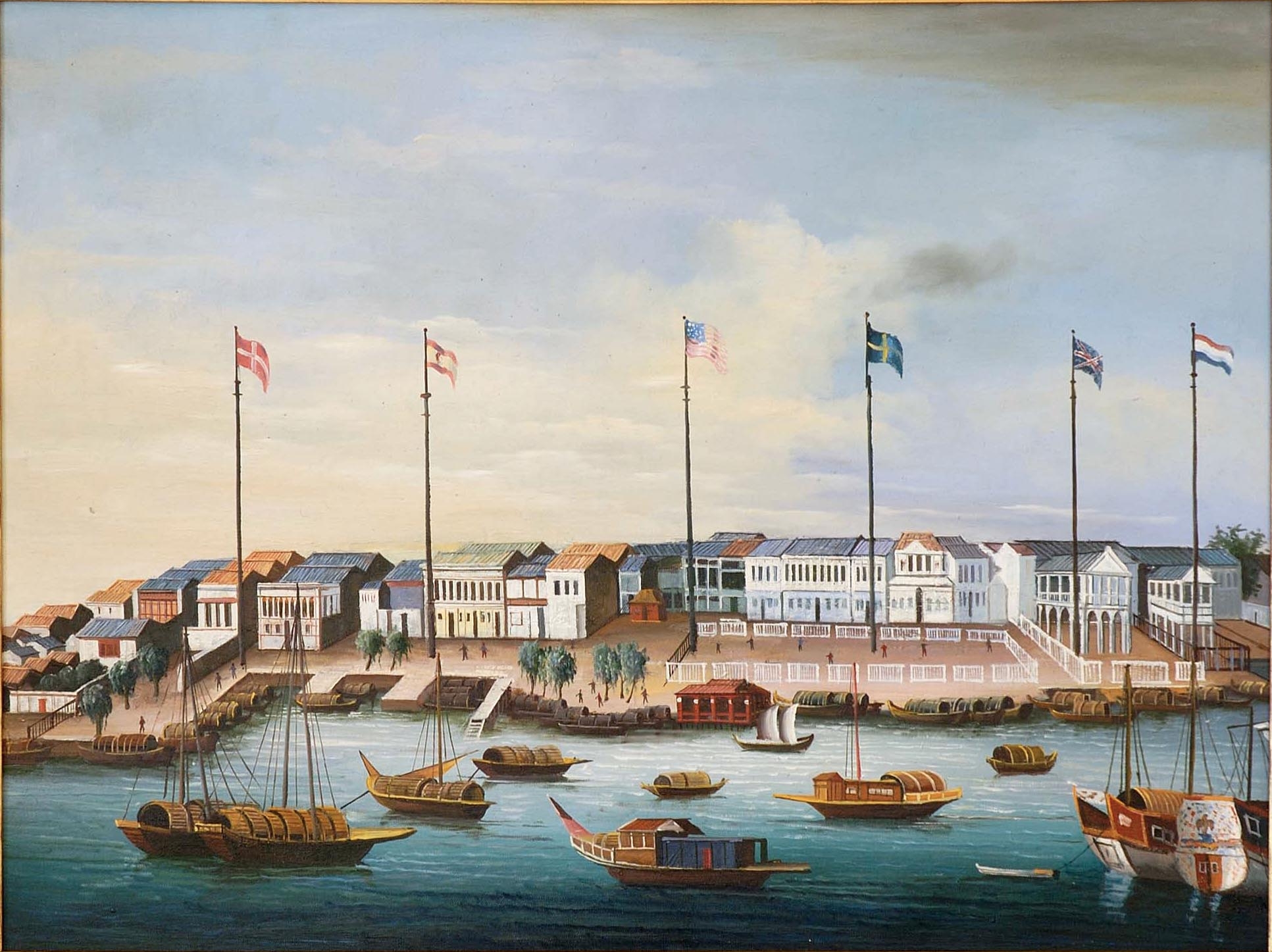
 Other European powers began to establish factories in the 17th century along the trade routes explored by Portugal and Spain, first the
Other European powers began to establish factories in the 17th century along the trade routes explored by Portugal and Spain, first the

 York Factory was founded by the chartered
York Factory was founded by the chartered
*Creek: ** Colerain, Georgia, Colerain, 1795–1797 **
Wisconsinhistory.org definition
{{DEFAULTSORT:Factory (Trading Post) History of international trade Medieval economics Age of Discovery History of European colonialism
 Factory was the common name during the
Factory was the common name during the medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
and early modern eras for an entrepôt
An ''entrepôt'' (; ) or transshipment port is a port, city, or trading post where merchandise may be imported, stored, or traded, usually to be exported again. Such cities often sprang up and such ports and trading posts often developed into c ...
– which was essentially an early form of free-trade zone
A free-trade zone (FTZ) is a class of special economic zone. It is a geographic area where goods may be imported, stored, handled, manufactured, or reconfigured and re-exported under specific customs regulation and generally not subject to cus ...
or transshipment
Transshipment, trans-shipment or transhipment is the shipment of goods or containers to an intermediate destination, then to another destination.
One possible reason for transshipment is to change the means of transport during the journey (e.g ...
point. At a factory, local inhabitants could interact with foreign merchants, often known as factors. First established in Europe, factories eventually spread to many other parts of the world. The origin of the word ''factory'' is ( pt, feitoria; nl, factorij; french: factorerie, ).
The factories established by European states in Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
, Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an are ...
and the Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World.
Along with th ...
from the 15th century
The 15th century was the century which spans the Julian dates from 1 January 1401 ( MCDI) to 31 December 1500 ( MD).
In Europe, the 15th century includes parts of the Late Middle Ages, the Early Renaissance, and the early modern period.
...
onward also tended to be official political dependencies of those states. These have been seen, in retrospect, as the precursors of colonial expansion.
A factory could serve simultaneously as market
Market is a term used to describe concepts such as:
*Market (economics), system in which parties engage in transactions according to supply and demand
*Market economy
*Marketplace, a physical marketplace or public market
Geography
*Märket, an ...
, warehouse
A warehouse is a building for storing goods. Warehouses are used by manufacturers, importers, exporters, wholesalers, transport businesses, customs, etc. They are usually large plain buildings in industrial parks on the outskirts of cities ...
, customs, defense and support to navigation
Navigation is a field of study that focuses on the process of monitoring and controlling the movement of a craft or vehicle from one place to another.Bowditch, 2003:799. The field of navigation includes four general categories: land navigation, ...
exploration, headquarters or ''de facto
''De facto'' ( ; , "in fact") describes practices that exist in reality, whether or not they are officially recognized by laws or other formal norms. It is commonly used to refer to what happens in practice, in contrast with ''de jure'' ("by la ...
'' government of local communities.
In North America, Europeans began to trade with the natives during the 16th century. Colonists created factories, known as trading post
A trading post, trading station, or trading house, also known as a factory, is an establishment or settlement where goods and services could be traded.
Typically the location of the trading post would allow people from one geographic area to tr ...
s, at which furs could be traded, in Native American territory.
European medieval factories

 Although European
Although European colonialism
Colonialism is a practice or policy of control by one people or power over other people or areas, often by establishing colony, colonies and generally with the aim of economic dominance. In the process of colonisation, colonisers may impose the ...
traces its roots from the classical era
Classical antiquity (also the classical era, classical period or classical age) is the period of cultural history between the 8th century BC and the 5th century AD centred on the Mediterranean Sea, comprising the interlocking civilizations of ...
, when Phoenicia
Phoenicia () was an ancient thalassocratic civilization originating in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily located in modern Lebanon. The territory of the Phoenician city-states extended and shrank throughout their histor ...
ns, Greeks
The Greeks or Hellenes (; el, Έλληνες, ''Éllines'' ) are an ethnic group and nation indigenous to the Eastern Mediterranean and the Black Sea regions, namely Greece, Cyprus, Albania, Italy, Turkey, Egypt, and, to a lesser extent, oth ...
and Romans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
established colonies of settlement around the Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western Europe, Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa ...
– "factories" were a unique institution born in medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
Europe.
Originally, factories were organizations of European merchants from a state, meeting in a foreign place. These organizations sought to defend their common interests, mainly economic (as well as organized insurance and protection), enabling the maintenance of diplomatic and trade relations within the foreign state where they were set.
The factories were established from 1356 onwards in the main trading centers, usually ports or central hubs that have prospered under the influence of the Hanseatic League and its guild
A guild ( ) is an association of artisans and merchants who oversee the practice of their craft/trade in a particular area. The earliest types of guild formed as organizations of tradesmen belonging to a professional association. They sometimes ...
s and kontor
A ''kontor'' () was a foreign trading post of the Hanseatic League.
In addition to the major ''kontore'' in London (the Steelyard), Bruges, Bergen (Bryggen), and Novgorod (Peterhof), some ports had a representative merchant and a warehouse.
E ...
s. The Hanseatic cities had their own law system and furnished their own protection and mutual aid. The Hanseatic League maintained factories, among others, in England (Boston
Boston (), officially the City of Boston, is the state capital and most populous city of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, as well as the cultural and financial center of the New England region of the United States. It is the 24th- mo ...
, King's Lynn), Norway (Tønsberg
Tønsberg , historically Tunsberg, is a city and municipality in Vestfold og Telemark county, eastern Norway, located around south-southwest of Oslo on the western coast of the Oslofjord near its mouth onto the Skagerrak. The administrative c ...
) and Finland (Åbo
Turku ( ; ; sv, Åbo, ) is a city and former capital on the southwest coast of Finland at the mouth of the Aura River, in the region of Finland Proper (''Varsinais-Suomi'') and the former Turku and Pori Province (''Turun ja Porin lääni''; ...
). Later, cities like Bruges
Bruges ( , nl, Brugge ) is the capital and largest city of the province of West Flanders in the Flemish Region of Belgium, in the northwest of the country, and the sixth-largest city of the country by population.
The area of the whole city a ...
and Antwerp actively tried to take over the monopoly of trade from the Hansa, inviting foreign merchants to join in.
Because foreigners were not allowed to buy land in these cities, merchants joined around factories, like the Portuguese in their Bruges factory: the factor(s) and his officers rented the housing and warehouses, arbitrated trade, and even managed insurance funds, working both as an association and an embassy, even administering justice within the merchant community.
Portuguese ''feitorias'' (c. 1445)
During the territorial and economic expansion of the Age of Discovery, the factory was adapted by thePortuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
and spread throughout from West Africa to Southeast Asia. The Portuguese ''feitorias'' were mostly fortified trading posts settled in coastal areas, built to centralize and thus dominate the local trade of products with the Portuguese kingdom (and thence to Europe). They served simultaneously as market
Market is a term used to describe concepts such as:
*Market (economics), system in which parties engage in transactions according to supply and demand
*Market economy
*Marketplace, a physical marketplace or public market
Geography
*Märket, an ...
, warehouse
A warehouse is a building for storing goods. Warehouses are used by manufacturers, importers, exporters, wholesalers, transport businesses, customs, etc. They are usually large plain buildings in industrial parks on the outskirts of cities ...
, support to the navigation
Navigation is a field of study that focuses on the process of monitoring and controlling the movement of a craft or vehicle from one place to another.Bowditch, 2003:799. The field of navigation includes four general categories: land navigation, ...
and customs and were governed by a ''feitor'' ("factor") responsible for managing the trade, buying and trading products on behalf of the king and collecting taxes (usually 20%).
 The first Portuguese ''feitoria'' overseas was established by Henry the Navigator in 1445 on the island of
The first Portuguese ''feitoria'' overseas was established by Henry the Navigator in 1445 on the island of Arguin
Arguin ( ar, أرغين, pt, Arguim) is an island off the western coast of Mauritania in the Bay of Arguin. It is approximately in size, with extensive and dangerous reefs around it. The island is now part of the Banc d'Arguin National Park.
H ...
, off the coast of Mauritania. It was built to attract Muslim traders and monopolize the business in the routes traveled in North Africa. It served as a model for a chain of African ''feitorias'', Elmina Castle being the most notorious.
Between the 15th and 16th centuries, a chain of about 50 Portuguese forts either housed or protected ''feitorias'' along the coasts of West and East Africa, the Indian Ocean, China, Japan, and South America. The main factories of the Portuguese East Indies, were in Goa, Malacca, Ormuz, Ternate
Ternate is a city in the Indonesian province of North Maluku and an island in the Maluku Islands. It was the ''de facto'' provincial capital of North Maluku before Sofifi on the nearby coast of Halmahera became the capital in 2010. It is off the ...
, Macao
Macau or Macao (; ; ; ), officially the Macao Special Administrative Region of the People's Republic of China (MSAR), is a city and special administrative region of China in the western Pearl River Delta by the South China Sea. With a po ...
, and the richest possession of Bassein that went on become the financial centre of India as Bombay (Mumbai). They were mainly driven by the trade of gold and slaves on the coast of Guinea, spices in the Indian Ocean, and sugar cane in the New World. They were also used for local triangular trade
Triangular trade or triangle trade is trade between three ports or regions. Triangular trade usually evolves when a region has export commodities that are not required in the region from which its major imports come. It has been used to offset ...
between several territories, like Goa-Macau-Nagasaki, trading products such as sugar, pepper, coconut, timber, horses, grain, feathers from exotic Indonesian birds, precious stones, silks and porcelain from the East, among many other products. In the Indian Ocean, the trade in Portuguese factories was enforced and increased by a merchant ship licensing system: the cartaz
The Cartaz (plural cartazes, in Portuguese) was a naval trade license or pass issued by the Portuguese empire in the Indian ocean during the sixteenth century (circa 1502–1750). Its name derives from the Portuguese term 'cartas', meaning letters. ...
es.
From the ''feitorias'', the products went to the main outpost in Goa, then to Portugal where they were traded in the Casa da Índia, which also managed exports to India. Diffie 1977, p. 316 There they were sold, or re-exported to the Royal Portuguese Factory in Antwerp, where they were distributed to the rest of Europe.
Easily supplied and defended by sea, the factories worked as independent colonial bases. They provided safety, both for the Portuguese, and at times for the territories in which they were built, protecting against constant rivalries and piracy. They allowed Portugal to dominate trade in the Atlantic and Indian oceans, establishing a vast empire with scarce human and territorial resources. Over time, the ''feitorias'' were sometimes licensed to private entrepreneurs, giving rise to some conflict between abusive private interests and local populations, such as in the Maldives
Maldives (, ; dv, ދިވެހިރާއްޖެ, translit=Dhivehi Raajje, ), officially the Republic of Maldives ( dv, ދިވެހިރާއްޖޭގެ ޖުމްހޫރިއްޔާ, translit=Dhivehi Raajjeyge Jumhooriyyaa, label=none, ), is an archipelag ...
.
Dutch ''factorij'' and other European factories (1600s)

 Other European powers began to establish factories in the 17th century along the trade routes explored by Portugal and Spain, first the
Other European powers began to establish factories in the 17th century along the trade routes explored by Portugal and Spain, first the Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
and then the English. They went on to establish in conquered Portuguese ''feitorias'' and further enclaves, as they explored the coasts of Africa, Arabia, India, and South East Asia in search of the source of the lucrative spice trade.
Factories were then established by chartered companies
A chartered company is an association with investors or shareholders that is incorporated and granted rights (often exclusive rights) by royal charter (or similar instrument of government) for the purpose of trade, exploration, and/or coloni ...
such as the Dutch East India Company
The United East India Company ( nl, Verenigde Oostindische Compagnie, the VOC) was a chartered company established on the 20th March 1602 by the States General of the Netherlands amalgamating existing companies into the first joint-stock ...
(VOC), founded in 1602, and the Dutch West India Company (WIC), founded in 1621. These factories provided for the exchange of products among European companies, local populations, and the colonies that often started as a factory with warehouses. Usually these factories had larger warehouses to fit the products resulting from the increasing agricultural development of colonies, which were boosted in the New World
The term ''New World'' is often used to mean the majority of Earth's Western Hemisphere, specifically the Americas."America." ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (). McArthur, Tom, ed., 1992. New York: Oxford University Press, p. ...
by the Atlantic slave trade.
In these factories, the products were checked, weighed, and packaged to prepare for the long sea voyage. In particular, spices, cocoa, tea
Tea is an aromatic beverage prepared by pouring hot or boiling water over cured or fresh leaves of ''Camellia sinensis'', an evergreen shrub native to East Asia which probably originated in the borderlands of southwestern China and north ...
, tobacco
Tobacco is the common name of several plants in the genus '' Nicotiana'' of the family Solanaceae, and the general term for any product prepared from the cured leaves of these plants. More than 70 species of tobacco are known, but the ...
, coffee
Coffee is a drink prepared from roasted coffee beans. Darkly colored, bitter, and slightly acidic, coffee has a stimulating effect on humans, primarily due to its caffeine content. It is the most popular hot drink in the world.
Seeds of ...
, sugar, porcelain
Porcelain () is a ceramic material made by heating substances, generally including materials such as kaolinite, in a kiln to temperatures between . The strength and translucence of porcelain, relative to other types of pottery, arises main ...
, and fur
Fur is a thick growth of hair that covers the skin of mammals. It consists of a combination of oily guard hair on top and thick underfur beneath. The guard hair keeps moisture from reaching the skin; the underfur acts as an insulating blanket t ...
were well protected against the salty sea air and against deterioration. The factor was present as the representative of the trading partners in all matters, reporting to the headquarters and being responsible for the products’ logistics (proper storage and shipping). Information took a long time to reach the company headquarters, and this was dependent on an absolute trust.
Some Dutch factories were located in Cape Town
Cape Town ( af, Kaapstad; , xh, iKapa) is one of South Africa's three capital cities, serving as the seat of the Parliament of South Africa. It is the legislative capital of the country, the oldest city in the country, and the second largest ...
in modern-day South Africa, Mocha in Yemen, Calicut
Kozhikode (), also known in English as Calicut, is a city along the Malabar Coast in the state of Kerala in India. It has a corporation limit population of 609,224 and a metropolitan population of more than 2 million, making it the second l ...
and the Coromandel Coast in southern India, Colombo
Colombo ( ; si, කොළඹ, translit=Koḷam̆ba, ; ta, கொழும்பு, translit=Koḻumpu, ) is the executive and judicial capital and largest city of Sri Lanka by population. According to the Brookings Institution, Colombo m ...
in Sri Lanka, Ambon
Ambon may refer to:
Places
* Ambon Island, an island in Indonesia
** Ambon, Maluku, a city on Ambon Island, the capital of Maluku province
** Governorate of Ambon, a colony of the Dutch East India Company from 1605 to 1796
* Ambon, Morbihan, a c ...
in Indonesia, Fort Zeelandia in Taiwan, Canton in southern China, Dejima
, in the 17th century also called Tsukishima ( 築島, "built island"), was an artificial island off Nagasaki, Japan that served as a trading post for the Portuguese (1570–1639) and subsequently the Dutch (1641–1854). For 220 years, i ...
Island in Japan (the only legal point of trade between Japan and the outside world during the Edo Period
The or is the period between 1603 and 1867 in the history of Japan, when Japan was under the rule of the Tokugawa shogunate and the country's 300 regional '' daimyo''. Emerging from the chaos of the Sengoku period, the Edo period was characte ...
), and Fort Orange
Fort Orange ( nl, Fort Oranje) was the first permanent Dutch settlement in New Netherland; the present-day city of Albany, New York developed at this site. It was built in 1624 as a replacement for Fort Nassau, which had been built on nearb ...
in modern-day Upstate New York
Upstate New York is a geographic region consisting of the area of New York State that lies north and northwest of the New York City metropolitan area. Although the precise boundary is debated, Upstate New York excludes New York City and Long Is ...
in the United States.
North American factories (1697 to 1822)
The American factories often played a strategic role as well, sometimes operating as forts, providing a degree of protection for colonists and their allies from hostile Indians and foreign colonists.
 York Factory was founded by the chartered
York Factory was founded by the chartered Hudson's Bay Company
The Hudson's Bay Company (HBC; french: Compagnie de la Baie d'Hudson) is a Canadian retail business group. A fur trading business for much of its existence, HBC now owns and operates retail stores in Canada. The company's namesake business di ...
in 1697. It was headquarters of the company for a long time, and was once the ''de facto'' government in parts of North America such as Rupert's Land
Rupert's Land (french: Terre de Rupert), or Prince Rupert's Land (french: Terre du Prince Rupert, link=no), was a territory in British North America which comprised the Hudson Bay drainage basin; this was further extended from Rupert's Land t ...
, before European-based colonies existed. It controlled the fur trade throughout much of British-controlled North America for several centuries, undertaking early exploration. Its traders and trappers forged early relationships with many groups of American Indians, and a network of trading posts formed the nucleus for later official authority in many areas of Western Canada and the United States.
The early coastal factory model contrasted with the system of the French, who established an extensive system of inland posts and sent traders to live among the tribes of the region. When war broke out in the 1680s between France and England, the two nations regularly sent expeditions to raid and capture each other's fur trading posts. In March 1686, the French sent a raiding party under Chevalier des Troyes over to capture the company's posts along James Bay. In 1697, Pierre Le Moyne d'Iberville
Pierre Le Moyne d'Iberville (16 July 1661 – 9 July 1706) or Sieur d'Iberville was a French soldier, explorer, colonial administrator, and trader. He is noted for founding the colony of Louisiana in New France. He was born in Montreal to French ...
, commander of the company's captured posts, defeated three ships of the Royal Navy in the Battle of the Bay on his way to capture York Factory by a ruse. York Factory changed hands several times in the next decade and was finally ceded permanently in the 1713 Treaty of Utrecht
The Peace of Utrecht was a series of peace treaties signed by the belligerents in the War of the Spanish Succession, in the Dutch city of Utrecht between April 1713 and February 1715. The war involved three contenders for the vacant throne ...
. After the treaty, the Hudson Bay Company rebuilt York Factory as a brick star fort at the mouth of the nearby Hayes River, its present location.
The United States government sanctioned a factory system from 1796 to 1822, with factories scattered through the mostly territorial portion of the country.
The factories were officially intended to protect Indians from exploitation through a series of legislation called the Indian Intercourse Acts. However, in practice, numerous tribes conceded extensive territory in exchange for the trading posts, as happened in the Treaty of Fort Clark in which the Osage Nation ceded most of Missouri
Missouri is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. Ranking 21st in land area, it is bordered by eight states (tied for the most with Tennessee): Iowa to the north, Illinois, Kentucky and Tennessee to the east, Arkansas t ...
at Fort Clark.
A blacksmith
A blacksmith is a metalsmith who creates objects primarily from wrought iron or steel, but sometimes from other metals, by forging the metal, using tools to hammer, bend, and cut (cf. tinsmith). Blacksmiths produce objects such as gates, gr ...
was usually assigned to the factory to repair utensils and build or maintain plows. The factories frequently also had some sort of milling operation associated with them.
The factories marked the United States' attempt to continue a process originally pioneered by the French and then by the Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Can ...
to officially license the fur trade in Upper Louisiana
Upper may refer to:
* Shoe upper or ''vamp'', the part of a shoe on the top of the foot
* Stimulant, drugs which induce temporary improvements in either mental or physical function or both
* ''Upper'', the original film title for the 2013 found fo ...
.
Factories were frequently called "fort
A fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is also used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ''fortis'' ("strong") and ''facere'' ...
s" and often had numerous unofficial names. Legislation was often passed calling for military garrisons at the fort but their de facto purpose was a trading post.
Examples
York Factory was founded by theHudson's Bay Company
The Hudson's Bay Company (HBC; french: Compagnie de la Baie d'Hudson) is a Canadian retail business group. A fur trading business for much of its existence, HBC now owns and operates retail stores in Canada. The company's namesake business di ...
in 1697.
In the United States factories under the Superintendent of Indian Tradebr>*Creek: ** Colerain, Georgia, Colerain, 1795–1797 **
Fort Wilkinson
Fort Wilkinson was a U.S. fort near Milledgeville, Georgia established in 1797 near the Oconee River. It supplanted Fort Fidius. A historical marker commemorates the site. The fort carried out trading relations with Creek people, Creek peoples thr ...
, 1797–1806
** Ocmulgee Old Fields, 1806–1809
** Fort Hawkins, 1809–1816
** Fort Mitchell, 1816–1820
*Cherokee:
** Fort Tellico, 1795–1807
** Fort Hiwassee, 1807–1810
** Fort Wayne, 1802–1812
*Choctaw:
** Fort St. Stephens, 1802–1815
** Fort Confederation, 1816–1822
* Fort Chickasaw Bluffs, 1802–1818
*Fort Detroit
Fort Pontchartrain du Détroit or Fort Detroit (1701–1796) was a fort established on the north bank of the Detroit River by the French officer Antoine de la Mothe Cadillac and the Italian Alphonse de Tonty in 1701. In the 18th century, Fre ...
, 1802–1805
* Fort Arkansas, 1805–1810
* Fort Chicago, 1805–1822
* Fort Belle Fontaine, 1805–1809
*Natchitoches—Sulphur Fork
** Fort Natchitoches, 1805–1818
** Fort Sulphur Fork, 1818–1822
* Fort Sandusky, 1806–1812
*Fort Madison, Iowa
Fort Madison is a city and a county seat of Lee County, Iowa, United States along with Keokuk. Of Iowa's 99 counties, Lee County is the only one with two county seats. The population was 10,270 at the time of the 2020 census. Located along the ...
1808–1815
* Fort Osage, 1808–1822
*Fort Mackinac
Fort Mackinac ( ) is a former British and American military outpost garrisoned from the late 18th century to the late 19th century in the city of Mackinac Island, Michigan, on Mackinac Island. The British built the fort during the American Re ...
(Michilimackinac), 1808–1812
* Fort Green Bay, 1815–1822
* Fort Praire du Chien, 1815–1822
* Fort Edwards, 1818–1822
* Fort Spadre Bluffs (Illinois Bayou), 1818–1822
References
Sources
* * * * *External links
Wisconsinhistory.org definition
{{DEFAULTSORT:Factory (Trading Post) History of international trade Medieval economics Age of Discovery History of European colonialism
Colonial
Colonial or The Colonial may refer to:
* Colonial, of, relating to, or characteristic of a colony or colony (biology)
Architecture
* American colonial architecture
* French Colonial
* Spanish Colonial architecture
Automobiles
* Colonial (1920 au ...
Overseas empires
Economic history of Portugal
Maritime history of Portugal
Native American history
Fur trade
Hudson's Bay Company
16th century
Trading posts