Ephor on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The ephors were a board of five magistrates in ancient
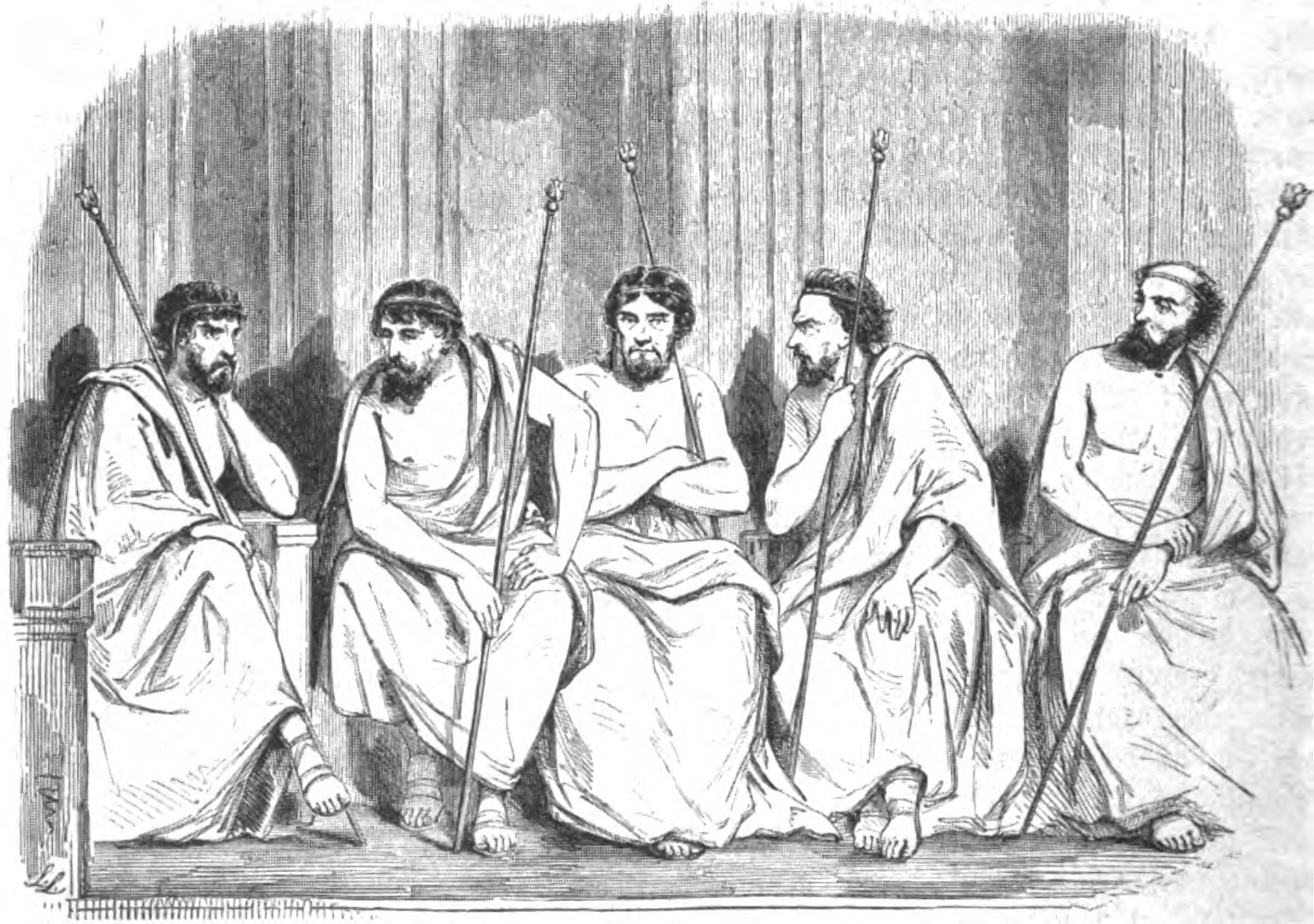 The ephors held numerous duties in legislative, judicial, financial, and executive matters. Following
The ephors held numerous duties in legislative, judicial, financial, and executive matters. Following 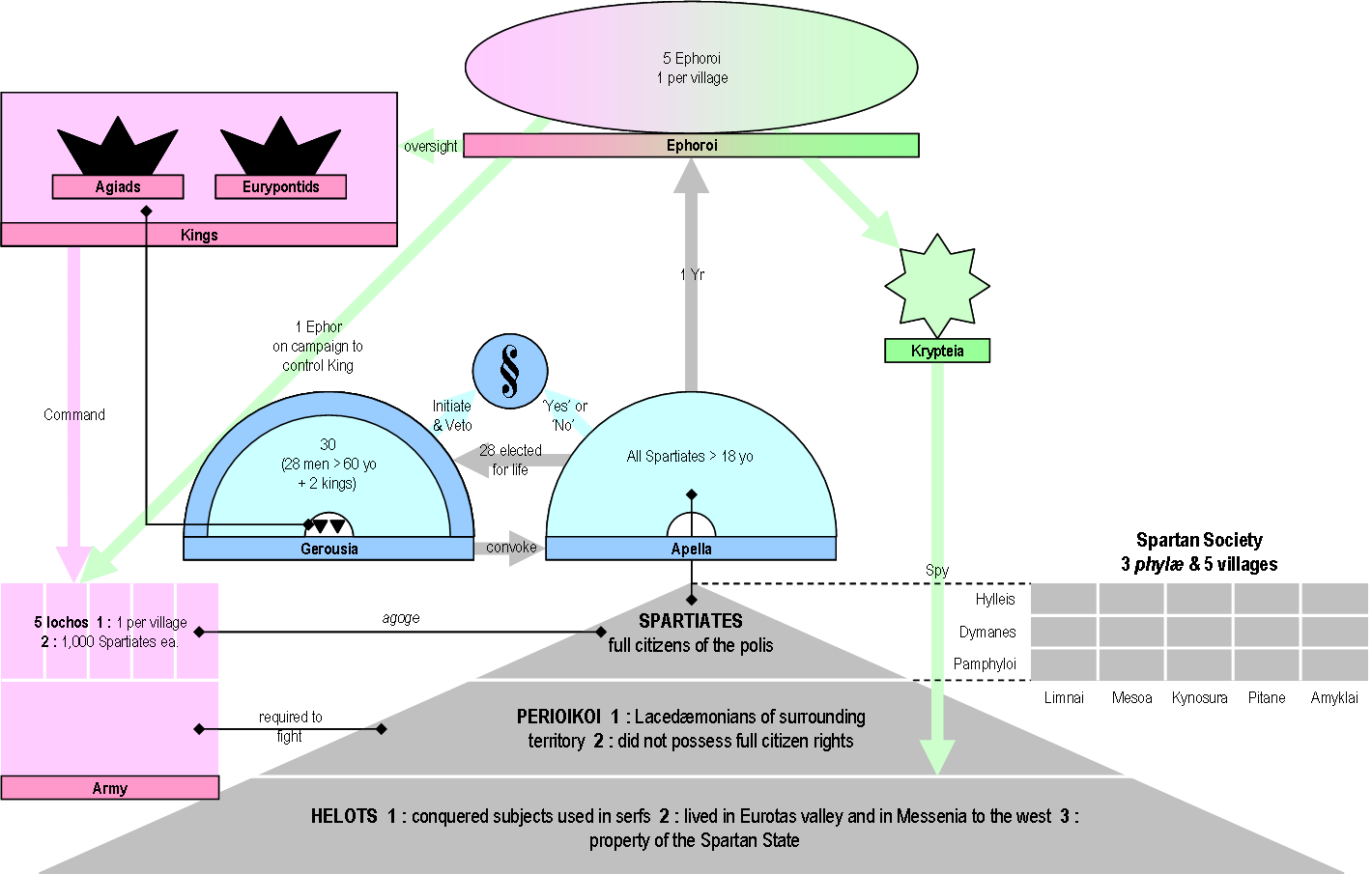 The ephors, along with the Gerousia, held the majority of the power within the Spartan government, as the two kings had to consult either with the ephors or the Gerousia in almost any official matter. The ephors also held power over the
The ephors, along with the Gerousia, held the majority of the power within the Spartan government, as the two kings had to consult either with the ephors or the Gerousia in almost any official matter. The ephors also held power over the
 *
*
The Hellenic Republic Ministry of Culture and Sports
contains several regional ephorates that carry out the administration of archaeological investigations in their respective regions The Neapolitan Republic's constitution of 1799, written by Francesco Mario Pagano, envisaged an organ of magistrates reviewing constitutional law, the ''eforato'', but lasted only 6 months. Zack Snyder's 2007 film adaptation of the Battle of Thermoplyae, '' 300'', features ephors throughout the movie. In the film they are dramatized as elderly lepers with pale skin and lesions. At the beginning of the movie, Leonidas is shown visiting the ephors and proposing a war strategy to them. The ephors then consult the Oracle and refuse Leonidas' plan, showing that they have been bribed by Xerxes I. King Leonidas thus leads his 300 'bodyguards' to Thermoplyae without their approval. Rudolph Maté's 1962 film '' The 300 Spartans'' also depicts the ephorate's role in the
Sparta
Sparta ( Doric Greek: Σπάρτα, ''Spártā''; Attic Greek: Σπάρτη, ''Spártē'') was a prominent city-state in Laconia, in ancient Greece. In antiquity, the city-state was known as Lacedaemon (, ), while the name Sparta referr ...
. They had an extensive range of judicial, religious, legislative, and military powers, and could shape Sparta's home and foreign affairs.
The word "''ephors''" (Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic pe ...
''éphoroi'', plural form of ''éphoros'') comes from the Ancient Greek ''epi'', "on" or "over", and ''horaō'', "to see", i.e., "one who oversees" or "overseer". The ephors were a council of five Spartan men elected annually who swore an oath monthly on the behalf of the state. The Spartan kings, however, would swear on behalf of themselves.
The ephors did not have to kneel before the Kings of Sparta, and were held in high esteem by the citizens because of the importance of their powers and because of the holy role that they earned throughout their functions. Donald Kagan, ''The Outbreak of the Peloponnesian War''. page 29. Ithaca/New York 1969, .
Several other Greek city-states with a Spartan ancestry also had ephors, such as Taras
Taras may refer to:
Geography
* Taras (ancient city) of Magna Graecia, modern-day Taranto
* Taras, Iran, a village in Tehran province
* Taras, Łódź Voivodeship, Poland
* Taraš, a village in Vojvodina, Serbia
* Taras, Kazakhstan, a village in ...
or Cyrene.
History
Creation
Two different accounts of the origins of the ephorate exist in ancient sources. The earliest account is found in the ''Histories
Histories or, in Latin, Historiae may refer to:
* the plural of history
* ''Histories'' (Herodotus), by Herodotus
* ''The Histories'', by Timaeus
* ''The Histories'' (Polybius), by Polybius
* ''Histories'' by Gaius Sallustius Crispus (Sallust), ...
'' of Herodotus
Herodotus ( ; grc, , }; BC) was an ancient Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus, part of the Persian Empire (now Bodrum, Turkey) and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria (Italy). He is known fo ...
, who traces its origins to the mythical Spartan lawgiver Lycurgus
Lycurgus or Lykourgos () may refer to:
People
* Lycurgus (king of Sparta) (third century BC)
* Lycurgus (lawgiver) (eighth century BC), creator of constitution of Sparta
* Lycurgus of Athens (fourth century BC), one of the 'ten notable orators' ...
—a version followed by Xenophon
Xenophon of Athens (; grc, Ξενοφῶν ; – probably 355 or 354 BC) was a Greek military leader, philosopher, and historian, born in Athens. At the age of 30, Xenophon was elected commander of one of the biggest Greek mercenary armies o ...
, Plato
Plato ( ; grc-gre, Πλάτων ; 428/427 or 424/423 – 348/347 BC) was a Greek philosopher born in Athens during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. He founded the Platonist school of thought and the Academy, the first institution ...
, or Isocrates
Isocrates (; grc, Ἰσοκράτης ; 436–338 BC) was an ancient Greek rhetorician, one of the ten Attic orators. Among the most influential Greek rhetoricians of his time, Isocrates made many contributions to rhetoric and education throu ...
. A diverging version first appears in the ''Politics
Politics (from , ) is the set of activities that are associated with making decisions in groups, or other forms of power relations among individuals, such as the distribution of resources or status. The branch of social science that studies ...
'', written in the middle of the 4th century by Aristotle
Aristotle (; grc-gre, Ἀριστοτέλης ''Aristotélēs'', ; 384–322 BC) was a Greek philosopher and polymath during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. Taught by Plato, he was the founder of the Peripatetic school of ...
, who tells that the ephorate was created by the Spartan king Theopompos. This version is then more prevalent in subsequent authors, such as Cicero
Marcus Tullius Cicero ( ; ; 3 January 106 BC – 7 December 43 BC) was a Roman statesman, lawyer, scholar, philosopher, and academic skeptic, who tried to uphold optimate principles during the political crises that led to the esta ...
, and especially Plutarch
Plutarch (; grc-gre, Πλούταρχος, ''Ploútarchos''; ; – after AD 119) was a Greek Middle Platonist philosopher, historian, biographer, essayist, and priest at the Temple of Apollo in Delphi. He is known primarily for hi ...
. Modern scholars have identified the source of the second version in a lost work written by the Agiad king Pausanias after he had been forced to abdicate and go into exile in 394. In this ''logos'', Pausanias likely published Lycurgus' laws, including the Rhetra, which details the different element of the Spartan constitution
The Spartan Constitution (or Spartan politeia) are the government and laws of the classical Greek city-state of Sparta. All classical Greek city-states had a politeia; the politeia of Sparta however, was noted by many classical authors for its ...
(kings
Kings or King's may refer to:
*Monarchs: The sovereign heads of states and/or nations, with the male being kings
*One of several works known as the "Book of Kings":
**The Books of Kings part of the Bible, divided into two parts
**The ''Shahnameh'' ...
, gerousia, ekklesia), but does not mention the ephors. It has therefore been suggested that Pausanias was hostile to the ephors, to whom he possibly attributed his banishment, and published the Rhetra to discredit their office. Although the contents of this ''logos'' and Pausanias' motivations remain disputed, most modern scholars think the ephors were created at the time of Theopompos, during the Messenian Wars.
According to Plutarch, the ephorate was born out of the necessity for leaders while the kings of Sparta were absent for long periods during the Messenian Wars. The ephors were elected by the popular assembly, and all citizens were eligible. The position of ephor was the only political office open to the whole ''damos'' (populace) of men between the ages of 30–60, so eligible Spartans highly sought after the position. They were forbidden to be re-elected and provided a balance for the two kings, who rarely co-operated. Plato
Plato ( ; grc-gre, Πλάτων ; 428/427 or 424/423 – 348/347 BC) was a Greek philosopher born in Athens during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. He founded the Platonist school of thought and the Academy, the first institution ...
called the ephors tyrant
A tyrant (), in the modern English usage of the word, is an absolute ruler who is unrestrained by law, or one who has usurped a legitimate ruler's sovereignty. Often portrayed as cruel, tyrants may defend their positions by resorting to ...
s, who ran Sparta as despots while the kings were little more than generals. Up to two ephors would accompany a king on extended military campaigns as a sign of control, and they held the authority to declare war during some periods in Spartan history.
Since political and economic decisions were made by majority vote, Sparta's policy could change quickly, when the vote of one ephor changed. For example, in 403 BCE, Pausanias convinced three of the ephors to send an army to Attica
Attica ( el, Αττική, Ancient Greek ''Attikḗ'' or , or ), or the Attic Peninsula, is a historical region that encompasses the city of Athens, the capital of Greece and its countryside. It is a peninsula projecting into the Aegean ...
, a complete reversal of the policy of Lysander. According to Aristotle, the ephors frequently came from poverty because any Spartan citizen could hold the position, and it was not exclusive to the upper-class. Aristotle stated that because of this they were often liable to corruption. There were times when the legal power of an ephor was taken advantage of, such as with Alcibiades
Alcibiades ( ; grc-gre, Ἀλκιβιάδης; 450 – 404 BC) was a prominent Athenian statesman, orator, and general. He was the last of the Alcmaeonidae, which fell from prominence after the Peloponnesian War. He played a major role in t ...
's use of Endius, who persuaded the Spartans to allow Alcibiades to take control of Sparta's peace mission to Athens
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates a ...
in 420 BCE.
Cleomenes III
Cleomenes III ( grc, Κλεομένης) was one of the two kings of Sparta from 235 to 222 BC. He was a member of the Agiad dynasty and succeeded his father, Leonidas II. He is known for his attempts to reform the Spartan state.
From 229 to ...
abolished the position of ephor in 227 BCE, and replaced them with a position called the ''patronomos''. Cleomenes's coup resulted in the death of four of the five ephors, along with ten other citizens. His abolition of the ephorship allowed him to cement his role as king and prevent anyone from stopping his political reforms. However, the ephorate was restored by the Macedonian King Antigonus III Doson
Antigonus III Doson ( el, Ἀντίγονος Γ΄ Δώσων, 263–221 BC) was king of Macedon from 229 BC to 221 BC. He was a member of the Antigonid dynasty.
Family background
Antigonus III Doson was a half-cousin of his predecessor, Demetr ...
after the Battle of Sellasia
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and for ...
in 222 BCE. Although Sparta fell under Roman rule in 146 BCE, the position existed into the 2nd century CE, when it was likely abolished by Roman Emperor Hadrian
Hadrian (; la, Caesar Trâiānus Hadriānus ; 24 January 76 – 10 July 138) was Roman emperor from 117 to 138. He was born in Italica (close to modern Santiponce in Spain), a Roman ''municipium'' founded by Italic settlers in Hispania ...
and superseded by imperial governance as part of the province of Achaea.
Election
The ephorate elections took place close to the Autumn equinox, because the term of the ephors matched the Spartan year, which started with the first full Moon after the equinox, therefore the end of September or October. There was probably an age requirement of at least 30 years old to be elected ephor, the age from which a Spartan citizen was no longer considered eromenos. The Spartan constitution is principally known through the work of Aristotle, who describes in detail the elections of the gerontes (the members of the Gerousia), but not the ephors. It is still assumed that the election procedure was similar. Candidates passed one by one before the assembled citizens, who shouted according to their preference, while several assessors who were confined into a windowless building declared winners the five candidates with the loudest shouts. As with the gerontes, this system ofvoice voting
In parliamentary procedure, a voice vote (from the Latin ''viva voce'', meaning "live voice") or acclamation is a voting method in deliberative assemblies (such as legislatures) in which a group vote is taken on a topic or motion by responding vo ...
was considered "childish" by Aristotle, because influential men could easily manipulate the results by pressurising the jury.
The kings played a prominent role during election campaigns by favouring their candidates, even though only one instance of such practice is known, when in 243/2 Lysander was elected ephor with the help of the king Agis IV
Agis IV ( grc-gre, Ἄγις; c. 265 BC – 241 BC), the elder son of Eudamidas II, was the 25th king of the Eurypontid dynasty of Sparta. Posterity has reckoned him an idealistic but impractical monarch.
Family background and accession
A ...
. The fact that influential kings such as Cleomenes I or Agesilaus II had no reported conflict with the ephors support the view that they could decide who would be the ephors. Some ephors were elected thanks to a famous deed that made them known among voters. For example, Leon, ephor in 419/8, had won the quadriga race at the Olympic Games
The modern Olympic Games or Olympics (french: link=no, Jeux olympiques) are the leading international sporting events featuring summer and winter sports competitions in which thousands of athletes from around the world participate in a multi ...
in 440, while his son Antalkidas had concluded a treaty with Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
in 387 before becoming ephor in 370/69. The famous general Brasidas
Brasidas ( el, Βρασίδας, died 422 BC) was the most distinguished Spartan officer during the first decade of the Peloponnesian War who fought in battle of Amphipolis and Pylos. He died during the Second Battle of Amphipolis while winning ...
was elected in 431 just after his victory against Athens at Methone.
Eponymous ephor
One of the ephors was eponymous, ie. he gave his name to the year, like theeponymous archon
In ancient Greece the chief magistrate in various Greek city states was called eponymous archon (ἐπώνυμος ἄρχων, ''epōnymos archōn''). "Archon" (ἄρχων, pl. ἄρχοντες, ''archontes'') means "ruler" or "lord", frequentl ...
in Athens. He was probably designated during the elections as the candidate with the loudest shouts overall. The eponymous ephor did not have any additional power compared to his colleagues; it was only a prestigious position. In 413/2, the ordinary ephor Endios is thus described by Thucydides as wielding a lot of influence within the college, even though the eponymous was Onomantios.
As the eponymous ephors were used as dates, a list compiling their names existed in Sparta, and is mentioned by Polybius. This list was perhaps published by Apollodoros and Sosicrates, whose lost works were used by Diogenes Laertius. The list went at least as far as 556 (the year of Chilon's ephorate) and possibly up to 754 (during the reign of Theopompos as ancient authors believed). However, Diogenes lived in the 3rd century AD, and even his sources dated from the Hellenistic era, long after the events.
Legal power
 The ephors held numerous duties in legislative, judicial, financial, and executive matters. Following
The ephors held numerous duties in legislative, judicial, financial, and executive matters. Following Lycurgus
Lycurgus or Lykourgos () may refer to:
People
* Lycurgus (king of Sparta) (third century BC)
* Lycurgus (lawgiver) (eighth century BC), creator of constitution of Sparta
* Lycurgus of Athens (fourth century BC), one of the 'ten notable orators' ...
's "Asteropus" in 620 BCE (increase in the power of the ephorate), the ephors became the ambassadors of Sparta. They handled all matters associated with foreign relations, including the creation of treaties with foreign powersMillender, E. (2001). Spartan Literacy Revisited. ''Classical Antiquity,'' ''20''(1), 121-164. doi:10.1525/ca.2001.20.1.121 and meeting with emissaries to discuss foreign politics. They held power within Sparta by also acting as the Presidents of the assembly and the justices of the supreme civil court as well as controlling army composition. The ephors needed a majority vote to make decisions binding and minority or dissenting decisions were not accepted by the assembly.
According to Plutarch
Plutarch (; grc-gre, Πλούταρχος, ''Ploútarchos''; ; – after AD 119) was a Greek Middle Platonist philosopher, historian, biographer, essayist, and priest at the Temple of Apollo in Delphi. He is known primarily for hi ...
, every autumn at the crypteia
The Crypteia, also referred to as Krypteia or Krupteia ( Greek: κρυπτεία ''krupteía'' from κρυπτός ''kruptós'', "hidden, secret"), was an ancient Spartan state institution involving young Spartan men. It was an exclusive element ...
, the ephors would '' pro forma'' declare war on the helot
The helots (; el, εἵλωτες, ''heílotes'') were a subjugated population that constituted a majority of the population of Laconia and Messenia – the territories ruled by Sparta. There has been controversy since antiquity as to their ...
population so that any Spartan citizen could kill a helot without fear of blood guilt. This was done to keep the large helot population in check. Plutarch also stated that every eight years the ephors would watch the skies on a moonless night. If shooting stars occurred, it was up to the ephors to decide whether one or both of the kings had transgressed in his dealings with the gods. A transgression could include any behavior that dishonored the Greek pantheon. Unless the oracle from Delphi or Olympia stated otherwise, the ephors had the ability to depose the offending king or kings. Plutarch also stated that the ephors tried cases involving contracts among citizens. He further reported that each ephor specialized in a different type of disputed contract.
According to Pausanias, the ephors served with the Gerousia on the Supreme criminal court of Sparta. This included presiding over treason, homicide, and other offenses that carried serious punishments. These punishments included exile, death, and disfranchisement.
Ephors had the authority to summon and preside over the assembly's regular meetings in the fifth century BCE. Initially this power was only assigned to kings in early years. However, with the passing of the Great Rhetra regular meetings became mandated. By the late sixth century BCE, the ephors had acquired this authority to oversee the assembly and could use this power against the kings of Sparta. For example, they used this authority to force King Anaxandridas II to change his conjugal arrangements to their advantage. King Anaxandridas' wife was barren but he refused to divorce her so the ephors forced him to marry a second wife to provide heirs.
Two ephors were always sent on military expeditions to ensure the king acted in line, and if not, could put the king on trial. Many kings were put on trial by the ephors, including Leotychidas, who was found to have accepted a bribe from the Thessalians during his military expedition to Thessaly
Thessaly ( el, Θεσσαλία, translit=Thessalía, ; ancient Thessalian: , ) is a traditional geographic and modern administrative region of Greece, comprising most of the ancient region of the same name. Before the Greek Dark Ages, Thes ...
.
 The ephors, along with the Gerousia, held the majority of the power within the Spartan government, as the two kings had to consult either with the ephors or the Gerousia in almost any official matter. The ephors also held power over the
The ephors, along with the Gerousia, held the majority of the power within the Spartan government, as the two kings had to consult either with the ephors or the Gerousia in almost any official matter. The ephors also held power over the Helots
The helots (; el, εἵλωτες, ''heílotes'') were a subjugated population that constituted a majority of the population of Laconia and Messenia – the territories ruled by Sparta. There has been controversy since antiquity as to their ...
and the Perioeci. They controlled the Crypteia
The Crypteia, also referred to as Krypteia or Krupteia ( Greek: κρυπτεία ''krupteía'' from κρυπτός ''kruptós'', "hidden, secret"), was an ancient Spartan state institution involving young Spartan men. It was an exclusive element ...
, the secret police who repressed the Helots
The helots (; el, εἵλωτες, ''heílotes'') were a subjugated population that constituted a majority of the population of Laconia and Messenia – the territories ruled by Sparta. There has been controversy since antiquity as to their ...
, and they were even able to sentence Perioeci to death without a trial.
Other duties
The congress of thePeloponnesian League
The Peloponnesian League was an alliance of ancient Greek city-states, dominated by Sparta and centred on the Peloponnese, which lasted from c.550 to 366 BC. It is known mainly for being one of the two rivals in the Peloponnesian War (431–404 ...
was always chaired by an ephor.
The ephors also had the authority to choose three ''hippagretai'' (Commanders of the Guard) every year from men over the age of thirty. The chosen ''hippagretes'' would then choose three hundred of the best ''hebontes'' to form a '' hippeis''. The ephors also were responsible for penalizing disobedience in the military using fines.
Ephors could also intervene in cases of "disturbing the peace." This included punishing underage Spartans indirectly for their offenses against Sparta. This form of retribution would include penalizing the boys' ''erastes'' (adult lovers). When men between the ages of twenty and thirty (known as ''hebontes'') committed offenses they were brought before the ''paidonomos'', a magistrate
The term magistrate is used in a variety of systems of governments and laws to refer to a civilian officer who administers the law. In ancient Rome, a '' magistratus'' was one of the highest ranking government officers, and possessed both judic ...
charged with supervising the education of the youth in the ''agoge
The ( grc-gre, ἀγωγή in Attic Greek, or , in Doric Greek) was the rigorous education and training program mandated for all male Spartan citizens, with the exception of the firstborn son in the ruling houses, Eurypontid and Agiad. The ...
''. Through this system the ephors could directly penalize the ''hebontes'' by giving them large fines.
The ephors paid close attention to the education of young Spartans, and played a significant role in ensuring the education was up to standard. According to Aelian, they would examine the naked bodies of the boys every ten days to ensure they were of proper complexion and fitness and not being overfed, as well as examining the boys' clothes daily to ensure that they fit.
The ephors had their own syssitia
The syssitia ( grc, συσσίτια ''syssítia'', plural of ''syssítion'') were, in ancient Greece, common meals for men and youths in social or religious groups, especially in Crete and Sparta, but also in Megara in the time of Theognis of ...
, the common meal of Spartan citizens.
Notable ephors
Only 67 ephors are known by name before the end of the third century BCE, out of potentially 3000. * Endius: Scion of wealthy family, son of Alcibiades (served in 413/2 BCE). *
* Brasidas
Brasidas ( el, Βρασίδας, died 422 BC) was the most distinguished Spartan officer during the first decade of the Peloponnesian War who fought in battle of Amphipolis and Pylos. He died during the Second Battle of Amphipolis while winning ...
: Came from higher class family (served in 431/0 BC).
* Leon: Became an ephor at an older age and was the founder of a Spartan colony and Olympic victor (served in 419/8 BCE).
* Antalcidas
Antalcidas ( grc-gre, Ἀνταλκίδας; died BC), son of Leon, was an ancient Greek soldier, politician, and diplomat from Sparta.
__NOTOC__
Life
Antalcidas came from a prominent family and was likely a relation by marriage to the Sp ...
: Known for being the negotiator of peace treaty, named after him (served in 387/6 BCE).
* Sthenelaidas: Known for causing physical division in the voting process by making voters stand in separate spaces to represent yes or no votes. This eliminated the secrecy of the voting process. (served in 432 BCE).
* Cleandridas
Cleandridas or Cleandrides (Greek: Κλεανδρίδας or Κλεανδρίδης) was a Spartan general of the 5th century BCE, who advised the young Agiad king Pleistoanax during the early part of the latter's reign. According to Plutarch, bot ...
: Known for abandoning the invasion of Athens and returning to Peloponnese in 446 BCE. He went voluntarily into exile
Exile is primarily penal expulsion from one's native country, and secondarily expatriation or prolonged absence from one's homeland under either the compulsion of circumstance or the rigors of some high purpose. Usually persons and peoples suf ...
, with the Spartans condemning him to death in absentia.
* Lysander: Was sent as an ambassador to King Agesilaus II on multiple campaigns but suffered a dispute with King Agesilaus over the locals' loyalty to him. Lysander returned home upon the end of term as ephor (served in 243 BCE).
* Nausikleidas: Accompanied and supported King Pausanias on expedition (served in 403 BCE).
* Epitadeus
Epitadeus was an early 4th-century BC Spartan ephor, who strengthened conservative class distinctions by allowing gifts of land to independent citizens (Spartiates). This 4th century rhetra allowed the Spartiatai to dispose of their private land at ...
: Introduced legislation that destroyed the equal distribution of land that Lukourgos made in the fourth century BCE.
* Chilon
Chilon of Sparta ( grc, Χείλων) (fl. 6th century BC) was a Spartan and one of the Seven Sages of Greece.
Life
Chilon was the son of Damagetus, and lived towards the beginning of the 6th century BC. Herodotus speaks of him as contemporary ...
: Served in 556/5 BCE.
* Agesilaos: Named eponymous ephor by his nephew Agis IV
Agis IV ( grc-gre, Ἄγις; c. 265 BC – 241 BC), the elder son of Eudamidas II, was the 25th king of the Eurypontid dynasty of Sparta. Posterity has reckoned him an idealistic but impractical monarch.
Family background and accession
A ...
and was charged with implementing a new bill which included debt-cancellation and land-redistribution.
Other Greek ''poleis'' with ephors
*Euesperides Libya's second largest city, Benghazi, has a history which extends from when the city was first inhabited in the 6th century BCE to the present day. Throughout its history, the city has been continuously conquered by different ancient and colonial f ...
(Benghazi
Benghazi () , ; it, Bengasi; tr, Bingazi; ber, Bernîk, script=Latn; also: ''Bengasi'', ''Benghasi'', ''Banghāzī'', ''Binghāzī'', ''Bengazi''; grc, Βερενίκη ('' Berenice'') and ''Hesperides''., group=note (''lit. Son of he Ghaz ...
, Libya): The city was a colony of Cyrene and adopted its institutions as a result. It therefore counted ephors and a gerousia.
* Herakleia ( Lucania, Italy): The eponymous magistrate of the city was an ephor, because it reproduced the institutions of its mother-city, Taras.
* Cyrene (Libya): Cyrene had a gerousia and a board of five ephors from an early date. It was a foundation of Thera.
* Messene (Peloponnese): Messene took its independence from Sparta in 370/69, but retained some of its institutions, such as the ephors, who are mentioned c.295.
* Taras (Taranto
Taranto (, also ; ; nap, label=Tarantino, Tarde; Latin: Tarentum; Old Italian: ''Tarento''; Ancient Greek: Τάρᾱς) is a coastal city in Apulia, Southern Italy. It is the capital of the Province of Taranto, serving as an important comme ...
, Italy): The ephorate is attested in the 3rd century, but considering that its colony Herakleia also had ephors, Taras probably had ephors since the Archaic Era. The office was eponymous in the 3rd century.
* Thera (Santorini Island): A board of three ephors were eponymous magistrates in the city.
Ephors in modern culture
The concept of an ephorate continues to be used by some contemporary organizations which require a monarchical element within a democratic framework. One such organization is the Ephorate of theRascals, Rogues, and Rapscallions
The Rascals, Rogues, and Rapscallions is a cigar-friendly men's fraternal society devoted to scholarly research on obscure topics. Dubbed "America's Most Interesting Men's Club", the RR&R meets for quarterly dinner meetings at which one or more me ...
, an American fraternal research society.The Hellenic Republic Ministry of Culture and Sports
contains several regional ephorates that carry out the administration of archaeological investigations in their respective regions The Neapolitan Republic's constitution of 1799, written by Francesco Mario Pagano, envisaged an organ of magistrates reviewing constitutional law, the ''eforato'', but lasted only 6 months. Zack Snyder's 2007 film adaptation of the Battle of Thermoplyae, '' 300'', features ephors throughout the movie. In the film they are dramatized as elderly lepers with pale skin and lesions. At the beginning of the movie, Leonidas is shown visiting the ephors and proposing a war strategy to them. The ephors then consult the Oracle and refuse Leonidas' plan, showing that they have been bribed by Xerxes I. King Leonidas thus leads his 300 'bodyguards' to Thermoplyae without their approval. Rudolph Maté's 1962 film '' The 300 Spartans'' also depicts the ephorate's role in the
Battle of Thermopylae
The Battle of Thermopylae ( ; grc, Μάχη τῶν Θερμοπυλῶν, label= Greek, ) was fought in 480 BC between the Achaemenid Persian Empire under Xerxes I and an alliance of Greek city-states led by Sparta under Leonidas I. Lastin ...
. They are shown conflicting with King Leotychidas over the decision to delay the battle until after the religious harvest festival of Carneia. The ephors decide to delay the battle but under the guise of having private bodyguards, King Leonidas marches into battle with 300 Spartans. The ephors are mentioned later in the film when Leonidas receives a letter from his wife informing him that the ephors have the remainder of the Spartan army will not be joining him. Xenathon is an named ephor in the film.
Ephors have appeared in Steven Pressfield's 1998 '' Gates of Fire,'' an historical fiction
Historical fiction is a literary genre in which the plot takes place in a setting related to the past events, but is fictional. Although the term is commonly used as a synonym for historical fiction literature, it can also be applied to other t ...
novel that recounts the Battle of Thermopylae. In Chapter 15, the ephors appear when a delegation of mothers and wives goes to the council, requesting they be allowed to join the battle.
In Kieron Gillen's graphic novel
A graphic novel is a long-form, fictional work of sequential art. The term ''graphic novel'' is often applied broadly, including fiction, non-fiction, and anthologized work, though this practice is highly contested by comic scholars and industry ...
'' Three'', ephors are referenced when Gillen describes the Krypteia
The Crypteia, also referred to as Krypteia or Krupteia ( Greek: κρυπτεία ''krupteía'' from κρυπτός ''kruptós'', "hidden, secret"), was an ancient Spartan state institution involving young Spartan men. It was an exclusive element o ...
and writes "Once a year, the masters declare war on the helots." The ephors were in charge of the Krypteia and declaring war on the helots in order to keep them terrified and controlled. The next scene depicts the ephor, Eurytos, being guided by his soldiers to a helot community where they demand hospitality. Eurytos is killed by a helot revolt and the only surviving soldier returns to Sparta to inform the remaining four ephors. The ephors send soldiers to kill the helots who killed Eurytos stating, "The only thing more unthinkable than a helot killing an ephor is that helot escaping punishment."
References
Bibliography
Ancient sources
*Aristotle
Aristotle (; grc-gre, Ἀριστοτέλης ''Aristotélēs'', ; 384–322 BC) was a Greek philosopher and polymath during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. Taught by Plato, he was the founder of the Peripatetic school of ...
, ''Politics
Politics (from , ) is the set of activities that are associated with making decisions in groups, or other forms of power relations among individuals, such as the distribution of resources or status. The branch of social science that studies ...
.''
* Cicero
Marcus Tullius Cicero ( ; ; 3 January 106 BC – 7 December 43 BC) was a Roman statesman, lawyer, scholar, philosopher, and academic skeptic, who tried to uphold optimate principles during the political crises that led to the esta ...
, ''De re publica
''De re publica'' (''On the Commonwealth''; see below) is a dialogue on Roman politics by Cicero, written in six books between 54 and 51 BC. The work does not survive in a complete state, and large parts are missing. The surviving sections derive ...
'', ''De Legibus
The ''De Legibus'' (''On the Laws'') is a dialogue written by Marcus Tullius Cicero during the last years of the Roman Republic. It bears the same name as Plato's famous dialogue, ''The Laws''. Unlike his previous work ''De re publica,'' in whi ...
.''
* Isocrates
Isocrates (; grc, Ἰσοκράτης ; 436–338 BC) was an ancient Greek rhetorician, one of the ten Attic orators. Among the most influential Greek rhetoricians of his time, Isocrates made many contributions to rhetoric and education throu ...
, ''Panathenaicus''.
* Plato
Plato ( ; grc-gre, Πλάτων ; 428/427 or 424/423 – 348/347 BC) was a Greek philosopher born in Athens during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. He founded the Platonist school of thought and the Academy, the first institution ...
, ''Epistles
An epistle (; el, ἐπιστολή, ''epistolē,'' "letter") is a writing directed or sent to a person or group of people, usually an elegant and formal didactic letter. The epistle genre of letter-writing was common in ancient Egypt as par ...
''.
* Plutarch
Plutarch (; grc-gre, Πλούταρχος, ''Ploútarchos''; ; – after AD 119) was a Greek Middle Platonist philosopher, historian, biographer, essayist, and priest at the Temple of Apollo in Delphi. He is known primarily for hi ...
, ''Parallel Lives
Plutarch's ''Lives of the Noble Greeks and Romans'', commonly called ''Parallel Lives'' or ''Plutarch's Lives'', is a series of 48 biographies of famous men, arranged in pairs to illuminate their common moral virtues or failings, probably writt ...
'' (''Cleomenes'', ''Lycurgus''), '' Moralia''.
* Xenophon
Xenophon of Athens (; grc, Ξενοφῶν ; – probably 355 or 354 BC) was a Greek military leader, philosopher, and historian, born in Athens. At the age of 30, Xenophon was elected commander of one of the biggest Greek mercenary armies o ...
, '' Constitution of the Lacedaemonians''.
Modern sources
* Paul Cartledge, ''Sparta and Lakonia, A Regional History 1300–362 BC'', London, Routledge, 2002 (originally published in 1979).ISBN
The International Standard Book Number (ISBN) is a numeric commercial book identifier that is intended to be unique. Publishers purchase ISBNs from an affiliate of the International ISBN Agency.
An ISBN is assigned to each separate edition a ...
0-415-26276-3
* G. E. M. de Ste. Croix
Geoffrey Ernest Maurice de Ste. Croix, (; 8 February 1910 – 5 February 2000), known informally as Croicks, was a British historian who specialised in examining Ancient Greece from a Marxist perspective. He was Fellow and Tutor in Ancient Histo ...
, ''The Origins of the Peloponnesian War'', London, Duckworth, 1972. {{ISBN, 0-7156-0640-9
* Mogens Herman Hansen & Thomas Heine Nielsen, ''An Inventory of Archaic and Classical Poleis'', Oxford University Press, 2004.
* G. L. Huxley, ''Early Sparta'', London, Faber & Faber, 1962. ISBN
The International Standard Book Number (ISBN) is a numeric commercial book identifier that is intended to be unique. Publishers purchase ISBNs from an affiliate of the International ISBN Agency.
An ISBN is assigned to each separate edition a ...
0-389-02040-0
* Anton Powell (editor), ''A Companion to Sparta'', Hoboken, Wiley, 2018. ISBN
The International Standard Book Number (ISBN) is a numeric commercial book identifier that is intended to be unique. Publishers purchase ISBNs from an affiliate of the International ISBN Agency.
An ISBN is assigned to each separate edition a ...
978-1-4051-8869-2
Ancient Greek titles
Government of Sparta