eosin methylene blue on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
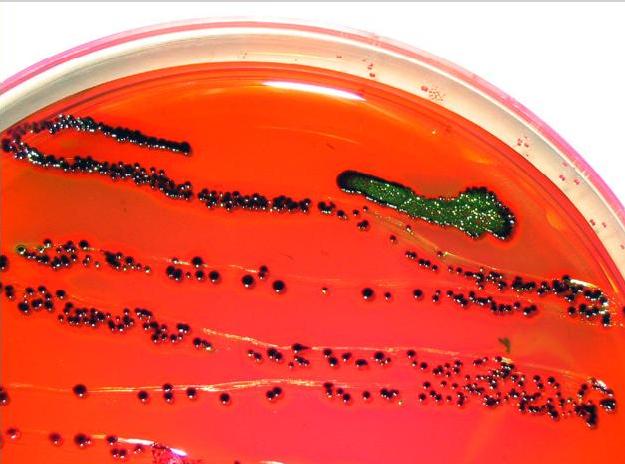 Eosin methylene blue (EMB, also known as "Levine's formulation") is a selective
Eosin methylene blue (EMB, also known as "Levine's formulation") is a selective
Uses of EMB AgarHistory of EMB AgarAcumedia - EMB AgarThe Scientist - EMB ExplanationMicrobugz - EMB Agar
{{DEFAULTSORT:Eosin Methylene Blue Biochemistry detection reactions Microbiological media ingredients Staining Microbiological media
stain
A stain is a discoloration that can be clearly distinguished from the surface, material, or medium it is found upon. They are caused by the chemical or physical interaction of two dissimilar materials. Accidental staining may make materials ap ...
for Gram-negative bacteria
Gram-negative bacteria are bacteria that do not retain the crystal violet stain used in the Gram staining method of bacterial differentiation. They are characterized by their cell envelopes, which are composed of a thin peptidoglycan cell wall ...
. EMB contains dyes that are toxic to Gram-positive bacteria
In bacteriology, gram-positive bacteria are bacteria that give a positive result in the Gram stain test, which is traditionally used to quickly classify bacteria into two broad categories according to their type of cell wall.
Gram-positive bac ...
. EMB is the selective and differential medium for coliforms. It is a blend of two stains, eosin
Eosin is the name of several fluorescent acidic compounds which bind to and form salts with basic, or eosinophilic, compounds like proteins containing amino acid residues such as arginine and lysine, and stains them dark red or pink as a resul ...
and methylene blue
Methylthioninium chloride, commonly called methylene blue, is a salt used as a dye and as a medication. Methylene blue is a thiazine dye. As a medication, it is mainly used to treat methemoglobinemia by converting the ferric iron in hemoglobin ...
in the ratio of 6:1. EMB is a differential microbiological medium, which slightly inhibits the growth of Gram-positive bacteria and provides a color indicator distinguishing between organisms that ferment lactose
Lactose is a disaccharide sugar synthesized by galactose and glucose subunits and has the molecular formula C12H22O11. Lactose makes up around 2–8% of milk (by mass). The name comes from ' (gen. '), the Latin word for milk, plus the suffix ' ...
(e.g., ''E. coli'') and those that do not (e.g., ''Salmonella'', ''Shigella''). Organisms that ferment lactose
Lactose is a disaccharide sugar synthesized by galactose and glucose subunits and has the molecular formula C12H22O11. Lactose makes up around 2–8% of milk (by mass). The name comes from ' (gen. '), the Latin word for milk, plus the suffix ' ...
display "nucleated colonies"—colonies with dark centers.
This medium is important in medical laboratories by distinguishing pathogenic microbes in a short period of time.
*Rapid lactose fermentation produces acids, which lower the pH. This encourages dye absorption by the colonies, which are now colored purple-black.
*Lactose non-fermenters may increase the pH by deamination of proteins. This ensures that the dye is not absorbed. The colonies will be colorless.
On EMB if '' E. coli'' is grown it will give a distinctive metallic green sheen (due to the metachromatic properties of the dyes, ''E. coli'' movement using flagella, and strong acid end-products of fermentation). Some species of ''Citrobacter'' and ''Enterobacter'' will also react this way to EMB.
This medium has been specifically designed to discourage the growth of Gram-positive bacteria.
EMB contains the following ingredients: peptone, lactose
Lactose is a disaccharide sugar synthesized by galactose and glucose subunits and has the molecular formula C12H22O11. Lactose makes up around 2–8% of milk (by mass). The name comes from ' (gen. '), the Latin word for milk, plus the suffix ' ...
, dipotassium phosphate, eosin Y
Eosin Y, also called C.I. 45380 or C.I. Acid Red 87, is a member of the triarylmethane dyes. It is produced from fluorescein by bromination.
Use
Eosin Y is commonly used as the red dye in red inks.
It is commonly used in histology, most notabl ...
(dye), methylene blue
Methylthioninium chloride, commonly called methylene blue, is a salt used as a dye and as a medication. Methylene blue is a thiazine dye. As a medication, it is mainly used to treat methemoglobinemia by converting the ferric iron in hemoglobin ...
(dye), and agar
Agar ( or ), or agar-agar, is a jelly-like substance consisting of polysaccharides obtained from the cell walls of some species of red algae, primarily from ogonori (''Gracilaria'') and "tengusa" (''Gelidiaceae''). As found in nature, agar i ...
.
There are also EMB agars that do not contain lactose.
References
External links
Uses of EMB Agar
{{DEFAULTSORT:Eosin Methylene Blue Biochemistry detection reactions Microbiological media ingredients Staining Microbiological media