Directional-change Intrinsic Time on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Directional-change intrinsic time is an event-based operator to dissect a data series into a sequence of alternating trends of defined size .
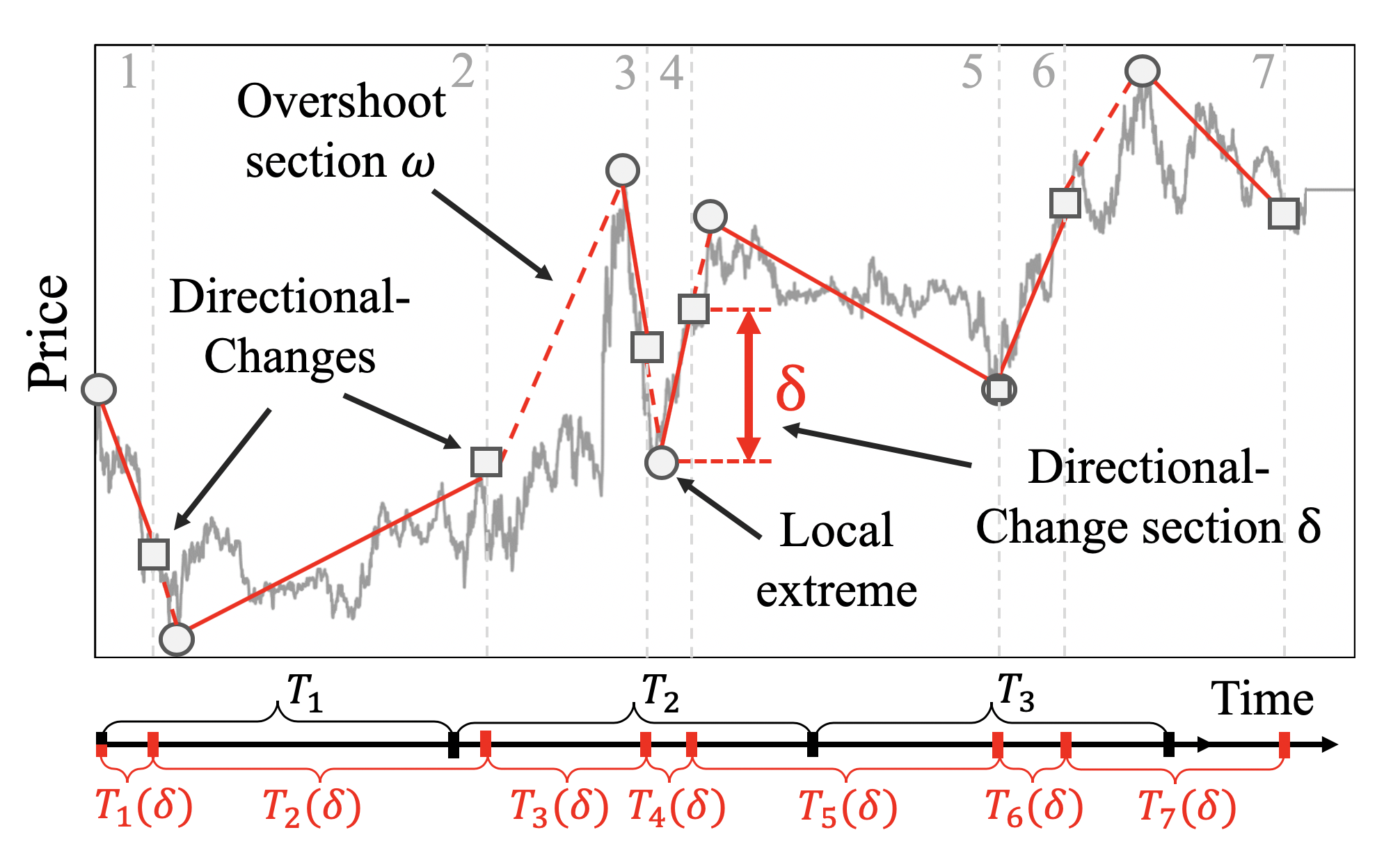 The directional-change intrinsic time operator was developed for the analysis of financial market data series. It is an alternative methodology to the concept of continuous time. Directional-change intrinsic time operator dissects a data series into a set of drawups and drawdowns or up and down trends that alternate with each other. An established trend comes to an end as soon as a trend reversal is observed. A price move that extends a trend is called overshoot and leads to new price extremes.
Figure 1 provides an example of a price curve dissected by the directional change intrinsic time operator.
The frequency of directional-change intrinsic events maps (1) the volatility of price changes conditional to (2) the selected threshold . The stochastic nature of the underlying process is mirrored in the non-equal number of intrinsic events observed over equal periods of physical time.
Directional-change intrinsic time operator is a noise filtering technique. It identifies regime shifts, when trend changes of a particular size occur and hides price fluctuations that are smaller than the threshold .
The directional-change intrinsic time operator was developed for the analysis of financial market data series. It is an alternative methodology to the concept of continuous time. Directional-change intrinsic time operator dissects a data series into a set of drawups and drawdowns or up and down trends that alternate with each other. An established trend comes to an end as soon as a trend reversal is observed. A price move that extends a trend is called overshoot and leads to new price extremes.
Figure 1 provides an example of a price curve dissected by the directional change intrinsic time operator.
The frequency of directional-change intrinsic events maps (1) the volatility of price changes conditional to (2) the selected threshold . The stochastic nature of the underlying process is mirrored in the non-equal number of intrinsic events observed over equal periods of physical time.
Directional-change intrinsic time operator is a noise filtering technique. It identifies regime shifts, when trend changes of a particular size occur and hides price fluctuations that are smaller than the threshold .
 Text in this draft was copied from , which is available under
Text in this draft was copied from , which is available under
Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
{{reflist Data analysis
 The directional-change intrinsic time operator was developed for the analysis of financial market data series. It is an alternative methodology to the concept of continuous time. Directional-change intrinsic time operator dissects a data series into a set of drawups and drawdowns or up and down trends that alternate with each other. An established trend comes to an end as soon as a trend reversal is observed. A price move that extends a trend is called overshoot and leads to new price extremes.
Figure 1 provides an example of a price curve dissected by the directional change intrinsic time operator.
The frequency of directional-change intrinsic events maps (1) the volatility of price changes conditional to (2) the selected threshold . The stochastic nature of the underlying process is mirrored in the non-equal number of intrinsic events observed over equal periods of physical time.
Directional-change intrinsic time operator is a noise filtering technique. It identifies regime shifts, when trend changes of a particular size occur and hides price fluctuations that are smaller than the threshold .
The directional-change intrinsic time operator was developed for the analysis of financial market data series. It is an alternative methodology to the concept of continuous time. Directional-change intrinsic time operator dissects a data series into a set of drawups and drawdowns or up and down trends that alternate with each other. An established trend comes to an end as soon as a trend reversal is observed. A price move that extends a trend is called overshoot and leads to new price extremes.
Figure 1 provides an example of a price curve dissected by the directional change intrinsic time operator.
The frequency of directional-change intrinsic events maps (1) the volatility of price changes conditional to (2) the selected threshold . The stochastic nature of the underlying process is mirrored in the non-equal number of intrinsic events observed over equal periods of physical time.
Directional-change intrinsic time operator is a noise filtering technique. It identifies regime shifts, when trend changes of a particular size occur and hides price fluctuations that are smaller than the threshold .
Application
The directional-change intrinsic time operator was used to analyze high frequency foreign exchange market data and has led to the discovery of a large set of scaling laws that have not been previously observed. The scaling laws identify properties of the underlying data series, such as the size of the expected price overshoot after an intrinsic time event or the number of expected directional-changes within a physical time interval or price threshold. For example, a scaling relating the expected number of directional-changes observed over the fixed period to the size of the threshold : , where and are thescaling law
In statistics, a power law is a functional relationship between two quantities, where a relative change in one quantity results in a proportional relative change in the other quantity, independent of the initial size of those quantities: one q ...
coefficients.
Other applications of the directional-change intrinsic time in finance include:
* trading strategy characterised by the annual Sharpe ratio
In finance, the Sharpe ratio (also known as the Sharpe index, the Sharpe measure, and the reward-to-variability ratio) measures the performance of an investment such as a security or portfolio compared to a risk-free asset, after adjusting for its ...
3.04
* tools designed to monitor liquidity
Liquidity is a concept in economics involving the convertibility of assets and obligations. It can include:
* Market liquidity, the ease with which an asset can be sold
* Accounting liquidity, the ability to meet cash obligations when due
* Liq ...
at multiple trend scales.
The methodology can also be used for applications beyond economics and finance. It can be applied to other scientific domains and opens a new avenue of research in the area of BigData.
References
*Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
{{reflist Data analysis