diapir on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A diapir (; , ) is a type of intrusion in which a more mobile and ductilely deformable material is forced into brittle overlying rocks. Depending on the tectonic environment, diapirs can range from idealized mushroom-shaped Rayleigh–Taylor instability structures in regions with low tectonic stress such as in the
A diapir (; , ) is a type of intrusion in which a more mobile and ductilely deformable material is forced into brittle overlying rocks. Depending on the tectonic environment, diapirs can range from idealized mushroom-shaped Rayleigh–Taylor instability structures in regions with low tectonic stress such as in the
 Differential loading causes salt deposits covered by
Differential loading causes salt deposits covered by
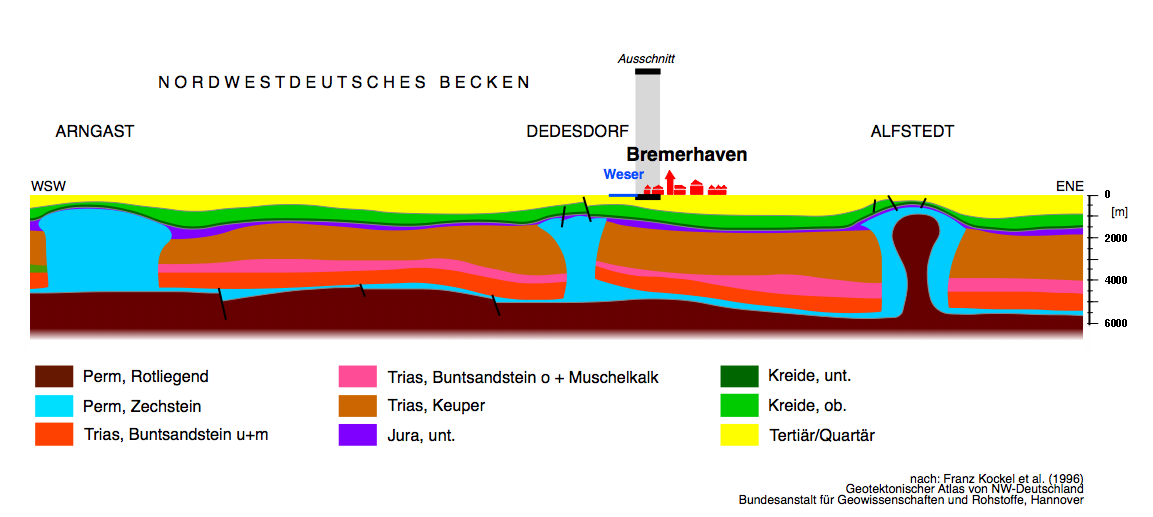 Diapirs or piercement structures are structures resulting from the penetration of overlaying material. By pushing upward and piercing overlying rock layers, diapirs can form
Diapirs or piercement structures are structures resulting from the penetration of overlaying material. By pushing upward and piercing overlying rock layers, diapirs can form
 There are many salt domes and salt glaciers in the
There are many salt domes and salt glaciers in the 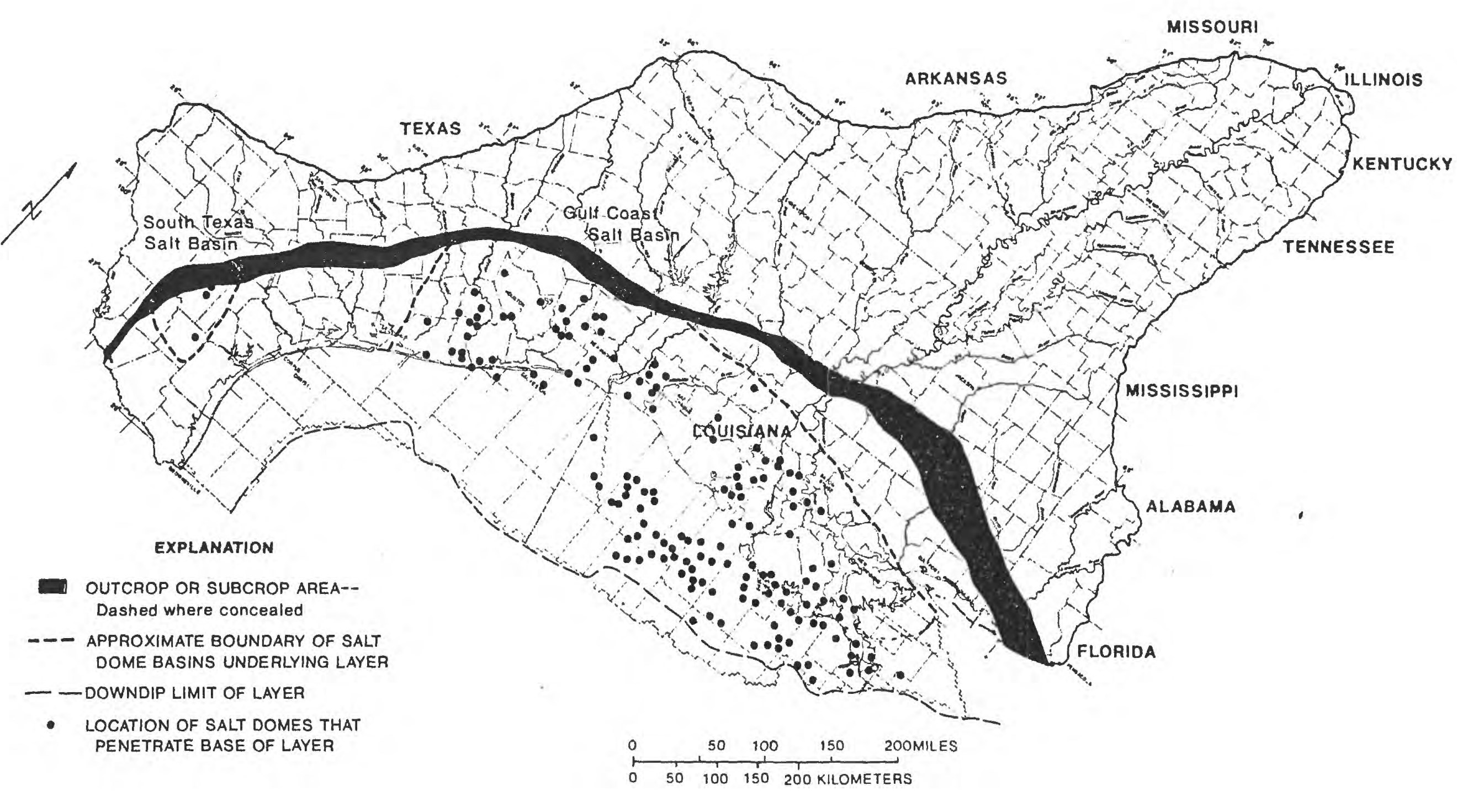
Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico () is an oceanic basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, mostly surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north, and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United States; on the southw ...
to narrow dikes of material that move along tectonically induced fractures in surrounding rock.
The term was introduced by Romanian geologist Ludovic Mrazek, who was the first to understand the principle of salt tectonics
upright=1.7
Salt tectonics, or halokinesis, or halotectonics, is concerned with the geometries and processes associated with the presence of significant thicknesses of evaporites containing rock salt within a stratigraphic sequence of rocks. This ...
and plasticity. The term ''diapir'' may be applied to '' igneous intrusions'', but it is more commonly applied to non-igneous, relatively cold materials, such as salt dome
A salt dome is a type of structural dome formed when salt (or other evaporite minerals) intrudes into overlying rocks in a process known as diapirism. Salt domes can have unique surface and subsurface structures, and they can be discovered us ...
s and mud
Mud (, or Middle Dutch) is loam, silt or clay mixed with water. Mud is usually formed after rainfall or near water sources. Ancient mud deposits hardened over geological time to form sedimentary rock such as shale or mudstone (generally cal ...
diapirs. If a salt diapir reaches the surface, it can flow because salt becomes ductile with a small amount of moisture, forming a salt glacier
A salt glacier (or namakier) is a rare flow of salt that is created when a rising diapir in a salt dome breaches the surface of Earth. The name ‘salt glacier’ was given to this phenomenon due to the similarity of movement when compared with ...
.
Occurrence
 Differential loading causes salt deposits covered by
Differential loading causes salt deposits covered by overburden
In mining, overburden (also called waste or spoil) is the material that lies above an area that lends itself to economical exploitation, such as the rock, soil, and ecosystem that lies above a coal seam or ore body. Overburden is distinct from tai ...
(sediment
Sediment is a solid material that is transported to a new location where it is deposited. It occurs naturally and, through the processes of weathering and erosion, is broken down and subsequently sediment transport, transported by the action of ...
) to rise upward toward the surface and pierce the overburden, forming diapirs (including salt dome
A salt dome is a type of structural dome formed when salt (or other evaporite minerals) intrudes into overlying rocks in a process known as diapirism. Salt domes can have unique surface and subsurface structures, and they can be discovered us ...
s), pillars, sheets, or other geological structures.
In addition to Earth-based observations, diapirism is thought to occur on Neptune's moon Triton, Jupiter's moon Europa, Saturn's moon Enceladus, and Uranus's moon Miranda.
Formation
Diapirs commonly intrude buoyantly upward along fractures or zones of structural weakness through denser overlying rocks. This process is known as ''diapirism''. The resulting structures are also referred to as ''piercement structures''. In the process, segments of the existingstrata
In geology and related fields, a stratum (: strata) is a layer of Rock (geology), rock or sediment characterized by certain Lithology, lithologic properties or attributes that distinguish it from adjacent layers from which it is separated by v ...
can be disconnected and pushed upwards. While moving higher, they retain many of their original properties, e.g. pressure; their pressure can be significantly different from the pressure of the shallower strata they get pushed into. Such overpressured "floaters" pose a significant risk when trying to drill
A drill is a tool used for making round holes or driving fasteners. It is fitted with a drill bit for making holes, or a screwdriver bit for securing fasteners. Historically, they were powered by hand, and later mains power, but cordless b ...
through them. There is an analogy to a Galilean thermometer.
Rock types such as evaporitic salt deposits, and gas charged muds are potential sources of diapirs. Diapirs also form in the Earth's mantle
Earth's mantle is a layer of silicate mineral, silicate rock between the Earth's crust, crust and the Earth's outer core, outer core. It has a mass of and makes up 67% of the mass of Earth. It has a thickness of making up about 46% of Earth's ...
when a sufficient mass of hot, less dense magma
Magma () is the molten or semi-molten natural material from which all igneous rocks are formed. Magma (sometimes colloquially but incorrectly referred to as ''lava'') is found beneath the surface of the Earth, and evidence of magmatism has also ...
assembles. Diapirism in the mantle is thought to be associated with the development of large igneous province
A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including intrusive ( sills, dikes) and extrusive (lava flows, tephra deposits), arising when magma travels through the crust towards the surface. The format ...
s and some mantle plume
A mantle plume is a proposed mechanism of convection within the Earth's mantle, hypothesized to explain anomalous volcanism. Because the plume head partially melts on reaching shallow depths, a plume is often invoked as the cause of volcanic ho ...
s.
Explosive, hot volatile rich magma or volcanic eruptions are referred to generally as diatremes. Diatremes are not usually associated with diapirs, as they are small-volume magmas which ascend by volatile plumes, not by density contrast with the surrounding mantle.
Economic importance
 Diapirs or piercement structures are structures resulting from the penetration of overlaying material. By pushing upward and piercing overlying rock layers, diapirs can form
Diapirs or piercement structures are structures resulting from the penetration of overlaying material. By pushing upward and piercing overlying rock layers, diapirs can form anticline
In structural geology, an anticline is a type of Fold (geology), fold that is an arch-like shape and has its oldest Bed (geology), beds at its core, whereas a syncline is the inverse of an anticline. A typical anticline is convex curve, c ...
s (arch-like shape folds), salt domes (mushroom/ dome-shaped diapirs), and other structures capable of trapping hydrocarbons
In organic chemistry, a hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon. Hydrocarbons are examples of group 14 hydrides. Hydrocarbons are generally colourless and hydrophobic; their odor is usually faint, and may b ...
such as petroleum
Petroleum, also known as crude oil or simply oil, is a naturally occurring, yellowish-black liquid chemical mixture found in geological formations, consisting mainly of hydrocarbons. The term ''petroleum'' refers both to naturally occurring un ...
and natural gas
Natural gas (also fossil gas, methane gas, and gas) is a naturally occurring compound of gaseous hydrocarbons, primarily methane (95%), small amounts of higher alkanes, and traces of carbon dioxide and nitrogen, hydrogen sulfide and helium ...
. Igneous intrusions themselves are typically too hot to allow the preservation of preexisting hydrocarbon
In organic chemistry, a hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon. Hydrocarbons are examples of group 14 hydrides. Hydrocarbons are generally colourless and Hydrophobe, hydrophobic; their odor is usually fain ...
s.
Occurrences
 There are many salt domes and salt glaciers in the
There are many salt domes and salt glaciers in the Zagros mountains
The Zagros Mountains are a mountain range in Iran, northern Iraq, and southeastern Turkey. The mountain range has a total length of . The Zagros range begins in northwestern Iran and roughly follows Iran's western border while covering much of s ...
, formed by the collision
In physics, a collision is any event in which two or more bodies exert forces on each other in a relatively short time. Although the most common use of the word ''collision'' refers to incidents in which two or more objects collide with great for ...
of two tectonic plates
Plate tectonics (, ) is the scientific theory that the Earth's lithosphere comprises a number of large tectonic plates, which have been slowly moving since 3–4 billion years ago. The model builds on the concept of , an idea developed durin ...
, the Eurasian Plate and the Arabian Plate. There are underwater salt domes in the Gulf of Mexico.
See also
* * *References
{{reflist Economic geology Geological processes Intrusions Salt domes Structural geology Structure of the Earth