creole people on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Creole peoples may refer to various ethnic groups around the world. The term's meaning exhibits regional variations, often sparking debate.
Creole peoples represent a diverse array of ethnicities, each possessing a distinct cultural identity that has been shaped over time. The emergence of
 In Africa, the term Creole refers to any ethnic group formed during the European colonial era, with some mix of African and non-African racial or cultural heritage. Creole communities are found on most African islands and along the continent's coastal regions where indigenous Africans first interacted with Europeans. As a result of these contacts, five major Creole types emerged in Africa: Portuguese,
In Africa, the term Creole refers to any ethnic group formed during the European colonial era, with some mix of African and non-African racial or cultural heritage. Creole communities are found on most African islands and along the continent's coastal regions where indigenous Africans first interacted with Europeans. As a result of these contacts, five major Creole types emerged in Africa: Portuguese,
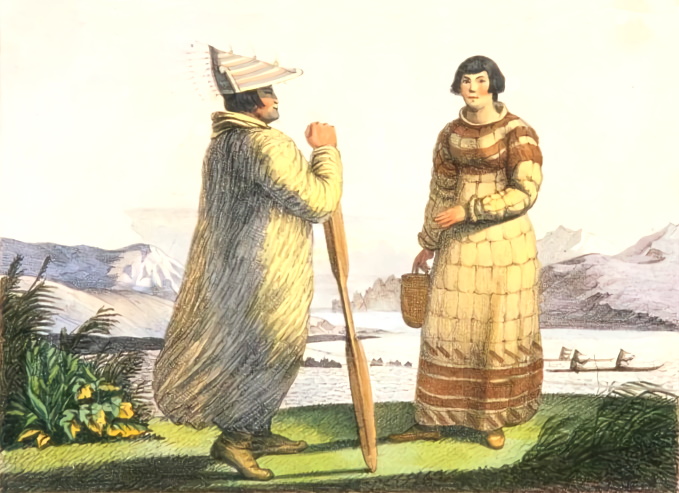 Alaskan Creole, sometimes colloquially spelled "Kriol" in English (from Russian креол), are a unique people who first came about through the intermingling of Sibero-Russian '' promyshlenniki'' men with
Alaskan Creole, sometimes colloquially spelled "Kriol" in English (from Russian креол), are a unique people who first came about through the intermingling of Sibero-Russian '' promyshlenniki'' men with
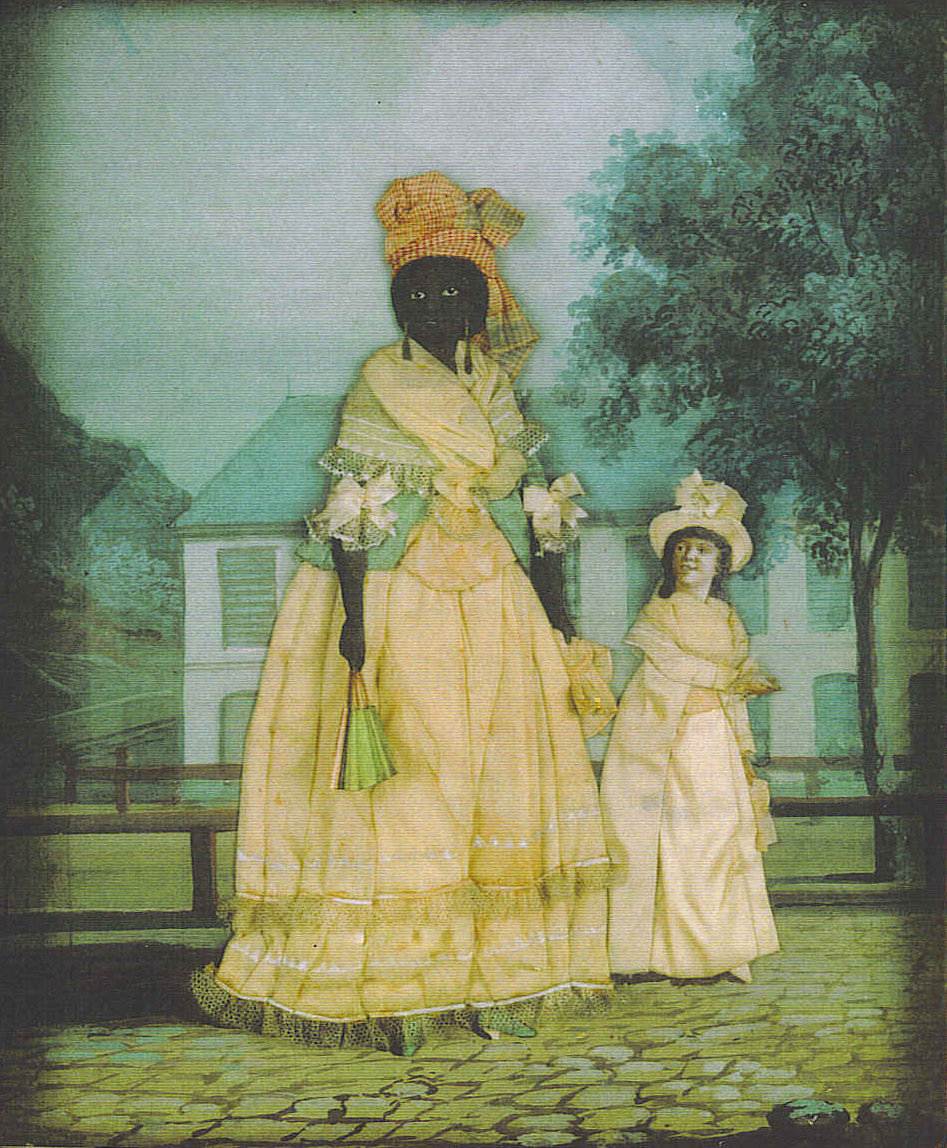 Louisiana Creoles historically spoke a variety of languages; today, the most prominent include Louisiana French and
Louisiana Creoles historically spoke a variety of languages; today, the most prominent include Louisiana French and
 In colonial Texas, the term "Creole" (''criollo'') distinguished old-world Africans and Europeans from their descendants born in the new world, Creoles; they composed the citizen class of
In colonial Texas, the term "Creole" (''criollo'') distinguished old-world Africans and Europeans from their descendants born in the new world, Creoles; they composed the citizen class of
 In
In
 The usage of creole in the islands of the southwest of the Indian Ocean varies according to the island. In
The usage of creole in the islands of the southwest of the Indian Ocean varies according to the island. In
 In the latter period of settlement of Latin America called ''La Colonia'', the Bourbon Spanish Crown preferred Spanish-born ''
In the latter period of settlement of Latin America called ''La Colonia'', the Bourbon Spanish Crown preferred Spanish-born ''
International Organization of Creole Peoples
{{DEFAULTSORT:Creole Peoples Creole culture African diaspora history African diaspora Ethnonyms
creole languages
A creole language, or simply creole, is a stable form of contact language that develops from the process of different languages simplifying and mixing into a new form (often a pidgin), and then that form expanding and elaborating into a full-fl ...
, frequently associated with Creole ethnicity, is a separate phenomenon.
In specific historical contexts, particularly during the European colonial era, the term ''Creole'' applies to ethnicities formed through large-scale population movements. These movements involved people from diverse linguistic
Linguistics is the scientific study of language. The areas of linguistic analysis are syntax (rules governing the structure of sentences), semantics (meaning), Morphology (linguistics), morphology (structure of words), phonetics (speech sounds ...
and cultural
Culture ( ) is a concept that encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and Social norm, norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, Social norm, customs, capabilities, Attitude (psychology), attitudes ...
backgrounds who converged upon newly established colonial territories. Often involuntarily separated from their ancestral homelands, these populations were forced to adapt and create a new way of life. Through a process of cultural amalgamation, they selectively adopted and merged desirable elements from their varied heritages. This resulted in the emergence of novel social norms, languages, and cultural practices that transcended their individual origins.
This process of cultural amalgamation, termed creolization
Creolization is the process through which creole languages and cultures emerge. Creolization was first used by linguists to explain how contact languages become creole languages, but now scholars in other social sciences use the term to describe ...
, is characterized by rapid social change that ultimately leads to the formation of a distinct Creole identity.
Etymology and overview
The English word creole derives from the French ''créole'', which in turn came from Portuguese ''crioulo'', a diminutive of ''cria'' meaning a person raised in one's house. ''Cria'' is derived from ''criar'', meaning "to raise or bring up", itself derived from the Latin ''creare'', meaning "to make, bring forth, produce, beget"; which is also the source of the English word "create". It originally referred to the descendants of European colonists who had been born in the colony. Creole is also known by cognates in other languages, such as ''crioulo'', ''criollo'', ''creolo'', ''kriolu'', ''criol'', ''kreyol'', ''kreol'', ''kriol'', ''krio'', and ''kriyoyo''. InLouisiana
Louisiana ( ; ; ) is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It borders Texas to the west, Arkansas to the north, and Mississippi to the east. Of the 50 U.S. states, it ranks 31st in area and 25 ...
, the term Creole has been used since 1792 to represent descendants of African or mixed heritage parents as well as children of French and Spanish descent with no racial mixing. Its use as in the name for languages started from 1879, while as an adjective for languages, its use began around 1748.
In Spanish-speaking countries, the word ''Criollo
Criollo or criolla (Spanish for creole) may refer to:
People
* Criollo people, a social class in the Spanish colonial system.
Animals
* Criollo duck, a species of duck native to Central and South America.
* Criollo cattle, a group of cattle bre ...
'' refers to the descendants of Europeans born in the Americas, but also in some countries, to describe something local or very typical of a particular Latin America
Latin America is the cultural region of the Americas where Romance languages are predominantly spoken, primarily Spanish language, Spanish and Portuguese language, Portuguese. Latin America is defined according to cultural identity, not geogr ...
n region.
In the Caribbean
The Caribbean ( , ; ; ; ) is a region in the middle of the Americas centered around the Caribbean Sea in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, mostly overlapping with the West Indies. Bordered by North America to the north, Central America ...
, the term broadly refers to all the people, whatever their class or ancestry — African, East Asian, European, Indian — who are part of the culture of the Caribbean. In Trinidad
Trinidad is the larger, more populous island of the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago, the country. The island lies off the northeastern coast of Venezuela and sits on the continental shelf of South America. It is the southernmost island in ...
, the term Creole is used to designate all Trinidadians except those of Asian origin. In Suriname
Suriname, officially the Republic of Suriname, is a country in northern South America, also considered as part of the Caribbean and the West Indies. It is a developing country with a Human Development Index, high level of human development; i ...
, the term refers only to the descendants of enslaved Africans and in neighboring French Guiana
French Guiana, or Guyane in French, is an Overseas departments and regions of France, overseas department and region of France located on the northern coast of South America in the Guianas and the West Indies. Bordered by Suriname to the west ...
the term refers to anyone, regardless of skin colour, who has adopted a European lifestyle.
 In Africa, the term Creole refers to any ethnic group formed during the European colonial era, with some mix of African and non-African racial or cultural heritage. Creole communities are found on most African islands and along the continent's coastal regions where indigenous Africans first interacted with Europeans. As a result of these contacts, five major Creole types emerged in Africa: Portuguese,
In Africa, the term Creole refers to any ethnic group formed during the European colonial era, with some mix of African and non-African racial or cultural heritage. Creole communities are found on most African islands and along the continent's coastal regions where indigenous Africans first interacted with Europeans. As a result of these contacts, five major Creole types emerged in Africa: Portuguese, African American
African Americans, also known as Black Americans and formerly also called Afro-Americans, are an Race and ethnicity in the United States, American racial and ethnic group that consists of Americans who have total or partial ancestry from an ...
, Dutch, French and British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies.
* British national identity, the characteristics of British people and culture ...
.
The ''Crioulos'' of African or mixed Portuguese and African descent eventually gave rise to several ethnic groups in Cape Verde
Cape Verde or Cabo Verde, officially the Republic of Cabo Verde, is an island country and archipelagic state of West Africa in the central Atlantic Ocean, consisting of ten volcanic islands with a combined land area of about . These islands ...
, Guinea-Bissau
Guinea-Bissau, officially the Republic of Guinea-Bissau, is a country in West Africa that covers with an estimated population of 2,026,778. It borders Senegal to Guinea-Bissau–Senegal border, its north and Guinea to Guinea–Guinea-Bissau b ...
, São Tomé e Príncipe, Angola
Angola, officially the Republic of Angola, is a country on the west-Central Africa, central coast of Southern Africa. It is the second-largest Portuguese-speaking world, Portuguese-speaking (Lusophone) country in both total area and List of c ...
and Mozambique
Mozambique, officially the Republic of Mozambique, is a country located in Southeast Africa bordered by the Indian Ocean to the east, Tanzania to the north, Malawi and Zambia to the northwest, Zimbabwe to the west, and Eswatini and South Afr ...
. The French-speaking Mauritian and Seychellois Creole
Seychellois Creole (), also known as Kreol, Seselwa Creole French, and Seselwa Creole is the French-based creole language spoken by the Seychellois Creole people, Seychelles Creole people of the Seychelles. It is one of the national language, na ...
s are both either African or ethnically mixed and Christianized
Christianization (or Christianisation) is a term for the specific type of change that occurs when someone or something has been or is being converted to Christianity. Christianization has, for the most part, spread through missions by individu ...
. On Réunion
Réunion (; ; ; known as before 1848) is an island in the Indian Ocean that is an overseas departments and regions of France, overseas department and region of France. Part of the Mascarene Islands, it is located approximately east of the isl ...
, the term Creole applies to all people born on the island, while in South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the Southern Africa, southernmost country in Africa. Its Provinces of South Africa, nine provinces are bounded to the south by of coastline that stretches along the Atlantic O ...
, the blending of East African and Southeast Asian slaves with Dutch settlers, later produced a creolized population. The Fernandino Creole peoples of Equatorial Guinea
Equatorial Guinea, officially the Republic of Equatorial Guinea, is a country on the west coast of Central Africa. It has an area of . Formerly the colony of Spanish Guinea, its post-independence name refers to its location both near the Equ ...
are a mix of Afro-Cubans
Afro-Cubans () or Black Cubans are Cubans of full or partial sub-Saharan African ancestry. The term ''Afro-Cuban'' can also refer to historical or cultural elements in Cuba associated with this community, and the combining of native African an ...
with Emancipados
Emancipado () was a term used for an African-descended social-political demographic within the population of Spanish Guinea (modern day Equatorial Guinea) that existed in the early to mid 1900s. This segment of the native population had become as ...
and English-speaking Liberated Africans, while the Americo-Liberian
Americo-Liberian people (also known as Congo people or Congau people),Cooper, Helene, ''The House at Sugar Beach: In Search of a Lost African Childhood'' (United States: Simon and Schuster, 2008), p. 6 are a Liberian ethnic group of African Am ...
s and Sierra Leone Creoles resulted from the intermingling of African Recaptives with Afro-Caribbean
Afro-Caribbean or African Caribbean people are Caribbean people who trace their full or partial ancestry to Sub-Saharan Africa. The majority of the modern Afro-Caribbean people descend from the Indigenous peoples of Africa, Africans (primarily fr ...
people and African American
African Americans, also known as Black Americans and formerly also called Afro-Americans, are an Race and ethnicity in the United States, American racial and ethnic group that consists of Americans who have total or partial ancestry from an ...
s.
Perhaps due to the range of divergent descriptions and lack of a coherent definition, Norwegian anthropologist T. H. Eriksen concludes:
The following ethnic groups have been historically characterized as "Creole" peoples:
* Afro-Brazilian Crioulos
* Aku Krio people
* Atlantic Creoles
* Belizean Kriol people
* Cape Verdeans (Crioulos)
* Criollo people
In Hispanic America, criollo () is a term used originally to describe people of full Spaniards, Spanish descent born in the Viceroyalty, viceroyalties. In different Latin American countries, the word has come to have different meanings, mostly ...
(European diaspora born in the Spanish colonies in the Americas)
* Fernandino Creole peoples
* Haitian Creole people
** Affranchi
''Affranchi'' (, ) is a former French legal term denoting a freedman or emancipated slave, but also a pejorative term for free people of color. It is used in the English language to describe the social class of freedmen in Saint-Domingue, and ...
s
* Afro-Honduran Creoles
* Liberian Creole people
* Louisiana Creole people
Louisiana Creoles (, , ) are a Louisiana French people, Louisiana French ethnic group descended from the inhabitants of colonial Louisiana (New France), Louisiana during the periods of French colonial empire, French and Spanish Empire, Spanis ...
** Creoles of color
The Creoles of color are a multiracial ethnic group of Louisiana Creoles that developed in the former French and Spanish colonies of Louisiana (especially in New Orleans), Mississippi, Alabama, and Northwestern Florida, in what is now the Unite ...
* Mauritian Creole people
** also Réunion Creole
Réunion Creole, or Reunionese Creole (; ), is a French-based creole languages, French-based creole language spoken on Réunion. It is derived mainly from French language, French and includes terms from Malagasy language, Malagasy, Hindi, Port ...
* Seychellois Creole people
* Sierra Leone Creole people
The Sierra Leone Creole people () are an ethnic group of Sierra Leone. The Sierra Leone Creole people are descendants of freed African-American, Afro-Caribbean, and Liberated African slaves who settled in the Western Area of Sierra Leone be ...
* Surinamese Creole people
United States
Alaska
 Alaskan Creole, sometimes colloquially spelled "Kriol" in English (from Russian креол), are a unique people who first came about through the intermingling of Sibero-Russian '' promyshlenniki'' men with
Alaskan Creole, sometimes colloquially spelled "Kriol" in English (from Russian креол), are a unique people who first came about through the intermingling of Sibero-Russian '' promyshlenniki'' men with Aleut
Aleuts ( ; (west) or (east) ) are the Indigenous people of the Aleutian Islands, which are located between the North Pacific Ocean and the Bering Sea. Both the Aleuts and the islands are politically divided between the US state of Alaska ...
and Eskimo
''Eskimo'' () is a controversial Endonym and exonym, exonym that refers to two closely related Indigenous peoples: Inuit (including the Alaska Native Iñupiat, the Canadian Inuit, and the Greenlandic Inuit) and the Yupik peoples, Yupik (or Sibe ...
women in the late 18th century and assumed a prominent position in the economy of Russian America
Russian(s) may refer to:
*Russians (), an ethnic group of the East Slavic peoples, primarily living in Russia and neighboring countries
*A citizen of Russia
*Russian language, the most widely spoken of the Slavic languages
*''The Russians'', a b ...
and the North Pacific Rim.
Chesapeake Colonies
Atlantic Creole is a term coined by historian Ira Berlin to describe a group of people from Angola and Central Africa in the 16th and 17th centuries with cultural or ethnic ties toAfrica
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent after Asia. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 20% of Earth's land area and 6% of its total surfac ...
, Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
, and sometimes the Caribbean
The Caribbean ( , ; ; ; ) is a region in the middle of the Americas centered around the Caribbean Sea in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, mostly overlapping with the West Indies. Bordered by North America to the north, Central America ...
. Some of these people arrived in the Chesapeake Colonies as the Charter Generation of slaves
Slavery is the ownership of a person as property, especially in regards to their labour. Slavery typically involves compulsory work, with the slave's location of work and residence dictated by the party that holds them in bondage. Enslavemen ...
during the European colonization of the Americas
During the Age of Discovery, a large scale colonization of the Americas, involving a number of European countries, took place primarily between the late 15th century and the early 19th century. The Norse explored and colonized areas of Europe a ...
before 1660. Some had lived and worked in Europe or the Caribbean before coming (or being transported) to North America. Examples of such men included John Punch and Emanuel Driggus (his surname was likely derived from Rodrigues
Rodrigues ( ; Mauritian Creole, Creole: ) is a Autonomous administrative division, autonomous Outer islands of Mauritius, outer island of the Republic of Mauritius in the Indian Ocean, about east of Mauritius. It is part of the Mascarene Isl ...
).
Also, during the early settlement of the colonies, children born of immigrants in the colonies were often referred to as "Creole". This is found more often in the Chesapeake Colonies.
Louisiana
In theUnited States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
, the words "Louisiana Creole" refers to people of any race or mixture thereof who are descended from colonial French La Louisiane and colonial Spanish Louisiana (New Spain)
Louisiana (, ), was a province of New Spain from 1762 to 1801. It was primarily located in the center of North America encompassing the western basin of the Mississippi River plus New Orleans. The area had originally been claimed and controlle ...
settlers before the Louisiana region became part of the United States in 1803 with the Louisiana Purchase
The Louisiana Purchase () was the acquisition of the Louisiana (New France), territory of Louisiana by the United States from the French First Republic in 1803. This consisted of most of the land in the Mississippi River#Watershed, Mississipp ...
. Both the word and the ethnic group derive from a similar usage, beginning in the Caribbean in the 16th century, which distinguished people born in the French, Spanish, and Portuguese colonies from the various new arrivals born in their respective, non-Caribbean homelands. Some writers from other parts of the country have mistakenly assumed the term to refer only to people of mixed racial descent, but this is not the traditional Louisiana
Louisiana ( ; ; ) is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It borders Texas to the west, Arkansas to the north, and Mississippi to the east. Of the 50 U.S. states, it ranks 31st in area and 25 ...
usage.Dominguez, Virginia R. ''White by Definition: Social Classification in Creole Louisiana.'' New Brunswick: Rutgers University Press, 1986.Eaton, Clement. ''A History of the Old South: The Emergence of a Reluctant Nation,'' third edition. New York: Macmillan, 1975.Fowler, H.W. (1926) ''A Dictionary of Modern English Usage'', Oxford University Press.
In Louisiana, the term "Creole" was first used to describe people born in Louisiana, who used the term to distinguish themselves from newly arrived immigrants. It was not a racial or ethnic identifier; it was simply synonymous with "born in the New World," meant to separate native-born people of any ethnic background—white, African, or any mixture thereof—from European immigrants and slaves imported from Africa. Later, the term was racialized after newly arrived Anglo-Americans began to associate créolité, or the quality of being Creole, with racially mixed ancestry. This caused many white Creoles to eventually abandon the label out of fear that the term would lead mainstream Americans to believe them to be of racially mixed descent (and thus endanger their livelihoods or social standing). Later writers occasionally make distinctions among French Creoles (of European ancestry), Creoles of Color (of mixed ethnic ancestry), and occasionally, African Creoles (of primarily African descendant); these categories, however, are later inventions, and most primary documents from the eighteenth, nineteenth and early twentieth centuries make use of the word "Creole" without any additional qualifier. Creoles of Spanish and German descent also exist, and Spanish Creoles survive today as Isleños
Isleños () are the Kinship, descendants of Canarian people, Canarian settlers and immigrants to present-day Louisiana, Puerto Rico, Texas, Cuba, the Dominican Republic, Venezuela, and other parts of the Americas. In these places, the name ''i ...
and Malagueños, both found in southern Louisiana. However, all racial categories of Creoles - from Caucasian, mixed racial, African, to Native American - tended to think and refer to themselves solely as Creole, a commonality in many other Francophone
The Francophonie or Francophone world is the whole body of people and organisations around the world who use the French language regularly for private or public purposes. The term was coined by Onésime Reclus in 1880 and became important a ...
and Iberoamerican cultures, who tend to lack strict racial separations common in United States History and other countries with large populations from Northern Europe
The northern region of Europe has several definitions. A restrictive definition may describe northern Europe as being roughly north of the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, which is about 54th parallel north, 54°N, or may be based on other ge ...
's various cultures. This racial neutrality persists to the modern day, as many Creoles do not use race as a factor for being a part of the ethno-culture.
Contemporary usage has again broadened the meaning of Louisiana Creoles to describe a broad cultural group of people of all races who share a colonial Louisianian background. Louisianians who identify themselves as "Creole" are most commonly from historically Francophone
The Francophonie or Francophone world is the whole body of people and organisations around the world who use the French language regularly for private or public purposes. The term was coined by Onésime Reclus in 1880 and became important a ...
and Hispanic
The term Hispanic () are people, Spanish culture, cultures, or countries related to Spain, the Spanish language, or broadly. In some contexts, Hispanic and Latino Americans, especially within the United States, "Hispanic" is used as an Ethnici ...
communities. Some of their ancestors came to Louisiana directly from France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
, Spain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Eur ...
, or Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
, while others came via the French and Spanish colonies in the Caribbean
The Caribbean ( , ; ; ; ) is a region in the middle of the Americas centered around the Caribbean Sea in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, mostly overlapping with the West Indies. Bordered by North America to the north, Central America ...
and Canada. Many Louisiana Creole families arrived in Louisiana from Saint-Domingue
Saint-Domingue () was a French colonization of the Americas, French colony in the western portion of the Caribbean island of Hispaniola, in the area of modern-day Haiti, from 1659 to 1803. The name derives from the Spanish main city on the isl ...
as refugees from the Haitian Revolution
The Haitian Revolution ( or ; ) was a successful insurrection by slave revolt, self-liberated slaves against French colonial rule in Saint-Domingue, now the sovereign state of Haiti. The revolution was the only known Slave rebellion, slave up ...
, along with other immigrants from Caribbean colonial centers like Santo Domingo
Santo Domingo, formerly known as Santo Domingo de Guzmán, is the capital and largest city of the Dominican Republic and the List of metropolitan areas in the Caribbean, largest metropolitan area in the Caribbean by population. the Distrito Na ...
and Havana
Havana (; ) is the capital and largest city of Cuba. The heart of La Habana Province, Havana is the country's main port and commercial center.Acadians
The Acadians (; , ) are an ethnic group descended from the French colonial empire, French who settled in the New France colony of Acadia during the 17th and 18th centuries. Today, most descendants of Acadians live in either the Northern Americ ...
of Canada are also Creoles in a strict sense, and there are many historical examples of people of full European ancestry and with Acadian surnames, such as the influential Alexandre and Alfred Mouton, being explicitly described as "Creoles." Today, however, the descendants of the Acadians are more commonly referred to as, and identify as, 'Cajuns
The Cajuns (; Louisiana French language, French: ''les Cadjins'' or ''les Cadiens'' ), also known as Louisiana ''Acadians'' (French: ''les Acadiens''), are a Louisiana French people, Louisiana French ethnic group, ethnicity mainly found in t ...
'—a derivation of the word Acadian, indicating French Canadian settlers as ancestors. The distinction between "Cajuns" and "Creoles" is stronger today than it was in the past because American racial ideologies have strongly influenced the meaning of the word "Creole" to the extent that there is no longer unanimous agreement among Louisianians on the word's precise definition. Today, many assume that any francophone person of European descent is Cajun and any francophone of African descent is Creole—a false assumption that would not have been recognized in the nineteenth century. Some assert that "Creole" refers to aristocratic urbanites whereas "Cajuns" are agrarian members of the francophone working class, but this is another relatively recent distinction. Creoles may be of any race and live in any area, rural or urban. The Creole culture of Southwest Louisiana is thus more similar to the culture dominant in Acadiana than it is to the Creole culture of New Orleans. Though the land areas overlap around New Orleans and down river, Cajun/Creole culture and language extend westward all along the southern coast of Louisiana, concentrating in areas southwest of New Orleans around Lafayette, and as far as Crowley, Abbeville, and into the rice belt of Louisiana nearer Lake Charles and the Texas border.
 Louisiana Creoles historically spoke a variety of languages; today, the most prominent include Louisiana French and
Louisiana Creoles historically spoke a variety of languages; today, the most prominent include Louisiana French and Louisiana Creole
Louisiana Creole is a French-based creole language spoken by fewer than 10,000 people, mostly in the U.S. state of Louisiana. Also known as Kouri-Vini, it is spoken today by people who may racially identify as white, black, mixed, and Native ...
. (There is a distinction between "Creole" people and the "creole" language. Not all Creoles speak creole—many speak French, Spanish, or English as primary languages.) Spoken creole is dying with continued 'Americanization' in the area. Most remaining Creole lexemes have drifted into popular culture. Traditional creole is spoken among those families determined to keep the language alive or in regions below New Orleans around St. James and St. John Parishes where German immigrants originally settled (also known as 'the German Coast', or La Côte des Allemands) and cultivated the land, keeping the ill-equipped French Colonists from starvation during the Colonial Period and adopting commonly spoken French and creole (arriving with the exiles) as a language of trade.
Creoles are largely Roman Catholic and influenced by traditional French and Spanish culture left from the first Colonial Period, officially beginning in 1722 with the arrival of the Ursuline Nuns, who were preceded by another order, the sisters of the Sacred Heart, with whom they lived until their first convent could be built with monies from the French Crown. (Both orders still educate girls in 2010). The "fiery Latin temperament" described by early scholars on New Orleans culture made sweeping generalizations to accommodate Creoles of Spanish heritage as well as the original French. The mixed-race Creoles, descendants of mixing of European colonists, slaves, and Native Americans or sometimes ''Gens de Couleur'' (free men and women of colour), first appeared during the colonial periods with the arrival of slave populations. Most Creoles, regardless of race, generally consider themselves to share a collective culture. Non-Louisianans often fail to appreciate this and assume that all Creoles are of mixed race, which is historically inaccurate.
Louisiane Creoles were also referred to as ''criollos'', a word from the Spanish language meaning "created" and used in the post-French governance period to distinguish the two groups of New Orleans area and down river Creoles. Both mixed race and European Creole groups share many traditions and language, but their socio-economic roots differed in the original period of Louisiana history. Actually, the French word Créole is derived from the Portuguese word ''Crioulo'', which described people born in the Americas as opposed to Spain.
The term is often used to mean simply "pertaining to the New Orleans
New Orleans (commonly known as NOLA or The Big Easy among other nicknames) is a Consolidated city-county, consolidated city-parish located along the Mississippi River in the U.S. state of Louisiana. With a population of 383,997 at the 2020 ...
area," but this, too, is not historically accurate. People all across the Louisiana territory, including the '' pays des Illinois,'' identified as Creoles, as evidenced by the continued existence of the term ''Créole'' in the critically endangered Missouri French
Missouri French () or Illinois Country French () also known as , and nicknamed " Paw-Paw French" often by individuals outside the community but not exclusively, is a variety of the French language spoken in the upper Mississippi River Valley in ...
.
Mississippi
The Mississippi Gulf Coast region has a significant population of Creoles—especially in Pass Christian, Gulfport,Biloxi
Biloxi ( ; ) is a city in Harrison County, Mississippi, United States. It lies on the Gulf Coast of the United States, Gulf Coast in southern Mississippi, bordering the city of Gulfport, Mississippi, Gulfport to its west. The adjacent cities ar ...
, and Pascagoula. A community known as Creoletown is located in Pascagoula, with its history on record. Many in this location are Catholic and have also used the Creole, French, and English languages.
Texas
 In colonial Texas, the term "Creole" (''criollo'') distinguished old-world Africans and Europeans from their descendants born in the new world, Creoles; they composed the citizen class of
In colonial Texas, the term "Creole" (''criollo'') distinguished old-world Africans and Europeans from their descendants born in the new world, Creoles; they composed the citizen class of New Spain
New Spain, officially the Viceroyalty of New Spain ( ; Nahuatl: ''Yankwik Kaxtillan Birreiyotl''), originally the Kingdom of New Spain, was an integral territorial entity of the Spanish Empire, established by Habsburg Spain. It was one of several ...
's Tejas province.
Texas Creole culture revolved around "ranchos''" (Creole ranches), attended mostly by ''vaqueros'' (cowboys) of African, Spaniard, or Mestizo descent, and Tlaxcalan Nahuatl settlers, who established a number of settlements in southeastern Texas and western Louisiana (e.g. Los Adaes).
Black Texas Creoles have been present in Texas ever since the 1600s; they served as soldiers in Spanish garrisons of eastern Texas. Generations of Black Texas Creoles, also known as "Black Tejanos", played a role in later phases of Texas history: Mexican Texas, Republic of Texas, and American Texas.
Africa
Southern Africa
Unlike the Americas, the term coloured is preferred in Southern Africa to refer to mixed people of African and European descent. The colonisation of theCape Colony
The Cape Colony (), also known as the Cape of Good Hope, was a British Empire, British colony in present-day South Africa named after the Cape of Good Hope. It existed from 1795 to 1802, and again from 1806 to 1910, when it united with three ...
by the Dutch East India Company
The United East India Company ( ; VOC ), commonly known as the Dutch East India Company, was a chartered company, chartered trading company and one of the first joint-stock companies in the world. Established on 20 March 1602 by the States Ge ...
led to the importation of Indonesian, East African and Southeast Asian slaves, who intermingled with Dutch settlers and the indigenous population leading to the development of a creolized population in the early 1700s. Additionally, Portuguese traders mixed with African communities, in what is now present day Mozambique and Zimbabwe, to create the Prazeros and Luso-Africans
Luso-Africans are people of mixed Portuguese and African ancestry who speak Portuguese. The vast majority of Luso-Africans live in former Portuguese Africa, now referred to as '' Lusophone Africa'', comprising the modern countries of Angola, Gu ...
, who were loyal to the Portuguese crown and served to advance its interests in southeastern Africa. A legacy of this era are the numerous Portuguese words that have entered Shona,
Tsonga and Makonde. Today, mixed race communities exist across the region, notably so in South Africa, Namibia and Zimbabwe. In colonial era Zambia, the term ''Eurafrican'' was often used though it has largely fallen out of use in the modern era and is no longer recognized at the national level. Today, South African Coloureds
Coloureds () are multiracial people in South Africa, Namibia and, to a smaller extent, Zimbabwe and Zambia. Their ancestry descends from the interracial mixing that occurred between Europeans, Africans and Asians. Interracial mixing in South ...
and Cape Malay
Cape Malays (, in Arabic Afrikaans, Arabic script) also known as Cape Muslims or Malays, are a Muslim community or ethnic group in South Africa. They are the descendants of enslaved and free Muslims from different parts of the world, specifi ...
form the majority of the population in the Western Cape
The Western Cape ( ; , ) is a provinces of South Africa, province of South Africa, situated on the south-western coast of the country. It is the List of South African provinces by area, fourth largest of the nine provinces with an area of , an ...
and a plurality in the Northern Cape
The Northern Cape ( ; ; ) is the largest and most sparsely populated Provinces of South Africa, province of South Africa. It was created in 1994 when the Cape Province was split up. Its capital is Kimberley, South Africa, Kimberley. It includes ...
.
In addition to Coloured people, the term mestiço
''Mestiço'' is a Portuguese term that referred to persons of mixed European and Indigenous non-European ancestry in the former Portuguese Empire.
Mestiço community in Brazil
In Colonial Brazil, it was initially used to refer to , persons b ...
is used in Angola and Mozambique to refer to mixed race people, who enjoyed a certain privilege during the Portuguese era.
West Africa
 In
In Sierra Leone
Sierra Leone, officially the Republic of Sierra Leone, is a country on the southwest coast of West Africa. It is bordered to the southeast by Liberia and by Guinea to the north. Sierra Leone's land area is . It has a tropical climate and envi ...
, the mingling of newly freed Africans and mixed heritage Nova Scotians and Jamaican Maroons
Jamaican Maroons descend from Africans who freed themselves from slavery in the Colony of Jamaica and established communities of Free black people in Jamaica, free black people in the island's mountainous interior, primarily in the eastern Pari ...
from the Western hemisphere and Liberated Africans - such as the Akan, Igbo people
The Igbo people ( , ; also spelled Ibo" and historically also ''Iboe'', ''Ebo'', ''Eboe'',
/
/
''Eboans'', ''Heebo'';
natively ) are an ethnic group found in Nigeria, Cameroon, Gabon, and Equatorial Guinea. Their primary origin is fo ...
, and Yoruba people
The Yoruba people ( ; , , ) are a West African ethnic group who inhabit parts of Nigeria, Benin, and Togo, which are collectively referred to as Yorubaland. The Yoruba constitute more than 50 million people in Africa, are over a million outsid ...
- over several generations in the late 18th and early 19th centuries led to the eventual creation of the
aristocratic
Aristocracy (; ) is a form of government that places power in the hands of a small, privileged ruling class, the aristocrats.
Across Europe, the aristocracy exercised immense economic, political, and social influence. In Western Christian co ...
ethnic group
An ethnicity or ethnic group is a group of people with shared attributes, which they collectively believe to have, and long-term endogamy. Ethnicities share attributes like language, culture, common sets of ancestry, traditions, society, re ...
now known as the '' Creoles''. Thoroughly westernized in their manners and bourgeois
The bourgeoisie ( , ) are a class of business owners, merchants and wealthy people, in general, which emerged in the Late Middle Ages, originally as a "middle class" between the peasantry and Aristocracy (class), aristocracy. They are tradition ...
in their methods, the Creoles established a comfortable dominance in the country through a combination of British colonial favouritism and political and economic activity. Their influence in the modern republic remains considerable, and their language Krio - an English-based creole language
An English-based creole language (often shortened to English creole) is a creole language for which English was the '' lexifier'', meaning that at the time of its formation the vocabulary of English served as the basis for the majority of the cr ...
- is the lingua franca
A lingua franca (; ; for plurals see ), also known as a bridge language, common language, trade language, auxiliary language, link language or language of wider communication (LWC), is a Natural language, language systematically used to make co ...
and de facto national language
'' ''
A national language is a language (or language variant, e.g. dialect) that has some connection— de facto or de jure—with a nation. The term is applied quite differently in various contexts. One or more languages spoken as first languag ...
spoken throughout the country.
The extension of these Sierra Leoneans' business and religious activities to neighbouring Nigeria
Nigeria, officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf of Guinea in the Atlantic Ocean to the south. It covers an area of . With Demographics of Nigeria, ...
in the late 19th and early 20th centuries - where many of them had ancestral ties - subsequently caused the creation of an offshoot in that country, the '' Saros''. Now often considered to be part of the wider Yoruba ethnicity, the Saros have been prominent in politics, the law, religion, the arts, and journalism.
Portuguese Africa
Atlantic Creole is a term coined by historian Ira Berlin to describe a group of people from Angola and Central Africa in the 16th and 17th centuries with cultural or ethnic ties toAfrica
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent after Asia. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 20% of Earth's land area and 6% of its total surfac ...
, Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
, and sometimes the Caribbean
The Caribbean ( , ; ; ; ) is a region in the middle of the Americas centered around the Caribbean Sea in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, mostly overlapping with the West Indies. Bordered by North America to the north, Central America ...
. They often had Portuguese names and were sometimes mixed race. Their knowledge of different cultures made them skilled traders and negotiators, but some were enslaved and arrived in the Chesapeake Colonies as the Charter Generation of slaves
Slavery is the ownership of a person as property, especially in regards to their labour. Slavery typically involves compulsory work, with the slave's location of work and residence dictated by the party that holds them in bondage. Enslavemen ...
during the Transatlantic Slave Trade
The Atlantic slave trade or transatlantic slave trade involved the transportation by slave traders of Slavery in Africa, enslaved African people to the Americas. European slave ships regularly used the triangular trade route and its Middle Pass ...
before 1660.
The ''Crioulos'' of mixed Portuguese and African descent eventually gave rise to several major ethnic groups in Africa, especially in Cape Verde
Cape Verde or Cabo Verde, officially the Republic of Cabo Verde, is an island country and archipelagic state of West Africa in the central Atlantic Ocean, consisting of ten volcanic islands with a combined land area of about . These islands ...
, Guinea-Bissau
Guinea-Bissau, officially the Republic of Guinea-Bissau, is a country in West Africa that covers with an estimated population of 2,026,778. It borders Senegal to Guinea-Bissau–Senegal border, its north and Guinea to Guinea–Guinea-Bissau b ...
, São Tomé e Príncipe, Equatorial Guinea
Equatorial Guinea, officially the Republic of Equatorial Guinea, is a country on the west coast of Central Africa. It has an area of . Formerly the colony of Spanish Guinea, its post-independence name refers to its location both near the Equ ...
(especially Annobón Province), Ziguinchor ( Casamance), Angola
Angola, officially the Republic of Angola, is a country on the west-Central Africa, central coast of Southern Africa. It is the second-largest Portuguese-speaking world, Portuguese-speaking (Lusophone) country in both total area and List of c ...
, Mozambique
Mozambique, officially the Republic of Mozambique, is a country located in Southeast Africa bordered by the Indian Ocean to the east, Tanzania to the north, Malawi and Zambia to the northwest, Zimbabwe to the west, and Eswatini and South Afr ...
. Only a few of these groups have retained the name ''crioulo'' or variations of it:
* Cape Verde
Cape Verde or Cabo Verde, officially the Republic of Cabo Verde, is an island country and archipelagic state of West Africa in the central Atlantic Ocean, consisting of ten volcanic islands with a combined land area of about . These islands ...
: the dominant ethnic group, called ''Kriolus'' or ''Kriols'' in the local language; the language itself is also called " Creole";
* Guinea-Bissau
Guinea-Bissau, officially the Republic of Guinea-Bissau, is a country in West Africa that covers with an estimated population of 2,026,778. It borders Senegal to Guinea-Bissau–Senegal border, its north and Guinea to Guinea–Guinea-Bissau b ...
: ''Crioulos''
* São Tomé and Príncipe
São Tomé and Príncipe, officially the Democratic Republic of São Tomé and Príncipe, is an island country in the Gulf of Guinea, off the western equatorial coast of Central Africa. It consists of two archipelagos around the two main isla ...
: ''Crioulos''
Indian Ocean
 The usage of creole in the islands of the southwest of the Indian Ocean varies according to the island. In
The usage of creole in the islands of the southwest of the Indian Ocean varies according to the island. In Mauritius
Mauritius, officially the Republic of Mauritius, is an island country in the Indian Ocean, about off the southeastern coast of East Africa, east of Madagascar. It includes the main island (also called Mauritius), as well as Rodrigues, Ag ...
, Mauritian Creoles will be identified based on both ethnicity and religion. Mauritian Creoles being either people
The term "the people" refers to the public or Common people, common mass of people of a polity. As such it is a concept of human rights law, international law as well as constitutional law, particularly used for claims of popular sovereignty. I ...
who are of Mauritian ancestry or those who are both racially mixed and Christian. The Mauritian Constitution identifies four communities namely, Hindu, Muslim, Chinese and the General Population. Creoles are included in the General Population category along with white Christians.
The term also indicates the same to the people of Seychelles
Seychelles (, ; ), officially the Republic of Seychelles (; Seychellois Creole: ), is an island country and archipelagic state consisting of 155 islands (as per the Constitution) in the Indian Ocean. Its capital and largest city, Victoria, ...
. On Réunion
Réunion (; ; ; known as before 1848) is an island in the Indian Ocean that is an overseas departments and regions of France, overseas department and region of France. Part of the Mascarene Islands, it is located approximately east of the isl ...
the term creole applies to all people born on the island.
In all three societies, creole also refers to the new languages derived from French and incorporating other languages.
Former Spanish colonies
In regions that were formerly colonies ofSpain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Eur ...
, the Spanish word ''criollo
Criollo or criolla (Spanish for creole) may refer to:
People
* Criollo people, a social class in the Spanish colonial system.
Animals
* Criollo duck, a species of duck native to Central and South America.
* Criollo cattle, a group of cattle bre ...
'' (implying "native born") historically denoted a class in the colonial caste system comprising people born in the colonies with total or mostly European, mainly Spanish, descent. Those with mostly European descent were considered on the basis of their “passing” for white. For example, many castizos could've gotten away with passing as criollo because their features would be strikingly European and so many of them would assume such identity in passing, mainly for economic reasons. "Criollo" came to refer to things distinctive of the region, as it is used today, in expressions such as "comida criolla" ("country" food from the area).
 In the latter period of settlement of Latin America called ''La Colonia'', the Bourbon Spanish Crown preferred Spanish-born ''
In the latter period of settlement of Latin America called ''La Colonia'', the Bourbon Spanish Crown preferred Spanish-born ''Peninsulares
In the context of the Spanish Empire, a ''peninsular'' (, pl. ''peninsulares'') was a Spaniard born in Spain residing in the New World, Spanish East Indies, or Spanish Guinea. In the context of the Portuguese Empire, ''reinóis'' (singular ''r ...
'' (literally "born in the Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula ( ), also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in south-western Europe. Mostly separated from the rest of the European landmass by the Pyrenees, it includes the territories of peninsular Spain and Continental Portugal, comprisin ...
") over Criollos for the top military, administrative, and religious offices due to the former mismanagement of the colonies on a previous Habsburg era.
In Argentina
Argentina, officially the Argentine Republic, is a country in the southern half of South America. It covers an area of , making it the List of South American countries by area, second-largest country in South America after Brazil, the fourt ...
, in an ambiguous ethnoracial way, ''criollo'' currently is used for people whose ancestors were already present in the territory in the colonial period, regardless their ethnicity. The exception are dark-skinned African people and current indigenous groups.
The word ''criollo'' is the origin and cognate of the French word ''creole''.
Spanish America
The racially-based caste system was in force throughout the Spanish viceroyalties in the Americas, since the 16th century. During the early Spanish colonial period the Spaniards had a policy selecting promising assimilationist Indigenous to educate and indoctrinate. They were accepted into the colonial leadership but sometimes remained in Spain. Among the descendants of these assimilated sons of chiefs are the Aztec descended Moctezuma de Tultengo. By the 19th century, this discrimination and the example of theAmerican Revolution
The American Revolution (1765–1783) was a colonial rebellion and war of independence in which the Thirteen Colonies broke from British America, British rule to form the United States of America. The revolution culminated in the American ...
and the ideals of the Enlightenment
The Age of Enlightenment (also the Age of Reason and the Enlightenment) was a European intellectual and philosophical movement active from the late 17th to early 19th century. Chiefly valuing knowledge gained through rationalism and empirici ...
eventually led the Spanish American Criollo elite to rebel against the Spanish rule. With the support of the lower classes, they engaged Spain in the Spanish American wars of independence
The Spanish American wars of independence () took place across the Spanish Empire during the early 19th century. The struggles in both hemispheres began shortly after the outbreak of the Peninsular War, forming part of the broader context of the ...
(1810–1826), which ended with the break-up of the former Spanish Empire in the Americas into a number of independent republics.
Spanish Philippines
Persons of pure Spanish descent born in the islands of theSpanish Philippines
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many countries in the Americas
**Spanish cuisine
** Spanish history
** Spanish cultur ...
were called Insulares ("islanders") or Criollos.
Although many of the Spanish Americans in the islands were also persons of pure Spanish descent, they, along with many Mestizos and Castizos from Spanish America living in the East Indies were also classified as "Americanos".
Caribbean
In many parts of the Southern Caribbean, the term Creole people is used to refer to the mixed-race descendants of Europeans and Africans born in the islands. Over time, there was intermarriage with Amerindians and residents from Asia, the Middle East and Latin America as well. They eventually formed a common culture based on their experience of living together in countries colonized by the French, Spanish, Dutch, and British. A typical Creole person from the Caribbean has French, Spanish, Portuguese, British, or Dutch ancestry, mixed with sub-Saharan African ethnicities, and sometimes mixed with Native Indigenous peoples of the Americas. As workers from Asia entered the Caribbean, Creole people of colour intermarried with Arabs, Indians, Chinese, Javanese, Filipinos, Koreans, and Hmongs. The latter combinations were especially common in Guadeloupe. The foods and cultures are the result of creolization of these influences.Caribbean Languages
"Kreyòl" or "Kwéyòl" or "Patois/Patwa" refers to the French-lexiconCreole languages
A creole language, or simply creole, is a stable form of contact language that develops from the process of different languages simplifying and mixing into a new form (often a pidgin), and then that form expanding and elaborating into a full-fl ...
in the Caribbean, including Antillean French Creole, Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole (; , ; , ), or simply Creole (), is a French-based creole languages, French-based creole language spoken by 10 to 12million people worldwide, and is one of the two official languages of Haiti (the other being French), where it ...
, and Trinidadian Creole
Trinidadian Creole is an creole language commonly spoken throughout the island of Trinidad in Trinidad and Tobago. It is distinct from Tobagonian Creole – particularly at the basilectal level – and from other Lesser Antillean creoles.
En ...
. Creole also refers to Bajan Creole
Bajan ( ), or Bajan Creole, is an English-based creole language with West/Central African and British influences spoken on the Caribbean island of Barbados. Bajan is primarily a spoken language, meaning that in general, standard English is used ...
, Bahamian Creole
Bahamian Dialect, also described as Bahamian dialect or simply Bahamian, is an English-based creole language spoken by both Black and White Bahamians, sometimes in slightly different forms. In comparison to many of the English-based dialects ...
, Belizean Creole
Belizean Creole (, ) is an English-based creole language spoken by the Belizean Creole people. It is closely related to Moskitian Creole, San Andrés-Providencia Creole, and Jamaican Patois.
Belizean Creole is a contact language that developed ...
, Guyanese Creole
Guyanese Creole (''Creolese'' by its speakers or simply ''Guyanese'') is an English-based creole language spoken by the Guyanese people. Linguistically, it is similar to other English dialects of the Caribbean region, based on 19th-century En ...
, Jamaican Patois
Jamaican Patois (; locally rendered Patwah and called Jamaican Creole by linguists) is an English-based creole language with influences from West African, Arawak, Spanish and other languages, spoken primarily in Jamaica and among the Jamaican ...
, Tobagonian Creole
Tobagonian Creole is a creole language that is generally spoken in Tobago. It is distinct from Trinidadian Creole
Trinidadian Creole is an creole language commonly spoken throughout the island of Trinidad in Trinidad and Tobago. It is distin ...
, Trinidadian Creole
Trinidadian Creole is an creole language commonly spoken throughout the island of Trinidad in Trinidad and Tobago. It is distinct from Tobagonian Creole – particularly at the basilectal level – and from other Lesser Antillean creoles.
En ...
and Sranan Tongo
Sranan Tongo (Sranantongo, "Surinamese tongue", Sranan, Surinamese Creole) is an English-based creole language from Suriname, in South America, where it is the first or second language for 519,600 Surinamese people (approximately 80% of the popu ...
(Surinamese Creole), among others.
People speak French-lexicon Antillean Creole
Antillean French Creole (also known as Lesser Antillean Creole, Kreyol, or Patois) is a French-based creole languages, French-based creole language that is primarily spoken in the Lesser Antilles caribbean. Its grammar and vocabulary include ele ...
in the following islands:
* St. Lucia
Saint Lucia is an island country of the West Indies in the eastern Caribbean. Part of the Windward Islands of the Lesser Antilles, it is located north/northeast of the island of Saint Vincent (Saint Vincent and the Grenadines), Saint Vincent ...
* Martinique
Martinique ( ; or ; Kalinago language, Kalinago: or ) is an island in the Lesser Antilles of the West Indies, in the eastern Caribbean Sea. It was previously known as Iguanacaera which translates to iguana island in Carib language, Kariʼn ...
* Dominica
Dominica, officially the Commonwealth of Dominica, is an island country in the Caribbean. It is part of the Windward Islands chain in the Lesser Antilles archipelago in the Caribbean Sea. The capital, Roseau, is located on the western side of t ...
* Guadeloupe
Guadeloupe is an Overseas departments and regions of France, overseas department and region of France in the Caribbean. It consists of six inhabited islands—Basse-Terre Island, Basse-Terre, Grande-Terre, Guadeloupe, Grande-Terre, Marie-Galant ...
* St. Martin
* Saint-Barthélemy
* Trinidad and Tobago
Trinidad and Tobago, officially the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago, is the southernmost island country in the Caribbean, comprising the main islands of Trinidad and Tobago, along with several List of islands of Trinidad and Tobago, smaller i ...
* Grenada
Grenada is an island country of the West Indies in the eastern Caribbean Sea. The southernmost of the Windward Islands, Grenada is directly south of Saint Vincent and the Grenadines and about north of Trinidad and Tobago, Trinidad and the So ...
See also
*Criollo people
In Hispanic America, criollo () is a term used originally to describe people of full Spaniards, Spanish descent born in the Viceroyalty, viceroyalties. In different Latin American countries, the word has come to have different meanings, mostly ...
* Creole nationalism
* Blanqueamiento
* Creolisation
* Indo people
The Indo people (, ) or Indos are Eurasian people living in or connected with Indonesia. In its narrowest sense, the term refers to people in the former Dutch East Indies who held European legal status but were of mixed Dutch and Native Indon ...
* Kristang people
* McGill family (Monrovia)
The McGill family of Monrovia, Liberia, was a free African-American family from Baltimore, Maryland, who emigrated to Monrovia in the 19th century. Among the early American settlers in Liberia, the McGills became established as one of the most p ...
* Mestizo
( , ; fem. , literally 'mixed person') is a term primarily used to denote people of mixed European and Indigenous ancestry in the former Spanish Empire. In certain regions such as Latin America, it may also refer to people who are culturall ...
* Métis
The Métis ( , , , ) are a mixed-race Indigenous people whose historical homelands include Canada's three Prairie Provinces extending into parts of Ontario, British Columbia, the Northwest Territories and the northwest United States. They ha ...
* Mulatto
( , ) is a Race (human categorization), racial classification that refers to people of mixed Sub-Saharan African, African and Ethnic groups in Europe, European ancestry only. When speaking or writing about a singular woman in English, the ...
Notes
References
External links
*International Organization of Creole Peoples
{{DEFAULTSORT:Creole Peoples Creole culture African diaspora history African diaspora Ethnonyms