credit crunch on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A credit crunch (a credit squeeze, credit tightening or credit crisis) is a sudden reduction in the general availability of loans (or credit) or a sudden tightening of the conditions required to obtain a loan from banks. A credit crunch generally involves a reduction in the availability of credit independent of a rise in official interest rates. In such situations the relationship between credit availability and interest rates changes. Credit becomes less available at any given official interest rate, or there ceases to be a clear relationship between interest rates and credit availability (i.e. credit rationing occurs). Many times, a credit crunch is accompanied by a flight to quality by lenders and investors, as they seek less risky investments (often at the expense of small to medium size enterprises).
 A credit crunch is often caused by a sustained period of careless and inappropriate lending which results in losses for lending institutions and investors in
A credit crunch is often caused by a sustained period of careless and inappropriate lending which results in losses for lending institutions and investors in
Wei Ding, Ilker Domac & Giovanni Ferri (World Bank)
 In a credit bubble, lending standards become less stringent. Easy credit drives up prices within a class of assets, usually
real estate or equities. These increased asset values then become the collateral for further borrowing.
During the upward phase in the credit cycle, asset prices may experience bouts of frenzied competitive, leveraged bidding, inducing
In a credit bubble, lending standards become less stringent. Easy credit drives up prices within a class of assets, usually
real estate or equities. These increased asset values then become the collateral for further borrowing.
During the upward phase in the credit cycle, asset prices may experience bouts of frenzied competitive, leveraged bidding, inducing
 Financial institutions facing losses may then reduce the availability of
Financial institutions facing losses may then reduce the availability of
Causes
 A credit crunch is often caused by a sustained period of careless and inappropriate lending which results in losses for lending institutions and investors in
A credit crunch is often caused by a sustained period of careless and inappropriate lending which results in losses for lending institutions and investors in debt
Debt is an obligation that requires one party, the debtor, to pay money Loan, borrowed or otherwise withheld from another party, the creditor. Debt may be owed by a sovereign state or country, local government, company, or an individual. Co ...
when the loans turn sour and the full extent of bad debts becomes known.
There are a number of reasons banks might suddenly stop or slow lending activity. For example, inadequate information about the financial condition of borrowers can lead to a boom in lending when financial institutions overestimate creditworthiness, while the sudden revelation of information suggesting that borrowers are or were less creditworthy can lead to a sudden contraction of credit. Other causes can include an anticipated decline in the value of the collateral used by the banks to secure the loans; an exogenous change in monetary conditions (for example, where the central bank
A central bank, reserve bank, national bank, or monetary authority is an institution that manages the monetary policy of a country or monetary union. In contrast to a commercial bank, a central bank possesses a monopoly on increasing the mo ...
suddenly and unexpectedly raises reserve requirement
Reserve requirements are central bank regulations that set the minimum amount that a commercial bank must hold in liquid assets. This minimum amount, commonly referred to as the Bank reserves, commercial bank's reserve, is generally determined ...
s or imposes new regulatory constraints on lending); the central government
A central government is the government that is a controlling power over a unitary state. Another distinct but sovereign political entity is a federal government, which may have distinct powers at various levels of government, authorized or deleg ...
imposing direct credit controls on the banking system; or even an increased perception of risk regarding the solvency
Solvency, in finance or business, is the degree to which the current assets of an individual or entity exceed the current liabilities of that individual or entity. Solvency can also be described as the ability of a corporation to meet its long- ...
of other banks within the banking system.''Is There A Credit Crunch in East Asia?''Wei Ding, Ilker Domac & Giovanni Ferri (World Bank)
Easy credit conditions
Easy credit conditions (sometimes referred to as "easy money" or "loose credit") are characterized by low interest rates for borrowers and relaxed lending practices by bankers, making it easy to get inexpensive loans. A credit crunch is the opposite, in which interest rates rise and lending practices tighten. Easy credit conditions mean that funds are readily available to borrowers, which results in asset prices rising if the loaned funds are used to buy assets in a particular market, such as real estate or stocks.Bubble formation
 In a credit bubble, lending standards become less stringent. Easy credit drives up prices within a class of assets, usually
real estate or equities. These increased asset values then become the collateral for further borrowing.
During the upward phase in the credit cycle, asset prices may experience bouts of frenzied competitive, leveraged bidding, inducing
In a credit bubble, lending standards become less stringent. Easy credit drives up prices within a class of assets, usually
real estate or equities. These increased asset values then become the collateral for further borrowing.
During the upward phase in the credit cycle, asset prices may experience bouts of frenzied competitive, leveraged bidding, inducing inflation
In economics, inflation is an increase in the average price of goods and services in terms of money. This increase is measured using a price index, typically a consumer price index (CPI). When the general price level rises, each unit of curre ...
in a particular asset market. This can then cause a speculative price "bubble
Bubble, Bubbles or The Bubble may refer to:
Common uses
* Bubble (physics), a globule of one substance in another, usually gas in a liquid
** Soap bubble
* Economic bubble, a situation where asset prices are much higher than underlying fundame ...
" to develop. As this upswing in new debt creation also increases the money supply
In macroeconomics, money supply (or money stock) refers to the total volume of money held by the public at a particular point in time. There are several ways to define "money", but standard measures usually include currency in circulation (i ...
and stimulates economic activity, this also tends to temporarily raise economic growth
In economics, economic growth is an increase in the quantity and quality of the economic goods and Service (economics), services that a society Production (economics), produces. It can be measured as the increase in the inflation-adjusted Outp ...
and employment
Employment is a relationship between two party (law), parties Regulation, regulating the provision of paid Labour (human activity), labour services. Usually based on a employment contract, contract, one party, the employer, which might be a cor ...
.
Economist Hyman Minsky described the types of borrowing and lending that contribute to a bubble. The "hedge borrower" can make debt payments (covering interest and principal) from current cash flows from investments. This borrower is not taking significant risk. However, the next type, the "speculative borrower", the cash flow from investments can service the debt, i.e., cover the interest due, but the borrower must regularly roll over, or re-borrow, the principal. The "Ponzi borrower" (named for Charles Ponzi
Charles Ponzi (; ; born Carlo Pietro Giovanni Guglielmo Tebaldo Ponzi; March 3, 1882 – January 18, 1949) was an Italians, Italian charlatan and Scam, con artist who operated in the United States and Canada. His Pseudonym, aliases included ''C ...
, see also Ponzi scheme
A Ponzi scheme (, ) is a form of fraud that lures investors and pays Profit (accounting), profits to earlier investors with Funding, funds from more recent investors. Named after Italians, Italian confidence artist Charles Ponzi, this type of s ...
) borrows based on the belief that the appreciation of the value of the asset will be sufficient to refinance the debt but could not make sufficient payments on interest or principal with the cash flow from investments; only the appreciating asset value can keep the Ponzi borrower afloat.
Often it is only in retrospect that participants in an economic bubble
An economy is an area of the Production (economics), production, Distribution (economics), distribution and trade, as well as Consumption (economics), consumption of Goods (economics), goods and Service (economics), services. In general, it is ...
realize that the point of collapse was obvious. In this respect, economic bubbles can have dynamic characteristics not unlike Ponzi scheme
A Ponzi scheme (, ) is a form of fraud that lures investors and pays Profit (accounting), profits to earlier investors with Funding, funds from more recent investors. Named after Italians, Italian confidence artist Charles Ponzi, this type of s ...
s or Pyramid scheme
A pyramid scheme is a business model which, rather than earning money (or providing Return on investment, returns on investments) by sale of legitimate product (business), products to an end consumer, mainly earns money by recruiting new members ...
s.
Psychological
Several psychological factors contribute to bubbles and related busts. *''Social herding'' refers to following the behavior of others, assuming they understand what is happening. AsJohn Maynard Keynes
John Maynard Keynes, 1st Baron Keynes ( ; 5 June 1883 – 21 April 1946), was an English economist and philosopher whose ideas fundamentally changed the theory and practice of macroeconomics and the economic policies of governments. Originall ...
observed in 1931 during the Great Depression
The Great Depression was a severe global economic downturn from 1929 to 1939. The period was characterized by high rates of unemployment and poverty, drastic reductions in industrial production and international trade, and widespread bank and ...
: "A sound banker, alas, is not one who foresees danger and avoids it, but one who, when he is ruined, is ruined in a conventional way along with his fellows, so that no one can really blame him."
*People may assume that unusually favorable trends (e.g., exceptionally low interest rates and prolonged asset price increases) will continue indefinitely.
*Incentives may also encourage risky behavior, particularly where the negative consequences if a bet goes sour are shared collectively. The tendency of government to bail out financial institutions that get into trouble (e.g., Long-term Capital Management
Long-Term Capital Management L.P. (LTCM) was a highly leveraged hedge fund. In 1998, it received a $3.6 billion bailout from a group of 14 banks, in a deal brokered and put together by the Federal Reserve Bank of New York.
LTCM was founded in ...
and the subprime mortgage crisis
The American subprime mortgage crisis was a multinational financial crisis that occurred between 2007 and 2010, contributing to the 2008 financial crisis. It led to a severe economic recession, with millions becoming unemployed and many busines ...
), provide examples of such moral hazard
In economics, a moral hazard is a situation where an economic actor has an incentive to increase its exposure to risk because it does not bear the full costs associated with that risk, should things go wrong. For example, when a corporation i ...
.
*People may assume that "this time is different", which psychologist Daniel Kahneman
Daniel Kahneman (; ; March 5, 1934 – March 27, 2024) was an Israeli-American psychologist best known for his work on the psychology of judgment and decision-making as well as behavioral economics, for which he was awarded the 2002 Nobel Memor ...
refers to as the ''inside view'', as opposed to the ''outside view'', which is based on historical or better objective information.
These and other cognitive biases
A cognitive bias is a systematic pattern of deviation from norm or rationality in judgment. Individuals create their own "subjective reality" from their perception of the input. An individual's construction of reality, not the objective input, ...
that impair judgment can contribute to credit bubbles and crunches.
Valuation of securities
The crunch is generally caused by a reduction in the market prices of previously "overinflated" assets and refers to thefinancial crisis
A financial crisis is any of a broad variety of situations in which some financial assets suddenly lose a large part of their nominal value. In the 19th and early 20th centuries, many financial crises were associated with Bank run#Systemic banki ...
that results from the price collapse. This can result in widespread foreclosure
Foreclosure is a legal process in which a lender attempts to recover the balance of a loan from a borrower who has Default (finance), stopped making payments to the lender by forcing the sale of the asset used as the Collateral (finance), coll ...
or bankruptcy
Bankruptcy is a legal process through which people or other entities who cannot repay debts to creditors may seek relief from some or all of their debts. In most jurisdictions, bankruptcy is imposed by a court order, often initiated by the deb ...
for those who came in late to the market, as the prices of previously inflated assets generally drop precipitously. In contrast, a liquidity crisis is triggered when an otherwise sound business finds itself temporarily incapable of accessing the bridge finance it needs to expand its business or smooth its cash flow payments. In this case, accessing additional credit lines and "trading through" the crisis can allow the business to navigate its way through the problem and ensure its continued solvency
Solvency, in finance or business, is the degree to which the current assets of an individual or entity exceed the current liabilities of that individual or entity. Solvency can also be described as the ability of a corporation to meet its long- ...
and viability. It is often difficult to know, in the midst of a crisis, whether distressed businesses are experiencing a crisis of solvency or a temporary liquidity crisis.
In the case of a credit crunch, it may be preferable to " mark to market" - and if necessary, sell or go into liquidation
Liquidation is the process in accounting by which a Company (law), company is brought to an end. The assets and property of the business are redistributed. When a firm has been liquidated, it is sometimes referred to as :wikt:wind up#Noun, w ...
if the capital of the business affected is insufficient to survive the post-boom phase of the credit cycle. In the case of a liquidity crisis on the other hand, it may be preferable to attempt to access additional lines of credit, as opportunities for growth may exist once the liquidity crisis is overcome.
Effects
 Financial institutions facing losses may then reduce the availability of
Financial institutions facing losses may then reduce the availability of credit
Credit (from Latin verb ''credit'', meaning "one believes") is the trust which allows one party to provide money or resources to another party wherein the second party does not reimburse the first party immediately (thereby generating a debt) ...
, and increase the cost of accessing credit by raising interest rates
An interest rate is the amount of interest due per period, as a proportion of the amount lent, deposited, or borrowed (called the principal sum). The total interest on an amount lent or borrowed depends on the principal sum, the interest rate, ...
. In some cases lenders may be unable to lend further, even if they wish, as a result of earlier losses. If participants themselves are highly leveraged (i.e., carrying a high debt burden) the damage done when the bubble bursts is more severe, causing recession
In economics, a recession is a business cycle contraction that occurs when there is a period of broad decline in economic activity. Recessions generally occur when there is a widespread drop in spending (an adverse demand shock). This may be tr ...
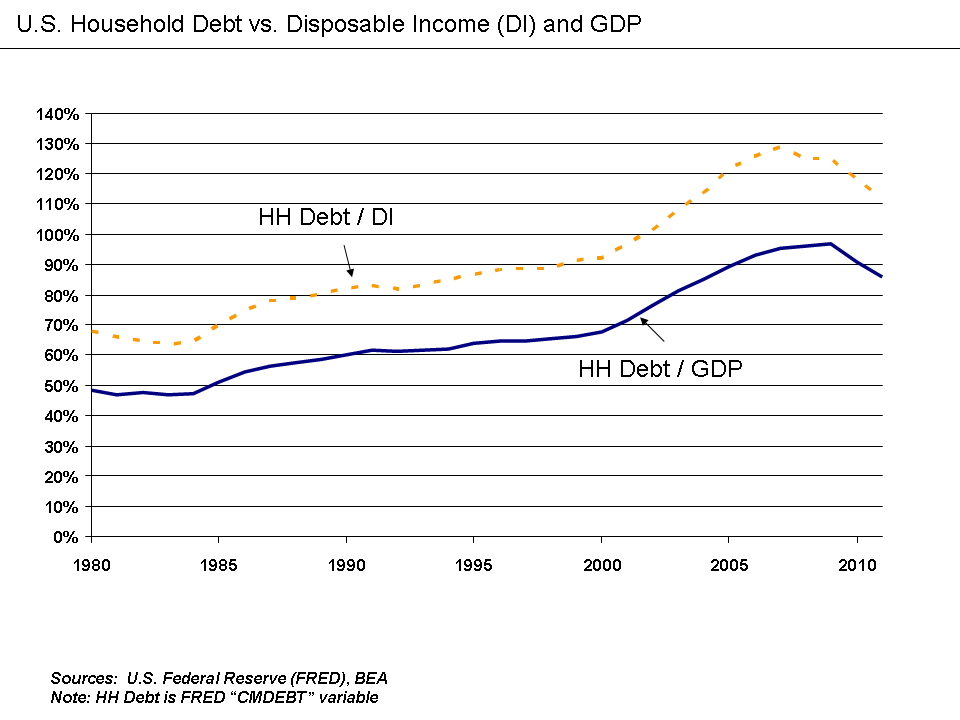
or depression. Financial institutions may fail, economic growth may slow, unemployment may rise, and social unrest may increase. For example, the ratio of household debt to after-tax income rose from 60% in 1984 to 130% by 2007, contributing to (and worsening) the Subprime mortgage crisis
The American subprime mortgage crisis was a multinational financial crisis that occurred between 2007 and 2010, contributing to the 2008 financial crisis. It led to a severe economic recession, with millions becoming unemployed and many busines ...
of 2007–2008.
Historical perspective
In recent decades credit crunches have not been rare orblack swan
The black swan (''Cygnus atratus'') is a large Anatidae, waterbird, a species of swan which breeds mainly in the southeast and southwest regions of Australia. Within Australia, the black swan is nomadic, with erratic migration patterns dependent ...
events. Although few economists have successfully predicted credit crunch events before they have occurred, Professor Richard Rumelt has written the following in relation to their surprising frequency and regularity in advanced economies around the world: "In fact, during the past fifty years there have been 28 severe house-price boom-bust cycles and 28 credit crunches in 21 advanced Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD; , OCDE) is an international organization, intergovernmental organization with 38 member countries, founded in 1961 to stimulate economic progress and international trade, wor ...
(OECD) economies."
See also
* Austrian business cycle theory * Debt deflation * Environmental credit crunch *Financial crisis
A financial crisis is any of a broad variety of situations in which some financial assets suddenly lose a large part of their nominal value. In the 19th and early 20th centuries, many financial crises were associated with Bank run#Systemic banki ...
* Minsky moment
* Liquidity crisis
References
Bibliography
* George Cooper, ''The Origin of Financial Crises'' (2008: London, Harriman House) * Graham Turner, ''The Credit Crunch: Housing Bubbles, Globalisation and the Worldwide Economic Crisis'' (2008: London, Pluto Press), {{Financial crises Credit Debt Financial crises United States housing bubble 2000s slang 2000s neologisms