
In
convex geometry
In mathematics, convex geometry is the branch of geometry studying convex sets, mainly in Euclidean space. Convex sets occur naturally in many areas: computational geometry, convex analysis, discrete geometry, functional analysis, geometry of ...
and
vector algebra, a convex combination is a
linear combination of
points
Point or points may refer to:
Places
* Point, Lewis, a peninsula in the Outer Hebrides, Scotland
* Point, Texas, a city in Rains County, Texas, United States
* Point, the NE tip and a ferry terminal of Lismore, Inner Hebrides, Scotland
* Points ...
(which can be
vectors,
scalars
Scalar may refer to:
* Scalar (mathematics), an element of a field, which is used to define a vector space, usually the field of real numbers
* Scalar (physics), a physical quantity that can be described by a single element of a number field such ...
, or more generally points in an
affine space) where all
coefficients are
non-negative and sum to 1.
In other words, the operation is equivalent to a standard
weighted average, but whose weights are expressed as a percent of the total weight, instead of as a fraction of the ''count'' of the weights as in a standard weighted average.
More formally, given a finite number of points
in a
real vector space, a convex combination of these points is a point of the form
:
where the real numbers
satisfy
and
[
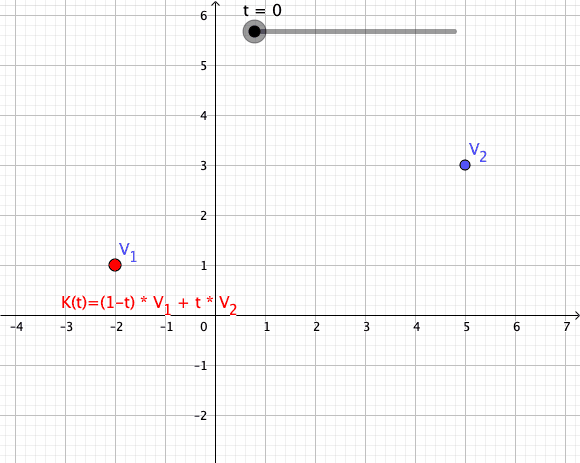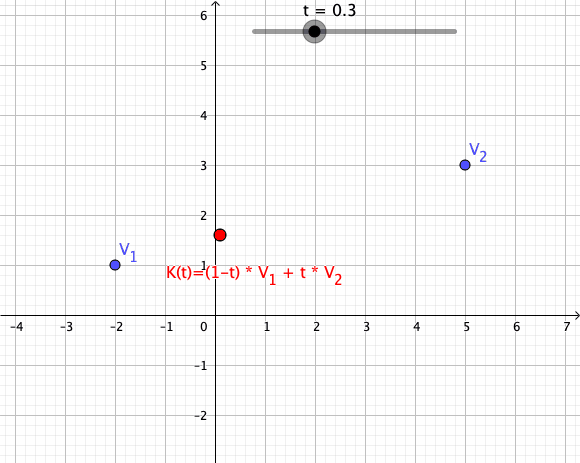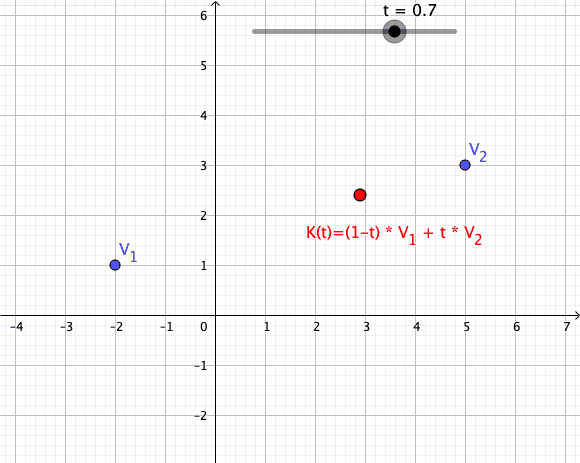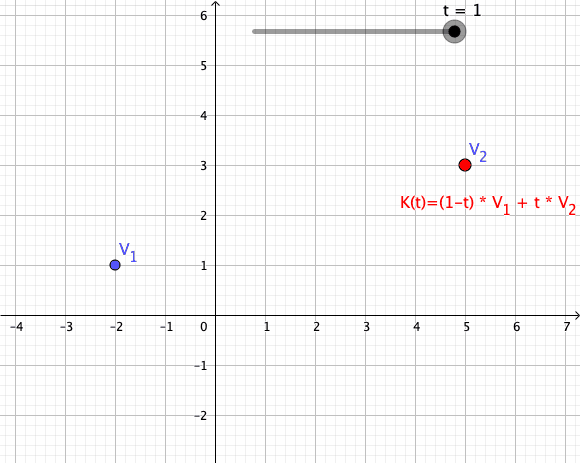
As a particular example, every convex combination of two points lies on the ]line segment
In geometry, a line segment is a part of a straight line that is bounded by two distinct end points, and contains every point on the line that is between its endpoints. The length of a line segment is given by the Euclidean distance between i ...
between the points.[
A set is ]convex
Convex or convexity may refer to:
Science and technology
* Convex lens, in optics
Mathematics
* Convex set, containing the whole line segment that joins points
** Convex polygon, a polygon which encloses a convex set of points
** Convex polytop ...
if it contains all convex combinations of its points.
The convex hull
In geometry, the convex hull or convex envelope or convex closure of a shape is the smallest convex set that contains it. The convex hull may be defined either as the intersection of all convex sets containing a given subset of a Euclidean space ...
of a given set of points is identical to the set of all their convex combinations.[
There exist subsets of a vector space that are not closed under linear combinations but are closed under convex combinations. For example, the interval ]

 In
In

 In
In