constellation on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A constellation is an area on the


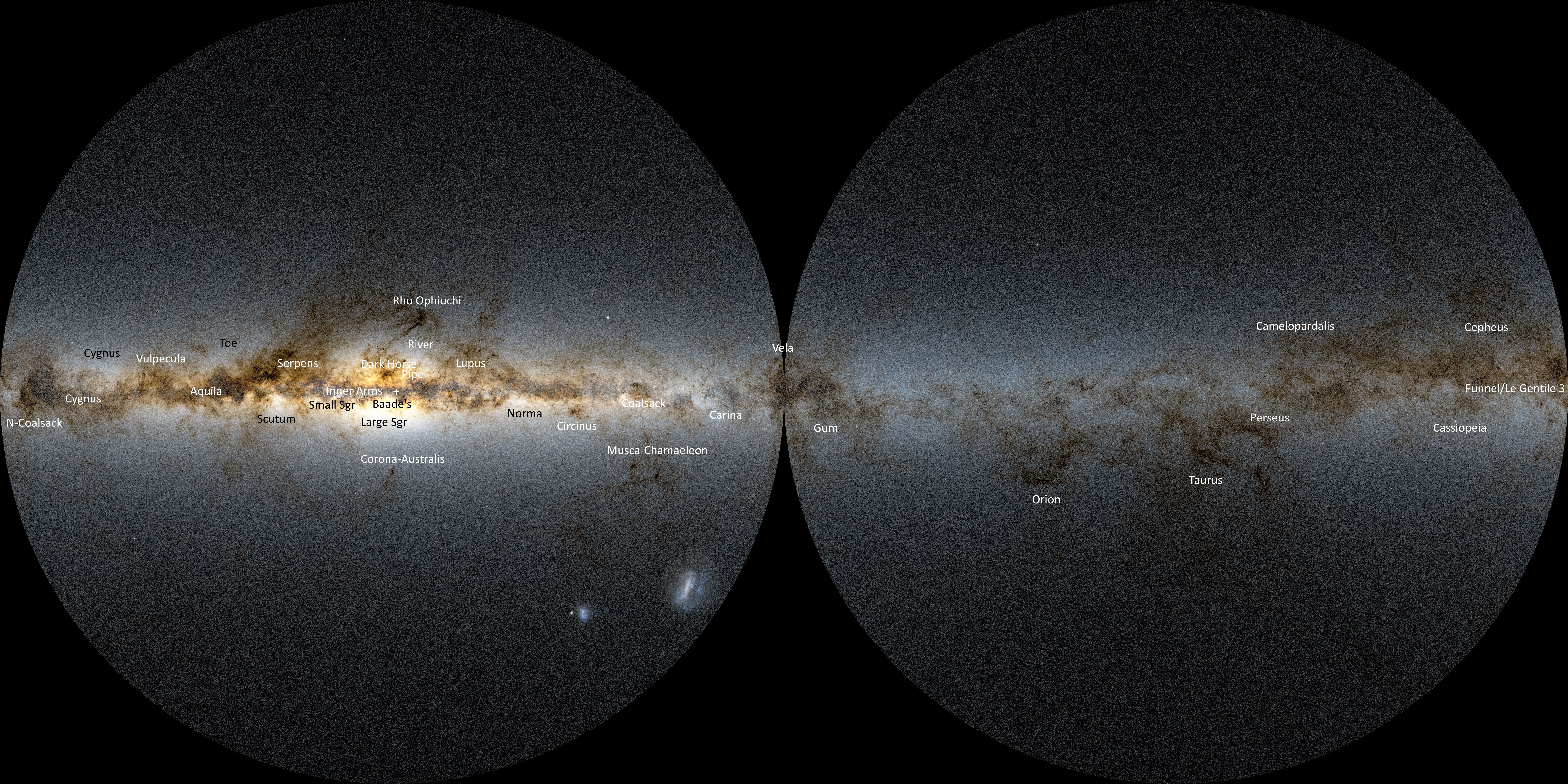 The Great Rift, a series of dark patches in the Milky Way, is most visible in the southern sky. Some cultures have discerned shapes in these patches. Members of the
The Great Rift, a series of dark patches in the Milky Way, is most visible in the southern sky. Some cultures have discerned shapes in these patches. Members of the
File:Emu public.jpg, The ''
IAU: The Constellations
including high quality maps.
Atlascoelestis
di Felice Stoppa.
Celestia
free 3D realtime space-simulation (OpenGL)
Stellarium
realtime sky rendering program (OpenGL)
Strasbourg Astronomical Data Center Files on official IAU constellation boundaries
Studies of Occidental Constellations and Star Names to the Classical Period: An Annotated Bibliography
Greco-Roman constellation myths
Neave Planetarium
Adobe Flash interactive web browser planetarium and stardome with realistic movement of stars and the planets. * Audio – Cain/Gay (2009
Astronomy Cast
Constellations
The Greek Star-Map
short essay by Gavin White
Bucur D. The network signature of constellation line figures
PLOS ONE 17(7): e0272270 (2022). A comparative analysis on the structure of constellation line figures across sky cultures. {{Authority control Constellations Celestial cartography Constellations Concepts in astronomy
celestial sphere
In astronomy and navigation, the celestial sphere is an abstract sphere that has an arbitrarily large radius and is concentric to Earth. All objects in the sky can be conceived as being projected upon the inner surface of the celestial sphere, ...
in which a group of visible star
A star is a luminous spheroid of plasma (physics), plasma held together by Self-gravitation, self-gravity. The List of nearest stars and brown dwarfs, nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked eye at night sk ...
s forms a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object.
The first constellations were likely defined in prehistory
Prehistory, also called pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the first known use of stone tools by hominins million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use ...
. People used them to relate stories of their beliefs, experiences, creation, and mythology
Myth is a genre of folklore consisting primarily of narratives that play a fundamental role in a society. For scholars, this is very different from the vernacular usage of the term "myth" that refers to a belief that is not true. Instead, the ...
. Different cultures and countries invented their own constellations, some of which lasted into the early 20th century before today's constellations were internationally recognized. The recognition of constellations has changed significantly over time. Many changed in size or shape. Some became popular, only to drop into obscurity. Some were limited to a single culture or nation. Naming constellations also helped astronomers and navigators identify stars more easily.
Twelve (or thirteen) ancient constellations belong to the zodiac
The zodiac is a belt-shaped region of the sky that extends approximately 8° north and south celestial latitude of the ecliptic – the apparent path of the Sun across the celestial sphere over the course of the year. Within this zodiac ...
(straddling the ecliptic
The ecliptic or ecliptic plane is the orbital plane of Earth's orbit, Earth around the Sun. It was a central concept in a number of ancient sciences, providing the framework for key measurements in astronomy, astrology and calendar-making.
Fr ...
, which the Sun, Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It Orbit of the Moon, orbits around Earth at Lunar distance, an average distance of (; about 30 times Earth diameter, Earth's diameter). The Moon rotation, rotates, with a rotation period (lunar ...
, and planet
A planet is a large, Hydrostatic equilibrium, rounded Astronomical object, astronomical body that is generally required to be in orbit around a star, stellar remnant, or brown dwarf, and is not one itself. The Solar System has eight planets b ...
s all traverse). The origins of the zodiac remain historically uncertain; its astrological divisions became prominent in Babylonian or Chaldean astronomy. Constellations appear in Western culture via Greece and are mentioned in the works of Hesiod, Eudoxus and Aratus. The traditional 48 constellations, consisting of the zodiac and 36 more (now 38, following the division of Argo Navis into three constellations) are listed by Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; , ; ; – 160s/170s AD) was a Greco-Roman mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were important to later Byzantine science, Byzant ...
, a Greco-Roman astronomer from Alexandria
Alexandria ( ; ) is the List of cities and towns in Egypt#Largest cities, second largest city in Egypt and the List of coastal settlements of the Mediterranean Sea, largest city on the Mediterranean coast. It lies at the western edge of the Nile ...
, Egypt, in his '' Almagest''. The formation of constellations was the subject of extensive mythology
Myth is a genre of folklore consisting primarily of narratives that play a fundamental role in a society. For scholars, this is very different from the vernacular usage of the term "myth" that refers to a belief that is not true. Instead, the ...
, most notably in the '' Metamorphoses'' of the Latin poet Ovid
Publius Ovidius Naso (; 20 March 43 BC – AD 17/18), known in English as Ovid ( ), was a Augustan literature (ancient Rome), Roman poet who lived during the reign of Augustus. He was a younger contemporary of Virgil and Horace, with whom he i ...
. Constellations in the far southern sky were added from the 15th century until the mid-18th century when European explorers began traveling to the Southern Hemisphere. Due to Roman and European transmission, each constellation has a Latin name.
In 1922, the International Astronomical Union
The International Astronomical Union (IAU; , UAI) is an international non-governmental organization (INGO) with the objective of advancing astronomy in all aspects, including promoting astronomical research, outreach, education, and developmen ...
(IAU) formally accepted the modern list of 88 constellations, and in 1928 adopted official constellation boundaries that together cover the entire celestial sphere. Any given point in a celestial coordinate system lies in one of the modern constellations. Some astronomical naming systems include the constellation where a given celestial object is found to convey its approximate location in the sky. The Flamsteed designation of a star, for example, consists of a number and the genitive form of the constellation's name.
Other star patterns or groups called asterisms are not constellations under the formal definition, but are also used by observers to navigate the night sky. Asterisms may be several stars within a constellation, or they may share stars with more than one constellation. Examples of asterisms include the teapot within the constellation Sagittarius, or the big dipper
The Big Dipper (American English, US, Canadian English, Canada) or the Plough (British English, UK, Hiberno-English, Ireland) is an asterism (astronomy), asterism consisting of seven bright stars of the constellation Ursa Major; six of them ar ...
in the constellation of Ursa Major
Ursa Major, also known as the Great Bear, is a constellation in the Northern Sky, whose associated mythology likely dates back into prehistory. Its Latin name means "greater (or larger) bear", referring to and contrasting it with nearby Ursa M ...
.
Terminology
The word ''constellation'' comes from theLate Latin
Late Latin is the scholarly name for the form of Literary Latin of late antiquity.Roberts (1996), p. 537. English dictionary definitions of Late Latin date this period from the 3rd to 6th centuries CE, and continuing into the 7th century in ...
term , which can be translated as "set of stars"; it came into use in Middle English
Middle English (abbreviated to ME) is a form of the English language that was spoken after the Norman Conquest of 1066, until the late 15th century. The English language underwent distinct variations and developments following the Old English pe ...
during the 14th century. The Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek (, ; ) includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the classical antiquity, ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Greek ...
word for constellation is ἄστρον (). These terms historically referred to any recognisable pattern of stars whose appearance was associated with mythological characters or creatures, earthbound animals, or objects. Over time, among European astronomers, the constellations became clearly defined and widely recognised. In the 20th century, the International Astronomical Union
The International Astronomical Union (IAU; , UAI) is an international non-governmental organization (INGO) with the objective of advancing astronomy in all aspects, including promoting astronomical research, outreach, education, and developmen ...
(IAU) recognized 88 constellations.
A constellation or star that never sets below the horizon
The horizon is the apparent curve that separates the surface of a celestial body from its sky when viewed from the perspective of an observer on or near the surface of the relevant body. This curve divides all viewing directions based on whethe ...
when viewed from a particular latitude
In geography, latitude is a geographic coordinate system, geographic coordinate that specifies the north-south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from −90° at t ...
on Earth is termed circumpolar. From the North Pole
The North Pole, also known as the Geographic North Pole or Terrestrial North Pole, is the point in the Northern Hemisphere where the Earth's rotation, Earth's axis of rotation meets its surface. It is called the True North Pole to distingu ...
or South Pole
The South Pole, also known as the Geographic South Pole or Terrestrial South Pole, is the point in the Southern Hemisphere where the Earth's rotation, Earth's axis of rotation meets its surface. It is called the True South Pole to distinguish ...
, all constellations south or north of the celestial equator are circumpolar. Depending on the definition, equatorial constellations may include those that lie between declinations 45° north and 45° south, or those that pass through the declination range of the ecliptic
The ecliptic or ecliptic plane is the orbital plane of Earth's orbit, Earth around the Sun. It was a central concept in a number of ancient sciences, providing the framework for key measurements in astronomy, astrology and calendar-making.
Fr ...
(or zodiac
The zodiac is a belt-shaped region of the sky that extends approximately 8° north and south celestial latitude of the ecliptic – the apparent path of the Sun across the celestial sphere over the course of the year. Within this zodiac ...
) ranging between 23.5° north and 23.5° south.
Stars in constellations can appear near each other in the sky, but they usually lie at a variety of distances away from the Earth. Since each star has its own independent motion, all constellations will change slowly over time. After tens to hundreds of thousands of years, familiar outlines will become unrecognizable. Astronomers can predict the past or future constellation outlines by measuring common proper motions of individual stars by accurate astrometry and their radial velocities by astronomical spectroscopy.
The 88 constellations recognized by the IAU as well as those by cultures throughout history are imagined figures and shapes derived from the patterns of stars in the observable sky. Many officially recognized constellations are based on the imaginations of ancient Near Eastern and Mediterranean mythologies. Some of these stories seem to relate to the appearance of the constellations, e.g. the assassination of Orion by Scorpius, their constellations appearing at opposite times of year.
Observation
Constellation positions change throughout the year due tonight
Night, or nighttime, is the period of darkness when the Sun is below the horizon. Sunlight illuminates one side of the Earth, leaving the other in darkness. The opposite of nighttime is daytime. Earth's rotation causes the appearance of ...
on Earth occurring at gradually different portions of its orbit around the Sun. As Earth rotates toward the east, the celestial sphere
In astronomy and navigation, the celestial sphere is an abstract sphere that has an arbitrarily large radius and is concentric to Earth. All objects in the sky can be conceived as being projected upon the inner surface of the celestial sphere, ...
appears to rotate west, with stars circling counterclockwise around the northern pole star and clockwise around the southern pole star.
Because of Earth's 23.5° axial tilt
In astronomy, axial tilt, also known as obliquity, is the angle between an object's rotational axis and its orbital axis, which is the line perpendicular to its orbital plane; equivalently, it is the angle between its equatorial plane and orbita ...
, the zodiac is distributed equally across hemispheres (along the ecliptic), approximating a great circle. Zodiacal constellations of the northern sky are Pisces, Aries, Taurus, Gemini, Cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Po ...
, and Leo. In the southern sky are Virgo
Virgo may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* Virgo (film), a 1970 Egyptian film
* Virgo (character), several Marvel Comics characters
* Virgo Asmita, a character in the manga ''Saint Seiya: The Lost Canvas''
* ''Virgo'' (album), by Virgo Four, ...
, Libra, Scorpius, Sagittarius, Capricornus, and Aquarius. The zodiac appears directly overhead from latitudes of 23.5° north to 23.5° south, depending on the time of year. In summer, the ecliptic appears higher up in the daytime and lower at night, while in winter the reverse is true, for both hemispheres.
Due to the Solar System
The Solar SystemCapitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Sola ...
's 60° tilt, the galactic plane
The galactic plane is the plane (geometry), plane on which the majority of a disk-shaped galaxy's mass lies. The directions perpendicular to the galactic plane point to the galactic poles. In actual usage, the terms ''galactic plane'' and ''galac ...
of the Milky Way
The Milky Way or Milky Way Galaxy is the galaxy that includes the Solar System, with the name describing the #Appearance, galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars in other arms of the galax ...
is inclined 60° from the ecliptic, between Taurus and Gemini (north) and Scorpius and Sagittarius (south and near which the Galactic Center
The Galactic Center is the barycenter of the Milky Way and a corresponding point on the rotational axis of the galaxy. Its central massive object is a supermassive black hole of about 4 million solar masses, which is called Sagittarius A*, a ...
can be found). The galaxy appears to pass through Aquila (near the celestial equator) and northern constellations Cygnus, Cassiopeia, Perseus, Auriga, and Orion (near Betelgeuse), as well as Monoceros (near the celestial equator), and southern constellations Puppis, Vela, Carina, Crux
CRUX is a lightweight x86-64 Linux distribution targeted at experienced Linux users and delivered by a tar.gz-based package system with BSD-style initscripts. It is not based on any other Linux distribution. It also utilizes a ports system ...
, Centaurus
Centaurus () is a bright constellation in the southern sky. One of the 88 modern constellations by area, largest constellations, Centaurus was included among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one ...
, Triangulum Australe, and Ara.
Northern hemisphere
Polaris
Polaris is a star in the northern circumpolar constellation of Ursa Minor. It is designated α Ursae Minoris (Latinisation of names, Latinized to ''Alpha Ursae Minoris'') and is commonly called the North Star or Pole Star. With an ...
, being the North Star, is the approximate center of the northern celestial hemisphere. It is part of Ursa Minor, constituting the end of the Little Dipper's handle.
From latitudes of around 35° north, in January, Ursa Major
Ursa Major, also known as the Great Bear, is a constellation in the Northern Sky, whose associated mythology likely dates back into prehistory. Its Latin name means "greater (or larger) bear", referring to and contrasting it with nearby Ursa M ...
(containing the Big Dipper
The Big Dipper (American English, US, Canadian English, Canada) or the Plough (British English, UK, Hiberno-English, Ireland) is an asterism (astronomy), asterism consisting of seven bright stars of the constellation Ursa Major; six of them ar ...
) appears to the northeast, while Cassiopeia is the northwest. To the west are Pisces (above the horizon) and Aries. To the southwest Cetus
Cetus () is a constellation, sometimes called 'the whale' in English. The Cetus (mythology), Cetus was a sea monster in Greek mythology which both Perseus and Heracles needed to slay. Cetus is in the region of the sky that contains other water- ...
is near the horizon. Up high and to the south are Orion and Taurus. To the southeast above the horizon is Canis Major
Canis Major is a constellation in the southern celestial hemisphere. In the second century, it was included in Ptolemy's 48 constellations, and is counted among the 88 modern constellations. Its name is Latin for "greater dog" in contrast to C ...
. Appearing above and to the east of Orion is Gemini: also in the east (and progressively closer to the horizon) are Cancer and Leo. In addition to Taurus, Perseus and Auriga appear overhead.
From the same latitude, in July, Cassiopeia (low in the sky) and Cepheus appear to the northeast. Ursa Major is now in the northwest. Boötes is high up in the west. Virgo is to the west, with Libra southwest and Scorpius south. Sagittarius and Capricorn are southeast. Cygnus (containing the Northern Cross) is to the east. Hercules is high in the sky along with Corona Borealis.
Southern hemisphere
January constellations include Pictor and Reticulum (near Hydrus and Mensa, respectively). In July, Ara (adjacent to Triangulum Australe) and Scorpius can be seen. Constellations near the pole star include Chamaeleon, Apus and Triangulum Australe (near Centaurus), Pavo, Hydrus, and Mensa. Sigma Octantis is the closest star approximating a southern pole star, but is faint in the night sky. Thus, the pole can be triangulated using the constellation Crux as well as the starsAlpha
Alpha (uppercase , lowercase ) is the first letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals, it has a value of one. Alpha is derived from the Phoenician letter ''aleph'' , whose name comes from the West Semitic word for ' ...
and Beta Centauri (about 30° counterclockwise from Crux) of the constellation Centaurus (arching over Crux).
History of the early constellations
Lascaux Caves, southern France
It has been suggested that the 17,000-year-old cave paintings inLascaux
Lascaux ( , ; , "Lascaux Cave") is a network of caves near the village of Montignac, Dordogne, Montignac, in the Departments of France, department of Dordogne in southwestern France. Over 600 Parietal art, parietal cave painting, wall paintin ...
, southern France, depict star constellations such as Taurus, Orion's Belt, and the Pleiades. However, this view is not generally accepted among scientists.
Mesopotamia
Inscribed stones and clay writing tablets fromMesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a historical region of West Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent. Today, Mesopotamia is known as present-day Iraq and forms the eastern geographic boundary of ...
(in modern Iraq
Iraq, officially the Republic of Iraq, is a country in West Asia. It is bordered by Saudi Arabia to Iraq–Saudi Arabia border, the south, Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq border, the east, the Persian Gulf and ...
) dating to 3000 BC provide the earliest generally accepted evidence for humankind's identification of constellations. It seems that the bulk of the Mesopotamian constellations were created within a relatively short interval from around 1300 to 1000 BC. Mesopotamian constellations appeared later in many of the classical Greek constellations.
Ancient Near East
The oldest Babylonian catalogues of stars and constellations date back to the beginning of the Middle Bronze Age, most notably the ''Three Stars Each'' texts and the '' MUL.APIN'', an expanded and revised version based on more accurate observation from around 1000 BC. However, the numerous Sumerian names in these catalogues suggest that they built on older, but otherwise unattested,Sumer
Sumer () is the earliest known civilization, located in the historical region of southern Mesopotamia (now south-central Iraq), emerging during the Chalcolithic and Early Bronze Age, early Bronze Ages between the sixth and fifth millennium BC. ...
ian traditions of the Early Bronze Age.
The classical Zodiac is a revision of Neo-Babylonian constellations from the 6th century BC. The Greeks adopted the Babylonian constellations in the 4th century BC. Twenty Ptolemaic constellations are from the Ancient Near East. Another ten have the same stars but different names.
Biblical scholar E. W. Bullinger interpreted some of the creatures mentioned in the books of Ezekiel and Revelation
Revelation, or divine revelation, is the disclosing of some form of Religious views on truth, truth or Knowledge#Religion, knowledge through communication with a deity (god) or other supernatural entity or entities in the view of religion and t ...
as the middle signs of the four-quarters of the Zodiac, with the Lion as Leo, the Bull as Taurus, the Man representing Aquarius, and the Eagle standing in for Scorpio. The biblical Book of Job
The Book of Job (), or simply Job, is a book found in the Ketuvim ("Writings") section of the Hebrew Bible and the first of the Poetic Books in the Old Testament of the Christian Bible. The language of the Book of Job, combining post-Babylonia ...
also makes reference to a number of constellations, including "bier", "fool" and "heap" (Job 9:9, 38:31–32), rendered as "Arcturus, Orion and Pleiades" by the KJV, but ''‘Ayish'' "the bier" actually corresponding to Ursa Major. The term '' Mazzaroth'' , translated as ''a garland of crowns'', is a '' hapax legomenon'' in Job 38:32, and it might refer to the zodiacal constellations.
Classical antiquity
There is only limited information on ancient Greek constellations, with some fragmentary evidence being found in the '' Works and Days'' of the Greek poet Hesiod, who mentioned the "heavenly bodies". Greek astronomy essentially adopted the older Babylonian system in the Hellenistic era, first introduced to Greece byEudoxus of Cnidus
Eudoxus of Cnidus (; , ''Eúdoxos ho Knídios''; ) was an Ancient Greece, ancient Greek Ancient Greek astronomy, astronomer, Greek mathematics, mathematician, doctor, and lawmaker. He was a student of Archytas and Plato. All of his original work ...
in the 4th century BC. The original work of Eudoxus is lost, but it survives as a versification by Aratus, dating to the 3rd century BC. The most complete existing works dealing with the mythical origins of the constellations are by the Hellenistic writer termed pseudo-Eratosthenes and an early Roman writer styled pseudo- Hyginus. The basis of Western astronomy as taught during Late Antiquity
Late antiquity marks the period that comes after the end of classical antiquity and stretches into the onset of the Early Middle Ages. Late antiquity as a period was popularized by Peter Brown (historian), Peter Brown in 1971, and this periodiza ...
and until the Early Modern period
The early modern period is a Periodization, historical period that is defined either as part of or as immediately preceding the modern period, with divisions based primarily on the history of Europe and the broader concept of modernity. There i ...
is the '' Almagest'' by Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; , ; ; – 160s/170s AD) was a Greco-Roman mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were important to later Byzantine science, Byzant ...
, written in the 2nd century.
In the Ptolemaic Kingdom
The Ptolemaic Kingdom (; , ) or Ptolemaic Empire was an ancient Greek polity based in Ancient Egypt, Egypt during the Hellenistic period. It was founded in 305 BC by the Ancient Macedonians, Macedonian Greek general Ptolemy I Soter, a Diadochi, ...
, native Egyptian tradition of anthropomorphic figures represented the planets, stars, and various constellations. Some of these were combined with Greek and Babylonian astronomical systems culminating in the Zodiac of Dendera, the oldest known depiction of the zodiac showing all the now familiar constellations, along with some original Egyptian constellations, decans, and planets
A planet is a large, rounded astronomical body that is generally required to be in orbit around a star, stellar remnant, or brown dwarf, and is not one itself. The Solar System has eight planets by the most restrictive definition of the te ...
. It remains unclear when this occurred, but most were placed during the Roman period between 2nd to 4th centuries AD. Ptolemy's ''Almagest'' remained the standard definition of constellations in the medieval period both in Europe and in Islamic astronomy.
Ancient China
Ancient China
The history of China spans several millennia across a wide geographical area. Each region now considered part of the Chinese world has experienced periods of unity, fracture, prosperity, and strife. Chinese civilization first emerged in the Y ...
had a long tradition of observing celestial phenomena. Nonspecific Chinese star names, later categorized in the twenty-eight mansions, have been found on oracle bones from Anyang
Anyang ( zh, s=安阳, t=安陽; ) is a prefecture-level city in Henan, China. Geographical coordinates are 35° 41'~ 36° 21' north latitude and 113° 38'~ 114° 59' east longitude. The northernmost city in Henan, Anyang borders Puyang to the eas ...
, dating back to the middle Shang dynasty
The Shang dynasty (), also known as the Yin dynasty (), was a Chinese royal dynasty that ruled in the Yellow River valley during the second millennium BC, traditionally succeeding the Xia dynasty and followed by the Western Zhou d ...
. These constellations are some of the most important observations of Chinese sky, attested from the 5th century BC. The Chinese system developed independently from the Greco-Roman system, although there may have been earlier mutual influence, suggested by parallels to ancient Babylonian astronomy
Babylonian astronomy was the study or recording of celestial objects during the early history of Mesopotamia. The numeral system used, sexagesimal, was based on 60, as opposed to ten in the modern decimal system. This system simplified the ca ...
.
Three schools of classical Chinese astronomy
Astronomy in China has a long history stretching from the Shang dynasty, being refined over a period of more than 3,000 years. The Ancient China, ancient Chinese people have identified stars from 1300 BCE, as Chinese star names later categori ...
in the Han period are attributed to astronomers of the earlier Warring States period
The Warring States period in history of China, Chinese history (221 BC) comprises the final two and a half centuries of the Zhou dynasty (256 BC), which were characterized by frequent warfare, bureaucratic and military reforms, and ...
. The constellations of the three schools were conflated into a single system by Chen Zhuo, an astronomer of the 3rd century ( Three Kingdoms period). Chen Zhuo's work has been lost, but information on his system of constellations survives in Tang period records, notably by Qutan Xida. The oldest extant Chinese star chart dates to that period and was preserved as part of the Dunhuang Manuscripts. Native Chinese astronomy flourished during the Song dynasty
The Song dynasty ( ) was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 960 to 1279. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Taizu of Song, who usurped the throne of the Later Zhou dynasty and went on to conquer the rest of the Fiv ...
, and during the Yuan dynasty
The Yuan dynasty ( ; zh, c=元朝, p=Yuáncháo), officially the Great Yuan (; Mongolian language, Mongolian: , , literally 'Great Yuan State'), was a Mongol-led imperial dynasty of China and a successor state to the Mongol Empire after Div ...
became increasingly influenced by medieval Islamic astronomy (see Treatise on Astrology of the Kaiyuan Era). As maps were prepared during this period on more scientific lines, they were considered as more reliable.
A well-known map from the Song period is the Suzhou Astronomical Chart, which was prepared with carvings of stars on the planisphere of the Chinese sky on a stone plate; it is done accurately based on observations, and it shows the 1054 supernova in Taurus.
Influenced by European astronomy during the late Ming dynasty
The Ming dynasty, officially the Great Ming, was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 1368 to 1644, following the collapse of the Mongol Empire, Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming was the last imperial dynasty of ...
, charts depicted more stars but retained the traditional constellations. Newly observed stars were incorporated as supplementary to old constellations in the southern sky, which did not depict the traditional stars recorded by ancient Chinese astronomers. Further improvements were made during the later part of the Ming dynasty by Xu Guangqi and Johann Adam Schall von Bell, the German Jesuit and was recorded in Chongzhen Lishu (Calendrical Treatise of Chongzhen period, 1628). Traditional Chinese star maps incorporated 23 new constellations with 125 stars of the southern hemisphere of the sky based on the knowledge of Western star charts; with this improvement, the Chinese Sky was integrated with the World astronomy.
Early modern astronomy
Historically, the origins of the constellations of the northern and southern skies are distinctly different. Most northern constellations date to antiquity, with names based mostly on Classical Greek legends. Evidence of these constellations has survived in the form of star charts, whose oldest representation appears on the statue known as the Farnese Atlas, based perhaps on the star catalogue of the Greek astronomerHipparchus
Hipparchus (; , ; BC) was a Ancient Greek astronomy, Greek astronomer, geographer, and mathematician. He is considered the founder of trigonometry, but is most famous for his incidental discovery of the precession of the equinoxes. Hippar ...
. Southern constellations are more modern inventions, sometimes as substitutes for ancient constellations (e.g. Argo Navis). Some southern constellations had long names that were shortened to more usable forms; e.g. Musca Australis became simply Musca.
Some of the early constellations were never universally adopted. Stars were often grouped into constellations differently by different observers, and the arbitrary constellation boundaries often led to confusion as to which constellation a celestial object belonged. Before astronomers delineated precise boundaries (starting in the 19th century), constellations generally appeared as ill-defined regions of the sky. Today they now follow officially accepted designated lines of right ascension
Right ascension (abbreviated RA; symbol ) is the angular distance of a particular point measured eastward along the celestial equator from the Sun at the equinox (celestial coordinates), March equinox to the (hour circle of the) point in questio ...
and declination
In astronomy, declination (abbreviated dec; symbol ''δ'') is one of the two angles that locate a point on the celestial sphere in the equatorial coordinate system, the other being hour angle. The declination angle is measured north (positive) or ...
based on those defined by Benjamin Gould in Equinox
A solar equinox is a moment in time when the Sun appears directly above the equator, rather than to its north or south. On the day of the equinox, the Sun appears to rise directly east and set directly west. This occurs twice each year, arou ...
B1875.0 in his star catalogue ''Uranometria Argentina''.
The 1603 star atlas " Uranometria" of Johann Bayer assigned stars to individual constellations and formalized the division by assigning a series of Greek and Latin letters to the stars within each constellation. These are known today as Bayer designation
A Bayer designation is a stellar designation in which a specific star is identified by a Greek alphabet, Greek or Latin letter followed by the genitive case, genitive form of its parent constellation's Latin name. The original list of Bayer design ...
s. Subsequent star atlases led to the development of today's accepted modern constellations.
Origin of the southern constellations
The southern sky, below about −65°declination
In astronomy, declination (abbreviated dec; symbol ''δ'') is one of the two angles that locate a point on the celestial sphere in the equatorial coordinate system, the other being hour angle. The declination angle is measured north (positive) or ...
, was only partially catalogued by ancient Babylonians, Egyptians, Greeks, Chinese, and Persian astronomers of the north. The knowledge that northern and southern star patterns differed goes back to Classical writers, who describe, for example, the African circumnavigation expedition commissioned by Egyptian Pharaoh Necho II in c. 600 BC and those of Hanno the Navigator in c. 500 BC.
The history of southern constellations is not straightforward. Different groupings and different names were proposed by various observers, some reflecting national traditions or designed to promote various sponsors. Southern constellations were important from the 14th to 16th centuries, when sailors used the stars for celestial navigation. Italian explorers who recorded new southern constellations include Andrea Corsali, Antonio Pigafetta, and Amerigo Vespucci.
Many of the 88 IAU-recognized constellations in this region first appeared on celestial globes developed in the late 16th century by Petrus Plancius, based mainly on observations of the Dutch navigators Pieter Dirkszoon Keyser
Pieter Dirkszoon Keyser (occasionally Petrus Theodorus; – 11 September 1596) was a Dutch navigator and celestial cartographer who mapped several constellations on the southern celestial hemisphere.
Voyages and star observation
Little is ...
and Frederick de Houtman. These became widely known through Johann Bayer's star atlas '' Uranometria'' of 1603. Fourteen more were created in 1763 by the French astronomer Nicolas Louis de Lacaille, who also split the ancient constellation Argo Navis into three; these new figures appeared in his star catalogue, published in 1756.
Several modern proposals have not survived. The French astronomers Pierre Lemonnier and Joseph Lalande, for example, proposed constellations that were once popular but have since been dropped. The northern constellation Quadrans Muralis survived into the 19th century (when its name was attached to the Quadrantid meteor shower), but is now divided between Boötes and Draco.
88 modern constellations
A list of 88 constellations was produced for the IAU in 1922. It is roughly based on the traditional Greek constellations listed by Ptolemy in his ''Almagest'' in the 2nd century and Aratus' work ''Phenomena'', with early modern modifications and additions (most importantly introducing constellations covering the parts of the southern sky unknown to Ptolemy) by Petrus Plancius (1592, 1597/98 and 1613), Johannes Hevelius (1690) and Nicolas Louis de Lacaille (1763), who introduced fourteen new constellations. Lacaille studied the stars of the southern hemisphere from 1751 until 1752 from theCape of Good Hope
The Cape of Good Hope ( ) is a rocky headland on the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic coast of the Cape Peninsula in South Africa.
A List of common misconceptions#Geography, common misconception is that the Cape of Good Hope is the southern tip of Afri ...
, when he was said to have observed more than 10,000 stars using a refracting telescope
A refracting telescope (also called a refractor) is a type of optical telescope that uses a lens (optics), lens as its objective (optics), objective to form an image (also referred to a dioptrics, dioptric telescope). The refracting telescope d ...
with an aperture of .
In 1922, Henry Norris Russell produced a list of 88 constellations with three-letter abbreviations for them. However, these constellations did not have clear borders between them. In 1928, the IAU formally accepted the 88 modern constellations, with contiguous boundaries along vertical and horizontal lines of right ascension
Right ascension (abbreviated RA; symbol ) is the angular distance of a particular point measured eastward along the celestial equator from the Sun at the equinox (celestial coordinates), March equinox to the (hour circle of the) point in questio ...
and declination
In astronomy, declination (abbreviated dec; symbol ''δ'') is one of the two angles that locate a point on the celestial sphere in the equatorial coordinate system, the other being hour angle. The declination angle is measured north (positive) or ...
developed by Eugene Delporte that, together, cover the entire celestial sphere; this list was finally published in 1930. Where possible, these modern constellations usually share the names of their Graeco-Roman predecessors, such as Orion, Leo, or Scorpius. The aim of this system is area-mapping, i.e. the division of the celestial sphere into contiguous fields. Out of the 88 modern constellations, 36 lie predominantly in the northern sky, and the other 52 predominantly in the southern.
The boundaries developed by Delporte used data that originated back to epoch B1875.0, which was when Benjamin A. Gould first made his proposal to designate boundaries for the celestial sphere, a suggestion on which Delporte based his work. The consequence of this early date is that because of the precession
Precession is a change in the orientation of the rotational axis of a rotating body. In an appropriate reference frame it can be defined as a change in the first Euler angle, whereas the third Euler angle defines the rotation itself. In o ...
of the equinox
A solar equinox is a moment in time when the Sun appears directly above the equator, rather than to its north or south. On the day of the equinox, the Sun appears to rise directly east and set directly west. This occurs twice each year, arou ...
es, the borders on a modern star map, such as epoch J2000
In astronomy, an epoch or reference epoch is a moment in time used as a reference point for some time-varying astronomical quantity. It is useful for the celestial coordinates or orbital elements of a celestial body, as they are subject to ...
, are already somewhat skewed and no longer perfectly vertical or horizontal. This effect will increase over the years and centuries to come.
Symbols
The constellations have no official symbols, though those of the ecliptic may take the signs of the zodiac. Symbols for the other modern constellations, as well as older ones that still occur in modern nomenclature, have occasionally been published.Dark cloud constellations
 The Great Rift, a series of dark patches in the Milky Way, is most visible in the southern sky. Some cultures have discerned shapes in these patches. Members of the
The Great Rift, a series of dark patches in the Milky Way, is most visible in the southern sky. Some cultures have discerned shapes in these patches. Members of the Inca
The Inca Empire, officially known as the Realm of the Four Parts (, ), was the largest empire in pre-Columbian America. The administrative, political, and military center of the empire was in the city of Cusco. The History of the Incas, Inca ...
civilization identified various dark areas or dark nebulae in the Milky Way as animals and associated their appearance with the seasonal rains. Australian Aboriginal astronomy also describes dark cloud constellations, the most famous being the "emu in the sky" whose head is formed by the Coalsack, a dark nebula, instead of the stars.
Emu
The emu (; ''Dromaius novaehollandiae'') is a species of flightless bird endemism, endemic to Australia, where it is the Tallest extant birds, tallest native bird. It is the only extant taxon, extant member of the genus ''Dromaius'' and the ...
in the sky'' – a constellation defined by dark clouds rather than by stars. The head of the emu is the Coalsack with Crux directly above. Scorpius is to the left.
File:Coricancha museum marker graphically explaining the Inca astronomical system.jpg, Inca dark cloud constellations in the Mayu (Celestial River), or the Milky Way; Crux is above Yutu, while the eyes of the Llama are Alpha
Alpha (uppercase , lowercase ) is the first letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals, it has a value of one. Alpha is derived from the Phoenician letter ''aleph'' , whose name comes from the West Semitic word for ' ...
and Beta Centauri.
List of dark cloud constellations
* Great Rift (astronomy) ** Cygnus Rift ** Serpens–Aquila Rift ** Dark Horse (astronomy) ** Rho Ophiuchi cloud complex ** Emu in the skySee also
* Celestial cartography * Constellation family * Former constellations * Lists of stars by constellation * Constellations listed by Johannes Hevelius * Constellations listed by Lacaille * Constellations listed by Petrus Plancius * Constellations listed by PtolemyReferences
Footnotes CitationsFurther reading
Mythology, lore, history, and archaeoastronomy
* Allen, Richard Hinckley. (1899) ''Star-Names And Their Meanings'', G. E. Stechert, New York, hardcover; reprint 1963 as ''Star Names: Their Lore and Meaning'', Dover Publications, Inc., Mineola, NY, softcover. * Olcott, William Tyler. (1911); ''Star Lore of All Ages'', G. P. Putnam's Sons, New York, hardcover; reprint 2004 as ''Star Lore: Myths, Legends, and Facts'', Dover Publications, Inc., Mineola, NY, softcover. * Kelley, David H. and Milone, Eugene F. (2004) ''Exploring Ancient Skies: An Encyclopedic Survey of Archaeoastronomy'', Springer, hardcover. * Ridpath, Ian. (2018) ''Star Tales'' 2nd ed., Lutterworth Press, softcover. * Staal, Julius D. W. (1988) ''The New Patterns in the Sky: Myths and Legends of the Stars'', McDonald & Woodward Publishing Co., hardcover, softcover. * *Atlases and celestial maps
* Becvar, Antonin. ''Atlas Coeli''. Published as ''Atlas of the Heavens'', Sky Publishing Corporation, Cambridge, MA, with coordinate grid transparency overlay. * Becvar, Antonin. (1962) ''Atlas Borealis 1950.0'', Czechoslovak Academy of Sciences (Ceskoslovenske Akademie Ved), Praha, Czechoslovakia, 1st Edition, elephant folio hardcover, with small transparency overlay coordinate grid square and separate paper magnitude legend ruler. 2nd Edition 1972 and 1978 reprint, Czechoslovak Academy of Sciences (Ceskoslovenske Akademie Ved), Prague, Czechoslovakia, and Sky Publishing Corporation, Cambridge, MA, oversize folio softcover spiral-bound, with transparency overlay coordinate grid ruler. *National Geographic Society
The National Geographic Society, headquartered in Washington, D.C., United States, is one of the largest nonprofit scientific and educational organizations in the world.
Founded in 1888, its interests include geography, archaeology, natural sc ...
. (1957, 1970, 2001, 2007) ''The Heavens'' (1970), Cartographic Division of the National Geographic Society (NGS), Washington, DC, two-sided large map chart depicting the constellations of the heavens; as a special supplement to the August 1970 issue of '' National Geographic''. Forerunner map as ''A Map of The Heavens'', as a special supplement to the December 1957 issue. Current version 2001 (Tirion), with 2007 reprint.
* Norton, Arthur Philip. (1910) '' Norton's Star Atlas'', 20th Edition 2003 as ''Norton's Star Atlas and Reference Handbook'', edited by Ridpath, Ian, Pi Press, , hardcover.
* Sinnott, Roger W. and Perryman, Michael A.C. (1997) '' Millennium Star Atlas'', Epoch 2000.0, Sky Publishing Corporation, Cambridge, MA, and European Space Agency (ESA), ESTEC, Noordwijk, The Netherlands. Subtitle: "An All-Sky Atlas Comprising One Million Stars to Visual Magnitude Eleven from the Hipparcos and Tycho Catalogues and Ten Thousand Nonstellar Objects". 3 volumes, hardcover, . Vol. 1, 0–8 Hours (Right Ascension), hardcover; Vol. 2, 8–16 Hours, hardcover; Vol. 3, 16–24 Hours, hardcover. Softcover version available. Supplemental separate purchasable coordinate grid transparent overlays.
* Tirion, Wil; et al. (1987) ''Uranometria 2000.0'', Willmann-Bell, Inc., Richmond, VA, 3 volumes, hardcover. Vol. 1 (1987): "The Northern Hemisphere to −6°", by Wil Tirion, Barry Rappaport, and George Lovi, hardcover, printed boards. Vol. 2 (1988): "The Southern Hemisphere to +6°", by Wil Tirion, Barry Rappaport and George Lovi, hardcover, printed boards. Vol. 3 (1993) as a separate added work: ''The Deep Sky Field Guide to Uranometria 2000.0'', by Murray Cragin, James Lucyk, and Barry Rappaport, hardcover, printed boards. 2nd Edition 2001 as collective set of 3 volumes – Vol. 1: ''Uranometria 2000.0 Deep Sky Atlas'', by Wil Tirion, Barry Rappaport, and Will Remaklus, hardcover, printed boards; Vol. 2: ''Uranometria 2000.0 Deep Sky Atlas'', by Wil Tirion, Barry Rappaport, and Will Remaklus, hardcover, printed boards; Vol. 3: ''Uranometria 2000.0 Deep Sky Field Guide'' by Murray Cragin and Emil Bonanno, , hardcover, printed boards.
* Tirion, Wil and Sinnott, Roger W. (1998) ''Sky Atlas 2000.0'', various editions. 2nd Deluxe Edition, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, England.
Catalogs
* Becvar, Antonin. (1959) ''Atlas Coeli II Katalog 1950.0'', Praha, 1960 Prague. Published 1964 as ''Atlas of the Heavens – II Catalogue 1950.0'', Sky Publishing Corporation, Cambridge, MA * Hirshfeld, Alan and Sinnott, Roger W. (1982) ''Sky Catalogue 2000.0'', Cambridge University Press and Sky Publishing Corporation, 1st Edition, 2 volumes. both vols., and vol. 1. "Volume 1: Stars to Magnitude 8.0", (Cambridge) and hardcover, softcover. Vol. 2 (1985) – "Volume 2: Double Stars, Variable Stars, and Nonstellar Objects", (Cambridge) hardcover, (Cambridge) softcover. 2nd Edition (1991) with additional third author François Ochsenbein, 2 volumes, . Vol. 1: (Cambridge) hardcover; (Cambridge) softcover . Vol. 2 (1999): (Cambridge) softcover and 0-933346-38-7 softcover – reprint of 1985 edition. * Yale University Observatory. (1908, et al.) '' Catalogue of Bright Stars'', New Haven, CN. Referred to commonly as "Bright Star Catalogue". Various editions with various authors historically, the longest term revising author as (Ellen) Dorrit Hoffleit. 1st Edition 1908. 2nd Edition 1940 by Frank Schlesinger and Louise F. Jenkins. 3rd Edition (1964), 4th Edition, 5th Edition (1991), and 6th Edition (pending posthumous) by Hoffleit.External links
IAU: The Constellations
including high quality maps.
Atlascoelestis
di Felice Stoppa.
Celestia
free 3D realtime space-simulation (OpenGL)
Stellarium
realtime sky rendering program (OpenGL)
Strasbourg Astronomical Data Center Files on official IAU constellation boundaries
Studies of Occidental Constellations and Star Names to the Classical Period: An Annotated Bibliography
Greco-Roman constellation myths
Neave Planetarium
Adobe Flash interactive web browser planetarium and stardome with realistic movement of stars and the planets. * Audio – Cain/Gay (2009
Astronomy Cast
Constellations
The Greek Star-Map
short essay by Gavin White
Bucur D. The network signature of constellation line figures
PLOS ONE 17(7): e0272270 (2022). A comparative analysis on the structure of constellation line figures across sky cultures. {{Authority control Constellations Celestial cartography Constellations Concepts in astronomy