constant of proportionality on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 In mathematics, two
In mathematics, two
 The concept of ''inverse proportionality'' can be contrasted with ''direct proportionality''. Consider two variables said to be "inversely proportional" to each other. If all other variables are held constant, the magnitude or absolute value of one inversely proportional variable decreases if the other variable increases, while their product (the constant of proportionality ''k'') is always the same. As an example, the time taken for a journey is inversely proportional to the speed of travel.
Formally, two variables are inversely proportional (also called varying inversely, in inverse variation, in inverse proportion) if each of the variables is directly proportional to the
The concept of ''inverse proportionality'' can be contrasted with ''direct proportionality''. Consider two variables said to be "inversely proportional" to each other. If all other variables are held constant, the magnitude or absolute value of one inversely proportional variable decreases if the other variable increases, while their product (the constant of proportionality ''k'') is always the same. As an example, the time taken for a journey is inversely proportional to the speed of travel.
Formally, two variables are inversely proportional (also called varying inversely, in inverse variation, in inverse proportion) if each of the variables is directly proportional to the
"Inversely Proportional"
''MathWorld'' – A Wolfram Web Resource. It follows that the variable ''y'' is inversely proportional to the variable ''x'' if there exists a non-zero constant ''k'' such that : or equivalently, Hence the constant "''k''" is the product of ''x'' and ''y''. The graph of two variables varying inversely on the Cartesian coordinate plane is a rectangular hyperbola. The product of the ''x'' and ''y'' values of each point on the curve equals the constant of proportionality (''k''). Since neither ''x'' nor ''y'' can equal zero (because ''k'' is non-zero), the graph never crosses either axis.
p. 34–35
* Brian Burrell: ''Merriam-Webster's Guide to Everyday Math: A Home and Business Reference''. Merriam-Webster, 1998,
p. 85–101
* Lanius, Cynthia S.; Williams Susan E.
''PROPORTIONALITY: A Unifying Theme for the Middle Grades''
Mathematics Teaching in the Middle School 8.8 (2003), p. 392–396. * Seeley, Cathy; Schielack Jane F.
''A Look at the Development of Ratios, Rates, and Proportionality''
Mathematics Teaching in the Middle School, 13.3, 2007, p. 140–142. * Van Dooren, Wim; De Bock Dirk; Evers Marleen; Verschaffel Lieven
''Students' Overuse of Proportionality on Missing-Value Problems: How Numbers May Change Solutions''
Journal for Research in Mathematics Education, 40.2, 2009, p. 187–211. {{DEFAULTSORT:Proportionality (Mathematics) Mathematical terminology Ratios
 In mathematics, two
In mathematics, two sequence
In mathematics, a sequence is an enumerated collection of objects in which repetitions are allowed and order matters. Like a set, it contains members (also called ''elements'', or ''terms''). The number of elements (possibly infinite) is called ...
s of numbers, often experimental data, are proportional or directly proportional if their corresponding elements have a constant ratio
In mathematics, a ratio shows how many times one number contains another. For example, if there are eight oranges and six lemons in a bowl of fruit, then the ratio of oranges to lemons is eight to six (that is, 8:6, which is equivalent to the ...
, which is called the coefficient of proportionality or proportionality constant. Two sequences are inversely proportional if corresponding elements have a constant product, also called the coefficient of proportionality.
This definition is commonly extended to related varying quantities, which are often called ''variables''. This meaning of ''variable'' is not the common meaning of the term in mathematics (see variable (mathematics)
In mathematics, a variable (from Latin '' variabilis'', "changeable") is a symbol that represents a mathematical object. A variable may represent a number, a vector, a matrix, a function, the argument of a function, a set, or an element of ...
); these two different concepts share the same name for historical reasons.
Two functions and are ''proportional'' if their ratio is a constant function
In mathematics, a constant function is a function whose (output) value is the same for every input value. For example, the function is a constant function because the value of is 4 regardless of the input value (see image).
Basic properti ...
.
If several pairs of variables share the same direct proportionality constant, the equation expressing the equality of these ratios is called a proportion, e.g., (for details see Ratio
In mathematics, a ratio shows how many times one number contains another. For example, if there are eight oranges and six lemons in a bowl of fruit, then the ratio of oranges to lemons is eight to six (that is, 8:6, which is equivalent to the ...
).
Proportionality is closely related to '' linearity''.
Direct proportionality
Given two variables ''x'' and ''y'', ''y'' is directly proportional to ''x'' if there is a non-zero constant ''k'' such that : The relation is often denoted using the symbols "∝" (not to be confused with the Greek letter alpha) or "~": : or For the proportionality constant can be expressed as the ratio : It is also called the constant of variation or constant of proportionality. A direct proportionality can also be viewed as a linear equation in two variables with a ''y''-intercept of and aslope
In mathematics, the slope or gradient of a line is a number that describes both the ''direction'' and the ''steepness'' of the line. Slope is often denoted by the letter ''m''; there is no clear answer to the question why the letter ''m'' is used ...
of ''k''. This corresponds to linear growth.
Examples
* If an object travels at a constantspeed
In everyday use and in kinematics, the speed (commonly referred to as ''v'') of an object is the magnitude of the change of its position over time or the magnitude of the change of its position per unit of time; it is thus a scalar quantity ...
, then the distance
Distance is a numerical or occasionally qualitative measurement of how far apart objects or points are. In physics or everyday usage, distance may refer to a physical length or an estimation based on other criteria (e.g. "two counties over"). ...
traveled is directly proportional to the time
Time is the continued sequence of existence and events that occurs in an apparently irreversible succession from the past, through the present, into the future. It is a component quantity of various measurements used to sequence events, t ...
spent traveling, with the speed being the constant of proportionality.
* The circumference
In geometry, the circumference (from Latin ''circumferens'', meaning "carrying around") is the perimeter of a circle or ellipse. That is, the circumference would be the arc length of the circle, as if it were opened up and straightened out t ...
of a circle
A circle is a shape consisting of all points in a plane that are at a given distance from a given point, the centre. Equivalently, it is the curve traced out by a point that moves in a plane so that its distance from a given point is const ...
is directly proportional to its diameter
In geometry, a diameter of a circle is any straight line segment that passes through the center of the circle and whose endpoints lie on the circle. It can also be defined as the longest chord of the circle. Both definitions are also valid fo ...
, with the constant of proportionality equal to .
* On a map of a sufficiently small geographical area, drawn to scale
Scale or scales may refer to:
Mathematics
* Scale (descriptive set theory), an object defined on a set of points
* Scale (ratio), the ratio of a linear dimension of a model to the corresponding dimension of the original
* Scale factor, a number ...
distances, the distance between any two points on the map is directly proportional to the beeline distance between the two locations represented by those points; the constant of proportionality is the scale of the map.
* The force
In physics, a force is an influence that can change the motion of an object. A force can cause an object with mass to change its velocity (e.g. moving from a state of rest), i.e., to accelerate. Force can also be described intuitively as a ...
, acting on a small object with small mass
Mass is an intrinsic property of a body. It was traditionally believed to be related to the quantity of matter in a physical body, until the discovery of the atom and particle physics. It was found that different atoms and different element ...
by a nearby large extended mass due to gravity
In physics, gravity () is a fundamental interaction which causes mutual attraction between all things with mass or energy. Gravity is, by far, the weakest of the four fundamental interactions, approximately 1038 times weaker than the str ...
, is directly proportional to the object's mass; the constant of proportionality between the force and the mass is known as gravitational acceleration
In physics, gravitational acceleration is the acceleration of an object in free fall within a vacuum (and thus without experiencing drag (physics), drag). This is the steady gain in speed caused exclusively by the force of gravitational attract ...
.
* The net force acting on an object is proportional to the acceleration of that object with respect to an inertial frame of reference. The constant of proportionality in this, Newton's second law
Newton's laws of motion are three basic Scientific law, laws of classical mechanics that describe the relationship between the motion of an object and the forces acting on it. These laws can be paraphrased as follows:
# A body remains at re ...
, is the classical mass of the object.
Computer encoding
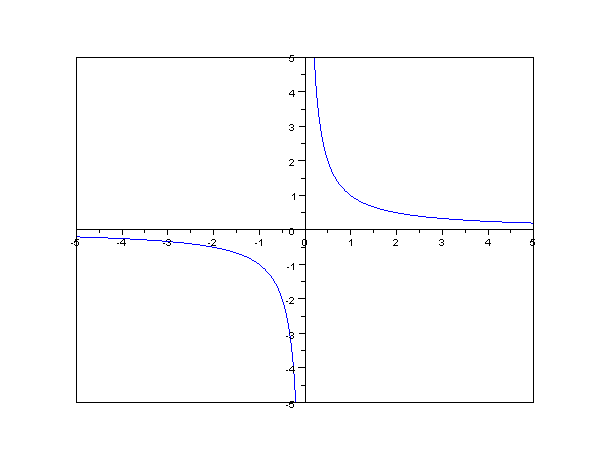
Inverse proportionality
 The concept of ''inverse proportionality'' can be contrasted with ''direct proportionality''. Consider two variables said to be "inversely proportional" to each other. If all other variables are held constant, the magnitude or absolute value of one inversely proportional variable decreases if the other variable increases, while their product (the constant of proportionality ''k'') is always the same. As an example, the time taken for a journey is inversely proportional to the speed of travel.
Formally, two variables are inversely proportional (also called varying inversely, in inverse variation, in inverse proportion) if each of the variables is directly proportional to the
The concept of ''inverse proportionality'' can be contrasted with ''direct proportionality''. Consider two variables said to be "inversely proportional" to each other. If all other variables are held constant, the magnitude or absolute value of one inversely proportional variable decreases if the other variable increases, while their product (the constant of proportionality ''k'') is always the same. As an example, the time taken for a journey is inversely proportional to the speed of travel.
Formally, two variables are inversely proportional (also called varying inversely, in inverse variation, in inverse proportion) if each of the variables is directly proportional to the multiplicative inverse
In mathematics, a multiplicative inverse or reciprocal for a number ''x'', denoted by 1/''x'' or ''x''−1, is a number which when multiplied by ''x'' yields the multiplicative identity, 1. The multiplicative inverse of a fraction ''a''/''b ...
(reciprocal) of the other, or equivalently if their product is a constant.Weisstein, Eric W"Inversely Proportional"
''MathWorld'' – A Wolfram Web Resource. It follows that the variable ''y'' is inversely proportional to the variable ''x'' if there exists a non-zero constant ''k'' such that : or equivalently, Hence the constant "''k''" is the product of ''x'' and ''y''. The graph of two variables varying inversely on the Cartesian coordinate plane is a rectangular hyperbola. The product of the ''x'' and ''y'' values of each point on the curve equals the constant of proportionality (''k''). Since neither ''x'' nor ''y'' can equal zero (because ''k'' is non-zero), the graph never crosses either axis.
Hyperbolic coordinates
The concepts of ''direct'' and ''inverse'' proportion lead to the location of points in the Cartesian plane by hyperbolic coordinates; the two coordinates correspond to the constant of direct proportionality that specifies a point as being on a particularray
Ray may refer to:
Fish
* Ray (fish), any cartilaginous fish of the superorder Batoidea
* Ray (fish fin anatomy), a bony or horny spine on a fin
Science and mathematics
* Ray (geometry), half of a line proceeding from an initial point
* Ray (g ...
and the constant of inverse proportionality that specifies a point as being on a particular hyperbola.
See also
* Linear map *Correlation
In statistics, correlation or dependence is any statistical relationship, whether causal or not, between two random variables or bivariate data. Although in the broadest sense, "correlation" may indicate any type of association, in statisti ...
* Eudoxus of Cnidus
Eudoxus of Cnidus (; grc, Εὔδοξος ὁ Κνίδιος, ''Eúdoxos ho Knídios''; ) was an ancient Greek astronomer, mathematician, scholar, and student of Archytas and Plato. All of his original works are lost, though some fragments a ...
* Golden ratio
In mathematics, two quantities are in the golden ratio if their ratio is the same as the ratio of their sum to the larger of the two quantities. Expressed algebraically, for quantities a and b with a > b > 0,
where the Greek letter phi ( ...
* Inverse-square law
In science, an inverse-square law is any scientific law stating that a specified physical quantity is inversely proportional to the square of the distance from the source of that physical quantity. The fundamental cause for this can be unde ...
* Proportional font
* Ratio
In mathematics, a ratio shows how many times one number contains another. For example, if there are eight oranges and six lemons in a bowl of fruit, then the ratio of oranges to lemons is eight to six (that is, 8:6, which is equivalent to the ...
* Rule of three (mathematics)
* Sample size
* Similarity
* Basic proportionality theorem
* ∷ the ''a'' is to ''b'' as ''c'' is to ''d'' symbol (U+2237 ''PROPORTION'')Growth
* Linear growth * Hyperbolic growthNotes
References
* Ya. B. Zeldovich,I. M. Yaglom
Isaak Moiseevich Yaglom (russian: Исаа́к Моисе́евич Ягло́м; 6 March 1921 – 17 April 1988) was a Soviet mathematician and author of popular mathematics books, some with his twin Akiva Yaglom.
Yaglom received a Ph.D. from M ...
: ''Higher math for beginners''p. 34–35
* Brian Burrell: ''Merriam-Webster's Guide to Everyday Math: A Home and Business Reference''. Merriam-Webster, 1998,
p. 85–101
* Lanius, Cynthia S.; Williams Susan E.
''PROPORTIONALITY: A Unifying Theme for the Middle Grades''
Mathematics Teaching in the Middle School 8.8 (2003), p. 392–396. * Seeley, Cathy; Schielack Jane F.
''A Look at the Development of Ratios, Rates, and Proportionality''
Mathematics Teaching in the Middle School, 13.3, 2007, p. 140–142. * Van Dooren, Wim; De Bock Dirk; Evers Marleen; Verschaffel Lieven
''Students' Overuse of Proportionality on Missing-Value Problems: How Numbers May Change Solutions''
Journal for Research in Mathematics Education, 40.2, 2009, p. 187–211. {{DEFAULTSORT:Proportionality (Mathematics) Mathematical terminology Ratios