Condensed matter physics on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Condensed matter physics is the field of
 One of the first studies of condensed states of matter was by
One of the first studies of condensed states of matter was by
 In 1879,
In 1879,
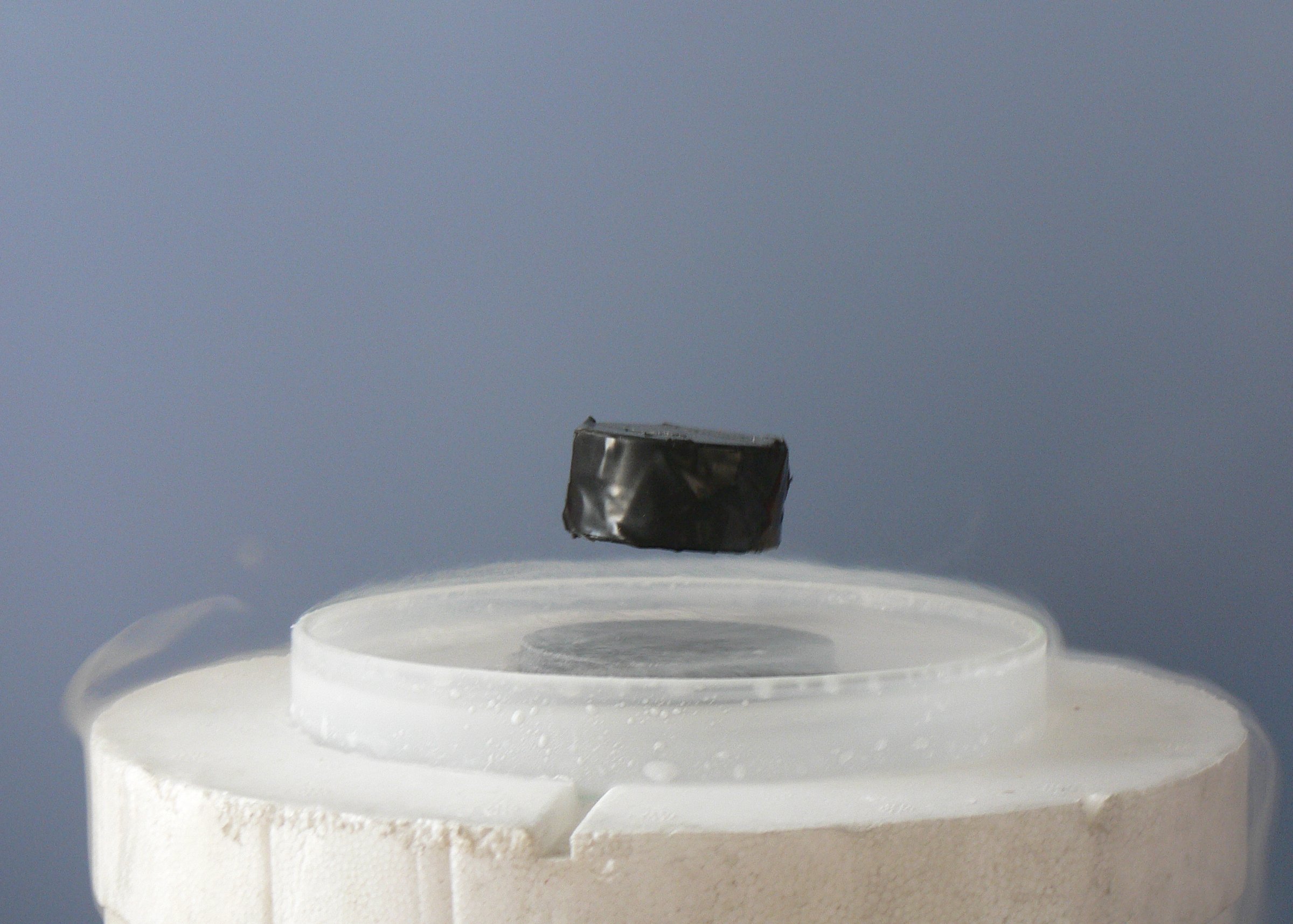 The Sommerfeld model and spin models for ferromagnetism illustrated the successful application of quantum mechanics to condensed matter problems in the 1930s. However, there still were several unsolved problems, most notably the description of
The Sommerfeld model and spin models for ferromagnetism illustrated the successful application of quantum mechanics to condensed matter problems in the 1930s. However, there still were several unsolved problems, most notably the description of  The study of phase transitions and the critical behavior of observables, termed critical phenomena, was a major field of interest in the 1960s. Leo Kadanoff, Benjamin Widom and Michael Fisher developed the ideas of
The study of phase transitions and the critical behavior of observables, termed critical phenomena, was a major field of interest in the 1960s. Leo Kadanoff, Benjamin Widom and Michael Fisher developed the ideas of
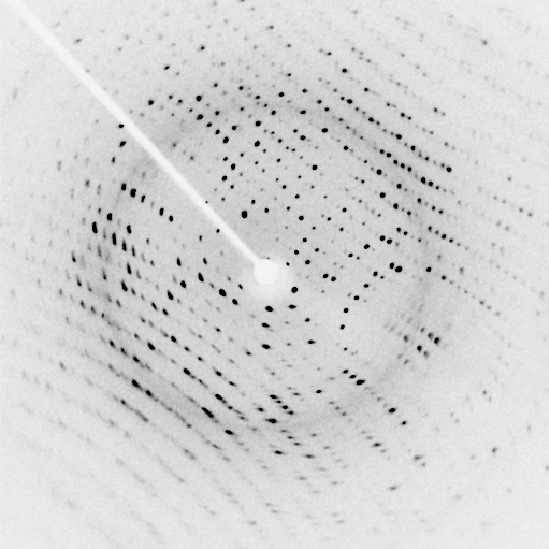

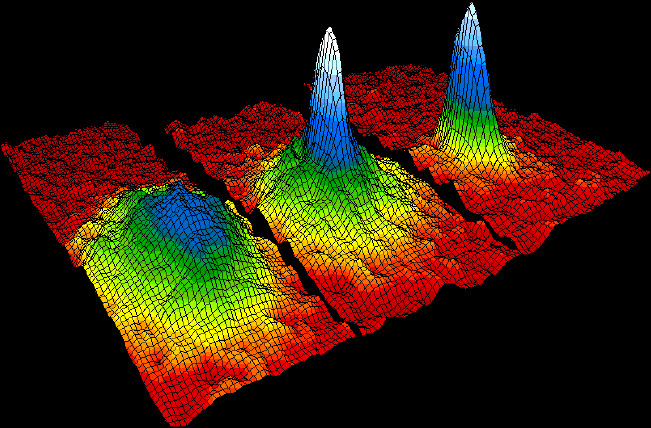 Ultracold atom trapping in optical lattices is an experimental tool commonly used in condensed matter physics, and in atomic, molecular, and optical physics. The method involves using optical lasers to form an interference pattern, which acts as a ''lattice'', in which ions or atoms can be placed at very low temperatures. Cold atoms in optical lattices are used as ''quantum simulators'', that is, they act as controllable systems that can model behavior of more complicated systems, such as frustrated magnets. In particular, they are used to engineer one-, two- and three-dimensional lattices for a
Ultracold atom trapping in optical lattices is an experimental tool commonly used in condensed matter physics, and in atomic, molecular, and optical physics. The method involves using optical lasers to form an interference pattern, which acts as a ''lattice'', in which ions or atoms can be placed at very low temperatures. Cold atoms in optical lattices are used as ''quantum simulators'', that is, they act as controllable systems that can model behavior of more complicated systems, such as frustrated magnets. In particular, they are used to engineer one-, two- and three-dimensional lattices for a
 Research in condensed matter physics has given rise to several device applications, such as the development of the
Research in condensed matter physics has given rise to several device applications, such as the development of the
physics
Physics is the natural science that studies matter, its fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge which ...
that deals with the macroscopic and microscopic physical properties of matter
In classical physics and general chemistry, matter is any substance that has mass and takes up space by having volume. All everyday objects that can be touched are ultimately composed of atoms, which are made up of interacting subatomic part ...
, especially the solid
Solid is one of the four fundamental states of matter (the others being liquid, gas, and plasma). The molecules in a solid are closely packed together and contain the least amount of kinetic energy. A solid is characterized by structur ...
and liquid
A liquid is a nearly incompressible fluid that conforms to the shape of its container but retains a (nearly) constant volume independent of pressure. As such, it is one of the four fundamental states of matter (the others being solid, gas, ...
phases which arise from electromagnetic forces between atom
Every atom is composed of a nucleus and one or more electrons bound to the nucleus. The nucleus is made of one or more protons and a number of neutrons. Only the most common variety of hydrogen has no neutrons.
Every solid, liquid, gas, a ...
s. More generally, the subject deals with "condensed" phases of matter: systems of many constituents with strong interactions between them. More exotic condensed phases include the superconducting phase exhibited by certain materials at low temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that expresses quantitatively the perceptions of hotness and coldness. Temperature is measured with a thermometer.
Thermometers are calibrated in various temperature scales that historically have relied o ...
, the ferromagnetic and antiferromagnet
In materials that exhibit antiferromagnetism, the magnetic moments of atoms or molecules, usually related to the spins of electrons, align in a regular pattern with neighboring spins (on different sublattices) pointing in opposite directions. ...
ic phases of spins
The spins (as in having "the spins")Diane Marie Leiva. ''The Florida State University College of Education''Women's Voices on College Drinking: The First-Year College Experience"/ref> is an adverse reaction of intoxication that causes a state of v ...
on crystal lattice
In geometry and crystallography, a Bravais lattice, named after , is an infinite array of discrete points generated by a set of discrete translation operations described in three dimensional space by
: \mathbf = n_1 \mathbf_1 + n_2 \mathbf_2 + n ...
s of atoms, and the Bose–Einstein condensate found in ultracold atomic systems. Condensed matter physicists seek to understand the behavior of these phases by experiments to measure various material properties, and by applying the physical law
Scientific laws or laws of science are statements, based on repeated experiments or observations, that describe or predict a range of natural phenomena. The term ''law'' has diverse usage in many cases (approximate, accurate, broad, or narro ...
s of quantum mechanics
Quantum mechanics is a fundamental theory in physics that provides a description of the physical properties of nature at the scale of atoms and subatomic particles. It is the foundation of all quantum physics including quantum chemistry, ...
, electromagnetism
In physics, electromagnetism is an interaction that occurs between particles with electric charge. It is the second-strongest of the four fundamental interactions, after the strong force, and it is the dominant force in the interactions o ...
, statistical mechanics
In physics, statistical mechanics is a mathematical framework that applies statistical methods and probability theory to large assemblies of microscopic entities. It does not assume or postulate any natural laws, but explains the macroscopic b ...
, and other theories to develop mathematical models.
The diversity of systems and phenomena available for study makes condensed matter physics the most active field of contemporary physics: one third of all American physicists self-identify as condensed matter physicists, and the Division of Condensed Matter Physics is the largest division at the American Physical Society
The American Physical Society (APS) is a not-for-profit membership organization of professionals in physics and related disciplines, comprising nearly fifty divisions, sections, and other units. Its mission is the advancement and diffusion of k ...
. The field overlaps with chemistry
Chemistry is the scientific study of the properties and behavior of matter. It is a natural science that covers the elements that make up matter to the compounds made of atoms, molecules and ions: their composition, structure, proper ...
, materials science, engineering
Engineering is the use of scientific principles to design and build machines, structures, and other items, including bridges, tunnels, roads, vehicles, and buildings. The discipline of engineering encompasses a broad range of more speciali ...
and nanotechnology
Nanotechnology, also shortened to nanotech, is the use of matter on an atomic, molecular, and supramolecular scale for industrial purposes. The earliest, widespread description of nanotechnology referred to the particular technological goal ...
, and relates closely to atomic physics
Atomic physics is the field of physics that studies atoms as an isolated system of electrons and an atomic nucleus. Atomic physics typically refers to the study of atomic structure and the interaction between atoms. It is primarily concerned wit ...
and biophysics. The theoretical physics
Theoretical physics is a branch of physics that employs mathematical models and abstractions of physical objects and systems to rationalize, explain and predict natural phenomena. This is in contrast to experimental physics, which uses experim ...
of condensed matter shares important concepts and methods with that of particle physics
Particle physics or high energy physics is the study of fundamental particles and forces that constitute matter and radiation. The fundamental particles in the universe are classified in the Standard Model as fermions (matter particles) an ...
and nuclear physics
Nuclear physics is the field of physics that studies atomic nuclei and their constituents and interactions, in addition to the study of other forms of nuclear matter.
Nuclear physics should not be confused with atomic physics, which studies t ...
.
A variety of topics in physics such as crystallography
Crystallography is the experimental science of determining the arrangement of atoms in crystalline solids. Crystallography is a fundamental subject in the fields of materials science and solid-state physics ( condensed matter physics). The wor ...
, metallurgy
Metallurgy is a domain of materials science and engineering that studies the physical and chemical behavior of metallic elements, their inter-metallic compounds, and their mixtures, which are known as alloys.
Metallurgy encompasses both the sc ...
, elasticity, magnetism
Magnetism is the class of physical attributes that are mediated by a magnetic field, which refers to the capacity to induce attractive and repulsive phenomena in other entities. Electric currents and the magnetic moments of elementary particles ...
, etc., were treated as distinct areas until the 1940s, when they were grouped together as ''solid-state physics
Solid-state physics is the study of rigid matter, or solids, through methods such as quantum mechanics, crystallography, electromagnetism, and metallurgy. It is the largest branch of condensed matter physics. Solid-state physics studies how th ...
''. Around the 1960s, the study of physical properties of liquid
A liquid is a nearly incompressible fluid that conforms to the shape of its container but retains a (nearly) constant volume independent of pressure. As such, it is one of the four fundamental states of matter (the others being solid, gas, ...
s was added to this list, forming the basis for the more comprehensive specialty of condensed matter physics. The Bell Telephone Laboratories was one of the first institutes to conduct a research program in condensed matter physics. According to founding director of the Max Planck Institute for Solid State Research, physics professor Manuel Cardona, it was Albert Einstein
Albert Einstein ( ; ; 14 March 1879 – 18 April 1955) was a German-born theoretical physicist, widely acknowledged to be one of the greatest and most influential physicists of all time. Einstein is best known for developing the theor ...
who created the modern field of condensed matter physics starting with his seminal 1905 article on the photoelectric effect and photoluminescence
Photoluminescence (abbreviated as PL) is light emission from any form of matter after the absorption of photons (electromagnetic radiation). It is one of many forms of luminescence (light emission) and is initiated by photoexcitation (i.e. photo ...
which opened the fields of photoelectron spectroscopy and photoluminescence spectroscopy, and later his 1907 article on the specific heat of solids which introduced, for the first time, the effect of lattice vibrations on the thermodynamic properties of crystals, in particular the specific heat. Deputy Director of the Yale Quantum Institute A. Douglas Stone makes a similar priority case for Einstein in his work on the synthetic history of quantum mechanics.
Etymology
According to physicist Philip Warren Anderson, the use of the term "condensed matter" to designate a field of study was coined by him andVolker Heine
Volker Heine FRS (born 19 September 1930 in Hamburg, Germany) is a New Zealand / British physicist. He is married to Daphne and they have three children. Volker Heine is considered a pioneer of theoretical and computational studies of the elect ...
, when they changed the name of their group at the Cavendish Laboratories, Cambridge
Cambridge ( ) is a university city and the county town in Cambridgeshire, England. It is located on the River Cam approximately north of London. As of the 2021 United Kingdom census, the population of Cambridge was 145,700. Cambridge bec ...
from ''Solid state theory'' to ''Theory of Condensed Matter'' in 1967, as they felt it better included their interest in liquids, nuclear matter, and so on. Although Anderson and Heine helped popularize the name "condensed matter", it had been used in Europe for some years, most prominently in the Springer-Verlag
Springer Science+Business Media, commonly known as Springer, is a German multinational publishing company of books, e-books and peer-reviewed journals in science, humanities, technical and medical (STM) publishing.
Originally founded in 1842 ...
journal ''Physics of Condensed Matter'', launched in 1963. The name "condensed matter physics" emphasized the commonality of scientific problems encountered by physicists working on solids, liquids, plasmas, and other complex matter, whereas "solid state physics" was often associated with restricted industrial applications of metals and semiconductors. In the 1960s and 70s, some physicists felt the more comprehensive name better fit the funding environment and Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because t ...
politics of the time.
References to "condensed" states can be traced to earlier sources. For example, in the introduction to his 1947 book ''Kinetic Theory of Liquids'', Yakov Frenkel proposed that "The kinetic theory of liquids must accordingly be developed as a generalization and extension of the kinetic theory of solid bodies. As a matter of fact, it would be more correct to unify them under the title of 'condensed bodies'".
History of condensed matter physics
Classical physics
 One of the first studies of condensed states of matter was by
One of the first studies of condensed states of matter was by English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ...
chemist
A chemist (from Greek ''chēm(ía)'' alchemy; replacing ''chymist'' from Medieval Latin ''alchemist'') is a scientist trained in the study of chemistry. Chemists study the composition of matter and its properties. Chemists carefully describe th ...
Humphry Davy
Sir Humphry Davy, 1st Baronet, (17 December 177829 May 1829) was a British chemist and inventor who invented the Davy lamp and a very early form of arc lamp. He is also remembered for isolating, by using electricity, several elements for ...
, in the first decades of the nineteenth century. Davy observed that of the forty chemical element
A chemical element is a species of atoms that have a given number of protons in their atomic nucleus, nuclei, including the pure Chemical substance, substance consisting only of that species. Unlike chemical compounds, chemical elements canno ...
s known at the time, twenty-six had metal
A metal (from ancient Greek, Greek μέταλλον ''métallon'', "mine, quarry, metal") is a material that, when freshly prepared, polished, or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electrical resistivity and conductivity, e ...
lic properties such as lustre, ductility
Ductility is a mechanical property commonly described as a material's amenability to drawing (e.g. into wire). In materials science, ductility is defined by the degree to which a material can sustain plastic deformation under tensile str ...
and high electrical and thermal conductivity. This indicated that the atoms in John Dalton
John Dalton (; 5 or 6 September 1766 – 27 July 1844) was an English chemist, physicist and meteorologist. He is best known for introducing the atomic theory into chemistry, and for his research into Color blindness, colour blindness, which ...
's atomic theory
Atomic theory is the scientific theory that matter is composed of particles called atoms. Atomic theory traces its origins to an ancient philosophical tradition known as atomism. According to this idea, if one were to take a lump of matter ...
were not indivisible as Dalton claimed, but had inner structure. Davy further claimed that elements that were then believed to be gases, such as nitrogen
Nitrogen is the chemical element with the symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a nonmetal and the lightest member of group 15 of the periodic table, often called the pnictogens. It is a common element in the universe, estimated at se ...
and hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-to ...
could be liquefied under the right conditions and would then behave as metals.
In 1823, Michael Faraday
Michael Faraday (; 22 September 1791 – 25 August 1867) was an English scientist who contributed to the study of electromagnetism and electrochemistry. His main discoveries include the principles underlying electromagnetic inducti ...
, then an assistant in Davy's lab, successfully liquefied chlorine
Chlorine is a chemical element with the symbol Cl and atomic number 17. The second-lightest of the halogens, it appears between fluorine and bromine in the periodic table and its properties are mostly intermediate between them. Chlorine i ...
and went on to liquefy all known gaseous elements, except for nitrogen, hydrogen, and oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements ...
. Shortly after, in 1869, Irish chemist Thomas Andrews studied the phase transition
In chemistry, thermodynamics, and other related fields, a phase transition (or phase change) is the physical process of transition between one state of a medium and another. Commonly the term is used to refer to changes among the basic states ...
from a liquid to a gas and coined the term critical point to describe the condition where a gas and a liquid were indistinguishable as phases, and Dutch physicist Johannes van der Waals supplied the theoretical framework which allowed the prediction of critical behavior based on measurements at much higher temperatures. By 1908, James Dewar
Sir James Dewar (20 September 1842 – 27 March 1923) was a British chemist and physicist. He is best known for his invention of the vacuum flask, which he used in conjunction with research into the liquefaction of gases. He also studied a ...
and Heike Kamerlingh Onnes
Heike Kamerlingh Onnes (21 September 1853 – 21 February 1926) was a Dutch physicist and Nobel laureate. He exploited the Hampson–Linde cycle to investigate how materials behave when cooled to nearly absolute zero and later to liquefy heliu ...
were successfully able to liquefy hydrogen and then newly discovered helium
Helium (from el, ἥλιος, helios, lit=sun) is a chemical element with the symbol He and atomic number 2. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, inert, monatomic gas and the first in the noble gas group in the periodic ta ...
, respectively.
Paul Drude
Paul Karl Ludwig Drude (; 12 July 1863 – 5 July 1906) was a German physicist specializing in optics. He wrote a fundamental textbook integrating optics with Maxwell's theories of electromagnetism.
Education
Born into an ethnic German family, D ...
in 1900 proposed the first theoretical model for a classical electron
The electron ( or ) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary electric charge. Electrons belong to the first generation of the lepton particle family,
and are generally thought to be elementary particles because they have n ...
moving through a metallic solid. Drude's model described properties of metals in terms of a gas of free electrons, and was the first microscopic model to explain empirical observations such as the Wiedemann–Franz law. However, despite the success of Drude's free electron model, it had one notable problem: it was unable to correctly explain the electronic contribution to the specific heat
In thermodynamics, the specific heat capacity (symbol ) of a substance is the heat capacity of a sample of the substance divided by the mass of the sample, also sometimes referred to as massic heat capacity. Informally, it is the amount of heat t ...
and magnetic properties of metals, and the temperature dependence of resistivity at low temperatures.
In 1911, three years after helium was first liquefied, Onnes working at University of Leiden discovered superconductivity
Superconductivity is a set of physical properties observed in certain materials where electrical resistance vanishes and magnetic flux fields are expelled from the material. Any material exhibiting these properties is a superconductor. Unlike ...
in mercury, when he observed the electrical resistivity of mercury to vanish at temperatures below a certain value. The phenomenon completely surprised the best theoretical physicists of the time, and it remained unexplained for several decades. Albert Einstein
Albert Einstein ( ; ; 14 March 1879 – 18 April 1955) was a German-born theoretical physicist, widely acknowledged to be one of the greatest and most influential physicists of all time. Einstein is best known for developing the theor ...
, in 1922, said regarding contemporary theories of superconductivity that "with our far-reaching ignorance of the quantum mechanics of composite systems we are very far from being able to compose a theory out of these vague ideas."
Advent of quantum mechanics
Drude's classical model was augmented byWolfgang Pauli
Wolfgang Ernst Pauli (; ; 25 April 1900 – 15 December 1958) was an Austrian theoretical physicist and one of the pioneers of quantum physics. In 1945, after having been nominated by Albert Einstein, Pauli received the Nobel Prize in Physics ...
, Arnold Sommerfeld
Arnold Johannes Wilhelm Sommerfeld, (; 5 December 1868 – 26 April 1951) was a German theoretical physicist who pioneered developments in atomic and quantum physics, and also educated and mentored many students for the new era of theoretic ...
, Felix Bloch and other physicists. Pauli realized that the free electrons in metal must obey the Fermi–Dirac statistics
Fermi–Dirac statistics (F–D statistics) is a type of quantum statistics that applies to the physics of a system consisting of many non-interacting, identical particles that obey the Pauli exclusion principle. A result is the Fermi–Dirac d ...
. Using this idea, he developed the theory of paramagnetism
Paramagnetism is a form of magnetism whereby some materials are weakly attracted by an externally applied magnetic field, and form internal, induced magnetic fields in the direction of the applied magnetic field. In contrast with this behavior ...
in 1926. Shortly after, Sommerfeld incorporated the Fermi–Dirac statistics
Fermi–Dirac statistics (F–D statistics) is a type of quantum statistics that applies to the physics of a system consisting of many non-interacting, identical particles that obey the Pauli exclusion principle. A result is the Fermi–Dirac d ...
into the free electron model and made it better to explain the heat capacity. Two years later, Bloch used quantum mechanics
Quantum mechanics is a fundamental theory in physics that provides a description of the physical properties of nature at the scale of atoms and subatomic particles. It is the foundation of all quantum physics including quantum chemistry, ...
to describe the motion of an electron in a periodic lattice. The mathematics of crystal structures developed by Auguste Bravais, Yevgraf Fyodorov
Evgraf Stepanovich Fedorov (russian: Евгра́ф Степа́нович Фёдоров, – 21 May 1919) was a Russian mathematician, crystallographer and mineralogist.
Fedorov was born in the Russian city of Orenburg. His father was a topo ...
and others was used to classify crystals by their symmetry group
In group theory, the symmetry group of a geometric object is the group of all transformations under which the object is invariant, endowed with the group operation of composition. Such a transformation is an invertible mapping of the amb ...
, and tables of crystal structures were the basis for the series ''International Tables of Crystallography'', first published in 1935. Band structure calculations was first used in 1930 to predict the properties of new materials, and in 1947 John Bardeen
John Bardeen (; May 23, 1908 – January 30, 1991) was an American physicist and engineer. He is the only person to be awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics twice: first in 1956 with William Shockley and Walter Brattain for the invention of the tra ...
, Walter Brattain and William Shockley
William Bradford Shockley Jr. (February 13, 1910 – August 12, 1989) was an American physicist and inventor. He was the manager of a research group at Bell Labs that included John Bardeen and Walter Brattain. The three scientists were jointl ...
developed the first semiconductor
A semiconductor is a material which has an electrical conductivity value falling between that of a conductor, such as copper, and an insulator, such as glass. Its resistivity falls as its temperature rises; metals behave in the opposite way ...
-based transistor
upright=1.4, gate (G), body (B), source (S) and drain (D) terminals. The gate is separated from the body by an insulating layer (pink).
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch ...
, heralding a revolution in electronics.
 In 1879,
In 1879, Edwin Herbert Hall
Edwin Herbert Hall (November 7, 1855 – November 20, 1938) was an American physicist, who discovered the eponymous Hall effect. Hall conducted thermoelectric research and also wrote numerous physics textbooks and laboratory manuals.
Biograp ...
working at the Johns Hopkins University
Johns Hopkins University (Johns Hopkins, Hopkins, or JHU) is a private research university in Baltimore, Maryland. Founded in 1876, Johns Hopkins is the oldest research university in the United States and in the western hemisphere. It consi ...
discovered a voltage developed across conductors transverse to an electric current in the conductor and magnetic field perpendicular to the current. This phenomenon arising due to the nature of charge carriers in the conductor came to be termed the Hall effect, but it was not properly explained at the time, since the electron was not experimentally discovered until 18 years later. After the advent of quantum mechanics, Lev Landau in 1930 developed the theory of Landau quantization and laid the foundation for the theoretical explanation for the quantum Hall effect discovered half a century later.
Magnetism as a property of matter has been known in China since 4000 BC. However, the first modern studies of magnetism only started with the development of electrodynamics by Faraday, Maxwell
Maxwell may refer to:
People
* Maxwell (surname), including a list of people and fictional characters with the name
** James Clerk Maxwell, mathematician and physicist
* Justice Maxwell (disambiguation)
* Maxwell baronets, in the Baronetage of ...
and others in the nineteenth century, which included classifying materials as ferromagnetic
Ferromagnetism is a property of certain materials (such as iron) which results in a large observed magnetic permeability, and in many cases a large magnetic coercivity allowing the material to form a permanent magnet. Ferromagnetic materials ...
, paramagnetic and diamagnetic based on their response to magnetization. Pierre Curie
Pierre Curie ( , ; 15 May 1859 – 19 April 1906) was a French physicist, a pioneer in crystallography, magnetism, piezoelectricity, and radioactivity. In 1903, he received the Nobel Prize in Physics with his wife, Marie Curie, and Henri Becq ...
studied the dependence of magnetization on temperature and discovered the Curie point phase transition in ferromagnetic materials. In 1906, Pierre Weiss
Pierre-Ernest Weiss (25 March 1865, Mulhouse – 24 October 1940, Lyon) was a French physicist who specialized in magnetism. He developed the domain theory of ferromagnetism in 1907. Weiss domains and the Weiss magneton are named after him ...
introduced the concept of magnetic domains to explain the main properties of ferromagnets. The first attempt at a microscopic description of magnetism was by Wilhelm Lenz
Wilhelm Lenz (February 8, 1888 in Frankfurt am Main – April 30, 1957 in Hamburg) was a German physicist, most notable for his invention of the Ising model and for his application of the Laplace–Runge–Lenz vector to the old quantum mechani ...
and Ernst Ising through the Ising model that described magnetic materials as consisting of a periodic lattice of spins
The spins (as in having "the spins")Diane Marie Leiva. ''The Florida State University College of Education''Women's Voices on College Drinking: The First-Year College Experience"/ref> is an adverse reaction of intoxication that causes a state of v ...
that collectively acquired magnetization. The Ising model was solved exactly to show that spontaneous magnetization
Spontaneous magnetization is the appearance of an ordered spin state ( magnetization) at zero applied magnetic field in a ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic material below a critical point called the Curie temperature or .
Overview
Heated to temper ...
cannot occur in one dimension but is possible in higher-dimensional lattices. Further research such as by Bloch on spin waves and Néel on antiferromagnetism led to developing new magnetic materials with applications to magnetic storage devices.
Modern many-body physics
 The Sommerfeld model and spin models for ferromagnetism illustrated the successful application of quantum mechanics to condensed matter problems in the 1930s. However, there still were several unsolved problems, most notably the description of
The Sommerfeld model and spin models for ferromagnetism illustrated the successful application of quantum mechanics to condensed matter problems in the 1930s. However, there still were several unsolved problems, most notably the description of superconductivity
Superconductivity is a set of physical properties observed in certain materials where electrical resistance vanishes and magnetic flux fields are expelled from the material. Any material exhibiting these properties is a superconductor. Unlike ...
and the Kondo effect
In physics, the Kondo effect describes the scattering of conduction electrons in a metal due to magnetic impurities, resulting in a characteristic change i.e. a minimum in electrical resistivity with temperature.
The cause of the effect was fi ...
. After World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, several ideas from quantum field theory were applied to condensed matter problems. These included recognition of collective excitation
In physics, quasiparticles and collective excitations are closely related emergent phenomena arising when a microscopically complicated system such as a solid behaves as if it contained different weakly interacting particles in vacuum.
For exa ...
modes of solids and the important notion of a quasiparticle. Russian physicist Lev Landau used the idea for the Fermi liquid theory wherein low energy properties of interacting fermion systems were given in terms of what are now termed Landau-quasiparticles. Landau also developed a mean-field theory for continuous phase transitions, which described ordered phases as spontaneous breakdown of symmetry. The theory also introduced the notion of an order parameter to distinguish between ordered phases. Eventually in 1956, John Bardeen
John Bardeen (; May 23, 1908 – January 30, 1991) was an American physicist and engineer. He is the only person to be awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics twice: first in 1956 with William Shockley and Walter Brattain for the invention of the tra ...
, Leon Cooper and John Schrieffer developed the so-called BCS theory of superconductivity, based on the discovery that arbitrarily small attraction between two electrons of opposite spin mediated by phonon
In physics, a phonon is a collective excitation in a periodic, elastic arrangement of atoms or molecules in condensed matter, specifically in solids and some liquids. A type of quasiparticle, a phonon is an excited state in the quantum mechani ...
s in the lattice can give rise to a bound state called a Cooper pair.
 The study of phase transitions and the critical behavior of observables, termed critical phenomena, was a major field of interest in the 1960s. Leo Kadanoff, Benjamin Widom and Michael Fisher developed the ideas of
The study of phase transitions and the critical behavior of observables, termed critical phenomena, was a major field of interest in the 1960s. Leo Kadanoff, Benjamin Widom and Michael Fisher developed the ideas of critical exponent
Critical or Critically may refer to:
*Critical, or critical but stable, medical states
**Critical, or intensive care medicine
* Critical juncture, a discontinuous change studied in the social sciences.
* Critical Software, a company specializing ...
s and widom scaling. These ideas were unified by Kenneth G. Wilson in 1972, under the formalism of the renormalization group
In theoretical physics, the term renormalization group (RG) refers to a formal apparatus that allows systematic investigation of the changes of a physical system as viewed at different scales. In particle physics, it reflects the changes in t ...
in the context of quantum field theory.
The quantum Hall effect was discovered by Klaus von Klitzing, Dorda and Pepper in 1980 when they observed the Hall conductance to be integer multiples of a fundamental constant .(see figure) The effect was observed to be independent of parameters such as system size and impurities. In 1981, theorist Robert Laughlin proposed a theory explaining the unanticipated precision of the integral plateau. It also implied that the Hall conductance is proportional to a topological invariant, called Chern number, whose relevance for the band structure of solids was formulated by David J. Thouless
David James Thouless (; 21 September 1934 – 6 April 2019) was a British condensed-matter physicist. He was the winner of the 1990 Wolf Prize and a laureate of the 2016 Nobel Prize for physics along with F. Duncan M. Haldane and J. Michael ...
and collaborators. Shortly after, in 1982, Horst Störmer
Horst may refer to:
Science
* Horst (geology), a raised fault block bounded by normal faults or graben
People
* Horst (given name)
* Horst (surname)
* ter Horst, Dutch surname
* van der Horst, Dutch surname
Places Settlements Germany
* Horst ...
and Daniel Tsui
Daniel Chee Tsui (, born February 28, 1939) is a Chinese-born American physicist, Nobel laureate, and the Arthur Legrand Doty Professor of Electrical Engineering, Emeritus, at Princeton University. Tsui's areas of research include electrical pro ...
observed the fractional quantum Hall effect
The fractional quantum Hall effect (FQHE) is a physical phenomenon in which the Hall conductance of 2-dimensional (2D) electrons shows precisely quantized plateaus at fractional values of e^2/h. It is a property of a collective state in which elec ...
where the conductance was now a rational multiple of the constant . Laughlin, in 1983, realized that this was a consequence of quasiparticle interaction in the Hall states and formulated a variational method solution, named the Laughlin wavefunction In condensed matter physics, the Laughlin wavefunction pp. 210-213 is an ansatz, proposed by Robert B. Laughlin, Robert Laughlin for the ground state of a two-dimensional electron gas placed in a uniform background magnetic field in the presence of ...
. The study of topological properties of the fractional Hall effect remains an active field of research. Decades later, the aforementioned topological band theory advanced by David J. Thouless
David James Thouless (; 21 September 1934 – 6 April 2019) was a British condensed-matter physicist. He was the winner of the 1990 Wolf Prize and a laureate of the 2016 Nobel Prize for physics along with F. Duncan M. Haldane and J. Michael ...
and collaborators was further expanded leading to the discovery of topological insulators.
In 1986, Karl Müller and Johannes Bednorz discovered the first high temperature superconductor
High-temperature superconductors (abbreviated high-c or HTS) are defined as materials that behave as superconductors at temperatures above , the boiling point of liquid nitrogen. The adjective "high temperature" is only in respect to previo ...
, a material which was superconducting at temperatures as high as 50 kelvin
The kelvin, symbol K, is the primary unit of temperature in the International System of Units (SI), used alongside its prefixed forms and the degree Celsius. It is named after the Belfast-born and University of Glasgow-based engineer and ...
s. It was realized that the high temperature superconductors are examples of strongly correlated materials where the electron–electron interactions play an important role. A satisfactory theoretical description of high-temperature superconductors is still not known and the field of strongly correlated material
Strongly correlated materials are a wide class of compounds that include insulators and electronic materials, and show unusual (often technologically useful) electronic and magnetic properties, such as metal-insulator transitions, heavy fermio ...
s continues to be an active research topic.
In 2009, David Field and researchers at Aarhus University
Aarhus University ( da, Aarhus Universitet, abbreviated AU) is a public research university with its main campus located in Aarhus, Denmark. It is the second largest and second oldest university in Denmark. The university is part of the Coimbra Gr ...
discovered spontaneous electric fields when creating prosaic films of various gases. This has more recently expanded to form the research area of spontelectrics
Spontelectrics is a form of solid state thin films with some peculiar physical properties.
Properties
When laid down as thin films tens to hundreds of molecular layers thick, a range of materials spontaneously generate large electric fields ...
.
In 2012, several groups released preprints which suggest that samarium hexaboride has the properties of a topological insulator in accord with the earlier theoretical predictions. Since samarium hexaboride is an established Kondo insulator, i.e. a strongly correlated electron material, it is expected that the existence of a topological Dirac surface state in this material would lead to a topological insulator with strong electronic correlations.
Theoretical
Theoretical condensed matter physics involves the use of theoretical models to understand properties of states of matter. These include models to study the electronic properties of solids, such as theDrude model
The Drude model of electrical conduction was proposed in 1900 by Paul Drude to explain the transport properties of electrons in materials (especially metals). Basically, Ohm's law was well established and stated that the current ''J'' and voltag ...
, the band structure
In solid-state physics, the electronic band structure (or simply band structure) of a solid describes the range of energy levels that electrons may have within it, as well as the ranges of energy that they may not have (called ''band gaps'' or ...
and the density functional theory. Theoretical models have also been developed to study the physics of phase transition
In chemistry, thermodynamics, and other related fields, a phase transition (or phase change) is the physical process of transition between one state of a medium and another. Commonly the term is used to refer to changes among the basic states ...
s, such as the Ginzburg–Landau theory, critical exponent
Critical or Critically may refer to:
*Critical, or critical but stable, medical states
**Critical, or intensive care medicine
* Critical juncture, a discontinuous change studied in the social sciences.
* Critical Software, a company specializing ...
s and the use of mathematical methods of quantum field theory
In theoretical physics, quantum field theory (QFT) is a theoretical framework that combines classical field theory, special relativity, and quantum mechanics. QFT is used in particle physics to construct physical models of subatomic particles and ...
and the renormalization group
In theoretical physics, the term renormalization group (RG) refers to a formal apparatus that allows systematic investigation of the changes of a physical system as viewed at different scales. In particle physics, it reflects the changes in t ...
. Modern theoretical studies involve the use of numerical computation of electronic structure and mathematical tools to understand phenomena such as high-temperature superconductivity, topological phase
In physics, topological order is a kind of order in the zero-temperature phase of matter (also known as quantum matter). Macroscopically, topological order is defined and described by robust ground state degeneracy and quantized non-Abelian ge ...
s, and gauge symmetries.
Emergence
Theoretical understanding of condensed matter physics is closely related to the notion ofemergence
In philosophy, systems theory, science, and art, emergence occurs when an entity is observed to have properties its parts do not have on their own, properties or behaviors that emerge only when the parts interact in a wider whole.
Emergenc ...
, wherein complex assemblies of particles behave in ways dramatically different from their individual constituents. For example, a range of phenomena related to high temperature superconductivity are understood poorly, although the microscopic physics of individual electrons and lattices is well known. Similarly, models of condensed matter systems have been studied where collective excitation
In physics, quasiparticles and collective excitations are closely related emergent phenomena arising when a microscopically complicated system such as a solid behaves as if it contained different weakly interacting particles in vacuum.
For exa ...
s behave like photon
A photon () is an elementary particle that is a quantum of the electromagnetic field, including electromagnetic radiation such as light and radio waves, and the force carrier for the electromagnetic force. Photons are massless, so they alwa ...
s and electron
The electron ( or ) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary electric charge. Electrons belong to the first generation of the lepton particle family,
and are generally thought to be elementary particles because they have n ...
s, thereby describing electromagnetism
In physics, electromagnetism is an interaction that occurs between particles with electric charge. It is the second-strongest of the four fundamental interactions, after the strong force, and it is the dominant force in the interactions o ...
as an emergent phenomenon. Emergent properties can also occur at the interface between materials: one example is the lanthanum aluminate-strontium titanate interface
The interface between lanthanum aluminate (LaAlO3) and strontium titanate (SrTiO3) is a notable materials interface because it exhibits properties not found in its constituent materials. Individually, LaAlO3 and SrTiO3 are non-magnetic insulators, ...
, where two band-insulators are joined to create conductivity and superconductivity
Superconductivity is a set of physical properties observed in certain materials where electrical resistance vanishes and magnetic flux fields are expelled from the material. Any material exhibiting these properties is a superconductor. Unlike ...
.
Electronic theory of solids
The metallic state has historically been an important building block for studying properties of solids. The first theoretical description of metals was given byPaul Drude
Paul Karl Ludwig Drude (; 12 July 1863 – 5 July 1906) was a German physicist specializing in optics. He wrote a fundamental textbook integrating optics with Maxwell's theories of electromagnetism.
Education
Born into an ethnic German family, D ...
in 1900 with the Drude model
The Drude model of electrical conduction was proposed in 1900 by Paul Drude to explain the transport properties of electrons in materials (especially metals). Basically, Ohm's law was well established and stated that the current ''J'' and voltag ...
, which explained electrical and thermal properties by describing a metal as an ideal gas of then-newly discovered electron
The electron ( or ) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary electric charge. Electrons belong to the first generation of the lepton particle family,
and are generally thought to be elementary particles because they have n ...
s. He was able to derive the empirical Wiedemann-Franz law and get results in close agreement with the experiments. This classical model was then improved by Arnold Sommerfeld
Arnold Johannes Wilhelm Sommerfeld, (; 5 December 1868 – 26 April 1951) was a German theoretical physicist who pioneered developments in atomic and quantum physics, and also educated and mentored many students for the new era of theoretic ...
who incorporated the Fermi–Dirac statistics
Fermi–Dirac statistics (F–D statistics) is a type of quantum statistics that applies to the physics of a system consisting of many non-interacting, identical particles that obey the Pauli exclusion principle. A result is the Fermi–Dirac d ...
of electrons and was able to explain the anomalous behavior of the specific heat
In thermodynamics, the specific heat capacity (symbol ) of a substance is the heat capacity of a sample of the substance divided by the mass of the sample, also sometimes referred to as massic heat capacity. Informally, it is the amount of heat t ...
of metals in the Wiedemann–Franz law. In 1912, The structure of crystalline solids was studied by Max von Laue
Max Theodor Felix von Laue (; 9 October 1879 – 24 April 1960) was a German physicist who received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1914 for his discovery of the diffraction of X-rays by crystals.
In addition to his scientific endeavors with con ...
and Paul Knipping, when they observed the X-ray diffraction
X-ray crystallography is the experimental science determining the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline structure causes a beam of incident X-rays to diffract into many specific directions. By measuring the angles ...
pattern of crystals, and concluded that crystals get their structure from periodic lattices of atoms. In 1928, Swiss physicist Felix Bloch provided a wave function solution to the Schrödinger equation
The Schrödinger equation is a linear partial differential equation that governs the wave function of a quantum-mechanical system. It is a key result in quantum mechanics, and its discovery was a significant landmark in the development of th ...
with a periodic potential, known as Bloch's theorem.
Calculating electronic properties of metals by solving the many-body wavefunction is often computationally hard, and hence, approximation methods are needed to obtain meaningful predictions. The Thomas–Fermi theory, developed in the 1920s, was used to estimate system energy and electronic density by treating the local electron density as a variational parameter. Later in the 1930s, Douglas Hartree
Douglas Rayner Hartree (27 March 1897 – 12 February 1958) was an English mathematician and physicist most famous for the development of numerical analysis and its application to the Hartree–Fock equations of atomic physics and the c ...
, Vladimir Fock and John Slater John Slater may refer to:
Business and government
*John Slater (industrialist) (1776–1843), (American) father of John Fox Slater, brother and partner of Samuel Slater
*John Fox Slater (1815–1884), American philanthropist, son of John Slater ( ...
developed the so-called Hartree–Fock wavefunction as an improvement over the Thomas–Fermi model. The Hartree–Fock method accounted for exchange statistics of single particle electron wavefunctions. In general, it is very difficult to solve the Hartree–Fock equation. Only the free electron gas case can be solved exactly. Finally in 1964–65, Walter Kohn, Pierre Hohenberg
Pierre C. Hohenberg (3 October 1934 – 15 December 2017) was a French-American theoretical physicist, who worked primarily on statistical mechanics. Hohenberg studied at Harvard, where he earned his bachelor's degree in 1956 and a master's degree ...
and Lu Jeu Sham
Lu Jeu Sham (Chinese: 沈呂九) (born April 28, 1938) is an American physicist. He is best known for his work with Walter Kohn on the Kohn–Sham equations.
Biography
Lu Jeu Sham's family was from Fuzhou, Fujian, but he was born in British Hong ...
proposed the density functional theory (DFT) which gave realistic descriptions for bulk and surface properties of metals. The density functional theory has been widely used since the 1970s for band structure calculations of variety of solids.
Symmetry breaking
Some states of matter exhibit ''symmetry breaking'', where the relevant laws of physics possess some form ofsymmetry
Symmetry (from grc, συμμετρία "agreement in dimensions, due proportion, arrangement") in everyday language refers to a sense of harmonious and beautiful proportion and balance. In mathematics, "symmetry" has a more precise definiti ...
that is broken. A common example is crystalline solid
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents (such as atoms, molecules, or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. In addition, macros ...
s, which break continuous translational symmetry
In geometry, to translate a geometric figure is to move it from one place to another without rotating it. A translation "slides" a thing by .
In physics and mathematics, continuous translational symmetry is the invariance of a system of equati ...
. Other examples include magnetized ferromagnets, which break rotational symmetry
Rotational symmetry, also known as radial symmetry in geometry, is the property a shape has when it looks the same after some rotation by a partial turn. An object's degree of rotational symmetry is the number of distinct orientations in which ...
, and more exotic states such as the ground state of a BCS superconductor, that breaks U(1) phase rotational symmetry.
Goldstone's theorem
In particle and condensed matter physics, Goldstone bosons or Nambu–Goldstone bosons (NGBs) are bosons that appear necessarily in models exhibiting spontaneous breakdown of continuous symmetries. They were discovered by Yoichiro Nambu in part ...
in quantum field theory
In theoretical physics, quantum field theory (QFT) is a theoretical framework that combines classical field theory, special relativity, and quantum mechanics. QFT is used in particle physics to construct physical models of subatomic particles and ...
states that in a system with broken continuous symmetry, there may exist excitations with arbitrarily low energy, called the Goldstone bosons. For example, in crystalline solids, these correspond to phonon
In physics, a phonon is a collective excitation in a periodic, elastic arrangement of atoms or molecules in condensed matter, specifically in solids and some liquids. A type of quasiparticle, a phonon is an excited state in the quantum mechani ...
s, which are quantized versions of lattice vibrations.
Phase transition
Phase transition refers to the change of phase of a system, which is brought about by change in an external parameter such astemperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that expresses quantitatively the perceptions of hotness and coldness. Temperature is measured with a thermometer.
Thermometers are calibrated in various temperature scales that historically have relied o ...
. Classical phase transition occurs at finite temperature when the order of the system was destroyed. For example, when ice melts and becomes water, the ordered crystal structure is destroyed.
In quantum phase transition
In physics, a quantum phase transition (QPT) is a phase transition between different quantum phases ( phases of matter at zero temperature). Contrary to classical phase transitions, quantum phase transitions can only be accessed by varying a phy ...
s, the temperature is set to absolute zero
Absolute zero is the lowest limit of the thermodynamic temperature scale, a state at which the enthalpy and entropy of a cooled ideal gas reach their minimum value, taken as zero kelvin. The fundamental particles of nature have minimum vibra ...
, and the non-thermal control parameter, such as pressure or magnetic field, causes the phase transitions when order is destroyed by quantum fluctuations originating from the Heisenberg uncertainty principle
In quantum mechanics, the uncertainty principle (also known as Heisenberg's uncertainty principle) is any of a variety of mathematical inequalities asserting a fundamental limit to the accuracy with which the values for certain pairs of physic ...
. Here, the different quantum phases of the system refer to distinct ground state
The ground state of a quantum-mechanical system is its stationary state of lowest energy; the energy of the ground state is known as the zero-point energy of the system. An excited state is any state with energy greater than the ground state. ...
s of the Hamiltonian matrix. Understanding the behavior of quantum phase transition is important in the difficult tasks of explaining the properties of rare-earth magnetic insulators, high-temperature superconductors, and other substances.
Two classes of phase transitions occur: ''first-order transitions'' and ''second-order'' or ''continuous transitions''. For the latter, the two phases involved do not co-exist at the transition temperature, also called the critical point. Near the critical point, systems undergo critical behavior, wherein several of their properties such as correlation length, specific heat
In thermodynamics, the specific heat capacity (symbol ) of a substance is the heat capacity of a sample of the substance divided by the mass of the sample, also sometimes referred to as massic heat capacity. Informally, it is the amount of heat t ...
, and magnetic susceptibility
In electromagnetism, the magnetic susceptibility (Latin: , "receptive"; denoted ) is a measure of how much a material will become magnetized in an applied magnetic field. It is the ratio of magnetization (magnetic moment per unit volume) to the ap ...
diverge exponentially. These critical phenomena present serious challenges to physicists because normal macroscopic laws are no longer valid in the region, and novel ideas and methods must be invented to find the new laws that can describe the system.
The simplest theory that can describe continuous phase transitions is the Ginzburg–Landau theory, which works in the so-called mean-field approximation. However, it can only roughly explain continuous phase transition for ferroelectrics and type I superconductors which involves long range microscopic interactions. For other types of systems that involves short range interactions near the critical point, a better theory is needed.
Near the critical point, the fluctuations happen over broad range of size scales while the feature of the whole system is scale invariant. Renormalization group
In theoretical physics, the term renormalization group (RG) refers to a formal apparatus that allows systematic investigation of the changes of a physical system as viewed at different scales. In particle physics, it reflects the changes in t ...
methods successively average out the shortest wavelength fluctuations in stages while retaining their effects into the next stage. Thus, the changes of a physical system as viewed at different size scales can be investigated systematically. The methods, together with powerful computer simulation, contribute greatly to the explanation of the critical phenomena associated with continuous phase transition.
Experimental
Experimental condensed matter physics involves the use of experimental probes to try to discover new properties of materials. Such probes include effects of electric andmagnetic field
A magnetic field is a vector field that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents, and magnetic materials. A moving charge in a magnetic field experiences a force perpendicular to its own velocity and to ...
s, measuring response functions, transport properties and thermometry. Commonly used experimental methods include spectroscopy
Spectroscopy is the field of study that measures and interprets the electromagnetic spectra that result from the interaction between electromagnetic radiation and matter as a function of the wavelength or frequency of the radiation. Matter ...
, with probes such as X-rays
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30&nbs ...
, infrared light and inelastic neutron scattering; study of thermal response, such as specific heat
In thermodynamics, the specific heat capacity (symbol ) of a substance is the heat capacity of a sample of the substance divided by the mass of the sample, also sometimes referred to as massic heat capacity. Informally, it is the amount of heat t ...
and measuring transport via thermal and heat conduction
Conductor or conduction may refer to:
Music
* Conductor (music), a person who leads a musical ensemble, such as an orchestra.
* ''Conductor'' (album), an album by indie rock band The Comas
* Conduction, a type of structured free improvisation ...
.

Scattering
Several condensed matter experiments involve scattering of an experimental probe, such asX-ray
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30&nb ...
, optical photon
A photon () is an elementary particle that is a quantum of the electromagnetic field, including electromagnetic radiation such as light and radio waves, and the force carrier for the electromagnetic force. Photons are massless, so they alwa ...
s, neutron
The neutron is a subatomic particle, symbol or , which has a neutral (not positive or negative) charge, and a mass slightly greater than that of a proton. Protons and neutrons constitute the atomic nucleus, nuclei of atoms. Since protons and ...
s, etc., on constituents of a material. The choice of scattering probe depends on the observation energy scale of interest. Visible light
Light or visible light is electromagnetic radiation that can be perceived by the human eye. Visible light is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400–700 nanometres (nm), corresponding to frequencies of 750–420 t ...
has energy on the scale of 1 electron volt (eV) and is used as a scattering probe to measure variations in material properties such as dielectric constant
The relative permittivity (in older texts, dielectric constant) is the permittivity of a material expressed as a ratio with the electric permittivity of a vacuum. A dielectric is an insulating material, and the dielectric constant of an insula ...
and refractive index
In optics, the refractive index (or refraction index) of an optical medium is a dimensionless number that gives the indication of the light bending ability of that medium.
The refractive index determines how much the path of light is bent, ...
. X-rays have energies of the order of 10 keV and hence are able to probe atomic length scales, and are used to measure variations in electron charge density.
Neutron
The neutron is a subatomic particle, symbol or , which has a neutral (not positive or negative) charge, and a mass slightly greater than that of a proton. Protons and neutrons constitute the atomic nucleus, nuclei of atoms. Since protons and ...
s can also probe atomic length scales and are used to study scattering off nuclei and electron spins
The spins (as in having "the spins")Diane Marie Leiva. ''The Florida State University College of Education''Women's Voices on College Drinking: The First-Year College Experience"/ref> is an adverse reaction of intoxication that causes a state of v ...
and magnetization (as neutrons have spin but no charge). Coulomb and Mott scattering measurements can be made by using electron beams as scattering probes. Similarly, positron
The positron or antielectron is the antiparticle or the antimatter counterpart of the electron. It has an electric charge of +1 '' e'', a spin of 1/2 (the same as the electron), and the same mass as an electron. When a positron collide ...
annihilation can be used as an indirect measurement of local electron density. Laser spectroscopy is an excellent tool for studying the microscopic properties of a medium, for example, to study forbidden transitions in media with nonlinear optical spectroscopy.
External magnetic fields
In experimental condensed matter physics, externalmagnetic field
A magnetic field is a vector field that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents, and magnetic materials. A moving charge in a magnetic field experiences a force perpendicular to its own velocity and to ...
s act as thermodynamic variables that control the state, phase transitions and properties of material systems. Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) is a method by which external magnetic fields are used to find resonance modes of individual electrons, thus giving information about the atomic, molecular, and bond structure of their neighborhood. NMR experiments can be made in magnetic fields with strengths up to 60 tesla. Higher magnetic fields can improve the quality of NMR measurement data. Quantum oscillations
In condensed matter physics, quantum oscillations describes a series of related experimental techniques used to map the Fermi surface of a metal in the presence of a strong magnetic field. These techniques are based on the principle of Landau quant ...
is another experimental method where high magnetic fields are used to study material properties such as the geometry of the Fermi surface. High magnetic fields will be useful in experimentally testing of the various theoretical predictions such as the quantized magnetoelectric effect, image magnetic monopole, and the half-integer quantum Hall effect.
Nuclear spectroscopy
The local structure, the structure of the nearest neighbour atoms, of condensed matter can be investigated with methods of nuclear spectroscopy, which are very sensitive to small changes. Using specific and radioactive nuclei, the nucleus becomes the probe that interacts with its surrounding electric and magnetic fields ( hyperfine interactions). The methods are suitable to study defects, diffusion, phase change, magnetism. Common methods are e.g. NMR, Mössbauer spectroscopy, or perturbed angular correlation (PAC). Especially PAC is ideal for the study of phase changes at extreme temperature above 2000 °C due to no temperature dependence of the method.Cold atomic gases
 Ultracold atom trapping in optical lattices is an experimental tool commonly used in condensed matter physics, and in atomic, molecular, and optical physics. The method involves using optical lasers to form an interference pattern, which acts as a ''lattice'', in which ions or atoms can be placed at very low temperatures. Cold atoms in optical lattices are used as ''quantum simulators'', that is, they act as controllable systems that can model behavior of more complicated systems, such as frustrated magnets. In particular, they are used to engineer one-, two- and three-dimensional lattices for a
Ultracold atom trapping in optical lattices is an experimental tool commonly used in condensed matter physics, and in atomic, molecular, and optical physics. The method involves using optical lasers to form an interference pattern, which acts as a ''lattice'', in which ions or atoms can be placed at very low temperatures. Cold atoms in optical lattices are used as ''quantum simulators'', that is, they act as controllable systems that can model behavior of more complicated systems, such as frustrated magnets. In particular, they are used to engineer one-, two- and three-dimensional lattices for a Hubbard model
The Hubbard model is an approximate model used to describe the transition between conducting and insulating systems.
It is particularly useful in solid-state physics. The model is named for John Hubbard.
The Hubbard model states that each el ...
with pre-specified parameters, and to study phase transitions for antiferromagnetic and spin liquid ordering.
In 1995, a gas of rubidium
Rubidium is the chemical element with the symbol Rb and atomic number 37. It is a very soft, whitish-grey solid in the alkali metal group, similar to potassium and caesium. Rubidium is the first alkali metal in the group to have a density higher ...
atoms cooled down to a temperature of 170 nK was used to experimentally realize the Bose–Einstein condensate, a novel state of matter originally predicted by S. N. Bose
Satyendra Nath Bose (; 1 January 1894 – 4 February 1974) was a Bengali mathematician and physicist specializing in theoretical physics. He is best known for his work on quantum mechanics in the early 1920s, in developing the foundation for ...
and Albert Einstein
Albert Einstein ( ; ; 14 March 1879 – 18 April 1955) was a German-born theoretical physicist, widely acknowledged to be one of the greatest and most influential physicists of all time. Einstein is best known for developing the theor ...
, wherein a large number of atoms occupy one quantum state
In quantum physics, a quantum state is a mathematical entity that provides a probability distribution for the outcomes of each possible measurement on a system. Knowledge of the quantum state together with the rules for the system's evolution i ...
.
Applications
 Research in condensed matter physics has given rise to several device applications, such as the development of the
Research in condensed matter physics has given rise to several device applications, such as the development of the semiconductor
A semiconductor is a material which has an electrical conductivity value falling between that of a conductor, such as copper, and an insulator, such as glass. Its resistivity falls as its temperature rises; metals behave in the opposite way ...
transistor
upright=1.4, gate (G), body (B), source (S) and drain (D) terminals. The gate is separated from the body by an insulating layer (pink).
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch ...
, laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word "laser" is an acronym for "light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation". The ...
technology, and several phenomena studied in the context of nanotechnology
Nanotechnology, also shortened to nanotech, is the use of matter on an atomic, molecular, and supramolecular scale for industrial purposes. The earliest, widespread description of nanotechnology referred to the particular technological goal ...
. Methods such as scanning-tunneling microscopy can be used to control processes at the nanometer
330px, Different lengths as in respect to the molecular scale.
The nanometre (international spelling as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures; SI symbol: nm) or nanometer (American and British English spelling differences#-re, ...
scale, and have given rise to the study of nanofabrication. Such molecular machines were developed for example by Nobel laurate in chemistry Ben Feringa
Bernard Lucas Feringa (, born 18 May 1951) is a Dutch synthetic organic chemist, specializing in molecular nanotechnology and homogeneous catalysis. He is the Jacobus van 't Hoff Distinguished Professor of Molecular Sciences, at the Strating ...
. He and his team developed multiple molecular machines such as molecular car, molecular windmill and many more.
In quantum computation
Quantum computing is a type of computation whose operations can harness the phenomena of quantum mechanics, such as superposition, interference, and entanglement. Devices that perform quantum computations are known as quantum computers. Though ...
, information is represented by quantum bits, or qubits. The qubits may decohere quickly before useful computation is completed. This serious problem must be solved before quantum computing may be realized. To solve this problem, several promising approaches are proposed in condensed matter physics, including Josephson junction qubits, spintronic qubits using the spin
Spin or spinning most often refers to:
* Spinning (textiles), the creation of yarn or thread by twisting fibers together, traditionally by hand spinning
* Spin, the rotation of an object around a central axis
* Spin (propaganda), an intentionally ...
orientation of magnetic materials, or the topological non-Abelian anyon
In physics, an anyon is a type of quasiparticle that occurs only in two-dimensional systems, with properties much less restricted than the two kinds of standard elementary particles, fermions and bosons. In general, the operation of exchan ...
s from fractional quantum Hall effect
The fractional quantum Hall effect (FQHE) is a physical phenomenon in which the Hall conductance of 2-dimensional (2D) electrons shows precisely quantized plateaus at fractional values of e^2/h. It is a property of a collective state in which elec ...
states.
Condensed matter physics also has important uses for biophysics, for example, the experimental method of magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes of the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio wave ...
, which is widely used in medical diagnosis.
See also
* * * * * * * * * *Notes
References
Further reading
* Anderson, Philip W. (2018-03-09). ''Basic Notions Of Condensed Matter Physics''. CRC Press. . *Girvin, Steven M.; Yang, Kun (2019-02-28). ''Modern Condensed Matter Physics''. Cambridge University Press. . *Coleman, Piers (2015). "Introduction to Many-Body Physics". ''Cambridge Core''. Retrieved 2020-04-18. *P. M. Chaikin and T. C. Lubensky (2000). ''Principles of Condensed Matter Physics'', Cambridge University Press; 1st edition, * * * Alexander Altland and Ben Simons (2006). ''Condensed Matter Field Theory'', Cambridge University Press, . * Michael P. Marder (2010). ''Condensed Matter Physics, second edition'', John Wiley and Sons, . *Lillian Hoddeson, Ernest Braun, Jürgen Teichmann and Spencer Weart, eds. (1992). ''Out of the Crystal Maze: Chapters from the History of Solid State Physics'', Oxford University Press, .External links
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Condensed Matter Physics Materials science