condensed matter on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Condensed matter physics is the field of
 One of the first studies of condensed states of matter was by English
One of the first studies of condensed states of matter was by English
 In 1879, Edwin Herbert Hall working at the
In 1879, Edwin Herbert Hall working at the
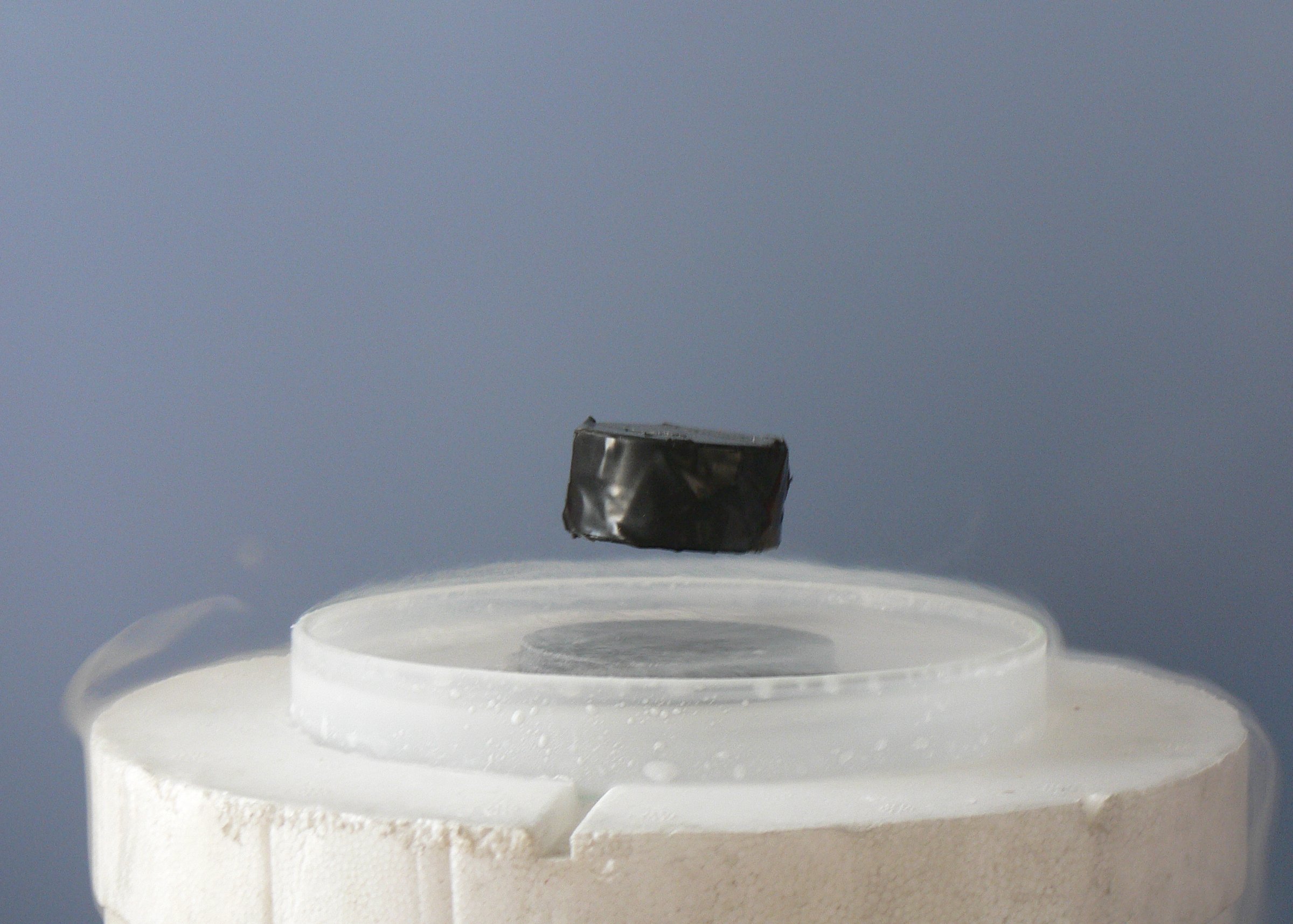 The Sommerfeld model and spin models for ferromagnetism illustrated the successful application of quantum mechanics to condensed matter problems in the 1930s. However, there still were several unsolved problems, most notably the description of superconductivity and the Kondo effect. After
The Sommerfeld model and spin models for ferromagnetism illustrated the successful application of quantum mechanics to condensed matter problems in the 1930s. However, there still were several unsolved problems, most notably the description of superconductivity and the Kondo effect. After  The study of phase transitions and the critical behavior of observables, termed critical phenomena, was a major field of interest in the 1960s. Leo Kadanoff, Benjamin Widom and Michael Fisher developed the ideas of critical exponents and widom scaling. These ideas were unified by Kenneth G. Wilson in 1972, under the formalism of the renormalization group in the context of quantum field theory.
The quantum Hall effect was discovered by Klaus von Klitzing, Dorda and Pepper in 1980 when they observed the Hall conductance to be integer multiples of a fundamental constant .(see figure) The effect was observed to be independent of parameters such as system size and impurities. In 1981, theorist Robert Laughlin proposed a theory explaining the unanticipated precision of the integral plateau. It also implied that the Hall conductance is proportional to a topological invariant, called Chern number, whose relevance for the band structure of solids was formulated by David J. Thouless and collaborators. Shortly after, in 1982, Horst Störmer and Daniel Tsui observed the fractional quantum Hall effect where the conductance was now a rational multiple of the constant . Laughlin, in 1983, realized that this was a consequence of quasiparticle interaction in the Hall states and formulated a variational method solution, named the Laughlin wavefunction. The study of topological properties of the fractional Hall effect remains an active field of research. Decades later, the aforementioned topological band theory advanced by David J. Thouless and collaborators was further expanded leading to the discovery of topological insulators.
In 1986, Karl Müller and Johannes Bednorz discovered the first high temperature superconductor, La2-xBaxCuO4, which is superconducting at temperatures as high as 39
The study of phase transitions and the critical behavior of observables, termed critical phenomena, was a major field of interest in the 1960s. Leo Kadanoff, Benjamin Widom and Michael Fisher developed the ideas of critical exponents and widom scaling. These ideas were unified by Kenneth G. Wilson in 1972, under the formalism of the renormalization group in the context of quantum field theory.
The quantum Hall effect was discovered by Klaus von Klitzing, Dorda and Pepper in 1980 when they observed the Hall conductance to be integer multiples of a fundamental constant .(see figure) The effect was observed to be independent of parameters such as system size and impurities. In 1981, theorist Robert Laughlin proposed a theory explaining the unanticipated precision of the integral plateau. It also implied that the Hall conductance is proportional to a topological invariant, called Chern number, whose relevance for the band structure of solids was formulated by David J. Thouless and collaborators. Shortly after, in 1982, Horst Störmer and Daniel Tsui observed the fractional quantum Hall effect where the conductance was now a rational multiple of the constant . Laughlin, in 1983, realized that this was a consequence of quasiparticle interaction in the Hall states and formulated a variational method solution, named the Laughlin wavefunction. The study of topological properties of the fractional Hall effect remains an active field of research. Decades later, the aforementioned topological band theory advanced by David J. Thouless and collaborators was further expanded leading to the discovery of topological insulators.
In 1986, Karl Müller and Johannes Bednorz discovered the first high temperature superconductor, La2-xBaxCuO4, which is superconducting at temperatures as high as 39

 Ultracold atom trapping in optical lattices is an experimental tool commonly used in condensed matter physics, and in atomic, molecular, and optical physics. The method involves using optical lasers to form an interference pattern, which acts as a ''lattice'', in which ions or atoms can be placed at very low temperatures. Cold atoms in optical lattices are used as ''quantum simulators'', that is, they act as controllable systems that can model behavior of more complicated systems, such as frustrated magnets. In particular, they are used to engineer one-, two- and three-dimensional lattices for a
Ultracold atom trapping in optical lattices is an experimental tool commonly used in condensed matter physics, and in atomic, molecular, and optical physics. The method involves using optical lasers to form an interference pattern, which acts as a ''lattice'', in which ions or atoms can be placed at very low temperatures. Cold atoms in optical lattices are used as ''quantum simulators'', that is, they act as controllable systems that can model behavior of more complicated systems, such as frustrated magnets. In particular, they are used to engineer one-, two- and three-dimensional lattices for a
 Research in condensed matter physics has given rise to several device applications, such as the development of the
Research in condensed matter physics has given rise to several device applications, such as the development of the
physics
Physics is the scientific study of matter, its Elementary particle, fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge whi ...
that deals with the macroscopic and microscopic physical properties of matter
In classical physics and general chemistry, matter is any substance that has mass and takes up space by having volume. All everyday objects that can be touched are ultimately composed of atoms, which are made up of interacting subatomic pa ...
, especially the solid
Solid is a state of matter where molecules are closely packed and can not slide past each other. Solids resist compression, expansion, or external forces that would alter its shape, with the degree to which they are resisted dependent upon the ...
and liquid
Liquid is a state of matter with a definite volume but no fixed shape. Liquids adapt to the shape of their container and are nearly incompressible, maintaining their volume even under pressure. The density of a liquid is usually close to th ...
phases, that arise from electromagnetic
In physics, electromagnetism is an interaction that occurs between particles with electric charge via electromagnetic fields. The electromagnetic force is one of the four fundamental forces of nature. It is the dominant force in the interacti ...
forces between atom
Atoms are the basic particles of the chemical elements. An atom consists of a atomic nucleus, nucleus of protons and generally neutrons, surrounded by an electromagnetically bound swarm of electrons. The chemical elements are distinguished fr ...
s and electrons
The electron (, or in nuclear reactions) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary charge, elementary electric charge. It is a fundamental particle that comprises the ordinary matter that makes up the universe, along with up qua ...
. More generally, the subject deals with condensed phases of matter: systems of many constituents with strong interactions among them. More exotic condensed phases include the superconducting phase exhibited by certain materials at extremely low cryogenic
In physics, cryogenics is the production and behaviour of materials at very low temperatures.
The 13th International Institute of Refrigeration's (IIR) International Congress of Refrigeration (held in Washington, DC in 1971) endorsed a univers ...
temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that quantitatively expresses the attribute of hotness or coldness. Temperature is measurement, measured with a thermometer. It reflects the average kinetic energy of the vibrating and colliding atoms making ...
s, the ferromagnetic and antiferromagnetic phases of spins
The spins (as in having "the spins") is an adverse reaction of Substance intoxication, intoxication that causes a state of vertigo and nausea, causing one to feel as if "spinning out of control", especially when lying down. It is most commonly as ...
on crystal lattice
In crystallography, crystal structure is a description of ordered arrangement of atoms, ions, or molecules in a crystal, crystalline material. Ordered structures occur from intrinsic nature of constituent particles to form symmetric patterns that ...
s of atoms, the Bose–Einstein condensates found in ultracold atomic systems, and liquid crystals. Condensed matter physicists seek to understand the behavior of these phases by experiments to measure various material properties, and by applying the physical law
Scientific laws or laws of science are statements, based on repeated experiments or observations, that describe or predict a range of natural phenomena. The term ''law'' has diverse usage in many cases (approximate, accurate, broad, or narrow) ...
s of quantum mechanics
Quantum mechanics is the fundamental physical Scientific theory, theory that describes the behavior of matter and of light; its unusual characteristics typically occur at and below the scale of atoms. Reprinted, Addison-Wesley, 1989, It is ...
, electromagnetism
In physics, electromagnetism is an interaction that occurs between particles with electric charge via electromagnetic fields. The electromagnetic force is one of the four fundamental forces of nature. It is the dominant force in the interacti ...
, statistical mechanics
In physics, statistical mechanics is a mathematical framework that applies statistical methods and probability theory to large assemblies of microscopic entities. Sometimes called statistical physics or statistical thermodynamics, its applicati ...
, and other physics theories to develop mathematical models and predict the properties of extremely large groups of atoms.
The diversity of systems and phenomena available for study makes condensed matter physics the most active field of contemporary physics: one third of all American physicists self-identify as condensed matter physicists, and the Division of Condensed Matter Physics is the largest division of the American Physical Society
The American Physical Society (APS) is a not-for-profit membership organization of professionals in physics and related disciplines, comprising nearly fifty divisions, sections, and other units. Its mission is the advancement and diffusion of ...
. These include solid state and soft matter
Soft matter or soft condensed matter is a type of matter that can be deformed or structurally altered by thermal or mechanical stress which is of similar magnitude to thermal fluctuations.
The science of soft matter is a subfield of condensed ...
physicists, who study quantum
In physics, a quantum (: quanta) is the minimum amount of any physical entity (physical property) involved in an interaction. The fundamental notion that a property can be "quantized" is referred to as "the hypothesis of quantization". This me ...
and non-quantum physical properties of matter respectively. Both types study a great range of materials, providing many research, funding and employment opportunities. The field overlaps with chemistry
Chemistry is the scientific study of the properties and behavior of matter. It is a physical science within the natural sciences that studies the chemical elements that make up matter and chemical compound, compounds made of atoms, molecules a ...
, materials science
Materials science is an interdisciplinary field of researching and discovering materials. Materials engineering is an engineering field of finding uses for materials in other fields and industries.
The intellectual origins of materials sci ...
, engineering
Engineering is the practice of using natural science, mathematics, and the engineering design process to Problem solving#Engineering, solve problems within technology, increase efficiency and productivity, and improve Systems engineering, s ...
and nanotechnology
Nanotechnology is the manipulation of matter with at least one dimension sized from 1 to 100 nanometers (nm). At this scale, commonly known as the nanoscale, surface area and quantum mechanical effects become important in describing propertie ...
, and relates closely to atomic physics
Atomic physics is the field of physics that studies atoms as an isolated system of electrons and an atomic nucleus. Atomic physics typically refers to the study of atomic structure and the interaction between atoms. It is primarily concerned wit ...
and biophysics
Biophysics is an interdisciplinary science that applies approaches and methods traditionally used in physics to study biological phenomena. Biophysics covers all scales of biological organization, from molecular to organismic and populations ...
. The theoretical physics
Theoretical physics is a branch of physics that employs mathematical models and abstractions of physical objects and systems to rationalize, explain, and predict List of natural phenomena, natural phenomena. This is in contrast to experimental p ...
of condensed matter shares important concepts and methods with that of particle physics
Particle physics or high-energy physics is the study of Elementary particle, fundamental particles and fundamental interaction, forces that constitute matter and radiation. The field also studies combinations of elementary particles up to the s ...
and nuclear physics
Nuclear physics is the field of physics that studies atomic nuclei and their constituents and interactions, in addition to the study of other forms of nuclear matter.
Nuclear physics should not be confused with atomic physics, which studies th ...
.
A variety of topics in physics such as crystallography
Crystallography is the branch of science devoted to the study of molecular and crystalline structure and properties. The word ''crystallography'' is derived from the Ancient Greek word (; "clear ice, rock-crystal"), and (; "to write"). In J ...
, metallurgy
Metallurgy is a domain of materials science and engineering that studies the physical and chemical behavior of metallic elements, their inter-metallic compounds, and their mixtures, which are known as alloys.
Metallurgy encompasses both the ...
, elasticity, magnetism
Magnetism is the class of physical attributes that occur through a magnetic field, which allows objects to attract or repel each other. Because both electric currents and magnetic moments of elementary particles give rise to a magnetic field, ...
, etc., were treated as distinct areas until the 1940s, when they were grouped together as ''solid-state physics
Solid-state physics is the study of rigid matter, or solids, through methods such as solid-state chemistry, quantum mechanics, crystallography, electromagnetism, and metallurgy. It is the largest branch of condensed matter physics. Solid-state phy ...
''. Around the 1960s, the study of physical properties of liquid
Liquid is a state of matter with a definite volume but no fixed shape. Liquids adapt to the shape of their container and are nearly incompressible, maintaining their volume even under pressure. The density of a liquid is usually close to th ...
s was added to this list, forming the basis for the more comprehensive specialty of condensed matter physics. The Bell Telephone Laboratories was one of the first institutes to conduct a research program in condensed matter physics. According to the founding director of the Max Planck Institute for Solid State Research, physics professor Manuel Cardona, it was Albert Einstein
Albert Einstein (14 March 187918 April 1955) was a German-born theoretical physicist who is best known for developing the theory of relativity. Einstein also made important contributions to quantum mechanics. His mass–energy equivalence f ...
who created the modern field of condensed matter physics starting with his seminal 1905 article on the photoelectric effect and photoluminescence which opened the fields of photoelectron spectroscopy and photoluminescence spectroscopy, and later his 1907 article on the specific heat of solids which introduced, for the first time, the effect of lattice vibrations on the thermodynamic properties of crystals, in particular the specific heat. Deputy Director of the Yale Quantum Institute A. Douglas Stone makes a similar priority case for Einstein in his work on the synthetic history of quantum mechanics
Quantum mechanics is the fundamental physical Scientific theory, theory that describes the behavior of matter and of light; its unusual characteristics typically occur at and below the scale of atoms. Reprinted, Addison-Wesley, 1989, It is ...
.
Etymology
According to physicistPhilip Warren Anderson
Philip Warren Anderson (December 13, 1923 – March 29, 2020) was an American theoretical physicist and Nobel laureate. Anderson made contributions to the theories of Anderson localization, localization, antiferromagnetism, symmetry breaking ( ...
, the use of the term "condensed matter" to designate a field of study was coined by him and Volker Heine, when they changed the name of their group at the Cavendish Laboratories, Cambridge
Cambridge ( ) is a List of cities in the United Kingdom, city and non-metropolitan district in the county of Cambridgeshire, England. It is the county town of Cambridgeshire and is located on the River Cam, north of London. As of the 2021 Unit ...
, from ''Solid state theory'' to ''Theory of Condensed Matter'' in 1967, as they felt it better included their interest in liquids, nuclear matter, and so on. Although Anderson and Heine helped popularize the name "condensed matter", it had been used in Europe for some years, most prominently in the Springer-Verlag
Springer Science+Business Media, commonly known as Springer, is a German multinational publishing company of books, e-books and peer-reviewed journals in science, humanities, technical and medical (STM) publishing.
Originally founded in 1842 in ...
journal ''Physics of Condensed Matter'', launched in 1963. The name "condensed matter physics" emphasized the commonality of scientific problems encountered by physicists working on solids, liquids, plasmas, and other complex matter, whereas "solid state physics" was often associated with restricted industrial applications of metals and semiconductors. In the 1960s and 70s, some physicists felt the more comprehensive name better fit the funding environment and Cold War
The Cold War was a period of global Geopolitics, geopolitical rivalry between the United States (US) and the Soviet Union (USSR) and their respective allies, the capitalist Western Bloc and communist Eastern Bloc, which lasted from 1947 unt ...
politics of the time.
References to "condensed" states can be traced to earlier sources. For example, in the introduction to his 1947 book ''Kinetic Theory of Liquids'', Yakov Frenkel proposed that "The kinetic theory of liquids must accordingly be developed as a generalization and extension of the kinetic theory of solid bodies. As a matter of fact, it would be more correct to unify them under the title of 'condensed bodies.
History
Classical physics
 One of the first studies of condensed states of matter was by English
One of the first studies of condensed states of matter was by English chemist
A chemist (from Greek ''chēm(ía)'' alchemy; replacing ''chymist'' from Medieval Latin ''alchemist'') is a graduated scientist trained in the study of chemistry, or an officially enrolled student in the field. Chemists study the composition of ...
Humphry Davy
Sir Humphry Davy, 1st Baronet (17 December 177829 May 1829) was a British chemist and inventor who invented the Davy lamp and a very early form of arc lamp. He is also remembered for isolating, by using electricity, several Chemical element, e ...
, in the first decades of the nineteenth century. Davy observed that of the forty chemical element
A chemical element is a chemical substance whose atoms all have the same number of protons. The number of protons is called the atomic number of that element. For example, oxygen has an atomic number of 8: each oxygen atom has 8 protons in its ...
s known at the time, twenty-six had metal
A metal () is a material that, when polished or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electrical resistivity and conductivity, electricity and thermal conductivity, heat relatively well. These properties are all associated wit ...
lic properties such as lustre, ductility
Ductility refers to the ability of a material to sustain significant plastic Deformation (engineering), deformation before fracture. Plastic deformation is the permanent distortion of a material under applied stress, as opposed to elastic def ...
and high electrical and thermal conductivity. This indicated that the atoms in John Dalton
John Dalton (; 5 or 6 September 1766 – 27 July 1844) was an English chemist, physicist and meteorologist. He introduced the atomic theory into chemistry. He also researched Color blindness, colour blindness; as a result, the umbrella term ...
's atomic theory were not indivisible as Dalton claimed, but had inner structure. Davy further claimed that elements that were then believed to be gases, such as nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a Nonmetal (chemistry), nonmetal and the lightest member of pnictogen, group 15 of the periodic table, often called the Pnictogen, pnictogens. ...
and hydrogen
Hydrogen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol H and atomic number 1. It is the lightest and abundance of the chemical elements, most abundant chemical element in the universe, constituting about 75% of all baryon, normal matter ...
could be liquefied under the right conditions and would then behave as metals.
In 1823, Michael Faraday
Michael Faraday (; 22 September 1791 – 25 August 1867) was an English chemist and physicist who contributed to the study of electrochemistry and electromagnetism. His main discoveries include the principles underlying electromagnetic inducti ...
, then an assistant in Davy's lab, successfully liquefied chlorine
Chlorine is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Cl and atomic number 17. The second-lightest of the halogens, it appears between fluorine and bromine in the periodic table and its properties are mostly intermediate between ...
and went on to liquefy all known gaseous elements, except for nitrogen, hydrogen, and oxygen
Oxygen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group (periodic table), group in the periodic table, a highly reactivity (chemistry), reactive nonmetal (chemistry), non ...
. Shortly after, in 1869, Irish chemist Thomas Andrews studied the phase transition
In physics, chemistry, and other related fields like biology, a phase transition (or phase change) is the physical process of transition between one state of a medium and another. Commonly the term is used to refer to changes among the basic Sta ...
from a liquid to a gas and coined the term critical point to describe the condition where a gas and a liquid were indistinguishable as phases, and Dutch physicist Johannes van der Waals supplied the theoretical framework which allowed the prediction of critical behavior based on measurements at much higher temperatures. By 1908, James Dewar and Heike Kamerlingh Onnes were successfully able to liquefy hydrogen and the then newly discovered helium
Helium (from ) is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol He and atomic number 2. It is a colorless, odorless, non-toxic, inert gas, inert, monatomic gas and the first in the noble gas group in the periodic table. Its boiling point is ...
respectively.
Paul Drude in 1900 proposed the first theoretical model for a classical electron
The electron (, or in nuclear reactions) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary charge, elementary electric charge. It is a fundamental particle that comprises the ordinary matter that makes up the universe, along with up qua ...
moving through a metallic solid. Drude's model described properties of metals in terms of a gas of free electrons, and was the first microscopic model to explain empirical observations such as the Wiedemann–Franz law. However, despite the success of Drude's model, it had one notable problem: it was unable to correctly explain the electronic contribution to the specific heat and magnetic properties of metals, and the temperature dependence of resistivity at low temperatures.
In 1911, three years after helium was first liquefied, Onnes working at University of Leiden discovered superconductivity in mercury, when he observed the electrical resistivity of mercury to vanish at temperatures below a certain value. The phenomenon completely surprised the best theoretical physicists of the time, and it remained unexplained for several decades. Albert Einstein
Albert Einstein (14 March 187918 April 1955) was a German-born theoretical physicist who is best known for developing the theory of relativity. Einstein also made important contributions to quantum mechanics. His mass–energy equivalence f ...
, in 1922, said regarding contemporary theories of superconductivity that "with our far-reaching ignorance of the quantum mechanics of composite systems we are very far from being able to compose a theory out of these vague ideas."
Advent of quantum mechanics
Drude's classical model was augmented by Wolfgang Pauli, Arnold Sommerfeld,Felix Bloch
Felix Bloch (; ; 23 October 1905 – 10 September 1983) was a Swiss-American physicist who shared the 1952 Nobel Prize in Physics with Edward Mills Purcell "for their development of new methods for nuclear magnetic precision measurements and di ...
and other physicists. Pauli realized that the free electrons in metal must obey the Fermi–Dirac statistics. Using this idea, he developed the theory of paramagnetism
Paramagnetism is a form of magnetism whereby some materials are weakly attracted by an externally applied magnetic field, and form internal, induced magnetic fields in the direction of the applied magnetic field. In contrast with this behavior, ...
in 1926. Shortly after, Sommerfeld incorporated the Fermi–Dirac statistics into the free electron model and made it better to explain the heat capacity. Two years later, Bloch used quantum mechanics
Quantum mechanics is the fundamental physical Scientific theory, theory that describes the behavior of matter and of light; its unusual characteristics typically occur at and below the scale of atoms. Reprinted, Addison-Wesley, 1989, It is ...
to describe the motion of an electron in a periodic lattice.
The mathematics of crystal structures developed by Auguste Bravais, Yevgraf Fyodorov and others was used to classify crystals by their symmetry group, and tables of crystal structures were the basis for the series ''International Tables of Crystallography'', first published in 1935. Band structure calculations were first used in 1930 to predict the properties of new materials, and in 1947 John Bardeen
John Bardeen (; May 23, 1908 – January 30, 1991) was an American solid-state physicist. He is the only person to be awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics twice: first in 1956 with William Shockley and Walter Houser Brattain for their inventio ...
, Walter Brattain and William Shockley
William Bradford Shockley ( ; February 13, 1910 – August 12, 1989) was an American solid-state physicist, electrical engineer, and inventor. He was the manager of a research group at Bell Labs that included John Bardeen and Walter Houser Brat ...
developed the first semiconductor
A semiconductor is a material with electrical conductivity between that of a conductor and an insulator. Its conductivity can be modified by adding impurities (" doping") to its crystal structure. When two regions with different doping level ...
-based transistor
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch electrical signals and electric power, power. It is one of the basic building blocks of modern electronics. It is composed of semicondu ...
, heralding a revolution in electronics.
 In 1879, Edwin Herbert Hall working at the
In 1879, Edwin Herbert Hall working at the Johns Hopkins University
The Johns Hopkins University (often abbreviated as Johns Hopkins, Hopkins, or JHU) is a private university, private research university in Baltimore, Maryland, United States. Founded in 1876 based on the European research institution model, J ...
discovered that a voltage developed across conductors which was transverse to both an electric current in the conductor and a magnetic field applied perpendicular to the current. This phenomenon, arising due to the nature of charge carriers in the conductor, came to be termed the Hall effect
The Hall effect is the production of a voltage, potential difference (the Hall voltage) across an electrical conductor that is wikt:transverse, transverse to an electric current in the conductor and to an applied magnetic field wikt:perpendicul ...
, but it was not properly explained at the time because the electron was not experimentally discovered until 18 years later. After the advent of quantum mechanics, Lev Landau in 1930 developed the theory of Landau quantization and laid the foundation for a theoretical explanation of the quantum Hall effect which was discovered half a century later.
Magnetism as a property of matter has been known in China since 4000 BC. However, the first modern studies of magnetism only started with the development of electrodynamics by Faraday, Maxwell
Maxwell may refer to:
People
* Maxwell (surname), including a list of people and fictional characters with the name
** James Clerk Maxwell, mathematician and physicist
* Justice Maxwell (disambiguation)
* Maxwell baronets, in the Baronetage of N ...
and others in the nineteenth century, which included classifying materials as ferromagnetic
Ferromagnetism is a property of certain materials (such as iron) that results in a significant, observable magnetic permeability, and in many cases, a significant magnetic coercivity, allowing the material to form a permanent magnet. Ferromagne ...
, paramagnetic and diamagnetic based on their response to magnetization. Pierre Curie
Pierre Curie ( ; ; 15 May 1859 – 19 April 1906) was a French physicist, Radiochemistry, radiochemist, and a pioneer in crystallography, magnetism, piezoelectricity, and radioactivity. He shared the 1903 Nobel Prize in Physics with his wife, ...
studied the dependence of magnetization on temperature and discovered the Curie point phase transition in ferromagnetic materials. In 1906, Pierre Weiss introduced the concept of magnetic domain
A magnetic domain is a region within a magnetic material in which the magnetization is in a uniform direction. This means that the individual magnetic moments of the atoms are aligned with one another and they point in the same direction. When c ...
s to explain the main properties of ferromagnets. The first attempt at a microscopic description of magnetism was by Wilhelm Lenz and Ernst Ising through the Ising model
The Ising model (or Lenz–Ising model), named after the physicists Ernst Ising and Wilhelm Lenz, is a mathematical models in physics, mathematical model of ferromagnetism in statistical mechanics. The model consists of discrete variables that r ...
that described magnetic materials as consisting of a periodic lattice of spins
The spins (as in having "the spins") is an adverse reaction of Substance intoxication, intoxication that causes a state of vertigo and nausea, causing one to feel as if "spinning out of control", especially when lying down. It is most commonly as ...
that collectively acquired magnetization. The Ising model was solved exactly to show that spontaneous magnetization can occur in one dimension and it is possible in higher-dimensional lattices. Further research such as by Bloch on spin waves and Néel on antiferromagnetism led to developing new magnetic materials with applications to magnetic storage
Magnetic storage or magnetic recording is the storage of data on a magnetized medium. Magnetic storage uses different patterns of magnetisation in a magnetizable material to store data and is a form of non-volatile memory. The information is acc ...
devices.
Modern many-body physics
 The Sommerfeld model and spin models for ferromagnetism illustrated the successful application of quantum mechanics to condensed matter problems in the 1930s. However, there still were several unsolved problems, most notably the description of superconductivity and the Kondo effect. After
The Sommerfeld model and spin models for ferromagnetism illustrated the successful application of quantum mechanics to condensed matter problems in the 1930s. However, there still were several unsolved problems, most notably the description of superconductivity and the Kondo effect. After World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, several ideas from quantum field theory were applied to condensed matter problems. These included recognition of collective excitation modes of solids and the important notion of a quasiparticle. Soviet physicist Lev Landau used the idea for the Fermi liquid theory wherein low energy properties of interacting fermion systems were given in terms of what are now termed Landau-quasiparticles. Landau also developed a mean-field theory for continuous phase transitions, which described ordered phases as spontaneous breakdown of symmetry. The theory also introduced the notion of an order parameter to distinguish between ordered phases. Eventually in 1956, John Bardeen
John Bardeen (; May 23, 1908 – January 30, 1991) was an American solid-state physicist. He is the only person to be awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics twice: first in 1956 with William Shockley and Walter Houser Brattain for their inventio ...
, Leon Cooper and Robert Schrieffer developed the so-called BCS theory of superconductivity, based on the discovery that arbitrarily small attraction between two electrons of opposite spin mediated by phonons in the lattice can give rise to a bound state called a Cooper pair.
 The study of phase transitions and the critical behavior of observables, termed critical phenomena, was a major field of interest in the 1960s. Leo Kadanoff, Benjamin Widom and Michael Fisher developed the ideas of critical exponents and widom scaling. These ideas were unified by Kenneth G. Wilson in 1972, under the formalism of the renormalization group in the context of quantum field theory.
The quantum Hall effect was discovered by Klaus von Klitzing, Dorda and Pepper in 1980 when they observed the Hall conductance to be integer multiples of a fundamental constant .(see figure) The effect was observed to be independent of parameters such as system size and impurities. In 1981, theorist Robert Laughlin proposed a theory explaining the unanticipated precision of the integral plateau. It also implied that the Hall conductance is proportional to a topological invariant, called Chern number, whose relevance for the band structure of solids was formulated by David J. Thouless and collaborators. Shortly after, in 1982, Horst Störmer and Daniel Tsui observed the fractional quantum Hall effect where the conductance was now a rational multiple of the constant . Laughlin, in 1983, realized that this was a consequence of quasiparticle interaction in the Hall states and formulated a variational method solution, named the Laughlin wavefunction. The study of topological properties of the fractional Hall effect remains an active field of research. Decades later, the aforementioned topological band theory advanced by David J. Thouless and collaborators was further expanded leading to the discovery of topological insulators.
In 1986, Karl Müller and Johannes Bednorz discovered the first high temperature superconductor, La2-xBaxCuO4, which is superconducting at temperatures as high as 39
The study of phase transitions and the critical behavior of observables, termed critical phenomena, was a major field of interest in the 1960s. Leo Kadanoff, Benjamin Widom and Michael Fisher developed the ideas of critical exponents and widom scaling. These ideas were unified by Kenneth G. Wilson in 1972, under the formalism of the renormalization group in the context of quantum field theory.
The quantum Hall effect was discovered by Klaus von Klitzing, Dorda and Pepper in 1980 when they observed the Hall conductance to be integer multiples of a fundamental constant .(see figure) The effect was observed to be independent of parameters such as system size and impurities. In 1981, theorist Robert Laughlin proposed a theory explaining the unanticipated precision of the integral plateau. It also implied that the Hall conductance is proportional to a topological invariant, called Chern number, whose relevance for the band structure of solids was formulated by David J. Thouless and collaborators. Shortly after, in 1982, Horst Störmer and Daniel Tsui observed the fractional quantum Hall effect where the conductance was now a rational multiple of the constant . Laughlin, in 1983, realized that this was a consequence of quasiparticle interaction in the Hall states and formulated a variational method solution, named the Laughlin wavefunction. The study of topological properties of the fractional Hall effect remains an active field of research. Decades later, the aforementioned topological band theory advanced by David J. Thouless and collaborators was further expanded leading to the discovery of topological insulators.
In 1986, Karl Müller and Johannes Bednorz discovered the first high temperature superconductor, La2-xBaxCuO4, which is superconducting at temperatures as high as 39 kelvin
The kelvin (symbol: K) is the base unit for temperature in the International System of Units (SI). The Kelvin scale is an absolute temperature scale that starts at the lowest possible temperature (absolute zero), taken to be 0 K. By de ...
. It was realized that the high temperature superconductors are examples of strongly correlated materials where the electron–electron interactions play an important role. A satisfactory theoretical description of high-temperature superconductors is still not known and the field of strongly correlated material
Strongly correlated materials are a wide class of compounds that include insulators and electronic materials, and show unusual (often technologically useful) electronic and magnetic properties, such as metal-insulator transitions, heavy fermi ...
s continues to be an active research topic.
In 2012, several groups released preprints which suggest that samarium hexaboride has the properties of a topological insulator in accord with the earlier theoretical predictions. Since samarium hexaboride is an established Kondo insulator, i.e. a strongly correlated electron material, it is expected that the existence of a topological Dirac surface state in this material would lead to a topological insulator with strong electronic correlations.
Theoretical
Theoretical condensed matter physics involves the use of theoretical models to understand properties of states of matter. These include models to study the electronic properties of solids, such as the Drude model, the band structure and the density functional theory. Theoretical models have also been developed to study the physics ofphase transition
In physics, chemistry, and other related fields like biology, a phase transition (or phase change) is the physical process of transition between one state of a medium and another. Commonly the term is used to refer to changes among the basic Sta ...
s, such as the Ginzburg–Landau theory, critical exponents and the use of mathematical methods of quantum field theory
In theoretical physics, quantum field theory (QFT) is a theoretical framework that combines Field theory (physics), field theory and the principle of relativity with ideas behind quantum mechanics. QFT is used in particle physics to construct phy ...
and the renormalization group. Modern theoretical studies involve the use of numerical computation
Numerical analysis is the study of algorithms that use numerical approximation (as opposed to symbolic manipulations) for the problems of mathematical analysis (as distinguished from discrete mathematics). It is the study of numerical methods t ...
of electronic structure and mathematical tools to understand phenomena such as high-temperature superconductivity, topological phases, and gauge symmetries.
Emergence
Theoretical understanding of condensed matter physics is closely related to the notion ofemergence
In philosophy, systems theory, science, and art, emergence occurs when a complex entity has properties or behaviors that its parts do not have on their own, and emerge only when they interact in a wider whole.
Emergence plays a central rol ...
, wherein complex assemblies of particles behave in ways dramatically different from their individual constituents. For example, a range of phenomena related to high temperature superconductivity are understood poorly, although the microscopic physics of individual electrons and lattices is well known. Similarly, models of condensed matter systems have been studied where collective excitations behave like photon
A photon () is an elementary particle that is a quantum of the electromagnetic field, including electromagnetic radiation such as light and radio waves, and the force carrier for the electromagnetic force. Photons are massless particles that can ...
s and electron
The electron (, or in nuclear reactions) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary charge, elementary electric charge. It is a fundamental particle that comprises the ordinary matter that makes up the universe, along with up qua ...
s, thereby describing electromagnetism
In physics, electromagnetism is an interaction that occurs between particles with electric charge via electromagnetic fields. The electromagnetic force is one of the four fundamental forces of nature. It is the dominant force in the interacti ...
as an emergent phenomenon. Emergent properties can also occur at the interface between materials: one example is the lanthanum aluminate-strontium titanate interface, where two band-insulators are joined to create conductivity and superconductivity.
Electronic theory of solids
The metallic state has historically been an important building block for studying properties of solids. The first theoretical description of metals was given by Paul Drude in 1900 with the Drude model, which explained electrical and thermal properties by describing a metal as anideal gas
An ideal gas is a theoretical gas composed of many randomly moving point particles that are not subject to interparticle interactions. The ideal gas concept is useful because it obeys the ideal gas law, a simplified equation of state, and is ...
of then-newly discovered electron
The electron (, or in nuclear reactions) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary charge, elementary electric charge. It is a fundamental particle that comprises the ordinary matter that makes up the universe, along with up qua ...
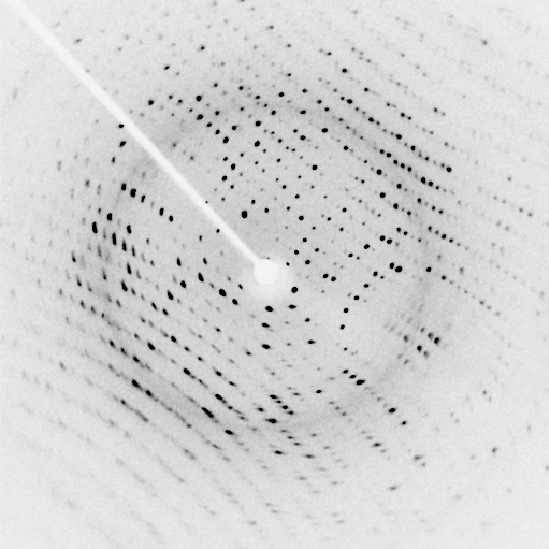
s. He was able to derive the empirical Wiedemann-Franz law and get results in close agreement with the experiments. This classical model was then improved by Arnold Sommerfeld who incorporated the Fermi–Dirac statistics of electrons and was able to explain the anomalous behavior of the specific heat of metals in the Wiedemann–Franz law. In 1912, The structure of crystalline solids was studied by Max von Laue and Paul Knipping, when they observed the X-ray diffraction
X-ray diffraction is a generic term for phenomena associated with changes in the direction of X-ray beams due to interactions with the electrons around atoms. It occurs due to elastic scattering, when there is no change in the energy of the waves. ...
pattern of crystals, and concluded that crystals get their structure from periodic lattices of atoms. In 1928, Swiss physicist Felix Bloch
Felix Bloch (; ; 23 October 1905 – 10 September 1983) was a Swiss-American physicist who shared the 1952 Nobel Prize in Physics with Edward Mills Purcell "for their development of new methods for nuclear magnetic precision measurements and di ...
provided a wave function solution to the Schrödinger equation
The Schrödinger equation is a partial differential equation that governs the wave function of a non-relativistic quantum-mechanical system. Its discovery was a significant landmark in the development of quantum mechanics. It is named after E ...
with a periodic potential, known as Bloch's theorem.
Calculating electronic properties of metals by solving the many-body wavefunction is often computationally hard, and hence, approximation methods are needed to obtain meaningful predictions. The Thomas–Fermi theory, developed in the 1920s, was used to estimate system energy and electronic density by treating the local electron density as a variational parameter. Later in the 1930s, Douglas Hartree, Vladimir Fock and John Slater developed the so-called Hartree–Fock wavefunction as an improvement over the Thomas–Fermi model. The Hartree–Fock method accounted for exchange statistics of single particle electron wavefunctions. In general, it is very difficult to solve the Hartree–Fock equation. Only the free electron gas case can be solved exactly. Finally in 1964–65, Walter Kohn, Pierre Hohenberg and Lu Jeu Sham proposed the density functional theory (DFT) which gave realistic descriptions for bulk and surface properties of metals. The density functional theory has been widely used since the 1970s for band structure calculations of variety of solids.
Symmetry breaking
Some states of matter exhibit ''symmetry breaking'', where the relevant laws of physics possess some form ofsymmetry
Symmetry () in everyday life refers to a sense of harmonious and beautiful proportion and balance. In mathematics, the term has a more precise definition and is usually used to refer to an object that is Invariant (mathematics), invariant und ...
that is broken. A common example is crystalline solids, which break continuous translational symmetry. Other examples include magnetized ferromagnets, which break rotational symmetry
Rotational symmetry, also known as radial symmetry in geometry, is the property a shape (geometry), shape has when it looks the same after some rotation (mathematics), rotation by a partial turn (angle), turn. An object's degree of rotational s ...
, and more exotic states such as the ground state of a BCS superconductor, that breaks U(1) phase rotational symmetry.
Goldstone's theorem in quantum field theory
In theoretical physics, quantum field theory (QFT) is a theoretical framework that combines Field theory (physics), field theory and the principle of relativity with ideas behind quantum mechanics. QFT is used in particle physics to construct phy ...
states that in a system with broken continuous symmetry, there may exist excitations with arbitrarily low energy, called the Goldstone boson
In particle physics, a boson ( ) is a subatomic particle whose spin quantum number has an integer value (0, 1, 2, ...). Bosons form one of the two fundamental classes of subatomic particle, the other being fermions, which have half odd-intege ...
s. For example, in crystalline solids, these correspond to phonons, which are quantized versions of lattice vibrations.
Phase transition
Phase transition refers to the change of phase of a system, which is brought about by change in an external parameter such astemperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that quantitatively expresses the attribute of hotness or coldness. Temperature is measurement, measured with a thermometer. It reflects the average kinetic energy of the vibrating and colliding atoms making ...
, pressure
Pressure (symbol: ''p'' or ''P'') is the force applied perpendicular to the surface of an object per unit area over which that force is distributed. Gauge pressure (also spelled ''gage'' pressure)The preferred spelling varies by country and eve ...
, or molar composition. In a single-component system, a classical phase transition occurs at a temperature (at a specific pressure) where there is an abrupt change in the order of the system. For example, when ice melts and becomes water, the ordered hexagonal crystal structure of ice is modified to a hydrogen bonded, mobile arrangement of water molecules.
In quantum phase transitions, the temperature is set to absolute zero
Absolute zero is the lowest possible temperature, a state at which a system's internal energy, and in ideal cases entropy, reach their minimum values. The absolute zero is defined as 0 K on the Kelvin scale, equivalent to −273.15 ° ...
, and the non-thermal control parameter, such as pressure or magnetic field, causes the phase transitions when order is destroyed by quantum fluctuations originating from the Heisenberg uncertainty principle
The uncertainty principle, also known as Heisenberg's indeterminacy principle, is a fundamental concept in quantum mechanics. It states that there is a limit to the precision with which certain pairs of physical properties, such as position a ...
. Here, the different quantum phases of the system refer to distinct ground states of the Hamiltonian matrix. Understanding the behavior of quantum phase transition is important in the difficult tasks of explaining the properties of rare-earth magnetic insulators, high-temperature superconductors, and other substances.
Two classes of phase transitions occur: ''first-order transitions'' and ''second-order'' or ''continuous transitions''. For the latter, the two phases involved do not co-exist at the transition temperature, also called the critical point. Near the critical point, systems undergo critical behavior, wherein several of their properties such as correlation length, specific heat, and magnetic susceptibility diverge exponentially. These critical phenomena present serious challenges to physicists because normal macroscopic
The macroscopic scale is the length scale on which objects or phenomena are large enough to be visible with the naked eye, without magnifying optical instruments. It is the opposite of microscopic.
Overview
When applied to physical phenome ...
laws are no longer valid in the region, and novel ideas and methods must be invented to find the new laws that can describe the system.
The simplest theory that can describe continuous phase transitions is the Ginzburg–Landau theory, which works in the so-called mean-field approximation. However, it can only roughly explain continuous phase transition for ferroelectrics and type I superconductors which involves long range microscopic interactions. For other types of systems that involves short range interactions near the critical point, a better theory is needed.
Near the critical point, the fluctuations happen over broad range of size scales while the feature of the whole system is scale invariant. Renormalization group methods successively average out the shortest wavelength fluctuations in stages while retaining their effects into the next stage. Thus, the changes of a physical system as viewed at different size scales can be investigated systematically. The methods, together with powerful computer simulation, contribute greatly to the explanation of the critical phenomena associated with continuous phase transition.
Experimental
Experimental condensed matter physics involves the use of experimental probes to try to discover new properties of materials. Such probes include effects ofelectric
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter possessing an electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described by Maxwel ...
and magnetic field
A magnetic field (sometimes called B-field) is a physical field that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents, and magnetic materials. A moving charge in a magnetic field experiences a force perpendicular ...
s, measuring response functions, transport properties and thermometry. Commonly used experimental methods include spectroscopy
Spectroscopy is the field of study that measures and interprets electromagnetic spectra. In narrower contexts, spectroscopy is the precise study of color as generalized from visible light to all bands of the electromagnetic spectrum.
Spectro ...
, with probes such as X-rays
An X-ray (also known in many languages as Röntgen radiation) is a form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than those of ultraviolet rays and longer than those of gamma rays. Roughly, X-rays have a wavelength ran ...
, infrared light and inelastic neutron scattering; study of thermal response, such as specific heat and measuring transport via thermal and heat conduction.

Scattering
Several condensed matter experiments involve scattering of an experimental probe, such asX-ray
An X-ray (also known in many languages as Röntgen radiation) is a form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than those of ultraviolet rays and longer than those of gamma rays. Roughly, X-rays have a wavelength ran ...
, optical photon
A photon () is an elementary particle that is a quantum of the electromagnetic field, including electromagnetic radiation such as light and radio waves, and the force carrier for the electromagnetic force. Photons are massless particles that can ...
s, neutron
The neutron is a subatomic particle, symbol or , that has no electric charge, and a mass slightly greater than that of a proton. The Discovery of the neutron, neutron was discovered by James Chadwick in 1932, leading to the discovery of nucle ...
s, etc., on constituents of a material. The choice of scattering probe depends on the observation energy scale of interest. Visible light has energy on the scale of 1 electron volt (eV) and is used as a scattering probe to measure variations in material properties such as the dielectric constant
The relative permittivity (in older texts, dielectric constant) is the permittivity of a material expressed as a ratio with the electric permittivity of a vacuum. A dielectric is an insulating material, and the dielectric constant of an insul ...
and refractive index
In optics, the refractive index (or refraction index) of an optical medium is the ratio of the apparent speed of light in the air or vacuum to the speed in the medium. The refractive index determines how much the path of light is bent, or refrac ...
. X-rays have energies of the order of 10 keV and hence are able to probe atomic length scales, and are used to measure variations in electron charge density and crystal structure.
Neutron
The neutron is a subatomic particle, symbol or , that has no electric charge, and a mass slightly greater than that of a proton. The Discovery of the neutron, neutron was discovered by James Chadwick in 1932, leading to the discovery of nucle ...
s can also probe atomic length scales and are used to study the scattering off nuclei and electron spins
The spins (as in having "the spins") is an adverse reaction of Substance intoxication, intoxication that causes a state of vertigo and nausea, causing one to feel as if "spinning out of control", especially when lying down. It is most commonly as ...
and magnetization (as neutrons have spin but no charge). Coulomb and Mott scattering measurements can be made by using electron beams as scattering probes. Similarly, positron
The positron or antielectron is the particle with an electric charge of +1''elementary charge, e'', a Spin (physics), spin of 1/2 (the same as the electron), and the same Electron rest mass, mass as an electron. It is the antiparticle (antimatt ...
annihilation can be used as an indirect measurement of local electron density. Laser spectroscopy is an excellent tool for studying the microscopic properties of a medium, for example, to study forbidden transitions in media with nonlinear optical spectroscopy.
External magnetic fields
In experimental condensed matter physics, externalmagnetic field
A magnetic field (sometimes called B-field) is a physical field that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents, and magnetic materials. A moving charge in a magnetic field experiences a force perpendicular ...
s act as thermodynamic variables that control the state, phase transitions and properties of material systems. Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) is a method by which external magnetic fields are used to find resonance modes of individual nuclei, thus giving information about the atomic, molecular, and bond structure of their environment. NMR experiments can be made in magnetic fields with strengths up to 60 tesla. Higher magnetic fields can improve the quality of NMR measurement data. Quantum oscillations is another experimental method where high magnetic fields are used to study material properties such as the geometry of the Fermi surface. High magnetic fields will be useful in experimental testing of the various theoretical predictions such as the quantized magnetoelectric effect, image magnetic monopole, and the half-integer quantum Hall effect.
Magnetic resonance spectroscopy
The local structure, as well as the structure of the nearest neighbour atoms, can be investigated in condensed matter with magnetic resonance methods, such as electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), which are very sensitive to the details of the surrounding of nuclei and electrons by means of the hyperfine coupling. Both localized electrons and specific stable or unstable isotopes of the nuclei become the probe of these hyperfine interactions), which couple the electron or nuclear spin to the local electric and magnetic fields. These methods are suitable to study defects, diffusion, phase transitions and magnetic order. Common experimental methods includeNMR
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) is a physical phenomenon in which atomic nucleus, nuclei in a strong constant magnetic field are disturbed by a weak oscillating magnetic field (in the near and far field, near field) and respond by producing ...
, nuclear quadrupole resonance (NQR), implanted radioactive probes as in the case of muon spin spectroscopy (SR), Mössbauer spectroscopy, NMR and perturbed angular correlation (PAC). PAC is especially ideal for the study of phase changes at extreme temperatures above 2000 °C due to the temperature independence of the method.
Cold atomic gases
 Ultracold atom trapping in optical lattices is an experimental tool commonly used in condensed matter physics, and in atomic, molecular, and optical physics. The method involves using optical lasers to form an interference pattern, which acts as a ''lattice'', in which ions or atoms can be placed at very low temperatures. Cold atoms in optical lattices are used as ''quantum simulators'', that is, they act as controllable systems that can model behavior of more complicated systems, such as frustrated magnets. In particular, they are used to engineer one-, two- and three-dimensional lattices for a
Ultracold atom trapping in optical lattices is an experimental tool commonly used in condensed matter physics, and in atomic, molecular, and optical physics. The method involves using optical lasers to form an interference pattern, which acts as a ''lattice'', in which ions or atoms can be placed at very low temperatures. Cold atoms in optical lattices are used as ''quantum simulators'', that is, they act as controllable systems that can model behavior of more complicated systems, such as frustrated magnets. In particular, they are used to engineer one-, two- and three-dimensional lattices for a Hubbard model
The Hubbard model is an Approximation, approximate model used to describe the transition between Conductor (material), conducting and Electrical insulation, insulating systems.
It is particularly useful in solid-state physics. The model is named ...
with pre-specified parameters, and to study phase transitions for antiferromagnetic and spin liquid ordering.
In 1995, a gas of rubidium atoms cooled down to a temperature of 170 nK was used to experimentally realize the Bose–Einstein condensate
In condensed matter physics, a Bose–Einstein condensate (BEC) is a state of matter that is typically formed when a gas of bosons at very low Density, densities is cooled to temperatures very close to absolute zero#Relation with Bose–Einste ...
, a novel state of matter originally predicted by S. N. Bose and Albert Einstein
Albert Einstein (14 March 187918 April 1955) was a German-born theoretical physicist who is best known for developing the theory of relativity. Einstein also made important contributions to quantum mechanics. His mass–energy equivalence f ...
, wherein a large number of atoms occupy one quantum state
In quantum physics, a quantum state is a mathematical entity that embodies the knowledge of a quantum system. Quantum mechanics specifies the construction, evolution, and measurement of a quantum state. The result is a prediction for the system ...
.
Applications
 Research in condensed matter physics has given rise to several device applications, such as the development of the
Research in condensed matter physics has given rise to several device applications, such as the development of the semiconductor
A semiconductor is a material with electrical conductivity between that of a conductor and an insulator. Its conductivity can be modified by adding impurities (" doping") to its crystal structure. When two regions with different doping level ...
transistor
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch electrical signals and electric power, power. It is one of the basic building blocks of modern electronics. It is composed of semicondu ...
, laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word ''laser'' originated as an acronym for light amplification by stimulated emission of radi ...
technology, magnetic storage
Magnetic storage or magnetic recording is the storage of data on a magnetized medium. Magnetic storage uses different patterns of magnetisation in a magnetizable material to store data and is a form of non-volatile memory. The information is acc ...
, liquid crystals, optical fibres and several phenomena studied in the context of nanotechnology
Nanotechnology is the manipulation of matter with at least one dimension sized from 1 to 100 nanometers (nm). At this scale, commonly known as the nanoscale, surface area and quantum mechanical effects become important in describing propertie ...
. Methods such as scanning-tunneling microscopy can be used to control processes at the nanometer scale, and have given rise to the study of nanofabrication. Such molecular machines were developed for example by Nobel laureates in chemistry Ben Feringa, Jean-Pierre Sauvage and Fraser Stoddart. Feringa and his team developed multiple molecular machines such as the molecular car, molecular windmill and many more.
In quantum computation, information is represented by quantum bits, or qubits. The qubits may decohere quickly before useful computation is completed. This serious problem must be solved before quantum computing may be realized. To solve this problem, several promising approaches are proposed in condensed matter physics, including Josephson junction qubits, spintronic qubits using the spin orientation of magnetic materials, and the topological non-Abelian anyon
In physics, an anyon is a type of quasiparticle so far observed only in two-dimensional physical system, systems. In three-dimensional systems, only two kinds of elementary particles are seen: fermions and bosons. Anyons have statistical proper ...
s from fractional quantum Hall effect states.
Condensed matter physics also has important uses for biomedicine. For example, magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to generate pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes inside the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and ...
is widely used in medical imaging of soft tissue and other physiological features which cannot be viewed with traditional x-ray imaging.
See also
* * * * * * * * * *Notes
References
Further reading
* Anderson, Philip W. (2018-03-09). ''Basic Notions Of Condensed Matter Physics''. CRC Press. . *Girvin, Steven M.; Yang, Kun (2019-02-28). ''Modern Condensed Matter Physics''. Cambridge University Press. . *Coleman, Piers (2015). '' Introduction to Many-Body Physics'', Cambridge University Press, . *P. M. Chaikin and T. C. Lubensky (2000). ''Principles of Condensed Matter Physics'', Cambridge University Press; 1st edition, * Alexander Altland and Ben Simons (2006). ''Condensed Matter Field Theory'', Cambridge University Press, . * Michael P. Marder (2010). ''Condensed Matter Physics, second edition'', John Wiley and Sons, . *Lillian Hoddeson, Ernest Braun, Jürgen Teichmann and Spencer Weart, eds. (1992). ''Out of the Crystal Maze: Chapters from the History of Solid State Physics'', Oxford University Press, .External links
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Condensed Matter Physics Materials science