computer representation of surfaces on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In technical applications of
 If one considers a local parametrization of a surface:
:
then the curves obtained by varying ''u'' while keeping ''v'' fixed are coordinate lines, sometimes called the ''u'' ''flow lines''. The curves obtained by varying ''v'' while ''u'' is fixed are called the ''v'' flow lines. These are generalizations of the ''x'' and ''y'' Cartesian coordinate lines in the plane coordinate system and of the meridians and circles of latitude on a
If one considers a local parametrization of a surface:
:
then the curves obtained by varying ''u'' while keeping ''v'' fixed are coordinate lines, sometimes called the ''u'' ''flow lines''. The curves obtained by varying ''v'' while ''u'' is fixed are called the ''v'' flow lines. These are generalizations of the ''x'' and ''y'' Cartesian coordinate lines in the plane coordinate system and of the meridians and circles of latitude on a
Image:spoon_wf.jpg , wireframe
hidden edges Image:spoon_uv.jpg , wireframe
uv isolines
*Faceted mode. In this mode each surface is drawn as a series of planar regions, usually rectangles. Hidden-line removal is typically used with such a representation. Static hidden-line removal does not update which lines are hidden during rotation, but only once the screen is refreshed. Dynamic hidden-line removal continuously updates which curves are hidden during rotations.
Image:spoon_fw.jpg , Facet wireframe
Image:spoon_fs.jpg , Facet shaded
*Shaded mode. Shading can then be added to the facets, possibly with blending between the regions for a smoother display. Shading can also be static or dynamic. A lower quality of shading is typically used for dynamic shading, while high quality shading, with multiple light sources, textures, etc., requires a delay for rendering.
Image:spoon_sh.jpg , shaded
Image:spoon_rl.jpg , reflection lines
Image:spoon_fi.jpg , reflected image
 CAD/
CAD/
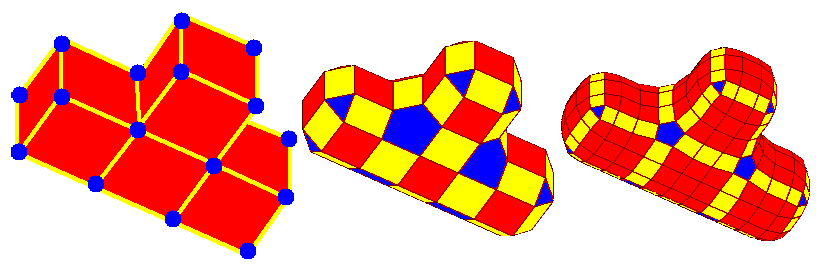 In
In
3D-XplorMath: Program to visualize many kinds of surfaces in wireframe, patch and anaglyph mode.
{{DEFAULTSORT:Computer Representation Of Surfaces 3D computer graphics Surfaces
3D computer graphics
3D computer graphics, sometimes called Computer-generated imagery, CGI, 3D-CGI or three-dimensional Computer-generated imagery, computer graphics, are graphics that use a three-dimensional representation of geometric data (often Cartesian coor ...
( CAx) such as computer-aided design
Computer-aided design (CAD) is the use of computers (or ) to aid in the creation, modification, analysis, or optimization of a design. This software is used to increase the productivity of the designer, improve the quality of design, improve c ...
and computer-aided manufacturing
Computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) also known as computer-aided modeling or computer-aided machining is the use of software to control machine tools in the manufacturing of work pieces. This is not the only definition for CAM, but it is the most ...
, surfaces are one way of representing objects. The other ways are wireframe (lines and curves) and solids. Point cloud
A point cloud is a discrete set of data Point (geometry), points in space. The points may represent a 3D shape or object. Each point Position (geometry), position has its set of Cartesian coordinates (X, Y, Z). Points may contain data other than ...
s are also sometimes used as temporary ways to represent an object, with the goal of using the points to create one or more of the three permanent representations.
Open and closed surfaces
 If one considers a local parametrization of a surface:
:
then the curves obtained by varying ''u'' while keeping ''v'' fixed are coordinate lines, sometimes called the ''u'' ''flow lines''. The curves obtained by varying ''v'' while ''u'' is fixed are called the ''v'' flow lines. These are generalizations of the ''x'' and ''y'' Cartesian coordinate lines in the plane coordinate system and of the meridians and circles of latitude on a
If one considers a local parametrization of a surface:
:
then the curves obtained by varying ''u'' while keeping ''v'' fixed are coordinate lines, sometimes called the ''u'' ''flow lines''. The curves obtained by varying ''v'' while ''u'' is fixed are called the ''v'' flow lines. These are generalizations of the ''x'' and ''y'' Cartesian coordinate lines in the plane coordinate system and of the meridians and circles of latitude on a spherical coordinate system
In mathematics, a spherical coordinate system specifies a given point in three-dimensional space by using a distance and two angles as its three coordinates. These are
* the radial distance along the line connecting the point to a fixed point ...
.
Open surfaces are not closed in either direction. This means moving in any direction along the surface will cause an observer to hit the edge of the surface. The top of a car hood is an example of a surface open in both directions.
Surfaces closed in one direction include a cylinder, cone, and hemisphere. Depending on the direction of travel, an observer on the surface may hit a boundary on such a surface or travel forever.
Surfaces closed in both directions include a sphere and a torus. Moving in any direction on such surfaces will cause the observer to travel forever without hitting an edge.
Places where two boundaries overlap (except at a point) are called a seam. For example, if one imagines a cylinder made from a sheet of paper rolled up and taped together at the edges, the boundaries where it is taped together are called the seam.
Flattening a surface
Some open surfaces and surfaces closed in one direction may be flattened into a plane without deformation of the surface. For example, a cylinder can be flattened into a rectangular area without distorting the surface distance between surface features (except for those distances across the split created by opening up the cylinder). A cone may also be so flattened. Such surfaces are linear in one direction and curved in the other (surfaces linear in both directions were flat to begin with). Sheet metal surfaces which have flat patterns can be manufactured by stamping a flat version, then bending them into the proper shape, such as with rollers. This is a relatively inexpensive process. Other open surfaces and surfaces closed in one direction, and all surfaces closed in both directions, can't be flattened without deformation. A hemisphere or sphere, for example, can't. Such surfaces are curved in both directions. This is why maps of the Earth are distorted. The larger the area the map represents, the greater the distortion. Sheet metal surfaces which lack a flat pattern must be manufactured by stamping using 3D dies (sometimes requiring multiple dies with different draw depths and/or draw directions), which tend to be more expensive.Regions
Patches
A surface may be composed of one or more ''patches'', where each patch has its own U-V coordinate system. These surface patches are analogous to the multiple polynomial arcs used to build a spline. They allow more complex surfaces to be represented by a series of relatively simple equation sets rather than a single set of complex equations. Thus, the complexity of operations such as surface intersections can be reduced to a series of patch intersections. Surfaces closed in one or two directions frequently must also be broken into two or more surface patches by the software.Faces
Surfaces and surface patches can only be trimmed at U and V coordinate lines. To overcome this severe limitation, surface ''faces'' allow a surface to be limited to a series of boundaries projected onto the surface in any orientation, so long as those boundaries are collectively closed. For example, trimming a cylinder at an angle would require such a surface face. A single surface face may span multiple surface patches on a single surface, but can't span multiple surfaces. Planar faces are similar to surface faces, but are limited by a collectively closed series of boundaries projected to an infinite plane, instead of a surface.Skins and volumes
As with surfaces, surface faces closed in one or two directions frequently must also be broken into two or more surface faces by the software. To combine them back into a single entity, a skin or volume is created. A ''skin'' is an open collection of faces and a ''volume'' is a closed set. The constituent faces may have the same support surface or face or may have different supports.Solids
Volumes can be filled in to build a solid model (possibly with other volumes subtracted from the interior). Skins and faces can also be offset to create solids of uniform thickness.Continuity
A surface's patches and the faces built on that surface typically have point continuity (no gaps) and tangent continuity (no sharp angles). Curvature continuity (no sharp radius changes) may or may not be maintained. Skins and volumes, however, typically only have point continuity. Sharp angles between faces built on different supports (planes or surfaces) are common.Visualization and display
Surfaces may be displayed in many ways: *Wireframe mode. In this representation the surface is drawn as a series of lines and curves, withouthidden-line removal
In 3D computer graphics, solid objects are usually modeled by polyhedra. A face of a polyhedron is a planar polygon bounded by straight line segments, called edges. Curved surfaces are usually approximated by a polygon mesh. Computer programs ...
. The boundaries and flow lines (isoparametric curves) may each be shown as solid or dashed curves. The advantage of this representation is that a great deal of geometry may be displayed and rotated on the screen with no delay needed for graphics processing.
hidden edges Image:spoon_uv.jpg , wireframe
uv isolines
CAD/CAM representation
CAM
Cam or CAM may refer to:
Science and technology
* Cam (mechanism), a mechanical linkage which translates motion
* Camshaft, a shaft with a cam
* Camera or webcam, a device that records images or video
In computing
* Computer-aided manufacturin ...
systems use primarily two types of surfaces:
*Regular (or canonical) surfaces include surfaces of revolution such as cylinders, cones, spheres, and tori, and ruled surfaces (linear in one direction) such as surfaces of extrusion.
* Freeform surfaces (usually NURBS
Non-uniform rational basis spline (NURBS) is a mathematical model using basis splines (B-splines) that is commonly used in computer graphics for representing curves and surfaces. It offers great flexibility and precision for handling both analy ...
) allow more complex shapes to be represented via freeform surface modeling
Freeform or free-form may refer to:
* Electron-beam freeform fabrication, an additive manufacturing process that builds near-net-shape parts
* Free-form radio, a radio station programming format in which the disc jockey is given either total or wi ...
.
Other surface forms such as facet
Facets () are flat faces on geometric shapes. The organization of naturally occurring facets was key to early developments in crystallography, since they reflect the underlying symmetry of the crystal structure. Gemstones commonly have facets cu ...
and voxel
In computing, a voxel is a representation of a value on a three-dimensional regular grid, akin to the two-dimensional pixel. Voxels are frequently used in the Data visualization, visualization and analysis of medical imaging, medical and scient ...
are also used in a few specific applications.
CAE/FEA representation
In computer-aided engineering andfinite element analysis
Finite element method (FEM) is a popular method for numerically solving differential equations arising in engineering and mathematical models, mathematical modeling. Typical problem areas of interest include the traditional fields of structural ...
, an object may be represented by a surface mesh of node points connected by triangles or quadrilaterals (polygon mesh
In 3D computer graphics and solid modeling, a polygon mesh is a collection of , s and s that defines the shape of a polyhedron, polyhedral object's surface. It simplifies Rendering (computer graphics), rendering, as in a wire-frame model. The fac ...
). More accurate, but also far more CPU-intensive, results can be obtained by using a solid mesh. The process of creating a mesh is called tessellation
A tessellation or tiling is the covering of a surface, often a plane, using one or more geometric shapes, called ''tiles'', with no overlaps and no gaps. In mathematics, tessellation can be generalized to higher dimensions and a variety ...
. Once tessellated, the mesh can be subjected to simulated stresses, strains, temperature differences, etc., to see how those changes propagate from node point to node point throughout the mesh.
VR/computer animation
 In
In virtual reality
Virtual reality (VR) is a Simulation, simulated experience that employs 3D near-eye displays and pose tracking to give the user an immersive feel of a virtual world. Applications of virtual reality include entertainment (particularly video gam ...
and computer animation
Computer animation is the process used for digitally generating Film, moving images. The more general term computer-generated imagery (CGI) encompasses both still images and moving images, while computer animation refers to moving images. Virtu ...
, an object may also be represented by a surface mesh of node points connected by triangles or quadrilaterals. If the goal is only to represent the visible portion of an object (and not show changes to the object) a solid mesh serves no purpose, for this application. The triangles or quadrilaterals can each be shaded differently depending on their orientation toward the light sources and/or viewer. This will give a rather faceted appearance, so an additional step is frequently added where the shading of adjacent regions is blended to provide smooth shading. There are several methods for performing this blending.
See also
*Animation
Animation is a filmmaking technique whereby still images are manipulated to create moving images. In traditional animation, images are drawn or painted by hand on transparent celluloid sheets to be photographed and exhibited on film. Animati ...
* Boundary representation
* Digital surface
* Digital surface model
* Mesh generation
Mesh generation is the practice of creating a polygon mesh, mesh, a subdivision of a continuous geometric space into discrete geometric and topological cells.
Often these cells form a simplicial complex.
Usually the cells partition the geometric ...
* Parametric surface
References
External links
3D-XplorMath: Program to visualize many kinds of surfaces in wireframe, patch and anaglyph mode.
{{DEFAULTSORT:Computer Representation Of Surfaces 3D computer graphics Surfaces